Lysine-Triggered Polymeric Hydrogels with Self-Adhesion, Stretchability, and Supportive Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis of DF-PEG and LysMA
2.3. Preparation of Hydrogels
2.4. Characterizations and Mechanical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
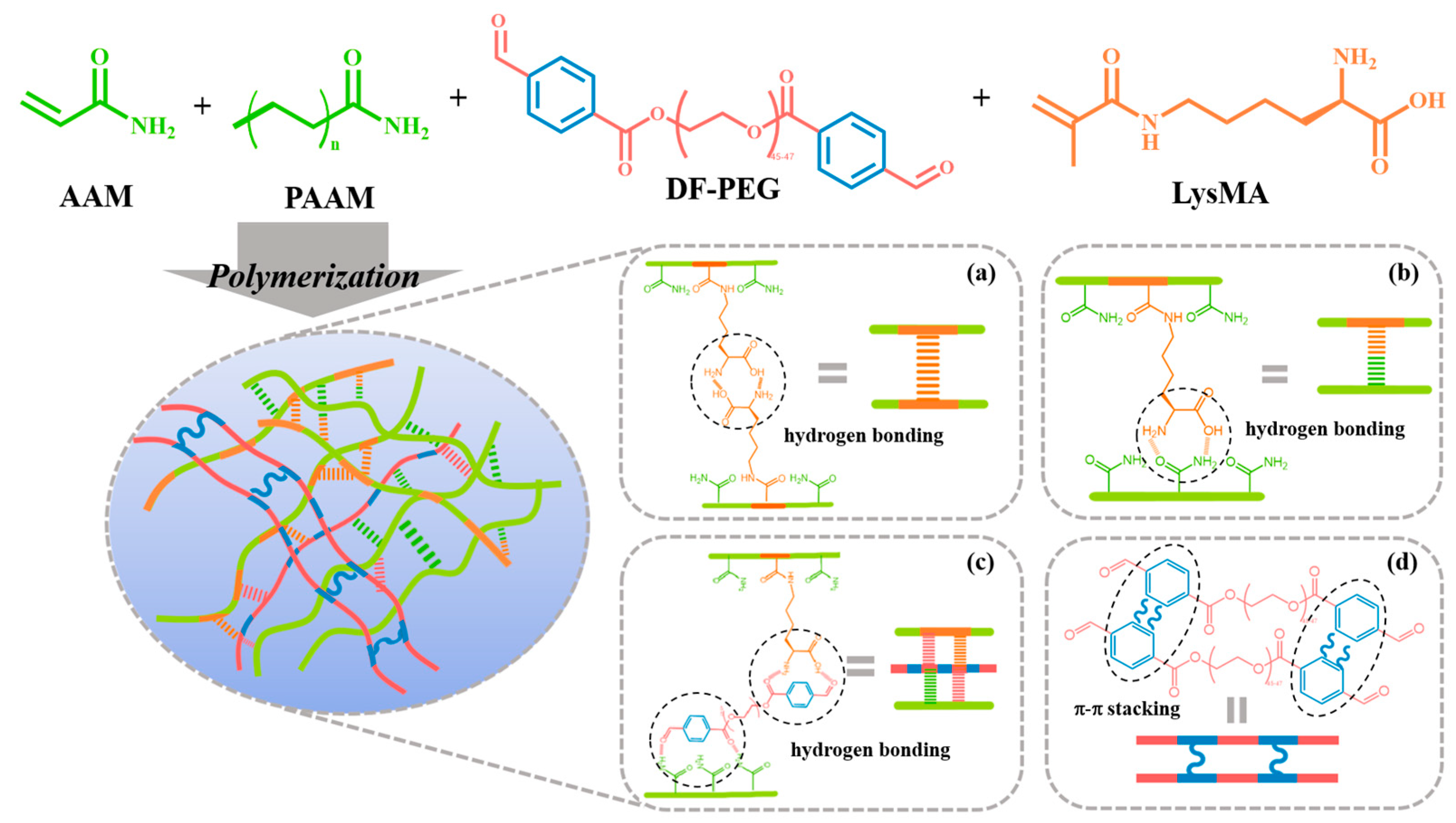
3.1. Design and Preparation of pADL Hydrogels
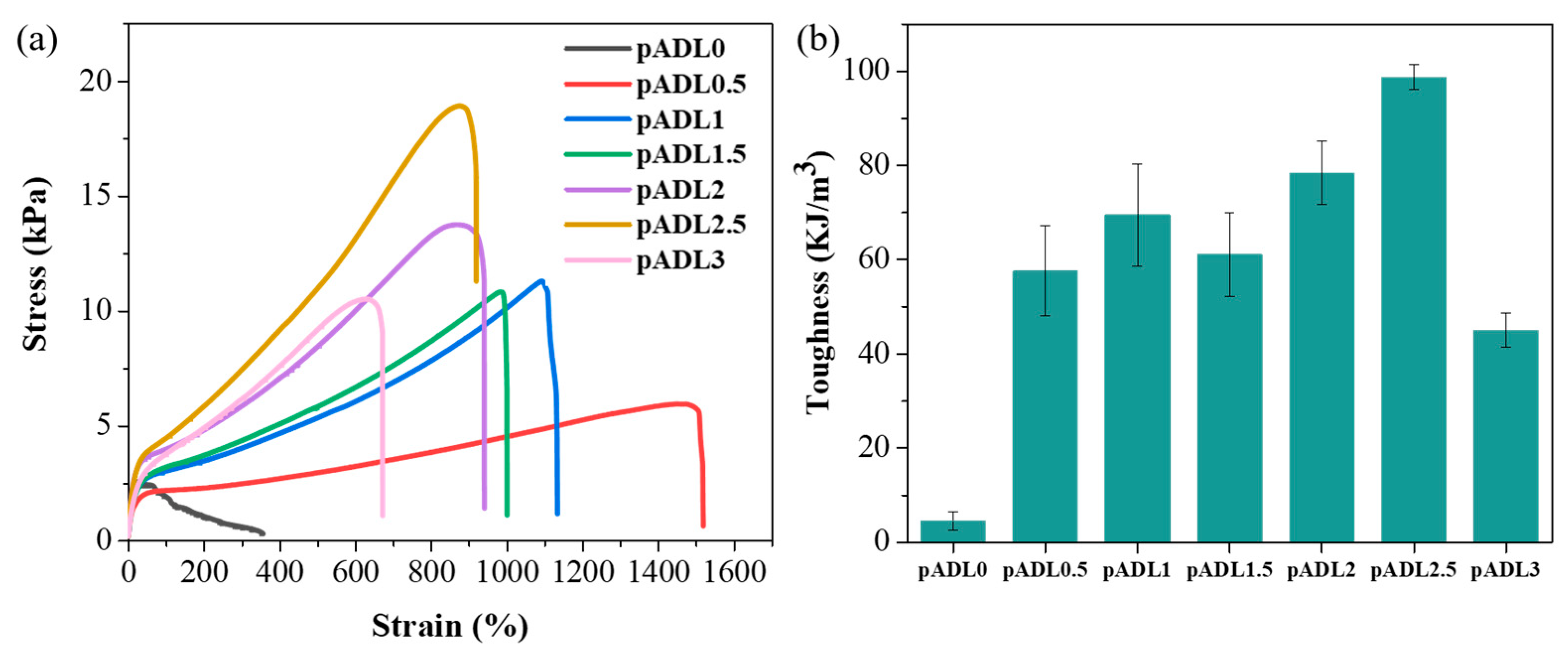
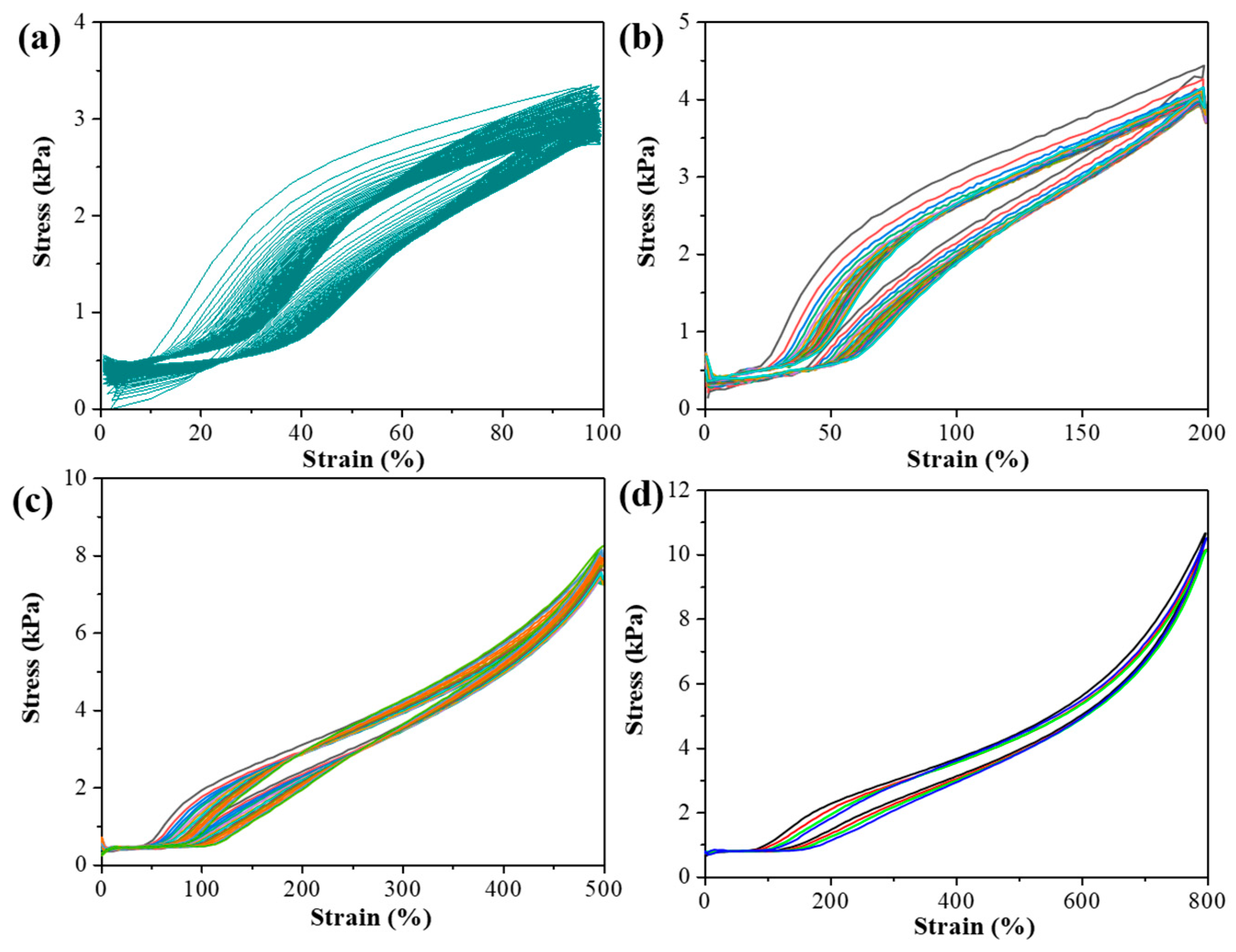
3.2. Mechanical Properties of pADL Hydrogels
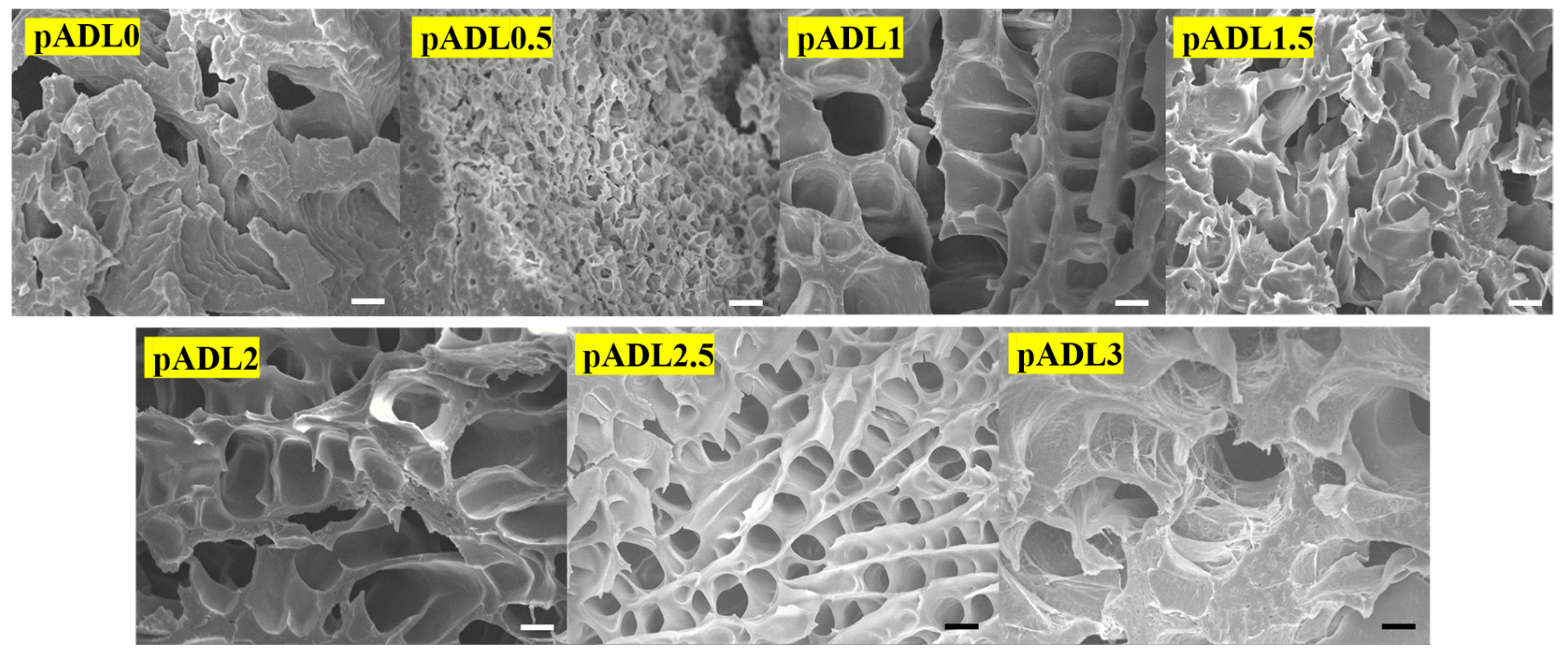
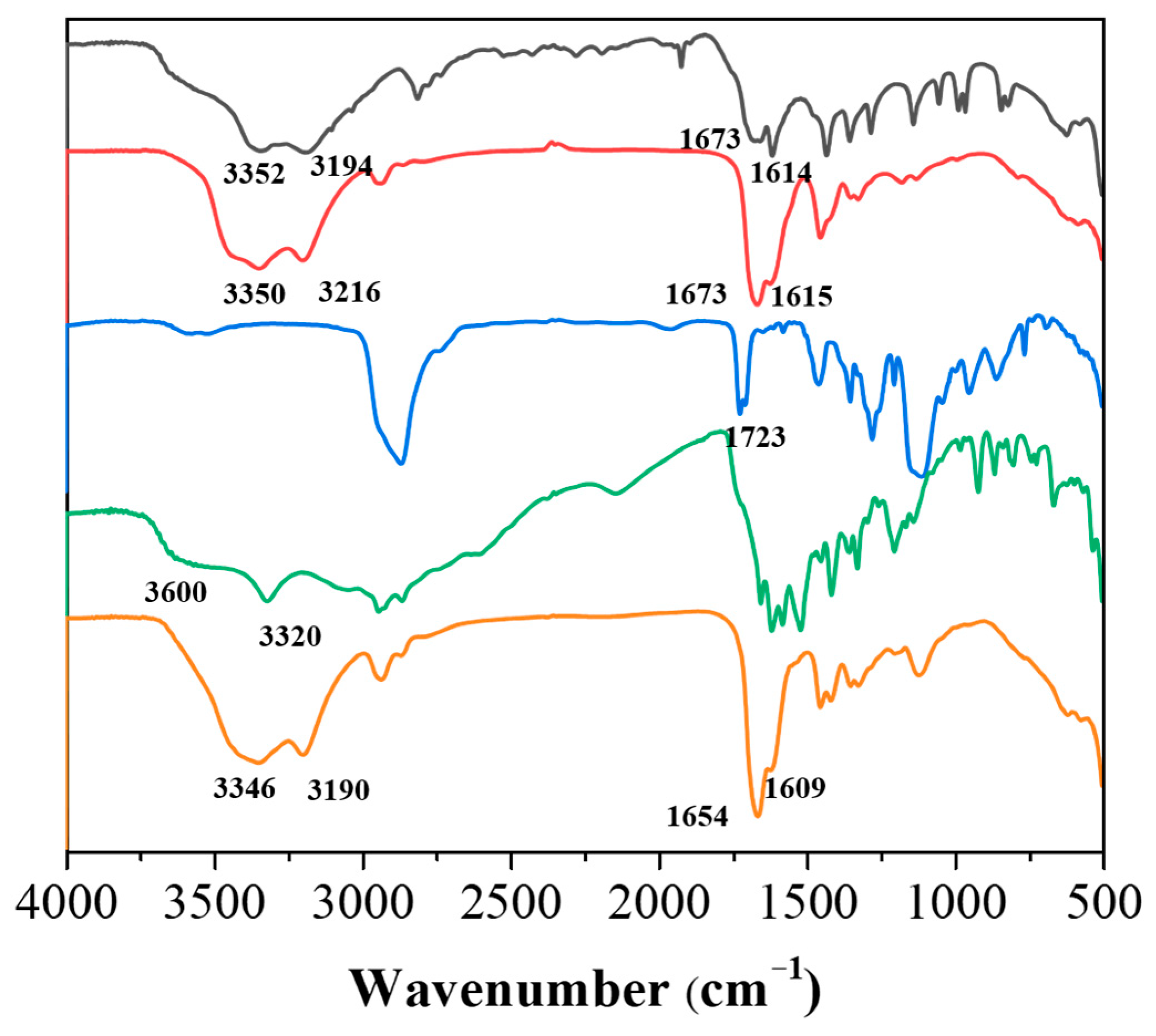
3.3. Morphologies and Spectral Analysis of pADL Hydrogels
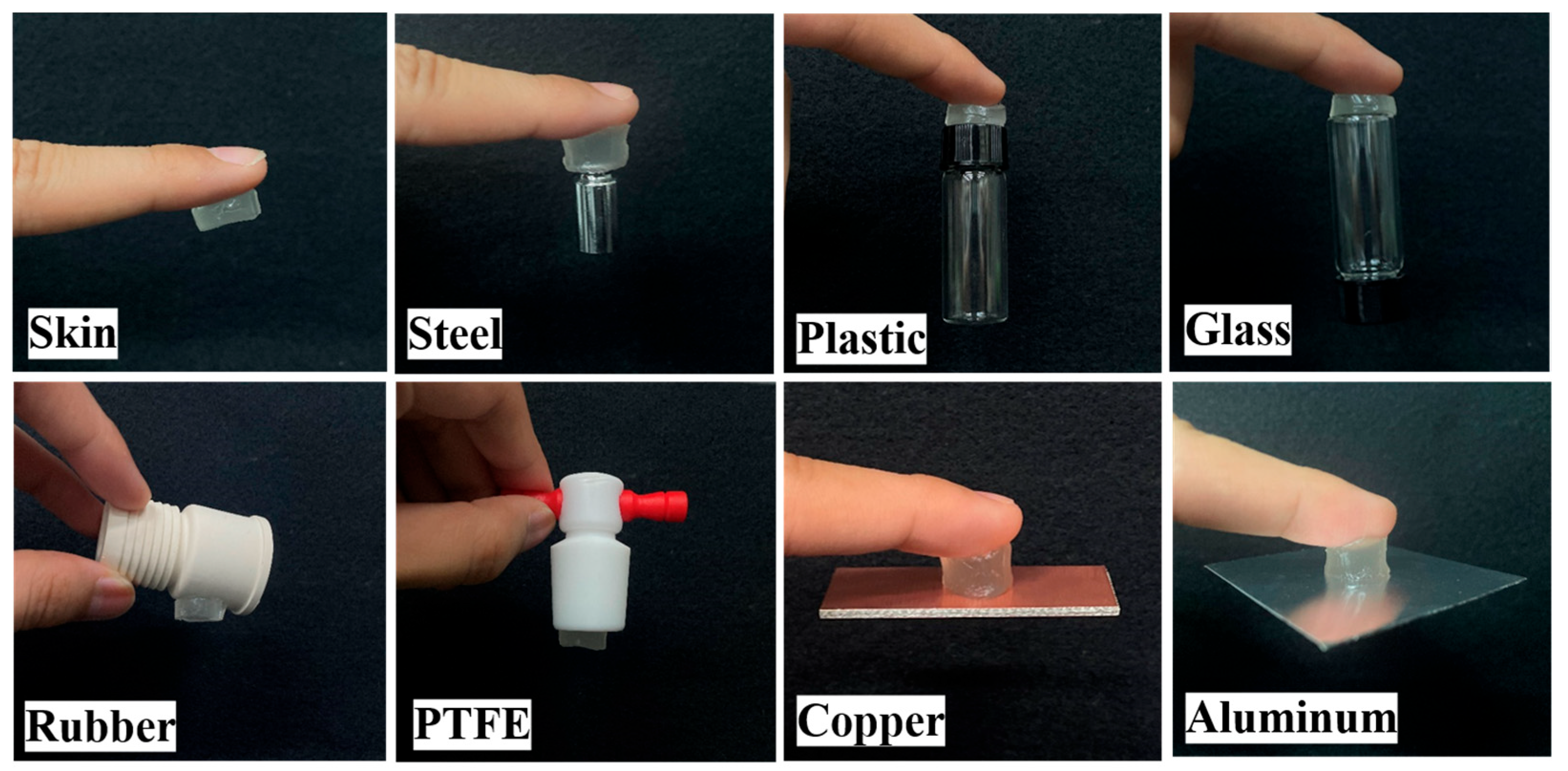
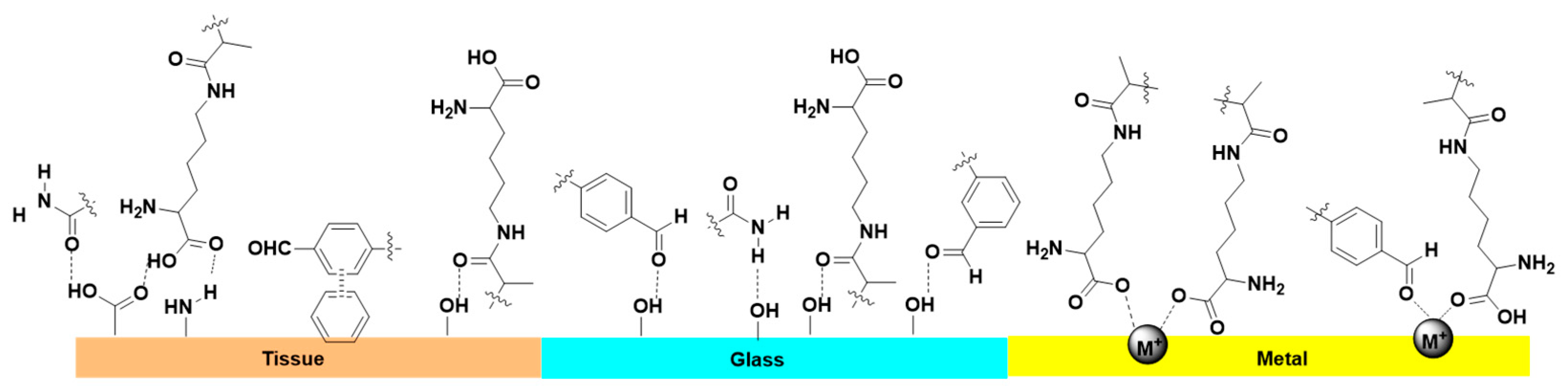
3.4. Adhesive Capacities of pADL Hydrogels
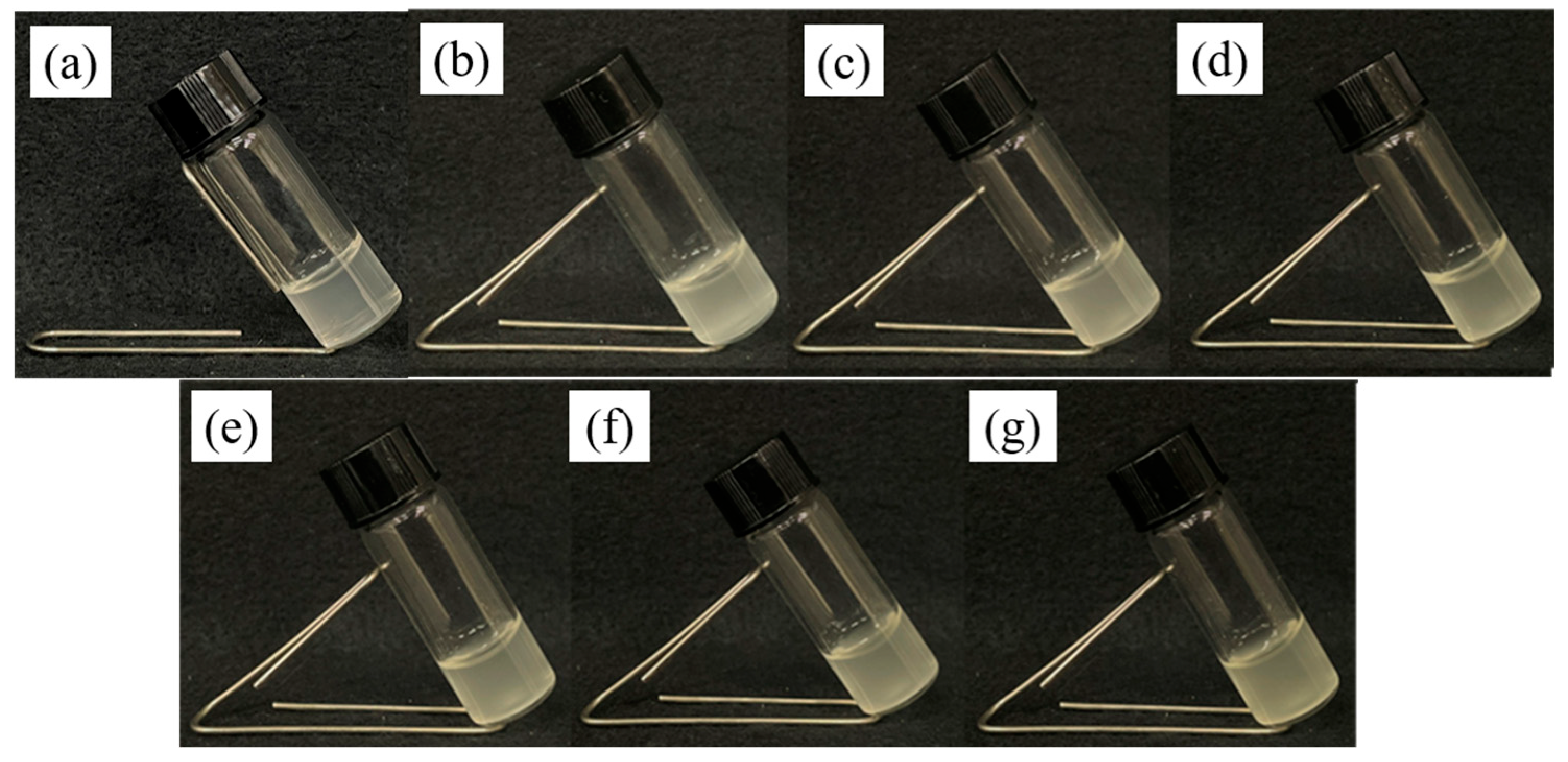
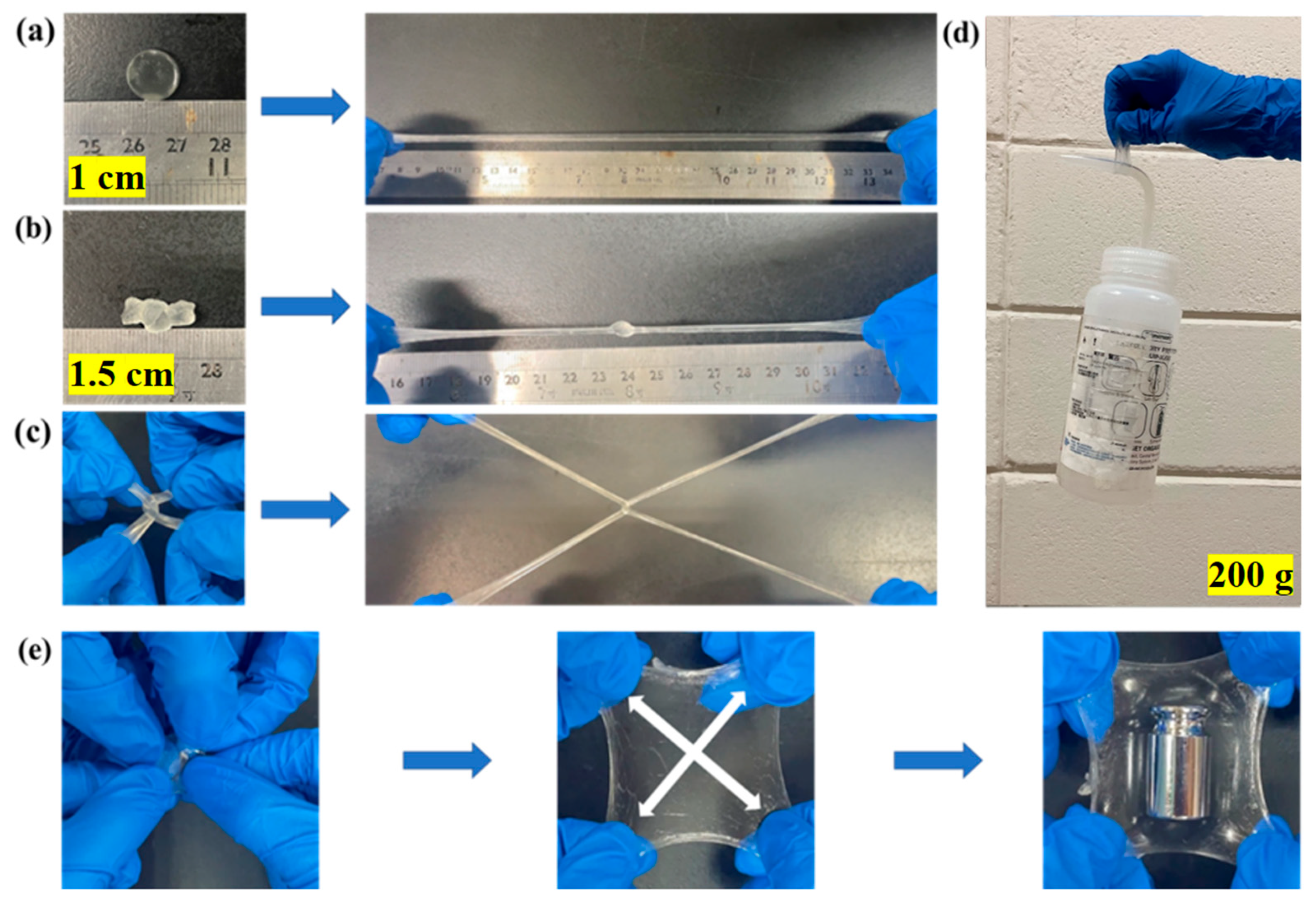
3.5. Stretchability and Supportiveness of pADL Hydrogels
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, G.; Zhu, K.; Guo, W.; Wu, D.; Quan, X.; Huang, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Fang, H.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Adhesive and Hydrophobic Bilayer Hydrogel Enabled On-Skin Biosensors for High-Fidelity Classification of Human Emotion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, Y.; He, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.A.; Ouyang, J. Wearable Stretchable Dry and Self-Adhesive Strain Sensors with Conformal Contact to Skin for High-Quality Motion Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 31, 2007495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, O.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Hou, M.; Zheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Cui, B. Spider-Web and Ant-Tentacle Doubly Bio-Inspired Multifunctional Self-Powered Electronic Skin with Hierarchical Nanostructure. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2004377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Jin, G.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W.; Yan, F. Poly(ionic liquid) hydrogel-based anti-freezing ionic skin for a soft robotic gripper. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallin, T.J.; Pikul, J.; Shepherd, R.F. 3D printing of soft robotic systems. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, K.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Weng, L.T.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Ren, F.; Zhao, C.; et al. Mussel-Inspired Adhesive and Tough Hydrogel Based on Nanoclay Confined Dopamine Polymerization. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2561–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.U.A.; Stojanovic, G.M.; Abdullah, M.F.B.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Marei, H.E.; Ashammakhi, N.; Hasan, A. Fundamental properties of smart hydrogels for tissue engineering applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantha, S.; Pillai, S.; Khayambashi, P.; Upadhyay, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, O.; Pham, H.M.; Tran, S.D. Smart Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Materials 2019, 12, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, W.; Yan, F.; Zhao, X.; Chu, X.; Xu, W.; Sun, C. A review of the properties and applications of bioadhesive hydrogels. Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 3721–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kováč, J.; Priščáková, P.; Gbelcová, H.; Heydari, A.; Žiaran, S. Bioadhesive and Injectable Hydrogels and Their Correlation with Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation for Cartilage Repair: A Mini-Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Xie, C.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, X. Self-adhesive hydrogels for tissue engineering. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 8739–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Yan, L.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Weng, L.-T.; Xu, J.; Weng, J.; et al. Tough, self-healable and tissue-adhesive hydrogel with tunable multifunctionality. NPG Asia Mater. 2017, 9, e372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fei, F.; Li, X.; Nie, Z.; Zhou, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Fei, Z.; Xu, T. A structure-supporting, self-healing, and high permeating hydrogel bioink for establishment of diverse homogeneous tissue-like constructs. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3580–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Li, J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Fatigue fracture of hydrogels. Extreme Mech. Lett. 2017, 10, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Liang, X.; Guo, J.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, L. Ultra-Stretchable and Force-Sensitive Hydrogels Reinforced with Chitosan Microspheres Embedded in Polymer Networks. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8037–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Sycks, D.; Chan, H.F.; Lin, S.; Lopez, G.P.; Guilak, F.; Leong, K.W.; Zhao, X. 3D Printing: 3D Printing of Highly Stretchable and Tough Hydrogels into Complex, Cellularized Structures. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Ren, X.; Gao, G. Ultrastretchable Wearable Strain and Pressure Sensors Based on Adhesive, Tough, and Self-healing Hydrogels for Human Motion Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 25613–25623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O.; Peppas, N.A.; Gurny, R. Structure and interactions in covalently and ionically crosslinked chitosan hydrogels for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Duan, L.; Ren, X.; Gao, G. Hydrophobic association hydrogels with excellent mechanical and self-healing properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, K.; Yan, C.; Zheng, G.; Huang, J.; Dai, K.; Liu, C.; Shen, C. Ultra-Stretchable, durable and conductive hydrogel with hybrid double network as high performance strain sensor and stretchable triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2020, 76, 105035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Qu, S.; Yang, W. A versatile hydrogel network-repairing strategy achieved by the covalent-like hydrogen bond interaction. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, 5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lin, S.; Zeng, H.; Liu, J.; Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, G. Dynamic intermolecular interactions through hydrogen bonding of water promote heat conduction in hydrogels. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 2936–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, N.; Lv, Z.; Jiang, Z. Ultra-stretchable hydrogels with hierarchical hydrogen bonds. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Huang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Du, Z.; Sun, T.L.; Guo, Z.H.; Yue, K. A Transparent, Highly Stretchable, Solvent-Resistant, Recyclable Multifunctional Ionogel with Underwater Self-Healing and Adhesion for Reliable Strain Sensors. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2105306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuddushi, M.; Pandey, D.K.; Singh, D.K.; Mata, J.; Malek, N. An ionic hydrogel with stimuli-responsive, self-healable and injectable characteristics for the targeted and sustained delivery of doxorubicin in the treatment of breast cancer. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 632–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Xu, X.; Song, Z.; Liu, H.; Chen, C. Strong, tough, ionic conductive, and freezing-tolerant all-natural hydrogel enabled by cellulose-bentonite coordination interactions. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, H.; Zhao, J.; Ma, X.; Li, H.; Fan, D. Antibacterial Dual Network Hydrogels for Sensing and Human Health Monitoring. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, e2101089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.K.; Chen, P.W.; Wang, H.J.; Yeh, M.Y. Alkyl Chain Length Effects of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids on Electrical and Mechanical Performances of Polyacrylamide/Alginate-Based Hydrogels. Gels 2021, 7, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Hanay, S.B.; Kimmins, S.D.; Cryan, S.A.; Hermida Merino, D.; Heise, A. Ion-Triggered Hydrogels Self-Assembled from Statistical Copolypeptides. ACS Macro Lett. 2022, 11, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xue, B.; Fan, Q.; Tao, R.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Qin, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, B.; et al. Molecular engineering of metal coordination interactions for strong, tough, and fast-recovery hydrogels. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, 9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Anderson, E.; Pera, R.R.; Pruitt, B.L.; Heilshorn, S.C. Hydrogel crosslinking density regulates temporal contractility of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes in 3D cultures. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10141–10148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, L.M.; Lopez, C.G.; Anseth, K.S. Effects of PEG hydrogel crosslinking density on protein diffusion and encapsulated islet survival and function. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 90, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, J.; Chen, W.; Xu, T.; Yun, S.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Sato, T.; Chi, B.; Xu, H. A Biomimetic Mussel-Inspired ε-Poly-l-lysine Hydrogel with Robust Tissue-Anchor and Anti-Infection Capacity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khunmanee, S.; Choi, A.; Ahn, I.Y.; Kim, W.J.; Bae, T.H.; Kang, S.H.; Park, H. Effective wound healing on diabetic mice by adhesive antibacterial GNPs-lysine composited hydrogel. iScience 2024, 27, 108860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Ou, J.; Cui, Z.; Yao, C.; Yang, D. A DNA/Poly-(L-lysine) Hydrogel with Long Shelf-Time for 3D Cell Culture. Small Methods 2024, 8, e2301236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Jia, F.; Gao, G. Transparent and conductive amino acid-tackified hydrogels as wearable strain sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 375, 121915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennakesavan, G.; Mostakhdemin, M.; Dkhar, L.K.; Seyfoddin, A.; Fatihhi, S.J. Acrylic acid/acrylamide-based hydrogels and its properties—A review. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 180, 109308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lv, T.; Sun, H.; Qian, G.; Li, N.; Yao, Y.; Chen, T. Ultrastretchable and superior healable supercapacitors based on a double cross-linked hydrogel electrolyte. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-J.; Chu, Y.-Z.; Chen, C.-K.; Liao, Y.-S.; Yeh, M.-Y. Preparation of conductive self-healing hydrogels via an interpenetrating polymer network method. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 6620–6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizhakkedathu, J.N.; Janzen, J.; Le, Y.; Kainthan, R.K.; Brooks, D.E. Poly(oligo(ethylene glycol)acrylamide) brushes by surface initiated polymerization: Effect of macromonomer chain length on brush growth and protein adsorption from blood plasma. Langmuir 2009, 25, 3794–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddow, P.; McAuley, W.J.; Kirton, S.B.; Cook, M.T. Poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide)–poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) as a thermoreversible gelator for topical administration. Mater. Adv. 2020, 1, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.-W.; Ji, D.-H.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Lee, C.; Yeh, M.-Y. Electroactive and Stretchable Hydrogels of 3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene/thiophene Copolymers. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 6753–6761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Mohamed, A.; Ji, Q.; Jia, H. High strength and flexible aramid nanofiber conductive hydrogels for wearable strain sensors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, X.; Liu, Y. Stretchable slide-ring supramolecular hydrogel for flexible electronic devices. Commun. Mater. 2022, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Gao, G. Bio-Based Hydrogel Transducer for Measuring Human Motion with Stable Adhesion and Ultrahigh Toughness. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 24173–24182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Zhang, H.; Ryu, S. Elastic Modulus Measurement of Hydrogels. In Cellulose-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogels; Mondal, M., Ed.; Polymers and Polymeric Composites: A Reference Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Lv, G.; Ren, X.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Dong, J.; Wang, Z.; Wu, G. Effect of size of latex particles on the mechanical properties of hydrogels reinforced by latex particles. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14701–14707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, C. Precise Analysis of Nanoparticle Size Distribution in TEM Image. Methods Protoc. 2023, 6, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Martins de Souza, A.L.; Carreteiro Damasceno, J.; Prado, C.B.; Magalhães Gurgel, M.A.; Carvalho Silva, R. Uncertainty model for automated gunshot residue particle length measurements obtained from electron microscopy images. J. Microsc. 2023, 292, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godwin Uranta, K.; Rezaei-Gomari, S.; Russell, P.; Hamad, F. Studying the Effectiveness of Polyacrylamide (PAM) Application in Hydrocarbon Reservoirs at Different Operational Conditions. Energies 2018, 11, 2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, S.; Kickelbick, G. Double Reversible Networks: Improvement of Self-Healing in Hybrid Materials via Combination of Diels–Alder Cross-Linking and Hydrogen Bonds. Macromol. 2018, 51, 6099–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.N.R.; Chaturvedi, G.C.; Gosavi, R.K. Infrared spectra and configurations of alkylurea derivatives: Normal vibrations on N, N′-dimethyl- and tetramethylurea. J. Mol. Spectrosc. 1968, 28, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.M.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, J.W.; Liu, Y.H.; Lin, H.C. Intramolecular interactions of a phenyl/perfluorophenyl pair in the formation of supramolecular nanofibers and hydrogels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Miao, L.; Kaur, P.; Men, S.; Wang, Q.; Gong, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhai, C.; Zhang, S.; et al. A highly sensitive and ultra-stretchable zwitterionic liquid hydrogel-based sensor as anti-freezing ionic skin. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 3970–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; He, J.; Bai, Y.; Zeng, H. Mussel-inspired adhesive and conductive hydrogel with tunable mechanical properties for wearable strain sensors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 585, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos-Perez, C.R.; White, J.D.; Wilker, J.J. Polymer composition and substrate influences on the adhesive bonding of a biomimetic, cross-linking polymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 9498–9505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, G.; Li, F.; He, S.; Li, W.; Wu, Q.; He, J.; Ruan, R.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H. Mussel- and Barnacle Cement Proteins-Inspired Dual-Bionic Bioadhesive with Repeatable Wet-Tissue Adhesion, Multimodal Self-Healing, and Antibacterial Capability for Nonpressing Hemostasis and Promoted Wound Healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y.; Zhao, X.; Illeperuma, W.R.; Chaudhuri, O.; Oh, K.H.; Mooney, D.J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature 2012, 489, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, S.; Xie, C.; Lu, X. Natural polymer-based adhesive hydrogel for biomedical applications. Biosurface Biotribology 2022, 8, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juan, C.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-S.; Cheng, J.-K.; Chen, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Yeh, M.-Y. Lysine-Triggered Polymeric Hydrogels with Self-Adhesion, Stretchability, and Supportive Properties. Polymers 2024, 16, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101388
Juan C-Y, Zhang Y-S, Cheng J-K, Chen Y-H, Lin H-C, Yeh M-Y. Lysine-Triggered Polymeric Hydrogels with Self-Adhesion, Stretchability, and Supportive Properties. Polymers. 2024; 16(10):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101388
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuan, Chieh-Yun, You-Sheng Zhang, Jen-Kun Cheng, Yu-Hsu Chen, Hsin-Chieh Lin, and Mei-Yu Yeh. 2024. "Lysine-Triggered Polymeric Hydrogels with Self-Adhesion, Stretchability, and Supportive Properties" Polymers 16, no. 10: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101388
APA StyleJuan, C.-Y., Zhang, Y.-S., Cheng, J.-K., Chen, Y.-H., Lin, H.-C., & Yeh, M.-Y. (2024). Lysine-Triggered Polymeric Hydrogels with Self-Adhesion, Stretchability, and Supportive Properties. Polymers, 16(10), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16101388






