Development of Highly Flexible Piezoelectric PVDF-TRFE/Reduced Graphene Oxide Doped Electrospun Nano-Fibers for Self-Powered Pressure Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Solution
2.2.2. Fabrication of Device
2.2.3. Vapor Phase Polymerization
2.2.4. Fabrication of Piezoelectric Pressure Sensor
3. Results
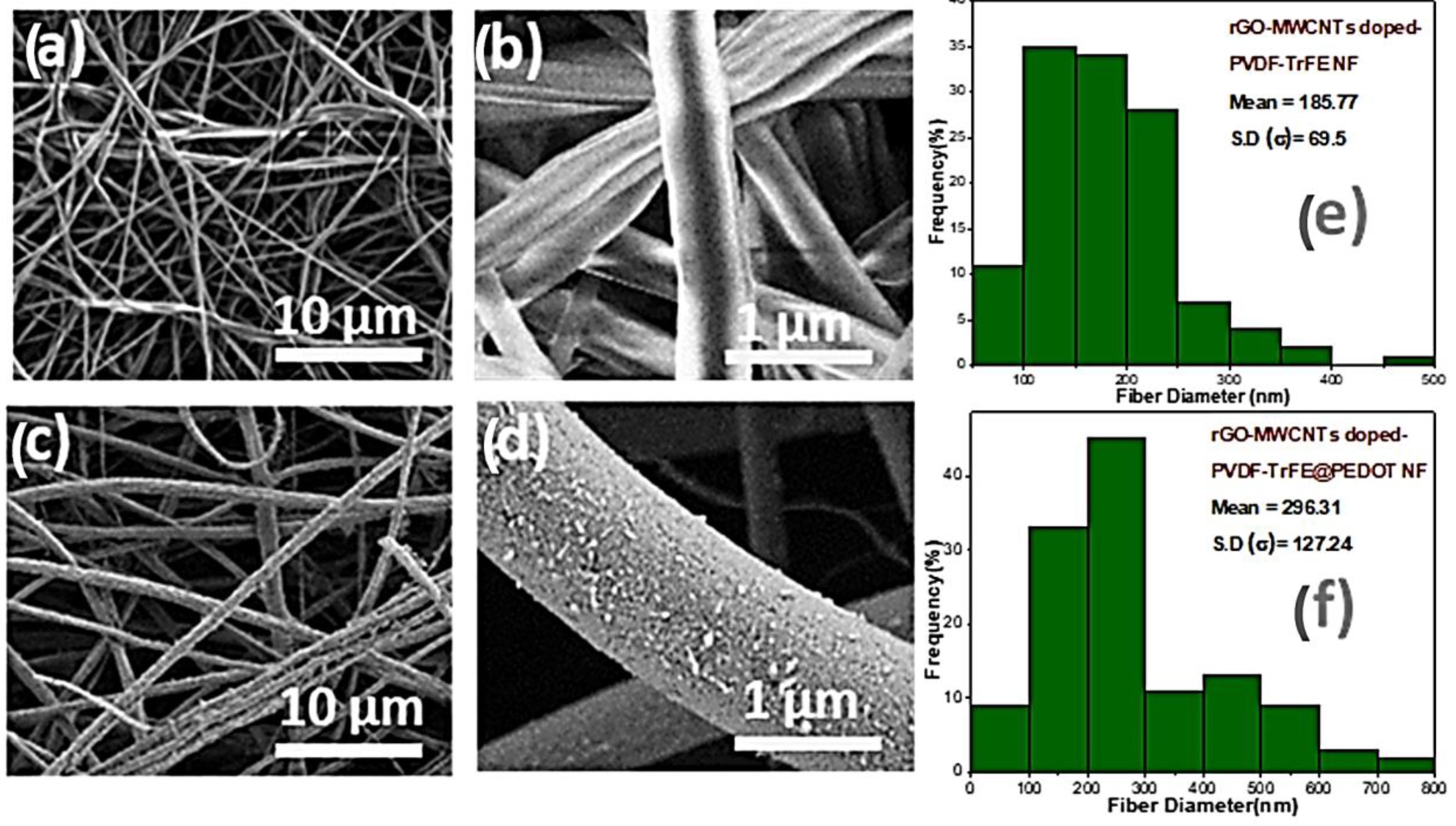
3.1. Morphological Analysis (FESEM and TEM)
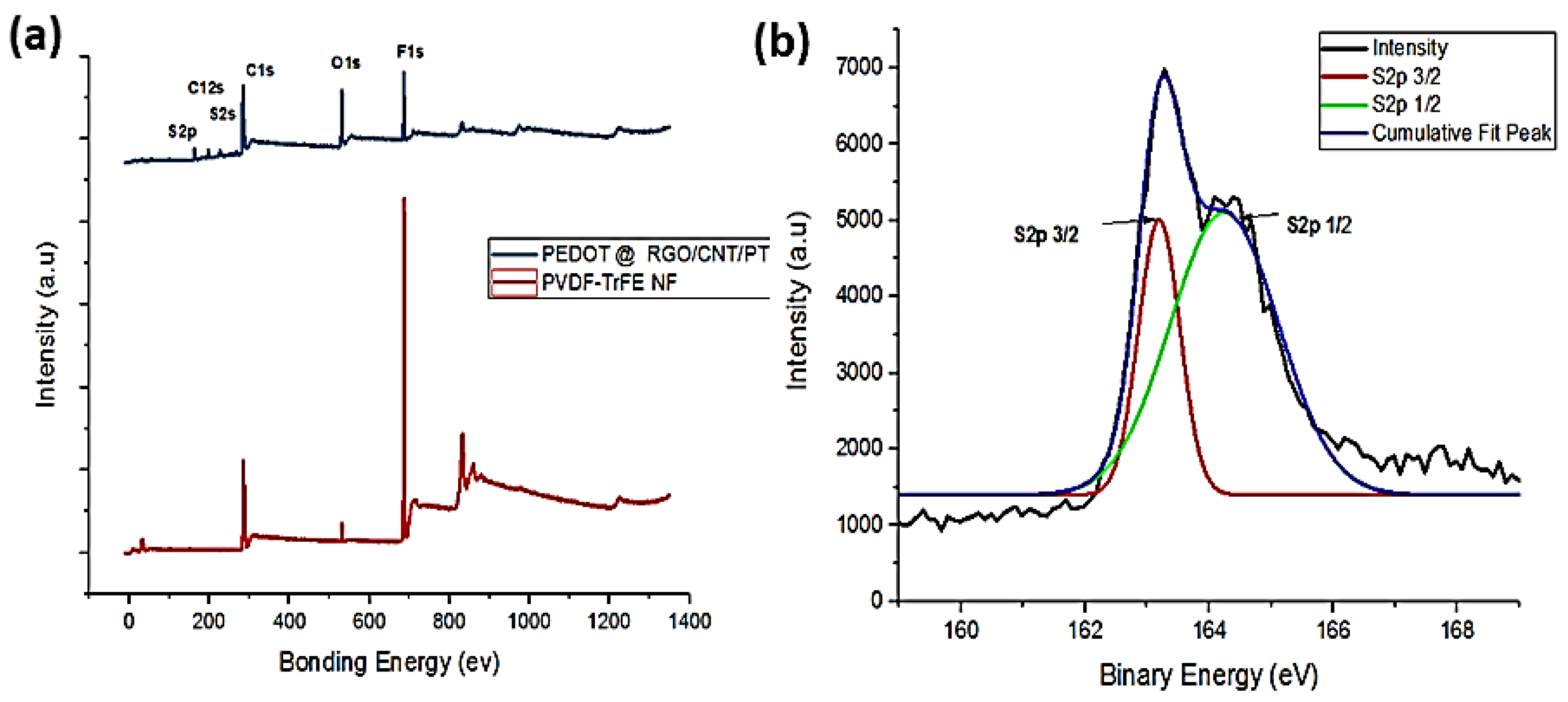
3.2. XPS Spectra Analysis
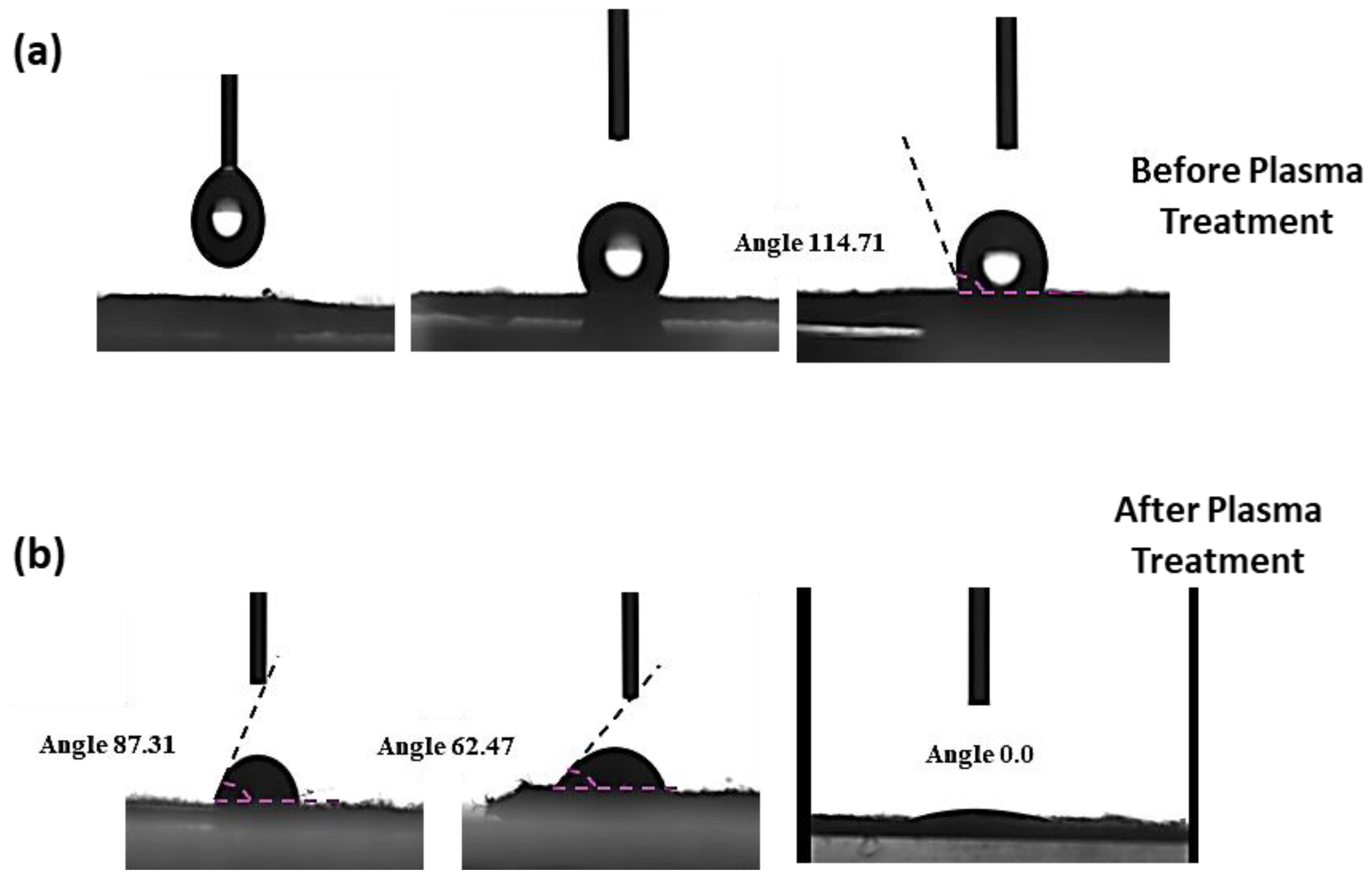
3.3. Contact Angle
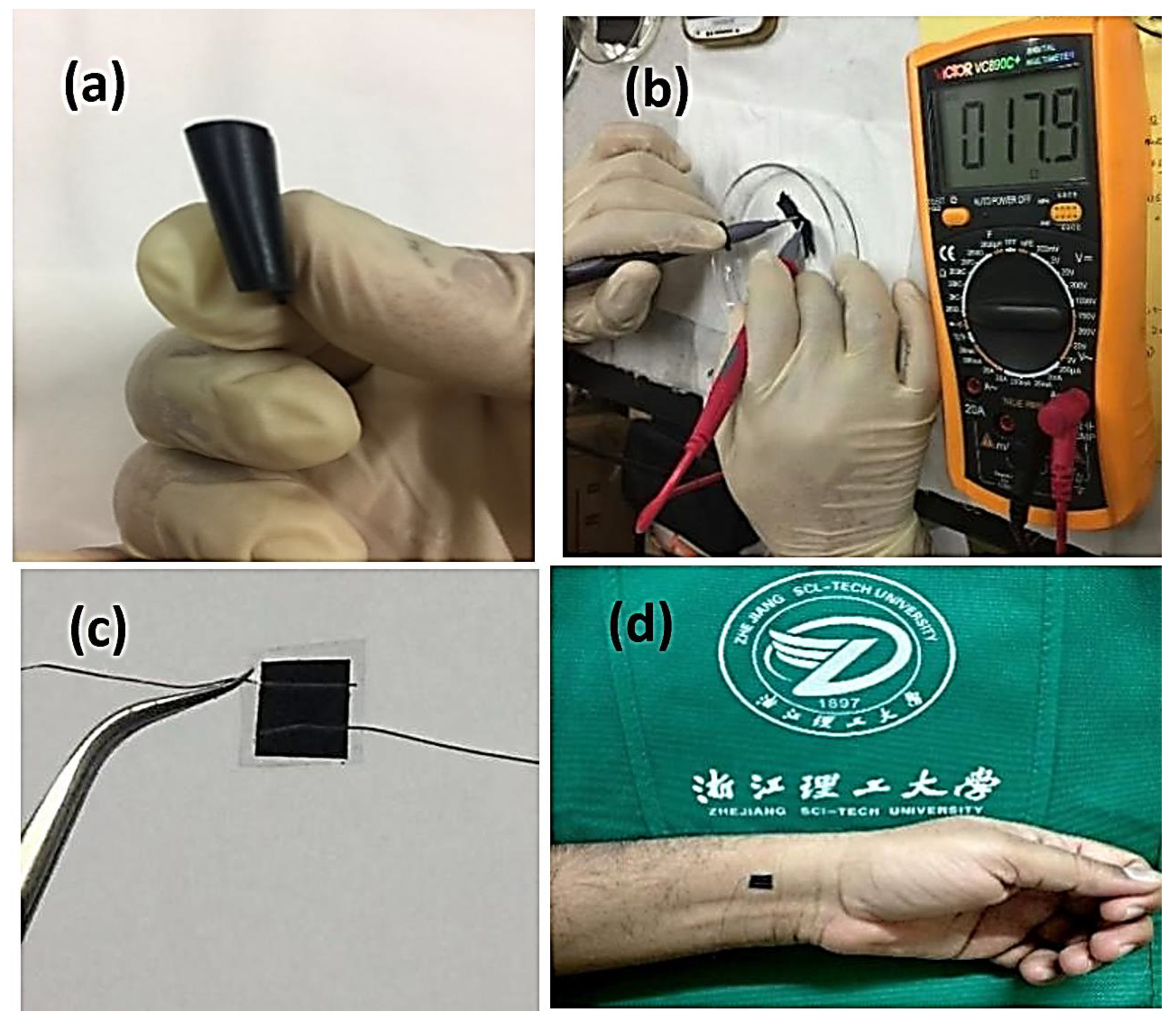
3.4. Resistivity
3.5. Durability
3.6. The Current–Voltage (I–V)
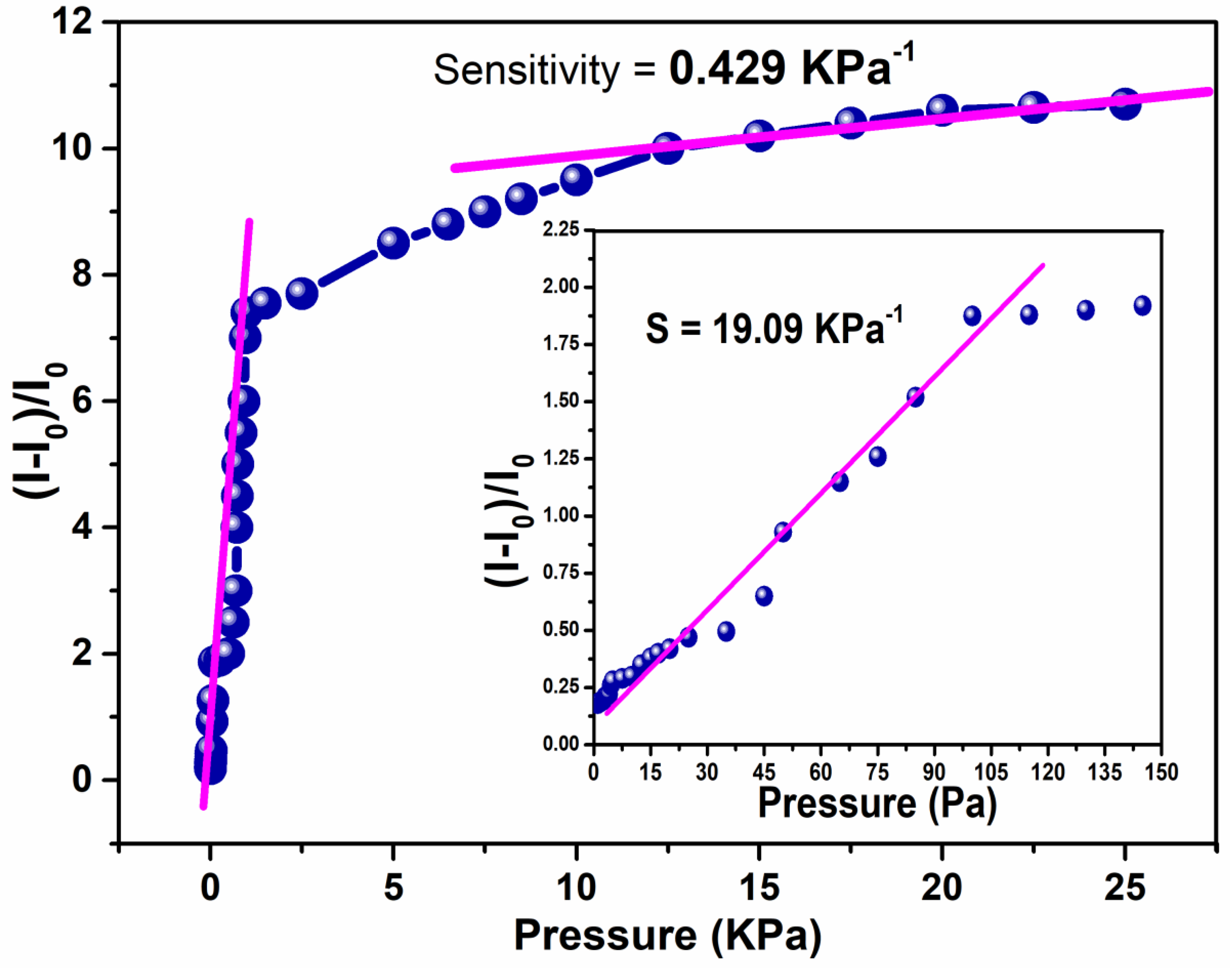
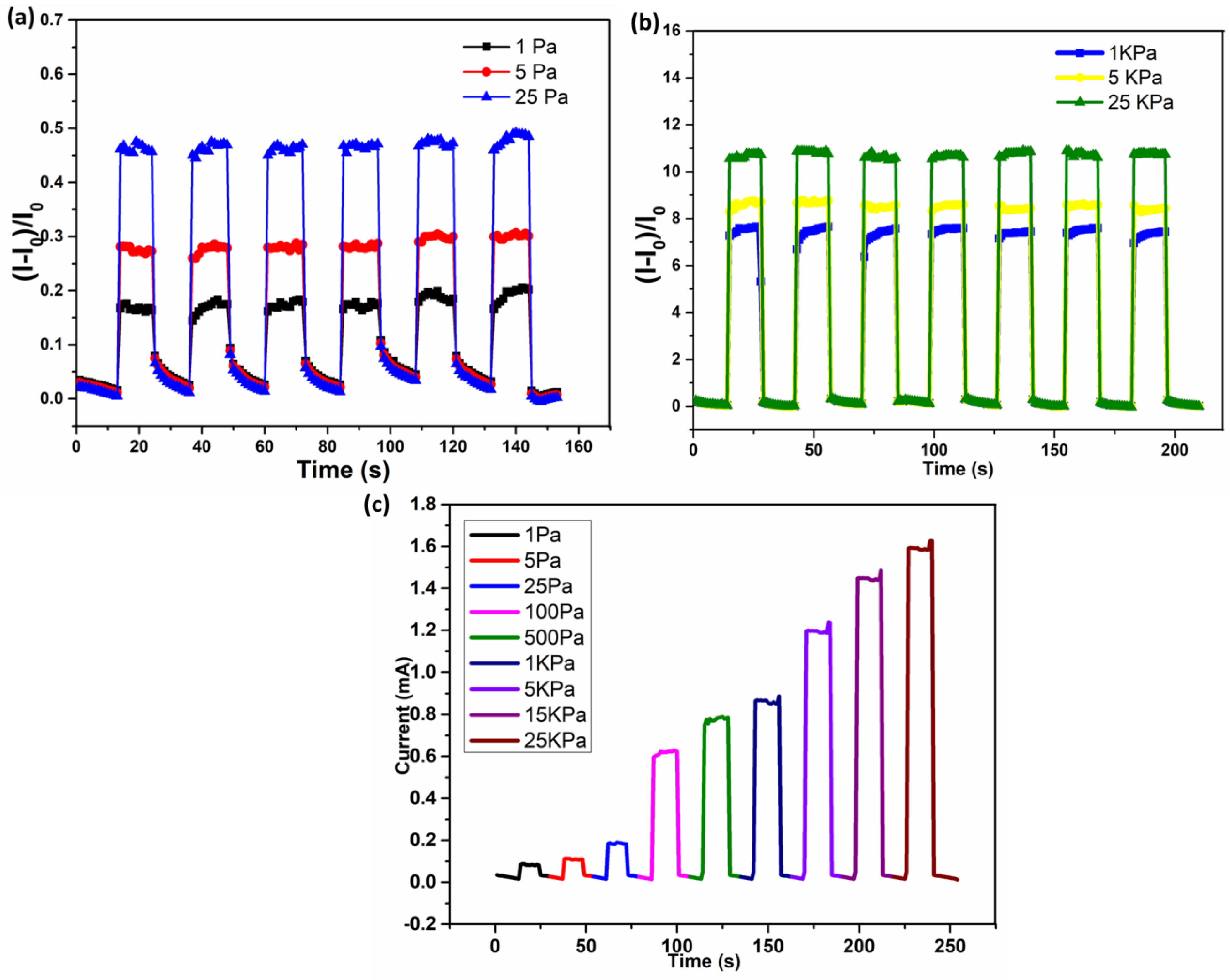
3.7. Sensing Performance
3.8. Pressure Response (Static and Dynamic)
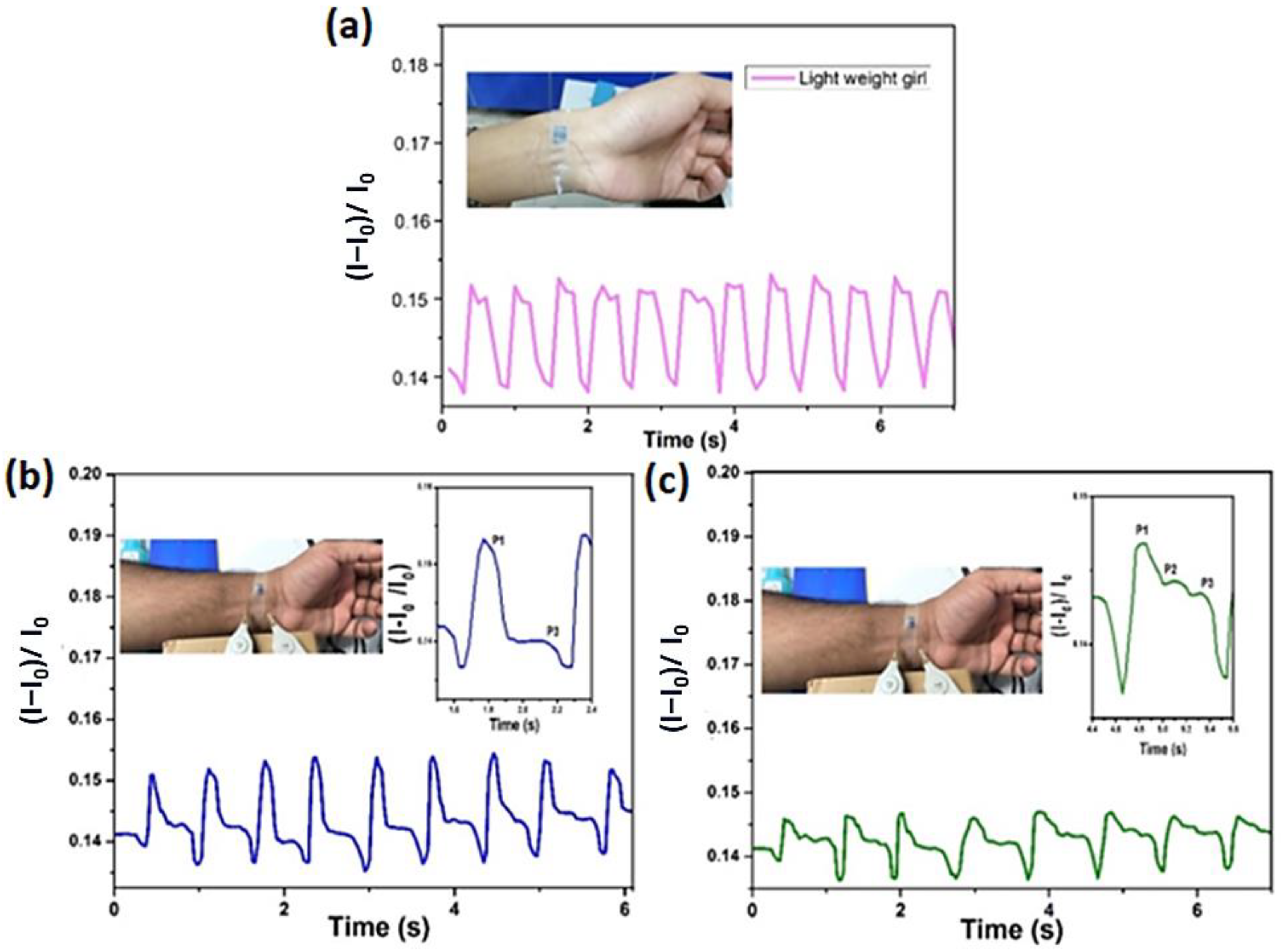
3.9. Human Physiological Response and Pulse Rate Response
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, C.; Li, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Xie, J.; Cao, Y.; Xue, M.; Lu, C. Highly Sensitive Wearable Pressure Sensors Based on Three-Scale Nested Wrinkling Microstructures of Polypyrrole Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 25811–25818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Jung, M.; Kim, B.; Kim, J.; Shin, K.; Kwon, O.-S.; Jeon, S. Low-voltage, high-sensitivity and high-reliability bimodal sensor array with fully inkjet-printed flexible conducting electrode for low power consumption electronic skin. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xia, K.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, Y. Advanced Carbon for Flexible and Wearable Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 31, e1801072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, G.; Tee, B.C.-K.; Mei, J.; Appleton, A.L.; Kim, D.H.; Wang, H.; Bao, Z. Flexible polymer transistors with high pressure sensitivity for application in electronic skin and health monitoring. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1859–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.-H.; Ma, S.-N.; Long, H.; Yuan, H.; Tang, C.Y.; Cheng, P.K.; Tsang, Y.H. Multifunctional Sensor Based on Porous Carbon Derived from Metal–Organic Frameworks for Real Time Health Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Shi, R.; Li, L.; Jiang, K.; Chen, D.; Shen, G. Ultrasensitive and ultraflexible e-skins with dual func-tionalities for wearable electronics. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, Y.S.; Bae, S.H.; Chen, H.; De Marco, N.; Yang, Y. Recent Progress in Materials and Devices toward Printable and Flexible Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4415–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Lou, Z.; Chen, S.; Chen, D.; Wang, Z.M.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G. All rGO-on-PVDF-nanofibers based self-powered electronic skins. Nano Energy 2017, 35, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Jiang, K.; Shen, G. An ultra-sensitive and rapid response speed graphene pressure sensors for electronic skin and health monitoring. Nano Energy 2016, 23, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, N.; Yue, Y.; Rao, J.; Cheng, F.; Su, J.; Liu, Z.; Gao, Y. Piezoresistive pressure sensor based on synergistical in-nerconnect polyvinyl alcohol nanowires/wrinkled graphene film. Small 2018, 14, 1704149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Meguro, H.; Okamoto, S.; Kimura, M. Flexible Tactile Sensor Using the Reversible Deformation of Poly(3-hexylthiophene) Nanofiber Assemblies. Langmuir 2012, 28, 17593–17596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, C.; Lee, G.-Y.; Kim, T.-I.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, H.N.; Ahn, S.-H.; Suh, K.-Y. A flexible and highly sensitive strain-gauge sensor using reversible interlocking of nanofibres. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, I.; Schulz, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Shanov, V.; Shi, D. A carbon nanotube strain sensor for structural health monitoring. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Wang, J.; Kang, W.; Cui, M.; Wang, X.; Foo, C.Y.; Chee, K.J.; Lee, P.S. Highly stretchable piezoresistive gra-phene-nanocellulose nanopaper for strain sensor. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, H.B.; Yeon, S.M.; Park, J.; Lee, N.K. Flexible and Stretchable Piezoelectric Sensor with Thickness-Tunable Configuration of Electrospun Nanofiber Mat and Elastomeric Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24773–24781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frutiger, A.; Muth, J.T.; Vogt, D.M.; Mengüç, Y.; Campo, A.; Valentine, A.D.; Walsh, C.J.; Lewis, J.A. Capacitive Soft Strain Sensors via Multicore–Shell Fiber Printing. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2440–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, W.; Jin, L.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.; Mao, L.; Zhang, H.; Yang, W. A flexible field-limited ordered ZnO nanorod-based self-powered tactile sensor array for electronic skin. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 16302–16306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, K.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; You, X.; Nan, N.; Shao, W.; Wang, L.; Ding, B.; Cui, S. A Highly Stretchable Nanofiber-Based Electronic Skin with Pressure-, Strain-, and Flexion-Sensitive Properties for Health and Motion Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 42951–42960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Reuveny, A.; Reeder, J.; Lee, S.; Jin, H.; Liu, Q.; Yokota, T.; Sekitani, T.; Isoyama, T.; Abe, Y. A transparent bend-ing-insensitive pressure sensor. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 11, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Park, J.; Lee, Y.; Ko, H. Triboelectric Generators and Sensors for Self-Powered Wearable Electronics. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3421–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jian, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y. Self-healable multifunctional electronic tattoos based on silk and graphene. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1605657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carponcin, D.; Dantras, E.; Dandurand, J.; Aridon, G.; Levallois, F.; Cadiergues, L.; Lacabanne, C. Electrical and Piezoelectric Behavior of Polyamide/PZT/CNT Multifunctional Nanocomposites. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2014, 16, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Scheinbeim, J.; Newman, B. Linear anhysteretic direct magnetoelectric effect in Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4/poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) 0-3 nanocomposites. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 56, 2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, N.; Elnabawy, E.; Abdelkader, M.; Hassanin, A.; Salah, M.; Nair, R.; Bhat, S.A. Static-aligned Piezoelectric poly (Vinyl-idene Fluoride) electrospun nanofibers/MWCNT composite membrane: Facile method. Polymers 2018, 10, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Zhuang, X.; Hu, J.; Lang, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y.; Jing, X. Synthesis of Biodegradable and Electroactive Multiblock Polylactide and Aniline Pentamer Copolymer for Tissue Engineering Applications. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, D.J.; Tang, J.B.; Doherty, S.A.; Hile, D.D.; Trantolo, D.J.; Wise, D.L.; Summerhayes, I.C. Enhanced peripheral nerve regeneration through a poled bioresorbable poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) guidance channel. J. Neural Eng. 2004, 1, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebrekrstos, A.; Madras, G.; Bose, S. Piezoelectric Response in Electrospun Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Fibers Containing Fluo-ro-Doped Graphene Derivatives. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovinger, A.J. Ferroelectric polymers. Science 1983, 220, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Unnikrishnan, L.; Nayak, S.K.; Mohanty, S. Advances in Piezoelectric Polymer Composites for Energy Harvesting Applications: A Systematic Review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Na, B.; Lv, R.; Li, C.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Z. Polar phase formation in poly(vinylidene fluoride) induced by melt annealing. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2012, 50, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradys, A.; Sajkiewicz, P.; Adamovsky, S.; Minakov, A.; Schick, C. Crystallization of poly(vinylidene fluoride) during ultra-fast cooling. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 461, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Hsu, S.L.; Honeker, C.; Bravet, D.J.; Williams, D.S. The Role of Surface Charge of Nucleation Agents on the Crystallization Behavior of Poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 7379–7388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, P.; Caparros, C.; Gonçalves, R.; Martins, P.; Benelmekki, M.; Botelho, G.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Role of nanoparticle surface charge on the nucleation of the electroactive β poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposites for sensor and actuator ap-plications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 15790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sencadas, V.; Moreira, M.V.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Pouzada, A.S.; Filho, R.G. α to β Transformation on PVDF films obtained by uniaxial stretch. Mater. Sci. Forum 2006, 514, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Sencadas, V.; Ribelles, J.L.G.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Influence of processing conditions on polymorphism and nan-ofiber morphology of electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride) electrospun membranes. Soft Mater. 2010, 8, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sencadas, V.; Filho, R.G.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Processing and characterization of a novel nonporous poly(vinilidene fluoride) films in the β phase. J. Non-Crystalline Solids 2006, 352, 2226–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajkiewicz, P.; Wasiak, A.; Gocłowski, Z. Phase transitions during stretching of poly(vinylidene fluoride). Eur. Polym. J. 1999, 35, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mohajir, B.-E.; Heymans, N. Changes in structural and mechanical behaviour of PVDF with processing and thermomechanical treatments. 1. Change in structure. Polymer 2001, 42, 5661–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Madras, G.; Bose, S. Process induced electroactive β-polymorph in PVDF: Effect on dielectric and ferroelectric properties. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 14792–14799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaka, S.; Miyata, S. Effects of crystal structure on piezoelectric and ferroelectric properties of copo-ly(vinylidenefluoride-tetrafluoroethylene). J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 57, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.A.; Davies, D.L.; Karim, M.M.; Nagle, J.K.; Wolf, M.O.; Patrick, B.O. Photophysical behaviour of cyclometalated irid-ium(iii) complexes with phosphino(terthiophene) ligands. Dalt. Trans. 2013, 42, 12354–12363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T. Piezoelectricity and pyroelectricity in polymers. IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul. 1989, 24, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doshi, J.; Reneker, D.H. Electrospinning process and applications of electrospun fibers. J. Electrost. 1995, 35, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, J. Preparation and properties of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride) mem-branes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.; Gustafsson, C.; Bertilsson, H.; Rychwalski, R.W. Enhancement of β phase crystals formation with the use of nanofillers in PVDF films and fibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2011, 71, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, K.; Lazareva, I.; Mandal, D.; Paloumpa, I.; Müller, K.; Koval, Y.; Müller, P.; Schmeißer, D. Electrical investigations on metal/ferroelectric/insulator/semiconductor structures using poly[vinylidene fluoride trifluoroethylene] as ferroelectric layer for organic nonvolatile memory applications. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. 2009, 27, 504–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Sung, E.-G.; Kim, E.-A.; Lee, T.-J. Gambogic acid induces apoptosis and sensitizes TRAIL-mediated apoptosis through downregulation of cFLIPL in renal carcinoma Caki cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 48, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Huang, S.; Yee, W.A.; Tjiu, W.C.; Liu, Y.; Kotaki, M.; Boey, Y.C.F.; Ma, J.; Liu, T.; Lu, X. Electrospinning of Polyvinylidene Difluoride with Carbon Nanotubes: Synergistic Effects of Extensional Force and Interfacial Interaction on Crystalline Structures. Langmuir 2008, 24, 13621–13626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, A.; Nandi, A.K. Noncovalent functionalization of multiwalled carbon nanotube by a polythiophene-based compati-bilizer: Reinforcement and conductivity improvement in poly (vinylidene fluoride) films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 9360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, D.; Kim, K.J.; Lee, J.S. Simple synthesis of palladium nanoparticles, β-phase formation, and the control of chain and dipole orientations in palladium-doped poly (vinylidene fluoride) thin. Angmuir 2012, 28, 10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, J.S.; Clarke, D.R. Effect of Electrospinning on the Ferroelectric Phase Content of Polyvinylidene Difluoride Fibers. Langmuir 2008, 24, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baji, A.; Mai, Y.-W.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y. Electrospinning induced ferroelectricity in poly(vinylidene fluoride) fibers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 3068–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Huang, B.; Zhang, J.; Wang, A.; Ren, K.; Wang, Z.L. Electrospun Poly(l -Lactic Acid) Nanofibers for Nanogenerator and Diagnostic Sensor Applications. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1600476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Yousefi, A.A. Electrospun PVDF/MWCNT/OMMT hybrid nanocomposites: Preparation and characterization. Iran. Polym. J. 2017, 26, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, F.; Yin, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Dong, M. Recent Study Advances in Flexible Sensors Based on Polyimides. Sensors 2018, 18, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, D.R.; Tenneti, K.K.; Li, C.Y.; Ko, F.K.; Sics, I.; Hsiao, B.S. On the structure and morphology of polyvinylidene fluo-ride-nanoclay nanocomposites. Polymer 2006, 47, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.-Y.; Cong, P.-H.; Liu, X.-J.; Liu, T.-X.; Huang, S.; Li, T.-S. The preparation of PVDF/clay nanocomposites and the inves-tigation of their tribological properties. Wear 2009, 266, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, P.; Dadbin, S.; Frounchi, M. Localized controlled release of stratifin reduces implantation-induced dermal fibrosis. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2012, 10, 745. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.-A.; Kim, M.-J.; Chen, S.-M.; Wu, Y.-S.; Lam, K.-H.; Chan, H.L.-W.; Fan, J.-T. Tough and porous piezoelectric P(VDF-TrFE)/organosilicate composite membrane. High Perform. Polym. 2016, 29, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaraiah, V.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Ramaprabhu, S. Functionalized Graphene–PVDF Foam Composites for EMI Shielding. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-M.; Liu, Y.-L. Conductivity and mechanical properties of well-dispersed single-wall carbon nanotube/polystyrene composite. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Martínez, G.; González-Domínguez, J.M.; Ansón, A.; Martínez, M.T.; Gómez, M.A. Grafting of a hydroxylated poly(ether ether ketone) to the surface of single-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 8285–8296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, W.A.; Kong, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Kotaki, M.; Lu, X. Polymorphism of electrospun polyvinylidene difluoride/carbon nanotube (CNT) nanocomposites: Synergistic effects of CNT surface chemistry, extensional force and supercritical carbon dioxide treatment. Polymer 2012, 53, 5097–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, S.; Nandi, A.K. Piezoelectric β Polymorph in Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposite Films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14670–14680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.; Lim, J.Y.; Hong, S.M.; Lee, J.; Ha, J.; Choi, H.J.; Seo, Y. Enhanced piezoelectric properties of electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride)/multiwalled carbon nanotube composites due to high β-phase formation in poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 11791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Liu, M.; Jeong, Y.G.; Kang, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, N.; Cheng, B.; Yang, G. Performance enhancements in poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based piezoelectric nanogenerators for efficient energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2018, 56, 662–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, N.B.; Afrooz, A.R.M.N.; Bisesi, J.H.; Aich, N.; Plazas-Tuttle, J.; Sabo-Attwood, T. Emergent Properties and Toxicological Considerations for Nanohybrid Materials in Aquatic Systems. Nanomaterials 2014, 4, 372–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, W.W. Clinical measurement of arterial stiffness obtained from noninvasive pressure waveforms. Am. J. Hypertens. 2005, 18, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM F43-99; Standard Test Methods for Resistivity of Semiconductor Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1999.
- Munir, S.; Jiang, B.; Guilcher, A.; Brett, S.; Redwood, S.; Marber, M.; Chowienczyk, P. Exercise reduces arterial pressure augmentation through vasodilation of muscular arteries in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2008, 294, H1645–H1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Hu, M.; Zhou, L.; Qiang, X. Self-Powered Wearable Pressure Sensors with Enhanced Piezoelectric Properties of Aligned P(VDF-TrFE)/MWCNT Composites for Monitoring Human Physiological and Muscle Motion Signs. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; He, J.; Wang, H.; Qi, K.; Nan, N.; You, X.; Shao, W.; Wang, L.; Ding, B.; Cui, S. Highly sensitive, self-powered and wearable electronic skin based on pressure-sensitive nanofiber woven fabric sensor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-M.; Chou, M.-H.; Zeng, W.-Y. Piezoelectric Response of Aligned Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Carbon Nanotube Nanofibrous Membranes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shao, J.; An, N.; Li, X.; Tian, H.; Xu, C.; Ding, Y. Self-powered flexible pressure sensors with vertically well-aligned piezoelectric nanowire arrays for monitoring vital signs. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 11806–11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material | Form | Sensitivity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF-TrFE/MWCNTs | Nano-fiber | 540 (mV/N) | [72] |
| PVDF-TrFE@PEDOT | Nonwoven | 18.376 kPa−1 | [73] |
| PVDF/CNT | Nano-fiber | 2.26 (mV/N) | [74] |
| CNT/rGO doped PDMS | Nonwoven | 11.02 kPa−1 | [69] |
| PVDF-TrFE | Nano-wire | 458.2 (mV/N) | [75] |
| GO doped PU@PEDOT | Nano-fiber | 20.6 KPa−1 | [18] |
| rGO-MWCNTs doped PVDF-TrFE@PEDOT | Nano-fiber | 19.09 kPa−1 | Present study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, A.; Khoso, N.A.; Arain, M.F.; Khan, I.A.; Javed, K.; Khan, A.; Memon, S.I.; Fan, Q.; Shao, J. Development of Highly Flexible Piezoelectric PVDF-TRFE/Reduced Graphene Oxide Doped Electrospun Nano-Fibers for Self-Powered Pressure Sensor. Polymers 2024, 16, 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131781
Ahmed A, Khoso NA, Arain MF, Khan IA, Javed K, Khan A, Memon SI, Fan Q, Shao J. Development of Highly Flexible Piezoelectric PVDF-TRFE/Reduced Graphene Oxide Doped Electrospun Nano-Fibers for Self-Powered Pressure Sensor. Polymers. 2024; 16(13):1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131781
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Arsalan, Nazakat Ali Khoso, Muhammad Fahad Arain, Imran Ahmad Khan, Kashif Javed, Asfandyar Khan, Sanam Irum Memon, Qinguo Fan, and Jianzhong Shao. 2024. "Development of Highly Flexible Piezoelectric PVDF-TRFE/Reduced Graphene Oxide Doped Electrospun Nano-Fibers for Self-Powered Pressure Sensor" Polymers 16, no. 13: 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131781
APA StyleAhmed, A., Khoso, N. A., Arain, M. F., Khan, I. A., Javed, K., Khan, A., Memon, S. I., Fan, Q., & Shao, J. (2024). Development of Highly Flexible Piezoelectric PVDF-TRFE/Reduced Graphene Oxide Doped Electrospun Nano-Fibers for Self-Powered Pressure Sensor. Polymers, 16(13), 1781. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16131781







