Ex Vivo Transdermal Delivery of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Using Polyvinyl Alcohol Microneedles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Microneedles
2.3. Patch Thickness
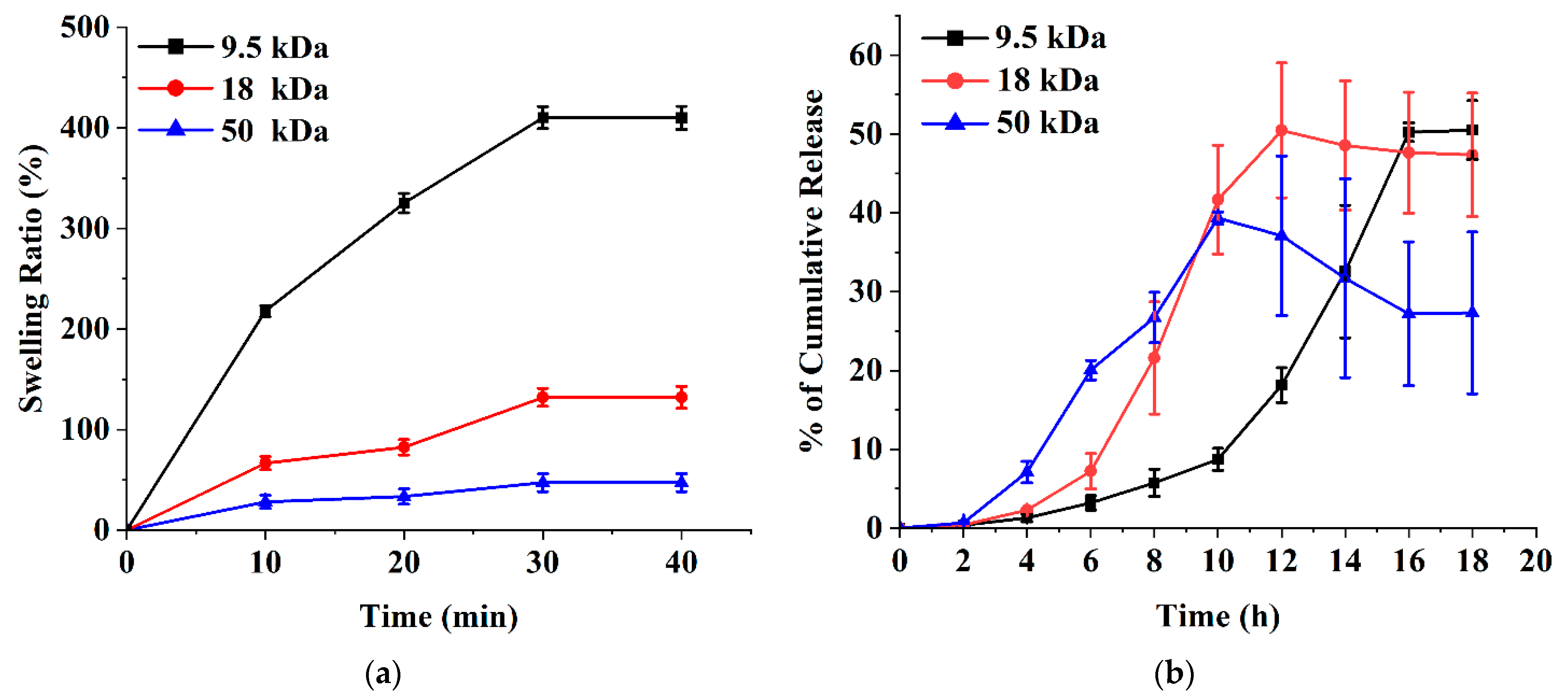
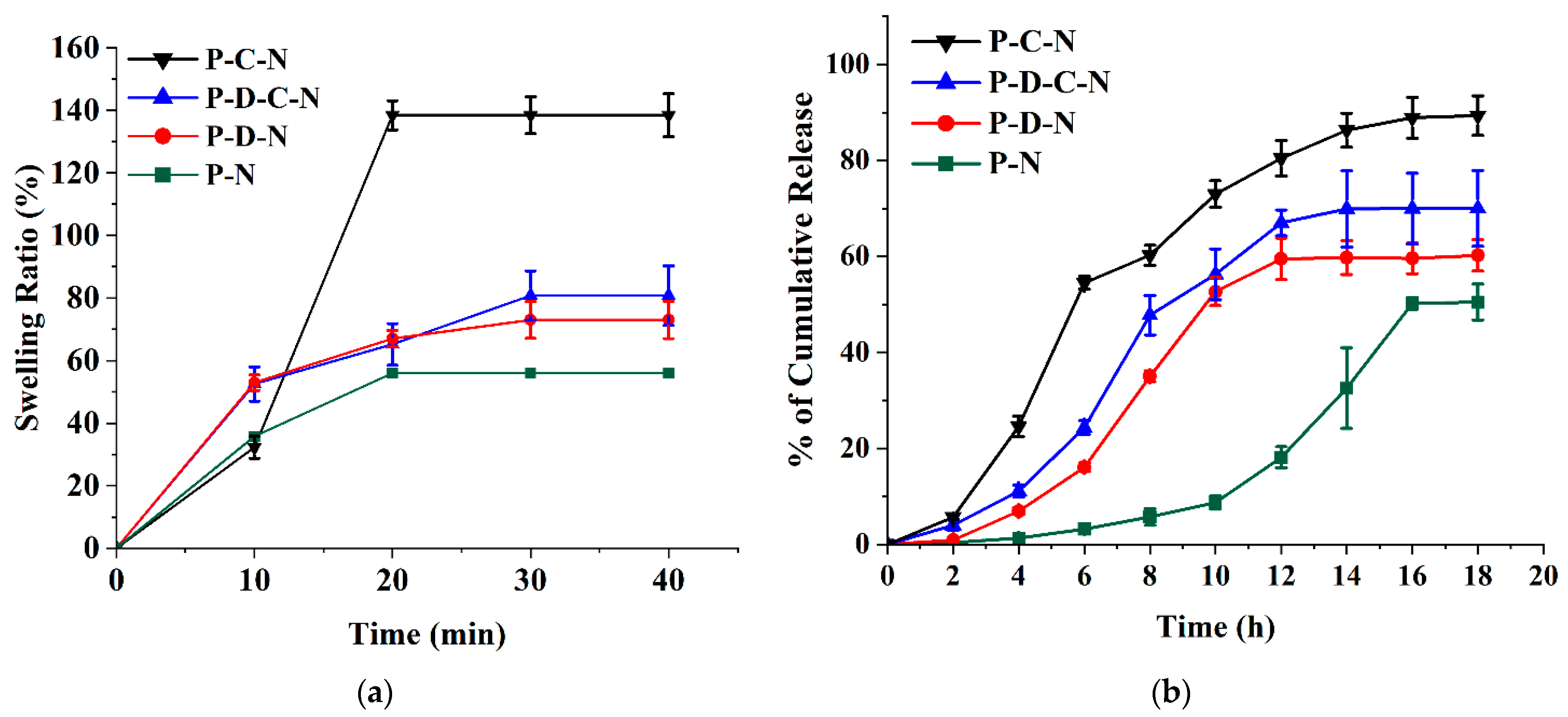
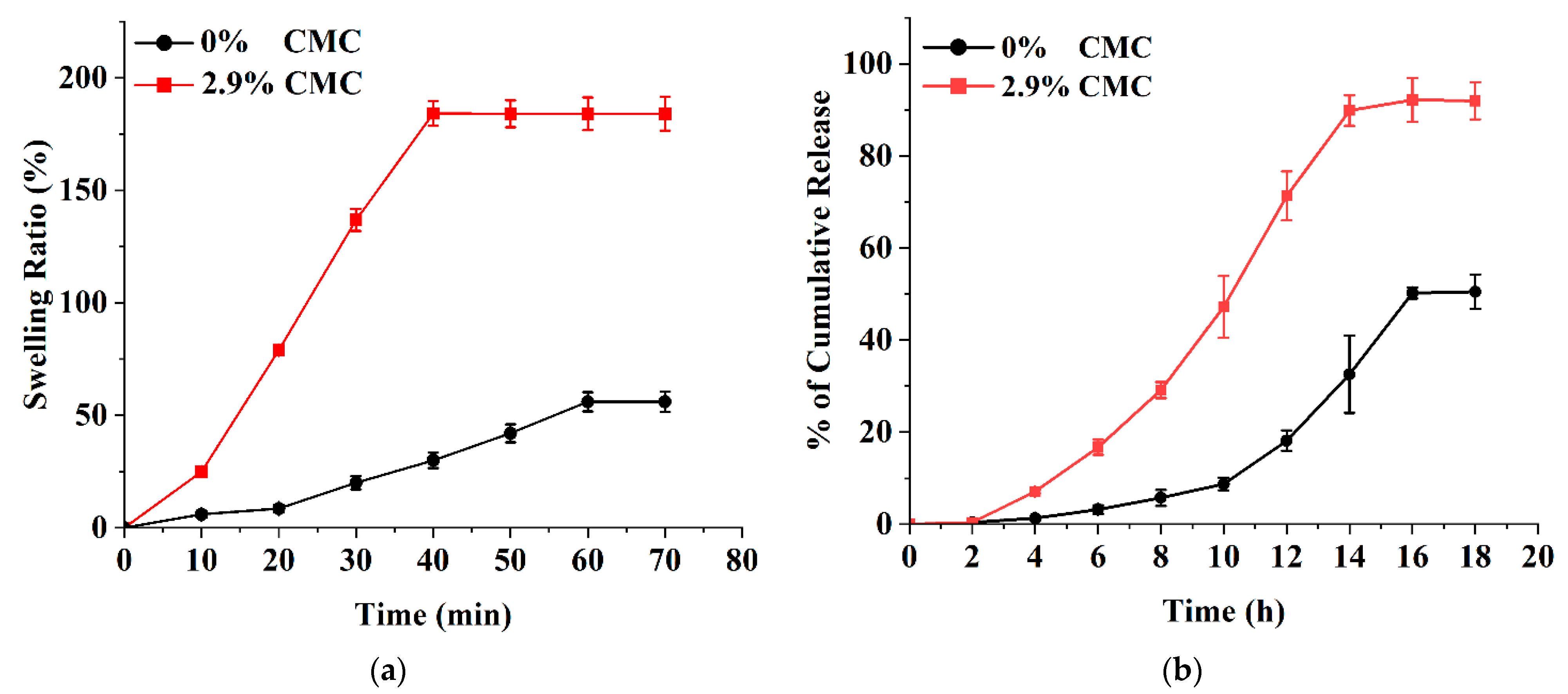
2.4. Swelling of Microneedle Patches
2.5. Determination of NMN Content in Microneedle
2.6. Ex Vivo Release Studies
3. Results and Discussion
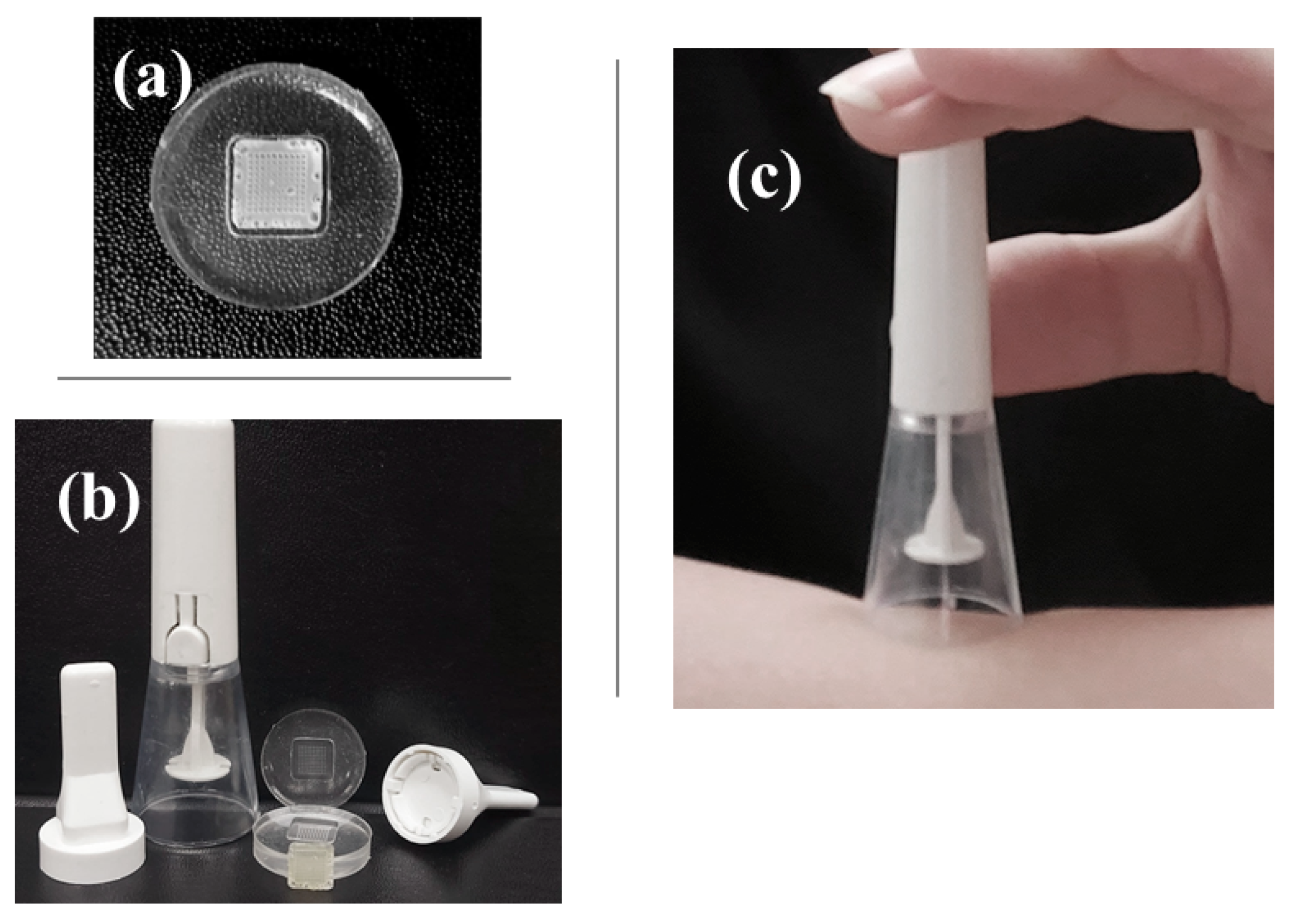
3.1. Preparation and Injection of Microneedles
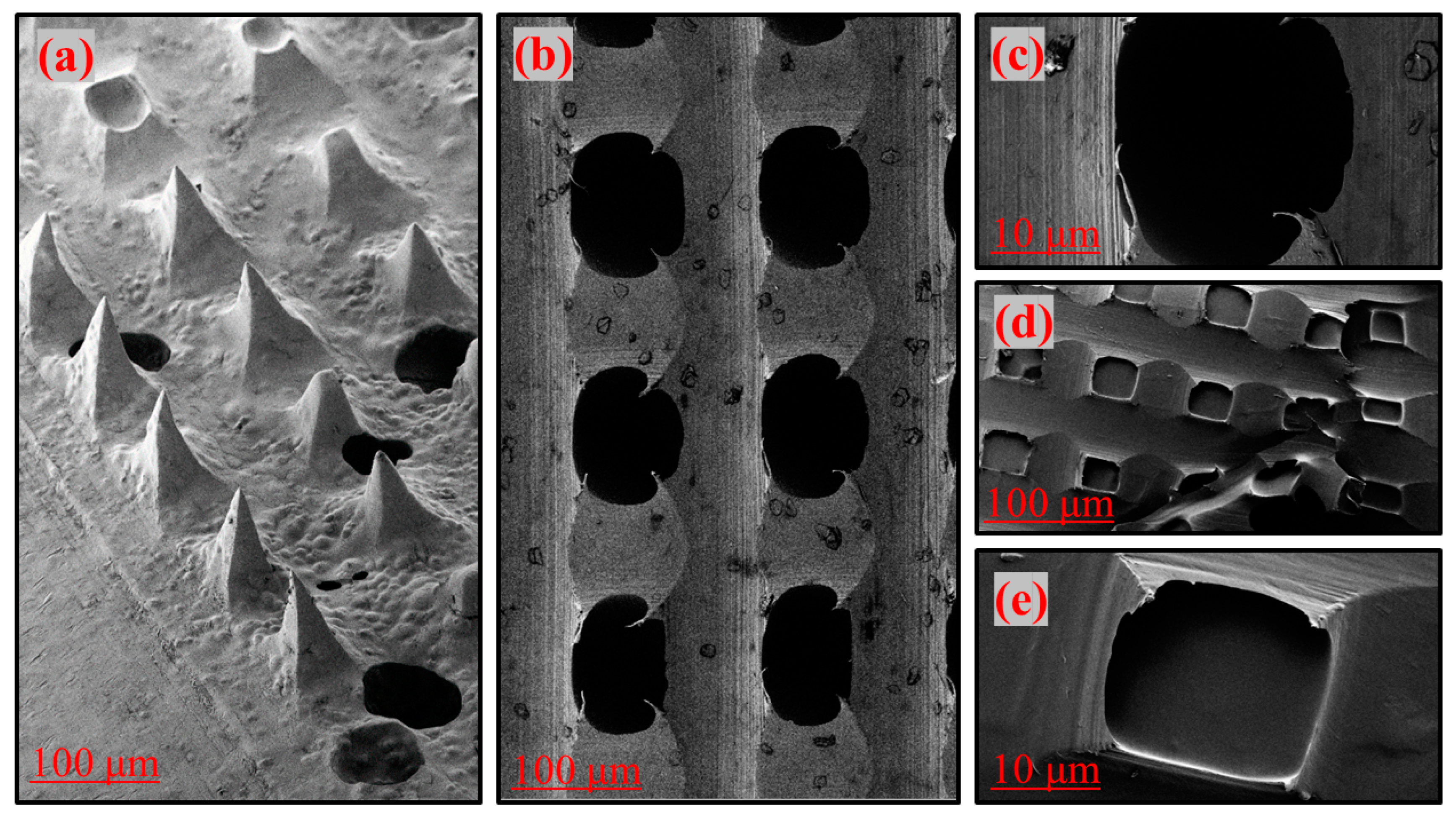
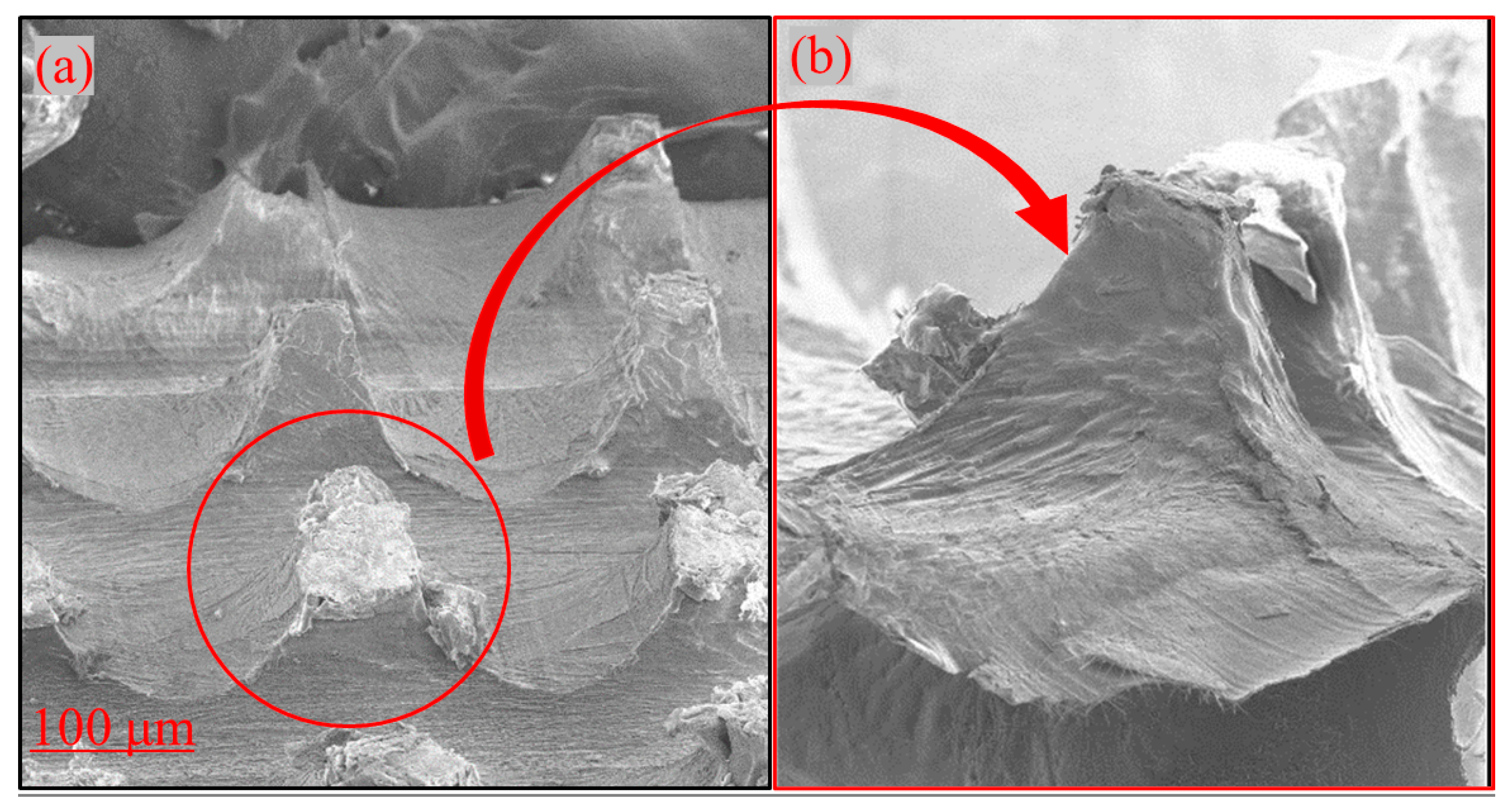
3.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy Studies
3.3. Entrapment Efficiency of NMN in Microneedle
3.4. Ex Vivo Release Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, A.; Hegarty, C.; Casimero, C.; Davis, J. Electrochemically Controlled Dissolution of Nanocarbon-Cellulose Acetate Phthalate Microneedle Arrays. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 35540–35547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xian, Y.; Singh, P.; Feng, J.; Cui, S.; Carrier, A.; Oakes, K.; Luan, T.; Zhang, X. Multifunctional Graphene-Oxide-Reinforced Dissolvable Polymeric Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, V.; Mishra, D.; Nahar, M.; Jain, V.; Jain, N.K. Enhanced Transdermal Delivery of an Anti-HIV Agent via Ethanolic Liposomes. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2010, 6, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestre, S.L.; Araújo, D.; Marques, A.C.; Pires, C.; Matos, M.; Alves, V.; Martins, R.; Freitas, F.; Reis, M.A.M.; Fortunato, E. Microneedle Arrays of Polyhydroxyalkanoate by Laser-Based Micromolding Technique. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 5856–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-Based Hydrogels for Controlled, Localized Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, D.F.S.; Vilela, C.; Pinto, R.J.B.; Bastos, V.; Oliveira, H.; Catarino, J.; Faísca, P.; Rosado, C.; Silvestre, A.J.D.; Freire, C.S.R. Bacterial Nanocellulose-Hyaluronic Acid Microneedle Patches for Skin Applications: In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.Y.; Degan, S.; Hall, R.P.; Boehm, R.D.; Jaipan, P.; Narayan, R.J. Use of Drawing Lithography-Fabricated Polyglycolic Acid Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery of Itraconazole to a Human Basal Cell Carcinoma Model Regenerated on Mice. JOM 2016, 68, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Chen, H.; Duan, B.; Lu, A.; Zhang, L. Swelling Behaviors of Superabsorbent Chitin/Carboxymethylcellulose Hydrogels. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basa, B.; Jakab, G.; Kállai-Szabó, N.; Borbás, B.; Fülöp, V.; Balogh, E.; Antal, I. Evaluation of Biodegradable PVA-Based 3D Printed Carriers during Dissolution. Materials 2021, 14, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Gupta, P.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Nandi, S.K.; Mandal, B.B. Immunomodulatory Injectable Silk Hydrogels Maintaining Functional Islets and Promoting Anti-Inflammatory M2 Macrophage Polarization. Biomaterials 2018, 187, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaaz, T.S.; Sulong, A.B.; Akhtar, M.N.; Kadhum, A.A.H.; Mohamad, A.B.; Al-Amiery, A.A.; McPhee, D.J. Properties and Applications of Polyvinyl Alcohol, Halloysite Nanotubes and Their Nanocomposites. Molecules 2015, 20, 22833–22847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poddar, S.K.; Sifat, A.E.; Haque, S.; Nahid, N.A.; Chowdhury, S.; Mehedi, I. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide: Exploration of Diverse Therapeutic Applications of a Potential Molecule. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, J.; Baur, J.A.; Imai, S.-I. NAD+ Intermediates: The Biology and Therapeutic Potential of NMN and NR. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, K.F.; Yoshida, S.; Stein, L.R.; Grozio, A.; Kubota, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Redpath, P.; Migaud, M.E.; Apte, R.S.; Uchida, K.; et al. Long-Term Administration of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Mitigates Age-Associated Physiological Decline in Mice. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Kim, B.S. Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery Using Clay-Based Composites. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2022, 19, 1099–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Su, X.; Quinn, W.J.; Hui, S.; Krukenberg, K.; Frederick, D.W.; Redpath, P.; Zhan, L.; Chellappa, K.; White, E.; et al. Quantitative Analysis of NAD Synthesis-Breakdown Fluxes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1067–1080.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.; Berg, J.; Mestayer, R.; Braidy, N.; Bennett, J.; Broom, S.; Watson, J. A Pilot Study Investigating Changes in the Human Plasma and Urine NAD+ Metabolome During a 6 Hour Intravenous Infusion of NAD+. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, P.; Jathar, S.; Kale, S.; Pal, K. Transdermal Drug Delivery System (TDDS)—A Multifaceted Approach For Drug Delivery. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 8, 1805–1835. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Quan, P.; Wan, X.C.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Fang, L. Mechanistic Insights of the Enhancement Effect of Sorbitan Monooleate on Olanzapine Transdermal Patch Both in Release and Percutaneous Absorption Processes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 107, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S. A Comprehensive Review on Recent Developments in Bentonite-Based Materials Used as Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 241, 1091–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, N.; Ishigooka, J.; Kim, W.H.; Yoon, B.H.; Lin, S.K.; Sulaiman, A.H.; Cosca, R.; Wang, L.; Suchkov, Y.; Agarkov, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Blonanserin Transdermal Patch in Patients with Schizophrenia: A 6-Week Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Study. Schizophr. Res. 2020, 215, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Hirono, M.; Fukushima, K.; Sugioka, N.; Takada, K. Two-Layered Dissolving Microneedles Formulated with Intermediate-Acting Insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganti, S.S.; Bhattaccharjee, S.A.; Murnane, K.S.; Blough, B.E.; Banga, A.K. Formulation and Evaluation of 4-Benzylpiperidine Drug-in-Adhesive Matrix Type Transdermal Patch. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavakoli, J.; Tang, Y. Honey/PVA Hybrid Wound Dressings with Controlled Release of AntibioticsStructural, Physico-Mechanical and in-Vitro Biomedical Studies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, L.K.; Donnelly, R.F.; Larrañeta, E.; González-Vázquez, P.; Thakur, R.R.S.; Vavia, P.R. Novel Bilayer Dissolving Microneedle Arrays with Concentrated PLGA Nano-Microparticles for Targeted Intradermal Delivery: Proof of Concept. J. Control. Release 2017, 265, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.-Y.; Chen, K.-S.; Run-Chu, L. Design and Evaluation of Drug-Loaded Wound Dressing Having Thermoresponsive, Adhesive, Absorptive and Easy Peeling Properties. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, V.N.; Chettiar, S.S.; Bhamore, J.R.; Kailasa, S.K.; Patel, R.M. Green Synthetic Approach for Synthesis of Fluorescent Carbon Dots for Lisinopril Drug Delivery System and Their Confirmations in the Cells. J. Fluoresc. 2017, 27, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Luo, H.; Lu, W.; Luan, H.; Wu, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Pi, J.; Lim, C.Y.; Wang, H. Rapidly Dissolvable Microneedle Patches for Transdermal Delivery of Exenatide. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 3348–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, C.; Hughes, H.; O’Reilly, N.J.; McLoughlin, P. Formulation and Characterisation of Dissolving Microneedles for the Transdermal Delivery of Therapeutic Peptides. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, M.G.; Vucen, S.; Vrdoljak, A.; Kelly, A.; O’Mahony, C.; Crean, A.M.; Moore, A. Production of Dissolvable Microneedles Using an Atomised Spray Process: Effect of Microneedle Composition on Skin Penetration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 200–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Ye, R.; Gao, J.; Ren, L.; Liu, B.; Liang, L.; Jiang, L. Fabrication of Gradient Porous Microneedle Array by Modified Hot Embossing for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 96, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Zheng, L.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, T.; Wang, Q. Dissolving Microneedle Patches-Mediated Percutaneous Delivery of Tetramethylpyrazine for Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 184, 106409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalid, A.; Shoaib Sarwar, H.; Sarfraz, M.; Farhan Sohail, M.; Jalil, A.; Bin Jardan, Y.A.; Arshad, R.; Tahir, I.; Ahmad, Z. Formulation and Characterization of Thiolated Chitosan/Polyvinyl Acetate Based Microneedle Patch for Transdermal Delivery of Dydrogesterone. Saudi Pharm. J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, C.M.; Peppas, N.A. Structure and Morphology of Freeze/Thawed PVA Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennink, W.E.; van Nostrum, C.F. Novel Crosslinking Methods to Design Hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, 13–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourjavadi, A.; Ghasemzadeh, H.; Soleyman, R. Synthesis, Characterization, and Swelling Behavior of Alginate-g-Poly (Sodium Acrylate)/Kaolin Superabsorbent Hydrogel Composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 105, 2631–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, L.F.; Correia, I.J.; Silva, A.S.; Mano, J.F. Biomaterials for Drug Delivery Patches. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 118, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Nawaz, A.; Akhlaq, M.; Shah, K.U.; Latif, M.S.; Doolaanea, A.A.; Alfatama, M. Transdermal Delivery of Gatifloxacin Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Based Patches: Preparation and Characterization. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 66, 102783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevc, G. Lipid Vesicles and Other Colloids as Drug Carriers on the Skin. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 675–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhu, D.D.; Chen, B.Z.; Ashfaq, M.; Guo, X.D. Insulin Delivery Systems Combined with Microneedle Technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabil, M.F.; Nasr, M.; Ibrahim, I.T.; Hassan, Y.A.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. New Repurposed Rolapitant in Nanovesicular Systems for Lung Cancer Treatment: Development, in-Vitro Assessment and in-Vivo Biodistribution Study. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 171, 106119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahsan, A.; Farooq, M.A. Therapeutic Potential of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Loaded PVA Hydrogel Patches for Wound Healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 101308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, F.; Muhamad, I.I.; Pa’e, N.; Hashim, Z. Strategies in Improving Properties of Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Smart Applications. In Cellulose-Based Superabsorbent Hydrogels; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 887–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, P. Hydrogels for Soft Machines. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, M.V.S.; Kaushal, A.M.; Garg, A.; Garg, S. Factors Affecting Mechanism and Kinetics of Drug Release from Matrix-Based Oral Controlled Drug Delivery Systems. Am. J. Drug Deliv. 2004, 2, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriamornsak, P.; Nunthanid, J.; Cheewatanakornkool, K.; Manchun, S. Effect of Drug Loading Method on Drug Content and Drug Release from Calcium Pectinate Gel Beads. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1315–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinescu, G.C.; Popescu, R.G.; Dinischiotu, A. Size Exclusion Chromatography Method for Purification of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) from Bacterial Cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesch, F.; Fabian, E.; Oesch-Bartlomowicz, B.; Werner, C.; Landsiedel, R. Drug-Metabolizing Enzymes in the Skin of Man, Rat, and Pig. Drug. Metab. Rev. 2007, 39, 659–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, A. Synthesis and Swelling Properties of PH-Sensitive Semi-IPN Superabsorbent Hydrogels Based on Sodium Alginate-g-Poly(Sodium Acrylate) and Polyvinylpyrrolidone. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 80, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Rajabnezhad, S.; Kohli, K. Hydrogels as Potential Drug Delivery Systems. Sci. Res. Essays 2009, 3, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, J.K.; Lee, D.I.; Park, J.M. Biopolymer-Based Microgels/Nanogels for Drug Delivery Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 1261–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Guo, X.; Temenoff, J.S.; Tabata, Y.; Caplan, A.I.; Kasper, F.K.; Mikos, A.G. Effect of Swelling Ratio of Injectable Hydrogel Composites on Chondrogenic Differentiation of Encapsulated Rabbit Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells In Vitro. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.O.; Ku, S.; Cho, H.; Han, D.H.; Huh, P. Fabrication of Poly(Ethylene Oxide) Hydrogels for Wound Dressing Application Using E-Beam. Macromol. Res. 2014, 22, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.Z.; Ashfaq, M.; Zhang, X.P.; Zhang, J.N.; Guo, X.D. In Vitro and in Vivo Assessment of Polymer Microneedles for Controlled Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Drug Target. 2018, 26, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Jeong, H.; Lee, D.Y. Synthesis and Biocompatibility of PVA/NaCMC Hydrogels Crosslinked by Cyclic Freezing/Thawing and Subsequent Gamma-Ray Irradiation. J. Biomed. Eng. Res. 2018, 39, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trieu, H.; Qutubuddin, S. Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Hydrogels: 2. Effects of Processing Parameters on Structure and Properties. Polymer 1995, 36, 2531–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, D.; Levina, M.; Nokhodchi, A.; Douroumis, D.; Farrell, T.; Rajabi-Siahboomi, A. The Influence of Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose on Drug Release from Polyethylene Oxide Extended Release Matrices. AAPS PharmSciTech 2011, 12, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzak, D.; Galiński, M. DMSO as an Auxiliary Solvent in the Fabrication of Homogeneous Chitin-Based Films Obtaining from an Ionic Liquid Process. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 158, 110681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, N.F.C.; Zainuddin, N.; Ahmad, M. Preparation and Swelling Study of CMC Hydrogel as Potential Superabsorbent. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 27, 489–498. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.W.; Park, J.-H.; Prausnitz, M.R. Dissolving Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2113–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabbagh, F.; Kim, B.-S. Ex Vivo Transdermal Delivery of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Using Polyvinyl Alcohol Microneedles. Polymers 2023, 15, 2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092031
Sabbagh F, Kim B-S. Ex Vivo Transdermal Delivery of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Using Polyvinyl Alcohol Microneedles. Polymers. 2023; 15(9):2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092031
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabbagh, Farzaneh, and Beom-Soo Kim. 2023. "Ex Vivo Transdermal Delivery of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Using Polyvinyl Alcohol Microneedles" Polymers 15, no. 9: 2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092031
APA StyleSabbagh, F., & Kim, B.-S. (2023). Ex Vivo Transdermal Delivery of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Using Polyvinyl Alcohol Microneedles. Polymers, 15(9), 2031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15092031






