Experimental Investigations on Shear Thickening Fluids as “Liquid Body Armors”: Non-Conventional Formulations for Ballistic Protection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. STF Formulations Preparation
2.2.2. Rheological Investigations on the STF Formulations
2.2.3. Analysis of STF Performances at Impact with a Free-Falling Blunt Object (Dynamic Loading at Moderate Impact Speed)
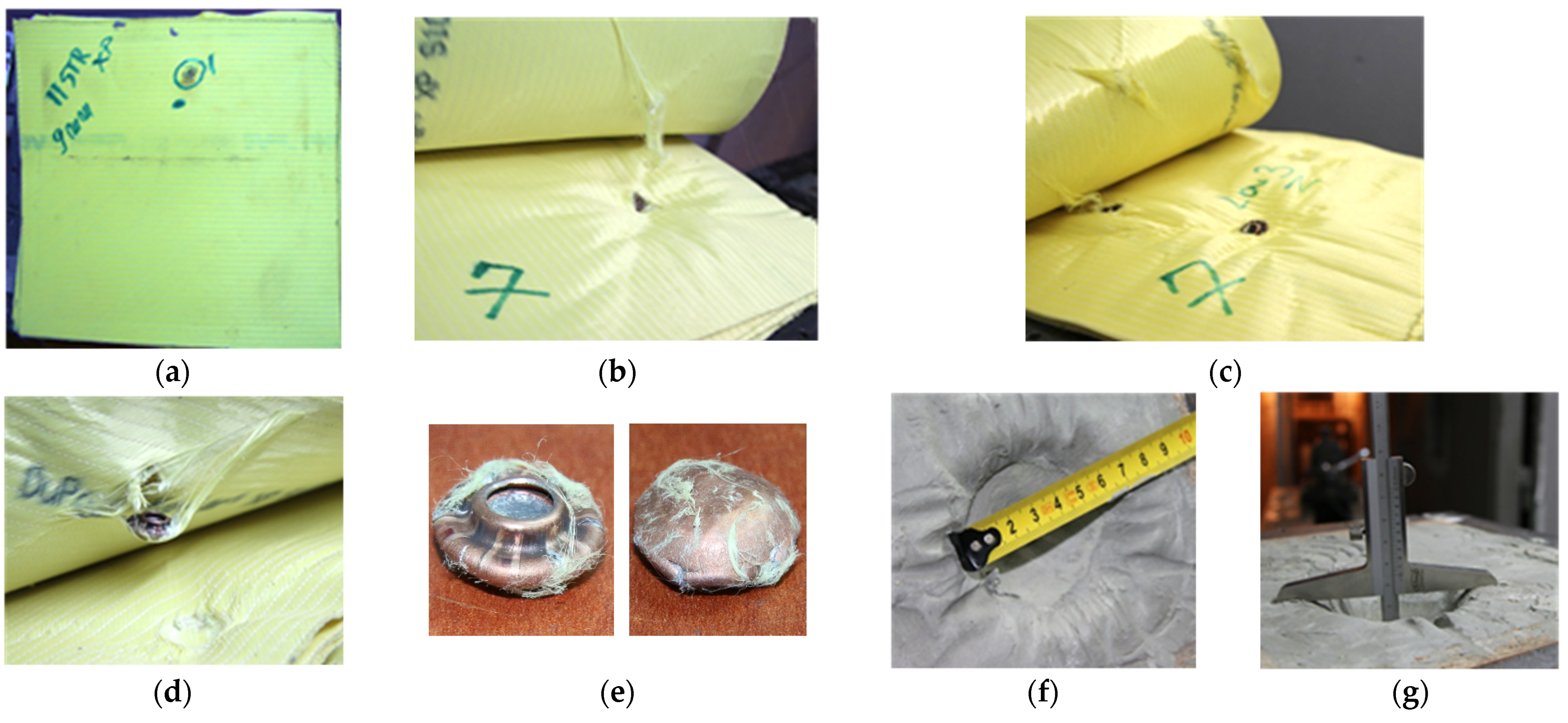
2.2.4. Assessment of Kinetic Energy Absorption at Impact with Standard Shrapnel
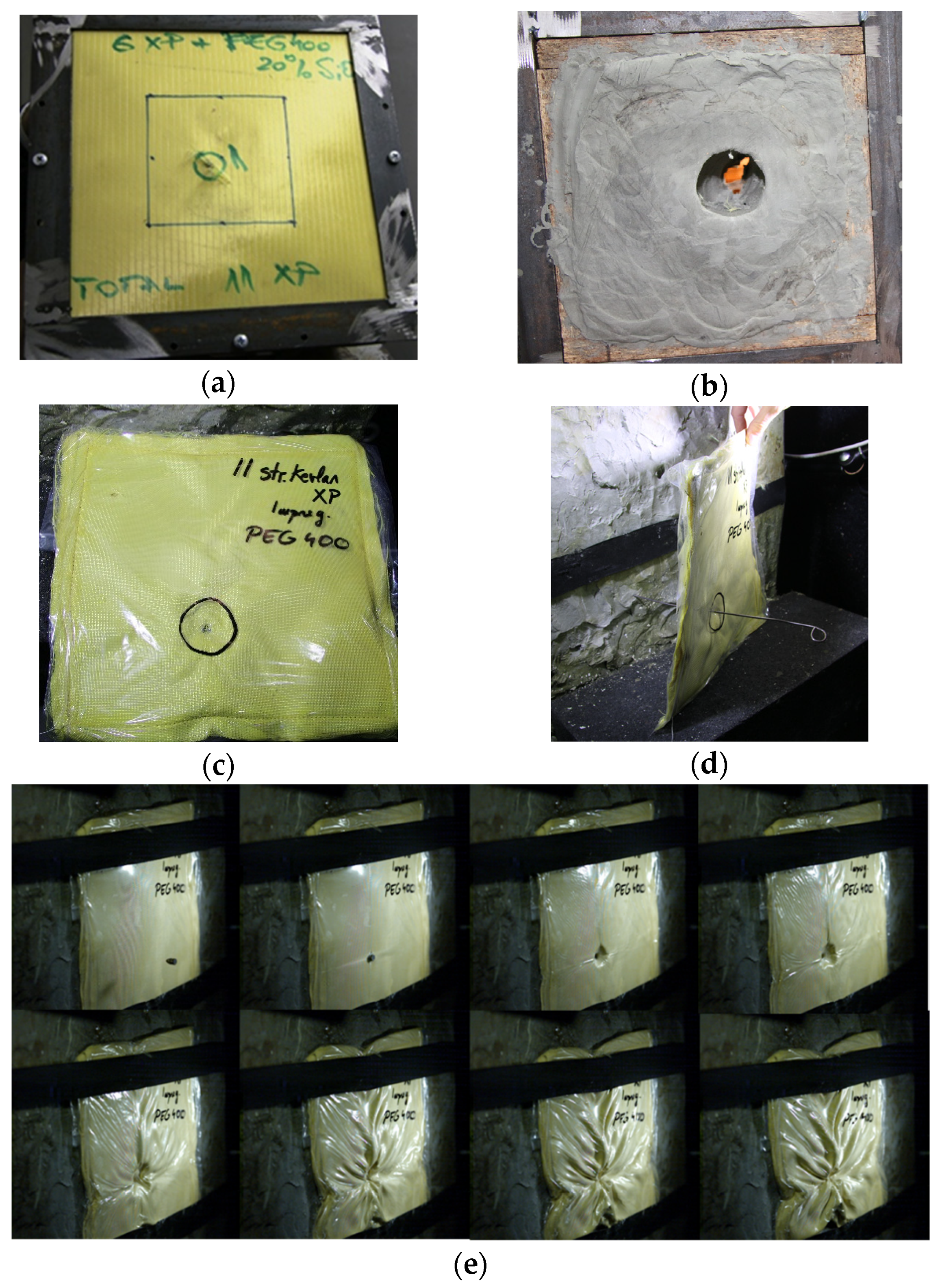
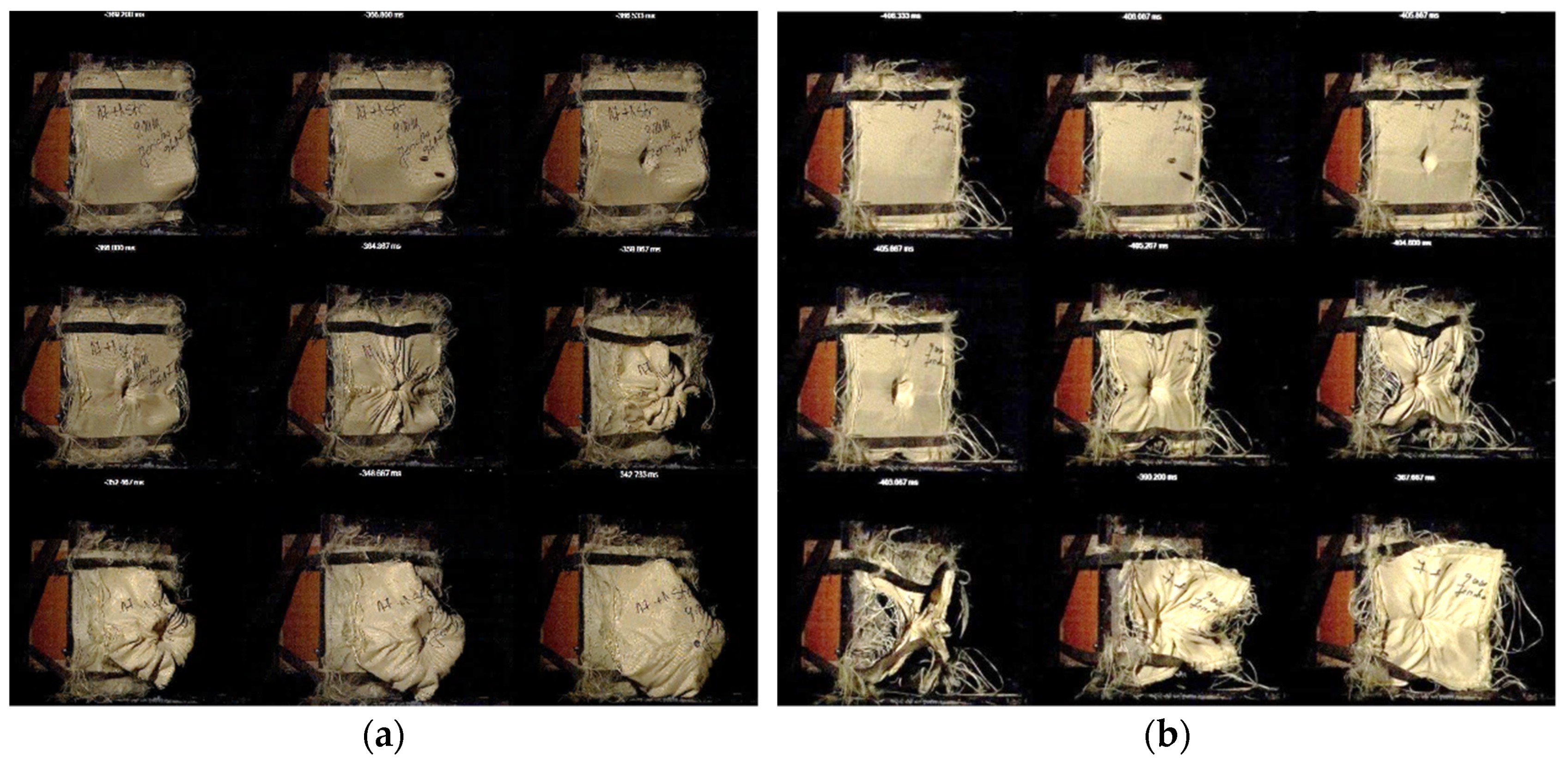
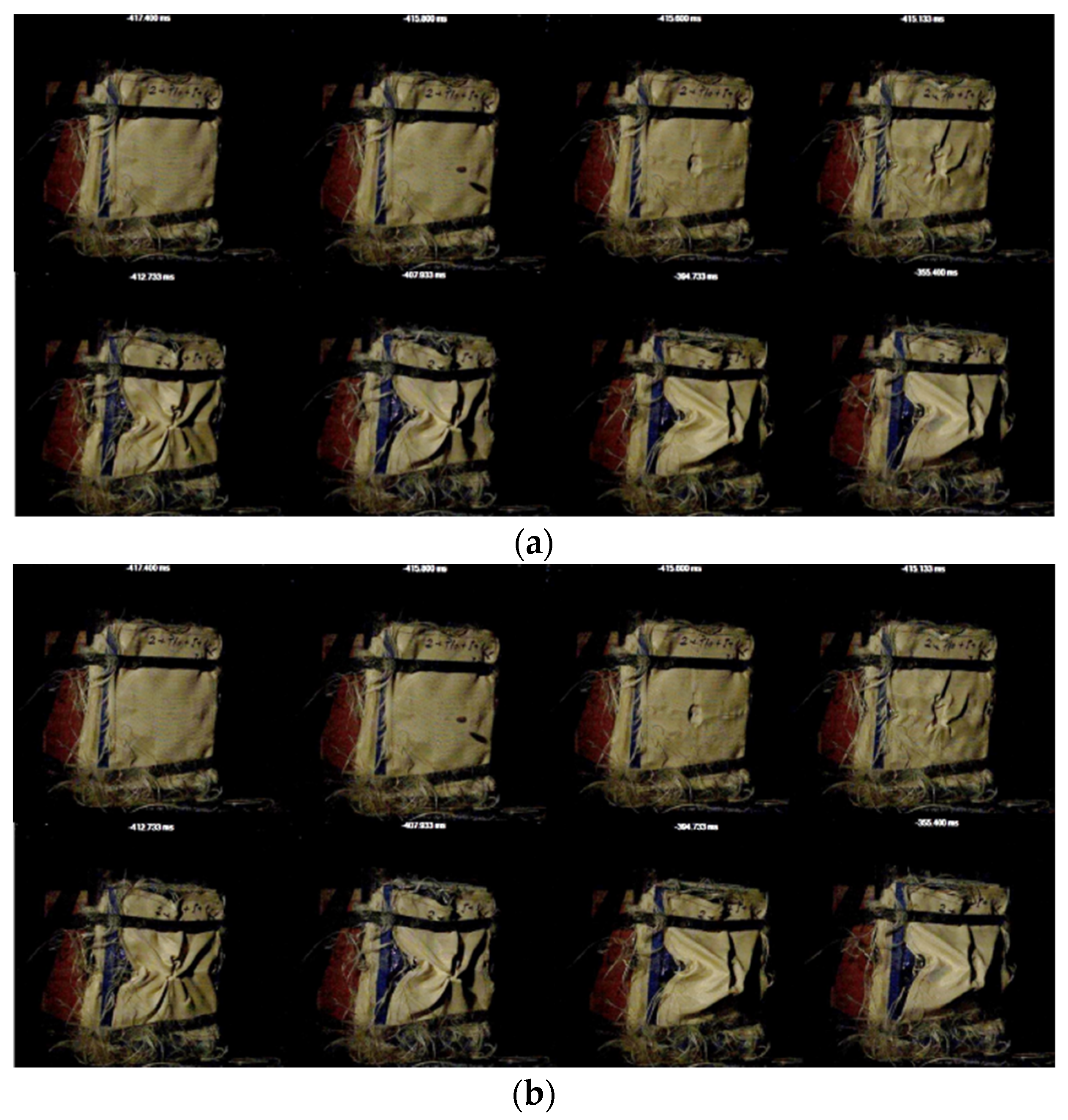
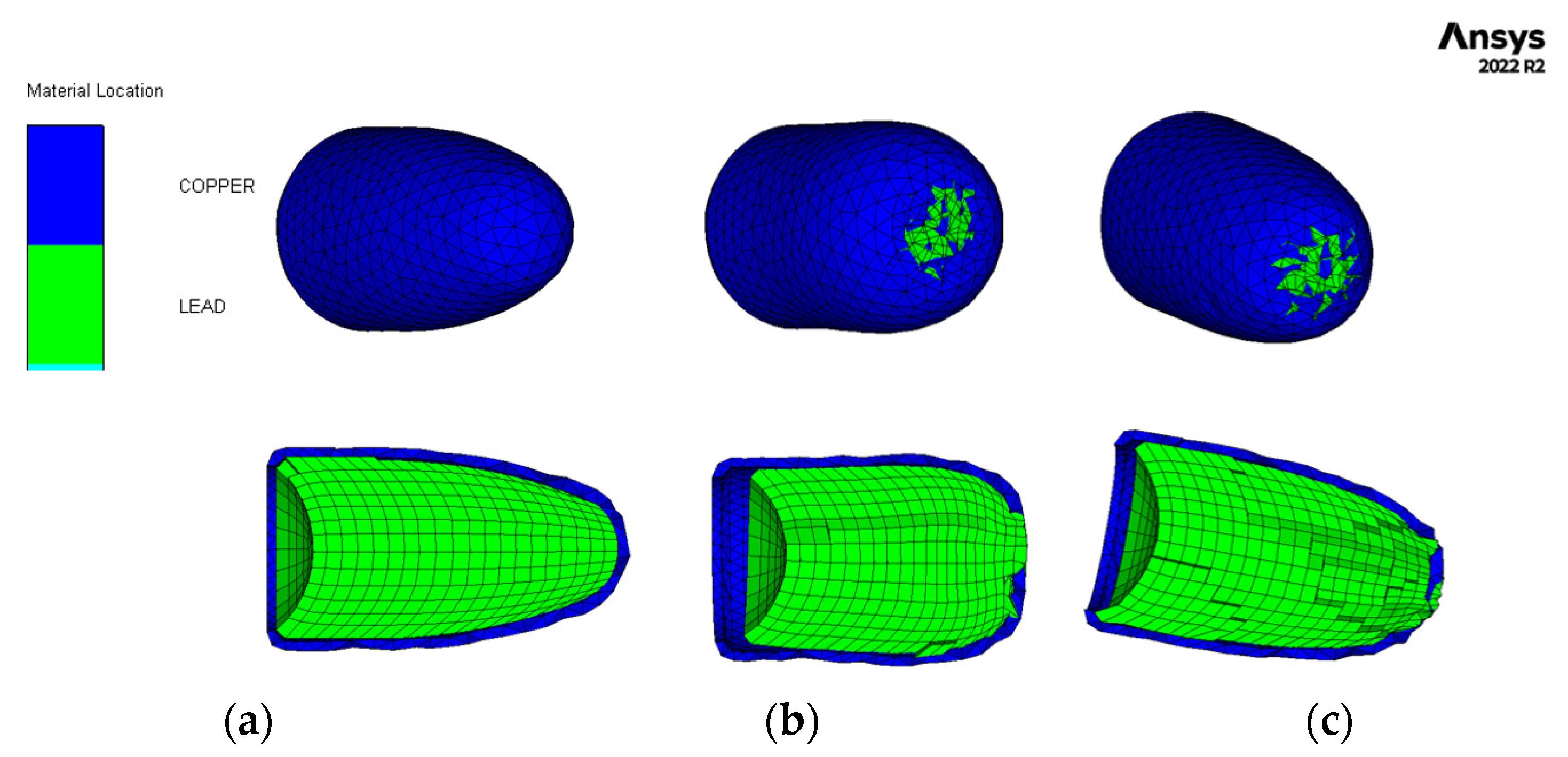
2.2.5. High-Velocity Impact Tests with 9 mm Bullet
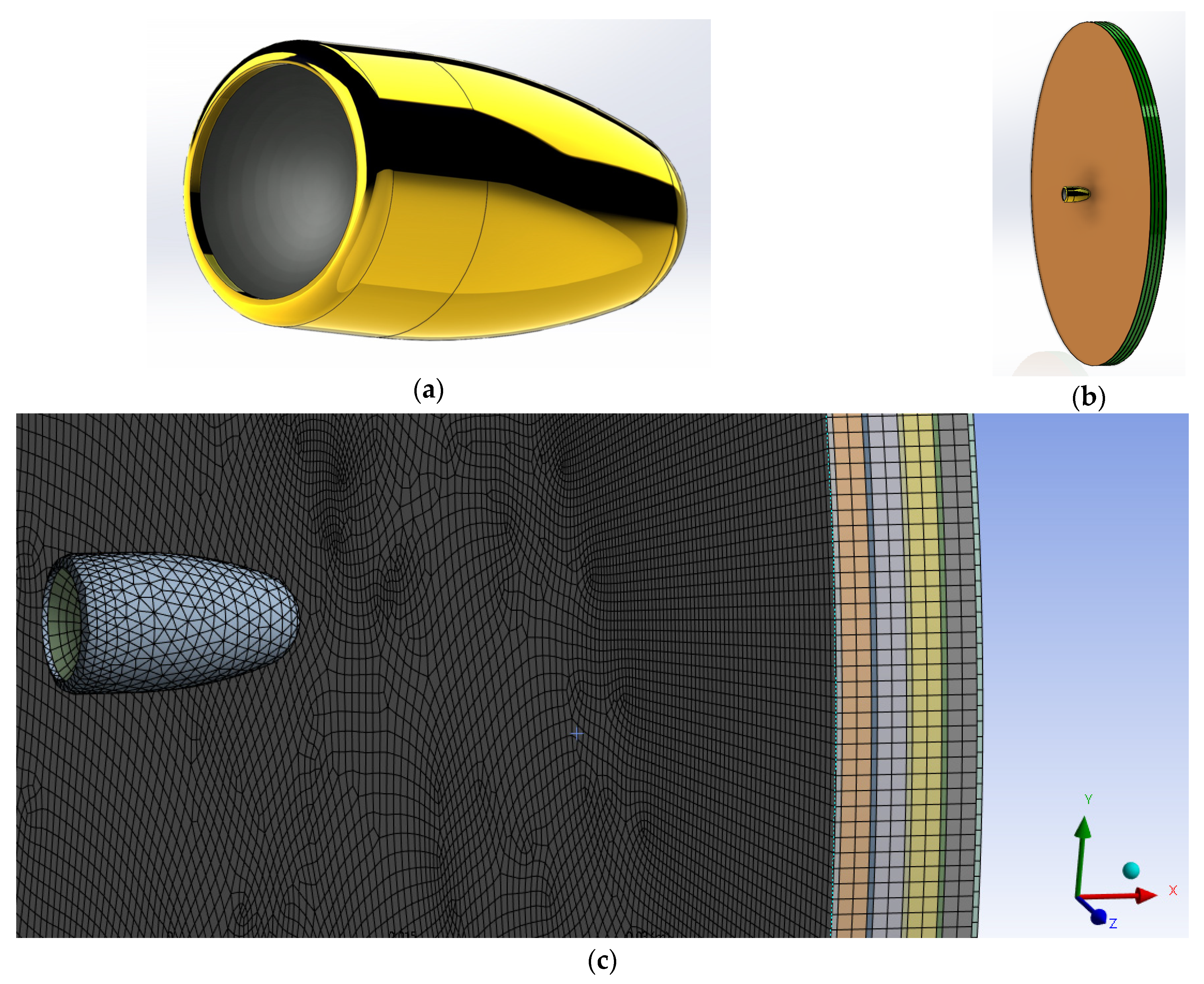
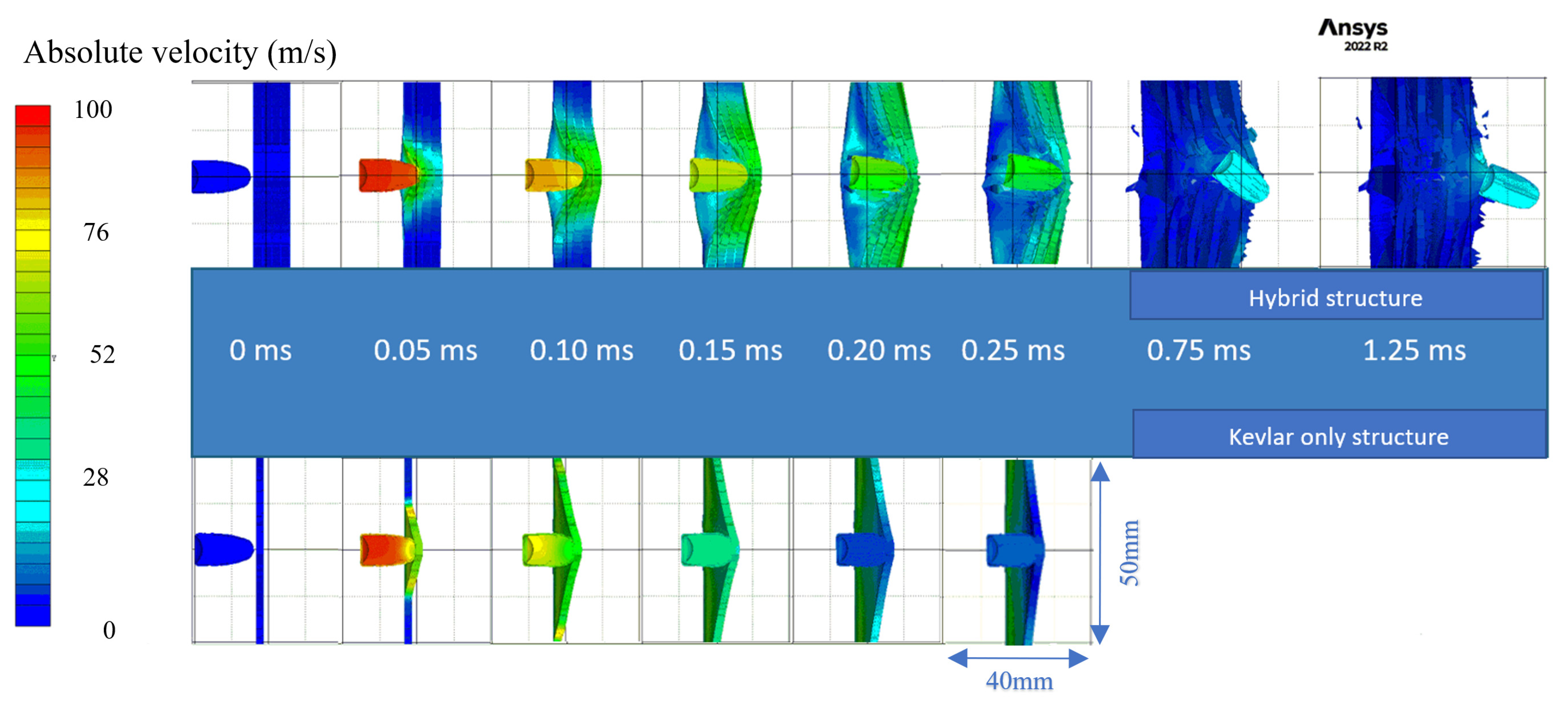
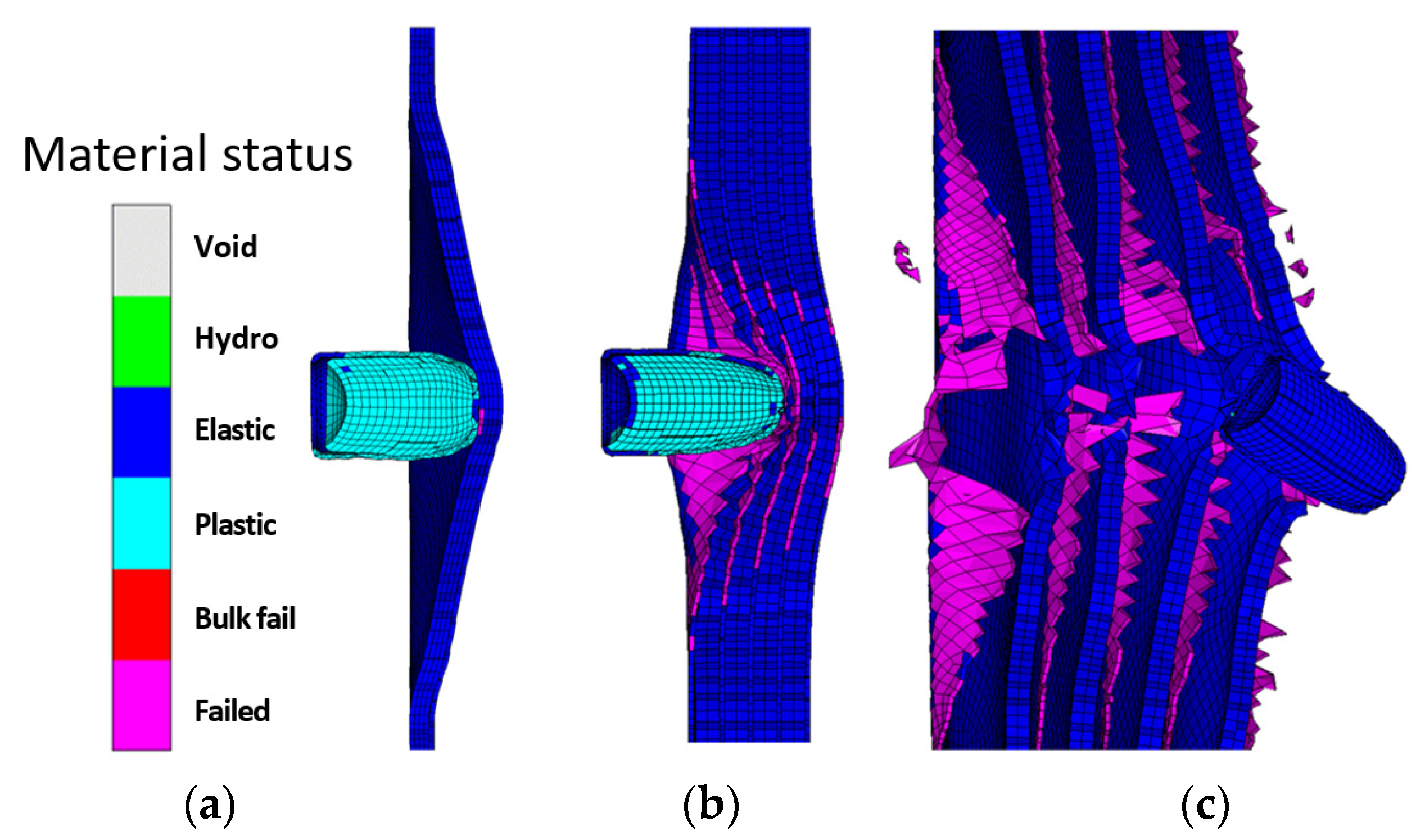
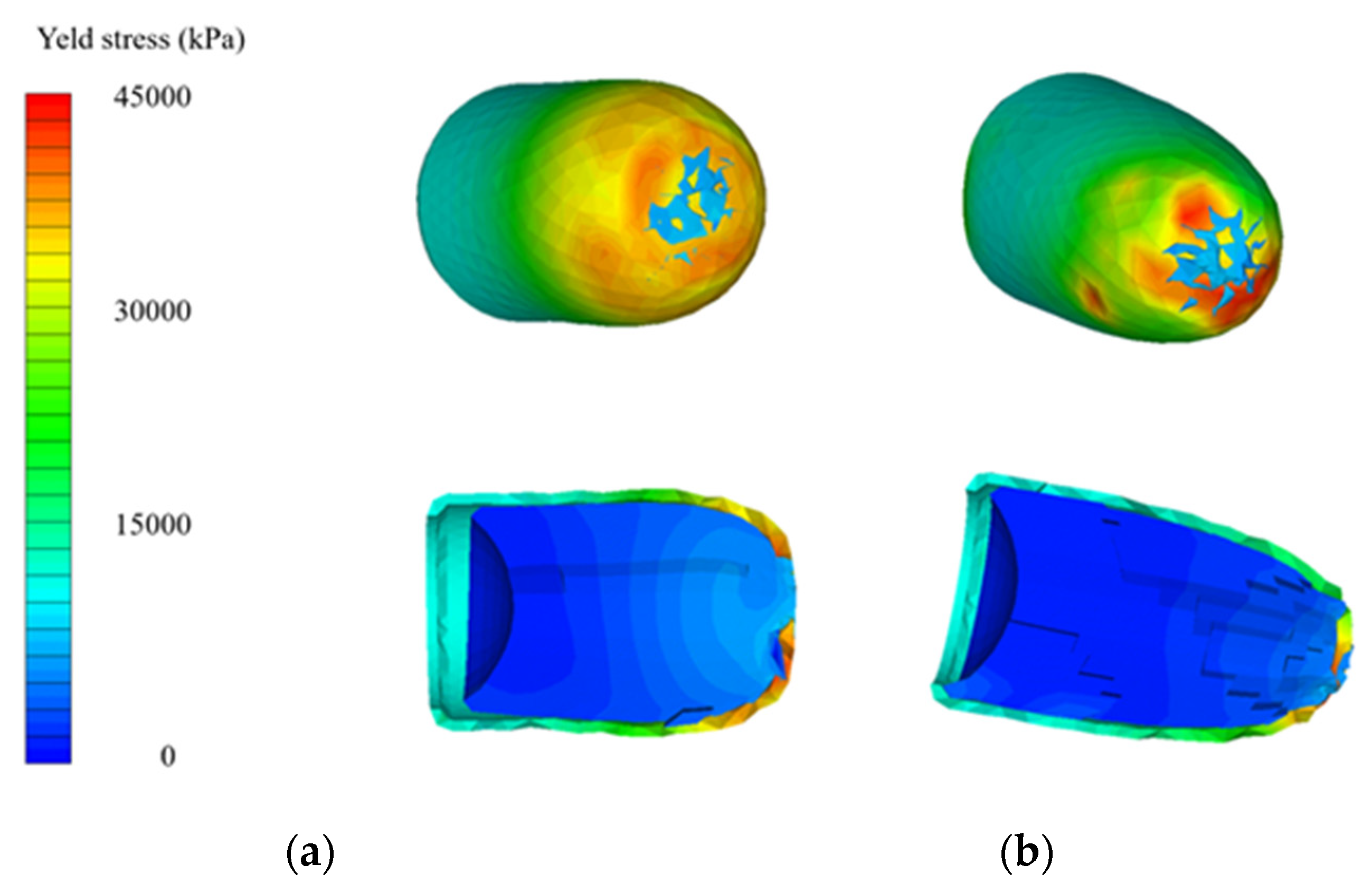
2.2.6. Modeling and Simulation of Kevlar/Shear Thickening Non-Newtonian Fluid Impact in Explicit Dynamics
3. Results
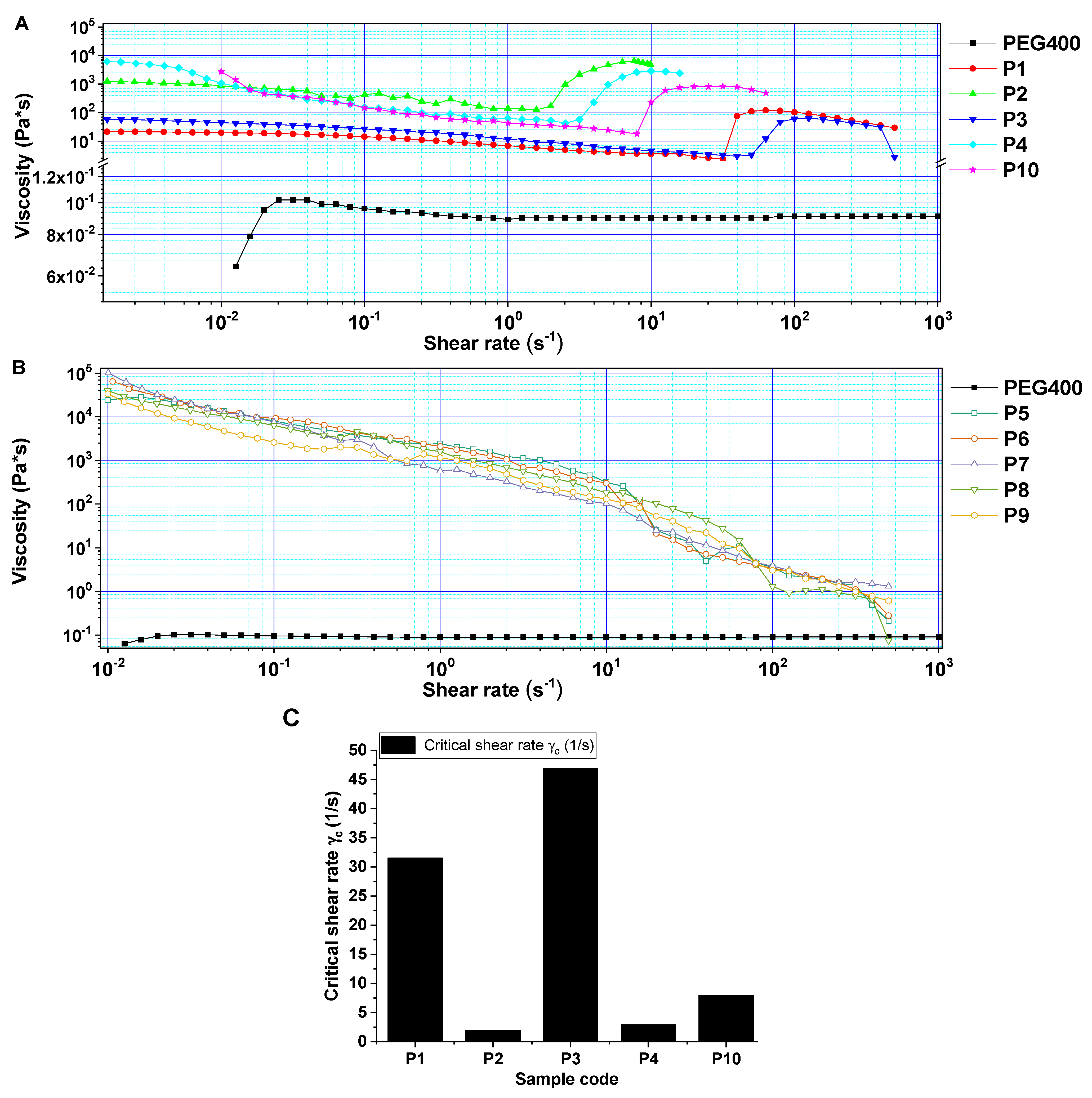
3.1. Rheological Investigations
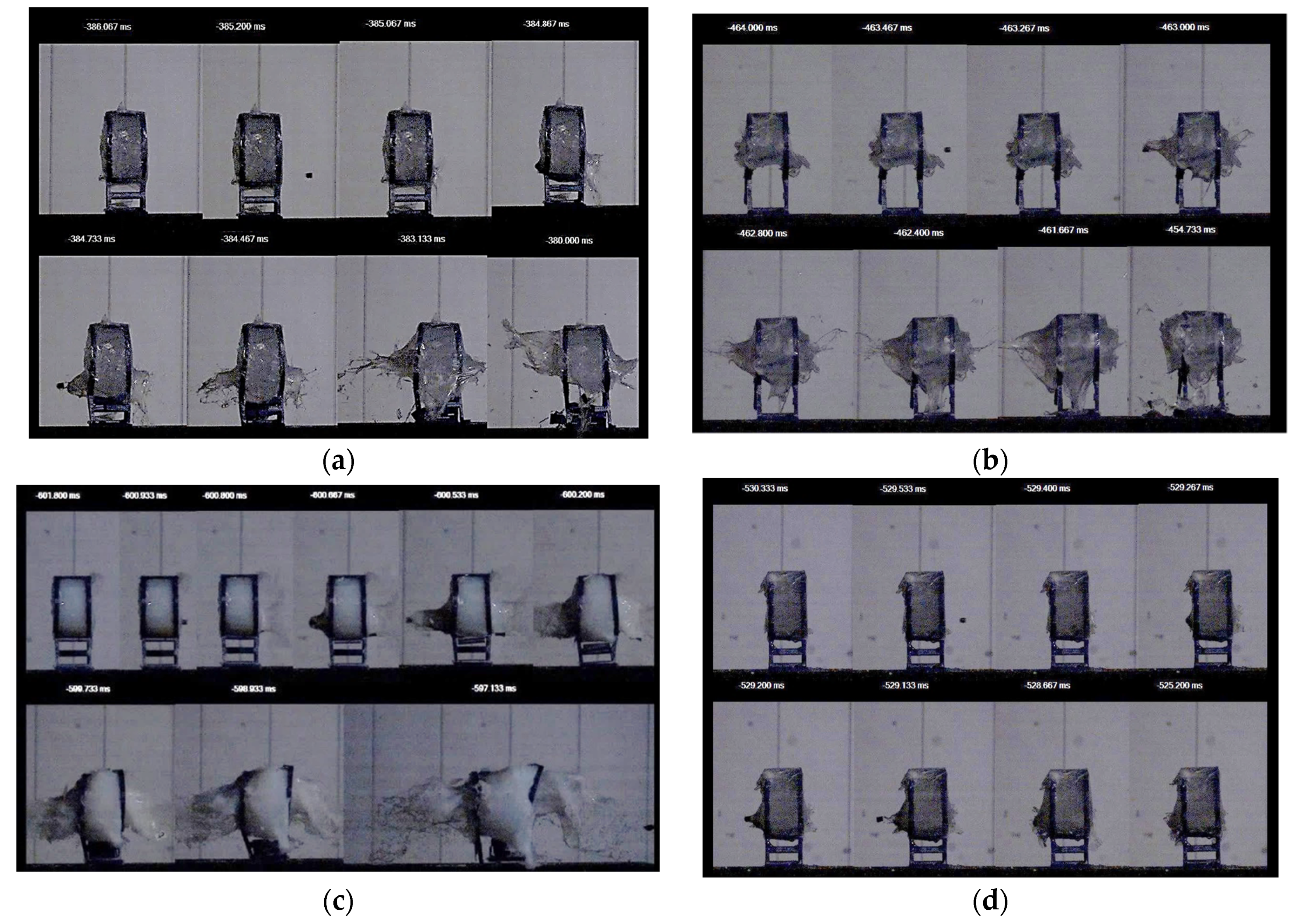
3.2. Analysis of STF Performances at Impact with a Free-Falling Blunt Object (Dynamic Loading at Moderate Impact Speed)
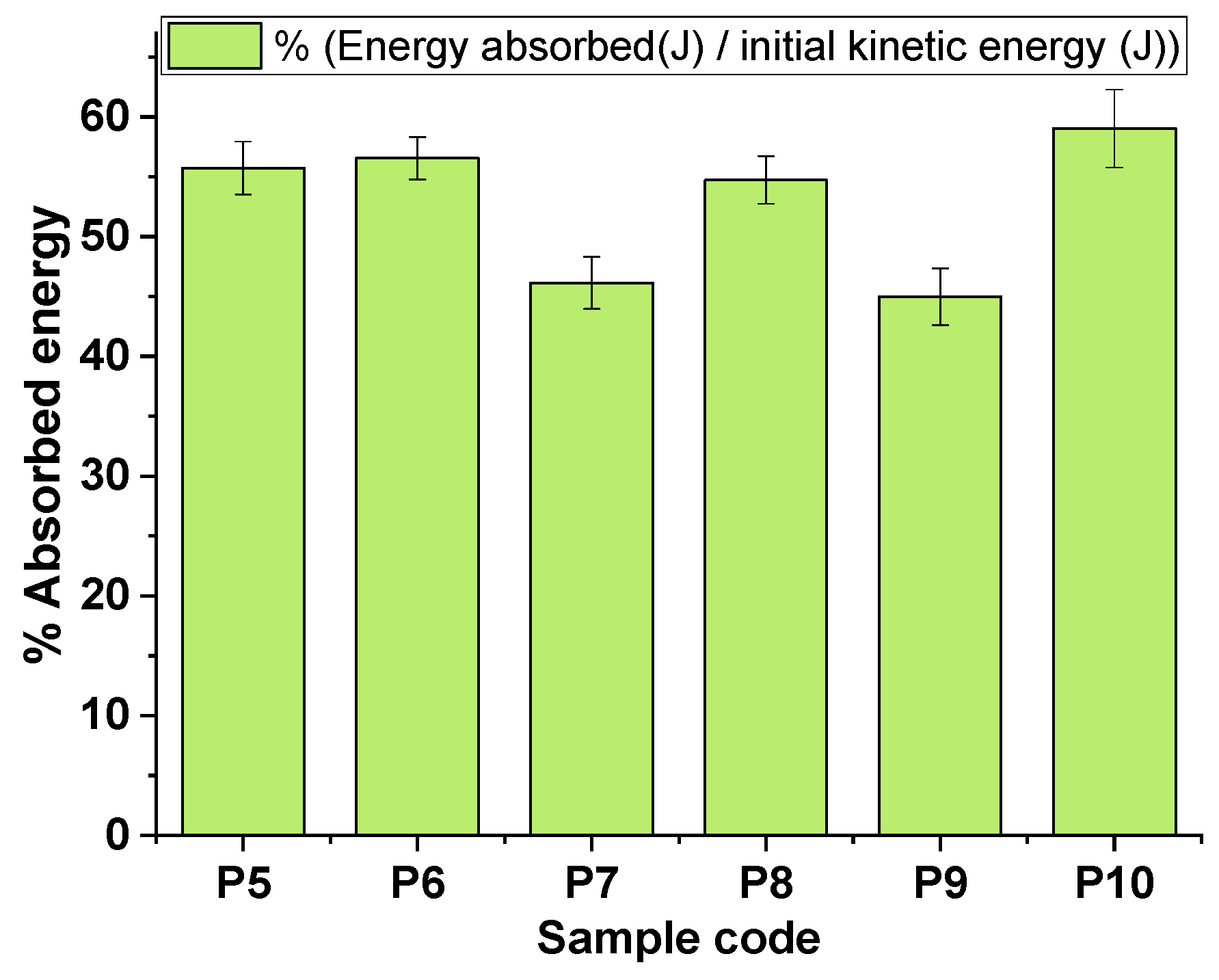
3.3. Assessment of Kinetic Energy Absorption at Impact with Standard Shrapnel
3.4. High-Velocity Impact Tests with 9 mm Bullet
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, Y.S.; Wetzel, E.D.; Wagner, N.J. The ballistic impact characteristics of Kevlar® woven fabrics impregnated with a colloidal shear thickening fluid. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 2825–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, P.J. Armour: Materials, Theory, and Design; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hudiakov, Y.; Filippovich, Y. Early medieval armor from southern Siberia. Archaeol. Ethnol. Anthropol. Eurasia 2017, 45, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.P.; da Silveira, P.H.; de Oliveira Braga, F.; Monteiro, S.N. Fabric Impregnation with Shear Thickening Fluid for Ballistic Armor Polymer Composites: An Updated Overview. Polymers 2022, 14, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Jia, X. From space to battlefield: A new breed of multifunctional fiber sheets for extreme environments. Matter 2020, 3, 602–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.G.; Satapathy, S.S.; Vargas-Gonzalez, L.R.; Walsh, S.M. Ballistic impact response of Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene (UHMWPE). Compos. Struct. 2015, 133, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, L.E., Jr. Evaluation and Development of Fluid Armor Systems; Hughes Aircraft Co Culver City Ca Aerospace Groups: Culver City, CA, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, N.J.; Wetzel, E.D. Advanced body armor utilizing shear thickening fluids. In Proceedings of the 23rd Army Science Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 2–5 December 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Grigoryan, V.; Kobylkin, I.; Marinin, V.; Bespalov, I. Ballistic performance of textile armor treated with shear thickening fluid. Tech. Wyr. Włókiennicze 2009, 17, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.; Ali, A.; Shah, S.K.; Shuaib, M. Advanced Body Armor Utilizing Shear Thickening Fluid Based on Nanosized Silica Particles. Mater. Sci. Forum 2022, 1068, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.F.; Santos, C.M.; Aquino, M.S.; Oliveira, F.R.; Medeiros, J.I. Statistical study of performance properties to impact of Kevlar® woven impregnated with Non-Newtonian Fluid (NNF). J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 3330–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, Ł.; Danelska, A.; Olszewska, K.; Tryznowski, M.; Zielińska, D.; Kucińska, I.; Szafran, M.; Leonowicz, M. Shear thickening fluids based on nanosized silica suspensions for advanced body armour. Compos. Theory Pr. 2013, 13, 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Tracey, P.J.; Li, W.; Peng, G.; Whitten, P.G.; Wallace, G.G. Review on shear thickening fluids and applications. Text. Light Ind. Sci. Technol. 2013, 2, 161–173. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, R. Discontinuous and dilatant viscosity behavior in concentrated suspensions. II. Theory and experimental tests. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1974, 46, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; McCoy, J.H.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Cohen, I. Imaging the microscopic structure of shear thinning and thickening colloidal suspensions. Science 2011, 333, 1276–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Nakano, M.; Li, W. Applications of shear thickening fluids: A review. Int. J. Hydromechatronics 2018, 1, 238–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisany, W.; Yousefi, S.; Soufiani, S.P.; Pashang, D.; McClements, D.J.; Ghasemlou, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: A versatile platform for encapsulation and delivery of essential oils for food applications. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2024, 325, 103116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, E.D.E.R.; Seyfaee, A.; Neville, F.; Moreno-Atanasio, R. Colloidal Silica Particle Synthesis and Future Industrial Manufacturing Pathways: A Review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8891–8913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankarious, R.A.; Radwan, M.A. Shear Thickening Fluids Comparative Analysis Composed of Silica Nanoparticles in Polyethylene Glycol and Starch in Water. J. Nanotechnol. 2020, 2020, 8839185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petel, O.E.; Ouellet, S.; Loiseau, J.; Frost, D.L.; Higgins, A.J. A comparison of the ballistic performance of shear thickening fluids based on particle strength and volume fraction. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2015, 85, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Qiao, X.; Dong, X.; Sun, K. Effect of particle modification on the shear thickening behaviors of the suspensions of silica nanoparticles in PEG. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2018, 296, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, G.; Verma, S.K.; Thakur, A.; Biswas, I.; Bhatacharjee, D. The effect of particle size and concentration on the ballistic resistance of different shear thickening fluids. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 28, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, E.D.; Lee, Y.; Egres, R.; Kirkwood, K.; Kirkwood, J.; Wagner, N. The effect of rheological parameters on the ballistic properties of shear thickening fluid (STF)-kevlar composites. AIP Conf. Proc. 2004, 712, 288–293. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, T.F.; Santos, C.M.S.; Aquino, M.S.; Ionesi, D.; Medeiros, J.I. Influence of silane coupling agent on shear thickening fluids (STF) for personal protection. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4032–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürgen, S.; Kuşhan, M.C.; Li, W. Shear thickening fluids in protective applications: A review. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2017, 75, 48–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, H. Shear-thickening (“Dilatancy”) in suspensions of nonaggregating solid particles dispersed in Newtonian liquids. J. Rheol. 1989, 33, 329–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, D.B. Shear rheology of hard-sphere, dispersed, and aggregated suspensions, and filler-matrix composites. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 171, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranzano, B.J.; Wagner, N.J. The effects of particle size on reversible shear thickening of concentrated colloidal dispersions. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 114, 10514–10527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriana, A.D. Fabrication, Characterisation and Optimisation of Shear Thickening Fluids; University of Wollongong: Wollongong, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, J.W.; Wagner, N.J. Optical Measurement of the Contributions of Colloidal Forces to the Rheology of Concentrated Suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1995, 172, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, W.H.; Laven, J.; Stein, H.N. Computer simulations of shear thickening of concentrated dispersions. J. Rheol. 1995, 39, 841–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellamuthu, M.; Arndt, E.M.; Rothstein, J.P. Extensional rheology of shear-thickening nanoparticle suspensions. Soft Matter 2009, 5, 2117–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durlofsky, L.; Brady, J.F.; Bossis, G. Dynamic simulation of hydrodynamically interacting particles. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 180, 21–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekiel-Jeżewska, M.L.; Gubiec, T.; Szymczak, P. Stokesian dynamics of close particles. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-D.; So, J.-H.; Yang, S.-M. Rheological behavior and stability of concentrated silica suspensions. J. Rheol. 1999, 43, 1117–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, Y.-L.; Gong, X.-L.; Peng, C.; Sun, Y.-Q.; Jiang, W.-Q.; Zhang, Z. Shear Thickening Fluids Based on Additives with Different Concentrations and Molecular Chain Lengths. Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2010, 23, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.L. Discontinuous and Dilatant Viscosity Behavior in Concentrated Suspensions. I. Observation of a Flow Instability. Trans. Soc. Rheol. 1972, 16, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, M.; Campo-Deaño, L.; Galindo-Rosales, F.J. Rheology of Shear Thickening Fluid. In Shear Thickening Fluid: Theory and Applications; Gürgen, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, F.; Wu, L.; Lu, Z.; Lin, J.-H.; Jiang, Q. Design of shear thickening fluid/polyurethane foam skeleton sandwich composite based on non-Newtonian fluid solid interaction under low-velocity impact. Mater. Des. 2022, 213, 110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, B.A.; Laufer, C.N.; Kalman, D.P.; Wetzel, E.D.; Wagner, N.J. Multi-threat performance of kaolin-based shear thickening fluid (STF)-treated fabrics. In Proceedings of the SAMPE 2007, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–7 June 2007; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Mawkhlieng, U.; Bajya, M.; Majumdar, A. Shear Thickening Fluid–Based Protective Structures against Low Velocity Impacts. In Shear Thickening Fluid: Theory and Applications; Gürgen, S., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 115–138. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, E.; Nebhani, L. Fabrication and Impact Properties of Shear-Thickening Fluid-Impregnated High-Performance Fabric Composites. In Shear Thickening Fluids in Protective Applications, Gürgen, S., Ed.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 39–68. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, X.; Qiu, J. Evaluation of ballistic performance of STF impregnated fabrics under high velocity impact. Compos. Struct. 2019, 227, 111208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y. Shear thickening fabric composites for impact protection: A review. Text. Res. J. 2022, 93, 1419–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Majumdar, A.; Butola, B.S. Improving the Impact Resistance of Textile Structures by using Shear Thickening Fluids: A Review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2012, 37, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, M.J.; Halbach, C.J.; Nam, C.H.; Wagner, N.J.; Wetzel, E.D. Stab resistance of shear thickening fluid (STF)-treated fabrics. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2007, 67, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decker, M.; Egres, R.; Wetzel, E.; Wagner, N. Low velocity ballistic properties of shear thickening fluid (STF)-fabric composites. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Symposium International Symposium on Ballistics, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 14–18 November 2005; pp. 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D7136/D7136M-15; Standard Test Method for Measuring the Damage Resistance of a Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Matrix Composite to a Drop-Weight Impact Event. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- ASTM D7766/D7766M-16; Standard Practice for Damage Resistance Testing of Sandwich Constructions. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2023.
- STANAG 2920; Ballistic Test Method for Personal Armour Materials and Combat Clothing. Nato Standardization Agency: Brussels, Belgium, 2003.
- Gotts, P.L. Personal Armour Testing versus Small Arms Ammunition when the Test Standard Doesn’t Fit. Probl. Mechatroniki: Uzbroj. Lot. Inżynieria Bezpieczeństwa 2015, 6, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Rosales, F.; Rubio-Hernández, F.; Sevilla, A. An apparent viscosity function for shear thickening fluids. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2011, 166, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Xiang, C.; Jia, Q.; Wang, F. A new view on improving the preparation efficiency of shear thickening fluid. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 295, 032088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bair, S.S. High Pressure Rheology for Quantitative Elastohydrodynamics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Panwar, P.; Michael, P.; Devlin, M.; Martini, A. Critical Shear Rate of Polymer-Enhanced Hydraulic Fluids. Lubricants 2020, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriana, A.D.; Tian, T.; Sencadas, V.; Li, W. Comparison of rheological behaviors with fumed silica-based shear thickening fluids. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2016, 28, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, S.; Meier, G.; Alig, I. Phase behaviour of mixtures of polyethylene glycol and polypropylene glycol: Influence of hydrogen bond clusters on the phase diagram. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2002, 4, 3743–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jorge, A.M.S.; Silva, G.M.C.; Coutinho, J.A.P.; Pereira, J.F.B. Unravelling the molecular interactions behind the formation of PEG/PPG aqueous two-phase systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 7308–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, U.; Seybold, H.J.; Floriancic, M.; Bertsch, P.; Jiménez-Martínez, J.; Andrade, J.S.; Holzner, M. Determination of the Effective Viscosity of Non-newtonian Fluids Flowing Through Porous Media. Front. Phys. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIJ Standard-0101.04; Ballistic Resistance of Body Armor. Department of Justice Washington Dc Office of Justice Programs: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Sen, S.; Jamal M, N.B.; Shaw, A.; Deb, A. Numerical investigation of ballistic performance of shear thickening fluid (STF)-Kevlar composite. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 164, 105174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilakantan, G.; Gillespie, J.W. Ballistic impact modeling of woven fabrics considering yarn strength, friction, projectile impact location, and fabric boundary condition effects. Compos. Struct. 2012, 94, 3624–3634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.; Offenberger, S.; Toghiani, H.; Pittman, C.U., Jr.; Lacy, T.E.; Kundu, S. Effect of Temperature on the Shear-Thickening Behavior of Fumed Silica Suspensions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 18650–18661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wu, Y.; Pei, X.; Zhou, F.; Xue, Q. Contribution of Surface Chemistry to the Shear Thickening of Silica Nanoparticle Suspensions. Langmuir 2017, 33, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toqueboeuf, W.; Mortaigne, B.; Cottenot, C. Dynamic behaviour of polycarbonate/polyurethane multi-layer for transparent armor. J. Phys. IV 1997, 7, C3-499–C3-504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal Elden, A.E.; Wafy, T.Z.; Tantawy, H.R. Shear Thickening Fluids for Blast Wave Mitigation Applications: Preparation, Characterization and Numerical Modeling. In The International Undergraduate Research Conference; The Military Technical College: Cairo, Egypt, 2021; Volume 5, pp. 228–234. [Google Scholar]
- Hiermaier, S.; Riedel, W.; Hayhurst, C.; Clegg, R.; Wentzel, C. Advanced Material Models for Hypervelocity Impact Simulations; ESA/ESTEC: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]




| Sample Code | Polymeric Matrix | Fumed Silica (0.2–0.3 μm) [wt.%] | Aerosil HDK® N20 Pyrogenic Silica (>40 μm) [wt.%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | PEG 400 | 20 | - |
| P2 | PEG 400 | 30 | - |
| P3 | PEG 400 | - | 20 |
| P4 | PEG 400 | - | 30 |
| P5 | PPG 400 | 20 | - |
| P6 | PPG 400 | - | 20 |
| P7 | PEG 400 * | - | 40 |
| P8 | PEG 200 * | - | 40 |
| P9 | PPG 400 * | - | 40 |
| P10 | PEG 400 | - | 27 |
| P-bk | PEG 400 | - | - |
| Impregnated Composite Sample Code | STF Code | Kevlar XP (No. of Layers) | Kevlar–Carbon Fiber (No. of Layers) | Specific Mass, Kg/m2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat | Impregnated with STF | Neat | Impregnated with STF | |||
| SC0 | - | 11 | - | - | - | 5.50 |
| SC1 | - | 5 | - | 6 | - | 3.49 |
| SC2 | P1 | 5 | 6 | - | - | 8.23 |
| SC3 | P10 | 5 | 6 | - | - | 9.75 |
| SC-bk | P-bk | 5 | 6 | - | - | 8.77 |
| Multilayered Composite Sample Code | STF Code | Kevlar XP (No. of Layers) | Twaron T730 WRT (No. of Layers) | Twaron LFT AT FLEX (No. of Layers) | Specific Mass, Kg/m2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neat | STF Packed Layer | Neat | STF Packed Layer | Neat | STF Packed Layer | |||
| SC4 | P2 | 11 | 1 (facing the bullet) | - | - | - | - | 13.51 |
| SC5 | P4 | 11 | 1 (facing the bullet) | - | - | - | - | 20.00 |
| SC6 | P4 | 11 | 1 (covered with one layer of Kevlar) | 20.00 | ||||
| SC7 | - | - | - | 17 | - | 1 | - | 4.91 |
| SC8 | - | - | - | 7 | - | 1 | - | 2.31 |
| SC9 | P10 | - | - | 7 | 1 (honeycomb structure) | 1 | - | 16.48 |
| SC10 | P10 | - | - | 7 | 1 (rectangular structure) | 1 | - | 16.48 |
| Sample Code | Projectile Initial Velocity, m/s | Initial Kinetic Energy, J | Projectile Residual Velocity, m/s | Residual Kinetic Energy, J | Absorbed Energy, J | Absorbed Energy, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P5 | 269 | 39.80 | 179 | 17.62 | 22.18 | 55.73 |
| P6 | 267 | 39.21 | 176 | 17.04 | 22.17 | 56.54 |
| P7 | 312 | 53.54 | 229 | 28.84 | 24.70 | 46.13 |
| P8 | 269 | 39.80 | 181 | 18.02 | 21.78 | 54.72 |
| P9 | 285 | 44.67 | 211.4 | 24.58 | 20.09 | 44.97 |
| P10 | 300 | 49.50 | 192 | 20.28 | 29.22 | 59.03 |
| Sample Code | Projectile Initial Velocity, m/s | Initial Kinetic Energy, J | Projectile Residual Velocity, m/s | Residual Kinetic Energy, J | Absorbed Energy, J | Absorbed Energy, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SC0 | 429 | 741.7 | N/A | N/A | 741.7 | 100 |
| SC1 | 428 | 738.2 | 234 | 220.7 | 517.5 | 70.1 |
| SC2 | 432 | 752.1 | 204 | 167.7 | 584.4 | 77.7 |
| SC3 | 430 | 745.1 | 178 | 127.7 | 617.4 | 82.9 |
| SC4 | 433 | 755.6 | 198 | 158.0 | 597.6 | 79.1 |
| SC5 | 438 | 773.1 | 169 | 115.1 | 658.0 | 85.1 |
| SC6 | 431 | 748.6 | N/A | N/A | 748.6 | 100 |
| SC7 | 435 | 762.6 | N/A | N/A | 762.6 | 100 |
| SC8 | 433 | 755.6 | N/A | N/A | 755.6 | 100 |
| SC9 | 434 | 759.1 | N/A | N/A | 759.1 | 100 |
| SC10 | 432 | 752.1 | N/A | N/A | 752.1 | 100 |
| SC-bk | 428 | 738.2 | 266 | 285.7 | 452.5 | 61.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alexe, F.; Sau, C.; Iorga, O.; Toader, G.; Diacon, A.; Rusen, E.; Lazaroaie, C.; Ginghina, R.E.; Tiganescu, T.V.; Teodorescu, M.; et al. Experimental Investigations on Shear Thickening Fluids as “Liquid Body Armors”: Non-Conventional Formulations for Ballistic Protection. Polymers 2024, 16, 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162305
Alexe F, Sau C, Iorga O, Toader G, Diacon A, Rusen E, Lazaroaie C, Ginghina RE, Tiganescu TV, Teodorescu M, et al. Experimental Investigations on Shear Thickening Fluids as “Liquid Body Armors”: Non-Conventional Formulations for Ballistic Protection. Polymers. 2024; 16(16):2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162305
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlexe, Florentina, Ciprian Sau, Ovidiu Iorga, Gabriela Toader, Aurel Diacon, Edina Rusen, Claudiu Lazaroaie, Raluca Elena Ginghina, Tudor Viorel Tiganescu, Mircea Teodorescu, and et al. 2024. "Experimental Investigations on Shear Thickening Fluids as “Liquid Body Armors”: Non-Conventional Formulations for Ballistic Protection" Polymers 16, no. 16: 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162305
APA StyleAlexe, F., Sau, C., Iorga, O., Toader, G., Diacon, A., Rusen, E., Lazaroaie, C., Ginghina, R. E., Tiganescu, T. V., Teodorescu, M., & Sobetkii, A. (2024). Experimental Investigations on Shear Thickening Fluids as “Liquid Body Armors”: Non-Conventional Formulations for Ballistic Protection. Polymers, 16(16), 2305. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16162305









