Novel and Facile Colorimetric Detection of Reducing Sugars in Foods via In Situ Formed Gelatin-Capped Silver Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
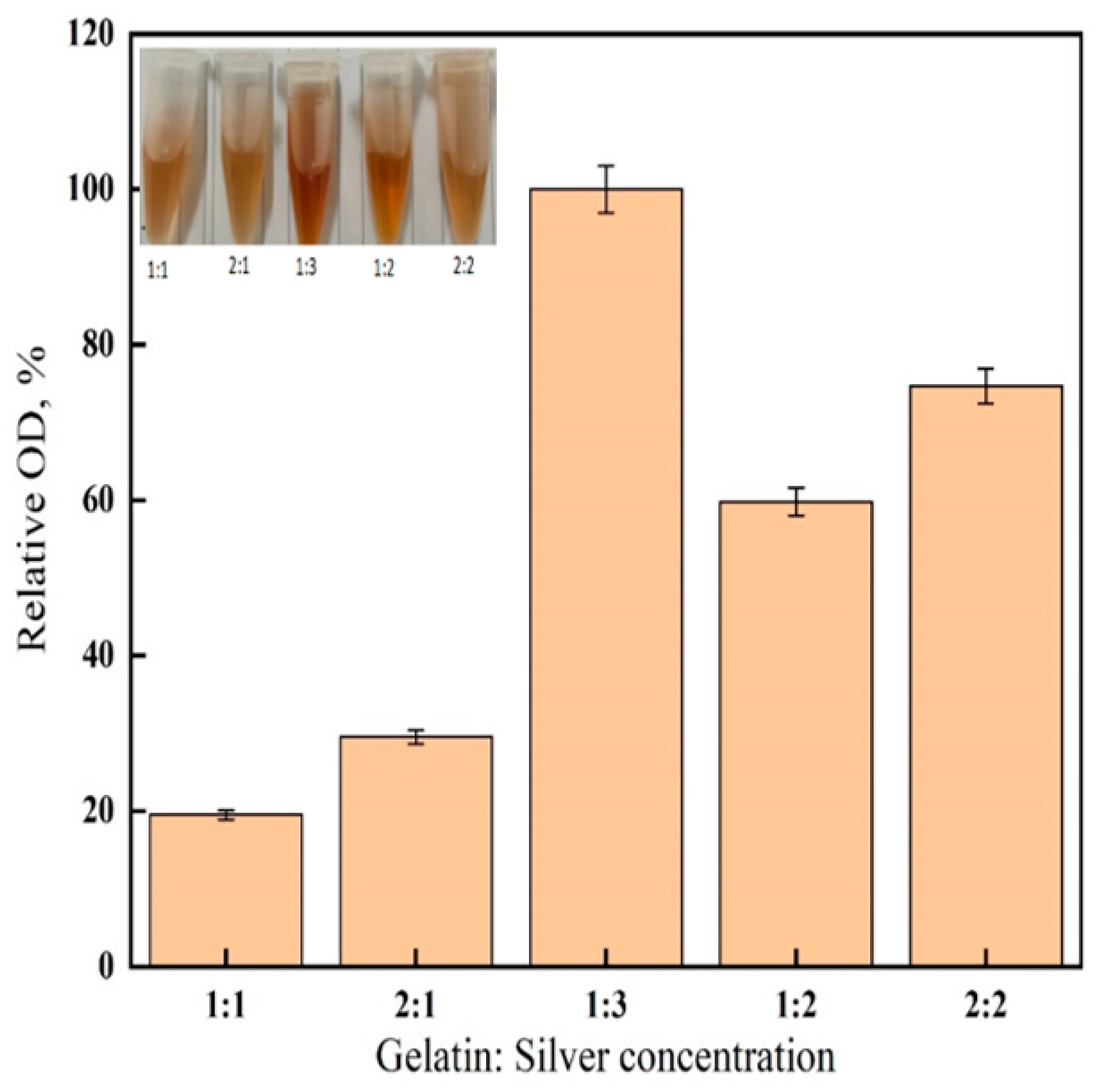
2.2. Effect of Gelatin-Silver Reagent Ratio
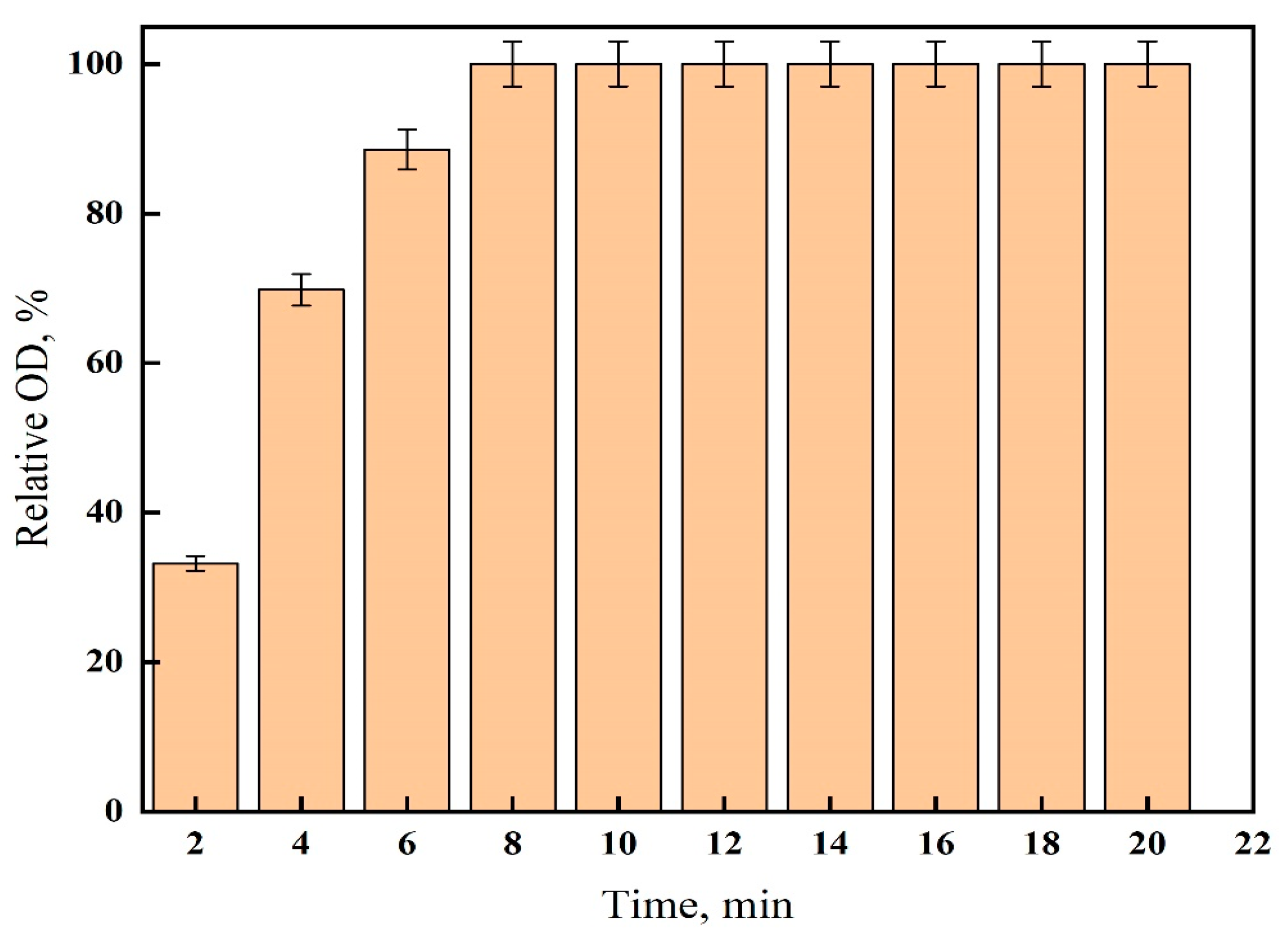
2.3. Effect of Time
2.4. Effect of PH on the Silver-Gelatin Reagent
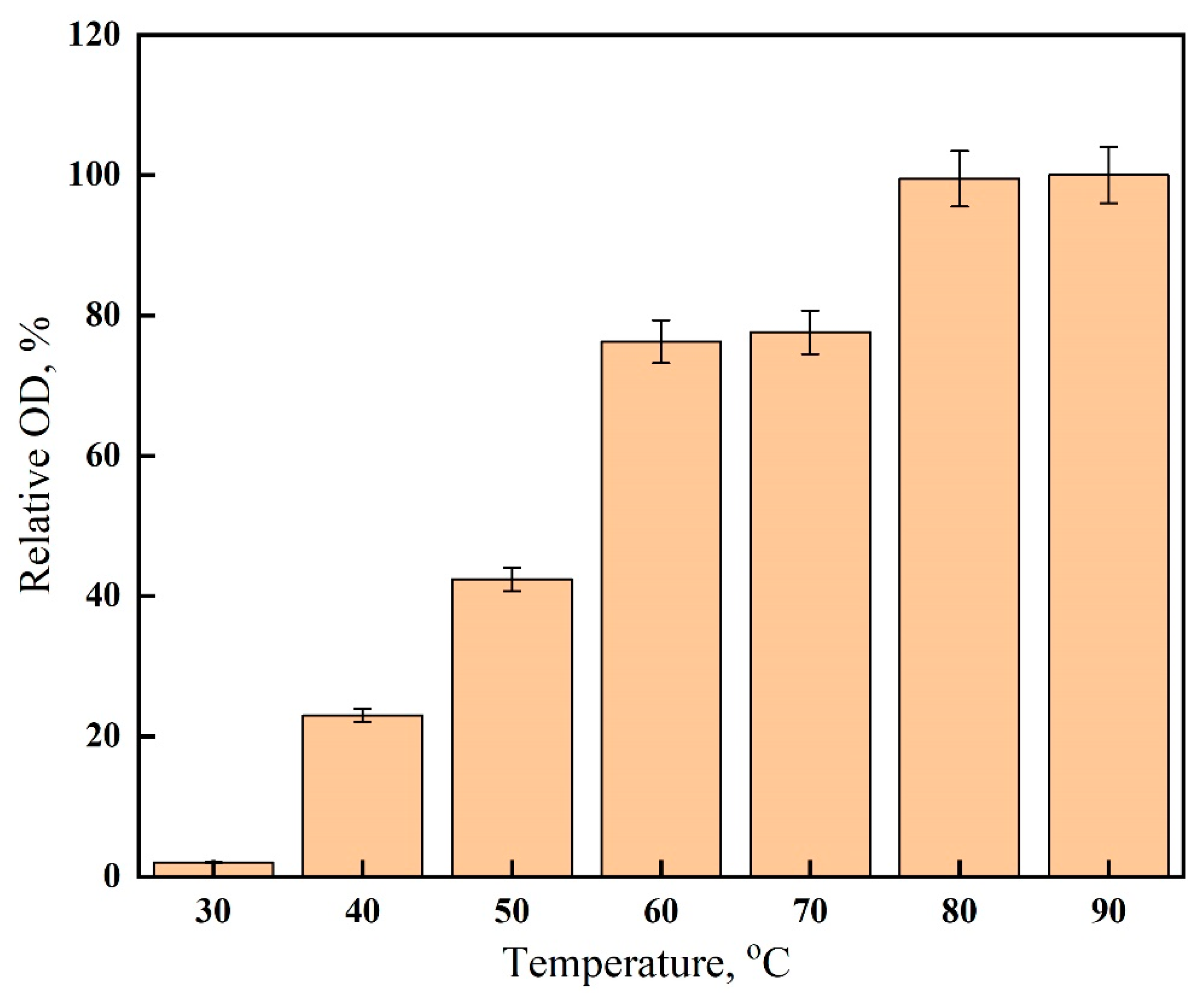
2.5. Effect of Temperature
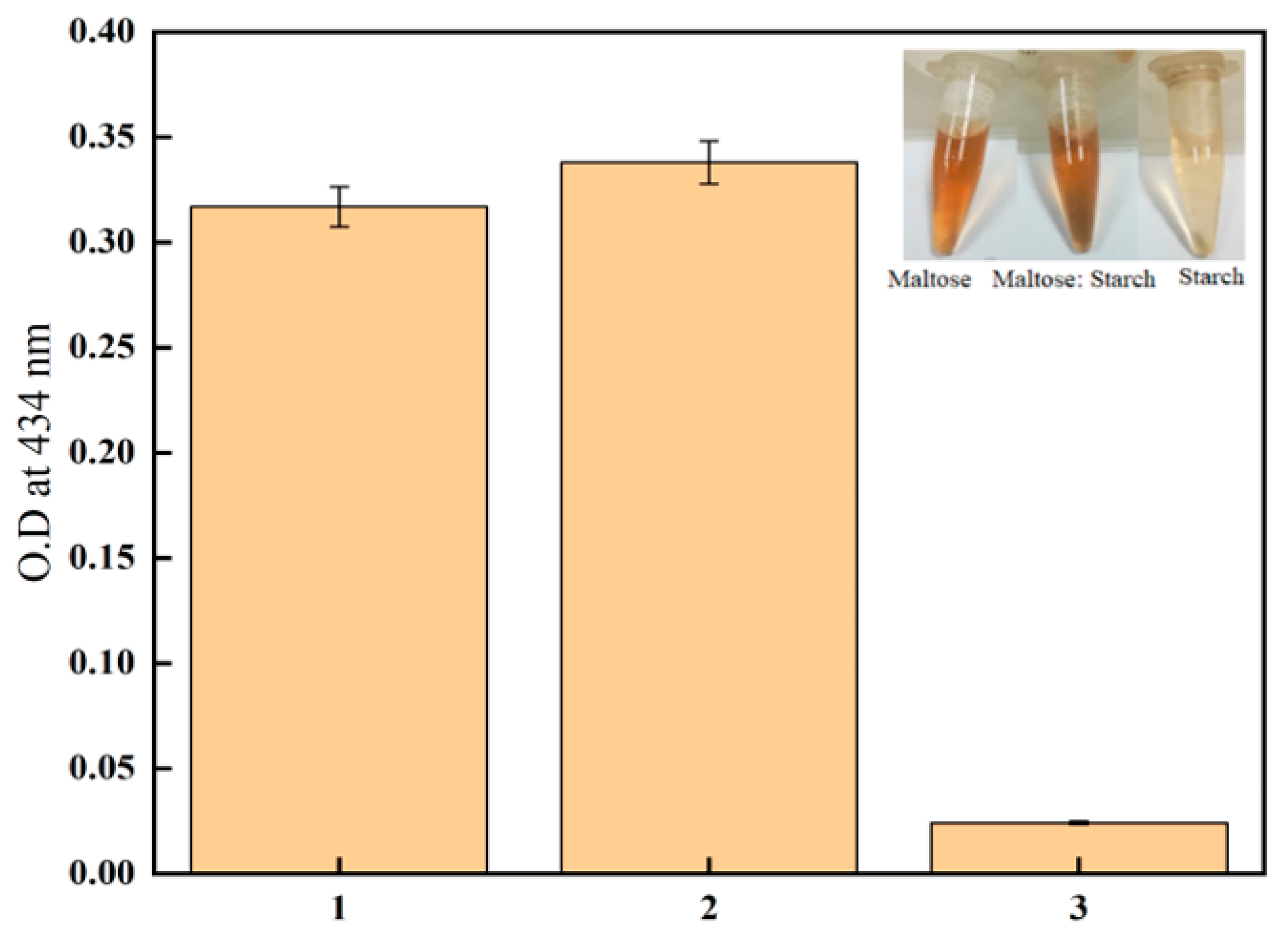
2.6. Maltose Selectivity
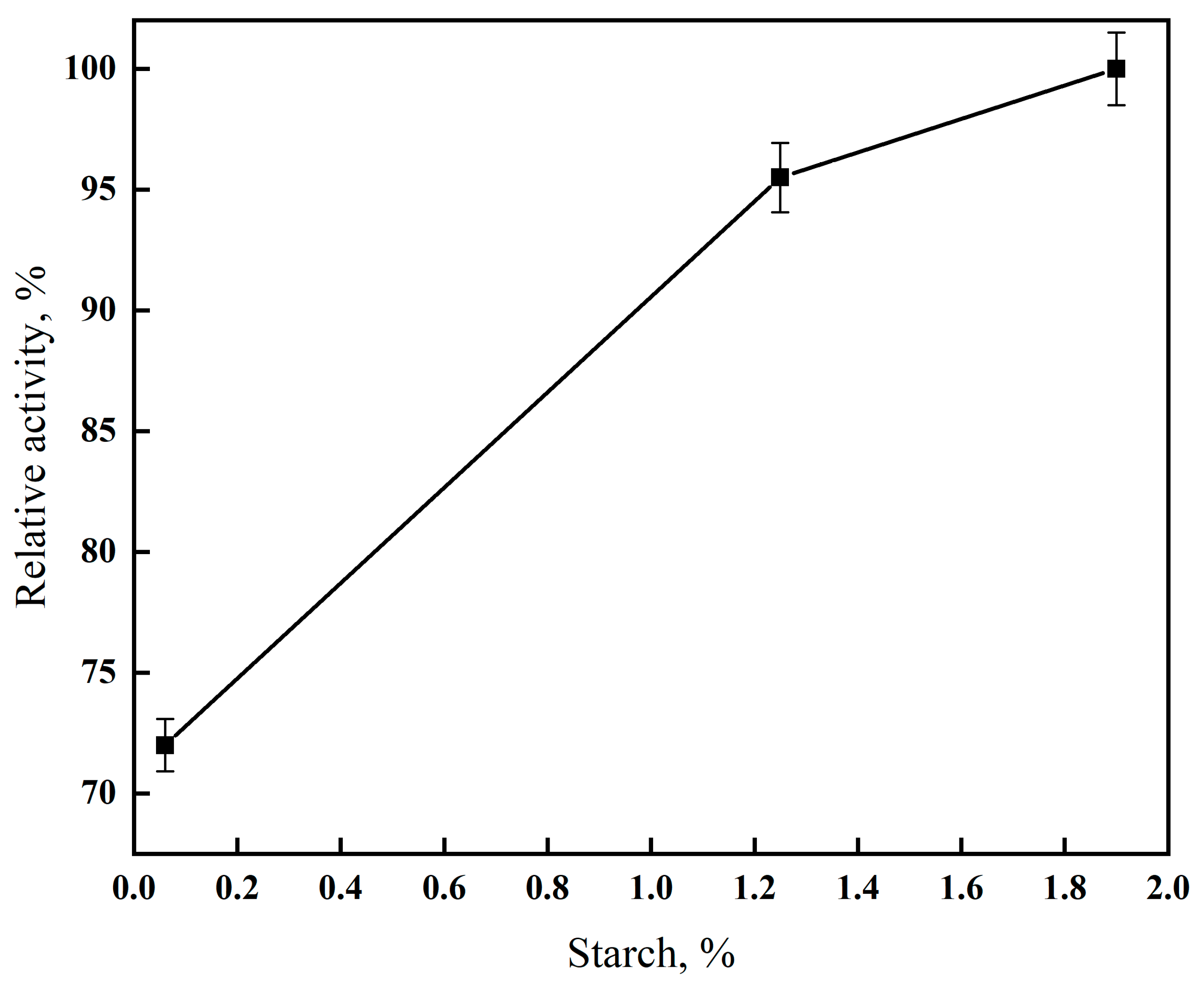
2.7. Hydrolysis of Starch with α-Amylase
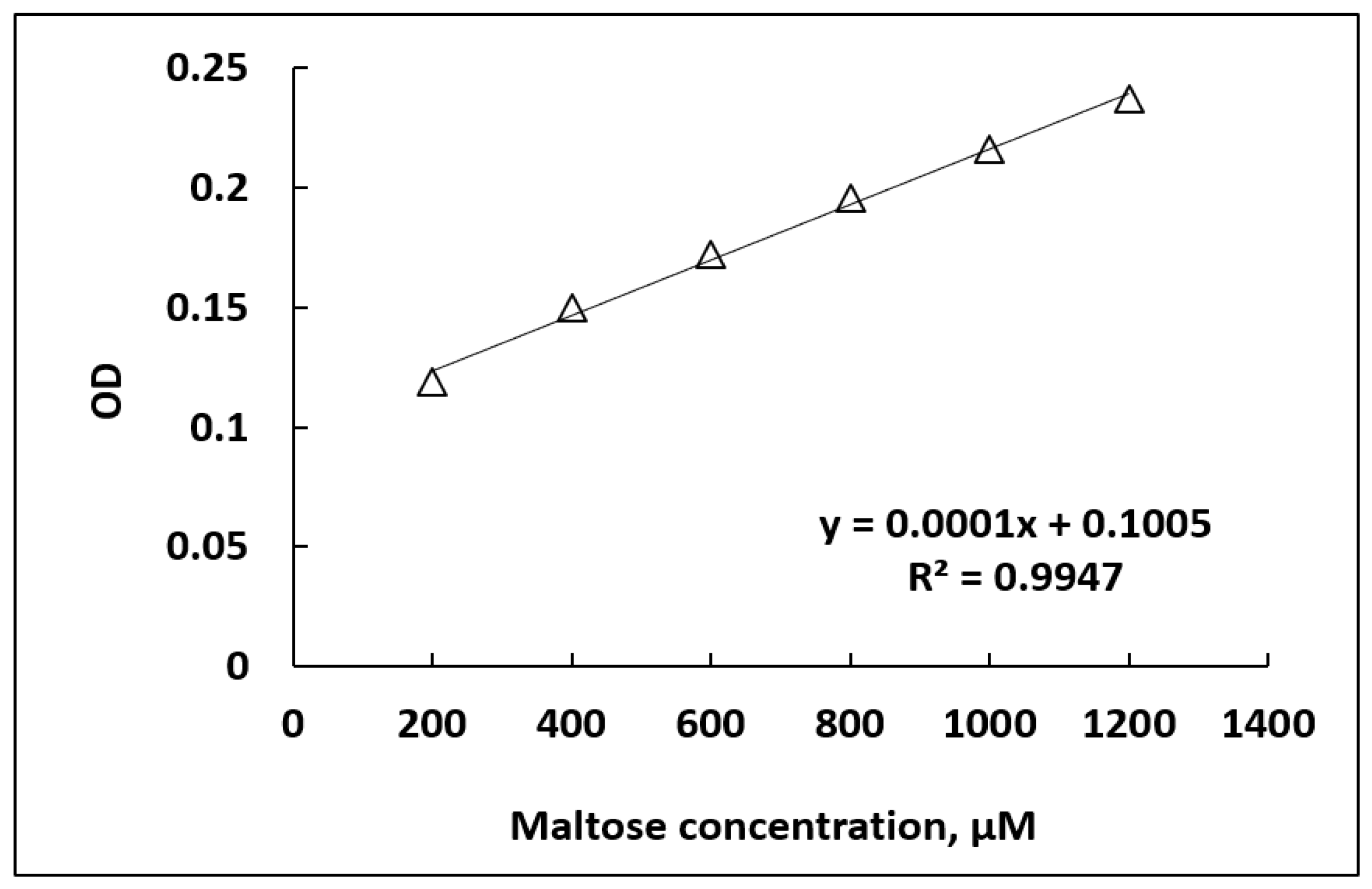
2.8. Effect of Maltose Concentration and Detection Limit
2.9. Real Samples Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
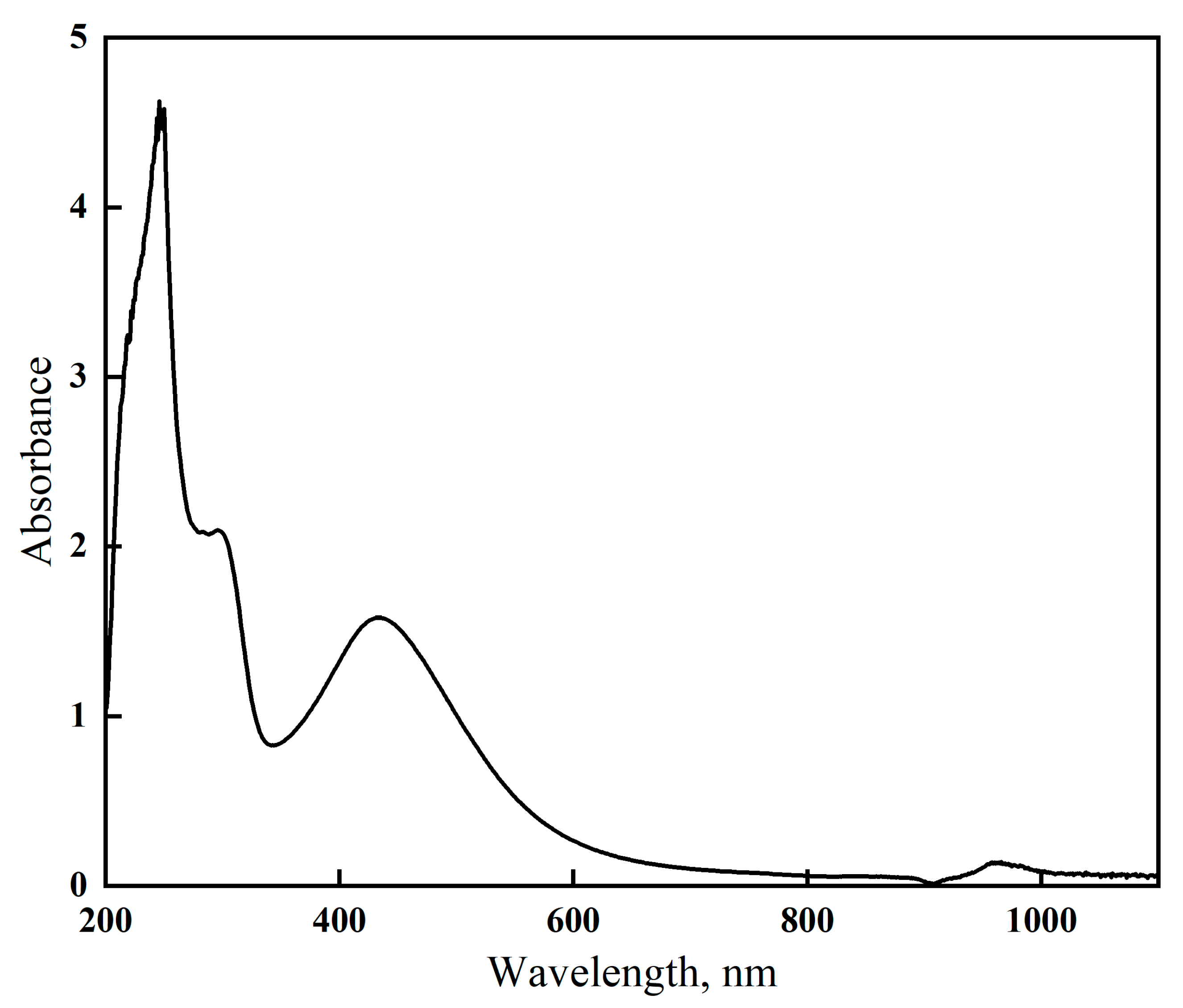
3.1. Gelatin-Silver Method Optimization
3.2. Possible Mechanism for Gelatin-Capped AgNPs
3.3. Maltose Selectivity and Starch Hydrolysis
3.4. Limit of Detection of Maltose
3.5. Real Samples Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Uhlig, H. (Ed.) . Industrial Enzymes and Their Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, N. A photometric adaptation of the Somogyi method for the determination of glucose. J. Biol. Chem. 1944, 153, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waffenschmidt, S.; Jaenicke, L. Assay of reducing sugars in the nanomole range with 2,2-bicinchoninate. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 165, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gropper, S.S.; Smith, J.L. Advanced Nutrition and Human Metabolism; Wadsworth Cengage Learning: Belmont, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, J.H.; Stephen, A.M. Carbohydrate terminology and classification. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 61, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis, D.B.; Tamayo, D.M.; Alonso, J.M. Determination of monosaccharides in cider by reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 436, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeley, W.E. Simple Automated Determination of Serum or Plasma Glucose by a Hexokinase/Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Method Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apovian, C.M. Sugar-sweetened soft drinks, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. JAMA 2004, 292, 978–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortacero-Ramirez, S.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Cruces-Blanco, C.; de Castro, M.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, A. Analysis of carbohydrates in beverages by cap-illary electrophoresis with precolumn derivatization and UV detection. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, B.S.; Slover, H.T. Gas-chromatographic method for the deter-mination of sugars in foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1971, 19, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, R.; Chang, X.; Jing, R. Development of near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy models for quantitative determination ofwater-soluble carbohydrate content in wheat stem and glume. Anal. Lett. 2011, 44, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duquesnoy, E.; Castola, V.; Casanova, J. Identification and quantitative determination of carbohydrates in ethanolic extracts of two conifers using C-13NMR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-L.; Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q. Determination of proteins and carbohydrates in the effluents from wastewater treatment bioreactors usingresonance light-scattering method. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3464–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.S. Phenol-sulfuric acid method for total carbohydrates. In Food Analysis Laboratory Manual; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Somani, B.L.; Khanade, J.; Sinha, R. A modified anthrone-sulfuric acid method for the determination of fructose in the presence of certain proteins. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 167, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 1995.
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalowicz, J.; Duda, W. Phenols—Sources and toxicity. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2007, 16, 347–362. [Google Scholar]
- Robyt, J.F.; Whelan, W.J. Reducing value methods for maltodextrins. I. Chain-length dependence of alkaline 3,5-dinitrosalicylate and chain-length independence of alkaline copper. Anal. Biochem. 1972, 45, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, W.A.; Dennison, C.; Quicke, G.V. Pitfalls in the assay of carboxymethylcellulase activity. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1983, 2, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuil, C.; Saddler, J.N. Comparison of the 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid and Nelson-Somogyi methods of assaying for reducing sugars and determining cellulase activity. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 1985, 7, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, T.K. Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure Appl. Chem. 1987, 2, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, P.; Rhim, J.W. Physicochemical properties of gelatin/silver nanoparticle antimicrobial composite films. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.T.; Hieu, M.H.; Phuong, N.T.M.; Thuan, T.D.B.; Thu, H.N.T.; Do Minh, T.; Thi, H.N. Optimization and characterization of electrospun polycaprolactone coated with gelatin-silver nanoparticles for wound healing application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ediyilyam, S.; George, B.; Shankar, S.S.; Dennis, T.T.; Wacławek, S.; Černík, M.; Padil, V.V. Chitosan/gelatin/silver nanoparticles composites films for biodegradable food packaging applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, L.; Park, W.H. Preparation and characterization of gelatin nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6857–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, P.K.; Dey, S. Effects and applications of silver nanoparticles in different fields. Int. J. Rec. Sci. Res. 2015, 28, 5880–5884. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shishtawy, R.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Al-Otaibi, M.M. Synthesis and spectroscopic studies of stable aqueous dispersion of silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 79, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Shishtawy, R.M.; Asiri, A.M.; Abdelwahed, N.A.M.; Al-Otaibi, M.M. In situ production of silver nanoparticle on cotton fabric and its antimicrobial evaluation. Cellulose 2011, 18, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bar, O.A.M.; El-Shishtawy, R.M.; Mohamed, S.A. Immobilization of camel liver catalase on nanosilver-coated cotton fabric. Catalysts 2021, 11, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zahrani, F.A.M.; AL-Zahrani, N.A.; Al-Ghamdi, S.N.; Lin, L.; Salem, S.S.; El-Shishtawy, R.M. Synthesis of Ag/Fe2O3 nanocomposite from essential oil of ginger via green method and its bactericidal activity. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Zahrani, F.A.M.; Salem, S.S.; Al-Ghamdi, H.A.; Nhari, L.M.; Lin, L.; El-Shishtawy, R.M. Green Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Ag/Fe2O3 Nanocomposite Using Buddleja lindleyana Extract. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darroudi, M.; Ahmad, M.B.; Abdullah, A.H.; Ibrahim, N.A. Green synthesis and characterization of gelatin-based and sugar-reduced silver nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, D.; Wei, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, J. A simple and sensitive assay of gallic acid based on localized surface plasmon resonance light scattering of silver nanoparticles through modified Tollens process. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Gu, Y.; Gao, M.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, D.; Li, Y.; Lin, R.; He, H. Colorimetric determination of o-phenylenediamine in water samples based on the formation of silver nanoparticles as a colorimetric probe. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2015, 140, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiendoo, K.; Sooksin, S.; Kulchat, S.; Promarak, V.; Tuntulani, T.; Ngeontae, W. A new formaldehyde sensor from silver nanoclusters modified Tollens’ reagent. Food Chem. 2018, 255, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durmazel, S.; Üzer, A.; Erbil, B.; Sayln, B.; Apak, R. Silver Nanoparticle Formation-Based Colorimetric Determination of Reducing Sugars in Food Extracts via Tollens’ Reagent. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 7596–7604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, G.; Facchini, L.; Mallardi, A. Colorimetric detection of sugars based on gold nanoparticle formation. Sens. Actuators B 2012, 161, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanoff, D.D., Jr.; Chumanov, G. Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanoparticles and arrays. ChemPhysChem 2005, 6, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Başkan, K.S.; Tütem, E.; Akyüz, E.; Özen, S.; Apak, R. Spectrophotometric total reducing sugars assay based on cupric reduction. Talanta 2016, 147, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrulescu, A.; Patrulea, V.; Mincea, M.M.; Ionascu, C.; Vlad-Oros, B.A.; Ostafe, V. Adapting the reducing sugars method with dinitrosalicylic acid to microtiter plates and microwave heating. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 2176–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Lang, Q.; Liang, B.; Shi, J. Sensitive detection of maltose and glucose based on dual enzyme-displayed bacteria electrochemical biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-López, A.; Felix, D.A.S.; Sierra, Z.Z.; Bravo, I.G.; Dinkova, T.D.; Alejandre, A.X.A. Quantification of Reducing Sugars Based on the Qualitative Technique of Benedict. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32403–32410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

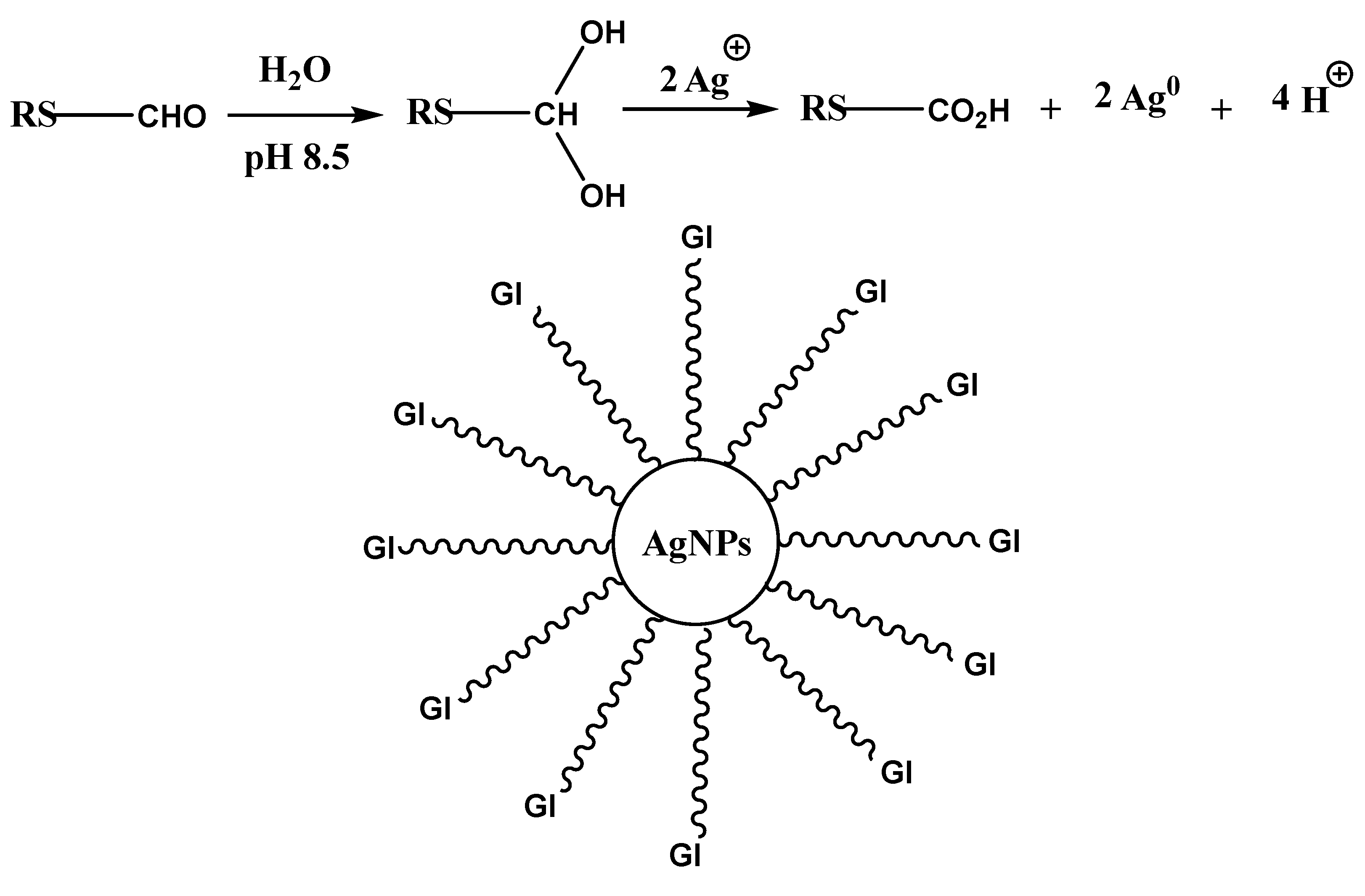
| Reference | Method | Analyte | LOD |
|---|---|---|---|
| [17,40] | DNS | Glucose | 80 µM |
| [37] | Tollens’ Reagent | Glucose | 40 nM |
| [41] | DNS | Honey | 83.3 µM |
| [40] | Alkaline Cu(II)-Nc | Glucose | 0.6 µM |
| [42] | Electrochemical Biosensor | Maltose | 100 µM |
| [43] | Benedict’s reagent | Maltose | 96.49 µM |
| [17] | DNS | Maltose | 80 µM |
| This work | Gelatin-silver | Maltose | 46.67 µM |
| mg Maltose Eq. g−1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sample | Gelatin-Silver Reagent | DNS |
| Fresh apple juice | 287 ± 1.05 | 284 ± 0.84 |
| Watermelon | 165 ± 0.95 | 169 ± 0.76 |
| Honey | 751 ± 1.12 | 723 ± 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El-Shishtawy, R.M.; Al Angari, Y.M.; Alotaibi, M.M.; Almulaiky, Y.Q. Novel and Facile Colorimetric Detection of Reducing Sugars in Foods via In Situ Formed Gelatin-Capped Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers 2023, 15, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051086
El-Shishtawy RM, Al Angari YM, Alotaibi MM, Almulaiky YQ. Novel and Facile Colorimetric Detection of Reducing Sugars in Foods via In Situ Formed Gelatin-Capped Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2023; 15(5):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051086
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl-Shishtawy, Reda M., Yasser M. Al Angari, Maha M. Alotaibi, and Yaaser Q. Almulaiky. 2023. "Novel and Facile Colorimetric Detection of Reducing Sugars in Foods via In Situ Formed Gelatin-Capped Silver Nanoparticles" Polymers 15, no. 5: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051086
APA StyleEl-Shishtawy, R. M., Al Angari, Y. M., Alotaibi, M. M., & Almulaiky, Y. Q. (2023). Novel and Facile Colorimetric Detection of Reducing Sugars in Foods via In Situ Formed Gelatin-Capped Silver Nanoparticles. Polymers, 15(5), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15051086








