Improving the Sustainability of Catalytic Glycolysis of Complex PET Waste through Bio-Solvolysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization of PET Waste
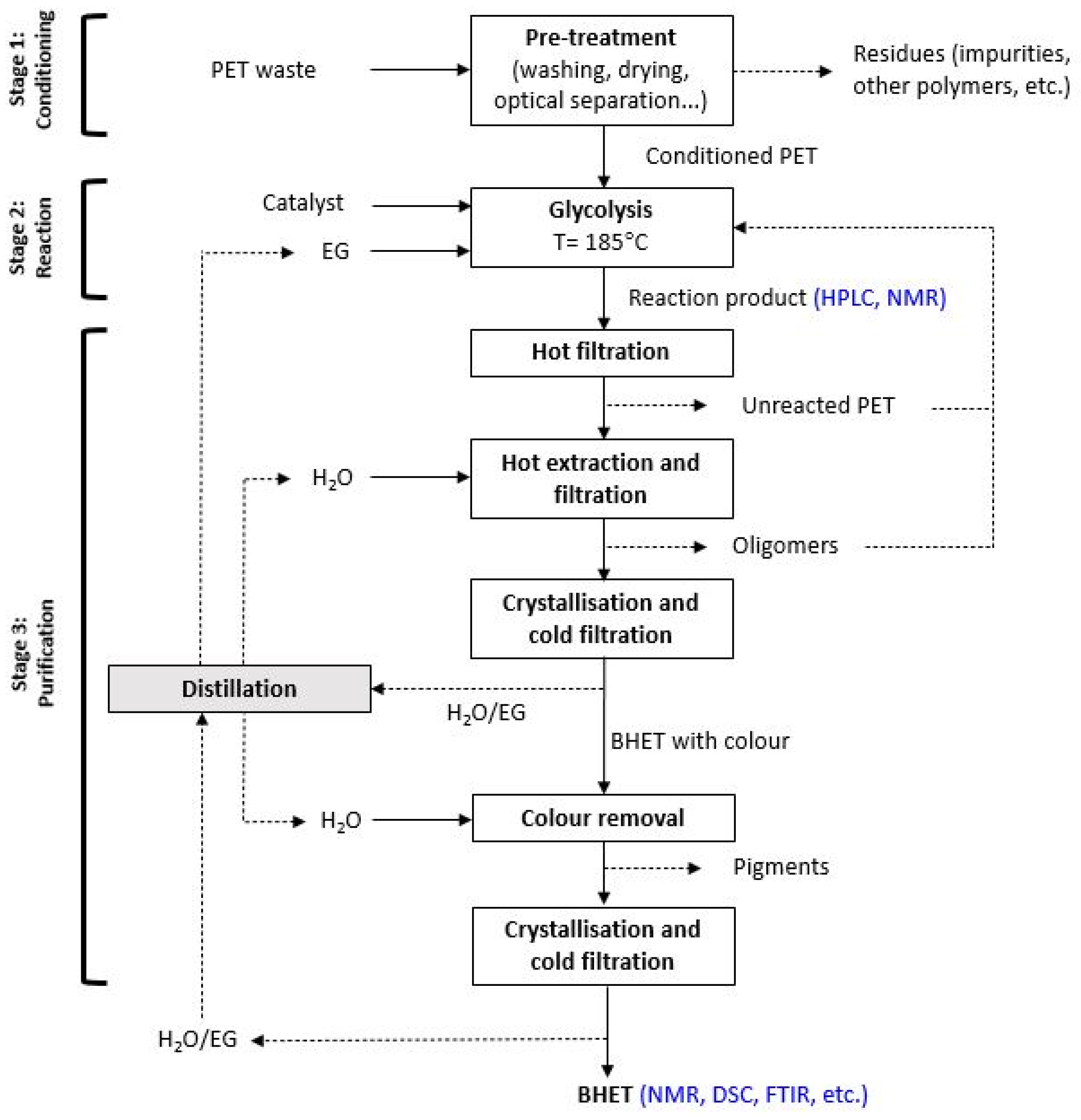
2.3. Catalytic Bio-Solvolysis of PET Waste
2.4. Purification of BHET Monomer
2.5. BHET Monomer Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
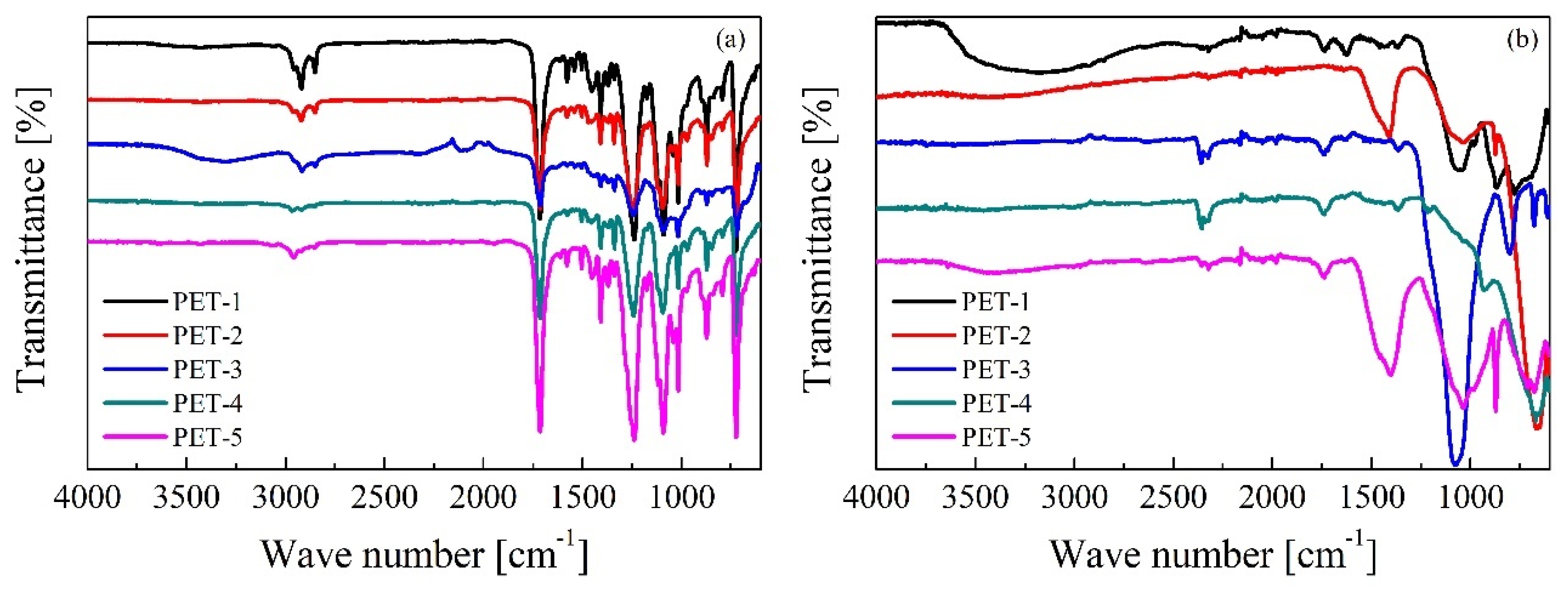
3.1. Characterization of PET Waste
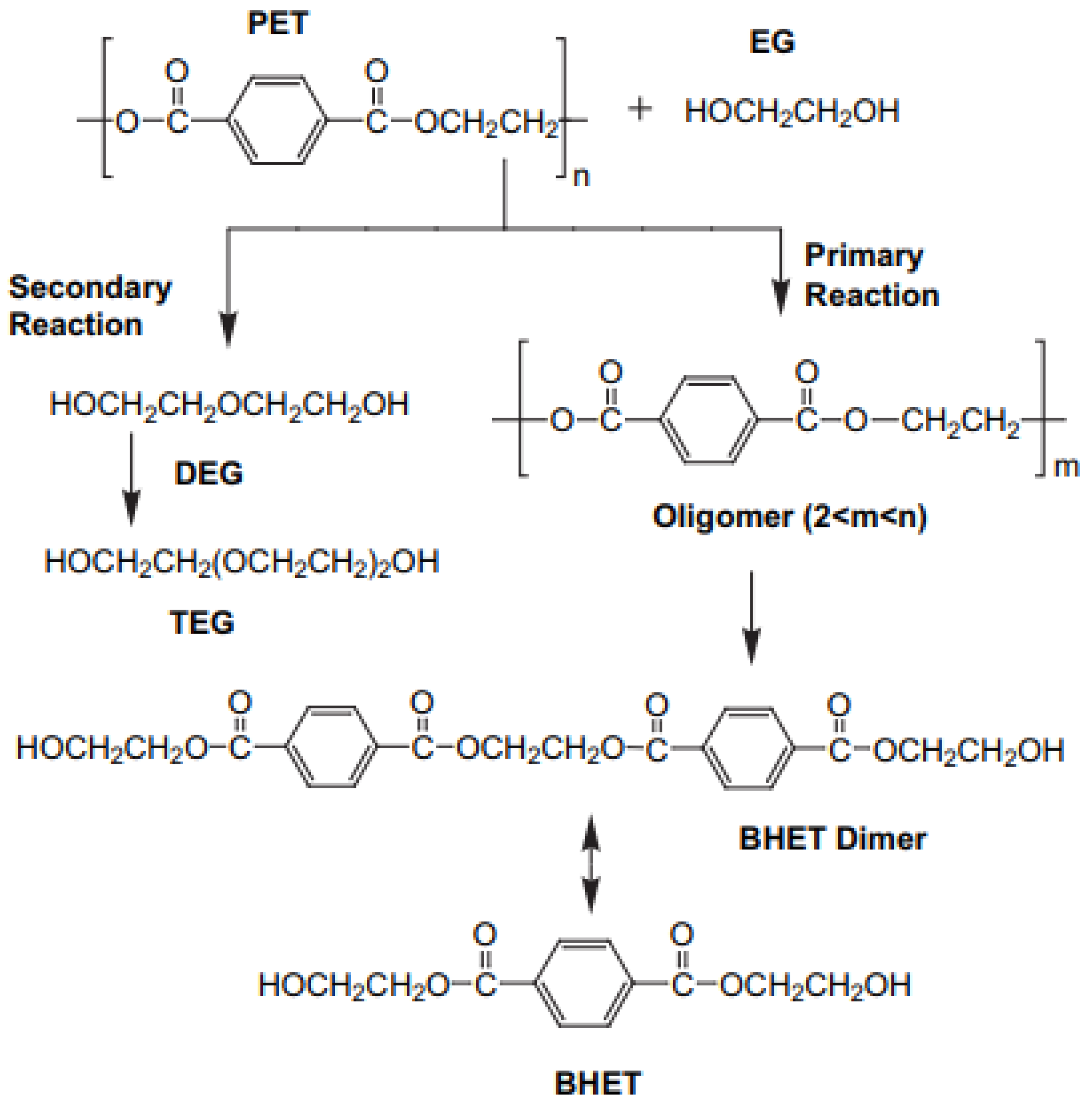
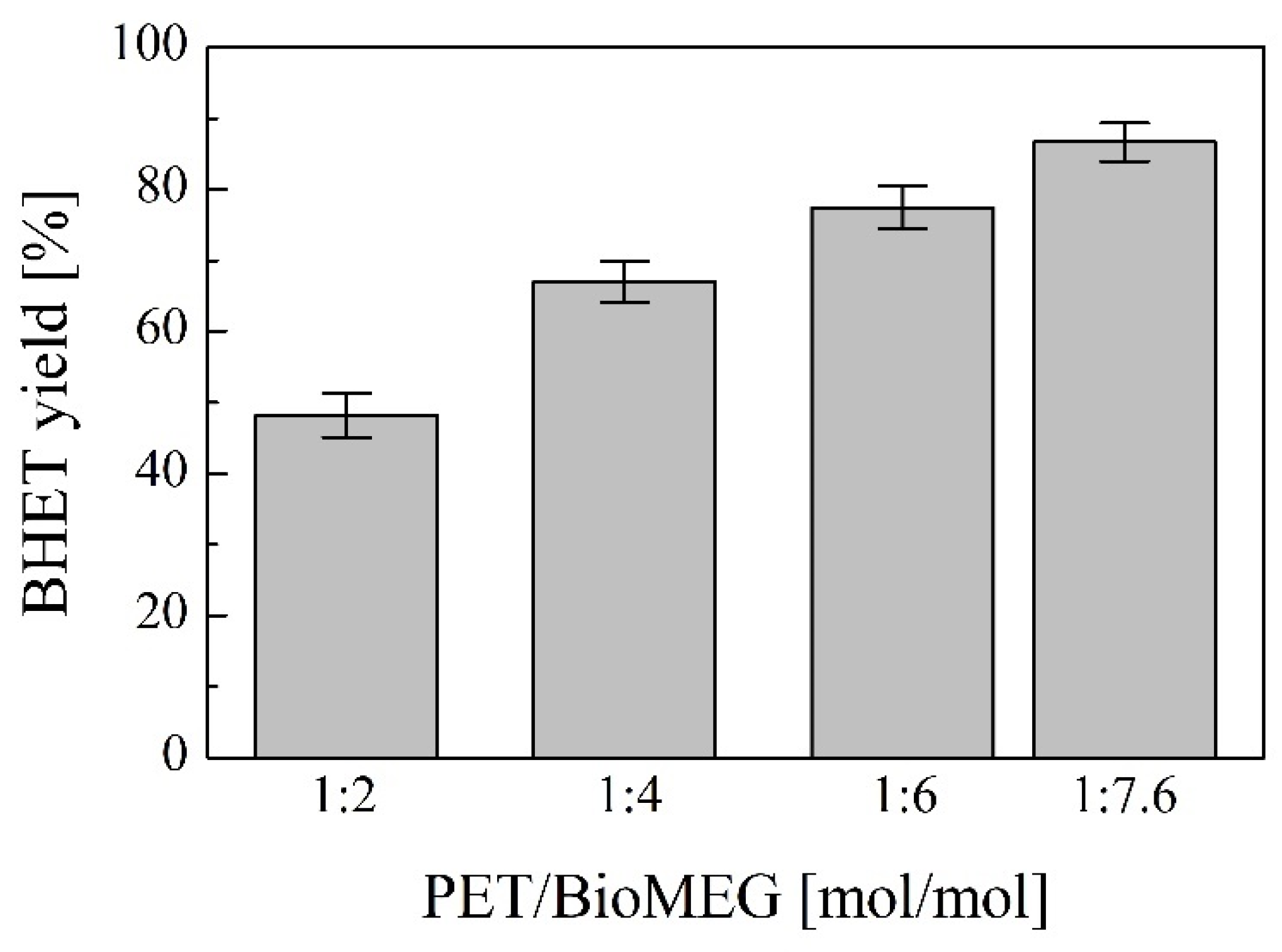
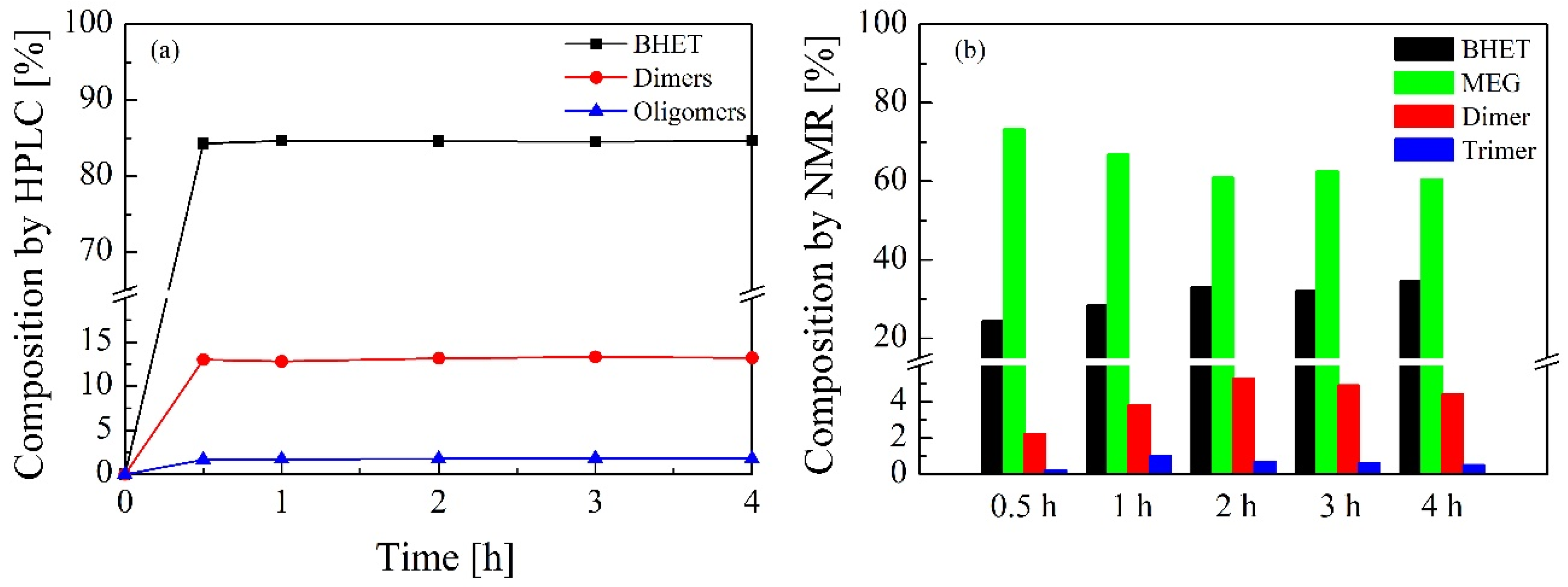
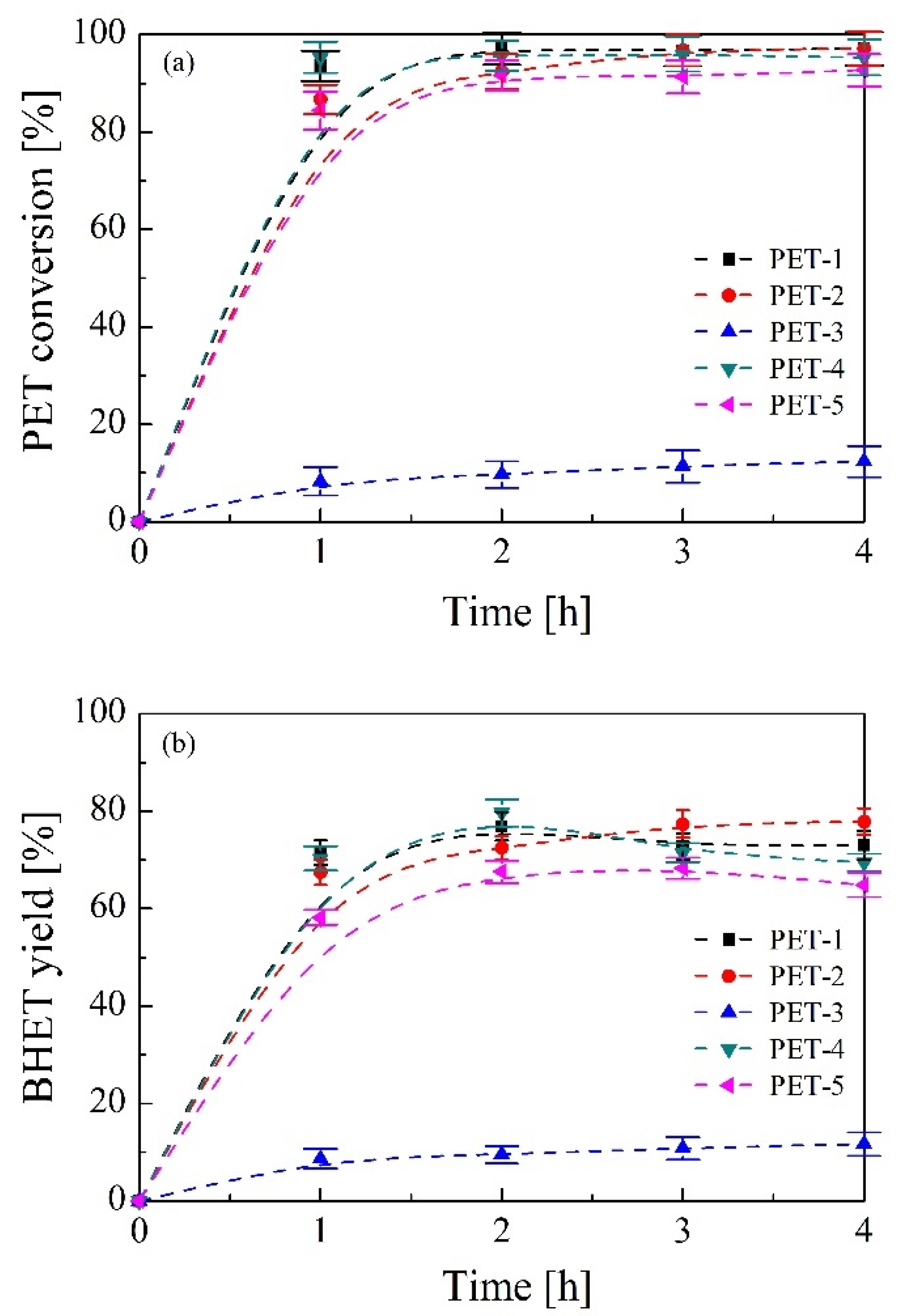
3.2. Bio-Solvolysis of PET Waste and Reaction Mechanism Determination
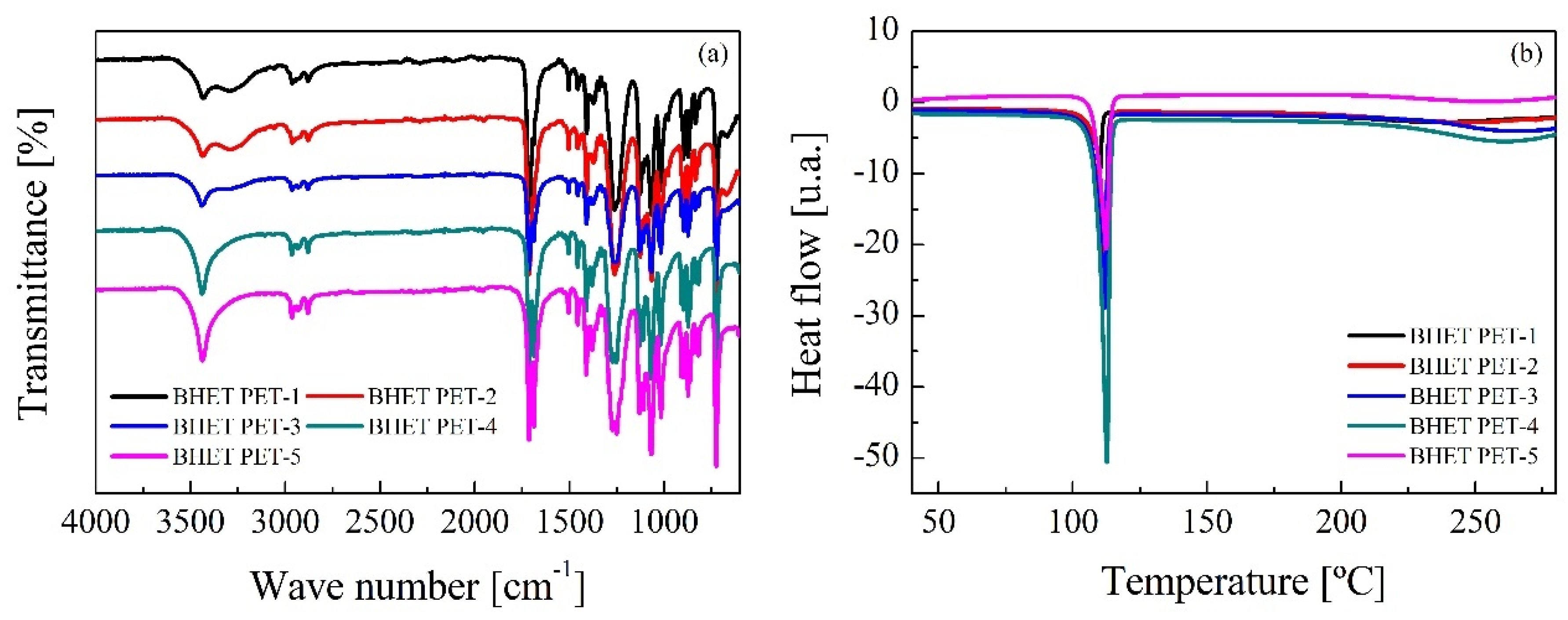
3.3. BHET Purification and Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- PlasticsEurope. Plastics—The Facts 2022. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-facts-2022/ (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- PlasticsEurope. Plastics—The Facts 2021. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-facts-2021/ (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Solis, M.; Silveira, S. Technologies for chemical recycling of household plastics—A technical review and TRL assessment. Waste Manag. 2020, 105, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vollmer, I.; Jenks, M.J.F.; Roelands, M.C.P.; White, R.J.; Harmelen, T.; Wild, P.; Laan, G.P.; Meirer, F.; Keurentjes, J.T.F.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Beyond mechanical recycling: Giving new life to plastic waste. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15402–15423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosal, K.; Nayak, C. Recent advances in chemical recycling of polyethylene terephthalate waste into value added products for sustainable coating solutions—Hope vs. hype. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1974–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; von Jouanne, A.; Yokochi, A. Current Technologies in Depolymerization Process and the Road Ahead. Polymers 2021, 13, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendiburu-Valor, E.; Mondragon, G.; González, N.; Kortaberria, G.; Eceiza, A.; Peña-Rodriguez, C. Improving the Efficiency for the Production of Bis-(2-Hydroxyethyl) Terephtalate (BHET) from the Glycolysis Reaction of Poly(Ethylene Terephtalate) (PET) in a Pressure Reactor. Polymers 2021, 13, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barredo, A.; Asueta, A.; Amundarain, I.; Leivar, J.; Miguel-Fernández, R.; Arnaiz, S.; Epelde, E.; López-Fonseca, R.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I. Chemical recycling of monolayer PET tray waste by alkaline hydrolysis. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, A.; Martínez, L.; Becerra, L.; Arieta-araunabeña, M.; Arnaiz, S.; Asueta, A.; Robertson, I. Chemical depolymerisation of PET complex waste: Hydrolysis vs. glycolysis. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2014, 16, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundarain, I.; Miguel-Fernández, R.; Asueta, A.; García-Fernández, S.; Arnaiz, S. Synthesis of Rigid Polyurethane Foams Incorporating Polyols from Chemical Recycling of Post-Industrial Waste Polyurethane Foams. Polymers 2022, 14, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel-Fernández, R.; Amundarain, I.; Asueta, A.; García-Fernández, S.; Arnaiz, S.; Miazza, N.L.; Montón, E.; Rodríguez-García, B.; Bianca-Benchea, E. Recovery of Green Polyols from Rigid Polyurethane Waste by Catalytic Depolymerization. Polymers 2022, 14, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, C.; Figueira, R.; Hofmann, M.; Koschke, S.; Enthaler, S. Chemical Recycling of End-of-Life Polyamide 6 via Ring Closing Depolymerization. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 12638–12642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, V.; Patel, M.R.; Patel, J.V. PET Waste Management by Chemical Recycling: A Review. J. Polym. Environ. 2010, 18, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petcore Europe. PET Market in Europe—State of Play 2022. Available online: https://www.petcore-europe.org/news-events/409-pet-market-in-europe-state-of-play-2022.html (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Chassignet, E.P.; Xu, X.; Zavala-Romero, O. Tracking Marine Litter with a Global Ocean Model: Where Does It Go? Where Does It Come From? Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 667591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolome, L.; Imran, M.; Cho, B.G.; Al-Masry, W.A.; Kim, D.H. Recent Developments in the Chemical Recycling of PET. Mater. Recycl.—Trends Perspect. 2012, 406, 576–596. [Google Scholar]
- Jeya, G.; Dhanalakshmi, R.; Anbarasu, M.; Vinitha, V.; Sivamurugan, V. A short review on latest developments in catalytic depolymerization of Poly (ethylene terephathalate) wastes. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, B.; Lorenz, G.; Kandelbauer, A. Recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate)—A review focusing on chemical methods. Express Polym. Lett. 2016, 10, 559–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiburu-Valor, E.; Mondragon, G.; González, N.; Kortaberria, G.; Martin, L.; Eceiza, A.; Peña-Rodriguez, C. Valorization of urban and marine PET waste by optimized chemical recycling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 184, 106413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.K.; Mathur, R.; Kumar, D.; Rajagopal, C. Tertiary recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate) wastes for production of polyurethane–polyisocyanurate foams. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2013, 1, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mejjatti, A.; Harit, T.; Riahi, A.; Khiari, R.; Bouabdallah, I.; Malek, F. Chemical recycling of poly(ethylene terephthalate). Application to the synthesis of multiblock copolyesters. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathalewar, M.; Dhopatkar, N.; Pacharane, B.; Sabnis, A.; Raut, P.; Bhave, V. Chemical recycling of PET using neopentyl glycol: Reaction kinetics and preparation of polyurethane coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimpan, V.; Sirisook, R.; Chuayjuljit, S. Synthesis of unsaturated polyester resin from postconsumer PET bottles: Effect of type of glycol on characteristics of unsaturated polyester resin. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 88, 788–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemy, M.; Mossaddegh, K. Depolymerisation of poly(ethylene terephthalate) fibre wastes using ethylene glycol. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 90, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carné Sánchez, A.; Collinson, S.R. The selective recycling of mixed plastic waste of polylactic acid and polyethylene terephthalate by control of process conditions. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fonseca, R.; Duque-Ingunza, I.; de Rivas, B.; Arnaiz, S.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I. Chemical recycling of post-consumer PET wastes by glycolysis in the presence of metal salts. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Surekha, P.; Kumar, D.; Rajagopal, C.; Roy, P.K. Microwave assisted glycolysis of poly(ethylene terepthalate) for preparation of polyester polyols. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 2779–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goje, A.S.; Mishra, S. Chemical kinetics, simulation and thermodynamics of glycolytic depolymerization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) waste with catalyst optimization for recycling of value added monomeric products. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2003, 288, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baliga, S.; Wong, W.T. Depolymerization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) recycled from post-consumer softdrink bottles. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 1989, 27, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Yehia, F.Z.; Eshaq, G.; Rabie, A.M.; ElMetwally, A.E. Greener routes for recycling of polyethylene terephthalate. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meys, R.; Frick, F.; Westhues, S.; Sternberg, A.; Klankermayer, J.; Bardow, A. Towards a circular economy for plastic packaging wastes—The environmental potential of chemical recycling. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 162, 105010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hann, S.; Connock, T. Chemical Recycling: State of Play. Report for CHEM Trust, Eunomia. 2020. Available online: https://www.eunomia.co.uk/reports-tools/final-report-chemical-recycling-state-of-play/ (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Eunomia. Chemical Recycling of Polymeric Materials from Waste in the Circular Economy: Final Report Prepared for The European Chemicals Agency; RPA Europe: Milan, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, C.T.D.M.; Ek, M.; Ostmark, E.; Gallstedt, M.; Karlsson, S. Recycling of multi-material multilayer plastic packaging: Current trends and future scenarios. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 176, 105905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damayanti; Wu, H.S. Strategic Possibility Routes of Recycled PET. Polymers 2021, 13, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Shi, K.; Zhang, X.; Yu, K.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; Ju, Y.; Liu, J. From plastic waste to wealth using chemical recycling: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 106867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Systemiq. Circularity of PET/Polyester Packaging and Textiles in Europe—Synthesis of Published Research. 2023. Available online: https://www.systemiq.earth/pet-polyester/ (accessed on 14 August 2023).
- Fehér, Z.; Kiss, J.; Kisszékelyi, P.; Molnár, J.; Huszthy, P.; Kárpáti, L.; Kupai, J. Optimisation of PET Glycolysis by Applying Recyclable Heterogeneous Organocatalysts. Green Chem. 2022, 24, 8447–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehanno, C.; Flores, I.; Dove, A.P.; Müller, A.J.; Ruipérez, F.; Sardon, H. Organocatalysed depolymerisation of PET in a fully sustainable cycle using thermally stable protic ionic salt. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, N.H.; Van, T.N.; Shong, B.; Cho, J. Low-Temperature Glycolysis of Polyethylene Terephthalate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 17261–17273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Mojtahedi, M.R.M.; Khosroshahi, A. Effect of spinning speed on the structure and physical properties of filament yarns produced from used PET bottles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 3972–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, H.; Lu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Yan, D. Ion-exchange resins for efficient removal of colorants in bis(hydroxyethyl) terephthalate. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 12351–12360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado Chacon, F.; Brouwer, M.T.; Thoden van Velzen, E.U. Effect of recycled content and rPET quality on the properties of PET bottles, part I: Optical and mechanical properties. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2020, 33, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Ingunza, I.; López-Fonseca, R.; de Rivas, B.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I. Process optimization for catalytic glycolysis of post-consumer PET wastes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Dong, T.; Fang, P.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, S. Fast and effective glycolysis of poly (ethylene terephthalate) catalyzed by polyoxometalate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 117, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Fisse, J.; Vogt, D. Optimization and Kinetic Evaluation for Glycolytic Depolymerization of Post-Consumer PET Waste with Sodium Methoxide. Polymers 2023, 15, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Huang, R.; Jaffery, Q.Z.; Yan, D.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, J.; Lu, X. Progress in the catalytic glycolysis of polyethylene terephthalate. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 296, 113267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirshanov, K.; Toms, R.; Melnikov, P.; Gervald, A. Investigation of Polyester Tire Cord Glycolysis Accompanied by Rubber Crumb Devulcanization. Polymers 2022, 14, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptiček Siročić, A.; Fijačko, A.; Hrnjak-Murgić, Z. Chemical recycling of postconsumer poly (ethylene-terephthalate) bottles—Depolymerization study. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2013, 27, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, P.; Liu, B.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J. High-efficiency glycolysis of poly (ethylene terephthalate) by sandwichstructure polyoxometalate catalyst with two active sites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 156, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza García, K.; Navarro, R.; Ramírez-Hernández, A.; Marcos-Fernández, Á. New routes to difunctional macroglycols using ethylene carbonate: Reaction with bis-(2-hydroxyethyl) terephthalate and degradation of poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 144, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Yan, D.; Dong, H.; Li, F.; Lu, X.; Xin, X. Removal of trace amount impurities in glycolytic monomer of polyethylene terephthalate by recrystallization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
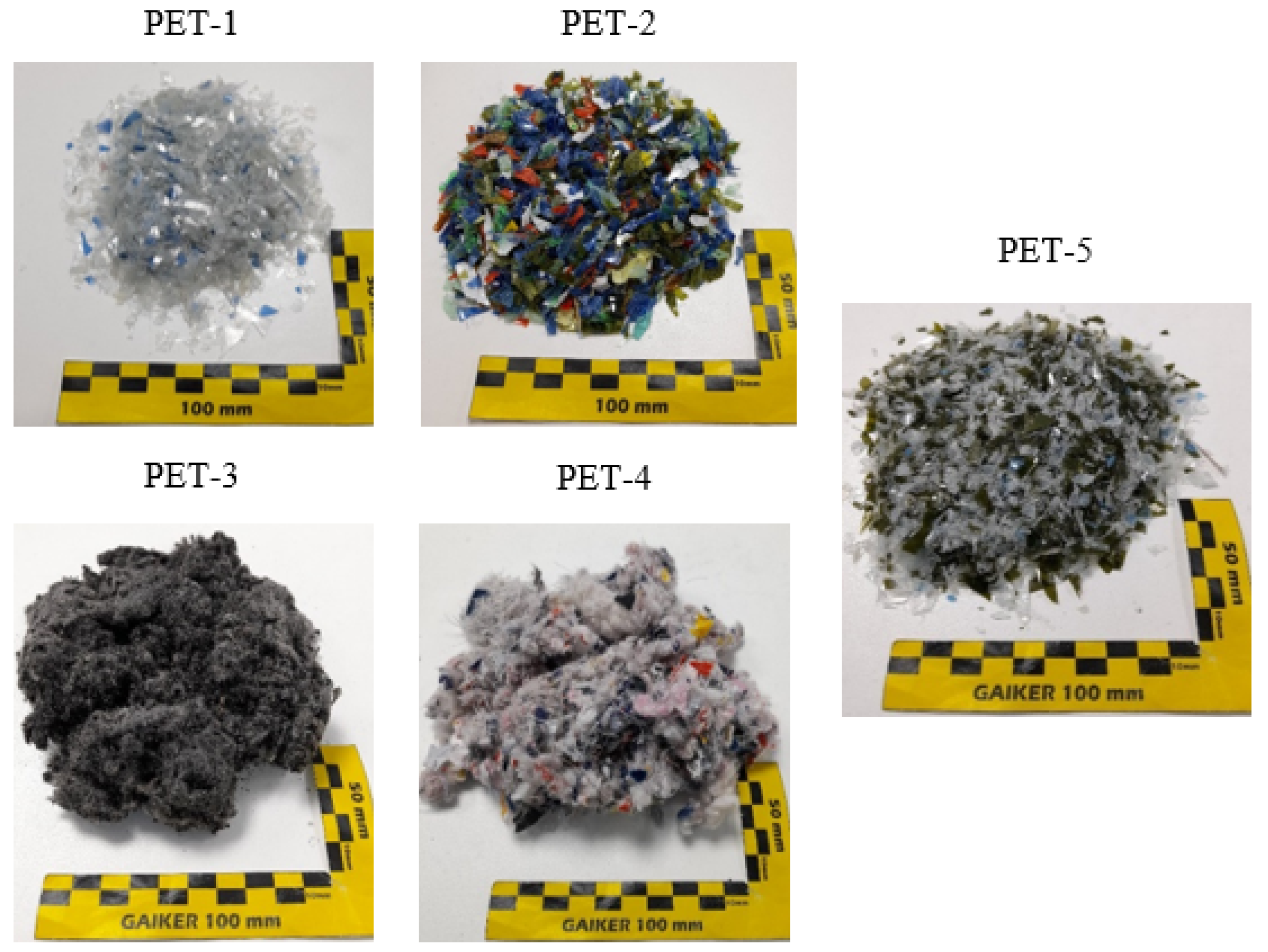

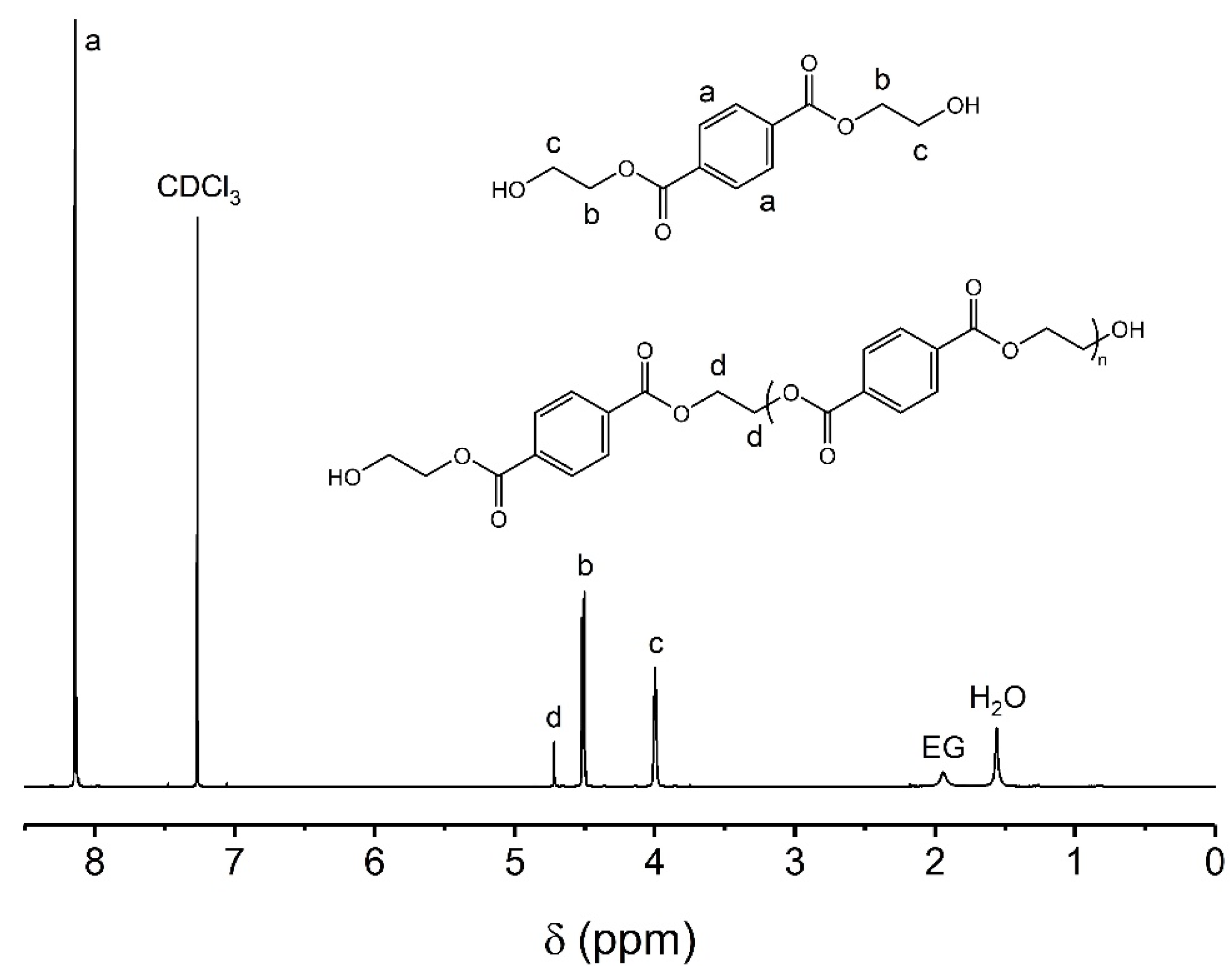
| PET | Material Description | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| PET-1 | Postconsumer monolayer trays | Low polyolefin concentration |
| PET-2 | Postconsumer coloured bottles | Highly coloured plastic |
| PET-3 | Textile from end-of-life tyres | Low density, presence of rubber |
| PET-4 | Textile from postconsumer clothing | Low density, presence of other fibres |
| PET-5 | Postconsumer multilayer trays | High polyolefin concentration |
| PET | Moisture (%) | Ash Content (%) | Bulk Density (g cm−3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PET-1 | 2.42 | 0.10 | 0.462 |
| PET-2 | 2.35 | 0.34 | 0.220 |
| PET-3 | 0.76 | 4.77 | 0.261 |
| PET-4 | 2.11 | 1.08 | 0.034 |
| PET-5 | 2.42 | 0.06 | 0.394 |
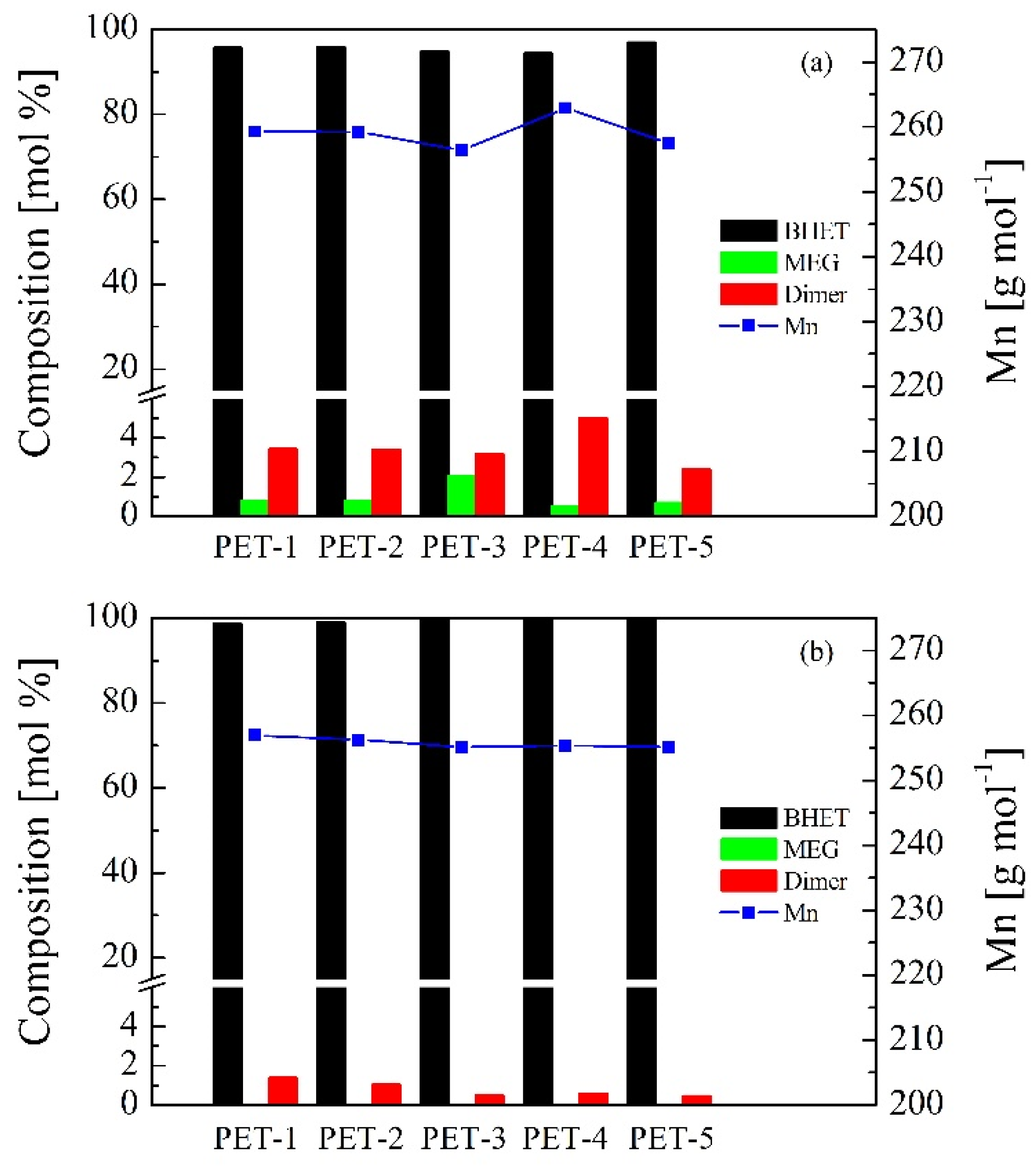
| PET | BHET (mol%) | MEG (mol%) | Dimer (mol%) | Trimer (mol%) | Mn (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET-1 | 95.74/98.61 | 0.81/0.00 | 3.45/1.39 | 0.00/0.00 | 259.30/256.91 |
| PET-2 | 95.82/98.94 | 0.80/0.00 | 3.38/1.06 | 0.00/0.00 | 259.21/256.28 |
| PET-3 | 94.79/99.52 | 2.04/0.00 | 3.17/0.48 | 0.00/0.00 | 256.40/255.16 |
| PET-4 | 94.48/99.41 | 0.51/0.00 | 5.00/0.59 | 0.00/0.00 | 262.87/255.37 |
| PET-5 | 96.93/99.53 | 0.69/0.00 | 2.38/0.47 | 0.00/0.00 | 257.47/255.14 |
| Sample | L* | a* | b* | Zn (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BHET PET-1 unpurified | 88.19 | −0.63 | 4.68 | 182.3 |
| BHET PET-1 purified | 95.23 | −0.12 | 1.43 | 1.9 |
| BHET PET-2 unpurified | 88.39 | −1.10 | 7.36 | 185.7 |
| BHET PET-2 purified | 95.68 | −0.02 | 1.12 | 2.5 |
| BHET PET-3 unpurified | 62.71 | 6.66 | 17.52 | 201.4 |
| BHET PET-3 purified | 91.44 | −0.23 | 2.32 | 4.3 |
| BHET PET-4 unpurified | 64.33 | 9.37 | 6.24 | 193.6 |
| BHET PET-4 purified | 93.33 | −0.13 | 1.39 | 3.6 |
| BHET PET-5 unpurified | 86.37 | −2.30 | 17.55 | 200.9 |
| BHET PET-5 purified | 93.80 | −0.18 | 1.52 | 2.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amundarain, I.; López-Montenegro, S.; Fulgencio-Medrano, L.; Leivar, J.; Iruskieta, A.; Asueta, A.; Miguel-Fernández, R.; Arnaiz, S.; Pereda-Ayo, B. Improving the Sustainability of Catalytic Glycolysis of Complex PET Waste through Bio-Solvolysis. Polymers 2024, 16, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010142
Amundarain I, López-Montenegro S, Fulgencio-Medrano L, Leivar J, Iruskieta A, Asueta A, Miguel-Fernández R, Arnaiz S, Pereda-Ayo B. Improving the Sustainability of Catalytic Glycolysis of Complex PET Waste through Bio-Solvolysis. Polymers. 2024; 16(1):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010142
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmundarain, Izotz, Sheila López-Montenegro, Laura Fulgencio-Medrano, Jon Leivar, Ana Iruskieta, Asier Asueta, Rafael Miguel-Fernández, Sixto Arnaiz, and Beñat Pereda-Ayo. 2024. "Improving the Sustainability of Catalytic Glycolysis of Complex PET Waste through Bio-Solvolysis" Polymers 16, no. 1: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010142
APA StyleAmundarain, I., López-Montenegro, S., Fulgencio-Medrano, L., Leivar, J., Iruskieta, A., Asueta, A., Miguel-Fernández, R., Arnaiz, S., & Pereda-Ayo, B. (2024). Improving the Sustainability of Catalytic Glycolysis of Complex PET Waste through Bio-Solvolysis. Polymers, 16(1), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym16010142








