Preparation of Waterborne Silicone-Modified Polyurethane Nanofibers and the Effect of Crosslinking Agents on Physical Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
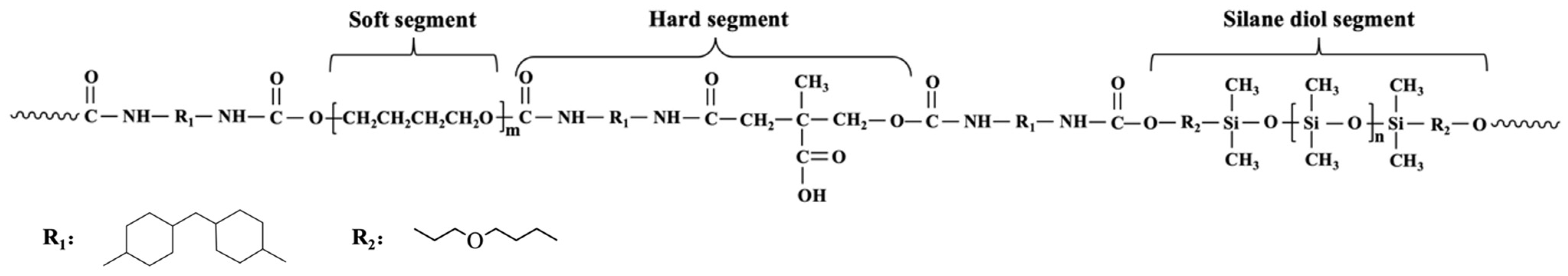
2.2. Synthesis of Waterborne PUSX and PU
2.3. Preparation of Waterborne PUSX and PU Nanofibrous Membranes
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4.2. Chemical Structure Analysis by FTIR
2.4.3. Water Performance Comprehensive Evaluation Test
2.4.4. Porosity Measurements
2.4.5. Tensile Tests
2.4.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fabrication of Waterborne PUSX and PU Nanofiber Membranes
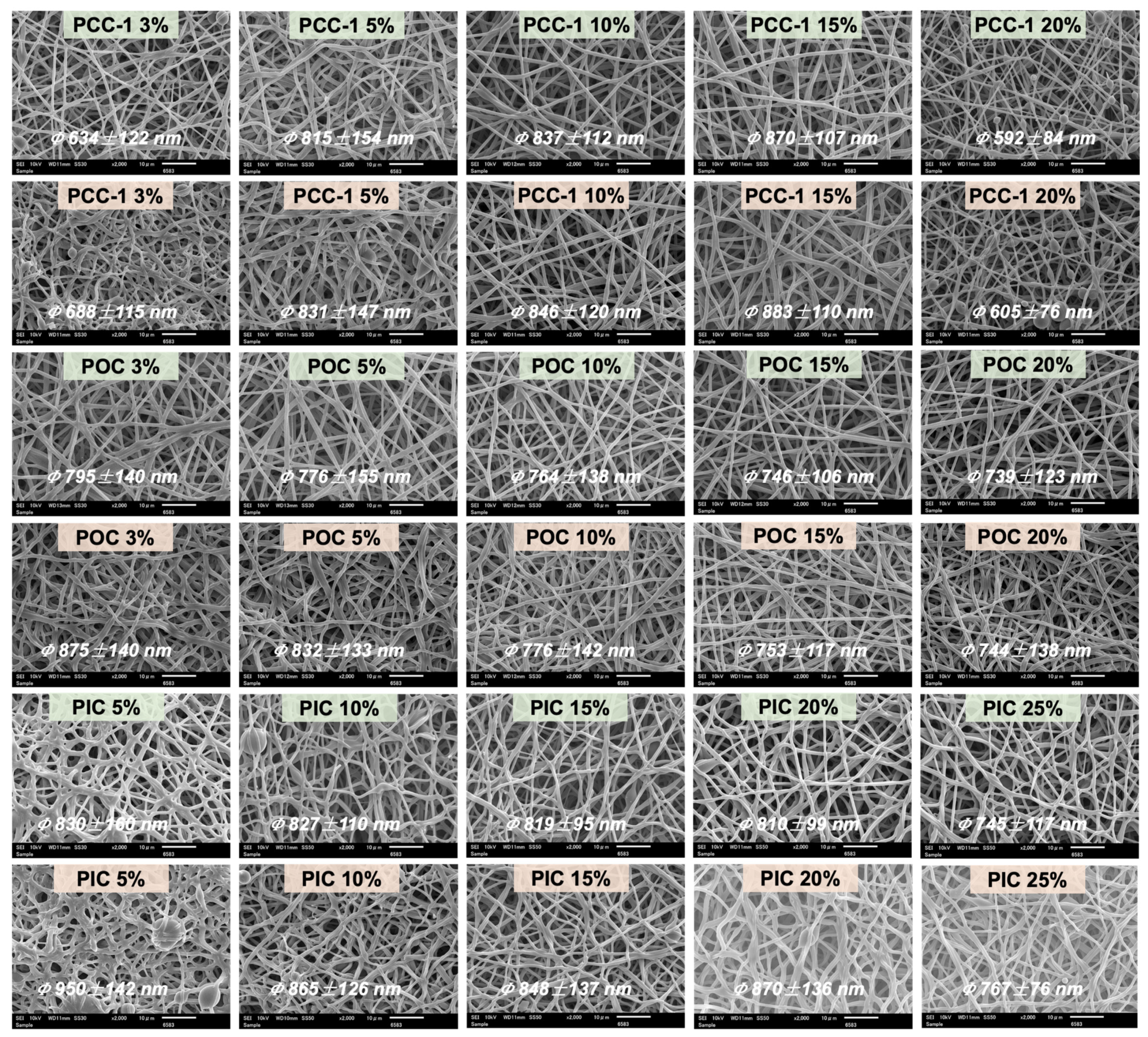
3.2. Morphological and Structure Characterization of PU and PUSX Nanofibers
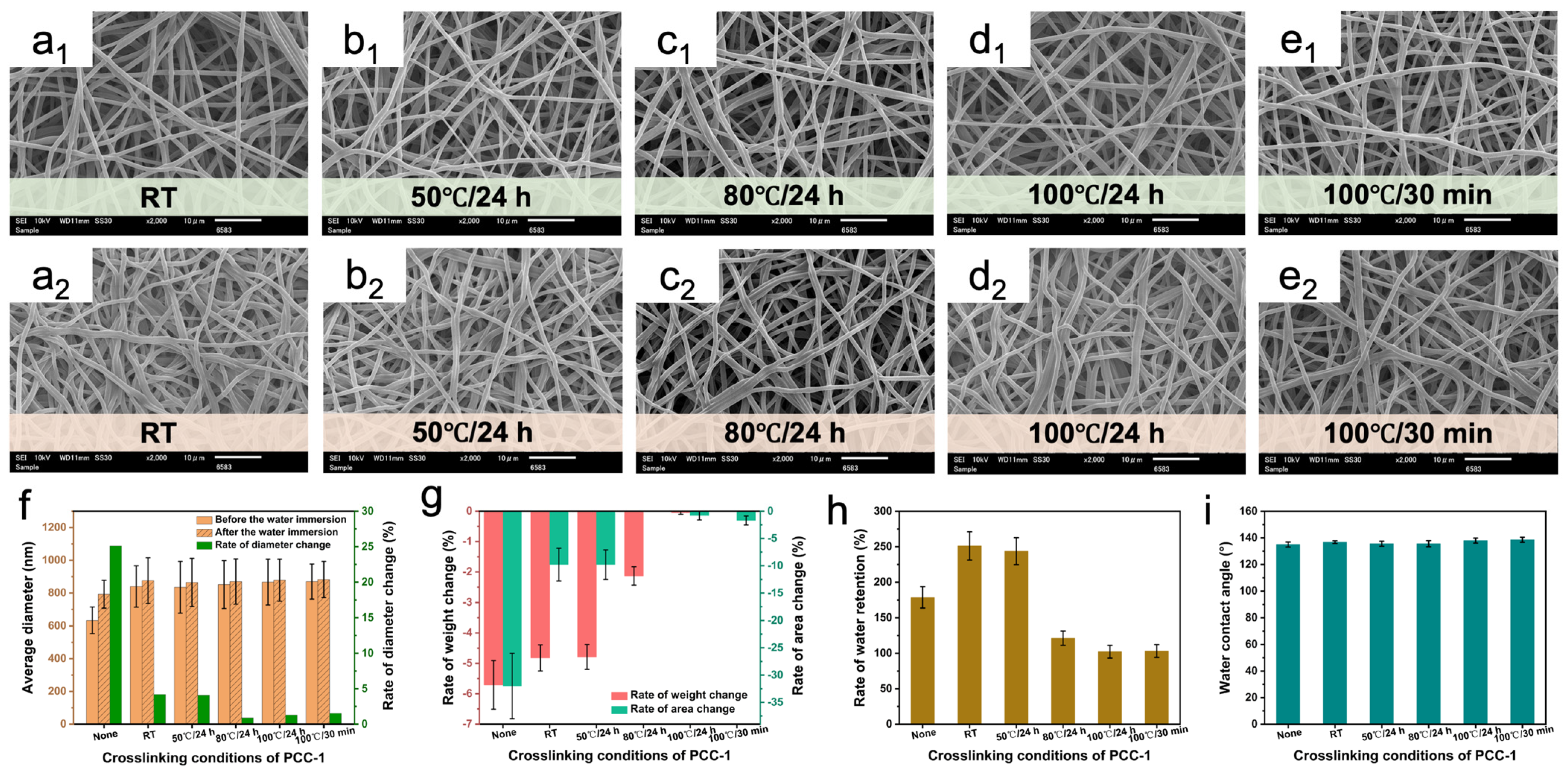
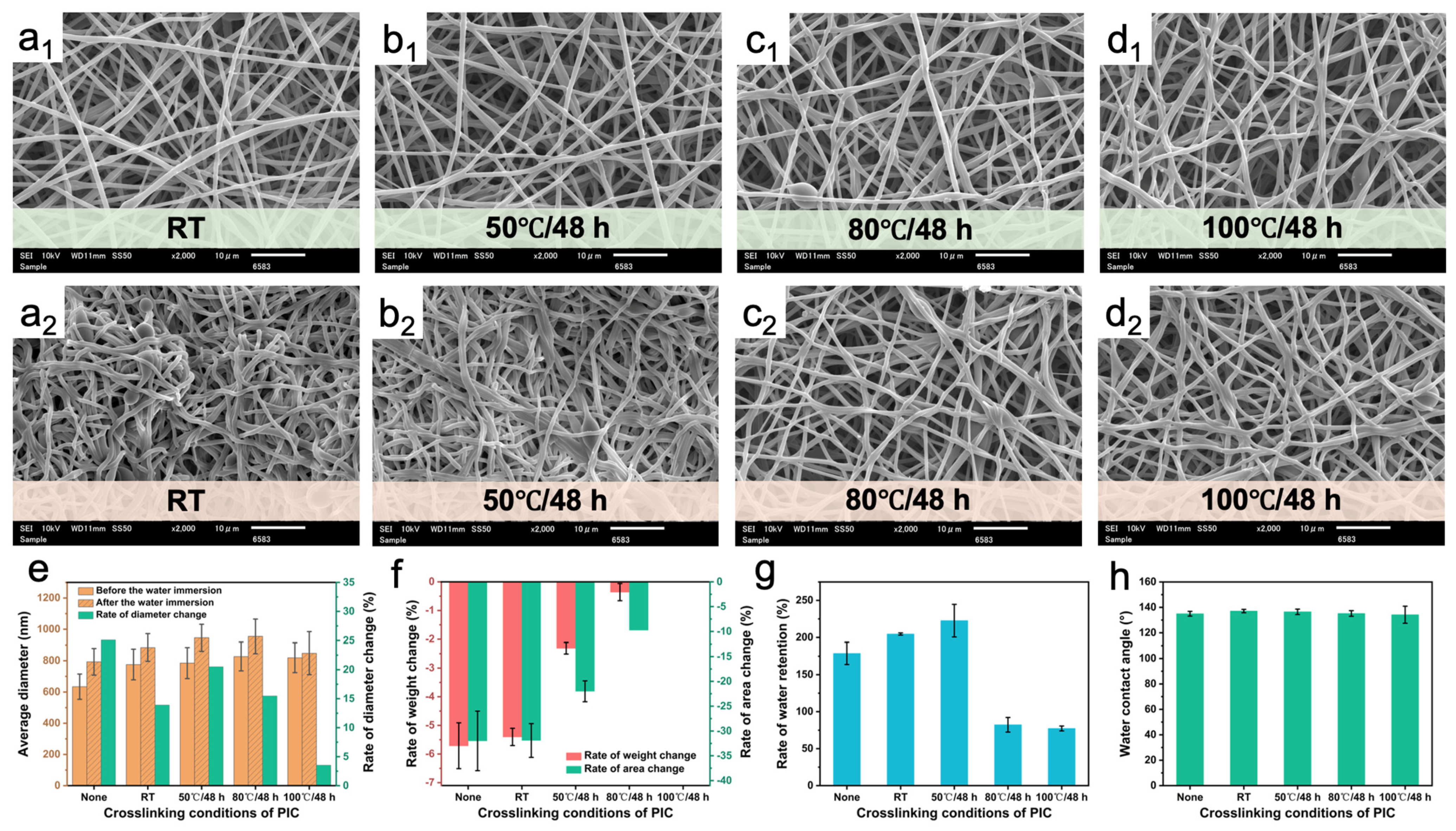
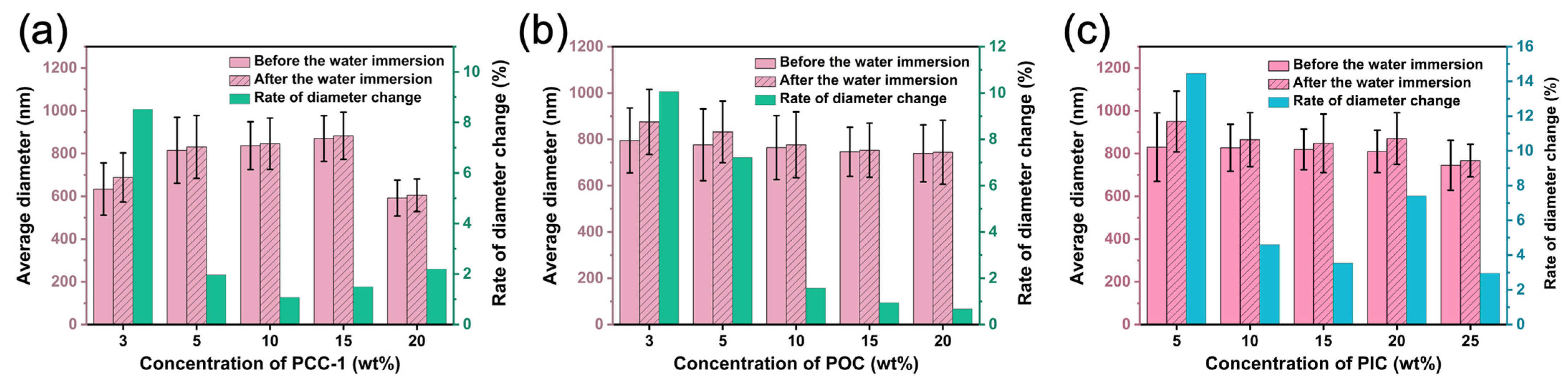
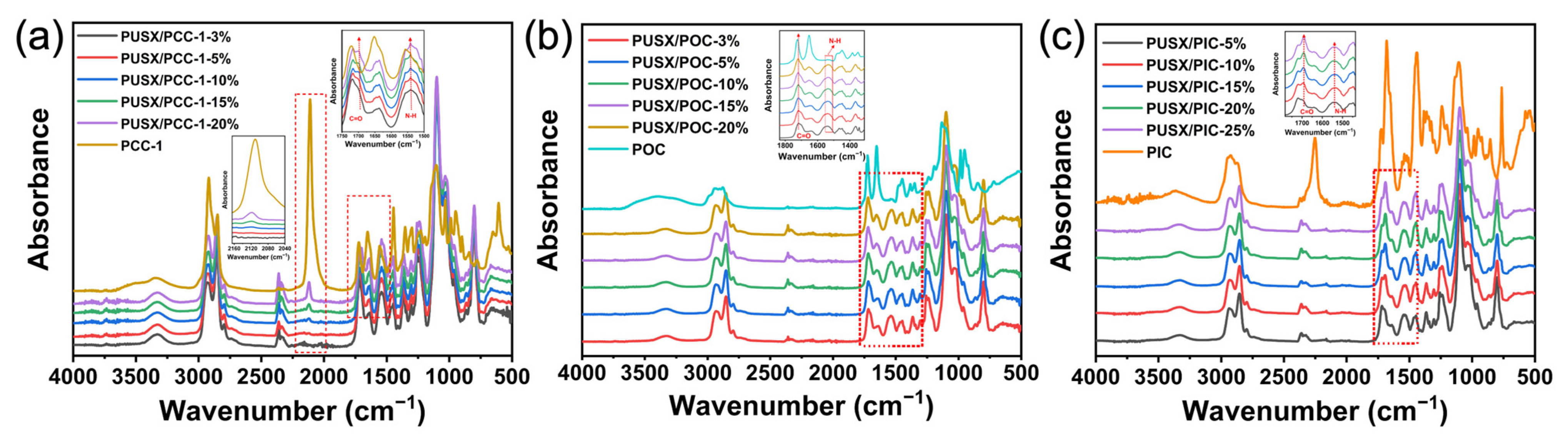
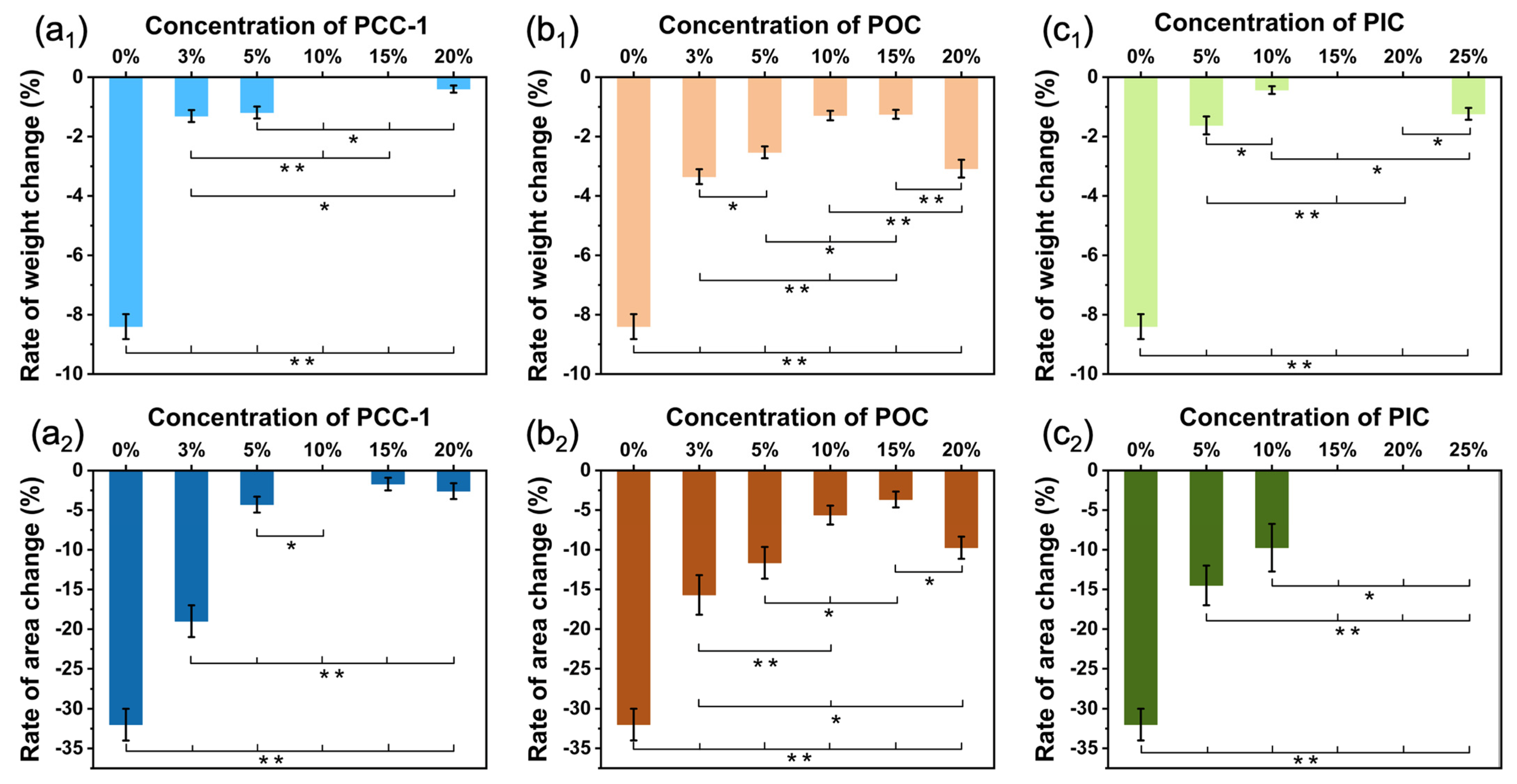
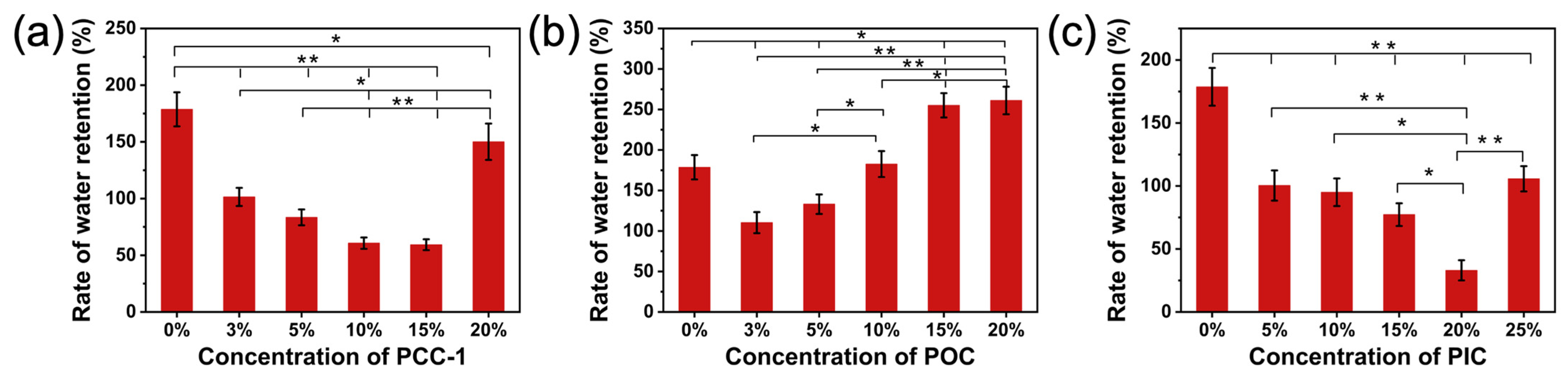
3.3. Optimization of the Crosslinking Conditions of Different Crosslinking Agents
3.4. Morphology of the PUSX-PyC Nanofiber Membranes
3.5. Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
3.6. Water Resistance Evaluation
3.7. Water Retention Evaluation
3.8. Water Contact Angle
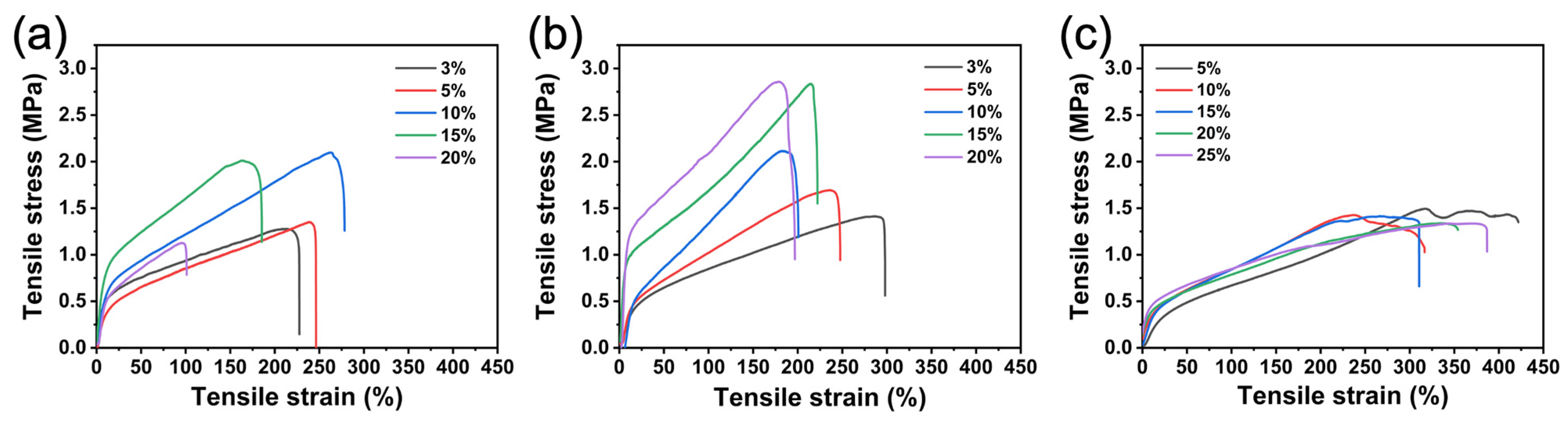
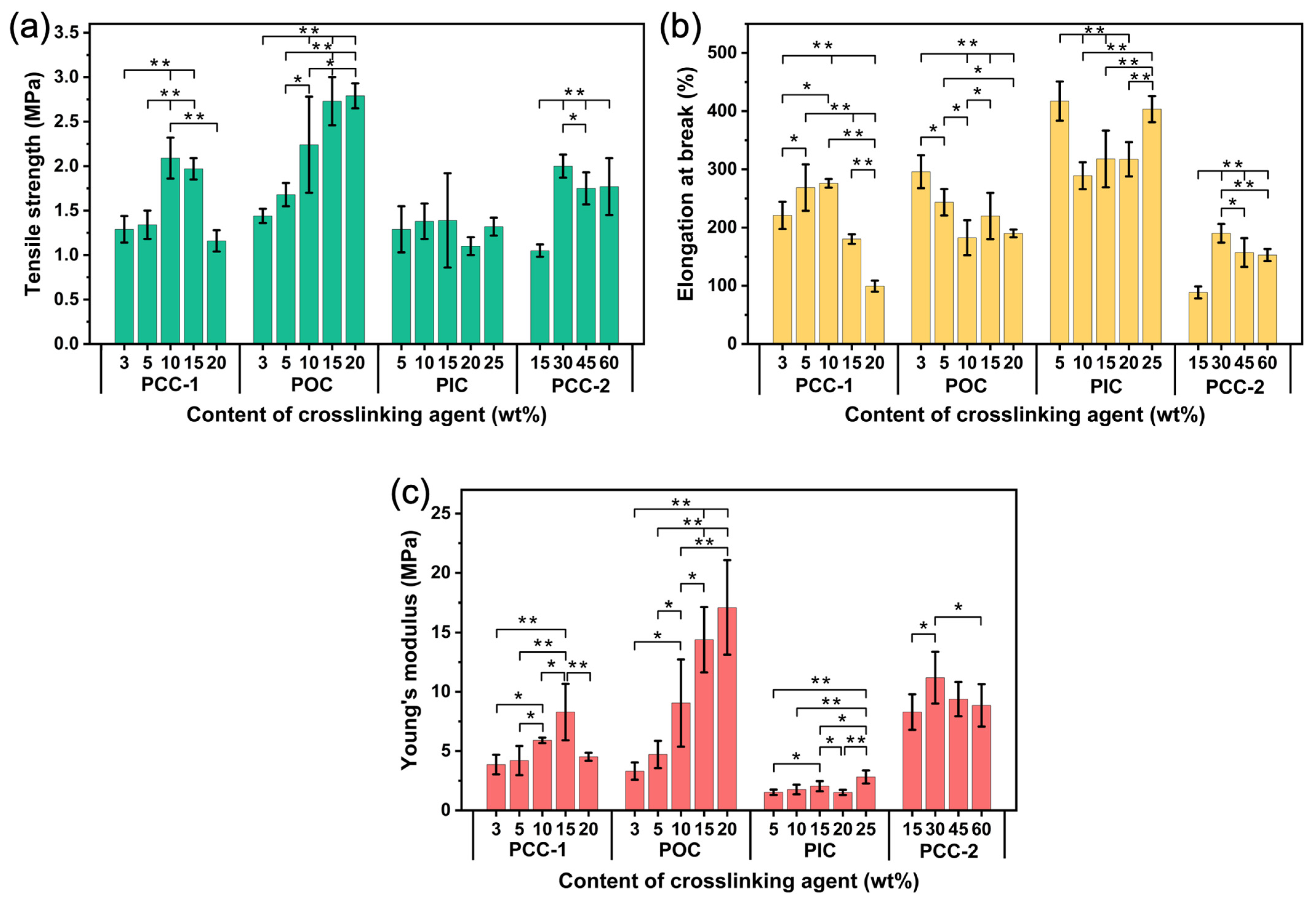
3.9. Characterization of Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, Z.; Liu, Z.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, A.; Lei, J. Effect of crystalline structure on water resistance of waterborne polyurethane. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 157, 110647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, L.; Feng, Y.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, T.; Yang, Z. A renewable and multifunctional eco-friendly coating from novel tung oil-based cationic waterborne polyurethane dispersions. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnol, L.D.; Dias, F.T.G.; Ornaghi, H.L., Jr.; Sangermano, M.; Bianchi, O. UV-curable waterborne polyurethane coatings: A state-of-the-art and recent advances review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 154, 106156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hong, W.; Chen, X. Continuous production of water-borne polyurethanes: A review. Polymers 2020, 12, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; OuYang, L.; Cai, Z.; Ren, Y.; Lu, S.; Shi, W. Effects of polyaminosiloxane on the structure and properties of modified waterborne polyurethane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Aziz, T.; Fan, H.; Bittencourt, C. Synthesis and characterization of eugenol-based silicone modified waterborne polyurethane with excellent properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 50515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lin, R.; Li, H.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, C. Investigation of the migration ability of silicone and properties of waterborne polyurethanes. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2020, 102, 102654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Kong, Z. Preparation and properties of super hydrophobic films from siloxane-modified two-component waterborne polyurethane and hydrophobic nano SiO2. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 127, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Han, K.; Song, S.; Pan, M.; Pan, Z. A novel fluorinated capping agent and silicone synergistically enhanced waterborne polyurethane. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 643, 128753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Okamoto, R.; Kondo, M.; Tanaka, T.; Hattori, H.; Tanaka, M.; Sato, H.; Iino, S.; Koshiro, Y. Electrospinning of block and graft type silicone modified polyurethane nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2018, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Improving water resistance of waterborne polyurethane coating with high transparency and good mechanical properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 601, 124994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Shaw, S.; Lind, K.R.; Cademartiri, L. Thermal Processing of Silicones for Green, Scalable, and Healable Superhydrophobic Coatings. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 3677–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, C.; Tang, L.; Yan, Y.; Qiu, H.; Pei, Y.; Sailor, M.J.; Wu, L. Stable electrically conductive, highly flame-retardant foam composites generated from reduced graphene oxide and silicone resin coatings. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, Y. A green approach to preparing hydrophobic, electrically conductive textiles based on waterborne polyurethane for electromagnetic interference shielding with low reflectivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 127749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Li, N.; Gu, H.; Xia, X.; Xiong, J. Polydimethylsiloxane-modified polyurethane–poly (ε-caprolactone) nanofibrous membranes for waterproof, breathable applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Facile fabrication of fluorine-free breathable poly (methylhydrosiloxane)/polyurethane fibrous membranes with enhanced water-resistant capability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 556, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Chadyagondo, T.T.; Li, G.; Gu, H.; Li, N. Designing waterproof and breathable fabric based on polyurethane/silica dioxide web fabricated by electrospinning. Fibers Polym. 2020, 21, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Rozet, S.; Okamoto, R.; Kondo, M.; Tamada, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Hattori, H.; Tanaka, M.; Sato, H.; Iino, S. Physical properties and in vitro biocompatible evaluation of silicone-modified polyurethane nanofibers and films. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Green electrospun nanofibers and their application in air filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gong, X.; Li, Y.; Si, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Environmentally friendly waterborne polyurethane nanofibrous membranes by emulsion electrospinning for waterproof and breathable textiles. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 130925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Gong, X.; Li, Y.; Si, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Waterborne electrospinning of fluorine-free stretchable nanofiber membranes with waterproof and breathable capabilities for protective textiles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 602, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.-X.; Wu, Y.-L.; Pu, C. Sericin grafting onto cashmere fiber and its properties investigation. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 2176–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Liang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yi, Z. Synthesis of waterborne polyurethane by inserting polydimethylsiloxane and constructing dual crosslinking for obtaining the superior performance of waterborne coatings. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 238, 109889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, K.-L. Waterborne polyurethanes. Prog. Org. Coat. 1997, 32, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, G. Post-crosslinking of Water-borne Urethanes. Prog. Org. Coat. 1997, 32, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tian, F.; Wang, W.; Wan, R.; Cao, J.; Chen, C.; Zhao, D.; Liu, J.; Zhong, J.; Wang, F. Design of highly conductive, intrinsically stretchable, and 3D printable PEDOT: PSS hydrogels via PSS-chain engineering for bioelectronics. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 5936–5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Jiao, W.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Green-solvent-processed fibrous membranes with water/oil/dust-resistant and breathable performances for protective textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 13, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, K.; Li, F.; Takayama, Y.; Nishijo, M.; Tanaka, T. Effects of Soaking Solvents by an Isothermal Crystallization Process on Physical Properties and Structures in One-Step-Drawing Films of Biodegradable P (3HB) Copolymers. Macromolecules 2023, 56, 8721–8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lin, W.; Hao, H.; Li, J.; Luo, F.; Tan, H. Nanofibrous scaffold from electrospinning biodegradable waterborne polyurethane/poly (vinyl alcohol) for tissue engineering application. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2017, 28, 648–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.H.; Yoon, N.S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, I.K.; Cheong, I.W.; Deng, Y.; Oh, W.; Yeum, J.H. Electrospinning fabrication and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol)/waterborne polyurethane nanofiber membranes in aqueous solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 2337–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Yan, J.; Long, F.; Qiu, W.; Meng, G.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Lin, N.; Liu, X.Y. Bioinspired Conductive Enhanced Polyurethane Ionic Skin as Reliable Multifunctional Sensors. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2300857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Li, X. Preparation of a wear-resistant, superhydrophobic SiO2/silicone-modified polyurethane composite coating through a two-step spraying method. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 146, 105710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, E.; Morales, G.; Spontón, M.; Estenoz, D. Design of thermosetting polymeric systems based on benzoxazines modified with maleic anhydride. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| PCC-1 | POC | PIC | PCC-2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | White opaque | Light yellow liquid | Light yellow liquid | Light yellow liquid |
| Solid content (%) | 40.0 ± 1.0 | 25.0 ± 1.5 | 70.0 ± 1.0 | 40.0 ± 1.0 |
| Viscosity (mPa·s/20 °C) | Below 500 | 10–100 | 150–620 | 50–200 |
| Ionicity | Nonionic | Nonionic | Nonionic | Nonionic |
| Functional group content | Carbodiimide (300 g·solid/eq) | Oxazoline (200 g·solid/eq) | NCO (8.7–9.7%) | Carbodiimide (600 g·solid/eq) |
| Solvent composition | Water | Water | Propylene glycol monomethyl ether acetate | Water |
| Crosslinking Agent | Content of Crosslinking Agent | Crosslinking Condition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCC-1 | 3% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 100 °C/30 min |
| POC | 3% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 80 °C/24 h |
| PIC | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 25% | 100 °C/48 h |
| PCC-2 | 15% | 30% | 45% | 60% | ---- | 100 °C/30 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Weng, K.; Nakamura, A.; Ono, K.; Tanaka, T.; Noda, D.; Tanaka, M.; Irifune, S.; Sato, H. Preparation of Waterborne Silicone-Modified Polyurethane Nanofibers and the Effect of Crosslinking Agents on Physical Properties. Polymers 2024, 16, 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111500
Li F, Weng K, Nakamura A, Ono K, Tanaka T, Noda D, Tanaka M, Irifune S, Sato H. Preparation of Waterborne Silicone-Modified Polyurethane Nanofibers and the Effect of Crosslinking Agents on Physical Properties. Polymers. 2024; 16(11):1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111500
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fang, Kai Weng, Asumi Nakamura, Keishiro Ono, Toshihisa Tanaka, Daisuke Noda, Masaki Tanaka, Shinji Irifune, and Hiromasa Sato. 2024. "Preparation of Waterborne Silicone-Modified Polyurethane Nanofibers and the Effect of Crosslinking Agents on Physical Properties" Polymers 16, no. 11: 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111500
APA StyleLi, F., Weng, K., Nakamura, A., Ono, K., Tanaka, T., Noda, D., Tanaka, M., Irifune, S., & Sato, H. (2024). Preparation of Waterborne Silicone-Modified Polyurethane Nanofibers and the Effect of Crosslinking Agents on Physical Properties. Polymers, 16(11), 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16111500







