Properties Comparison of Oxidized and Heat Moisture Treated (HMT) Starch-Based Biodegradable Films
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Edible Film
2.1. Definition
2.2. Function and Properties
2.3. Edible Film Preparation
3. Starch as a Material for Edible Film
3.1. Native Starch and Its Drawbacks for Edible Film Application
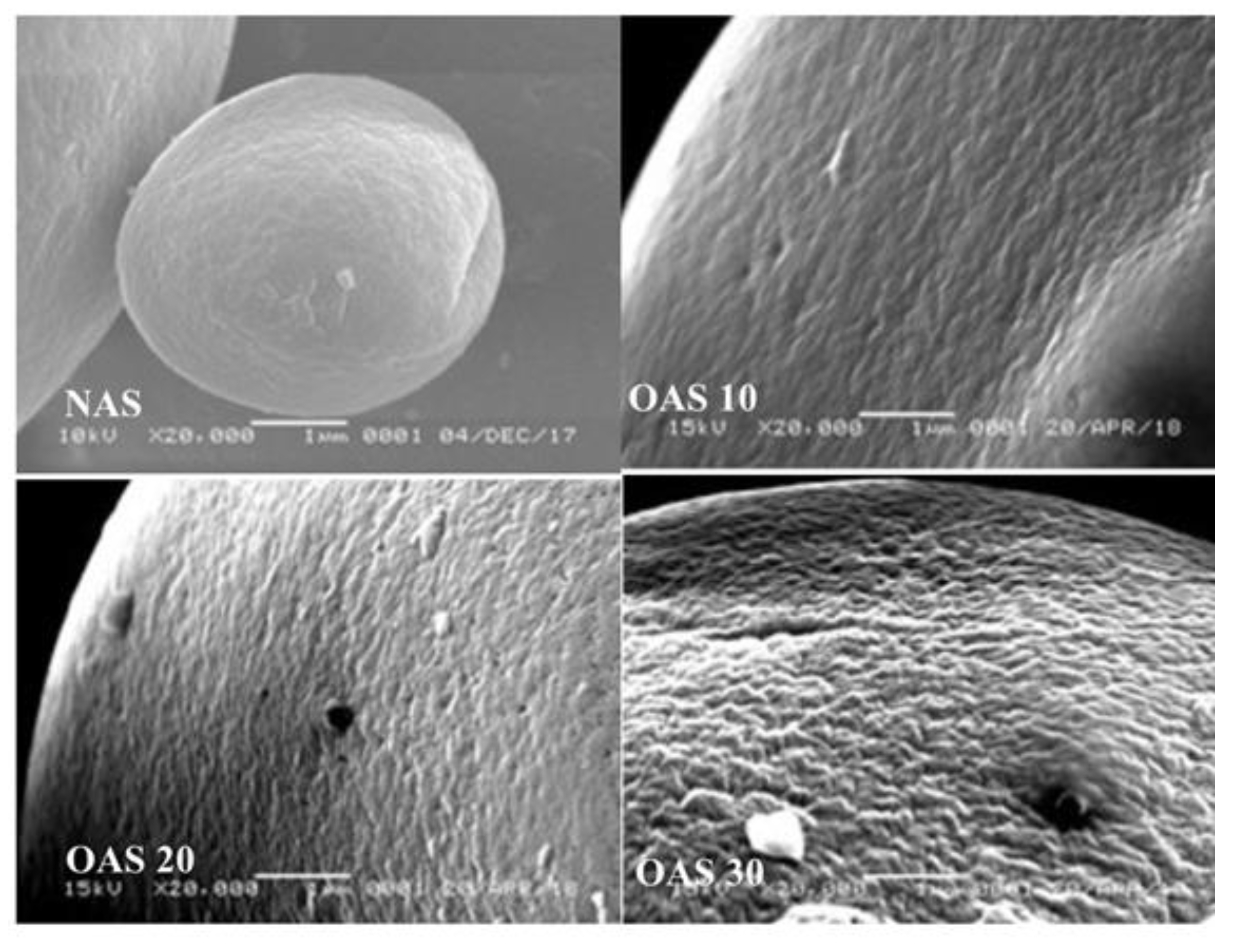
3.2. Starch Modification (Oxidation and Heat Moisture Treatment)
3.2.1. Oxidation
3.2.2. Heat Moisture Treatment (HMT)
4. Starch Modification Effect on Edible Film Properties
4.1. Gas (O2) and Water Vapor Permeability (WVP)
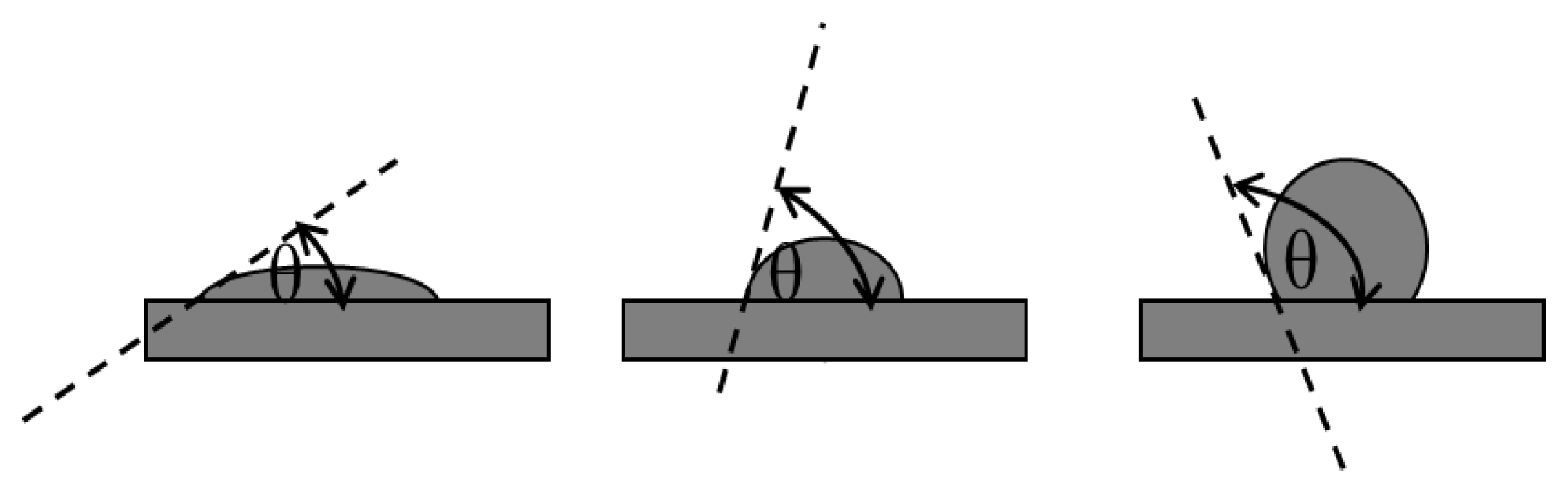
4.2. Contact Angle
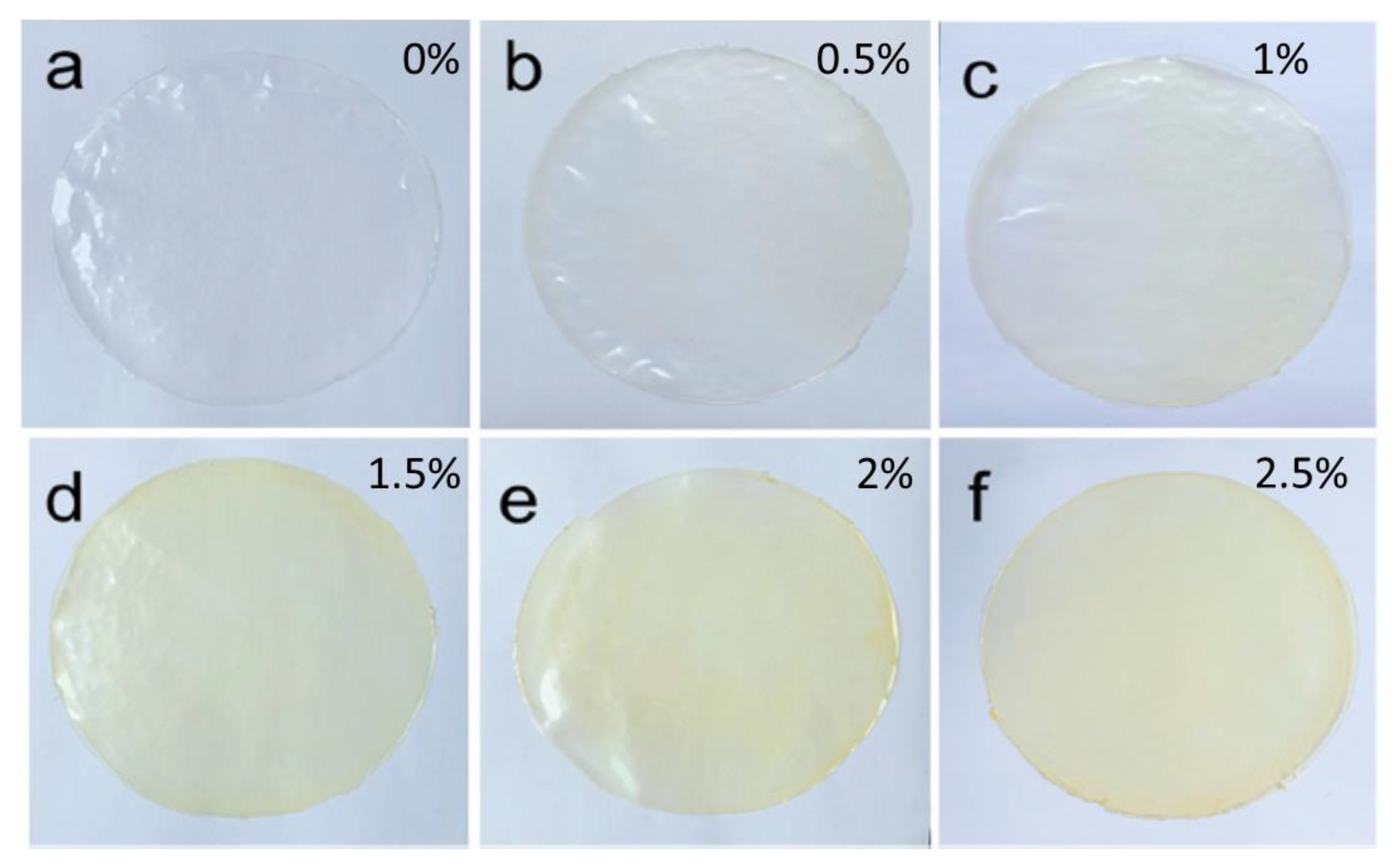
4.3. Transparency
4.4. Mechanical Strength (Modulus, Elongation, and Tensile Strength)
4.5. Thermal Properties and Crystallinity
4.5.1. Crystallinity
4.5.2. Thermal Properties
5. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohamed, S.A.A.; El-Sakhawy, M.; El-Sakhawy, M.A.-M. Polysaccharides, Protein and Lipid -Based Natural Edible Films in Food Packaging: A Review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 238, 116178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marta, H.; Cahyana, Y.; Bintang, S.; Soeherman, G.P.; Djali, M. Physicochemical and pasting properties of corn starch as affected by hydrothermal modification by various methods. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 792–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handarini, K.; Hamdani, J.S.; Cahyana, Y.; Setiasih, I.S. Gaseous Ozonation at Low Concentration Modifies Functional, Pasting, and Thermal Properties of Arrowroot Starch (Maranta arundinaceae). Starch—Stärke 2020, 72, 1900106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Composition, structure, physicochemical properties, and modifications of cassava starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 122, 456–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Mhaske, P.; Farahnaky, A.; Kasapis, S.; Majzoobi, M. Cassava starch: Chemical modification and its impact on functional properties and digestibility, a review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, H.; Hasya, H.N.L.; Lestari, Z.I.; Cahyana, Y.; Arifin, H.R.; Nurhasanah, S. Study of Changes in Crystallinity and Functional Properties of Modified Sago Starch (Metroxylon sp.) Using Physical and Chemical Treatment. Polymers 2022, 14, 4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakody, L.; Hoover, R.; Liu, Q.; Donner, E. Studies on tuber starches III. Impact of annealing on the molecular structure, composition and physicochemical properties of yam (Dioscorea sp.) starches grown in Sri Lanka. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, H.; Cahyana, Y.; Djali, M.; Arcot, J.; Tensiska, T. A comparative study on the physicochemical and pasting properties of starch and flour from different banana (Musa spp.) cultivars grown in Indonesia. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 1562–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, H.; Cahyana, Y.; Djali, M. Pectin interaction with thermally modified starch affects physicochemical properties and digestibility of starch as revealed by logarithm of slop plot. CyTA—J. Food 2021, 19, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fida, R.; Pramafisi, G.; Cahyana, Y. Application of banana starch and banana flour in various food product: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 443, 012057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.-T.; Zhou, D.-N.; Jin, Z.-Y.; Xu, X.-M.; Chen, H.-Q. Effect of repeated heat-moisture treatments on digestibility, physicochemical and structural properties of sweet potato starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waduge, R.N.; Hoover, R.; Vasanthan, T.; Gao, J.; Li, J. Effect of annealing on the structure and physicochemical properties of barley starches of varying amylose content. Food Res. Int. 2006, 39, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebowale, K.O.; Afolabi, T.A.; Olu-Owolabi, B.I. Hydrothermal treatments of Finger millet (Eleusine coracana) starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2005, 19, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, H.; Cahyana, Y.; Arifin, H.R.; Khairani, L. Comparing the effect of four different thermal modifications on physicochemical and pasting properties of breadfruit (Artocarpus altilis) starch. Int. Food Res. J. 2019, 26, 269–276. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Hasan, M.; Mangaraj, S.; Pravitha, M.; Verma, D.K.; Srivastav, P.P. Trends in Edible Packaging Films and its Prospective Future in Food: A Review. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.; Shin, D.; Lyu, J.S.; Lee, J.-S.; Song, H.-G.; Chung, M.-N.; Han, J. Physicochemical properties and solubility of sweet potato starch-based edible films. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 33, 100867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhai, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Sun, C.; Wang, W.; Hou, H. Effects of natural wax types on the physicochemical properties of starch/gelatin edible films fabricated by extrusion blowing. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, H.; Wijaya, C.; Sukri, N.; Cahyana, Y.; Mohammad, M. A Comprehensive Study on Starch Nanoparticle Potential as a Reinforcing Material in Bioplastic. Polymers 2022, 14, 4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falua, K.J.; Pokharel, A.; Babaei-Ghazvini, A.; Ai, Y.; Acharya, B. Valorization of Starch to Biobased Materials: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Chen, J.; He, J.; Li, H.; Jia, Q.; Hossen, M.A.; Dai, J.; Qin, W.; Liu, Y. Preparation of corn starch/rock bean protein edible film loaded with d-limonene particles and their application in glutinous rice cake preservation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongphan, P.; Khowthong, M.; Supatrawiporn, T.; Harnkarnsujarit, N. Novel edible starch films incorporating papain for meat tenderization. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 31, 100787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmasari, Y.; Yemiş, G.P. Characterization of ginger starch-based edible films incorporated with coconut shell liquid smoke by ultrasound treatment and application for ground beef. Meat Sci. 2022, 188, 108799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoshal, G.; Shivani. Thyme essential oil nano-emulsion/Tamarind starch/Whey protein concentrate novel edible films for tomato packaging. Food Control 2022, 138, 108990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzahedi, S.M.T.; Ahmadigol, A.; Khubber, S.; Altintas, Z. Whey protein isolate/jujube polysaccharide-based edible nanocomposite films reinforced with starch nanocrystals for the shelf-life extension of banana: Optimization and characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1063–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanmani, P.; Rhim, J.-W. Properties and characterization of bionanocomposite films prepared with various biopolymers and ZnO nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 106, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, H.; Cahyana, Y.; Djali, M.; Pramafisi, G. The Properties, Modification, and Application of Banana Starch. Polymers 2022, 14, 3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C.; Deng, Y.; Xie, P.; Liu, L.; Cheng, J. Research advances in chemical modifications of starch for hydrophobicity and its applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 240, 116292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Prado Cordoba, L.; Ribeiro, L.S.; Rosa, L.S.; Lacerda, L.G.; Schnitzler, E. Effect of enzymatic treatments on thermal, rheological and structural properties of pinhão starch. Thermochim. Acta 2016, 642, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, V.Z.; Vanier, N.L.; Deon, V.G.; Moomand, K.; El Halal, S.L.M.; Zavareze, E.d.R.; Lim, L.-T.; Dias, A.R.G. Effects of single and dual physical modifications on pinhão starch. Food Chem. 2015, 187, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handarini, K.; Hamdani, J.S.; Cahyana, Y.; Setiasih, I.S. Functional, thermal, and molecular properties of ozonated starches. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 443, 012102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Montes, E.; Castro-Muñoz, R. Edible Films and Coatings as Food-Quality Preservers: An Overview. Foods 2021, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajkovska Petkoska, A.; Daniloski, D.; D’Cunha, N.M.; Naumovski, N.; Broach, A.T. Edible packaging: Sustainable solutions and novel trends in food packaging. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 109981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zibaei, R.; Hasanvand, S.; Hashami, Z.; Roshandel, Z.; Rouhi, M.; Guimarães, J.d.T.; Mortazavian, A.M.; Sarlak, Z.; Mohammadi, R. Applications of emerging botanical hydrocolloids for edible films: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 256, 117554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhedi, O.; Salem, A.; Nasri, R.; Nasri, M.; Jridi, M. Food applications of bioactive marine gelatin films. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 43, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, B.H.; Yildirim, F.K.; Hecer, C. Edible Films and Coatings: A Good Idea from Past to Future Technology. J. Food Technol. Res. 2018, 5, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, B.W.S.; Cerqueira, M.A.; Teixeira, J.A.; Vicente, A.A. The Use of Electric Fields for Edible Coatings and Films Development and Production: A Review. Food Eng. Rev. 2010, 2, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, Y.W.; Putri, S.Y.; Intan, N.; Bahtiar, A.; Kurniati, M. The effect of sorbitol and sweet sorghum to carrageenan ratio on the physicochemical properties of sweet sorghum/carrageenan bioplastics. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 2719–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falguera, V.; Quintero, J.P.; Jiménez, A.; Muñoz, J.A.; Ibarz, A. Edible films and coatings: Structures, active functions and trends in their use. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 22, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, H.; Cahyana, Y.; Djali, M. The effect of starch-hydrocolloid interaction on starch digestibility, pasting and physicochemical properties: A review. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 443, 012084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, J.; He, J. Effects of cinnamon essential oil on the physical, mechanical, structural and thermal properties of cassava starch-based edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Ramakanth, D.; Akhila, K.; Gaikwad, K.K. Edible films and coatings for food packaging applications: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2022, 20, 875–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Fu, Y.; He, J. Preparation and physical properties of soy protein isolate and gelatin composite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellinas, C.; Valdés, A.; Ramos, M.; Burgos, N.; Garrigós, M.d.C.; Jiménez, A. Active edible films: Current state and future trends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 42631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebalia, I.; Maigret, J.E.; Réguerre, A.L.; Novales, B.; Guessasma, S.; Lourdin, D.; Della Valle, G.; Kristiawan, M. Morphology and mechanical behaviour of pea-based starch-protein composites obtained by extrusion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 223, 115086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Yepes, O.; Di Giogio, L.; Goyanes, S.; Mauri, A.; Famá, L. Influence of process (extrusion/thermo-compression, casting) and lentil protein content on physicochemical properties of starch films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, V.; Felix, M.; Romero, A.; Guerrero, A. Characterization of pea protein-based bioplastics processed by injection moulding. Food Bioprod. Process. 2016, 97, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, K.S.; Sharma, L.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, R. Physical, structural and thermal properties of composite edible films prepared from pearl millet starch and carrageenan gum: Process optimization using response surface methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Min, S.C. Trout skin gelatin-based edible film development. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, E240–E246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouki, M.; Khazaei, N.; Ghasemlou, M.; HadiNezhad, M. Effect of glycerol concentration on edible film production from cress seed carbohydrate gum. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.M.; Radünz, M.; dos Santos Hackbart, H.C.; da Silva, F.T.; Camargo, T.M.; Bruni, G.P.; Monks, J.L.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Dias, A.R. Electrospun potato starch nanofibers for thyme essential oil encapsulation: Antioxidant activity and thermal resistance. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4263–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, L.; Cai, J.; Dong, Q.; Din, Z.-U.; Hu, Z.-Z.; Wang, G.-Z.; Ding, W.-P.; He, J.-R.; Cheng, S.-Y. Starch/tea polyphenols nanofibrous films for food packaging application: From facile construction to enhance mechanical, antioxidant and hydrophobic properties. Food Chem. 2021, 360, 129922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, L.C.B.; de Souza, C.O.; da Silva, J.B.A.; Martins, A.C.; Nunes, I.L.; Druzian, J.I. Active biocomposites of cassava starch: The effect of yerba mate extract and mango pulp as antioxidant additives on the properties and the stability of a packaged product. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 94, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, H.; Rizki, D.I.; Mardawati, E.; Djali, M.; Mohammad, M.; Cahyana, Y. Starch Nanoparticles: Preparation, Properties and Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, U.; Naqash, F.; Gani, A.; Masoodi, F.A. Art and Science behind Modified Starch Edible Films and Coatings: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 568–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabetzadeh, M.; Bagheri, R.; Masoomi, M. Study on ternary low density polyethylene/linear low density polyethylene/thermoplastic starch blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 119, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogstad, T.M.; Konings, G.; Buwalda, P.L.; Boxtel, A.J.B.; Kiewidt, L.; Bitter, J.H. The effect of polydispersity on the conversion kinetics of starch oxidation and depolymerisation. Chem. Eng. Sci. X 2019, 4, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhija, S.; Singh, S.; Riar, C.S. Molecular characteristics of oxidized and cross-linked lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) rhizome starch. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S1065–S1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handarini, K.; Hamdani, J.S.; Cahyana, Y.; Setiasih, I.S. Functional and pasting properties of a starch–lipid complex formed with gaseous ozone and palm oil. Int. J. Food Prop. 2020, 23, 1361–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyana, Y.; Titipanillah, R.; Mardawati, E.; Sukarminah, E.; Rialita, T.; Andoyo, R.; Djali, M.; Hanidah, I.-I.; Setiasih, I.S.; Handarini, K. Non-starch contents affect the susceptibility of banana starch and flour to ozonation. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ji, G.; Gao, F.; Qian, J.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C. Effect of heat-moisture treatment on the structural and physicochemical characteristics of sand rice (Agriophyllum squarrosum) starch. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 6720–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, H.; Delcour, J.A. Hydrothermal Modifications of Granular Starch, with Retention of the Granular Structure: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2895–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavareze, E.d.R.; Pinto, V.Z.; Klein, B.; El Halal, S.L.M.; Elias, M.C.; Prentice-Hernández, C.; Dias, A.R.G. Development of oxidised and heat–moisture treated potato starch film. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca, L.M.; Halal, S.L.M.E.; Dias, A.R.G.; Zavareze, E.d.R. Physical modification of starch by heat-moisture treatment and annealing and their applications: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 274, 118665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahyana, Y.; Wijaya, E.; Halimah, T.S.; Marta, H.; Suryadi, E.; Kurniati, D. The effect of different thermal modifications on slowly digestible starch and physicochemical properties of green banana flour (Musa acuminata colla). Food Chem. 2019, 274, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahyana, Y.; Rangkuti, A.; Halimah, T.S.; Marta, H.; Yuliana, T. Application of heat-moisture-treated banana flour as composite material in hard biscuit. CyTA—J. Food 2020, 18, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marta, H.; Cahyana, Y.; Djali, M. Densely packed-matrices of heat moisture treated-starch determine the digestion rate constant as revealed by logarithm of slope plots. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 2237–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, S. Barley starch modifications: Physical, chemical and enzymatic—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahyana, Y.; Nugraha, T.; Aprilira, N.; Ayuningtias, K.; Soeherman, G.P.; Marta, H.; Tensiska, T. Interplay Role of Heat-Moisture Treatment and Lipid from Egg yolk and Margarine on Functional and Pasting Properties of Banana Flour. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2021, 71, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fuente, C.I.A.; de Souza, A.T.; Tadini, C.C.; Augusto, P.E.D. Ozonation of cassava starch to produce biodegradable films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 141, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzoobi, M.; Pesaran, Y.; Mesbahi, G.; Golmakani, M.T.; Farahnaky, A. Physical properties of biodegradable films from heat-moisture-treated rice flour and rice starch. Starch—Stärke 2015, 67, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.M.; Gonçalves, J.R.; El Halal, S.L.M.; Pinto, V.Z.; Dias, A.R.G.; Jacques, A.C.; Zavareze, E.d.R. Oxidation of potato starch with different sodium hypochlorite concentrations and its effect on biodegradable films. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Torres, B.; Robles-García, M.Á.; Gutiérrez-Lomelí, M.; Padilla-Frausto, J.J.; Navarro-Villarruel, C.L.; Del-Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Rodríguez-Félix, F.; Barrera-Rodríguez, A.; Reyna-Villela, M.Z.; Avila-Novoa, M.G.; et al. Combination of Sorbitol and Glycerol, as Plasticizers, and Oxidized Starch Improves the Physicochemical Characteristics of Films for Food Preservation. Polymers 2021, 13, 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritu, S.; Bhupendar Singh, K. Amaranth Starch Isolation, Oxidation, Heat-Moisture Treatment and Application in Edible Film Formation. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Res. Sci. 2018, 5, 237406. [Google Scholar]
- Viana, E.B.M.; Oliveira, N.L.; Ribeiro, J.S.; Almeida, M.F.; Souza, C.C.E.; Resende, J.V.; Santos, L.S.; Veloso, C.M. Development of starch-based bioplastics of green plantain banana (Musa paradisiaca L.) modified with heat-moisture treatment (HMT). Food Packag. Shelf Life 2022, 31, 100776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüello-García, E.; Solorza-Feria, J.; Rendón-Villalobos, J.R.; Rodríguez-González, F.; Jiménez-Pérez, A.; Flores-Huicochea, E. Properties of Edible Films Based on Oxidized Starch and Zein. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2014, 2014, 292404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamudio-Flores, P.B.; Vargas-Torres, A.; Pérez-González, J.; Bosquez-Molina, E.; Bello-Pérez, L.A. Films Prepared with Oxidized Banana Starch: Mechanical and Barrier Properties. Starch—Stärke 2006, 58, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Halal, S.L.M.; Colussi, R.; Deon, V.G.; Pinto, V.Z.; Villanova, F.A.; Carreño, N.L.V.; Dias, A.R.G.; Zavareze, E.d.R. Films based on oxidized starch and cellulose from barley. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, A.M.P.; Santoso, U.; Pranoto, Y.; Marseno, D.W. Dual Modification of Sago Starch via Heat Moisture Treatment and Octenyl Succinylation to Improve Starch Hydrophobicity. Polymers 2022, 14, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrianti, N.; Pranoto, Y.; Abbas, A. Preparation and Characterization of Edible Films Made from Modified Sweet Potato Starch through Heat Moisture Treatment. Indones. J. Chem. 2018, 18, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biduski, B.; Silva, F.T.d.; Silva, W.M.d.; Halal, S.L.d.M.E.; Pinto, V.Z.; Dias, A.R.G.; Zavareze, E.d.R. Impact of acid and oxidative modifications, single or dual, of sorghum starch on biodegradable films. Food Chem. 2017, 214, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillard, V.; Broyart, B.; Bonazzi, C.; Guilbert, S.; Gontard, N. Preventing Moisture Transfer in a Composite Food Using Edible Films: Experimental and Mathematical Study. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 2267–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talja, R.A.; Helén, H.; Roos, Y.H.; Jouppila, K. Effect of various polyols and polyol contents on physical and mechanical properties of potato starch-based films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2007, 67, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuzzi, M.A.; Castro Vidaurre, E.F.; Armada, M.; Gottifredi, J.C. Water vapor permeability of edible starch based films. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mali, S.; Grossmann, M.V.E.; García, M.A.; Martino, M.N.; Zaritzky, N.E. Barrier, mechanical and optical properties of plasticized yam starch films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CUQ, B.; GONTARD, N.; CUQ, J.-L.; GUILBERT, S. Functional Properties of Myofibrillar Protein-based Biopackaging as Affected by Film Thickness. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.B.; Müller, C.M.O.; Larotonda, F.D.S.; Laurindo, J.B. Biodegradable films based on rice starch and rice flour. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 51, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-D.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z. High Carbonyl Content Oxidized Starch Prepared by Hydrogen Peroxide and Its Thermoplastic Application. Starch—Stärke 2009, 61, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuakpetoon, D.; Wang, Y.-J. Characterization of Different Starches Oxidized by Hypochlorite. Starch—Stärke 2001, 53, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.J.; Liu, Q.; Thompson, M.R. Characterization of structure and properties of thermoplastic potato starch film surface cross-linked by UV irradiation. Starch—Stärke 2013, 65, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basiak, E.; Lenart, A.; Debeaufort, F. Effect of starch type on the physico-chemical properties of edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, X.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Lv, M.; Peng, Q.; Wang, M. Changes in physicochemical properties and in vitro digestibility of common buckwheat starch by heat-moisture treatment and annealing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 132, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adawiyah, D.R.; Akuzawa, S.; Sasaki, T.; Kohyama, K. A comparison of the effects of heat moisture treatment (HMT) on rheological properties and amylopectin structure in sago (Metroxylon sago) and arenga (Arenga pinnata) starches. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3404–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khunae, P.; Tran, T.; Sirivongpaisal, P. Effect of Heat-Moisture Treatment on Structural and Thermal Properties of Rice Starches Differing in Amylose Content. Starch—Stärke 2007, 59, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, N.L.; Ribba, L.; Dufresne, A.; Aranguren, M.I.; Goyanes, S. Physico-Mechanical Properties of Biodegradable Starch Nanocomposites. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2009, 294, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Starch Source | Modification Type and Method | Effect on Film Properties | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cassava starch | Oxidation with ozone |
| [69] |
| Rice Starch | HMT |
| [70] |
| Potato Starch | HMT |
| [62] |
| Oxidation by sodium hypochlorite |
| [62] | |
| Oxidation by sodium hypochlorite |
| [71] | |
| Oxidation by sodium hypochlorite |
| [72] | |
| Amaranth Starch | HMT |
| [73] |
| Oxidation with sodium hypochlorite |
| ||
| Green plantain banana | HMT |
| [74] |
| Oxidation with hypochlorite |
| [75] | |
| Oxidation with hypochlorite |
| [76] | |
| Barley | Oxidation with sodium hypochlorite |
| [77] |
| Sago | Heat moisture treatment (HMT) |
| [78] |
| Sweet potato | Heat moisture treatment (HMT) |
| [79] |
| Sorghum | Oxidation with chlorine |
| [80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cahyana, Y.; Verrell, C.; Kriswanda, D.; Aulia, G.A.; Yusra, N.A.; Marta, H.; Sukri, N.; Esirgapovich, S.J.; Abduvakhitovna, S.S. Properties Comparison of Oxidized and Heat Moisture Treated (HMT) Starch-Based Biodegradable Films. Polymers 2023, 15, 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092046
Cahyana Y, Verrell C, Kriswanda D, Aulia GA, Yusra NA, Marta H, Sukri N, Esirgapovich SJ, Abduvakhitovna SS. Properties Comparison of Oxidized and Heat Moisture Treated (HMT) Starch-Based Biodegradable Films. Polymers. 2023; 15(9):2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092046
Chicago/Turabian StyleCahyana, Yana, Christoper Verrell, Dodo Kriswanda, Ghina Almira Aulia, Namira Azkia Yusra, Herlina Marta, Nandi Sukri, Safarov Jasur Esirgapovich, and Sultanova Shakhnoza Abduvakhitovna. 2023. "Properties Comparison of Oxidized and Heat Moisture Treated (HMT) Starch-Based Biodegradable Films" Polymers 15, no. 9: 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092046
APA StyleCahyana, Y., Verrell, C., Kriswanda, D., Aulia, G. A., Yusra, N. A., Marta, H., Sukri, N., Esirgapovich, S. J., & Abduvakhitovna, S. S. (2023). Properties Comparison of Oxidized and Heat Moisture Treated (HMT) Starch-Based Biodegradable Films. Polymers, 15(9), 2046. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092046







