Effects of Carbon/Kevlar Hybrid Ply and Intercalation Sequence on Mechanical Properties and Damage Resistance of Composite Laminates under Quasi-Static Indentation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Composite Fabrication
2.1.2. Specimens
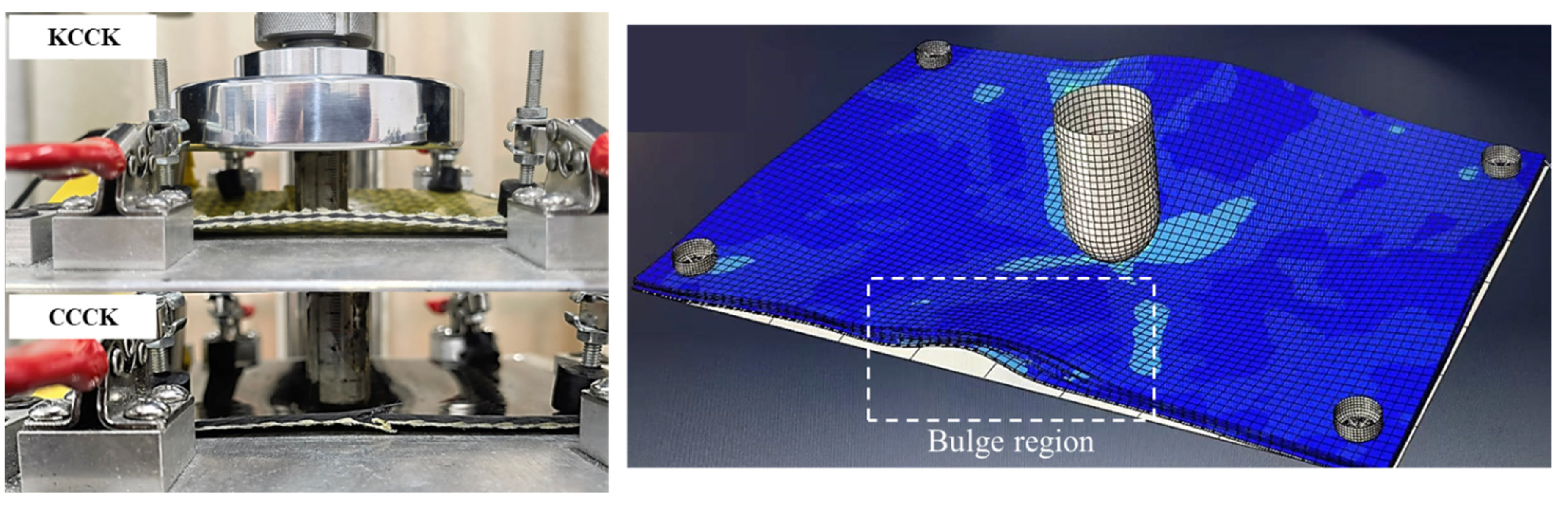
2.2. Quasi-Static Indentation (QSI) Tests
3. Results and Discussion
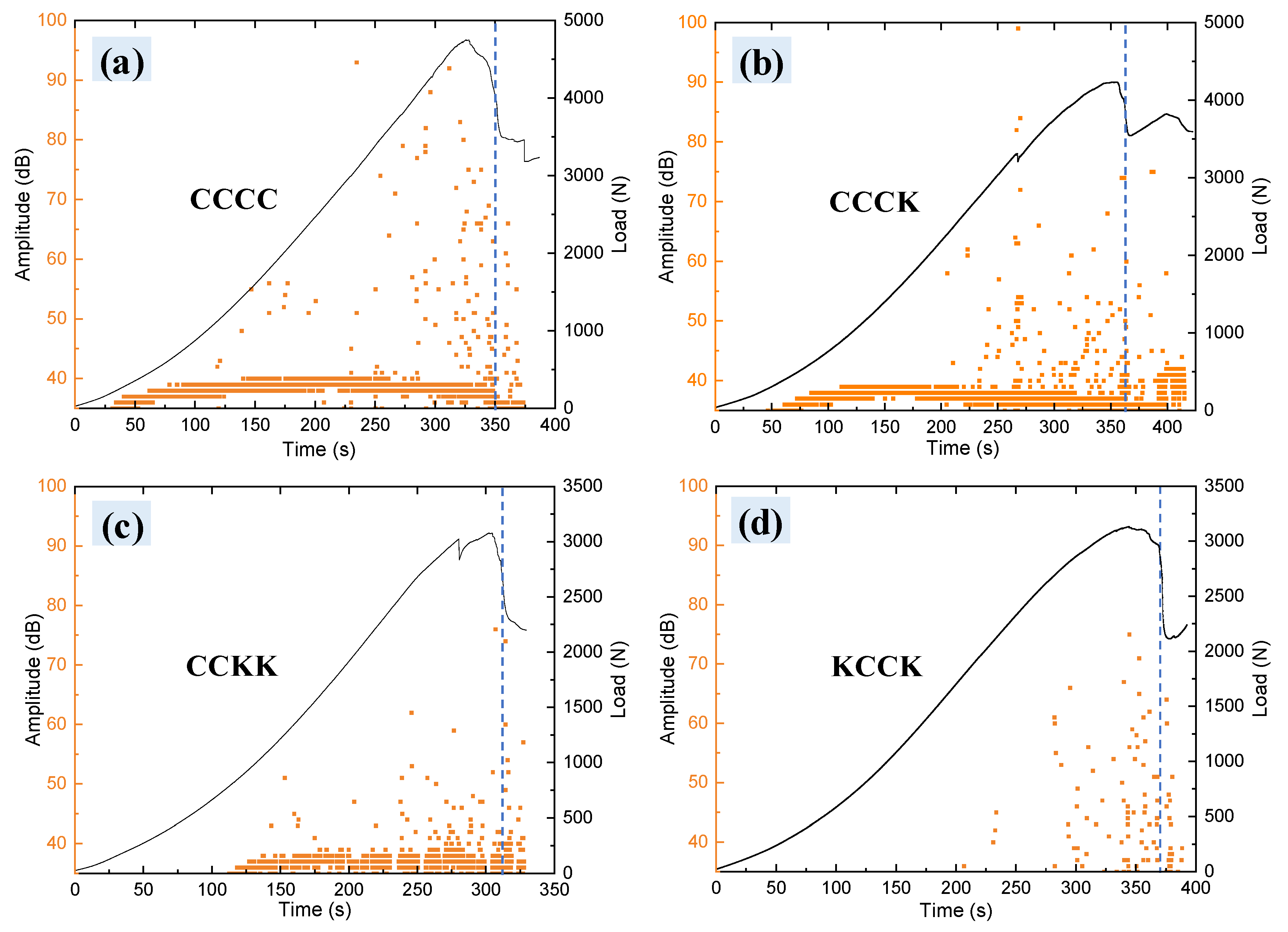
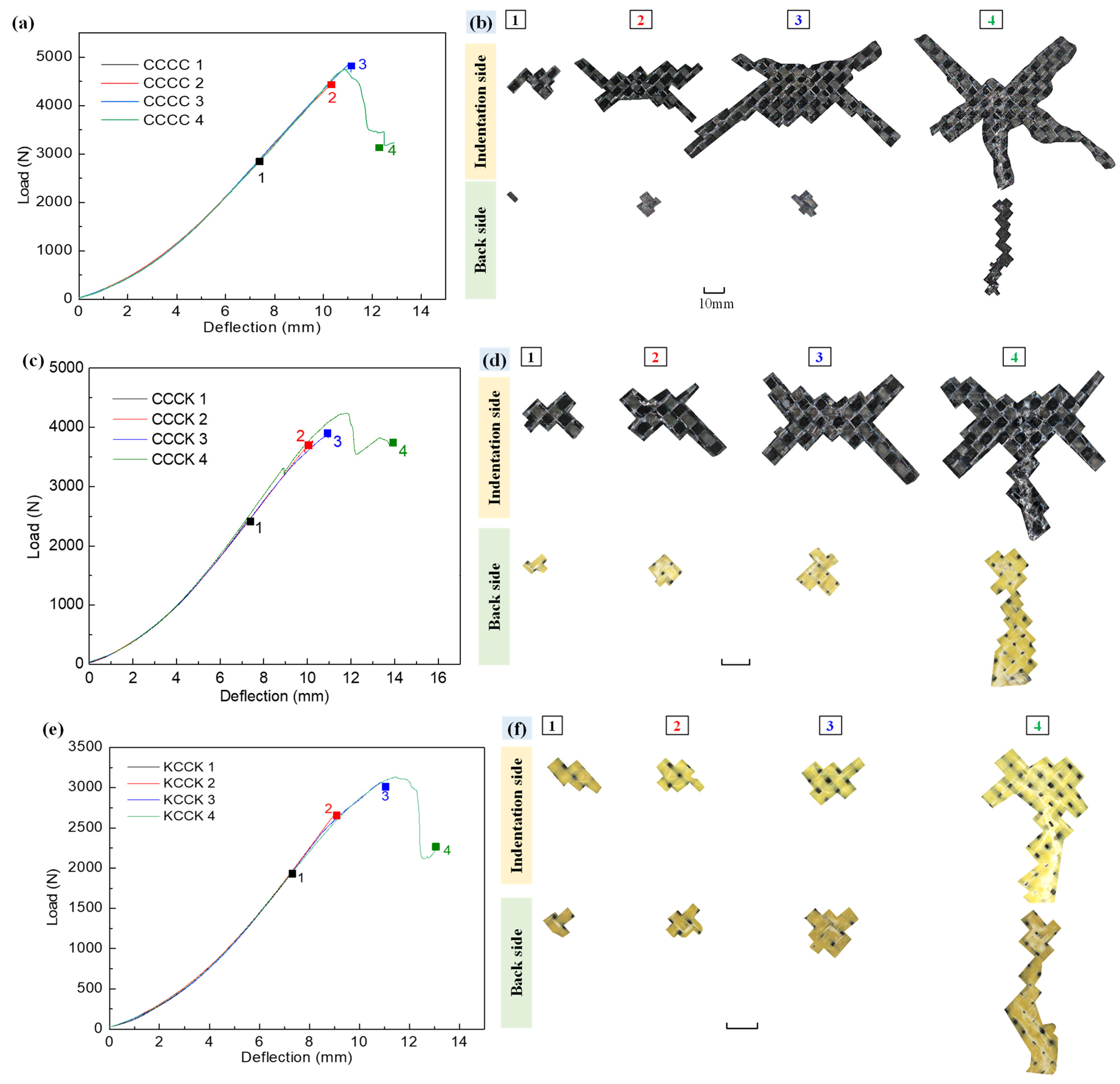
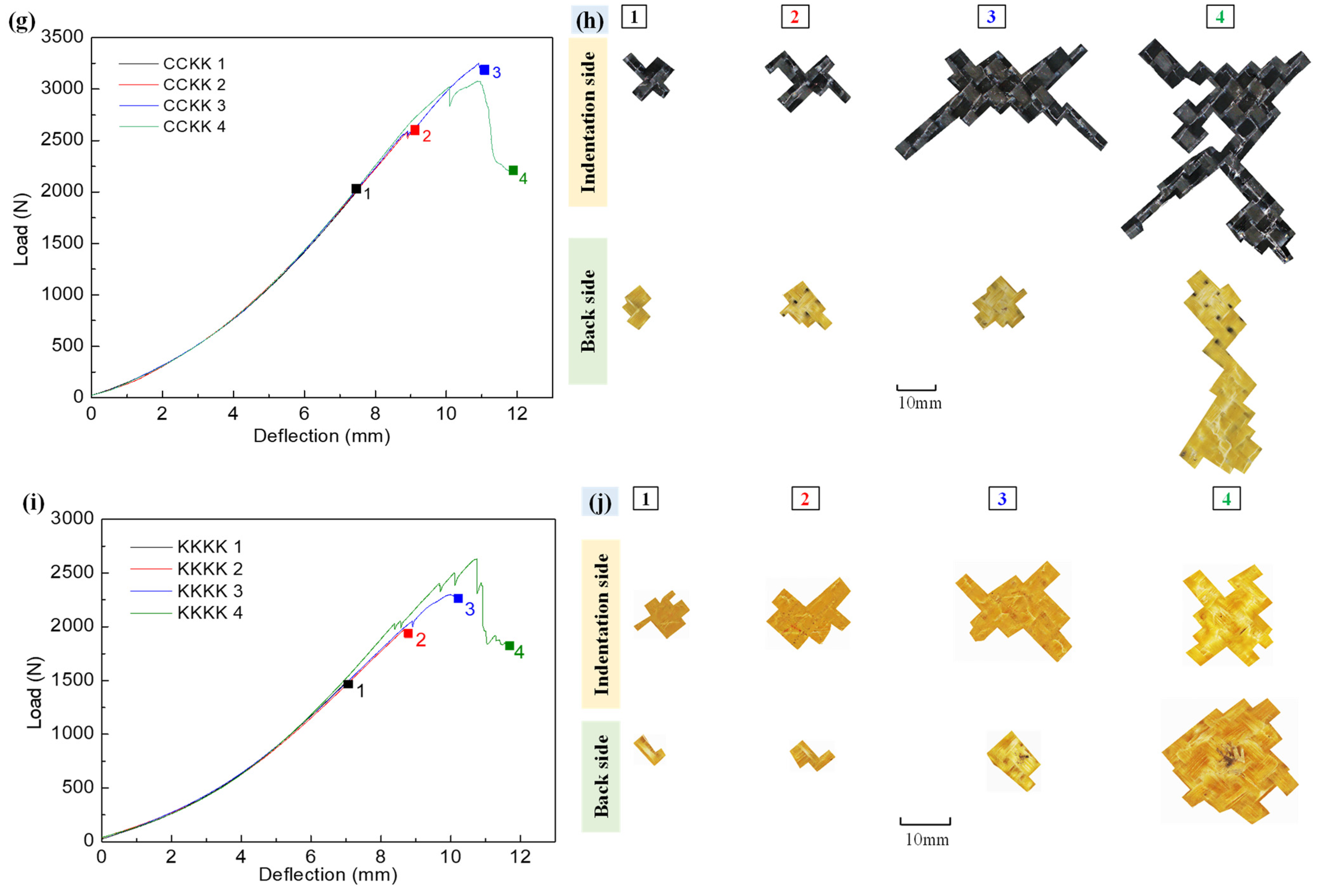
3.1. Load–Deflection Curve
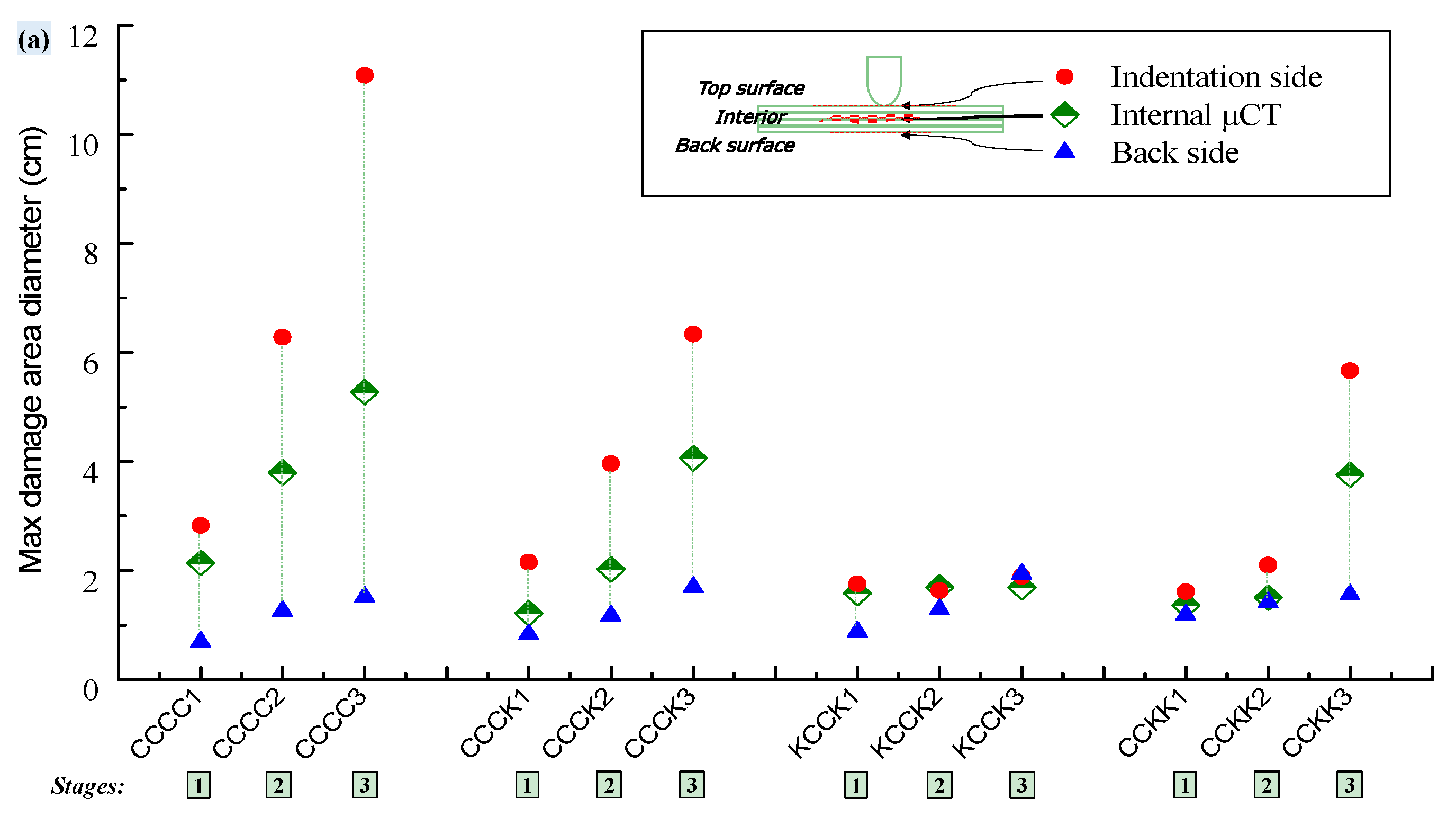
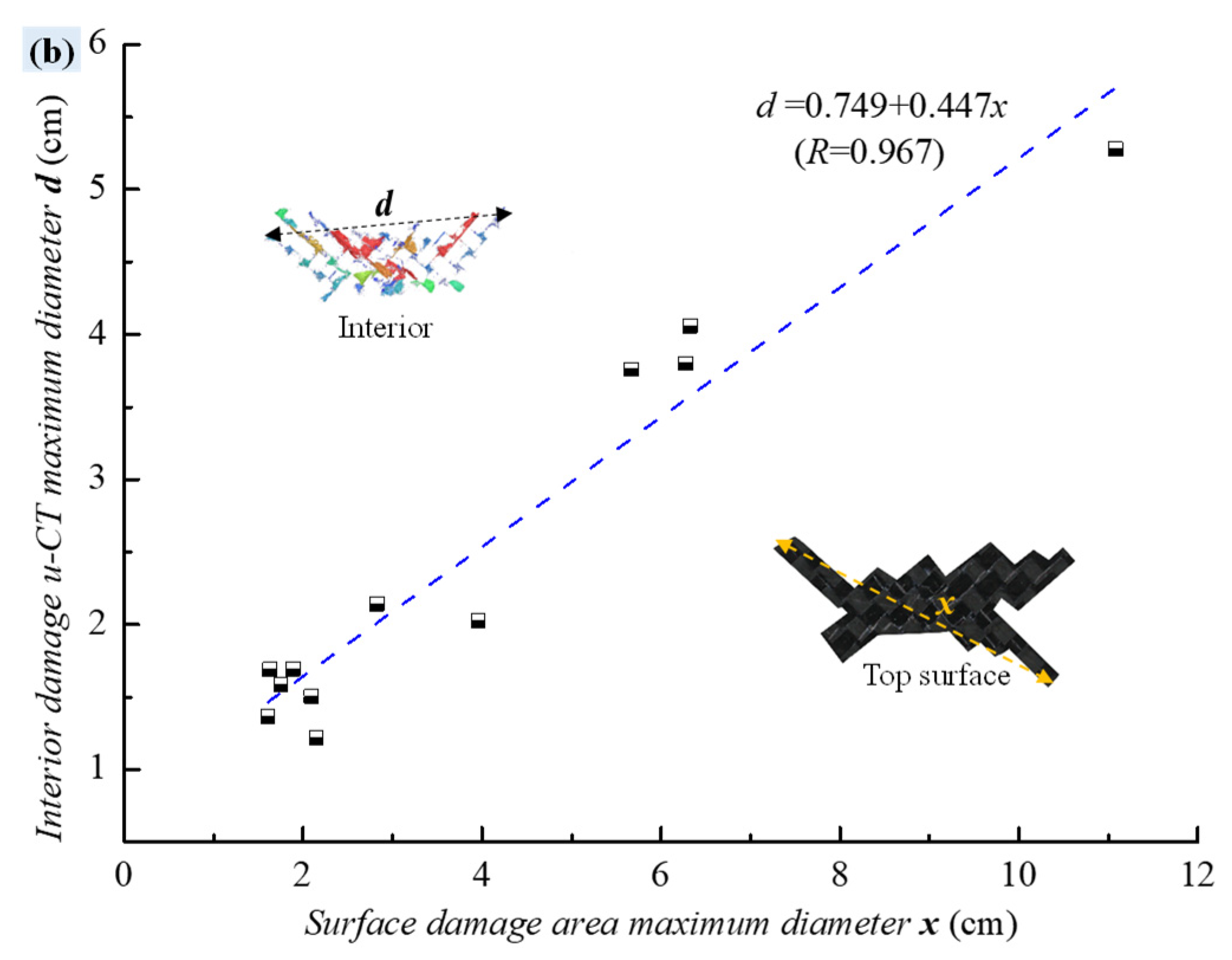
3.2. Damage Morphology
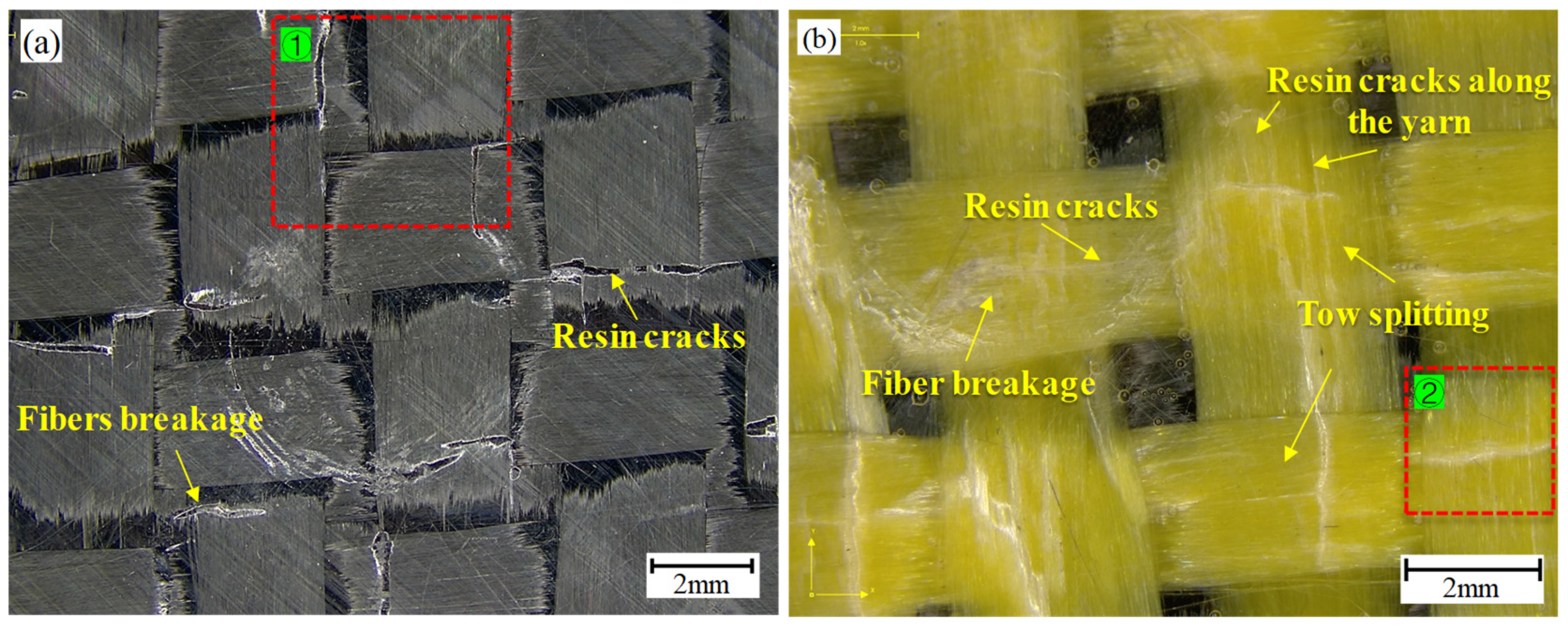
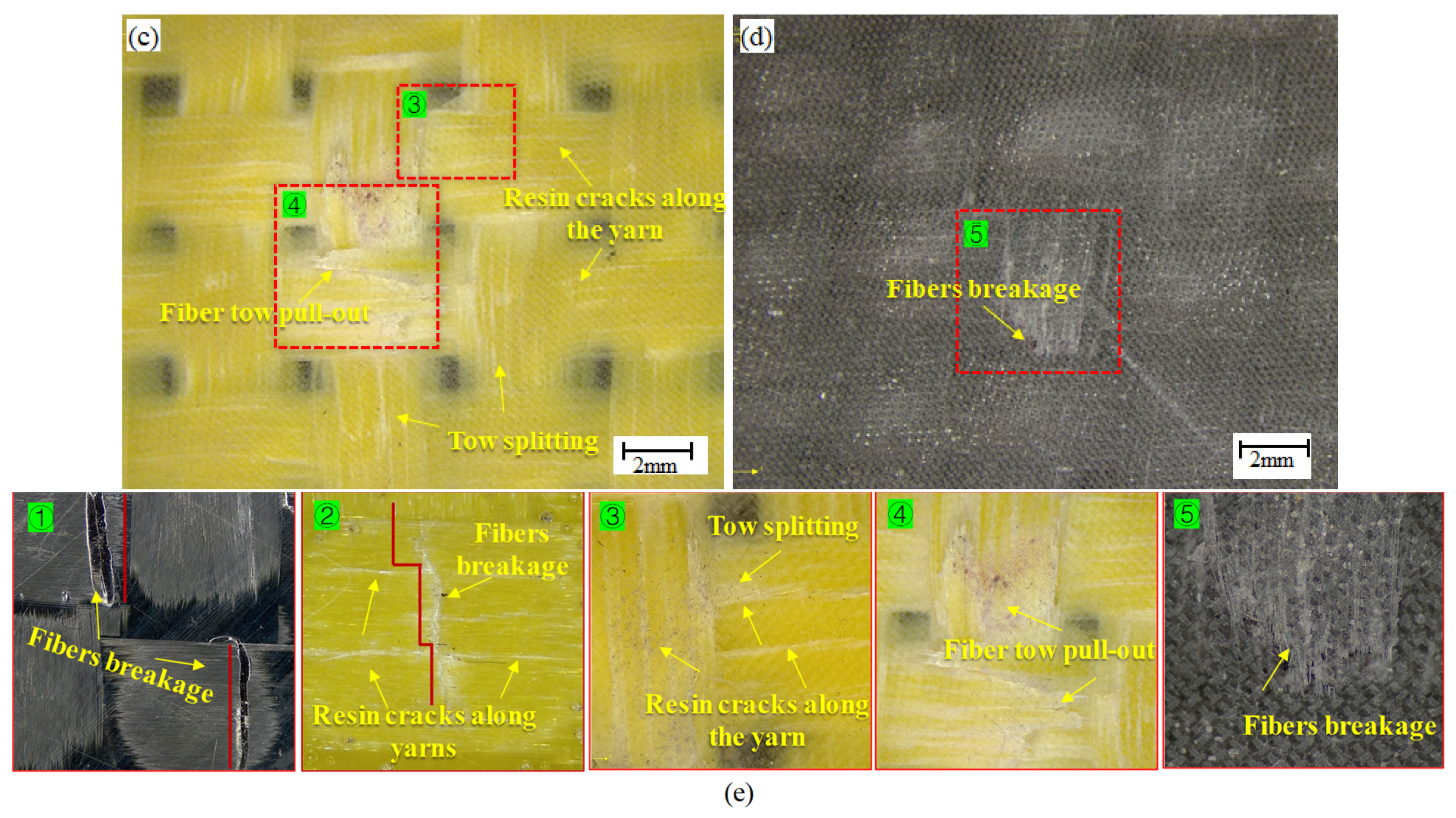
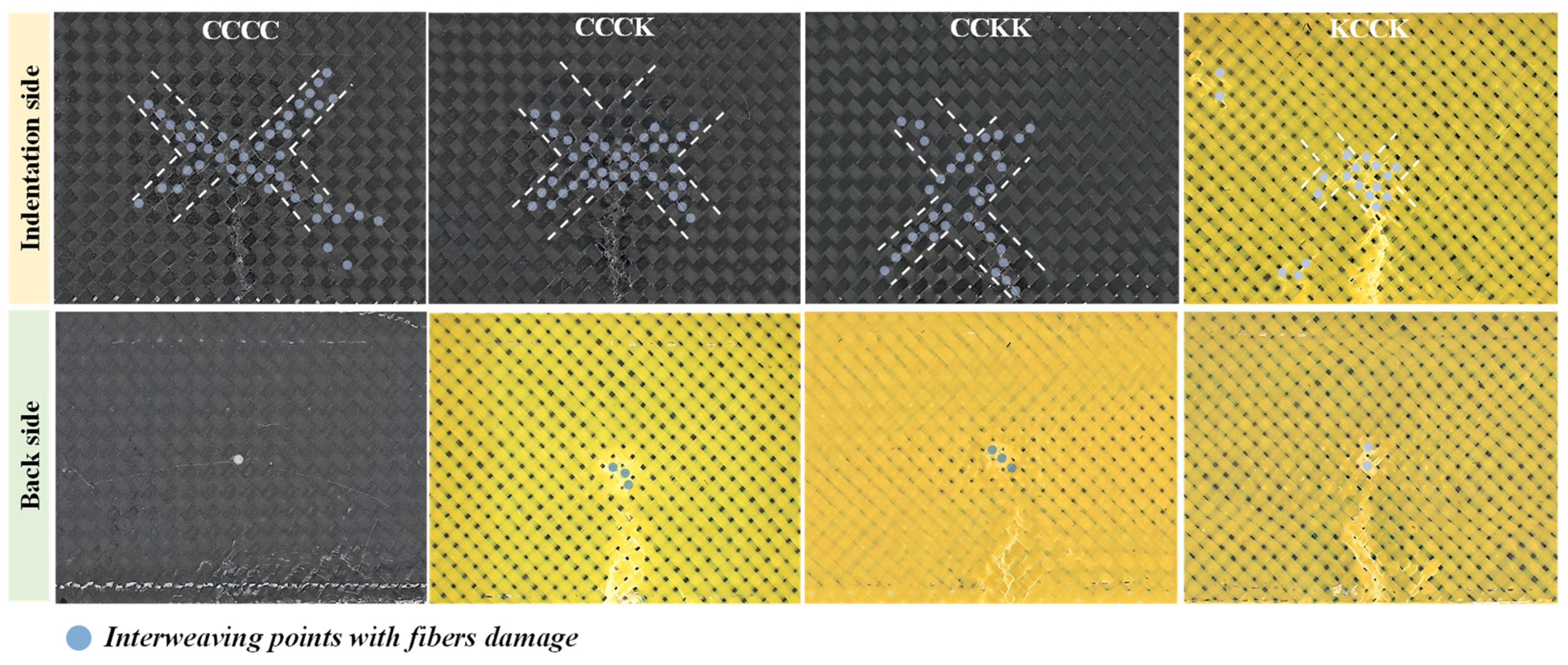
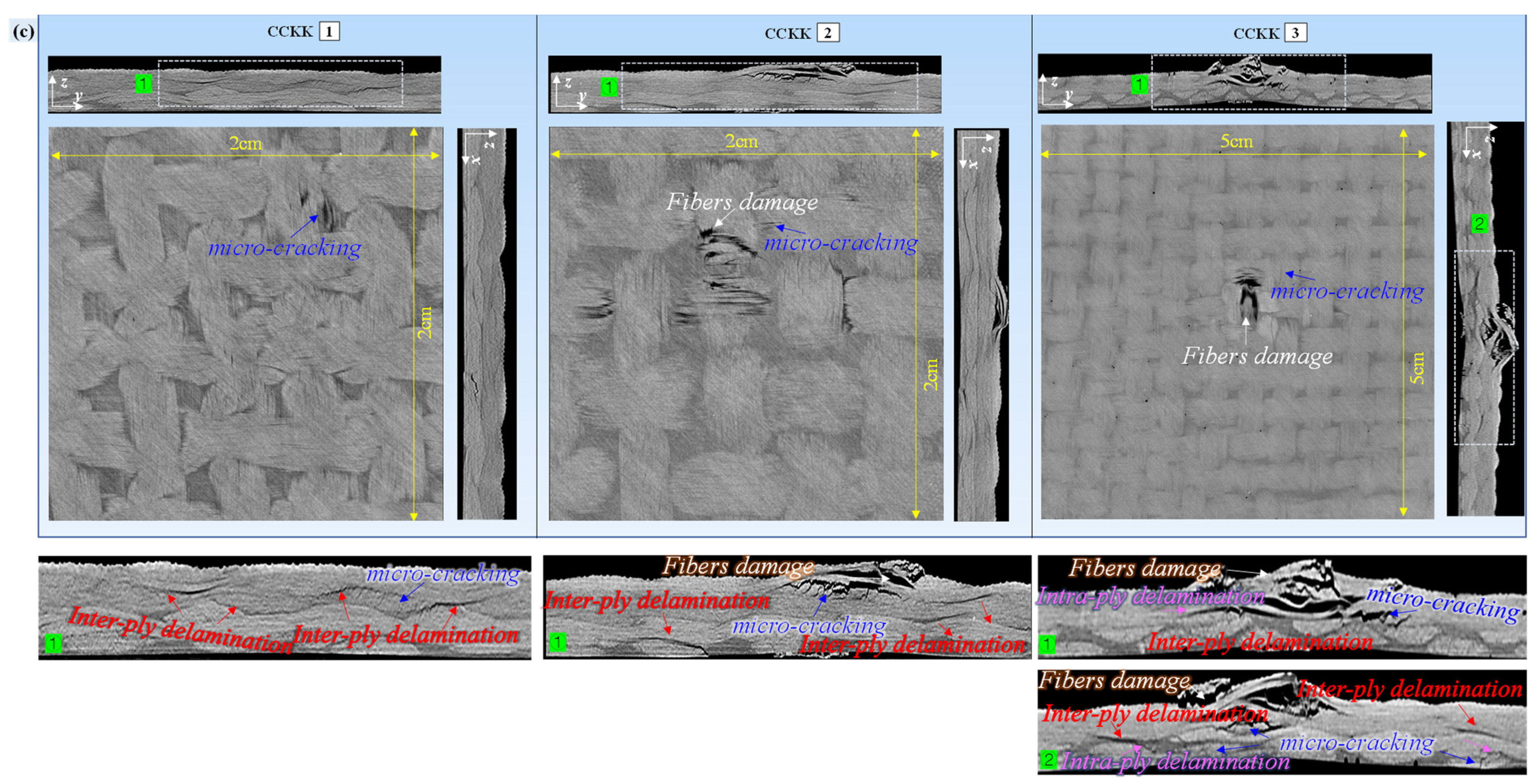
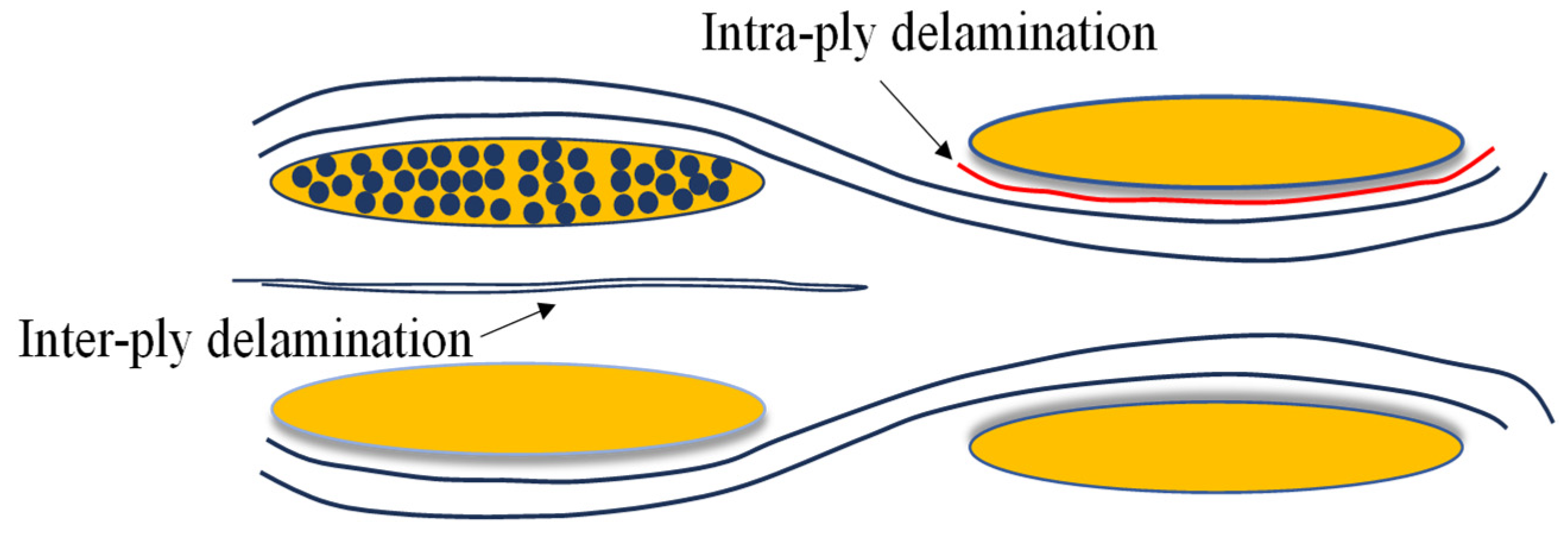
3.3. Microscopic Damage of Plain Woven Structure
3.4. Development of Indentation Damage
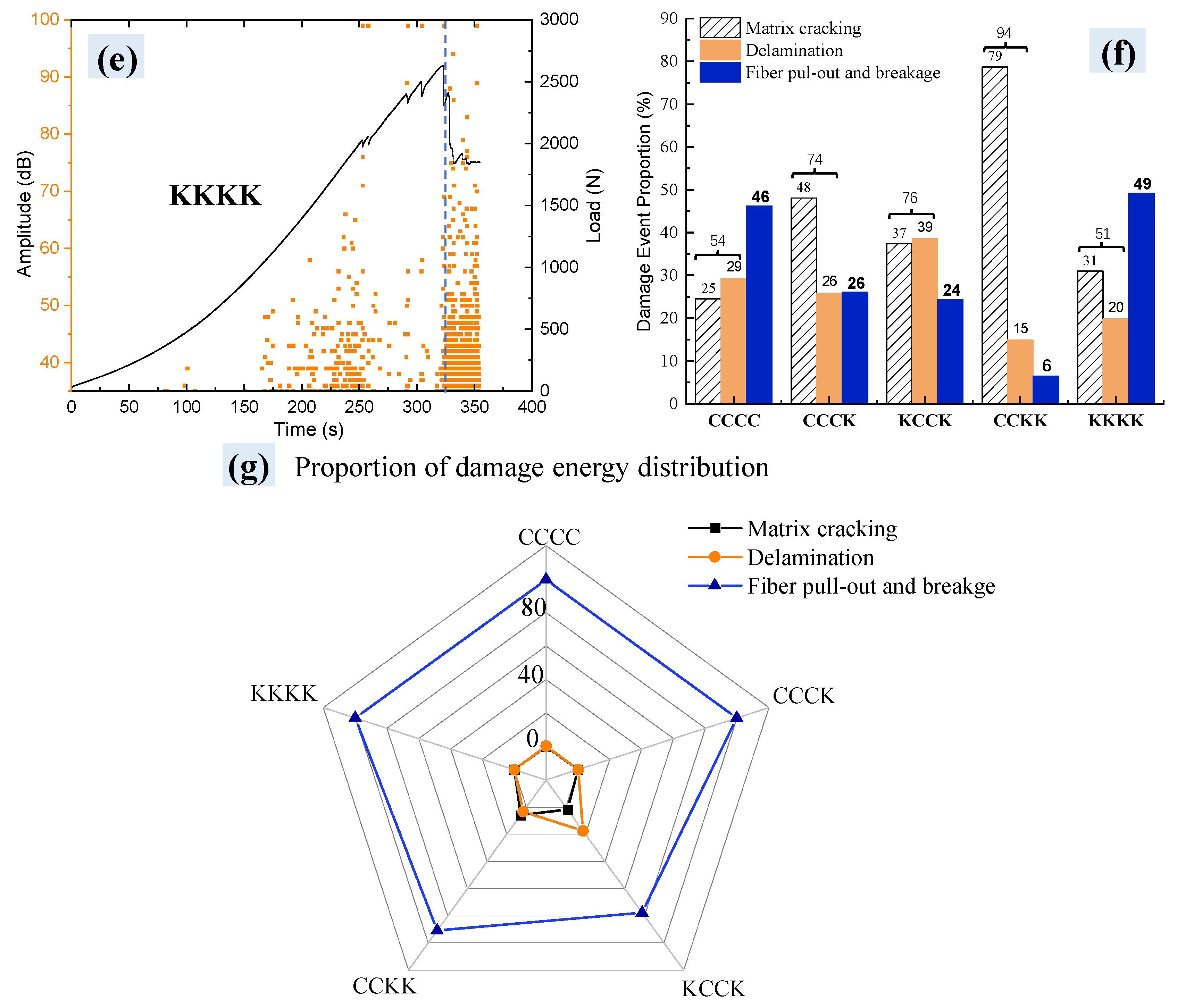
3.4.1. Acoustic Emission (AE) from Initial Load to Final Failure
3.4.2. Staged Characterization of Progressive Damage
- (1)
- Load–deflection curve and macroscopic progressive damage morphology
- (2)
- Microscopic progressive damage morphology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verma, L.; Andrew, J.J.; Sivakumar, S.M.; Balaganesan, G.; Vedantam, S.; Dhakal, H.N. Evaluation of quasi-static indentation response of superelastic shape memory alloy embedded GFRP laminates using AE monitoring. Polym. Test. 2020, 93, 106942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, L.; Andrew, J.J.; Sivakumar, M.S.; Balaganesan, G.; Vedantam, S.; Dhakal, H.N. Compression after high-velocity impact behavior of pseudo-elastic shape memory alloy embedded glass/epoxy composite laminates. Compos. Struct. 2020, 259, 113519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajmohammad, M.H.; Farrokhian, A.; Kolahchi, R. Dynamic analysis in beam element of wave-piercing Catamarans undergoing slamming load based on mathematical modelling. Ocean. Eng. 2021, 234, 109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Furjan, M.S.H.; Hajmohammad, M.H.; Shen, X.; Rajak, D.K.; Kolahchi, R. Evaluation of tensile strength and elastic modulus of 7075-T6 aluminum alloy by adding SiC reinforcing particles using vortex casting method. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 886, 161261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davood, R.; Elyas, S.; Mahshid, F.; Mohammad, A.; Kianoosh, S.; Ismaeil, G.; Majid, B.; Karen, A.; Mahdi, B.; Mostafa, B. 4D printing and annealing of PETG composites reinforced withshort carbonfibers. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 055957. [Google Scholar]
- Szeluga, U.; Kumanek, B.; Trzebicka, B. Synergy in hybrid polymer/nanocarbon composites. A review. Compos. Part A 2015, 73, 204–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safri, S.N.A.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Jawaid, M.; Jayakrishna, K. Impact Behaviour of Hybrid Composites for Structural Applications: A Review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 133, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armin, K.; Davood, R.K.; Mostafa, B. Various FDM Mechanisms Used in the Fabrication of Continuous-Fiber Reinforced Composites: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorey, G.; Sidey, G.R.; Hutchings, J. Impact properties of carbon fibre/Kevlar 49 fibre hydrid composites. Composites 1978, 9, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Kang, K.-H.; Park, O. Response of hybrid laminated composite plates under low-velocity impact. Comput. Struct. 1997, 65, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustin, J.; Joneson, A.; Mahinfalah, M.; Stone, J. Low velocity impact of combination Kevlar/carbon fiber sandwich composites. Compos. Struct. 2005, 69, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Zheng, X.; Yan, L.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X. Influence of asymmetric hybridization on impact response of 3D orthogonal woven composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 199, 108326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Xue, Y.S.; Sun, B.Z.; Gu, B.H. Ballistic penetration damages of hybrid plain-woven laminates with carbon, Kevlar and UHMWPE fibers in different stacking sequences. Def. Technol. 2023, 26, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia, A.A.; Tian, X.; Liu, T.; Zhou, J.; Ghouri, M.A.; Yun, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Li, D.; Malakhov, A.V. Mechanical and energy absorption behaviors of 3D printed continuous carbon/Kevlar hybrid thread reinforced PLA composites. Compos. Struct. 2023, 303, 116386. [Google Scholar]
- Zachariah, S.A.; Shenoy, B.S.; Jayan, J.; Pai, K.D. Experimental investigation on dynamic and static transverse behaviour of thin woven Carbon/Aramid hybrid laminates. J. King Saud Univ.-Eng. Sci. 2020, 9, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson, A.J.; Srinivasan, S.M.; Arockiarajan, A. Effect of multiphase fiber system and stacking sequence on low velocity impact and residual tensile behavior of glass/epoxy composite laminates. Polym. Compos. 2018, 40, 24884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pan, Z.; Wu, Z.; Ying, Z. Effect of carbon/Kevlar asymmetric hybridization ratio on the low-velocity impact response of plain woven laminates. Compos. Struct. 2021, 276, 114574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pan, Z.; Ying, Z.; Wu, Z. Symmetric and asymmetric intercalation effect on the low-velocity impact behavior of carbon/Kevlar hybrid woven laminates. Compos. Struct. 2022, 297, 115919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motezaker, M.; Kolahchi, R.; Rajak, D.K.; Mahmoud, S.R. Influences of fiber reinforced polymer layer on the dynamic deflection of concrete pipes containing nanoparticle subjected to earthquake load. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 26118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolahchi, R.; Keshtegar, B.; Trung, N.T. Optimization of dynamic properties for laminated multiphase nanocomposite sandwich conical shell in thermal and magnetic conditions. J. Sandw. Struct. Mater. 2022, 24, 643–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, J.J.; Srinivasan, S.M.; Arockiarajan, A.; Dhakal, H.N. Parameters influencing the impact response of fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composite materials: A critical review. Compos. Struct. 2019, 224, 111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigit, A.S.; Christoforou, A.P. Limits of asymptotic solutions in low-velocity impact of composite plates. Compos. Struct. 2007, 81, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasegeran, M.; Vasudevan, M.; Ramamoorthy, M.; Arumugam, A. Investigation of quasi-static indentation on sandwich structure with GFRP face sheets and PLA bio-inspired core: Numerical and experimental study. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 184, 110501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh Kumar, C.; Arumugam, V.; Santulli, C. Characterization of indentation damage resistance of hybrid composite laminates using acoustic emission monitoring. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 111, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoblom, P.O.; Hartness, J.T.; Cordell, T.M. On Low-Velocity Impact Testing of Composite Materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1988, 22, 30–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagih, A.; Maimí, P.; Blanco, N.; Costa, J. A quasi-static indentation test to elucidate the sequence of damage events in low velocity impacts on composite laminates. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 82, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettles, A.T.; Douglas, M.J. A Comparison of Quasi-Static Indentation Testing to Low Velocity Impact Testing. In Composite Materials: Testing, Design, and Acceptance Criteria; ED34, MSFC. AL 35812; NASA Marshall Space Flight Center: Phoenix, AZ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lammerant, L.; Verpoest, I. The interaction between matrix cracks and delaminations during quasi-static impact of composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1994, 51, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, F.; Re, V.D.; Minak, G.; Zucchelli, A. Damage and residual strength of laminated carbon–epoxy composite circular plates loaded at the centre. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2007, 38, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirichantra, J.; Ogin, S.L.; Jesson, D.A. The use of a controlled multiple quasi-static indentation test to characterise through-thickness penetration of composite panels. Compos. Part B Eng. 2012, 43, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiary Davijani, A.A.; Hajikhani, M.; Ahmadi, M. Acoustic Emission based on sentry function to monitor the initiation of delamination in composite materials. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3059–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morokov, E.; Levin, V.; Ryzhova, T.; Dubovikov, E.; Petronyuk, Y.; Gulevsky, I. Bending damage evolution from micro to macro level in CFRP laminates studied by high-frequency acoustic microscopy and acoustic emission. Compos. Struct. 2022, 288, 115427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léonard, F.; Stein, J.; Soutis, C.; Withers, P. The quantification of impact damage distribution in composite laminates by analysis of X-ray computed tomograms. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 152, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, R.; Seltzer, R.; Sket, F.; González, C.; Llorca, J. Influence of hybridisation on energy absorption of 3D woven composites under low-velocity impact loading. Modelling and experimental validation. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2022, 165, 104229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.T.; Yoshimura, A.; Watanabe, N.; Iwahori, Y.; Ishikawa, T. Further investigation of Delamination Reduction Trend for stitched composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 118, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Rao, Y.; Li, W. Low-velocity impact behavior of intraply hybrid composites based on carbon and glass non-crimp fabric. Compos. Struct. 2020, 234, 111713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marec, A.; Thomas, J.-H.; Guerjouma, R.E. Investigation of damage mechanisms of composite materials: Multivariable analysis based on temporal and wavelet features extracted from acoustic emission signals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ameur, M.; El Mahi, A.; Rebiere, J.-L.; Gimenez, I.; Beyaoui, M.; Abdennadher, M.; Haddar, M. Investigation and identification of damage mechanisms of unidirectional carbon/flax hybrid composites using acoustic emission. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2019, 216, 106511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Type | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T700 | 4900 | 220 | 1.52 |
| Kelvar49 | 2814 | 117 | 2.14 |
| Fabric | Configuration | Kevlar Quantity | Ply Ratio (Carbon–Kevlar) | Aerial Density (kg/m2) | Thickness (mm) | Fiber Volume Fraction (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain (±45°) | CCCC |  | 0-ply | 4:0 | 2.41 | 1.84 ± 0.05 | 40.7 ± 2.1 |
| CCCK |  | 1-ply | 3:1 | 2.32 | 1.86 ± 0.03 | 39.8 ± 1.9 | |
| CCKK | 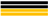 | 2-ply | 2:2 | 2.30 | 1.86 ± 0.04 | 41.7 ± 1.7 | |
| KCCK |  | 2-ply | 2:2 | 2.30 | 1.88 ± 0.05 | 40.8 ± 1.5 | |
| KKKK |  | 4-ply | 0:4 | 2.28 | 1.90 0.05 | 40.4 ± 2.0 | |
| Triaxial (±60/0°) | cccc |  | 0-ply | 4:0 | 3.47 | 2.62 0.06 | 38.2 ± 2.2 |
| ccck |  | 1-ply | 3:1 | 3.41 | 2.61 0.05 | 39.5 ± 1.2 | |
| cckk | 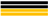 | 2-ply | 2:2 | 3.22 | 2.56 0.08 | 39.1 ± 3.1 | |
| kcck |  | 2-ply | 2:2 | 3.22 | 2.70 0.07 | 39.7 ± 2.0 | |
| kkkk |  | 4-ply | 0:4 | 3.22 | 2.71 0.06 | 40.3 ± 1.9 | |
| Fabric | Index | CCCC | CCCK | KCCK | CCKK | KKKK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain | Peak load | 0% | −10.72% | −33.86% | −35.42% | −44.51% |
| Stiffness | 0% | −7.35% | −27.58% | −25.59% | −35.55% | |
| Fabric | Index | cccc | Ccck | kcck | cckk | kkkk |
| Triaxial | Peak load | 0% | −9.97% | −16.31% | −20.69% | −46.03% |
| Stiffness | 0% | −6.23% | −22.27% | −19.95% | −41.43% |
| Type | CCCC | CCCK | CCKK | KCCK |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indentation side | 48 | 41 | 36 | 19 |
| Reverse side | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 |
| Damage Side | Type | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 | Stage 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indentation side | CCCC | ○ | ○√ | ○√ | ○ √ |
| CCCK | ○√ | ○√ | ○ √ | ○ √ | |
| KCCK | ○ ■# | ○ ■# | ○ ■# | ○ √ ■# | |
| CCKK | ○√ | ○√ | ○√ | ○ √ | |
| KKKK | ○ ■# | ○ √ ■# | ○ √☆ ■# | ○ √☆ ■# | |
| Reverse side | CCCC | ○ | ○√☆ | ○√☆ | ○√☆ |
| CCCK | ○ ■# | ○ √☆ ■# | ○ √☆ ■# | ○ √☆■# | |
| KCCK | ○ ■# | ○ √■# | ○ √☆ ■# | ○ √☆ ■# | |
| CCKK | ○ ■# | ○ √☆■# | ○ √☆■# | ○ √☆■# | |
| KKKK | ○ ■# | ○ √ ■# | ○ √☆■# | ○ √☆■# |
| Delamination | Stage 1 | Stage 2 | Stage 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCCC | IV and III | IV and III and I | IV and III and II and I |
| KCCK | IV and III and II | IV and III and II | IV and III and II |
| CCKK | IV and III and II | IV and III and II and I | IV and III and II and I |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, M.; Pan, Z.; Cai, Q.; Zhao, L.; Wu, Z. Effects of Carbon/Kevlar Hybrid Ply and Intercalation Sequence on Mechanical Properties and Damage Resistance of Composite Laminates under Quasi-Static Indentation. Polymers 2024, 16, 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131801
Wang M, Pan Z, Cai Q, Zhao L, Wu Z. Effects of Carbon/Kevlar Hybrid Ply and Intercalation Sequence on Mechanical Properties and Damage Resistance of Composite Laminates under Quasi-Static Indentation. Polymers. 2024; 16(13):1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131801
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Mingling, Zhongxiang Pan, Qimao Cai, Lei Zhao, and Zhenyu Wu. 2024. "Effects of Carbon/Kevlar Hybrid Ply and Intercalation Sequence on Mechanical Properties and Damage Resistance of Composite Laminates under Quasi-Static Indentation" Polymers 16, no. 13: 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131801
APA StyleWang, M., Pan, Z., Cai, Q., Zhao, L., & Wu, Z. (2024). Effects of Carbon/Kevlar Hybrid Ply and Intercalation Sequence on Mechanical Properties and Damage Resistance of Composite Laminates under Quasi-Static Indentation. Polymers, 16(13), 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131801






