Wood Sponge for Oil–Water Separation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Sewage Treatment Mechanism of Adsorption of Crude Oil by Wood Sponge
2.1. Characteristics of Wood Sponge
2.2. Mechanism of Crude Oil Adsorption
3. Preparation Methods of Hydrophobic Wood Sponge
3.1. Chemical Vapor Deposition Method
3.2. Chemical Liquid Deposition Method
3.3. Improving the Preparation Method by Utilizing Solar Energy and Light Energy
4. Limitation of Wood Sponge Used in Oil–Water Separation
5. Summary and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ventikos, N.P.; Vergetis, E.; Psaraftis, H.N.; Triantafyllou, G. A high-level synthesis of oil spill response equipment and countermeasures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 107, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Wang, B.; Zeng, J.; Cheng, Z.; Li, J.; Xu, J.; Gao, W.; Chen, K. Degradable dual superlyophobic lignocellulosic fibers for high-efficiency oil/water separation. Green Chem. 2020, 22, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Removal of Organic Pollutants from Water Using Superwetting Materials. Chem. Rec. 2018, 18, 118–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higaki, Y.; Hatae, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Takanohashi, T.; Hayashi, J.; Takahara, A. Adsorption and Desorption Behavior of Asphaltene on Polymer-Brush-Immobilized Surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20385–20389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ge-Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Song, Y.; Ding, Y.; Cui, J. Computer Simulation of Polyethylene Terephthalate Carbonated Beverage Bottle Bottom Structure Based on Manual–Automatic Double-Adjustment Optimization. Polymers 2022, 14, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.-L.; An, W.-L.; Zhao, X.; Xu, S.; Wang, Y.-Z. From waste epoxy resins to efficient oil/water separation materials via a microwave assisted pore-forming strategy. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 1733–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge-Zhang, S.; Song, M.; Huang, Z.; Li, M.; Mu, L. Comparison and Optimization: Research on the Structure of the PET Bottle Bottom Based on the Finite Element Method. Polymers 2022, 14, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibrous materials: A versatile medium for effective oil/water separation. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Superelastic and Superhydrophobic Nanofiber-Assembled Cellular Aerogels for Effective Separation of Oil/Water Emulsions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge-Zhang, S.; Liu, H.; Song, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Fan, H.; Ding, Y.; Mu, L. Advances in Polyethylene Terephthalate Beverage Bottle Optimization: A Mini Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Yuan, H.; Su, M.; Shao, C.; Liu, C.; Guo, Z.; Shen, C.; Liu, X. Simple fabrication of superhydrophobic PLA with honeycomb-like structures for high-efficiency oil-water separation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 365–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, M.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Fu, G. Nature-inspired chemistry toward hierarchical superhydrophobic, antibacterial and biocompatible nanofibrous membranes for effective UV-shielding, self-cleaning and oil-water separation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Qin, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Shao, Q.; Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Shen, C.; et al. Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Polycarbonate/Carbon Nanotubes Porous Monolith for Selective Oil Adsorption from Water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13747–13755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villacañas, F.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Órfão, J.J.; Figueiredo, J.L. Adsorption of simple aromatic compounds on activated carbons. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 293, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Ma, Q.; Tan, C.; Lim, T.T.; Huang, L.; Zhang, H.J.S. Carbon-based sorbents with three-dimensional architectures for water remediation. Small 2015, 11, 3319–3336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guo, C.; Shi, R.; Zhang, H.; Gong, L.; Dai, L. Chitosan/nanofibrillated cellulose aerogel with highly oriented microchannel structure for rapid removal of Pb (II) ions from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Sèbe, G.; Rentsch, D.; Zimmermann, T.; Tingaut, P. Ultralightweight and Flexible Silylated Nanocellulose Sponges for the Selective Removal of Oil from Water. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 2659–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.; Gao, H.; He, M.; Zhang, L. Hydrophobic Modification on Surface of Chitin Sponges for Highly Effective Separation of Oil. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 19933–19942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Chu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, N.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Pan, Q. Robust superhydrophobic polyurethane sponge as a highly reusable oil-absorption material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5386–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A. Magnetic, durable, and superhydrophobic polyurethane@ Fe3O4@ SiO2@ fluoropolymer sponges for selective oil absorption and oil/water separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4936–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Ai, K.; Li, X.; Lu, L. A Superhydrophobic Sponge with Excellent Absorbency and Flame Retardancy. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 5662–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-B.; Huang, S.; Liu, C.; Wu, J.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Xu, Z.-K. Carboxylated wood-based sponges with underoil superhydrophilicity for deep dehydration of crude oil. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 11354–11361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shamrani, A.; James, A.; Xiao, H. Separation of oil from water by dissolved air flotation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2002, 209, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Su, Y.-L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z. Free-Standing Graphene Oxide-Palygorskite Nanohybrid Membrane for Oil/Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 8247–8256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padaki, M.; Murali, R.S.; Abdullah, M.S.; Misdan, N.; Moslehyani, A.; Kassim, M.; Hilal, N.; Ismail, A.F. Membrane technology enhancement in oil–water separation. A review. Desalination 2015, 357, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, G.; Xu, N.; Shi, J. Preparation and application in oil–water separation of ZrO2/α-Al2O3 MF membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 1998, 142, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Na, S.-H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Latthe, S.S.; Swihart, M.T.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Yoon, S.S. Gravity-Driven Hybrid Membrane for Oleophobic–Superhydrophilic Oil–Water Separation and Water Purification by Graphene. Langmuir 2014, 30, 11761–11769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, M.H.; Gao, P.; Tan, B.Y.L.; Sun, D.D.; Leckie, J.O. Highly Efficient and Flexible Electrospun Carbon–Silica Nanofibrous Membrane for Ultrafast Gravity-Driven Oil–Water Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 9393–9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Fu, J.; Cai, Z.; O’Reilly, S.; Zhao, D. Dispersion, sorption and photodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbons in dispersant-seawater-sediment systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 526–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Yang, Q.; Yang, F. Flexible Underwater Oleophobic Cellulose Aerogels for Efficient Oil/Water Separation. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8181–8187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Two-dimensional membrane and three-dimensional bulk aerogel materials via top-down wood nanotechnology for multibehavioral and reusable oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F. Design and fabrication of superwetting fiber-based membranes for oil/water separation applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 364, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Guan, Q.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yu, S. Macroscopic-Scale Template Synthesis of Robust Carbonaceous Nanofiber Hydrogels and Aerogels and Their Applications. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5101–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, N.; Cao, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, L. Superwetting Porous Materials for Wastewater Treatment: From Immiscible Oil/Water Mixture to Emulsion Separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayase, G.; Kanamori, K.; Fukuchi, M.; Kaji, H.; Nakanishi, K. Facile Synthesis of Marshmallow-like Macroporous Gels Usable under Harsh Conditions for the Separation of Oil and Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1986–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Chen, M.; Du, C.; Guo, H.; Bai, H.; Li, L. Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Oil Absorbent with a Three-Dimensionally Interconnected Porous Structure and Swellable Skeleton. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10201–10206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yu, C.; Cui, L.; Song, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, L. Facile Preparation of the Porous PDMS Oil-Absorbent for Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 4, 1600862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, C.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H.; Shi, G.; Qu, L. A versatile, ultralight, nitrogen-doped graphene framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 11371–11375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Xie, X.; Yin, K.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, S.; He, L.; Xu, F.; Banhart, F.; Sun, L.; Ruoff, R.S. Spongy Graphene as a Highly Efficient and Recyclable Sorbent for Oils and Organic Solvents. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4421–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ge-Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Mu, H. A Wooden Carbon-Based Photocatalyst for Water Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Pan, C.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Lightweight, Superelastic, and Hydrophobic Polyimide Nanofiber/MXene Composite Aerogel for Wearable Piezoresistive Sensor and Oil/Water Separation Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2008006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Du, E.; He, Y.; Fan, Y.; Ye, Y.; Tang, B. Preparation of Carbonized Kapok Fiber/Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel for Oil-Water Separation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2020, 43, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.K.; Tsai, Y.B.; Gebremedhin, K.F.; Chien, T.Y.; Chang, R.Y.; Tung, K.L. Preparation of polypropylene/high-melt-strength PP open-cell foam for oil absorption. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 1139–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, R.; Chen, L.; Fan, M. A robust salt-tolerant superoleophobic chitosan/nanofibrillated cellulose aerogel for highly efficient oil/water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 200, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Betti, M.; Chen, L. Highly porous, hydrophobic, and compressible cellulose nanocrystals/poly(vinyl alcohol) aerogels as recyclable absorbents for oil–water separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 11118–11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, K.R.; Dora, D.; Pant, K.; Roy, S. An ultra-light flexible aerogel-based on methane derived CNTs as a reinforcing agent in silica-CMC matrix for efficient oil adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Yang, X.; Cranston, E.D.; Zhu, S. Flexible and Porous Nanocellulose Aerogels with High Loadings of Metal–Organic-Framework Particles for Separations Applications. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 7652–7657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Meng, G.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Magnetic Cellulose Sponge for Removing Oil from Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Yang, H. Wood-inspired polyacrylonitrile foam with hierarchically aligned porous structure for application in water purification. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Jiang, F.; Yang, Z.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Lacey, S.D.; Dai, J.; Wang, C. Tree-inspired design for high-efficiency water extraction. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1704107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, W.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y. Wood-Based Mesoporous Filter Decorated with Silver Nanoparticles for Water Purification. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 5134–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jin, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Sun, F.; Ma, H.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Xia, C. A comprehensive review of lignocellulosic biomass derived materials for water/oil separation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 876, 162549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, X. Highly Compressible Wood Sponges with a Spring-like Lamellar Structure as Effective and Reusable Oil Absorbents. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 10365–10373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Yang, F.; Gan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. Wood Sponge Reinforced with Polyvinyl Alcohol for Sustainable Oil–Water Separation. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 12866–12876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Liang, Y.; Hong, S.; Zuo, S.; Wu, Y.; Shi, J.; Cai, L.; Li, J.; Mao, H.; Ge, S.; et al. Novel Low-Temperature Chemical Vapor Deposition of Hydrothermal Delignified Wood for Hydrophobic Property. Polymers 2020, 12, 1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, C.; Shen, M.; Ren, X.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. A Versatile and Scalable Approach toward Robust Superhydrophobic Porous Materials with Excellent Absorbency and Flame Retardancy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, L.; Lai, X.; Li, H.; Zeng, X. Highly hydrophobic F-rGO@ wood sponge for efficient clean-up of viscous crude oil. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 386, 123994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chen, C.; Brozena, A.H.; Zhu, J.Y.; Xu, L.; Driemeier, C.; Dai, J.; Rojas, O.J.; Isogai, A.; Wågberg, L.; et al. Developing fibrillated cellulose as a sustainable technological material. Nature 2021, 590, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lin, S.; Li, X.; Zou, H.; Zhuo, B.; Ti, P.; Yuan, Q. Optimization and absorption performance of wood sponge. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 8479–8496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge-Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Mu, H. Interfacial solar steam generator by MWCNTs/carbon black nanoparticles coated wood. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 63, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Li, B.; Yang, K.; Chao, Y.; Luo, R.; Zhou, S.; Li, H. Superhydrophobic wood sponge with intelligent pH responsiveness for efficient and continuous oil-water separation. Mater. Res. Express 2023, 10, 055101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mei, C.; Li, Y.; Duan, G.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Ma, C.; Jiang, S. Wood-Inspired Anisotropic Cellulose Nanofibril Composite Sponges for Multifunctional Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 35513–35522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, H.; Zhang, C.; Tu, K.; Dai, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Wet-Stable Lamellar Wood Sponge with High Elasticity and Fatigue Resistance Enabled by Chemical Cross-Linking. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 18173–18183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Qiang, H.; Liang, S.; Guo, F.; Wang, R.; Cao, J.; Guo, Z.; Pang, Q.; Wei, B.; Sun, J. Hierarchically porous wood aerogel/polypyrrole(PPy) composite thick electrode for supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, N.; Lu, X.; Yan, B.; Chen, G.; Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, S. Co/N co-doped carbonized wood sponge with 3D porous framework for efficient peroxymonosulfate activation: Performance and internal mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Credou, J.; Berthelot, T. Cellulose: From biocompatible to bioactive material. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4767–4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Guo, H.; Ribera, J.; Wu, C.; Tu, K.; Binelli, M.; Panzarasa, G.; Schwarze, F.W.; Wang, Z.L.; Burgert, I. Sustainable and biodegradable wood sponge piezoelectric nanogenerator for sensing and energy harvesting applications. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 14665–14674. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, W.; Li, H.; Hui, D.; Gaff, M.; Lorenzo, R.; Corbi, I.; Corbi, O.; Ashraf, M. Effects of chemical modification and nanotechnology on wood properties. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2021, 10, 978–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farid, T.; Rafiq, M.I.; Ali, A.; Tang, W. Transforming wood as next-generation structural and functional materials for a sustainable future. EcoMat 2022, 4, e12154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suppanucroa, N. Development and Characterization of Natural Rubber-Cellulose Sponge. Master’s Thesis, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.; Shi, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, R.; Shi, L.; Jin, Y.; Qing, W.; Tang, C.; Wang, P. Solar-assisted fast cleanup of heavy oil spills using a photothermal sponge. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 9192–9199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, X.; Tang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Scalable fabrication of efficient and recycling wood residue-derived sponge for crude oil adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 441, 129979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, W.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Cao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, C.; Ho, S.-H. Natural sponge-like wood-derived aerogel for solar-assisted adsorption and recovery of high-viscous crude oil. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 400, 125865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jin, P.; Wang, M.; Wu, G.; Dong, C.; Wu, A. Biomass-Derived Porous Carbonaceous Aerogel as Sorbent for Oil-Spill Remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32862–32868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatum, O.; Steiner, S.A., III; Griffin, J.S.; Shi, W.; Plata, D.L. Flexible, Mechanically Durable Aerogel Composites for Oil Capture and Recovery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Zhang, R.; Ge, W.; Xie, A.; Chang, Z.; Tian, S.; Zhou, Z.; Yan, Y. 3D macroscopic superhydrophobic magnetic porous carbon aerogel converted from biorenewable popcorn for selective oil-water separation. Mater. Des. 2018, 139, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.T.; Feng, J.; Le, N.T.; Le, A.T.T.; Hoang, N.; Tan, V.B.C.; Duong, H.M. Cellulose Aerogel from Paper Waste for Crude Oil Spill Cleaning. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 18386–18391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Huang, G.; Qiu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Gao, J. Cost-Effective Reduced Graphene Oxide-Coated Polyurethane Sponge As a Highly Efficient and Reusable Oil-Absorbent. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 10018–10026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceylan, D.; Dogu, S.; Karacik, B.; Yakan, S.D.; Okay, O.S.; Okay, O. Evaluation of Butyl Rubber as Sorbent Material for the Removal of Oil and Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons from Seawater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3846–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Chen, P. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic hybrid foam of graphene and carbon nanotube for selective removal of oils or organic solvents from the surface of water. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10660–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Li, H.; Wang, K.; Wei, J.; Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, L.; Cao, A.; Zhu, H.; Wu, D. Recyclable carbon nanotube sponges for oil absorption. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 4798–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Zhou, Y.; Ling, Z.; Qiu, J. Synthesis of a carbon nanofiber/carbon foam composite from coal liquefaction residue for the separation of oil and water. Carbon 2013, 59, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-P.; Wang, H.-N.; Kang, F.-Y.; Wang, L.-N.; Inagaki, M. Sorption capacity of exfoliated graphite for oils-sorption in and among worm-like particles. Carbon 2004, 42, 2603–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, M.; Kawahara, A.; Konno, H. Sorption and recovery of heavy oils using carbonized fir fibers and recycling. Carbon 2002, 40, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-Q.; Huang, J.-Q.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, W.-L.; Wei, F. Improvement of oil adsorption performance by a sponge-like natural vermiculite-carbon nanotube hybrid. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011, 53, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husseien, M.; Amer, A.; El-Maghraby, A.; Hamedallah, N. A comprehensive characterization of corn stalk and study of carbonized corn stalk in dye and gas oil sorption. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2009, 86, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.; Rahmah, A.U.; Man, Z. Physicochemical and sorption characteristics of Malaysian Ceiba pentandra (L.) Gaertn. as a natural oil sorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 177, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, H.-J.; Kappl, M. Normal capillary forces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 146, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Sanchez, J.F.; Palacio-Perez, A.; Suarez-Dominguez, E.J.; Diaz-Zavala, N.P.; Izquierdo-Kulich, E. Evaluation of surface tension modifiers for crude oil transport through porous media. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 192, 107319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, E.K.; Liu, J.; Lv, X. Surface Engineering Materials of Superhydrophobic Sponges for Oil/Water Separation: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 2353–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjahro, N.; Yunus, R.; Abdullah, L.C.; Rashid, S.A.; Asis, A.J.; Akhlisah, Z.N. Recent advances in the application of cellulose derivatives for removal of contaminants from aquatic environments. Cellulose 2021, 28, 7521–7557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, F.; Lin, M.; Zhang, J.; Lv, Q.; Dong, Z. Wood-Inspired Compressible Superhydrophilic Sponge for Efficient Removal of Micron-Sized Water Droplets from Viscous Oils. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 11789–11802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Thabit, N.Y.; Uwaezuoke, O.J.; Abu Elella, M.H. Superhydrophobic nanohybrid sponges for separation of oil/water mixtures. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.-Y.; Jing, X.; Politowicz, A.L.; Chen, E.; Huang, H.-X.; Turng, L.-S. Highly compressible ultra-light anisotropic cellulose/graphene aerogel fabricated by bidirectional freeze drying for selective oil absorption. Carbon 2018, 132, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Yan, N.; Cai, Z.; Yu, Y. Ultralight, hydrophobic, anisotropic bamboo-derived cellulose nanofibrils aerogels with excellent shape recovery via freeze-casting. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, P.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, F. Sustainable, Reusable, and Superhydrophobic Aerogels from Microfibrillated Cellulose for Highly Effective Oil/Water Separation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 6409–6416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J. Roles of silanes and silicones in forming superhydrophobic and superoleophobic materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13677–13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Yang, J.; Fang, X.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wu, H.; Guo, S. Facile fabrication of wood-inspired aerogel from chitosan for efficient removal of oil from Water. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprea, M.; Voicu, S.I. Recent advances in composites based on cellulose derivatives for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 247, 116683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, D.N.-S. Cellulose and its derivatives: Structures, reactions, and medical uses. In Polysaccharides in Medicinal Applications; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2017; pp. 87–105. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.; Wei, B.; Liang, S.; Wang, R.; Ji, Q.; Hu, G.; Li, W.; He, L.; Yu, J.; Zhu, H.; et al. Highly nanostructured and carboxylated wood aerogel-based adsorption membrane reconstructed by grafting of polyacrylic acid for efficient removal of heavy-metal ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Fang, X.; Sun, J.; Xia, R.; Guo, H.; Liu, Y. Processing wood into a phase change material with high solar-thermal conversion efficiency by introducing stable polyethylene glycol-based energy storage polymer. Energy 2022, 254, 124206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, R.K.; Padil, V.V.; Škodová, M.; Wacławek, S.; Černík, M.; Agarwal, S. Hierarchically porous bio-based sustainable conjugate sponge for highly selective oil/organic solvent absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2100640. [Google Scholar]
- Deki, S.; Béléké, A.B.; Kotani, Y.; Mizuhata, M. Synthesis of tungsten oxide thin film by liquid phase deposition. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 123, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janesch, J.; Arminger, B.; Gindl-Altmutter, W.; Hansmann, C. Superhydrophobic coatings on wood made of plant oil and natural wax. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 148, 105891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Yang, W.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X. Preparation of highly hydrophobic and anti-fouling wood using poly(methylhydrogen)siloxane. Cellulose 2018, 25, 7341–7353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zheng, R.; Chen, J.; Huang, H. Investigation on the determination of lignocellulosics components by NREL method. Chin. J. Anal. Lab. 2010, 29, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Zhao, L.; Yu, J.; Liu, G. The effect of calcination temperature on the microstructure and photocatalytic activity of TiO2-based composite nanotubes prepared by an in situ template dissolution method. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 6597–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kuang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Burgert, I.; Keplinger, T.; Gong, A.; Li, T.; Berglund, L.; Eichhorn, S.J.; Hu, L. Structure–property–function relationships of natural and engineered wood. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 642–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artus, G.R.J.; Jung, S.; Zimmermann, J.; Gautschi, H.; Marquardt, K.; Seeger, S. Silicone Nanofilaments and Their Application as Superhydrophobic Coatings. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2758–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.T.; Kettunen, M.; Ras, R.H.A.; Ikkala, O. Hydrophobic Nanocellulose Aerogels as Floating, Sustainable, Reusable, and Recyclable Oil Absorbents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 1813–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, K.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H.; Liu, Z.; Dai, J.; Andreasen, J.; Hu, L. A cellulose based hydrophilic, oleophobic hydrated filter for water/oil separation. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 13296–13299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Li, F.; Liu, X. Liquid-phase deposition functionalized wood sponges for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 19075–19092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, O.; Hädicke, E.; Koltzenburg, S.; Müller-Plathe, F. Hydrophilicity and Lipophilicity of Cellulose Crystal Surfaces. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 3822–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettunen, M.; Silvennoinen, R.J.; Houbenov, N.; Nykänen, A.; Ruokolainen, J.; Sainio, J.; Pore, V.; Kemell, M.; Ankerfors, M.; Lindström, T.; et al. Photoswitchable Superabsorbency Based on Nanocellulose Aerogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 510–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Tong, Z.; Wang, C. Renewable Lignin-Based Xerogels with Self-Cleaning Properties and Superhydrophobicity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1729–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yi, H.; Wang, C. Oil Absorbents Based on Melamine/Lignin by a Dip Adsorbing Method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3012–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donath, S.; Militz, H.; Mai, C. Wood modification with alkoxysilanes. Wood Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Gu, B.; Pennefather, M.P.; Nguyen, T.X.; Phan-Thien, N.; Duong, H.M. Cotton aerogels and cotton-cellulose aerogels from environmental waste for oil spillage cleanup. Mater. Des. 2017, 130, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.-L.; Ma, C.; Yuan, Q.; Mai, T.; Ma, M.-G. Novel Ti3C2Tx MXene wrapped wood sponges for fast cleanup of crude oil spills by outstanding Joule heating and photothermal effect. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 606, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, F.; Alhabeb, M.; Hatter, C.B.; Anasori, B.; Hong, S.M.; Koo, C.M.; Gogotsi, Y. Electromagnetic interference shielding with 2D transition metal carbides (MXenes). Science 2016, 353, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Luo, F.; Qiang, Z.; Ren, J. Solar-assisted, fast, and in situ recovery of crude oil spill by a superhydrophobic and photothermal sponge. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21175–21185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, L.; Yu, W.; Sun, Z.; Guan, J.; Zhang, J.; Lin, J.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Murugadoss, V.; et al. Low optical dosage heating-reduced viscosity for fast and large-scale cleanup of spilled crude oil by reduced graphene oxide melamine nanocomposite adsorbents. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 225402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Peng, G.; Chen, M.; Zhao, M.; He, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qin, Y.; Lin, S. Reduced graphene oxide composites and its real-life application potential for in-situ crude oil removal. Chemosphere 2020, 249, 126141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, X.; Yang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, T.; Qin, L.; Yu, Z.-Z. Photothermal hierarchical carbon nanotube/reduced graphene oxide microspherical aerogels with radially orientated microchannels for efficient cleanup of crude oil spills. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 570, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Shi, L.-A.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Yao, H.-B.; Zhu, Y.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.-W.; Wu, H.-A.; Yu, S.-H. Joule-heated graphene-wrapped sponge enables fast clean-up of viscous crude-oil spill. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, M.-B.; Wu, B.-H.; Yang, J.; Xu, Z.-K. Solar-driven self-heating sponges for highly efficient crude oil spill remediation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 8880–8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Cui, M.; Huang, R.; Su, R.; Qi, W.; He, Z. Polydopamine-Assisted Surface Coating of MIL-53 and Dodecanethiol on a Melamine Sponge for Oil–Water Separation. Langmuir 2020, 36, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wang, D.Y.; Wang, M.Z.; Dan, X.X.; Che, L.M.; Xu, H.H.; Zhou, H.; Liu, H.; Singh, L.; Wu, X.E. Functional photothermal sponges for efficient solar steam generation and accelerated cleaning of viscous crude-oil spill. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 204, 110203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Su, Y.; Fan, Q.; Li, Z.; Cui, W.; Yu, M.; Ning, X.; Ramakrishna, S.; Long, Y. Robust Graphene@PPS Fibrous Membrane for Harsh Environmental Oil/Water Separation and All-Weather Cleanup of Crude Oil Spill by Joule Heat and Photothermal Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 19377–19386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Lei, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, J.; Teng, L.; Chen, Z.; Lai, Y. Photothermal and Joule heating-assisted thermal management sponge for efficient cleanup of highly viscous crude oil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Sun, Q.; Li, Y.; Wu, T.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Huang, F. Solar-heating crassula perforata-structured superoleophilic CuO@ CuS/PDMS nanowire arrays on copper foam for fast remediation of viscous crude oil spill. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 19476–19482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Huang, S.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Xu, Z. Compressible Carbon Sponges from Delignified Wood for Fast Cleanup and Enhanced Recovery of Crude Oil Spills by Joule Heat and Photothermal Effect. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2006806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, G.; Pei, Y.; Pastel, G.; Jia, C.; Song, J.; Mi, R.; Yang, B.; Das, S.; et al. Bioinspired Solar-Heated Carbon Absorbent for Efficient Cleanup of Highly Viscous Crude Oil. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1900162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Lai, X.; Su, X.; Liang, T.; Zeng, X. Thiolated graphene-based superhydrophobic sponges for oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Jia, Y.; Xiao, L.; Chen, H.; Zhao, K.; Chen, Y.; Ma, Y. Three dimensional cross-linked and flexible graphene composite paper with ultrafast electrothermal response at ultra-low voltage. Carbon 2019, 154, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Lao, J.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Gao, J.; Wan, Y.; Sun, X.; Guo, R.; Luo, J. Fast and all-weather cleanup of viscous crude-oil spills with Ti 3 C 2 TX MXene wrapped sponge. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 20162–20167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yi, G.; Fu, Z.; Yu, H.; Chen, S.; Quan, X. Vertically Aligned Janus MXene-Based Aerogels for Solar Desalination with High Efficiency and Salt Resistance. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13196–13207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Kang, S.; Ma, J.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wei, A.; Xiang, X.; Wei, L.; Gu, J. Ultraflexible and mechanically strong double-layered aramid nanofiber–Ti3C2Tx mxene/silver nanowire nanocomposite papers for high-performance electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8368–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Niu, J.; Heon, M.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-dimensional nanocrystals produced by exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. In MXenes; Jenny Stanford Publishing: London, UK, 2011; pp. 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Shi, L.; Wang, P.J. MXene Ti3C2: An effective 2D light-to-heat conversion material. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3752–3759. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Chen, C.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Kierzewski, I.; Liu, B.; He, S.; et al. Highly Compressible, Anisotropic Aerogel with Aligned Cellulose Nanofibers. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, O.; Suopajärvi, T.; Österberg, M.; Liimatainen, H. Hydrophobic, Superabsorbing Aerogels from Choline Chloride-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent Pretreated and Silylated Cellulose Nanofibrils for Selective Oil Removal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 25029–25037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Cai, Z.; Gong, S. Green synthesis of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA)–cellulose nanofibril (CNF) hybrid aerogels and their use as superabsorbents. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 3110–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Ren, W.; Gao, L.; Liu, B.; Pei, S.; Cheng, H.-M. Three-dimensional flexible and conductive interconnected graphene networks grown by chemical vapour deposition. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Jing, C.; Li, G.; Ling, S.; Wang, Z.; Lu, P.; Li, Q.; Dai, C.; Gao, S.; Chen, B.; et al. Wood-Derived Systems for Sustainable Oil/Water Separation. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, M.J. Preservation, protection and modification of wood composites. In Wood Composites; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2015; pp. 253–310. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Xu, M.; Shi, Q.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, L.; James, T.D. An upcycled wood sponge adsorbent for drinking water purification by solar steam generation. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 2559–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Z.; Lü, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Qiu, F. Recent progress and future prospects of oil-absorbing materials. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 27, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge-Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Ni, H.; Mu, H.; Zhang, M. Biomimetic superhydrophobic metal/nonmetal surface manufactured by etching methods: A mini review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 958095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge-Zhang, S.; Cai, T.; Yang, H.; Ding, Y.; Song, M. Biology and nature: Bionic superhydrophobic surface and principle. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1033514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ge-Zhang, S.; Mu, P.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Qiao, L.; Mu, H. Advances in Sol-Gel-Based Superhydrophobic Coatings for Wood: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
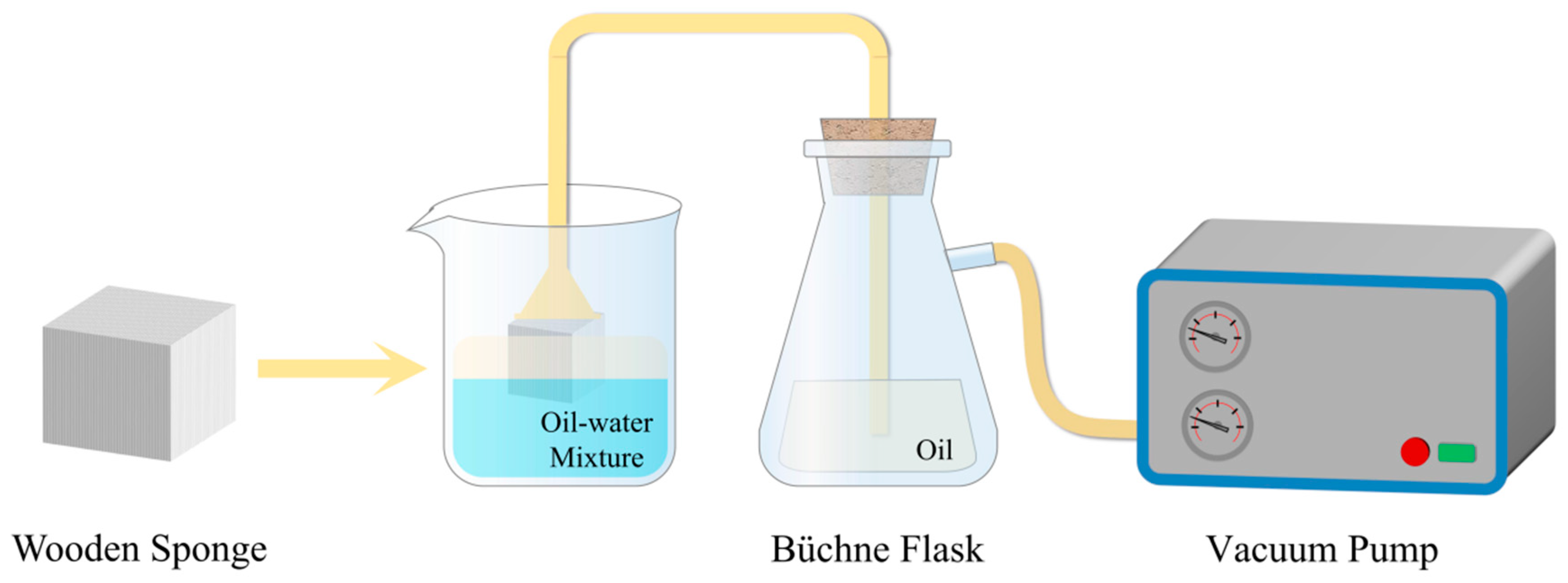
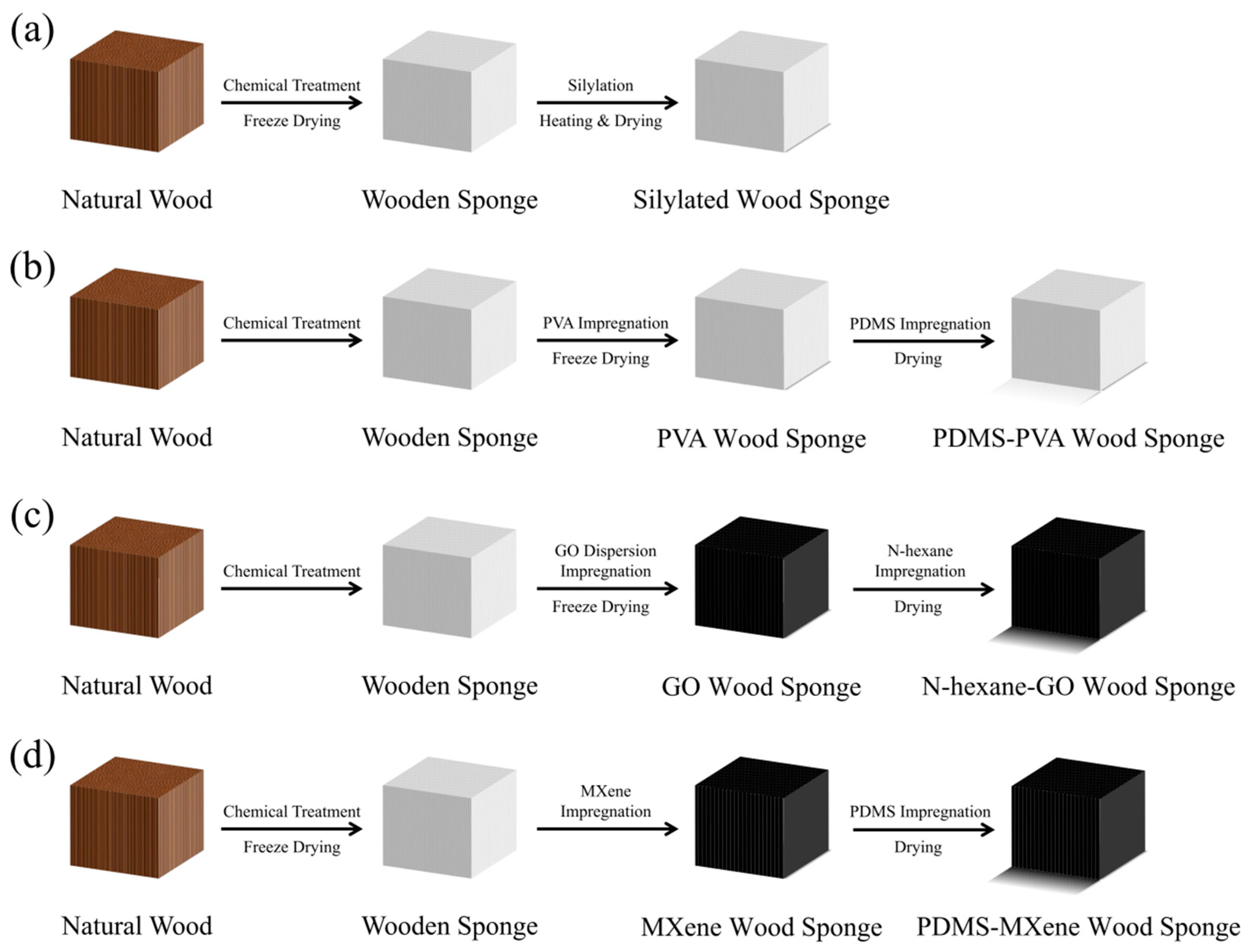
| Ref. | Material | Oil | Absorption Capacity | Porosity | WCA | Cycles of Reuse |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [59] | Modified wood sponge | Cuclohexane | 17,300 mg g−1 | 96.47% | 121.37° | More than 10 times |
| [74] | Carbonaceous aerogel | Peanut oil | 11,400 mg g−1 | Volume of 4.13 g cm−3 | 144.2° | Not reported |
| [75] | Cabot thermal wrap | Dichloromethane | 13,000 mg g−1 | 92.1% | 127.6° | More than 10 times |
| [75] | Aspen Aerogels Spaceloft | Dichloromethane | 16,000 mg g−1 | 86.1% | 130.9° | More than 10 times |
| [76] | Popcorn-based carbon aerogel | Chloroethane | 10,830 mg g−1 | Volume of 0.095 g cm−3 | 151.6° | Not reported |
| [18] | Chitin sponge | Phenisin | 58,000 mg g−1 | Pore sizes of 20–50 μm | 148.7° | Above 93% after 10 cycles |
| [39] | Spongy graphene | Toluene | 86,000 mg g−1 | Density of 12.5 mg cm−3 | 114.2° | Basically unchanged after 10 cycles |
| [77] | Cellulose aerogel | Ruby | 18,400 mg g−1 | 97.3% | 145° | Above 96.4% after 5 cycles |
| [78] | Polyurethane sponge | Chloroform | 160,000 mg g−1 | 99.3% | 127° | Basically unchanged after 50 cycles |
| [79] | Butyl rubber | Crude oil | 23,000 mg g−1 | Volume of 8.9 mL g−1 | Not reported | Above 70% after 8 cycles |
| [79] | Polypropylene | Fuel oil | 15,700 mg g−1 | Pore sizes of 10 μm | Not reported | Above 10% after 8 cycles |
| [19] | Modified PU sponge | Lubricate oil | 25,000 mg g−1 | Not reported | Not reported | More than 300 times |
| [39] | Graphene sponge | Castor oil | 75,000 mg g−1 | Pore sizes of 570–620 μm | 114.2° | More than 10 times |
| [80] | Graphene–CNT hybrid foam | Sesame oil | 105,000 mg g−1 | Pore sizes of 100 μm | 152.3° | More than 6 times |
| [81] | CNT sponge | Mineral oil | 126,000 mg g−1 | 98% | 156° | Above 96% after 10 cycles |
| [82] | CNF/carbon foam | Wash oil | 28,400 mg g−1 | 95% | 140° | Not reported |
| [83] | Exfoliate graphite | Heavy oil | 75,000 mg g−1 | 73–77% | Not reported | Not reported |
| [84] | Fir fibers | Grade-C oil | 15,000 mg g−1 | Not reported | Not reported | Above 78% after 8 cycles |
| [85] | EV/CNT | Diesel oil | 26,700 mg g−1 | Pore sizes of 5–10 nm | Not reported | Above 94% after 10 cycles |
| [81] | CNT sponges | Vegetable oil | 130,100 mg g−1 | Density of 5.8 mg cm−3 | Not reported | More than 10 times |
| [81] | CNT sponges | Vegetable oil | 32,300 mg g−1 | Density of 25.5 mg cm−3 | Not reported | More than 10 times |
| [86] | Corn stalk | Diesel oil | 8600 mg g−1 | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported |
| [87] | Kapok | Diesel oil | 36,700 mg g−1 | Pore sizes of 16.5 μm | 102° | Basically unchanged after 15 cycles |
| Ref. | Preparation Method | Wood Sponge Species | WCA | Absorption Capacity | Compression | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [94] | CVD | Cellulose/graphene aerogel | 153° | 80–197 | Compressible to 90% | Strong hydrophobic ability, diverse materials, and good mechanical properties | Uneven deposition and harsh reaction conditions |
| [143] | Silylated cellulose fibers | 142° | 51–142.9 | Compressible in diesel oil | |||
| [53] | Silylated wood sponge | 151° | 16–41 | Compressible to 60% | |||
| [17] | Silylated nanocellulose sponge | 136° | 49–102 | Compressible to 96% | |||
| [113] | LPD | Superhydrophobic wood sponge | 159° | 23–60 | Compressible | Simple treatment process, mild reaction conditions, uniform deposition; durability and accurate quantification | Slow reaction speed and low product purity |
| [96] | Superhydrophobic microfibrillated cellulose aerogel | 151.8° | 116–260 | Compressible | |||
| [73] | Utilizing solar energy and light energy | Graphene–wood sponge | 134.2° | 7.28 | Compressible to 90% | Rare radial pore structure; excellent compressibility, recyclability, and high adsorption rate | Complex technology, stability problems, and high cost |
| [144] | Methyltrichlorosilane treated PVA-CNF aerogel | 150.2° | 44–96 | Compressible to 80% | |||
| [145] | CNT sponge | 156° | 87–176 | Compressible in ethanol | |||
| [144] | PVA/cellulose nanofibril aerogels | Not reported | 44–96 | Compressible |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Cai, T.; Ge-Zhang, S.; Mu, P.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J. Wood Sponge for Oil–Water Separation. Polymers 2024, 16, 2362. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162362
Zhang C, Cai T, Ge-Zhang S, Mu P, Liu Y, Cui J. Wood Sponge for Oil–Water Separation. Polymers. 2024; 16(16):2362. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162362
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Chang, Taoyang Cai, Shangjie Ge-Zhang, Pingxuan Mu, Yuwen Liu, and Jingang Cui. 2024. "Wood Sponge for Oil–Water Separation" Polymers 16, no. 16: 2362. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162362
APA StyleZhang, C., Cai, T., Ge-Zhang, S., Mu, P., Liu, Y., & Cui, J. (2024). Wood Sponge for Oil–Water Separation. Polymers, 16(16), 2362. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162362






