Optimization Design of a Multi-String Standing Wave Electrospinning Apparatus Based on Electric Field Simulations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PVA Solution
2.3. Multi-String Standing Wave Electrospinning Apparatus
2.4. Electric Field Simulation
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Process Parameters Optimization Based on Electric Fields Simulations
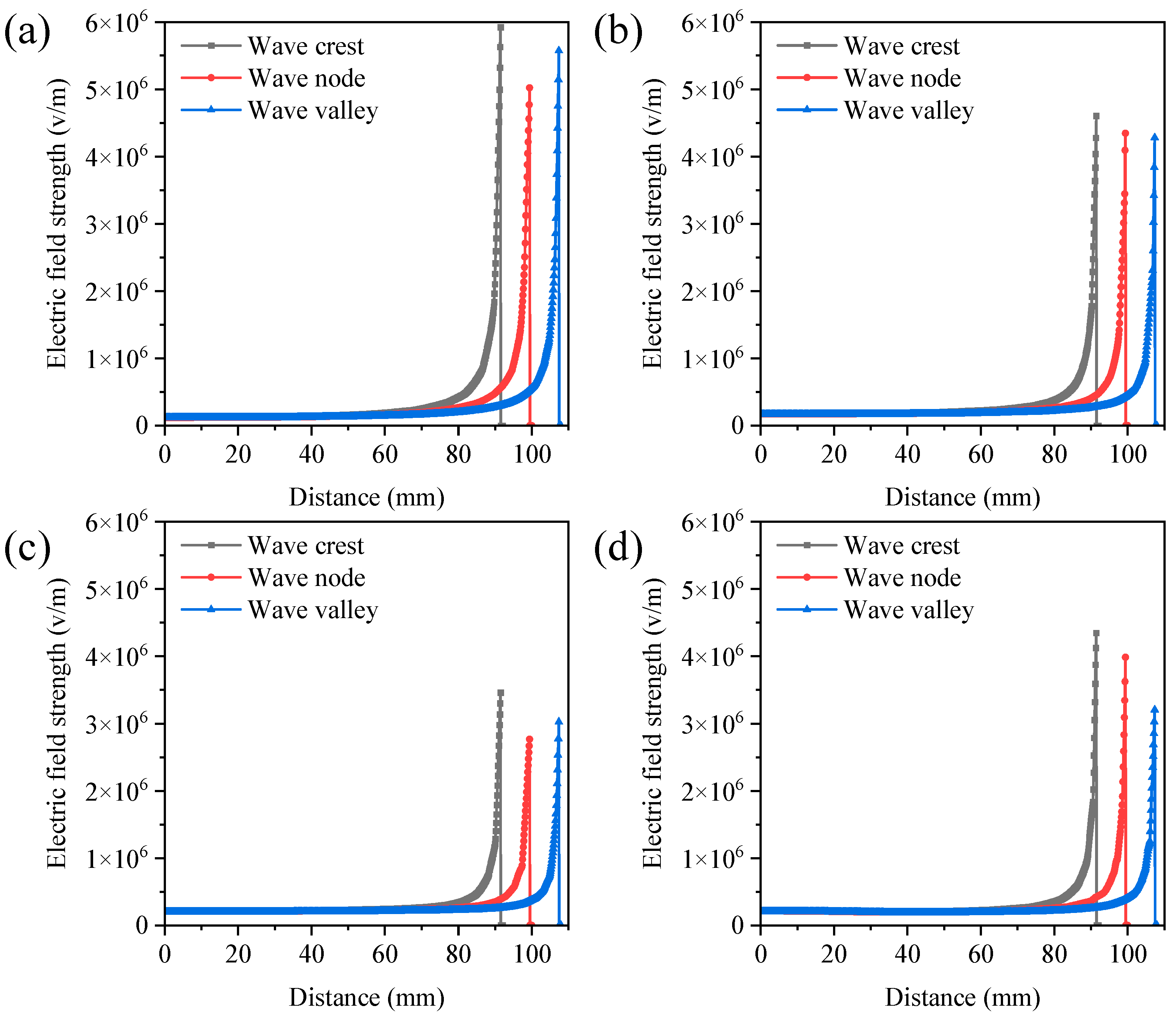
3.1.1. Parallel Spacing of Strings
3.1.2. The Number of Strings
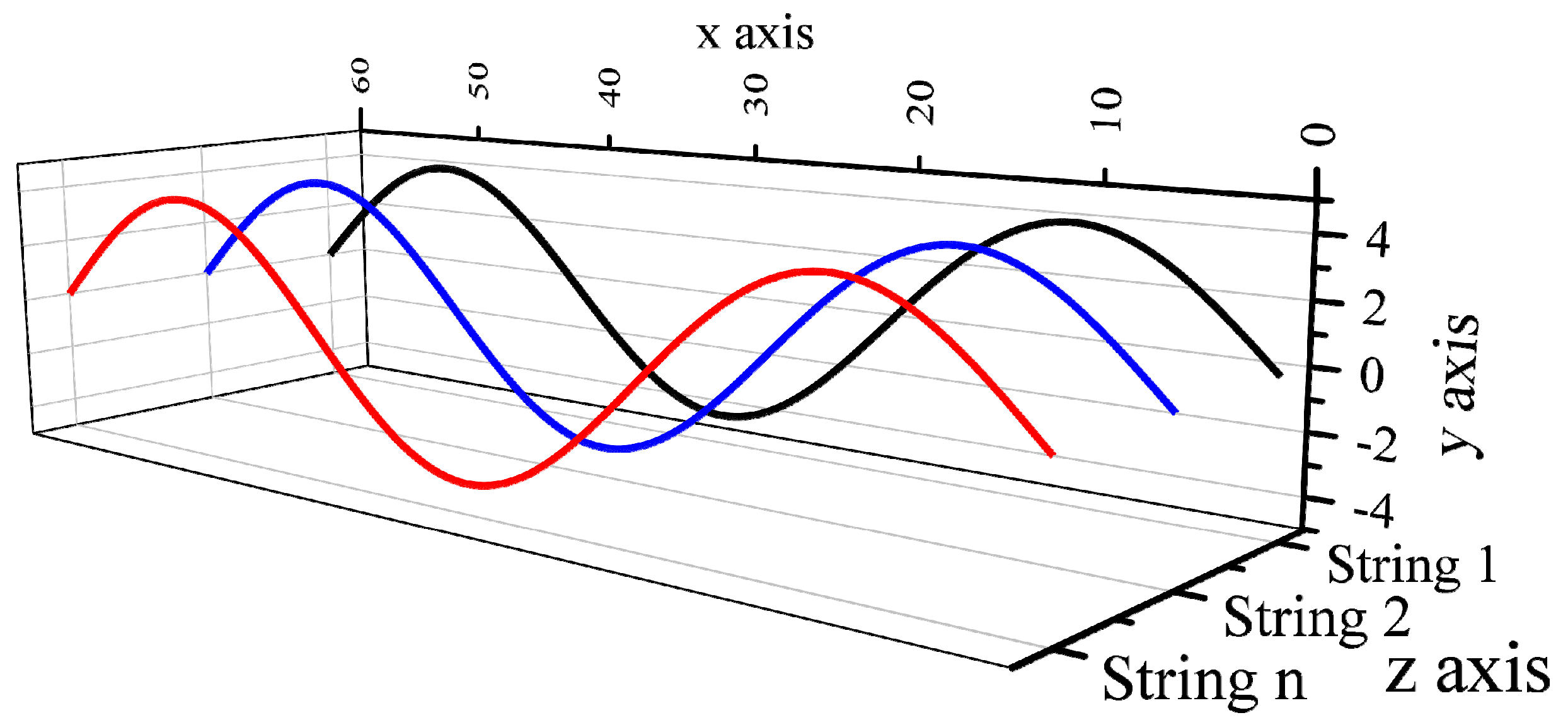
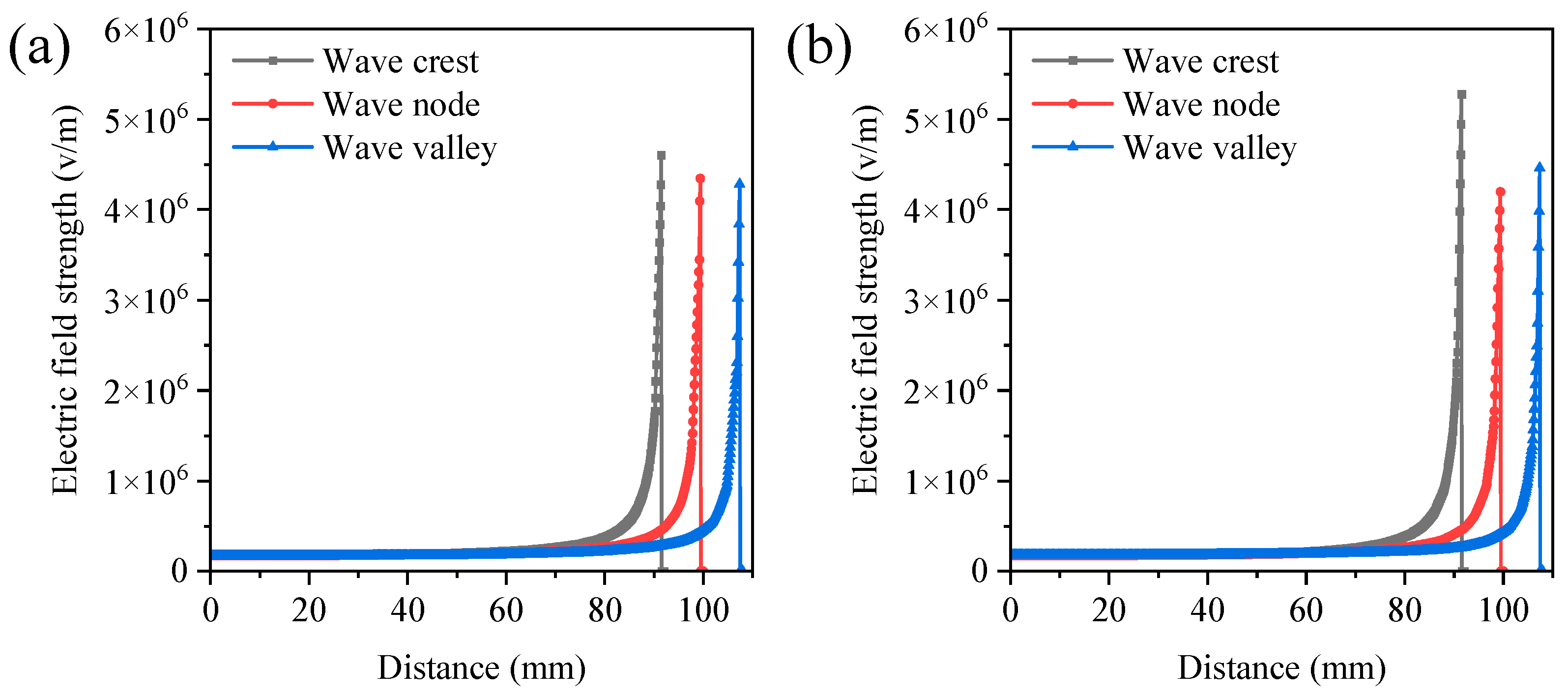
3.1.3. Phase Difference in String Standing Waves
3.2. Nanofiber Quality and Production of Multi-String Standing Wave Electrospinning
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Li, H.; Wei, B.; Yang, W. Electrospinning on a plucked string. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Xie, J.; Liao, J.; Zhang, T.; Lin, S.; Lin, Y. Nanomaterials and bone regeneration. Bone Res. 2015, 3, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaf, S.S.; El-Shafei, A.M.; Refaie, R.; Gibriel, A.A.; Abdel-Sattar, R. Antibacterial and wound healing properties of cellulose acetate electrospun nanofibers loaded with bioactive glass nanoparticles; in-vivo study. Cellulose 2022, 29, 4565–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Jin, G.; Li, L.; Li, K.; Srinivasan, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chen, J. Multi-functional electrospun nanofibres for advances in tissue regeneration, energy conversion & storage, and water treatment. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 1225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Low, Z.-X.; Xie, Z.; Wang, H. TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibers: A Renewable Nanomaterial for Environmental and Energy Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2001180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Reuveny, A.; Reeder, J.; Lee, S.; Jin, H.; Liu, Q.; Yokota, T.; Sekitani, T.; Isoyama, T.; Abe, Y. A transparent bending-insensitive pressure sensor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rianjanu, A.; Fauzi, F.; Triyana, K.; Wasisto, H.S. Electrospun Nanofibers for Quartz Crystal Microbalance Gas Sensors: A Review. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 9957–9975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yan, B.; Liu, B.; Gu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Shang, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, S.; Lan, J. Aminated Polyacrylonitrile Nanofiber Membranes for the Removal of Organic Dyes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeongan, C.; Byeong Joon, Y.; Gwi-Nam, B.; Jae Hee, J. Herbal Extract Incorporated Nanofiber Fabricated by an Electrospinning Technique and its Application to Antimicrobial Air Filtration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 25313–25320. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, E.; Sabantina, L.; Weber, M.O.; Finsterbusch, K.; Ehrmann, A. Preliminary Study of Ultrasonic Welding as a Joining Process for Electrospun Nanofiber Mats. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-C.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wu, T.-H.; Tseng, C.-H.; Yen, F.-L. Myricetin Nanofibers Enhanced Water Solubility and Skin Penetration for Increasing Antioxidant and Photoprotective Activities. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.L.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.D.; Sun, B.; Zhang, J.C.; Long, Y.Z. Needleless electrospinning for large scale production of ultrathin polymer fibres. Mater. Res. Innov. 2014, 18, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Dong, R.H.; Yan, X.; Yu, G.F.; You, M.H.; Ning, X.; Long, Y.Z. Recent advances in needleless electrospinning of ultrathin fibers: From academia to industrial production. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, W.; Yi, B. Comparative Study of Traditional Single-Needle Electrospinning and Novel Spiral-Vane Electrospinning: Influence on the Properties of Poly(caprolactone)/Gelatin Nanofiber Membranes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 847800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Ang, K.K.J.; He, J. Needle-disk electrospinning inspired by natural point discharge. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, B.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Ren, L.; Jiao, J.; Zhuang, L.; Luo, J.; Jiang, L. Fabrication of Magnetic Nanofibers by Needleless Electrospinning from a Self-Assembling Polymer Ferrofluid Cone Array. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Ye, C.; Ahmed, A.; Xu, L. Batch preparation of nanofibers containing nanoparticles by an electrospinning device with multiple air inlets. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2023, 14, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; He, J.H.; Yu, J.Y. Bubble-electrospinning: A novel method for making nanofibers. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2008, 96, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Niu, H.; Lin, T.; Wang, X. Needleless electrospinning of nanofibers with a conical wire coil. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2009, 49, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kılıç, A.; Yıldırım, B.; İçoğlu, H.İ.; Türkoğlu, M.; Topalbekiroğlu, M. Production of continuous nanofiber bundles by multi parallel electrodes in needleless electrospinning. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 109025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Niu, H.; Shao, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, H.; Lin, T. Curved convex slot: An effective needleless electrospinning spinneret. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 11749–11758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Li, H.; Chen, M.; Cheng, L.; He, X.; Yang, W. String electrospinning based on the standing wave vibration. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 9518–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Yu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Xin, B.; Kan, C.W. Preparation and Characterization of Electrospun PAN/PSA Carbonized Nanofibers: Experiment and Simulation Study. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabu, G.T.V.; Dhurai, B. A Novel Profiled Multi-Pin Electrospinning System for Nanofiber Production and Encapsulation of Nanoparticles into Nanofibers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D.H. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.M.H.; Song, W.Y.; Kim, T.Y. Characterization of Spray Modes and Factors Affecting the Ionization Efficiency of Paper Spray Ionization. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 864184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Zhang, S.; Qin, X. High throughput of quality nanofibers via one stepped pyramid-shaped spinneret. Mater. Lett. 2013, 106, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoppey, N.M.; Bochinski, J.R.; Clarke, L.I.; Gorga, R.E. Edge electrospinning for high throughput production of quality nanofibers. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 345301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.G. Mass Production of Nanofibers from a Spiral Coil. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 821–822, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Niu, H.; Aslam, S.; Jabbar, A.; Rajput, A.W.; Lin, T. Needleless electrospinning using sprocket wheel disk spinneret. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 7567–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, I.; Wang, L.; Wang, X. Needleless Electrospinning from a Tube with an Embedded Wire Loop. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2019, 304, 1800588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriyanti, I.; Jauhari, J. Synthesis of polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) fibers using needleless electrospinning technique with straight wire electrode. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1166, 012012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prahasti, G.; Zulfi, A.; Munir, M.M. Needleless electrospinning system with wire spinneret: An alternative way to control morphology, size, and productivity of nanofibers. Nano Express 2020, 1, 010046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Liu, C.; Dong, J.; Fan, X.; Zhi, C.; Sun, R. Process investigation of nanofiber diameter based on linear needleless spinneret by response surface methodology. Polym. Test. 2022, 110, 107577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Spinning Method | Spinning Solution | Fiber Diameter | Spinning Voltage | Fiber Production | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pyramid-shaped spinneret electrospinning | PA-6 | 205 ± 84 nm | 55 kV | 2.30 g/h | [29] |
| Conical wire coil electrospinning | PVA | 327 ± 123 nm | 45 kV | 0.86 g/h | [21] |
| Edge electrospinning | PCL | 344 ± 67 nm | 55 kV | 0.68 g/h | [30] |
| Curved convex slot electrospinning | PVA | 556 nm | 50 kV | 0.76 g/h | [23] |
| Spiral coil electrospinning | PVA | 300 ± 110 nm | 45 kV | 2.94 g/h | [31] |
| Sprocket wheel disk electrospinning | PVA | 426 ± 89 nm | 50 kV | 2.09 g/h | [32] |
| Embedded wire loop electrospinning | PAN | 126 ± 79 nm | 28 kV | 0.48 g/h | [33] |
| Straight wire electrospinning | PVAc | 1.21 μm | 40 kV | / | [34] |
| Wire spinneret electrospinning | PVP | 1.3 μm | 40 kV | 0.34 g/h | [35] |
| Linear flume electrospinning | PAN | 171 ± 6.5 nm | 60 kV | / | [36] |
| Multi-string standing wave electrospinning | PVA | 178 ± 72 nm | 28 kV | 2.17 g/h | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Liang, J.; Tan, X.; Ding, J.; Xie, W.; Li, C.; Cai, Y. Optimization Design of a Multi-String Standing Wave Electrospinning Apparatus Based on Electric Field Simulations. Polymers 2024, 16, 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162330
Chen X, Liang J, Tan X, Ding J, Xie W, Li C, Cai Y. Optimization Design of a Multi-String Standing Wave Electrospinning Apparatus Based on Electric Field Simulations. Polymers. 2024; 16(16):2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162330
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaoqing, Jiahao Liang, Xiang Tan, Jiazheng Ding, Wenyu Xie, Changgang Li, and Yebin Cai. 2024. "Optimization Design of a Multi-String Standing Wave Electrospinning Apparatus Based on Electric Field Simulations" Polymers 16, no. 16: 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162330
APA StyleChen, X., Liang, J., Tan, X., Ding, J., Xie, W., Li, C., & Cai, Y. (2024). Optimization Design of a Multi-String Standing Wave Electrospinning Apparatus Based on Electric Field Simulations. Polymers, 16(16), 2330. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162330






