An Approach to a Silver Conductive Ink for Inkjet Printer Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Conductive Ink Preparation
2.3. Physico-Chemical Methods in the Research and Printing Processes
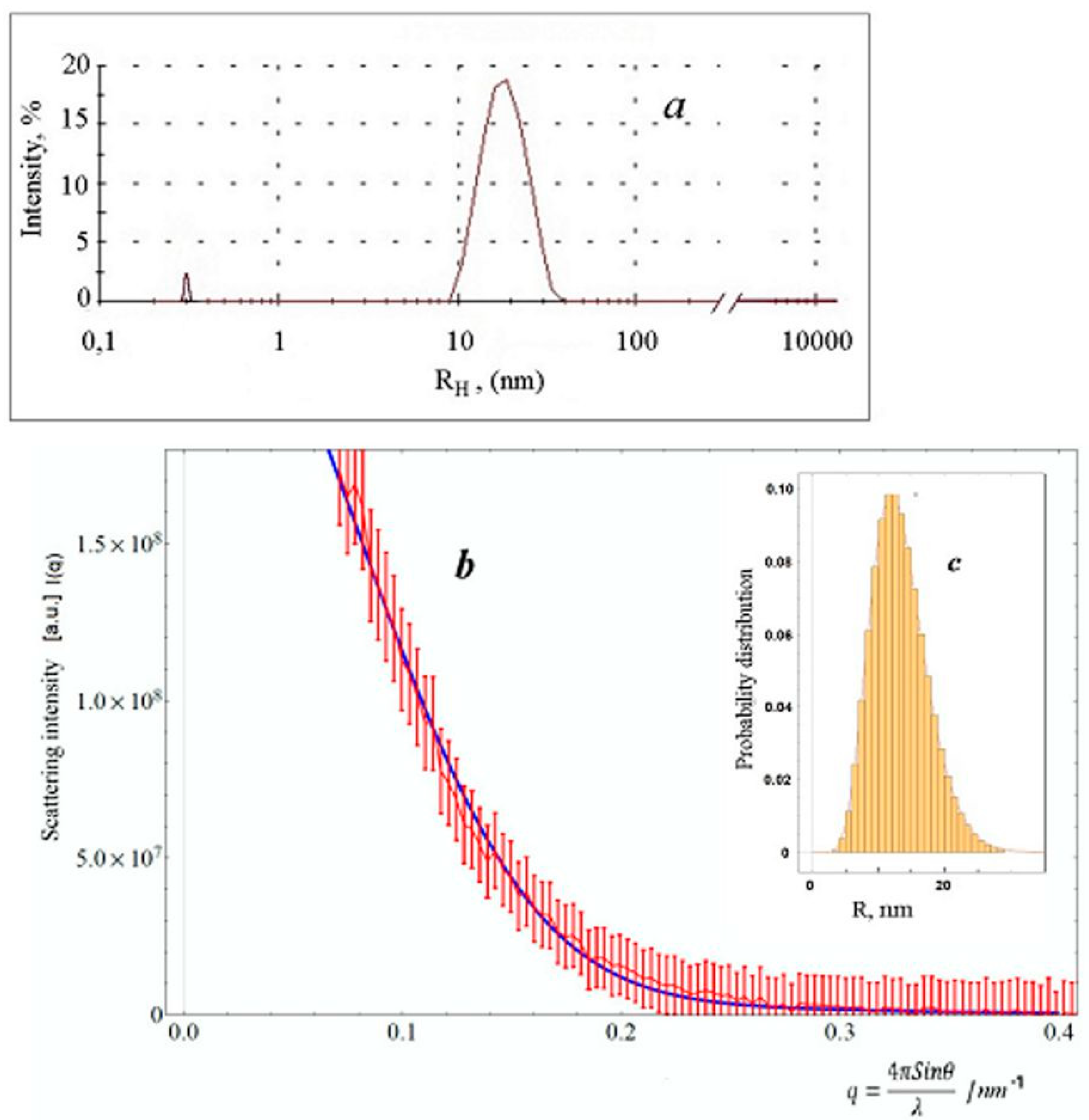
2.4. SAXS Studies of Colloid Particles
2.5. Theoretical Model of SAXS: Model of Aggregated Polydisperse Spheres (APSs)
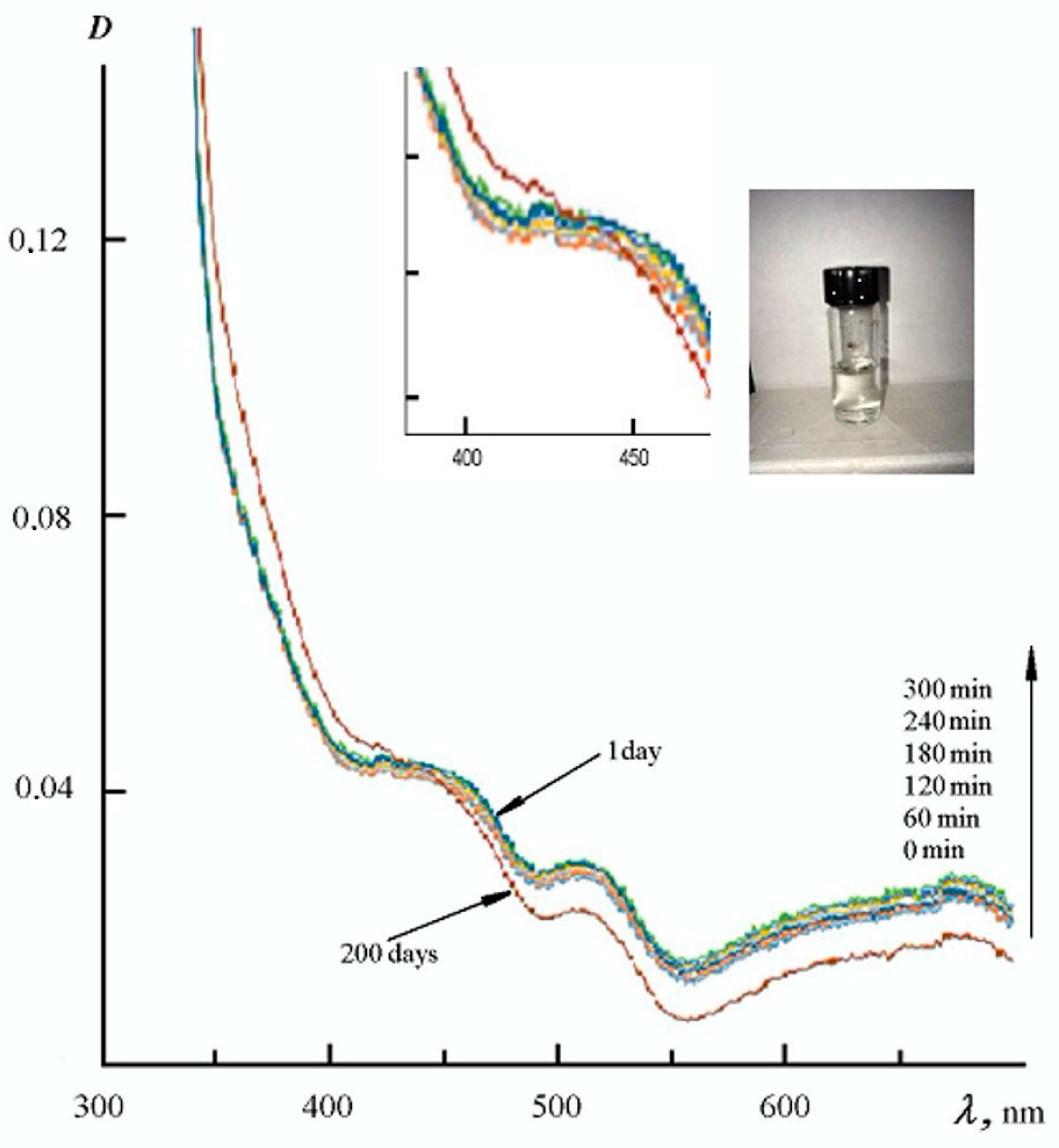
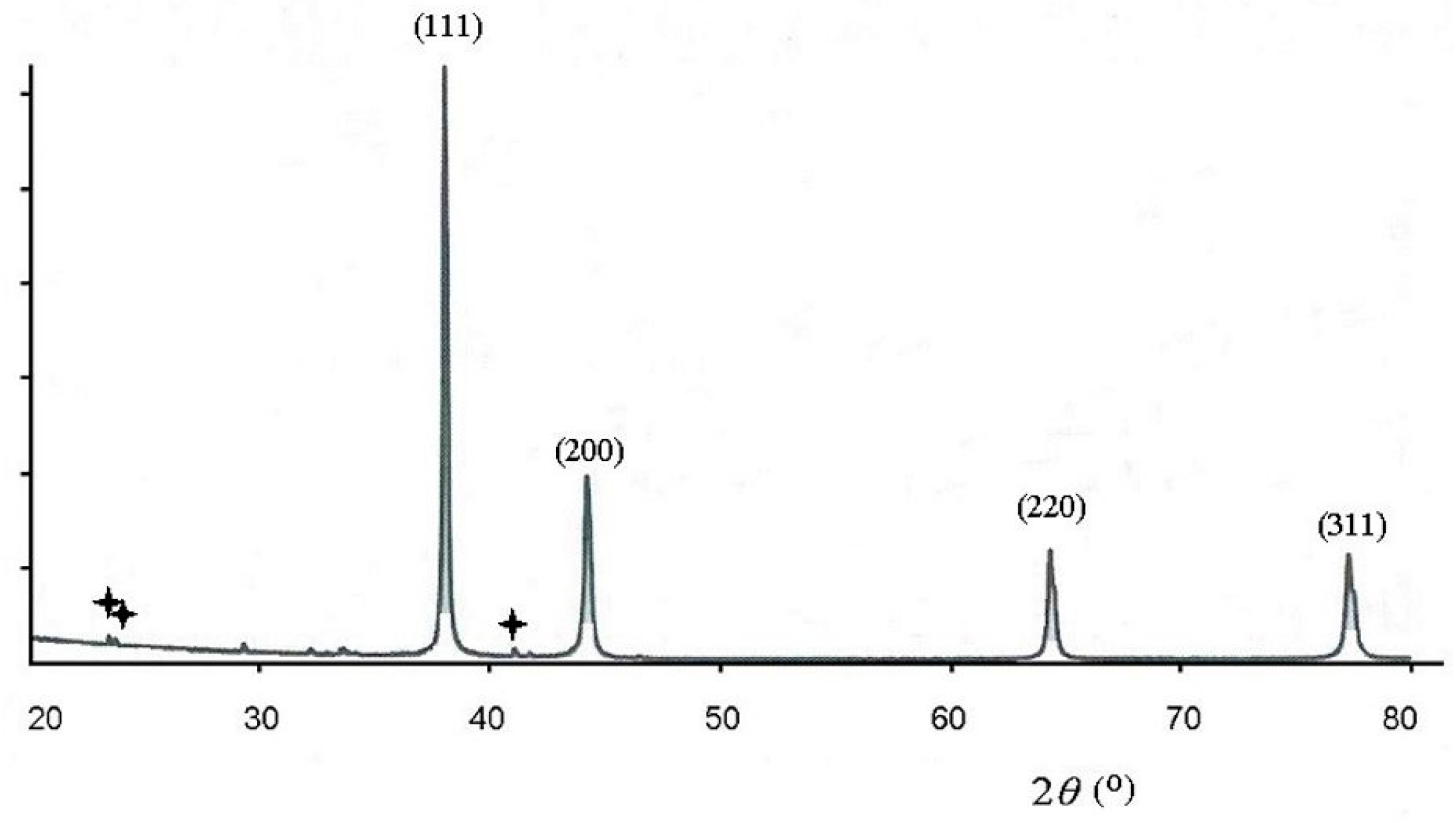
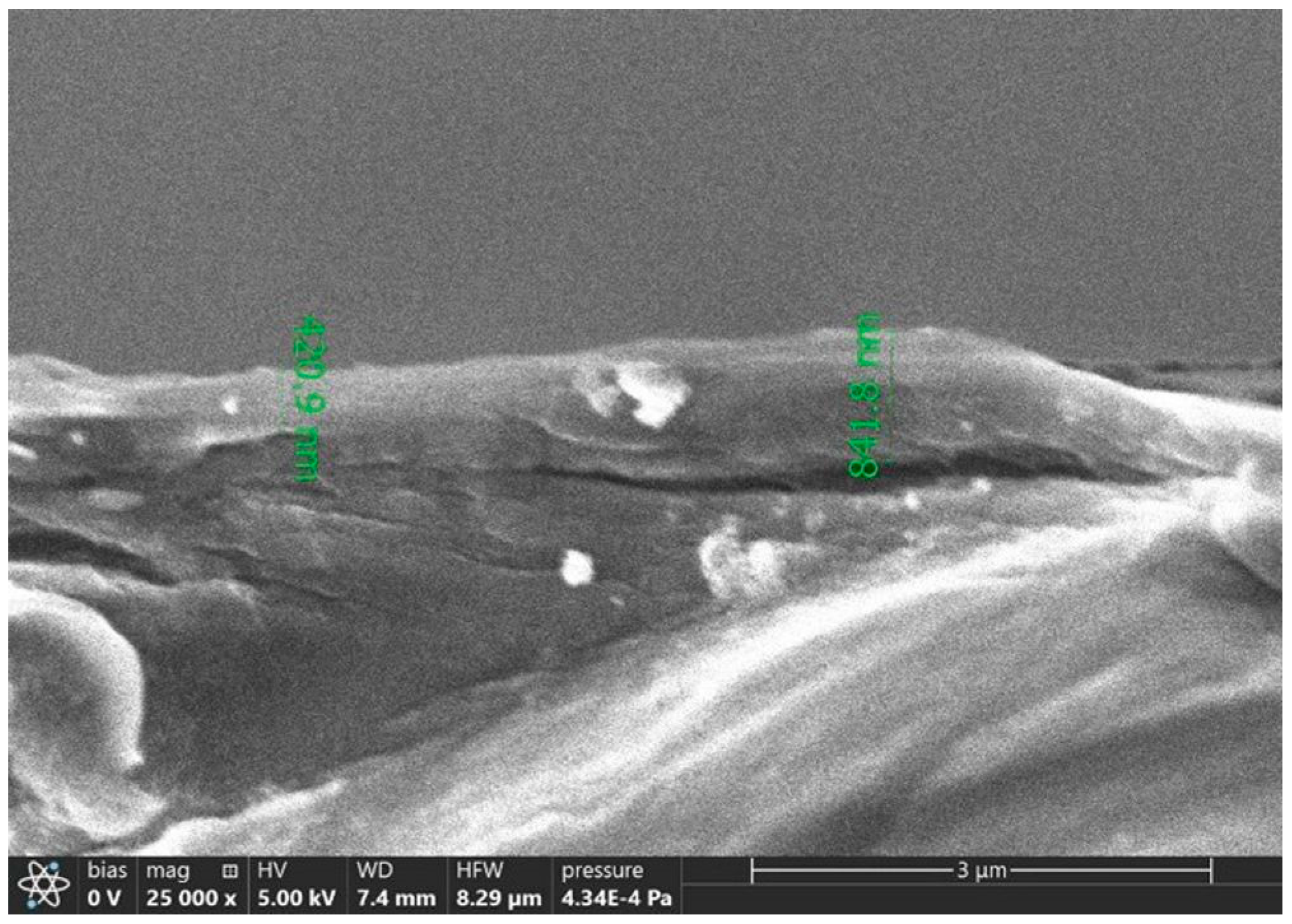
3. Results and Discussion
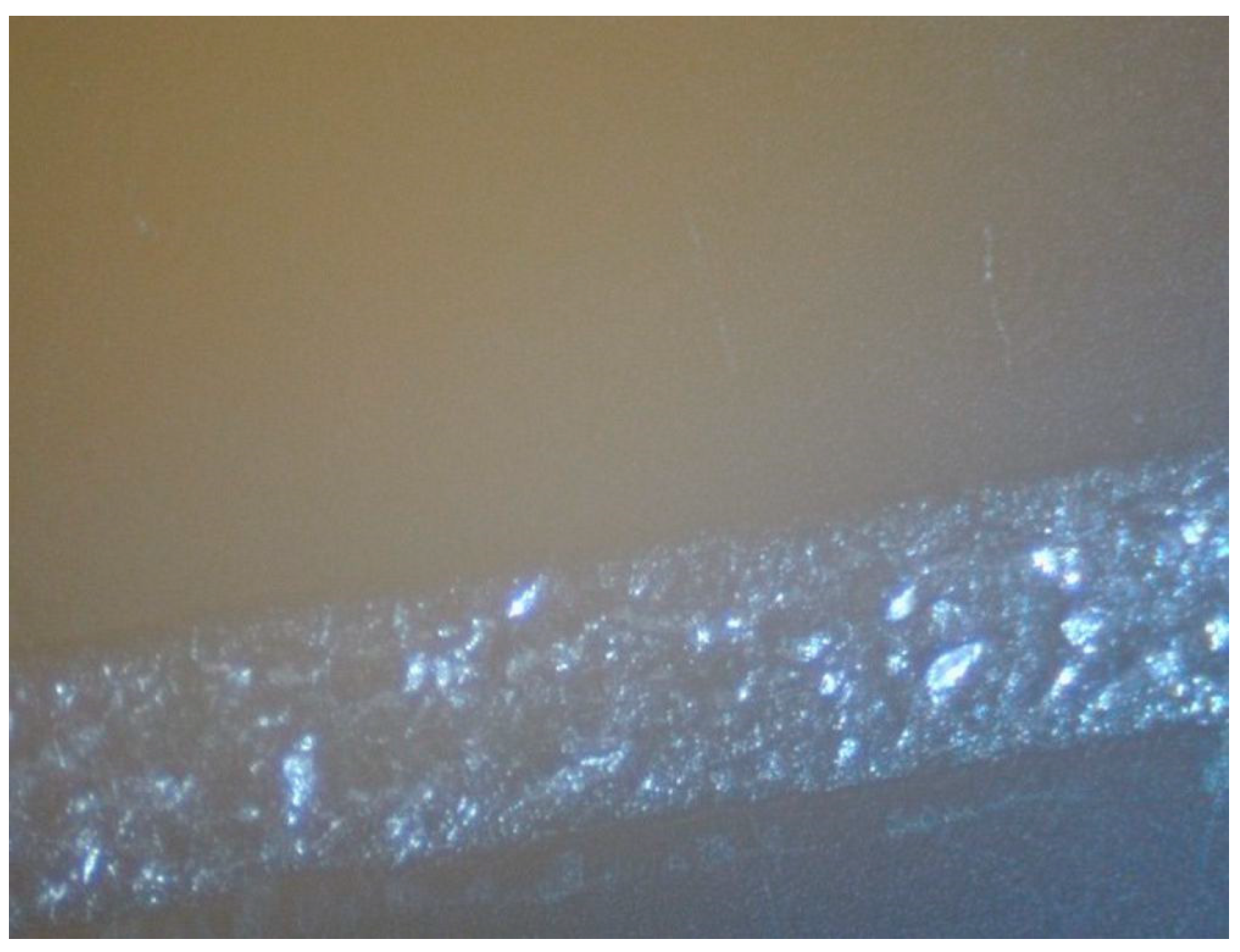
4. Inkjet Printing and Heat Treatment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bastola, A.; He, Y.; Im, J.; Rivers, G.; Wang, F.; Worsley, R.; Austin, J.S.; Nelson-Dummett, O.; Wildman, R.D.; Hague, R.; et al. Formulation of functional materials for inkjet printing: A pathway towards fully 3D printed electronics. Mater. Today Electron. 2023, 6, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Foralosso, R.; Trindade, G.F.; Ilchev, A.; Ruiz-Cantu, L.; Clark, E.A.; Khaled, S.; Hague, R.J.M.; Tuck, C.J.; Rose, F.R.A.J.; et al. A reactive prodrug ink formulation strategy for inkjet 3D printing of controlled release dosage forms and implants. Adv. Therap. 2020, 3, 1900187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Li, H.; Song, Y. Inkjet printing-based high-throughput DNA synthesis. Giant 2024, 17, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, X. Inkjet-printed flexible sensors: From function materials, manufacture process, and applications perspective. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minemawari, H. Inkjet printing of single-crystal films of organic molecular semiconductors for flexible and printed electronics. In Proceedings of the International Display Workshops (IDW 22), Fukuoka, Japan, 14–16 December 2022; pp. 111–113. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, H.; McKernan, C.; Elliott, C.; Dean, M. Consumer purchase intention towards a quick response (QR) code for antibiotic information: An exploratory study. Sci. Food 2022, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, A.; Levato, R.; D’Este, M.; Piluso, S.; Eglin, D.; Malda, J. Printability and shape fidelity of bioinks in 3D bioprinting. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 11028–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Park, M.J.; Choo, Y.W.; Huang, Y.; Phuntsho, S.; Shon, H.K. Inkjet printing technique for membrane fabrication and modification: A review. Desalination 2023, 565, 116841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, W.; Guo, Y.; Kashani, A.; Wang, K.; Ferrara, L.; Agudelo, I. Concrete 3D printing technology in sustainable construction: A review on raw materials, concrete types and performances. Dev. Built Environ. 2024, 17, 100378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, D.; Clemens, W.; Breitung, S.; Hecker, K. OE-A roadmap for organic and printed electronics. In Applications of Organic and Printed Electronics; Cantatore, E., Ed.; Springer US: Secaucus, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, R.; Song, L.; Dong, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Chen, X. Synthesis and self-assembly of large-area Cu nanosheets and their application as an aqueous conductive ink on flexible electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-Y.; Chang, Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Z.-G. Green water-based silver nanoplate conductive ink for flexible printed circuit. Mater. Technol. 2016, 31, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, E.; Nalwa, H.S. Inkjet printed nanomaterial based flexible radio frequency identification (RFID) tag sensors for the internet of nano things. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 48597–48630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yin, Y.; Ali, M.U.; Peng, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, D.; Zou, T.; Li, Y.; Jiao, S.; Chen, S.; et al. Inkjet printed uniform quantum dots as color conversion layers for full-color OLED displays. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, A.M.; Mamidanna, M.; Ding, L.; Hildreth, O.J.; Bertoni, M.I. Low-temperature drop-on-demand reactive silver inks for solar cell front-metallization. IEEE J. Photovolt. 2017, 7, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankoco, M.; Tesfay, G.; Benevent, E.; Bendahan, M. Temperature sensor realized by inkjet printing process on flexible substrate. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2016, 205, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Ogbeide, O.; Macadam, N.; Sun, Q.; Yu, W.; Li, Y.; Su, B.-L.; Hasan, T.; Huang, X.; Huang, W. Printed gas sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1756–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.-H.; Ahn, D.B.; Lee, S.-Y. Current status and challenges in printed batteries: Toward form factor-free, monolithic integrated power sources. ACS Energy Lett. 2018, 3, 220–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, F.; Operamolla, A.; Castro-Hermosa, S.; Lucarelli, G.; Manca, V.; Farinola, G.M.; Brown, T.M. Printed solar cells and energy storage devices on paper substrates. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.Y.; Hu, H.J.; Zhou, S.; Xu, S. Soft wearable devices for deep-tissue sensing. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 850–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Mun, J.; Kwon, S.Y.; Park, S.; Bao, Z.N.; Park, S. Electronic skin: Recent progress and future prospects for skin-attachable devices for health monitoring, robotics, and prosthetics. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1970337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshny, A.; Steinke, J.; Magdassi, S. Metal-based inkjet inks for printed electronics. Open Appl. Phys. J. 2011, 4, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, G.; Desmulliez, M.P. Inkjet printing of conductive materials: A review. Circuit World 2012, 38, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-K.; Lee, M.-T. Laser direct synthesis and patterning of silver nano/microstructures on a polymer substrate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14576–14582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lee, H.; Yeo, J.; Ko, S.H. Digital selective laser methods for nanomaterials: From synthesis to processing. Nano Today 2016, 11, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Huang, Y.; Liang, J.; Wan, X.; Chen, Y. Graphene-based conducting inks for direct inkjet printing of flexible conductive patterns and their applications in electric circuits and chemical sensors. Nano Res. 2011, 4, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shboul, A.; Trudeau, C.; Cloutier, S.; Siaj, M.; Claverie, J. Graphene dispersions in alkanes: Toward fast drying conducting inks. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 9893–9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrisi, F.; Hasan, T.; Wu, W.; Sun, Z.; Lombardo, A.; Kulmala, T.S.; Hsieh, G.-W.; Jung, S.; Bonaccorso, F.; Paul, P.J.; et al. Inkjet-printed graphene electronics. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2992–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majee, S.; Liu, C.; Wu, B.; Zhang, S.-L.; Zhang, Z.-B. Ink-jet printed highly conductive pristine graphene patterns achieved with water-based ink and aqueous doping processing. Carbon 2017, 114, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-W.; Kim, B.; Li, J.; Meyyappan, M. Ink for writing on cellulose paper. Mater. Res. Bull. 2014, 50, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perinka, N.; Kim, C.H.; Kaplanova, M.; Bonnassieux, Y. Preparation and characterization of thin conductive polymer films on the base of PEDOT:PSS by inkjet printing. Phys. Procedia 2013, 44, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, T.; Constantino, C.; Lopes, E.; Job, A.E.; Alves, N. Thermal inkjet printing of polyaniline on paper. Thin Solid Film 2012, 520, 7200–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.P.; Mrig, S.; Knapp, C.E. MODs vs. NPs: Vying for the future of printed electronics. Chem. Eur. J. 2021, 27, 8062–8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, W.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, P. The laser writing of highly conductive and anti-oxidative copper structures in liquid. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.K.; Kim, D.; Jeong, S.; Moon, J.; Kim, J. Direct writing of copper conductive patterns by ink-jet printing. Thin Solid Film 2007, 515, 7707–7711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshny, A.; Magdassi, S. Conductive nanomaterials for 2D and 3D printed flexible electronics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1712–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhu, Y. Printing conductive nanomaterials for flexible and stretchable electronics: A review of materials, processes, and applications. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.Y.; Duoss, E.B.; Motala, M.J.; Xiaoying, G.; Sang-Il, P.; Yujie, X.; Johgseung, Y.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Rogers, J.A.; Lewis, J.A. Omnidirectional printing of flexible, stretchable, and spanning silver microelectrodes. Science 2009, 323, 1590–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachev, S.V.; Kim, V.P.; Kushnir, A.E.; Kornilov, D.Y.; Gubin, S.P. The dispersions of nanoparticles in water-organic solvents as the basis for the silver nano-ink for inkjet printing. RENSIT 2016, 8, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ji, H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, W.; Huang, Y.; Feng, H.; Wei, J.; Li, M. Enhanced electrical and mechanical properties of a printed bimodal silver nanoparticle ink for flexible electronics. Phys. Status Solidi A 2018, 215, 1800007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htwe, Y.Z.N.; Mariatti, M. Performance of water-based printed hybrid graphene/silver nanoparticle conductive inks for flexible strain sensor applications. Synth. Met. 2023, 300, 117495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Gao, M.; Guo, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Song, Y.; Li, Y. Transparent Ag@Au-graphenepatterns with conductive stability via inkjet printing. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2017, 5, 2800–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, D.; Zhang, T.; Guo, J.; Fang, X.; Wei, J. Water-based ultraviolet curable conductive inkjet ink containing silver nano-colloids for flexible electronics. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2013, 424, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, S.Y.; Kwak, C.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.; Cho, H.; Lee, J. 3D-printable, lightweight, and electrically conductive metal inks based on evaporable emulsion templates jammed with natural rheology modifiers. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 628, 758–767. [Google Scholar]
- Dearden, A.L.; Smith, P.J.; Shin, D.Y.; Reis, N.; Derby, B.; O’Brien, P. A low curing temperature silver ink for use in ink-jet printing and subsequent production of conductive tracks. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2005, 26, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeton, J.J.; Hermans, K.; Bastiaansen, C.W.; Broer, D.J.; Perelaer, J.; Schubert, U.S.; Crawford, G.P.; Smith, P.J. Room temperature preparation of conductive silver features using spin-coating and inkjet printing. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-T.; Hsu, S.L.-C.; Tsai, M.-H.; Hwang, W.-S. Inkjet printing of low-temperature cured silver patterns by using AgNO3/1-dimethylamino-2-propanol Inks on polymer substrates. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 10940–10945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zeng, X.; Liu, J. Laser direct writing of conductive silver film on polyimide surface from decomposition of organometallic ink. J. Electron. Mater. 2011, 40, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-P.; Kao, Z.-K.; Lin, J.-L.; Liao, Y.-C. Silver conductive features on flexible substrates from a thermally accelerated chain reaction at low sintering temperatures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 7064–7068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.B.; Lewis, J.A. Reactive silver inks for patterning high-conductivity features at mild temperatures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1419–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaseem, M.; McKerricher, G.; Shamim, A. Robust design of a particle-free silver-organo-complex ink with high conductivity and inkjet stability for flexible electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, H.; Sun, Q.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Chen, M. Facile preparation of stable reactive silver ink for highly conductive and flexible electrodes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 475, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xu, Z.; Bai, H.; Knapp, C.E. Room Temperature electronic functionalization of thermally sensitive substrates by inkjet printing of a reactive silver-based MOD ink. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Ouyang, S.; Wang, D.; Lee, W.-Y.; Fong, H.H. Highly smooth and conductive silver film with metallo-organic decomposition ink for all-solution-processed flexible organic thin-film transistors. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 15908–15918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Wang, D.; Tai, Y.; Yang, Z. Preparation, characterization and reaction mechanism of a novel silver-organic conductive ink. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 25296–25301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, K.S.; Ahmad, R.; Wang, Y.; Hahn, Y.-B. Low-temperature sintering of highly conductive silver ink for flexible electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 8522–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Wang, H.; Zou, J. Inkjet printing of silver citrate conductive ink on PET substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Li, J.-G.; Sun, X. Facile synthesis of high silver content MOD ink by using silver oxalate precursor for inkjet printing applications. Thin Solid Film. 2015, 589, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.-G.; Sun, X. Optimizing formulations of silver organic decomposition ink for producing highly-conductive features on flexible substrates: The case study of amines. Thin Solid Film. 2016, 616, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Tao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Tai, Y. A facile approach to a silver conductive ink with high performance for macroelectronics. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempien, Z.; Rybicki, E.; Rybicki, T.; Lesnikowski, J. Inkjet-printing deposition of silver electro-conductive layers on textile substrates at low sintering temperature by using an aqueous silver ions-containing ink for textronic. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 224, 714–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, C.E.; Chemin, J.-B.; Douglas, S.P.; Ondo, D.A.; Guillot, J.; Choquet, P.; Boscher, N.D. Room-temperature plasma-assisted inkjet printing of highly conductive silver on paper. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, Y.; Guo, W.; Jin, J.; Mei, L.; Peng, P. Low-temperature sintering of silver patterns on polyimide substrate printed with particle-free ink. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 305301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Arrighi, V. An organic silver complex conductive ink using both decomposition and self-reduction mechanisms in film formation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 2771–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Arrighi, V. Silver oxalate ink with low sintering temperature and good electrical property. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 47, 2824–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, P.; Zemb, T. (Eds.) Neutron, X-ray and Light-Scattering: Introduction to an Investigative Tool for Colloidal and Polymeric Systems; North Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1991; 375p. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, R. Theory of the optical properties of ionic crystal cubes. Phys. Rev. B 1975, 11, 1732–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Carrol, D.L. Silver nanoplates: Size control in two dimensions and formation mechanisms. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 5500–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramelle, D.; Sadovoy, A.; Gorelik, S.; Free, P.; Hobley, J.; Fernig, D.G. A rapid method to estimate the concentration of citrate capped silver nanoparticles from UV-visible light spectra. Analyst 2014, 139, 4855–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarnavalli, G.C.J.; Joseph, V.; Kannappan, V.; Roopsingh, D.A. Simple approach to the synthesis of hexagonal-shaped silver nanoplates. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 825637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, M.C.; Dang, T.M.D.; Fribourg-Blanc, E. Silver nanoparticles ink synthesis for conductive patterns fabrication using inkjet printing technology. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Ahn, B.Y.; Adams, J.J.; Duoss, E.B.; Bernhard, J.T.; Lewis, J. Pen-on-paper flexible electronics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3426–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastner, J.; Faury, T.; Außerhuber, H.M.; Obermüller, T.; Leichtfried, H.; Yaslinger, M.; Liftinger, E.; Innerhonger, J.; Gnatiuk, I.; Hilzinger, D.; et al. Silver-based reactive ink for inkjet-printing of conductive lines on textiles. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 176, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| T, °C | ρsq, Ω/sq |
|---|---|
| 100 | 8.9 |
| 120 | 3.54 |
| 150 | 3.91 |
| 180 | 3.55 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kholuiskaya, S.N.; Siracusa, V.; Mukhametova, G.M.; Wasserman, L.A.; Kovalenko, V.V.; Iordanskii, A.L. An Approach to a Silver Conductive Ink for Inkjet Printer Technology. Polymers 2024, 16, 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121731
Kholuiskaya SN, Siracusa V, Mukhametova GM, Wasserman LA, Kovalenko VV, Iordanskii AL. An Approach to a Silver Conductive Ink for Inkjet Printer Technology. Polymers. 2024; 16(12):1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121731
Chicago/Turabian StyleKholuiskaya, Svetlana N., Valentina Siracusa, Gulnaz M. Mukhametova, Luybov A. Wasserman, Vladislav V. Kovalenko, and Alexey L. Iordanskii. 2024. "An Approach to a Silver Conductive Ink for Inkjet Printer Technology" Polymers 16, no. 12: 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121731
APA StyleKholuiskaya, S. N., Siracusa, V., Mukhametova, G. M., Wasserman, L. A., Kovalenko, V. V., & Iordanskii, A. L. (2024). An Approach to a Silver Conductive Ink for Inkjet Printer Technology. Polymers, 16(12), 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16121731








