Study on the Discoloration Mechanism of Eucalyptus Wood during Thermal Treatment in Different Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wood Samples
2.2. Thermal Treatment
2.3. Color Measurement
2.4. UV–Vis Spectrum
2.5. FTIR Analysis
2.6. NMR Spectrum
2.7. XPS Spectrum
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Color Change and UV–Vis Analysis
3.2. FTIR Analysis
3.3. XPS Analysis
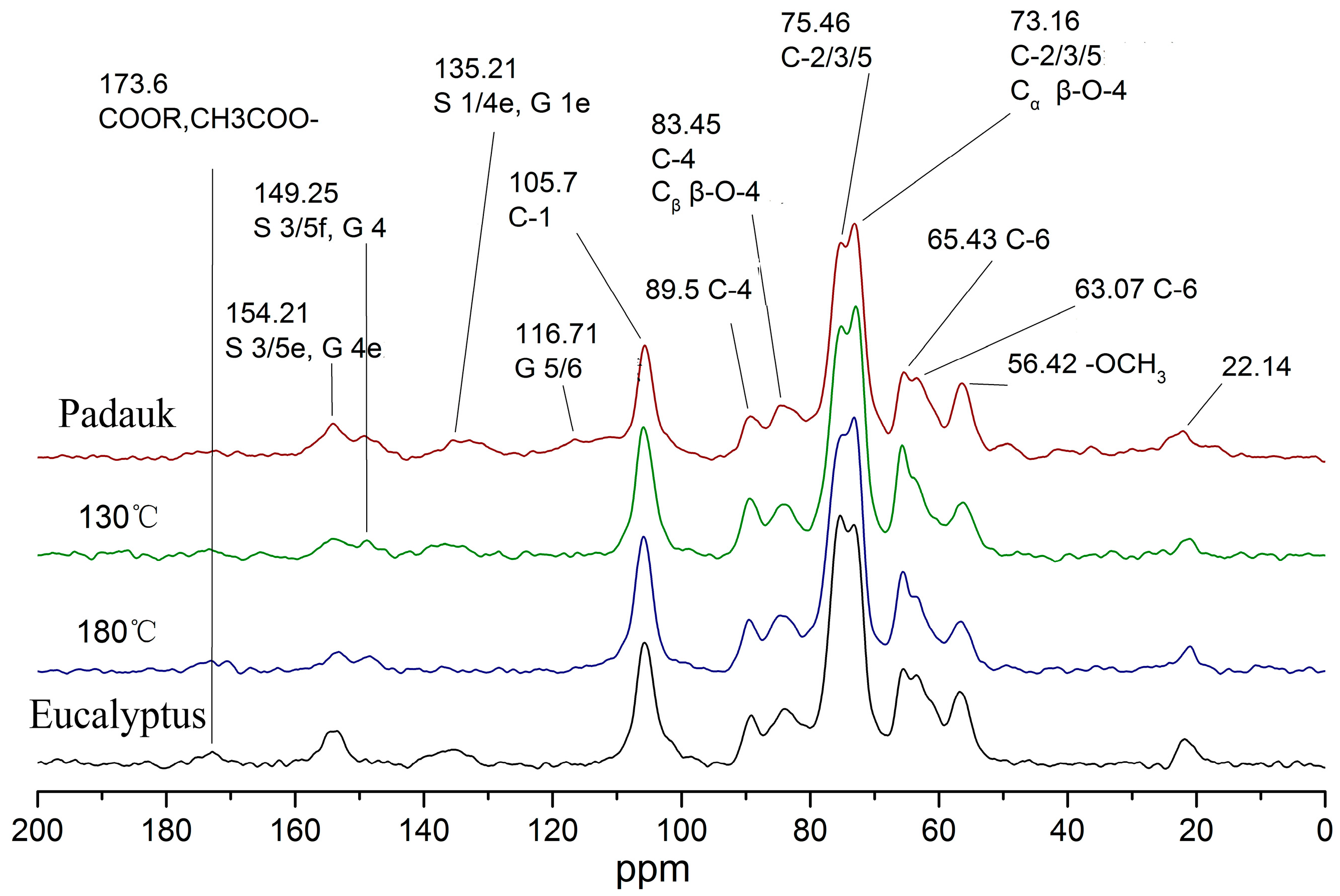
3.4. CPMAS 13C-NMR Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Y. Newly advances in wood science and technology. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 2021, 41, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Gan, W.-T.; Wang, L.-J. Research Progress on Wood Biomimetic Intelligent Materials. Chin. J. Wood Sci. Technol. 2021, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H. Wood Chemical Modification: The State of the Art of Technologies and Commercialization. Sci. Silvae Sin. 2012, 48, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- Laine, K.; Segerholm, K.; Wålinder, M.; Rautkari, L.; Hughes, M. Wood densification and thermal modification: Hardness, set-recovery and micromorphology. Wood Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 883–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Microbial dyeing for inoculation and pigment used in wood processing: Opportunities and challenges. Dye. Pigment. 2021, 186, 109021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.-J. Development of Bamboo-Fiber based Composites. China Wood Ind. 2011, 25, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Kamperidou, V.; Barboutis, I.; Vasileiou, V. Effect of thermal treatment on colour and hygroscopic properties of poplar wood. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Scientific Conference: Wood is Good—With Knowledge and Technology to a Competitive Forestry and Wood Technology Sector, Zagreb, Croatia, 12 October 2012; pp. 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Mechanism of the Formation of Chromophore System of Heat-Induced Color Change of Wood. Ph.D. Dissertation, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gonultas, O.; Candan, Z. Chemical characterization and ftir spectroscopy of thermally compressed eucalyptus wood panels. Maderas. Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2018, 20, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogu, D.; Tuncer, F.D.; Bakir, D.; Candan, Z. Characterizing Microscopic Changes of Paulownia Wood under Thermal Compression. Bioresources 2017, 12, 5279–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, B. Color response of Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris), Norway spruce (Picea abies) and birch (Betula pubescens) subjected to heat treatment in capillary phase. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2002, 60, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneque, L.N.; de Lima, I.L.; Florsheim, S.M.B.; Sakita, M.N. Temperature of thermal modification in some properties and characteristics of wood eucalyptus. Sci. Agrar. Parana. 2019, 18, 15–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tolvaj, L.; Nemeth, R.; Varga, D.; Molnar, S. Colour Homogenisation of Beech Wood by Steam Treatment. Drewno 2009, 52, 5–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi, S.; Iijima, Y.; Doi, S. Spectrochemical characterization by FT-Raman spectroscopy of wood heat-treated at low temperatures: Japanese larch and beech. J. Wood Sci. 2005, 51, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazaki, Y.; Bauch, J.; Endeward, R. Extractive components responsible for the discoloration of Ilombl wood. Holz Als Roh- Und Werkst. 1985, 43, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windeisen, E.; Strobel, C.; Wegener, G. Chemical changes during the production of thermo-treated beech wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratsuka, Y.; Chakravarty, P.; Miao, S.; Ayer, W.A. Potential for biological protection against blue stain in Populus tremuloides with a hyphomycetous fungus, Stachybotrys cylindrospora. Can. J. For. Res. 1994, 24, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windeisen, E.; Wegener, G. Behaviour of lignin during thermal treatments of wood. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2008, 27, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-Y.; Oh, S.; Hwang, H.; Kim, U.-J.; Choi, J.W. Structural features and thermal degradation properties of various lignin macromolecules obtained from poplar wood (Populus albaglandulosa). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2013, 98, 1671–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikberg, H.; Maunu, S.L. Characterisation of thermally modified hard- and softwoods by 13C CPMAS NMR. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 58, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, B.; Marques, A.V.; Domingos, I.; Pereira, H. Chemical changes of heat treated pine and eucalypt wood monitored by ftir. Maderas-Cienc. Y Tecnol. 2013, 15, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuong, V.M.; Li, J. Changes caused by heat treatment in chemical composition and some physical properties of acacia hybrid sapwood. Holzforschung 2011, 65, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yongming, F.; Jianmin, G.; Houkun, L. Coloring characteristics of in situ lignin during heat treatment. Wood Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Tshabalala, M.A.; Gao, J.; Stark, N.M.; Fan, Y. Color and surface chemistry changes of extracted wood flour after heating at 120 °C. Wood Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kačíková, D.; Kačík, F.; Čabalová, I.; Ďurkovič, J. Effects of thermal treatment on chemical, mechanical and colour traits in Norway spruce wood. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Peña, M.M.; Hale, M.D.C. Colour in thermally modified wood of beech, Norway spruce and Scots pine. Part 1: Colour evolution and colour changes. Holzforschung 2009, 63, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcginnes, E.A.J.; Rosen, H.N. Macroscopic and microscopic analyses of color changes of wood pressure steam-dried above atmospheric pressure. Wood Fiber Sci. J. Soc. Wood Sci. Technol. 1984, 16, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, B. Discoloration mechanism of Acer buergerianum during drying process. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2004, 26, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- McMillen, J.M. Physical Characteristics of Seasoning Discolorations in Sugar Maple Sapwood; Forest Products Laboratory: Madison, WI, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Hillis, W.E. High temperature and chemical effects on wood stability. Wood Sci. Technol. 1984, 18, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreber, B.; Fernandez, M.; McDonald, A.G. Migration of Kiln Brown Stain Precursors During the Drying of Radiata Pine Sapwood. Holzforschung 1998, 52, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mononen, K.; Alvila, L.; Pakkanen, T.T. CIEL*a*b* Measurements to Determine the Role of Felling Season, Log Storage and Kiln Drying on Coloration of Silver Birch Wood. Scand. J. For. Res. 2002, 17, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanciu, M.D.; Sova, D.; Savin, A.; Ilias, N.; Gorbacheva, G.A. Physical and Mechanical Properties of Ammonia-Treated Black Locust Wood. Polymers 2020, 12, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimer, P.J.; Hackney, J.M.; French, A.D. Effects of chemical treatments and heating on the crystallinity of celluloses and their implications for evaluating the effect of crystallinity on cellulose biodegradation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 48, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.-J.; Colin, B.; Chen, W.-H.; Pétrissans, A.; Rousset, P.; Pétrissans, M. Thermal degradation and compositional changes of wood treated in a semi-industrial scale reactor in vacuum. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 130, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xu, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, C. Modeling and predicting of the color changes of wood surface during CO2 laser modification. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, C.; Tang, R.; Zhao, B.; Wang, H.; Han, Y. Microbial dyeing—Infection behavior and influence of Lasiodiplodia theobromae in poplar veneer. Dye. Pigment. 2020, 173, 107988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Xiao, D. Adsorption of cadmium ion from aqueous solution by ground wheat stems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1359–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y.; Fan, Y. Heat-Induced Discoloration of Chromophore Structures in Eucalyptus Lignin. Materials 2018, 11, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melkior, T.; Jacob, S.; Gerbaud, G.; Hediger, S.; Le Pape, L.; Bonnefois, L.; Bardet, M. NMR analysis of the transformation of wood constituents by torrefaction. Fuel 2012, 92, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, D.; Xu, F.; Geng, Z.; Sun, R.; Jones, G.L.; Baird, M.S. Physicochemical characterization of extracted lignin from sweet sorghum stem. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2010, 32, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimz, H.; Robert, D.; Faix, O.; Nemr, M. Carbon-13 NMR Spectra of Lignins, 8. Structural Differences between Lignins of Hardwoods, Softwoods, Grasses and Compression Wood. Holzforschung 1981, 35, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
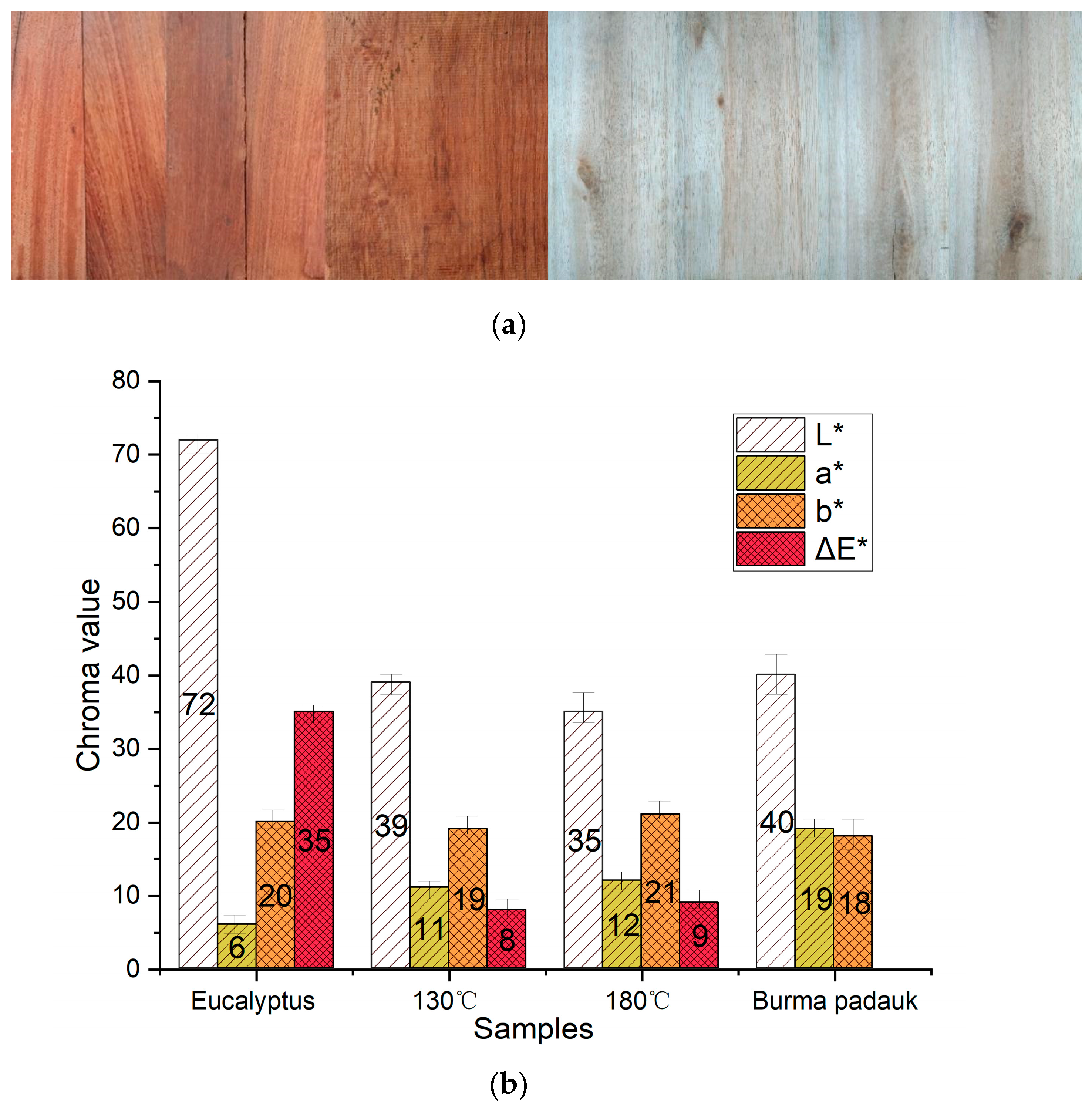
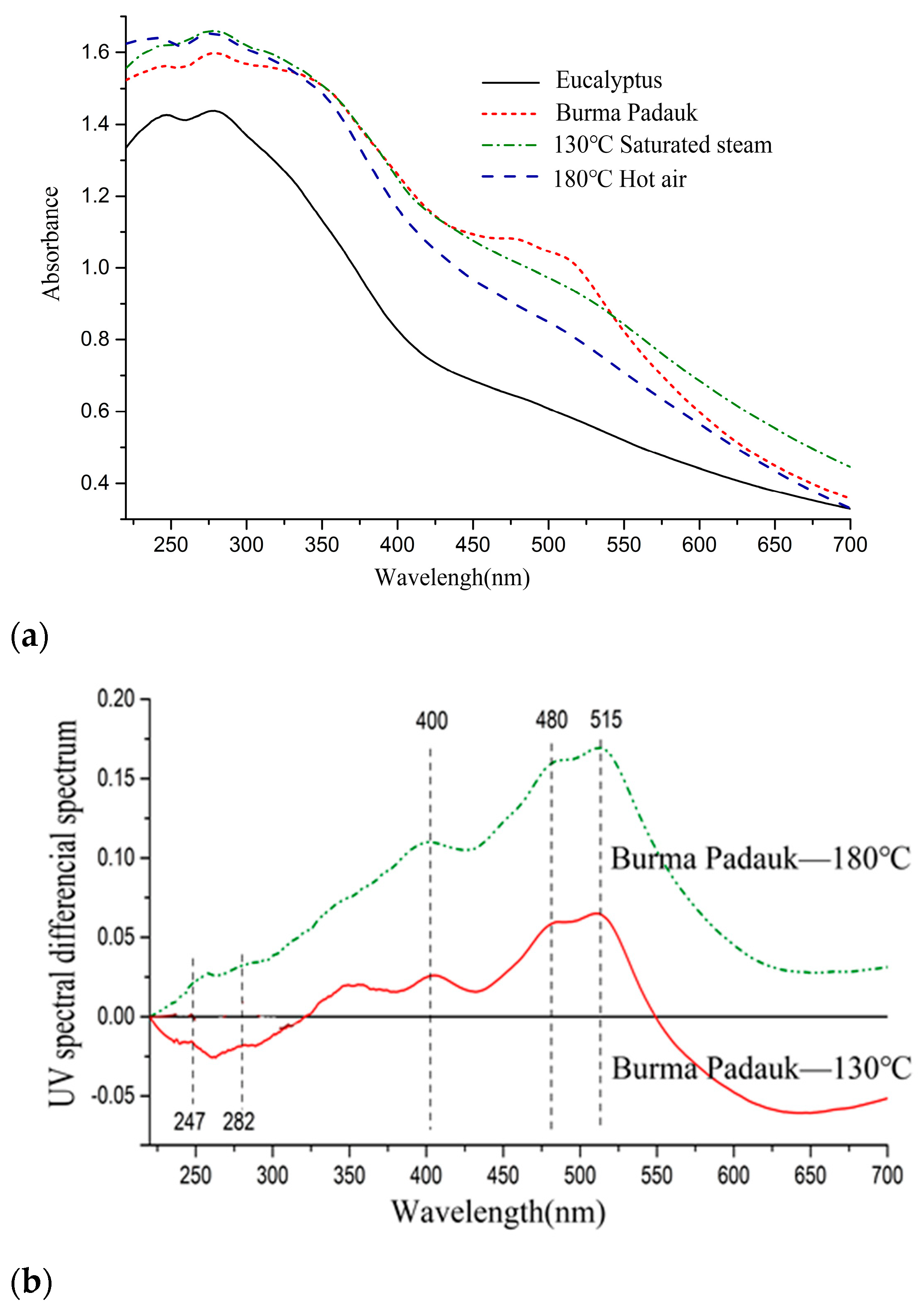
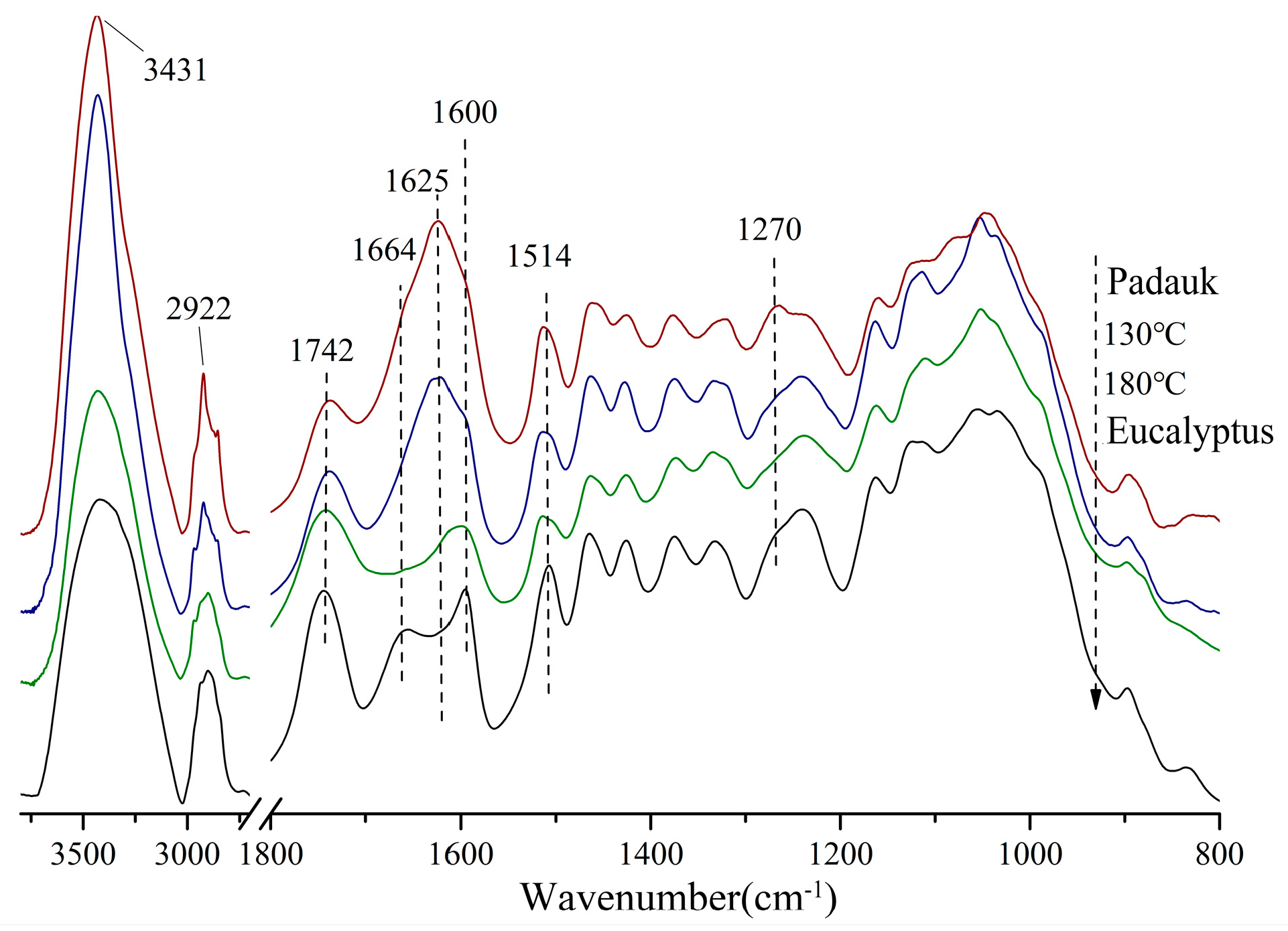

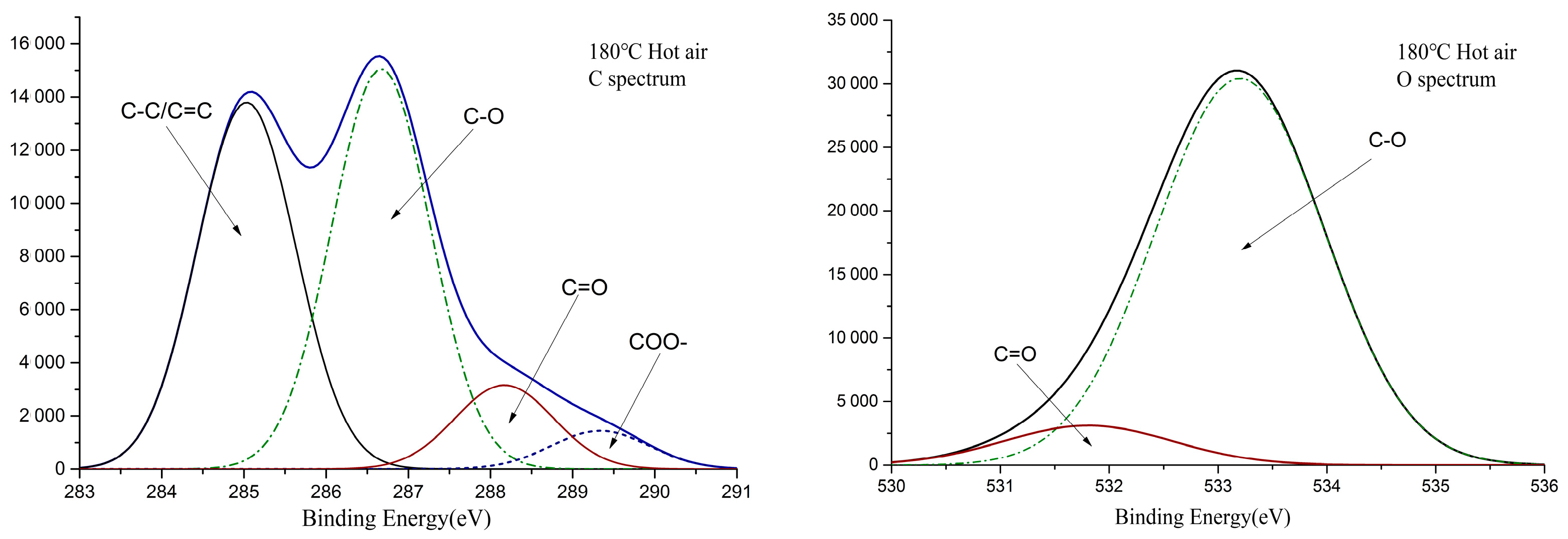
| Wavenumber/cm−1 | 3431 | 1742 | 1664 | 1625 | 1600 | 1270 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treated Samples | Hydroxyl | Non-Conjugated Carbonyl | Carbonyl Group Conjugated to Aromatic Ring | Conjugated Double Bond | Benzene Ring | Guaiacol |
| Burma padauk | 2.51 | 0.63 | 1.01 | 1.51 | 1.29 | 1.33 |
| 130 °C | 2.84 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 1.29 | 1.12 | 1.17 |
| 180 °C | 1.76 | 1.04 | 0.66 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 1.11 |
| Eucalyptus | 1.27 | 0.89 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.86 | 1.09 |
| Treated Samples | C1s Relative Peak Area | O1s Relative Peak Area | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C3/C2 | O1 (531.7 eV) | O2 (532.8 eV) | O1/O2 | |
| (284.7 eV) | (286.2 eV) | (287.6 eV) | (289 eV) | |||||
| Burma padauk | 66.04 | 27.62 | 3.56 | 2.76 | 0.13 | 9.99 | 90.00 | 0.11 |
| 130 °C | 47.66 | 45.58 | 4.40 | 2.34 | 0.10 | 8.96 | 91.03 | 0.10 |
| 180 °C | 41.24 | 45.00 | 9.45 | 4.30 | 0.21 | 9.26 | 90.73 | 0.10 |
| Eucalyptus | 31.85 | 44.37 | 18.56 | 5.20 | 0.42 | 6.61 | 93.38 | 0.07 |
| ppm | Peak Attribution | Relative Number (/C1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Burma Padauk | 130 | 180 | Eucalyptus | ||
| 173.6 | COOR, CH3COO-hemicellulose | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.09 |
| 154.21 | S 3/5 lignin | 0.36 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.3 |
| 149.25 | G 4 lignin | 0.19 | 0.07 | 0.08 | —— |
| 135.21 | S 1/4e, G 1e lignin | 0.29 | 0.13 | -0.01 | 0.17 |
| 116.71 | G 5/6 lignin | 0.39 | —— | 0.05 | —— |
| 89.5 | C-4 crystalline region cellulose | 0.34 | 0.35 | 0.27 | 0.24 |
| 83.45 | C-4 Amorphous Region cellulose; Cβ β-O-4 lignin | 0.58 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.5 |
| 75.46 | C-2/C-3/C-5 cellulose Cα β-O-4 lignin | 3.39 | 3 | 2.97 | 2.91 |
| 65.43 | C6 crystalline region cellulose | 0.4 | 0.57 | 0.46 | 0.39 |
| 63.07 | C6 amorphous region cellulose | 0.64 | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.64 |
| 56.42 | -OCH3 lignin | 0.1 | 0.46 | 0.35 | 0.51 |
| 22.14 | Acetyl | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.17 | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Gao, J.; Liu, F.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Y. Study on the Discoloration Mechanism of Eucalyptus Wood during Thermal Treatment in Different Media. Polymers 2023, 15, 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071599
Zhang P, Gao J, Liu F, Chen Y, Peng Y. Study on the Discoloration Mechanism of Eucalyptus Wood during Thermal Treatment in Different Media. Polymers. 2023; 15(7):1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071599
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Peng, Jianmin Gao, Fu Liu, Yao Chen, and Yao Peng. 2023. "Study on the Discoloration Mechanism of Eucalyptus Wood during Thermal Treatment in Different Media" Polymers 15, no. 7: 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071599
APA StyleZhang, P., Gao, J., Liu, F., Chen, Y., & Peng, Y. (2023). Study on the Discoloration Mechanism of Eucalyptus Wood during Thermal Treatment in Different Media. Polymers, 15(7), 1599. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15071599






