Self-Floating Polydopamine/Polystyrene Composite Porous Structure via a NaCl Template Method for Solar-Driven Interfacial Water Evaporation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Characterization
2.2. Synthesis of PDA Nanoparticles
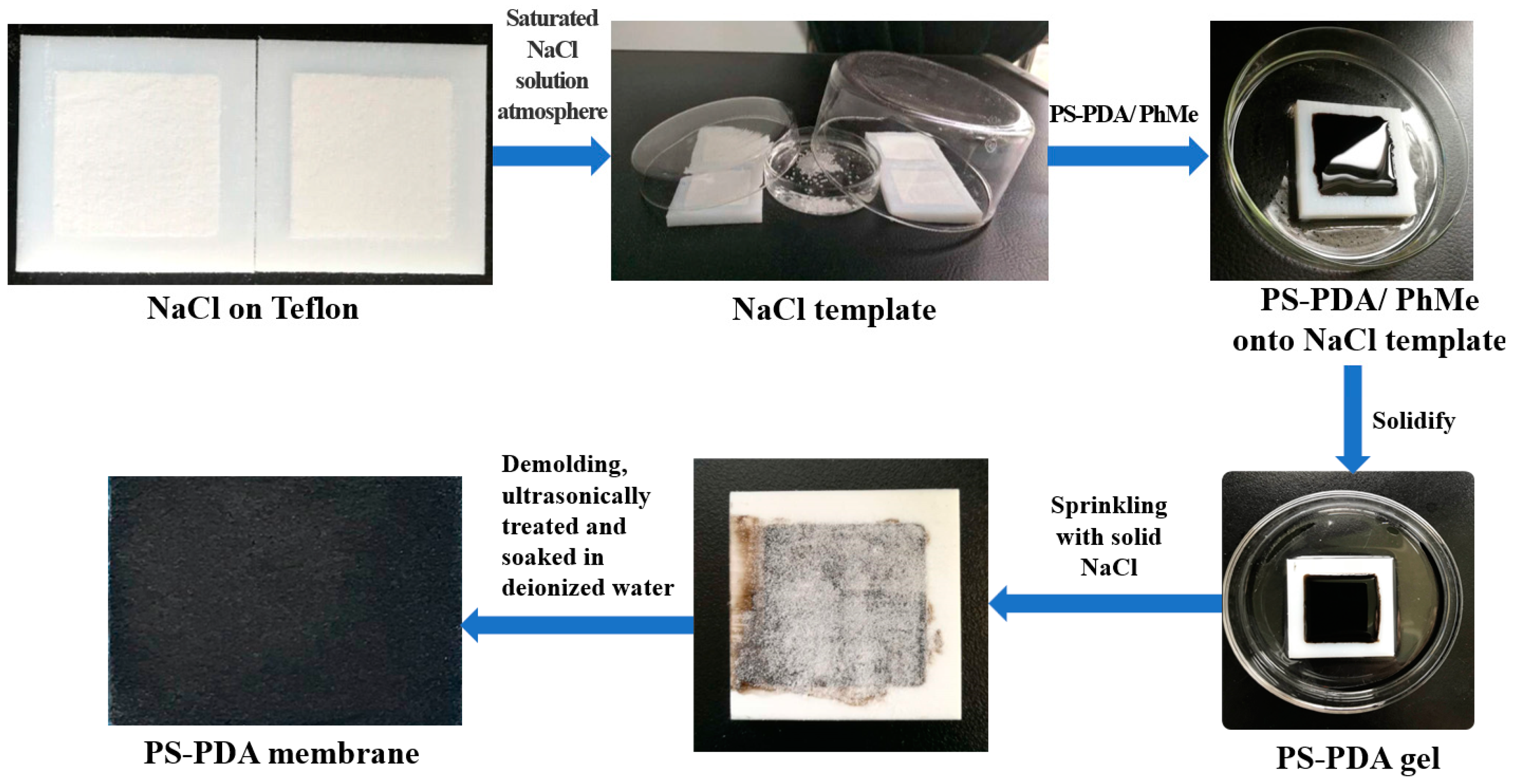
2.3. Fabrication of PS-PDA Material
2.4. Solar-Driven Interfacial Water Evaporation Measurements
3. Results
3.1. Morphology of PS-PDA Materials
3.2. Wettability of PS-PDA Materials
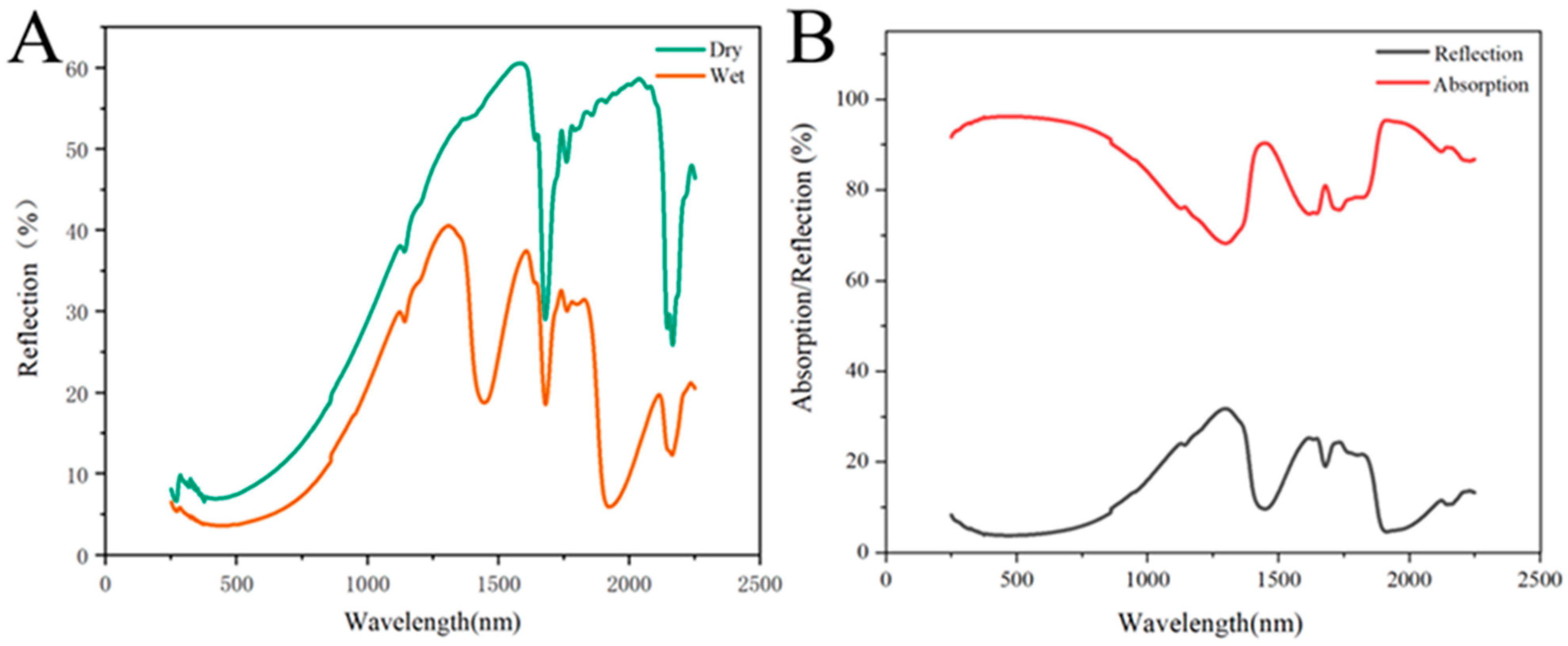
3.3. Light Absorption Property of PS-PDA Materials
3.4. Water Evaporation Test under Simulated Solar Radiation Indoors
3.5. Solar-Driven Interfacial Water Evaporation Test Outdoors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, F.E.; Hashaikeh, R.; Hilal, N. Solar powered desalination—Technology, energy and future outlook. Desalination 2019, 453, 54–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.S.; Derami, H.G.; Ghim, D.; Cao, S.S.; Jun, Y.S.; Singamaneni, S. Polydopamine-filled bacterial nanocellulose as a biodegradable interfacial photothermal evaporator for highly efficient solar steam generation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 18397–18402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Marinas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elimelech, M. The global challenge for adequate and safe water. J. Water Supply Res. Technol. 2006, 55, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Deng, T. Solar steam generation: Steam by thermal concentration. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, H.; Ni, G.; Marconnet, A.M.; Loomis, J.; Yerci, S.; Miljkovic, N.; Chen, G. Solar steam generation by heat localization. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, W.; Tang, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. Graphene oxide-based efficient and scalable solar desalination under one sun with a confined 2D water path. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13953–13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Tanabe, Y.; Han, J.; Fujita, T.; Tanigaki, K.; Chen, M. Multifunctional Porous Graphene for High-Efficiency Steam Generation by Heat Localization. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4302–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.T.; Qin, Y.J.; Pan, W.; Wang, Z.B.; Qi, Y.; He, J.X.; Zhang, H.Q. Dual-Driven Functional Fabric with High Electrothermal and Photothermal Conversion Efficiency Modified by CuS Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 5747–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simayee, M.; Zad, A.I.; Esfandiar, A. Green synthesize of copper nanoparticles on the cotton fabric as a self-regenerating and high-efficient plasmonic solar evaporator. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simayee, M.; Zad, A.I.; Esfandiar, A. Boosting-photothermal properties of Cu/Black TiO2 nanoparticles on biomimetics texture structure as high-performance and self-regenerating solar-evaporator. Sol. Energy 2023, 265, 112097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaee, M.; Niazi, Z.; Asarnia, M.; Goharshadi, E.K.; Dehghani, R. Modified pine cone with MnO2 nanoparticles as a photoabsorber for highly efficient seawater desalination and wastewater treatment. Appl. Phys. A 2023, 129, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Chanda, K.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Bairi, P.; Chattopadhyay, K.K.; Chattopadhyay, P. Enhanced interfacial evaporation and desalination by solar heat localisation using nitrogenated graphitic carbon and Co3O4 nanorods. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2023, 257, 112361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Fang, X.; Yu, W.; Xie, H.; Lei, H. Magnetic recyclable Fe3O4@Ti3C2TX nanoparticles for high-efficiency solar membrane distillation. Desalination 2023, 564, 116784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, B.S.; Kim, I.S.; Han, I.K.; Ko, H.; Kang, J.G.; Kang, G. Plasmonic silicon nanowires for enhanced heat localization and interfacial solar steam generation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 583, 152563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wang, X.; Gan, Q.M.; Zhang, T.Q.; Zhu, K.H.; Ye, M.M. A bifunctional MoS2-based solar evaporator for both efficient water evaporation and clean freshwater collection. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 11177–11185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Yuan, Y.; Cai, W.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. 3D self-assembly of aluminium nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced solar desalination. Nat. Photonics 2016, 10, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Feng, R.; Bernard, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, H.; Shang, W.; Tao, P.; Song, C.; et al. A Bioinspired, Reusable, Paper-Based System for High-Performance Large-Scale Evaporation. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tao, P.; Shen, Q.; Yi, N.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Song, C.; Zhang, D.; Shang, W.; et al. Bio-Inspired Evaporation Through Plasmonic Film of Nanoparticles at the Air-Water Interface. Small 2014, 10, 3234–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lead, J.R.; Batley, G.E.; Alvarez, P.J.J.; Croteau, M.-N.; Handy, R.D.; McLaughlin, M.J.; Judy, J.D.; Schirmer, K. Nanomaterials in the environment: Behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effectsAn updated review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 2029–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selck, H.; Handy, R.D.; Fernandes, T.F.; Klaine, S.J.; Petersen, E.J. Nanomaterials in the Aquatic Environment: A European Union-United States Perspective on the Status of Ecotoxicity Testing, Research Priorities, and Challenges Ahead. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Lee, Y.; Kong, W.H.; Kim, T.G.; Park, T.G.; Lee, H. Catechol-Functionalized Chitosan/Pluronic Hydrogels for Tissue Adhesives and Hemostatic Materials. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 2653–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, H.; Zhong, S. Controlled preparation and photothermal properties of polydopamine submicrospheres. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 124, 108395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Lu, L. Polydopamine and Its Derivative Materials: Synthesis and Promising Applications in Energy, Environmental, and Biomedical Fields. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 5057–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, D.R.; Higginson, C.J.; Korpusik, A.B.; Gonthier, A.R.; Messersmith, P.B. Untemplated Resveratrol-Mediated Polydopamine Nanocapsule Formation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 34792–34801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, D.R.; Sugnaux, C.; Lau, K.H.A.; Messersmith, P.B. Size Control and Fluorescence Labeling of Polydopamine Melanin-Mimetic Nanoparticles for Intracellular Imaging. Biomimetics 2017, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ai, K.; Liu, J.; Deng, M.; He, Y.; Lu, L. Dopamine-Melanin Colloidal Nanospheres: An Efficient Near-Infrared Photothermal Therapeutic Agent for In Vivo Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 1353–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, K.-Y.; Lee, Y.; Lee, S.; Park, S.B.; Lee, J.-K. Bioinspired Polymerization of Dopamine to Generate Melanin-Like Nanoparticles Having an Excellent Free-Radical-Scavenging Property. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, M.K.; Zare, M.; Khodadadi, A.; Seidi, F.; Sajadi, S.M.; Zarrintaj, P.; Arefi, A.; Saeb, M.R.; Mozafari, M. Polydopamine Biomaterials for Skin Regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8, 2196–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Gao, C.; Xu, J. Reductant-assisted polydopamine-modified membranes for efficient water purification. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 15, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, A.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zelikin, A.N.; Tjipto, E.; Caruso, F. Self-Polymerization of Dopamine as a Versatile and Robust Technique to Prepare Polymer Capsules. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 3042–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthier, E.; Young, E.W.K.; Beebe, D. Engineers are from PDMS-land, Biologists are from Polystyrenia. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1224–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.; Lim, J.; Choi, D.; Hong, H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, S.M.; Rhie, J.W.; Kim, D.S. Fabrication of polystyrene-based multi-well screening platform for micrometer-scale surface topographies promoting stem cell functions. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 174, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, C.; Martin, C.; Linares, N.; De Vos, D. Catalytic routes towards polystyrene recycling. Mater. Horiz. 2023, 10, 1625–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, D.S.; El-Hiti, G.A.; Yousif, E.; Hameed, A.S. Polyphosphates as Inhibitors for Poly(vinyl Chloride) Photodegradation. Molecules 2017, 22, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Shi, Y.; Xia, Y. Polydopamine Nanobottles with Photothermal Capability for Controlled Release and Related Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2104729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Weng, W.; Cheng, K. A facile synthesis of polydopamine/TiO2 composite films for cell sheet harvest application. Colloids Surf. B 2018, 172, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Long, Y.H.; Zhu, T.; Guo, J.; Cai, C.; Zhao, N.; Xu, J. Fabrication of oriented wrinkles on polydopamine/polystyrene bilayer films. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 498, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.; Lee, W.; Ahn, Y. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surface on Polydopamine-coated Al Plate by Using Modified SiO2 Nanoparticles/Polystyrene Nano-Composite Coating. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2016, 37, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Qian, X.; Liu, N.; Wei, Y.; Ji, Y. Polydopamine nanoparticles doped in liquid crystal elastomers for producing dynamic 3D structures. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 6740–6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Polydopamine Based Photo-Responsive Shape Memory Polymer and the Achievement of Specific 3D Structures. Ph.D. Thesis, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Salt Fusion: An Approach to Improve Pore Interconnectivity within Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2002, 8, 43–52. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.Y.; Zhu, L.P.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, B.K. A facile method of surface modification for hydrophobic polymer membranes based on the adhesive behavior of poly(DOPA) and poly(dopamine). J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.M.; Pei, Z.Q.; Xu, Y.S.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Ji, Y. A durable monolithic polymer foam for efficient solar steam generation. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


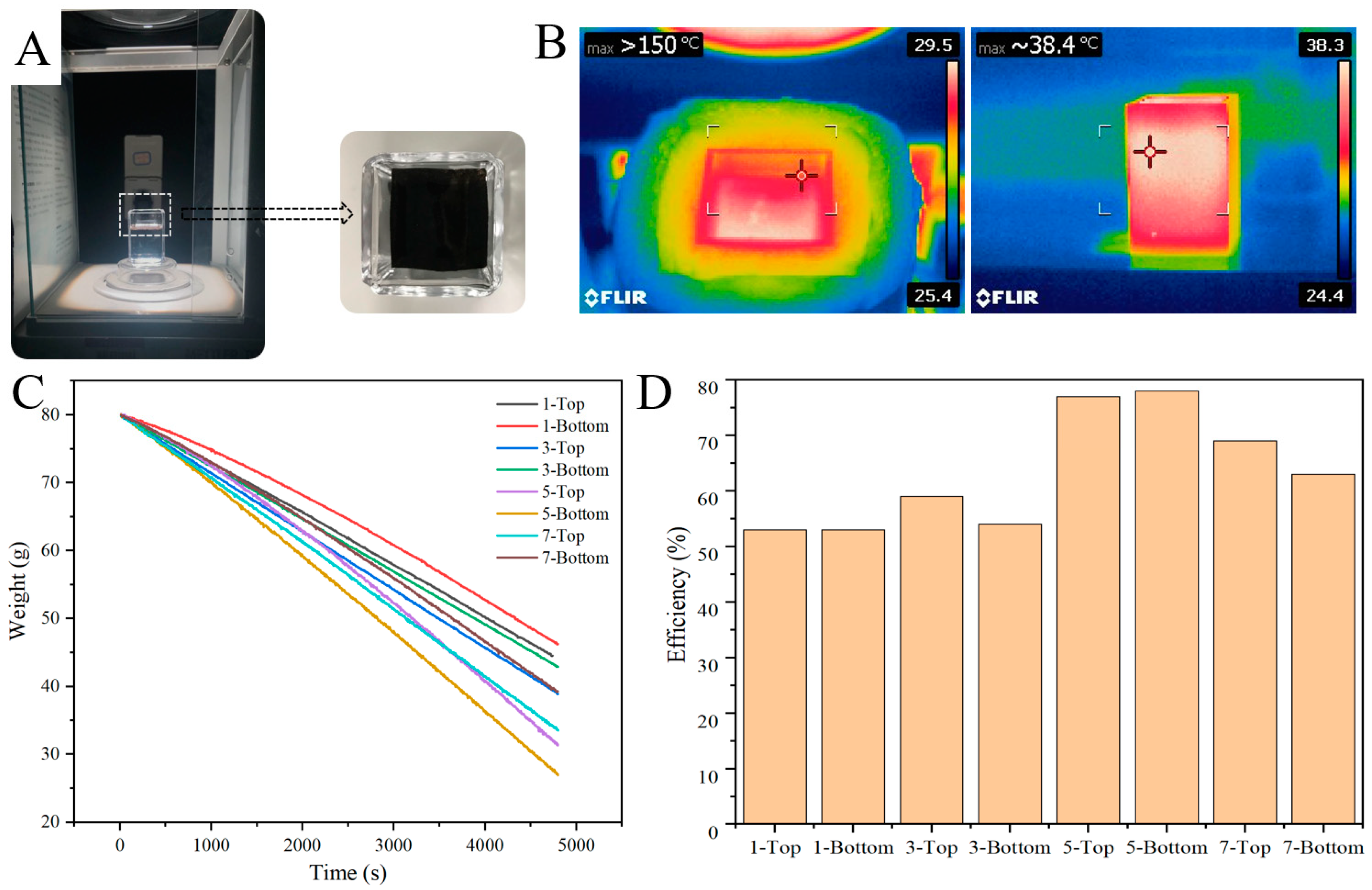

| Group | 1-Top | 1-Bottom | 3-Top | 3-Bottom | 5-Top | 5-Bottom | 7-Top | 7-Bottom |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 53% | 53% | 59% | 54% | 77% | 78% | 69% | 63% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, B.; Tian, T.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Dai, C. Self-Floating Polydopamine/Polystyrene Composite Porous Structure via a NaCl Template Method for Solar-Driven Interfacial Water Evaporation. Polymers 2024, 16, 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152231
Wang X, Li Z, Wu X, Liu B, Tian T, Ding Y, Zhang H, Li Y, Liu Y, Dai C. Self-Floating Polydopamine/Polystyrene Composite Porous Structure via a NaCl Template Method for Solar-Driven Interfacial Water Evaporation. Polymers. 2024; 16(15):2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152231
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiao, Zhen Li, Xiaojing Wu, Bingjie Liu, Tian Tian, Yi Ding, Haibo Zhang, Yuanli Li, Ye Liu, and Chunai Dai. 2024. "Self-Floating Polydopamine/Polystyrene Composite Porous Structure via a NaCl Template Method for Solar-Driven Interfacial Water Evaporation" Polymers 16, no. 15: 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152231
APA StyleWang, X., Li, Z., Wu, X., Liu, B., Tian, T., Ding, Y., Zhang, H., Li, Y., Liu, Y., & Dai, C. (2024). Self-Floating Polydopamine/Polystyrene Composite Porous Structure via a NaCl Template Method for Solar-Driven Interfacial Water Evaporation. Polymers, 16(15), 2231. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16152231







