Soy Protein/Polyvinyl-Alcohol (PVA)-Based Packaging Films Reinforced by Nano-TiO2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Film Composition
2.3. Film Preparation
2.4. Physical Properties Evaluation
2.5. Water Absorption
2.6. Comprehensive Film Property Evaluation
2.7. Water Vapor Transmission and O2 Permeation
2.8. Thermal Properties
2.9. Visualization of Film Structure
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Particle Size of Nano-TiO2 on the Film Properties
3.2. Effect of Nano-TiO2 Concentration
3.3. Effect of PVP Concentration
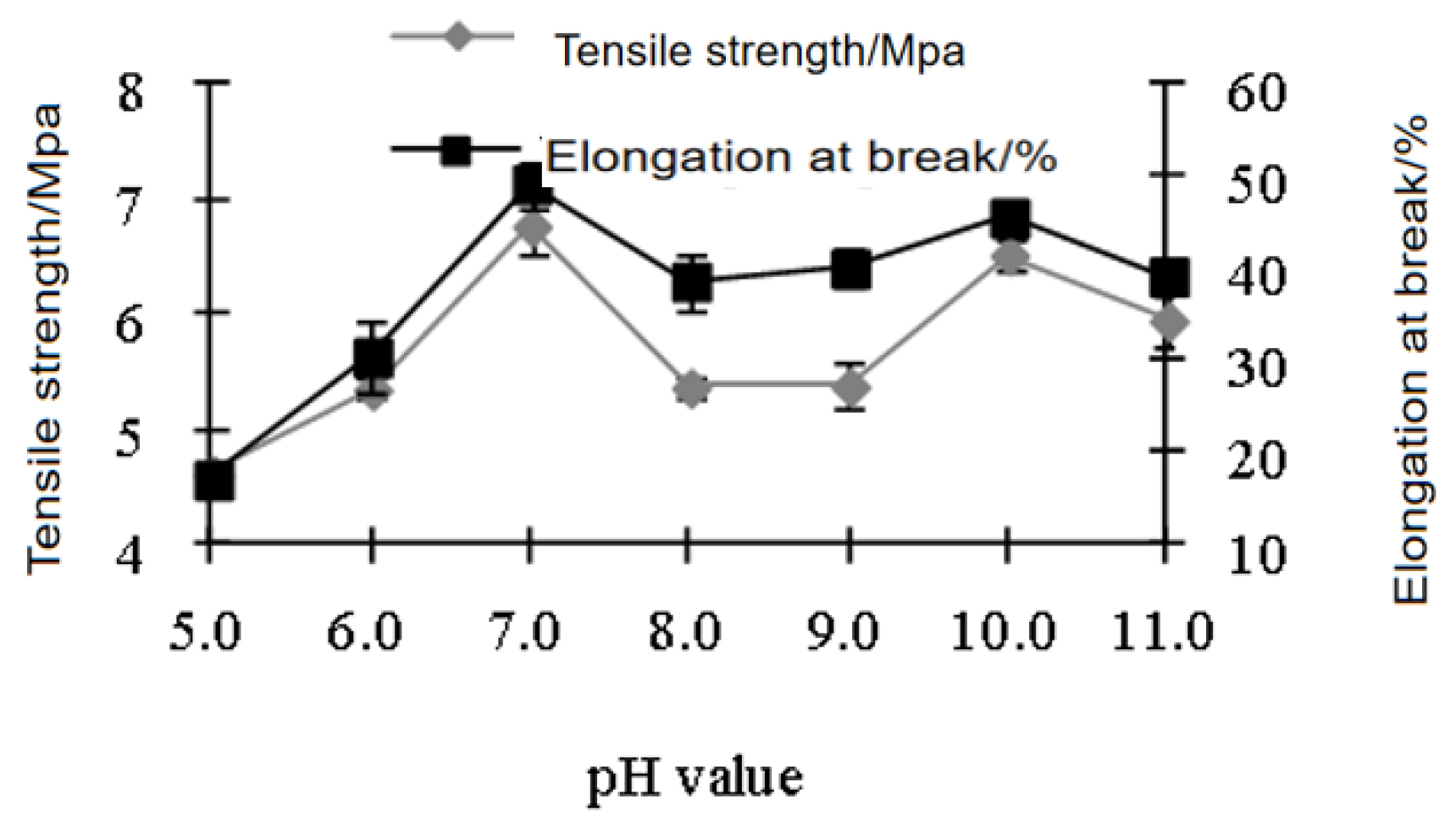
3.4. Effects of pH of Film Casting Solution
3.5. Orthogonal Array Design Experiment
- The optimum condition was A2B3C1, which contains 2.5 wt% nano-TiO2 (30 nm) and 1.5 wt% PVP in the film, and the processing pH is 6.0.
- In the optimized film A2B3C1, the most important factor that affects the film properties should be PVP concentration, followed by nano-TiO2 (30 nm) concentration and pH.
3.6. Validation of the Optimum Condition
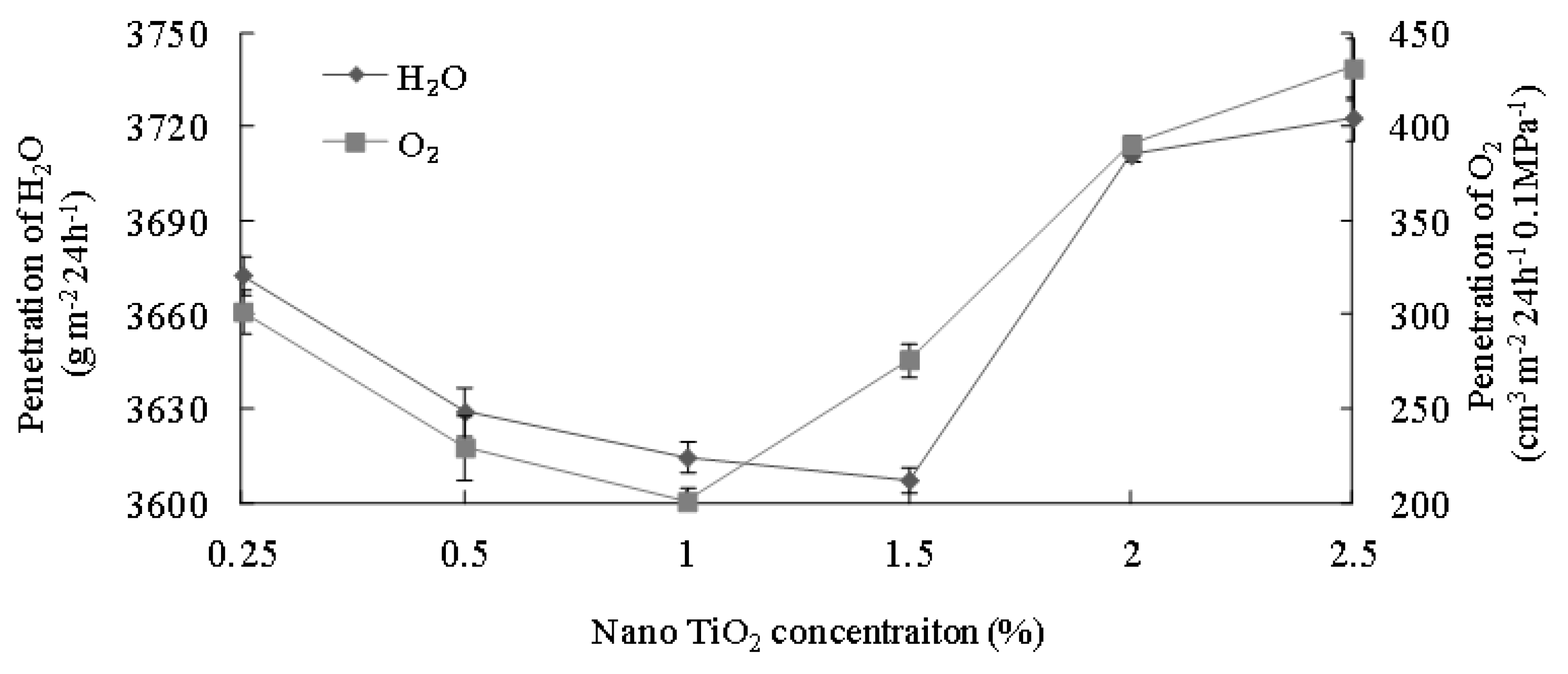
3.7. Effects of Nano-TiO2 on Water Vapor Transmission Rate and O2 Permeation
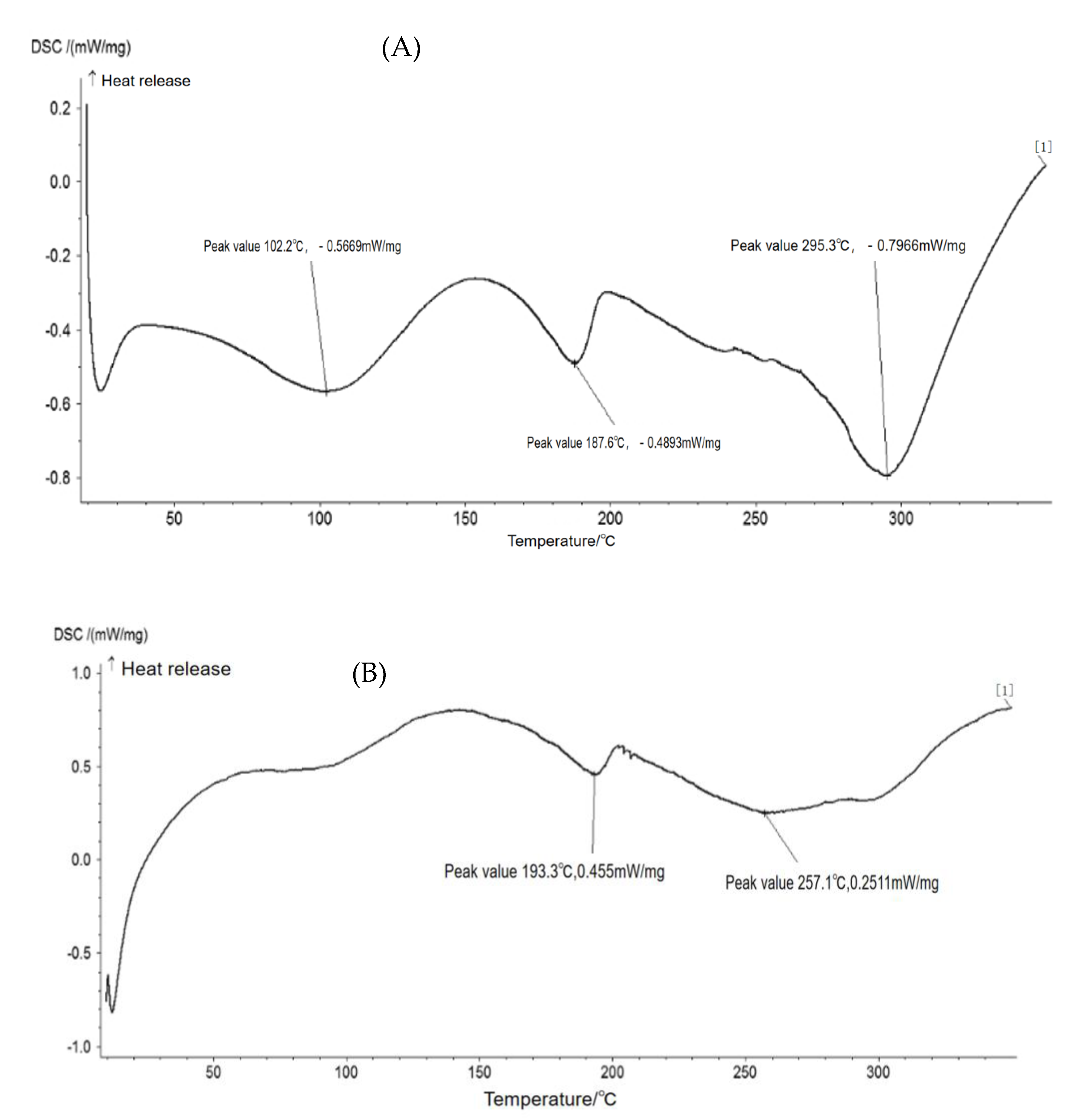
3.8. Effect of Nano-TiO2 on Thermal Properties of Soy Protein/PVA Film
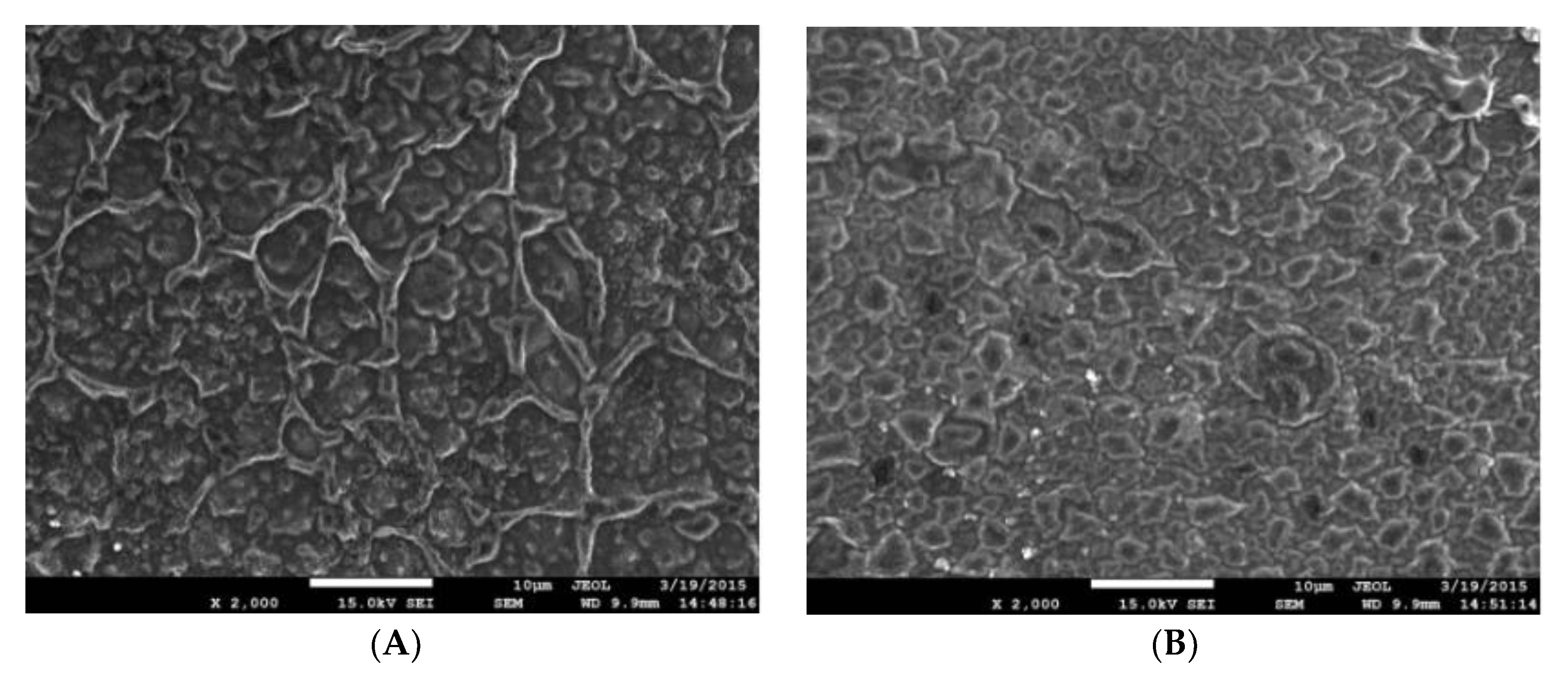
3.9. Effect of Nano-TiO2 on Soy Protein/PVA Film Morphology
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guan, Q.F.; Yang, H.B.; Han, Z.M.; Ling, Z.C.; Yu, S.H. An all-natural bioinspired structural material for plastic replacement. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-G.; Shen, T.-L.; Yang, Y.-C.; Ma, X.-X.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.-C.-C.; Wang, P.-F. Novel environment-friendly superhydrophobic bio-based polymer derived from liquefied corncob for controlled-released fertilizer. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 151, 106018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, L.A. Future opportunities for bio-based adhesives–advantages beyond renewability. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1866–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L. Current Progress in the Utilization of Soy-Based Emulsifiers in Food Applications—A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-S.; Fang, C.-Q.; Zhang, W.; Lei, W.-Q.; Wang, D.; Zhou, X. Novel grasshopper protein/soy protein isolate/pullulan ternary blend with hesperidin derivative for antimicrobial edible film. Arab. J. Chem. 2023, 16, 104563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Izquierdo, V.M.; Krochta, J.M. Thermoplastic processing of proteins for film formation—A review. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, R30–R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S.-Z.; Huang, C.-H.; Jackson, M.G. Role of ferulic acid in preparing edible films from soy protein isolate. J. Food Eng. 2005, 70, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sandeep, K.P.; Alavi, S.; Truong, V.D.; Gorga, R.E. Preparation and characterization of bio-nanocomposite films based on soy protein isolate and montmorillonite using melt extrusion. J. Food Eng. 2010, 100, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.-H.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, C.-B.; Yang, X.-Q. Effect of transglutaminase treatment on the properties of cast films of soy protein isolates. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 120, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Anjum, K.N.; Rani, S.; Sharma, K.; Tiwary, K.P.; Kumar, K.D. Material properties of ZnS nanoparticles incorporated soy protein isolate biopolymeric film. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2019, 48, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Fan, L.; Huang, J.; Chen, Y. Role of Star-Like Hydroxylpropyl Lignin in Soy-Protein Plastics. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbin, E.; Riviere, G.N.; Foulon, L.; Frapart, Y.M.; Cottyn, B.; Pernes, M.; Marcuello, C.; Godon, B.; Gainvors-Claisse, A.; Crônier, D.; et al. Tuning the functional properties of lignocellulosic films by controlling the molecular and supramolecular structure of lignin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 181, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doustkhah, E.; Ide, Y. Microporous layered silicates: Old but new microporous materials. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 9957–9968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, T.S.; Mali, S.S.; Korade, S.D.; Shaikh, J.S.; Karanjkar, M.M.; Hong, C.K.; Kim, J.H.; Patil, P.S. Mesoporous architecture of TiO2 microspheres via controlled template assisted route and their photoelectrochemical properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2016, 28, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saari, J.; Ali-Löytty, H.; Lahtonen, K.; Hannula, M.; Palmolahti, L.; Tukiainen, A.; Valden, M. Low-Temperature Route to Direct Amorphous to Rutile Crystallization of TiO2 Thin Films Grown by Atomic Layer Deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 15357–15366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Lim, J.; Baek, M.; Choi, W.; Kim, W.; Yong, K. Investigating the Unrevealed Photocatalytic Activity and Stability of Nanostructured Brookite TiO2 Film as an Environmental Photocatalyst. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16252–16260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirai, K.; Fazio, G.; Sugimoto, T.; Sell, D.; Ferraro, L.; Watanabe, K.; Haruta, M.; Ohtani, B.; Kurata, H.; Valentin, C.D.; et al. Water-Assisted Hole Trapping at the Highly Curved Surface of Nano-TiO2 Photocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wang, H.-Y.; Sui, S.-Y.; Sun, X.-X.; Ma, Z.-S. The effects of ultrasonic/microwave assisted treatment on the properties of soy protein isolate/titanium dioxide films. LWT–Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, M.R.; Aouada, F.A.; Avena-Bustillos, R.J.; McHugh, T.H.; Krochta, J.M.; Mattoso, L.H.C. Improved barrier and mechanical properties of novel hydroxypropyl methylcellulose edible films with chitosan/tripolyphosphate nanoparticles. J. Food Eng. 2009, 92, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, S.; Caratto, V.; Locardi, F.; Alberti, S.; Sturini, M.; Speltini, A.; Maraschi, F.; Canepa, F.; Ferretti, M. Enhancement of TiO2 NPs Activity by Fe3O4 Nano-Seeds for Removal of Organic Pollutants in Water. Materials 2016, 9, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rehman, K.; Zaman, U.; Tahir, K.; Khan, D.; Khattak, N.S.; Khan, S.U.; Khan, W.U.; Nazir, S.; Bibi, R.; Gul, R. A Coronopus didymus based eco-benign synthesis of Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) with enhanced photocatalytic and biomedical applications. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 137, 109179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-J.; Chen, J.; He, M.; Yao, J.-F. Cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membranes reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals: Preparation and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.; Zhuravlev, E.; Wurm, A.; Schick, C.; Cebe, P. Fundamental thermal properties of polyvinyl alcohol by fast scanning calorimetry. Polymer 2018, 137, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, N.; Jiang, B.; Wang, X.-J.; Shang, Z.-F.; Jiang, D.-W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, C.-Y.; Wu, Z.-J.; Yan, H.; Liu, C.-T.; et al. Overview of Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Electro-Skin, Actuator, Supercapacitor and Fuel Cell. Chem. Rec. 2020, 20, 773–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molki, B.; Heidarian, P.; Mohammadi Aframehr, W.; Nasri-Nasrabadi, B.; Bahrami, B.; Ahmadi, M.; Komeily-Nia, Z.; Bagheri, R. Properties investigation of polyvinyl alcohol barrier films reinforced by calcium carbonate nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 055311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jin, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Dong, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Lv, X.-P.; He, M. Novel high strength PVA/soy protein isolate composite hydrogels and their properties. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 984652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezati, P.; Riahi, Z.; Rhim, J.-W. CMC-based functional film incorporated with copper-doped TiO2 to prevent banana browning. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 122, 107104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, R.; Zhang, W.; Qi, C.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Development of Eco-friendly Soy Protein Isolate Films with High Mechanical Properties through HNTs, PVA, and PTGE Synergism Effect. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, H.C.; Abba, M.U.; Abdulsalam, M.; Azis, R.S.; Idris, A.L.; Hamzah, M.H. Utilization of Nano-TiO2 as an Influential Additive for Complementing Separation Performance of a Hybrid PVDF-PVP Hollow Fiber: Boron Removal from Leachate. Polymers 2020, 12, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wu, Y.; Wu, D.; Gao, C.; Meng, L.; Feng, X.; Cheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; et al. Effect of nano-TiO2 particle size on the bonding performance and film-forming properties of starch-based wood adhesives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, J. A new approach for morphology control of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) and soy protein blends. Polymer 2009, 50, 3770–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangal, S.; Meiser, F.; Lakio, S.; Morton, D.; Larson, L. The role of physico-chemical and bulk characteristics of co-spray dried L-leucine and polyvinylpyrrolidone on glidant and binder properties in interactive mixtures. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hada, N.M.; Al-Ghaili, A.M.; Kasim, H.; Saleh, M.A.; Flaifel, M.H.; Kamari, H.M.; Baqiah, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. The Effect of PVP Concentration on Particle Size, Morphological and Optical Properties of Cassiterite Nanoparticles. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 93444–93454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Tang, D.-L.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z. Biodegradable soy protein isolate-based materials: A review. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3369–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Yang, L.; Song, H.; Zhang, G.; He, Y.; Liu, H. Application of soy protein isolate fiber and soy soluble polysaccharide non-covalent complex: A potential way for pH-triggered release. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Kelly, A.L.; Miao, S. The impact of pH on mechanical properties, storage stability and digestion of alginate-based and soy protein isolate-stabilized emulsion gel beads with encapsulated lycopene. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, M.M.G.; De Souza Silva, K.; Mauro, M.A. Evaluation of Interactions Between Carboxymethylcellulose and Soy Protein Isolate and their Effects on the Preparation and Characterization of Composite Edible Films. Food Biophys. 2021, 16, 214–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, F.J.; Tsou, M.J.; Kao, H.C.; Chiang, W.D. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis conditions for producing soy protein hydrolysate with maximum lipolysis-stimulating activity. J. Food Drug Anal. 2020, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yu, B.; Tao, H.; Liu, P.; Zhao, H.; Tan, C.; Cui, B. Effects of soy protein isolate on mechanical and hydrophobic properties of oxidized corn starch film. LWT 2021, 147, 111529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.-P.; Chen, C.-W.; Xie, J. Development of antimicrobial active films based on poly(vinyl alcohol) containing nano-TiO2 and its application in Macrobrachium rosenbergii packaging. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, e13702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Ma, L.; Cai, H.; Cheng, Q. Molecular arrangement mechanisms within phosphate films on Ti6Al4V regulated by intermolecular forces based on sum frequency generation vibrational spectroscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 521, 146364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Cao, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Soy Protein Isolate Films Incorporating Modified Nano-TiO2. Int. J. Food Eng. 2019, 15, 20180278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Tronstad, Z.C.; Yang, Y.; Green, M.D. Characterization of PVC-soy protein nonwoven mats prepared by electrospinning. AIChE J. 2018, 64, 2737–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, S.K.; Schick, C.; Málek, J. A fast scanning calorimetry study of nucleation in a Se90Te10 glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2019, 249, 114425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Dai, Y.; Hou, H.; Dong, H. Effects of various nanomaterials on the properties of starch/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite films formed by blow extrusion process. Iran. Polym. J. 2015, 24, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.; Sun, H.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, B.; Shi, J.; Jiang, R.; Dong, Y. Effect of bovine bone collagen and nano-TiO2 on the properties of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 158, 937–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramian, A. Poly(ethylene terephthalate)-based nanocomposite films as greenhouse covering material: Environmental sustainability, mechanical durability, and thermal stability. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 138, 49991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Particle Size | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Water Absorption (%) | Comprehensive Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 nm | 4.08 ± 0.45 b | 38.64 ± 2.98 b | 59.22 ± 1.98 a | 15.52 ± 2.31 c |
| 30 nm | 5.69 ± 0.53 a | 53.40 ± 2.80 a | 45.00 ± 2.01 c | 90.00 ± 0.87 a |
| 50 nm | 4.63 ± 0.54 b | 51.20 ± 3.62 a | 54.71 ± 4.32 ab | 50.10 ± 1.03 b |
| Control | 3.85 ± 0.18 b | 38.38 ± 2.09 b | 52.77 ± 2.36 b | 12.40 ± 2.43 c |
| Experimental Number | Factor | Comprehensive Evaluation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano-TiO2 | PVP | pH | Error | ||
| A [%] | B [%] | C | D | ||
| 1 | 1 (2.0%) | 1 (0.5%) | 1 (6) | 1 | 38.15 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 (1.0%) | 2 (7) | 2 | 41.01 |
| 3 | 1 | 3 (1.5%) | 3 (8) | 3 | 43.99 |
| 4 | 2 (2.5%) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 41.36 |
| 5 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 45.41 |
| 6 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 88.60 |
| 7 | 3 (3.0%) | 1 | 3 | 2 | 13.14 |
| 8 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 37.66 |
| 9 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 59.34 |
| T1 | 123.15 | 92.65 | 164.41 | 142.90 | |
| T2 | 175.38 | 124.08 | 141.72 | 142.76 | |
| T3 | 110.15 | 191.94 | 102.54 | 123.02 | |
| R1 | 41.05 | 30.88 | 54.80 | 47.63 | |
| R2 | 58.46 | 41.36 | 47.24 | 47.59 | |
| R3 | 36.72 | 63.98 | 34.18 | 41.01 | |
| M | 21.74 | 33.10 | 20.62 | 6.58 | |
| Combination | Tensile Strength(MPa) | Elongation (%) | Water Absorption (%) | Comprehensive Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2B3C1 | 6.77 ± 0.10 | 58.91 ± 3.12 | 44.89 ± 2.85 | 88.79 ± 1.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, X.; Chen, Z.; Lu, X.; Mu, J.; Ma, Q.; Li, X. Soy Protein/Polyvinyl-Alcohol (PVA)-Based Packaging Films Reinforced by Nano-TiO2. Polymers 2023, 15, 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071764
Tian X, Chen Z, Lu X, Mu J, Ma Q, Li X. Soy Protein/Polyvinyl-Alcohol (PVA)-Based Packaging Films Reinforced by Nano-TiO2. Polymers. 2023; 15(7):1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071764
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Xueying, Zhizhou Chen, Xiaomeng Lu, Jianlou Mu, Qianyun Ma, and Xiaoyuan Li. 2023. "Soy Protein/Polyvinyl-Alcohol (PVA)-Based Packaging Films Reinforced by Nano-TiO2" Polymers 15, no. 7: 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071764
APA StyleTian, X., Chen, Z., Lu, X., Mu, J., Ma, Q., & Li, X. (2023). Soy Protein/Polyvinyl-Alcohol (PVA)-Based Packaging Films Reinforced by Nano-TiO2. Polymers, 15(7), 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071764






