Designing a Coupling Agent with Aliphatic Polyether Chain and Exploring Its Effect on Silica/Natural Rubber Nanocomposites under the Action of Non-Rubber Contents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
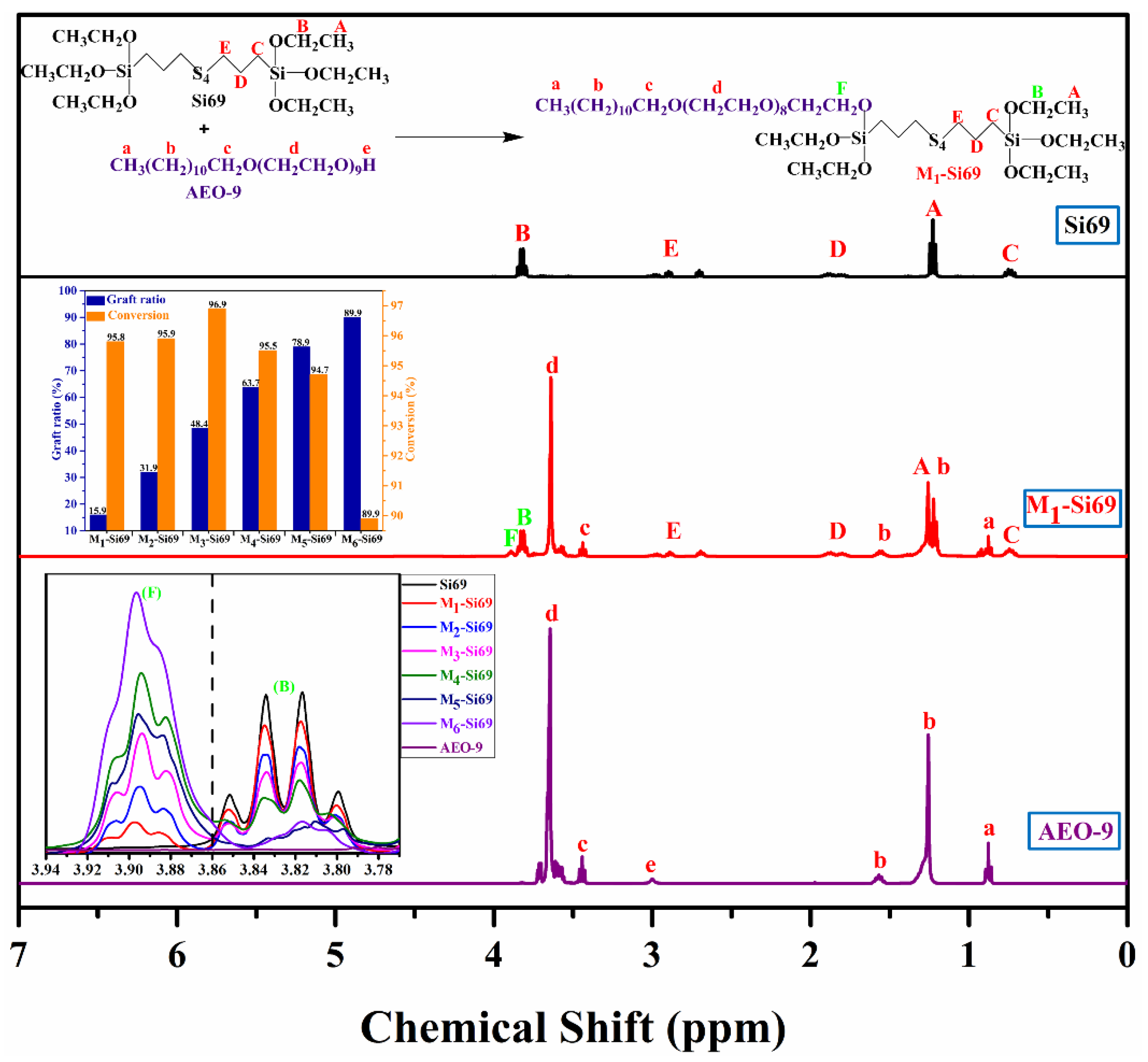
2.2. Preparation of Mx–Si69 Coupling Agent
2.3. Characteristics of Coupling Agents
2.4. Preparation of Rubber Nanocomposites
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of Silica/NR Nanocomposites Containing Mx–Si69
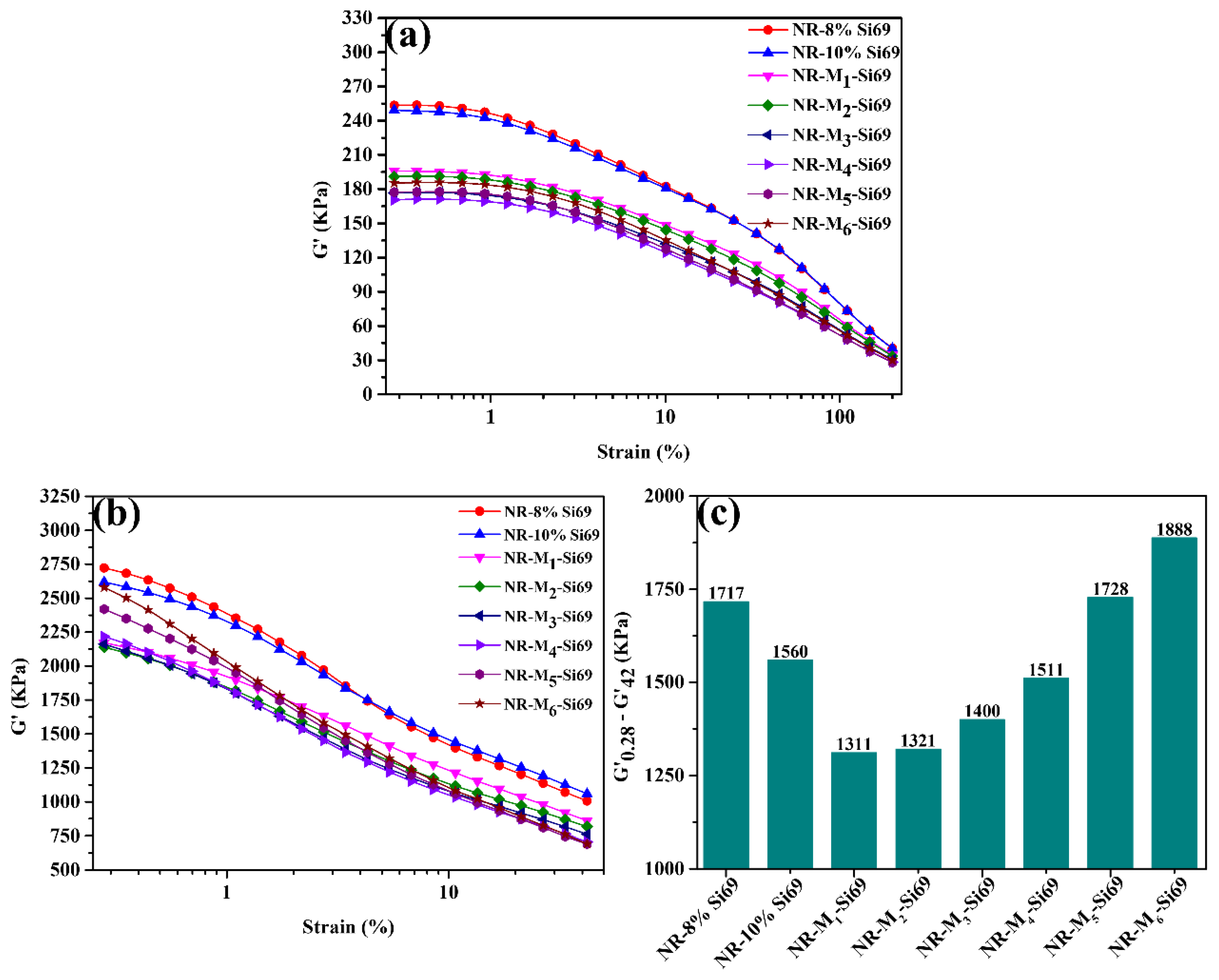
3.1.1. Crosslink Density and Filler Network of Silica/NR Nanocomposites
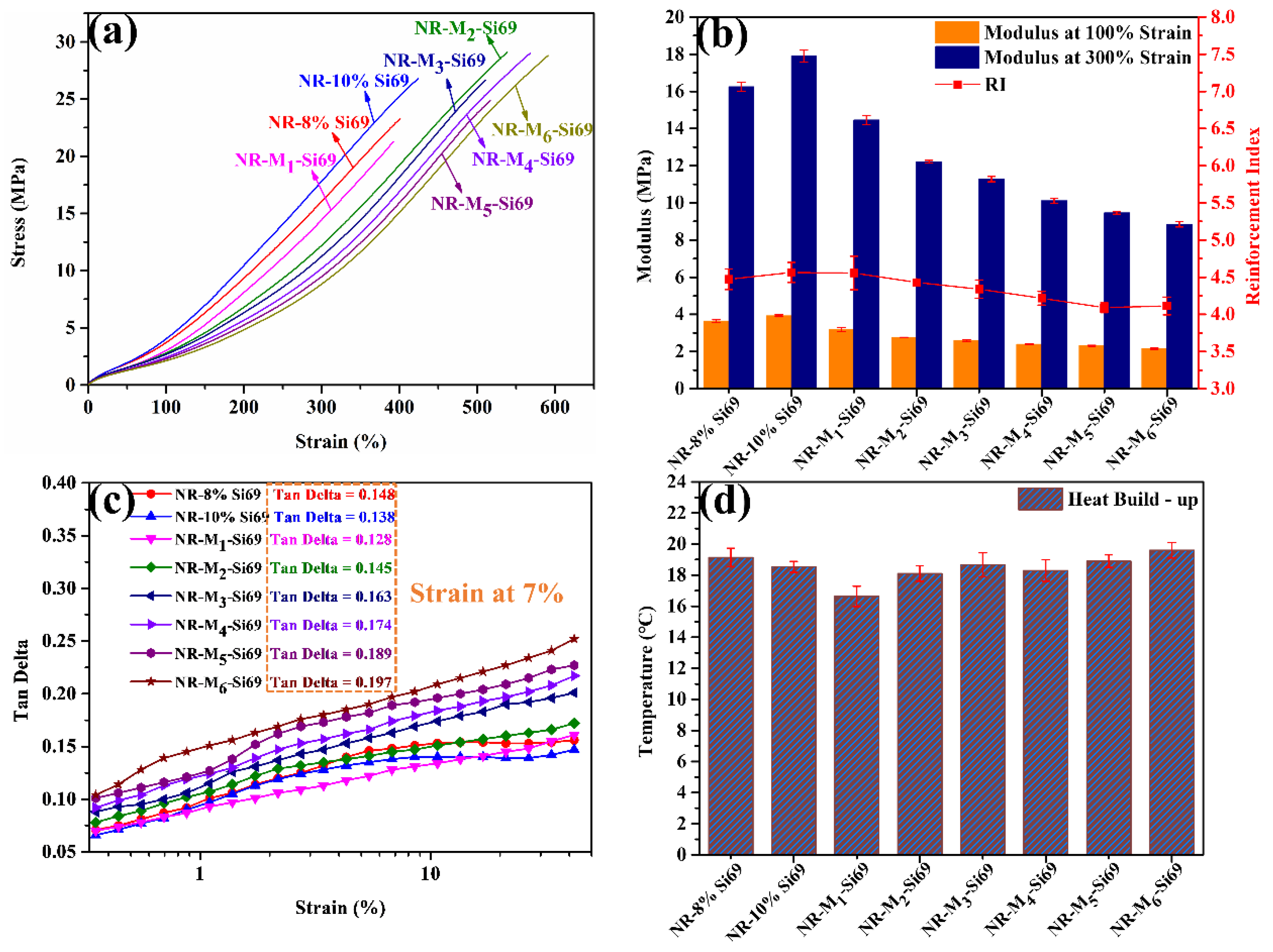
3.1.2. Static and Dynamic Properties of Silica/NR Nanocomposites
3.2. Mechanism of Mx–Si69 on Silica Modification in NR Nanocomposites
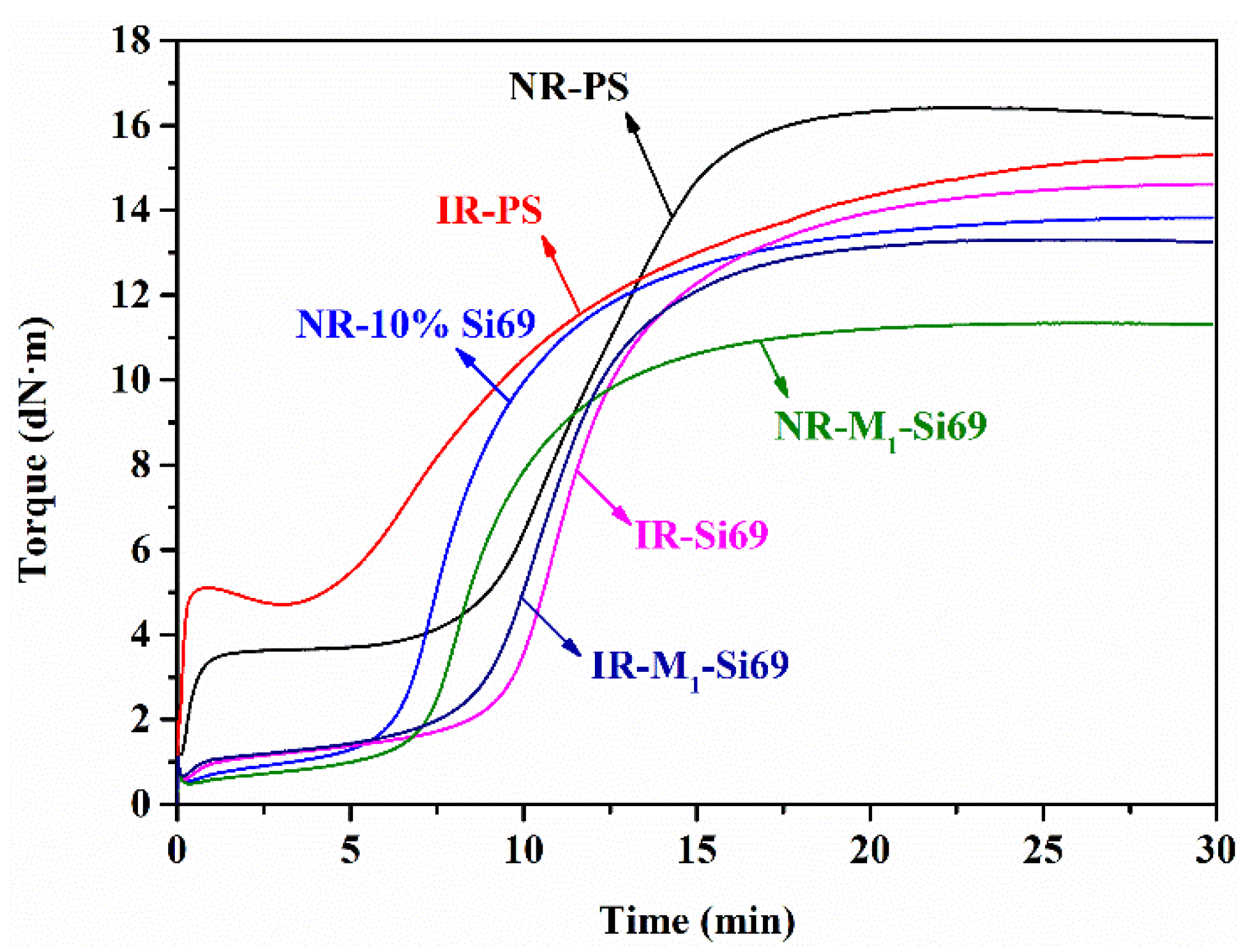
3.2.1. Cure Characteristics of Silica/NR Nanocomposites and Silica/IR Nanocomposites
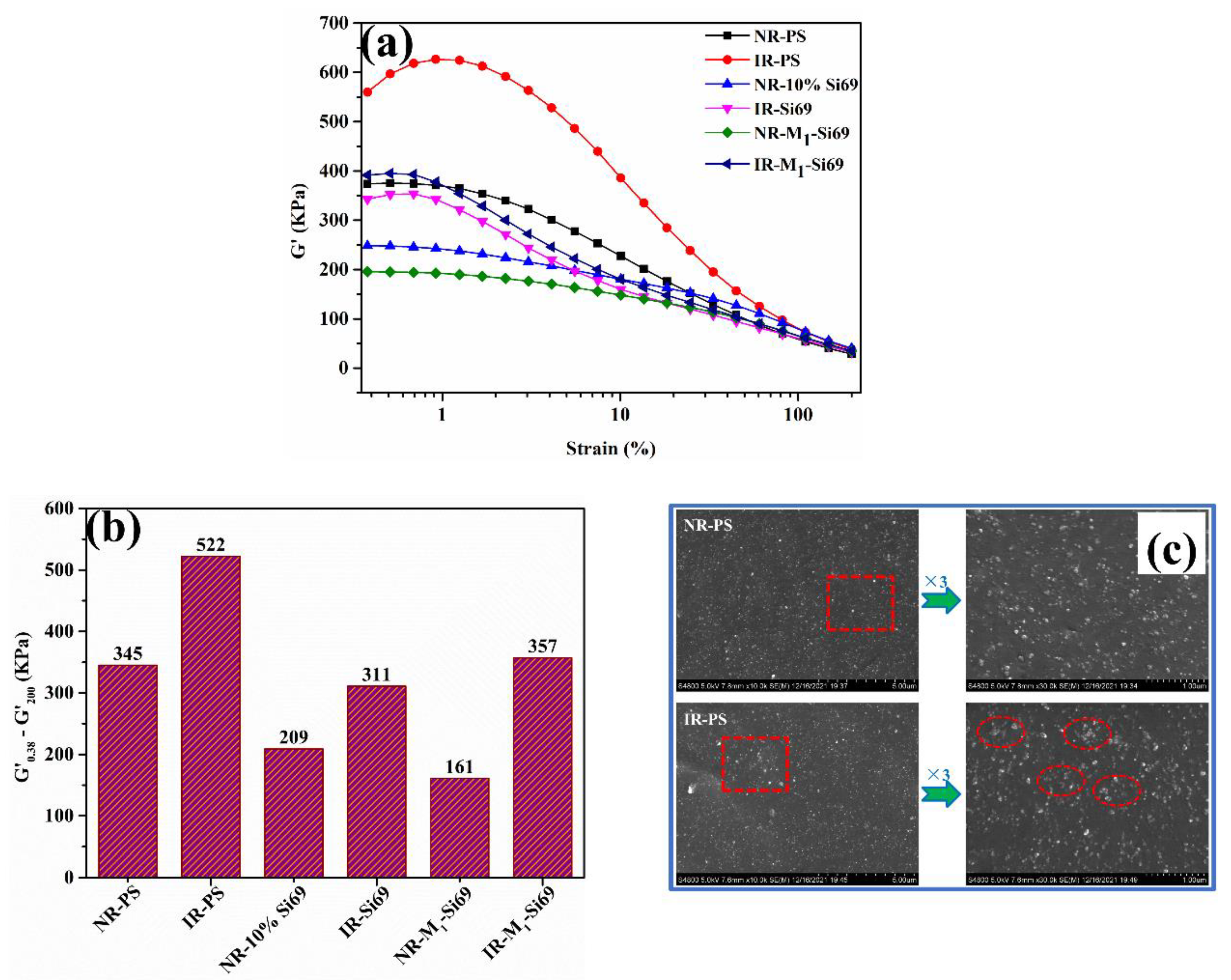
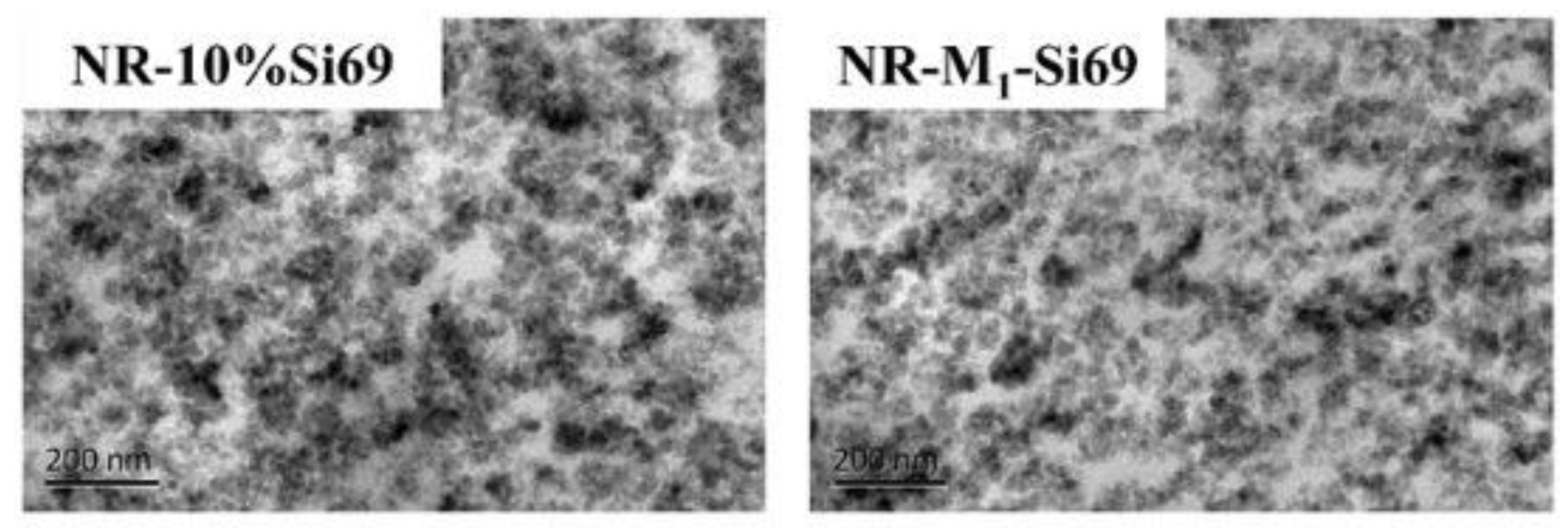
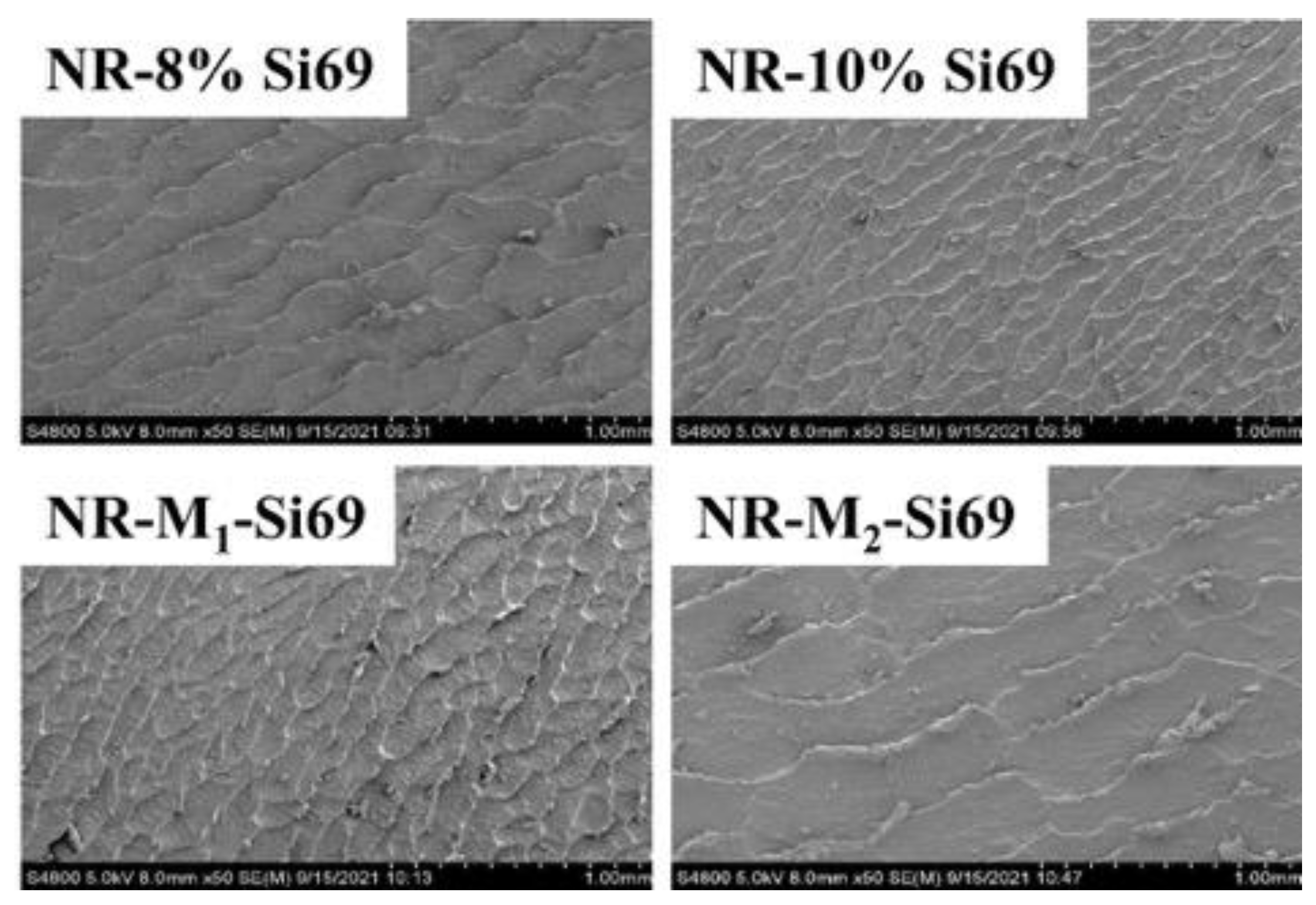
3.2.2. Filler Network and Micromorphology of Silica/NR Nanocomposites and Silica/IR Nanocomposites
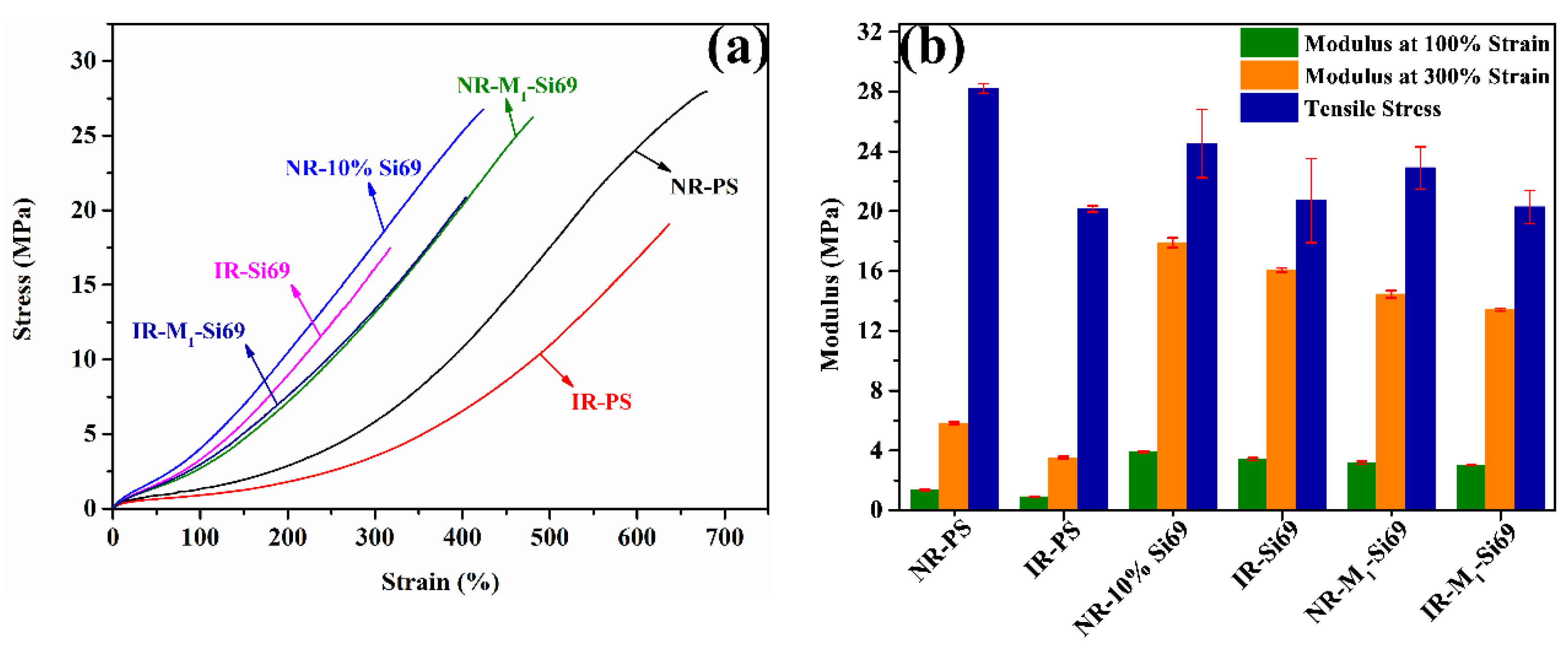
3.2.3. Static and Dynamic Performance of Silica/NR Nanocomposites and Silica/IR Nanocomposites
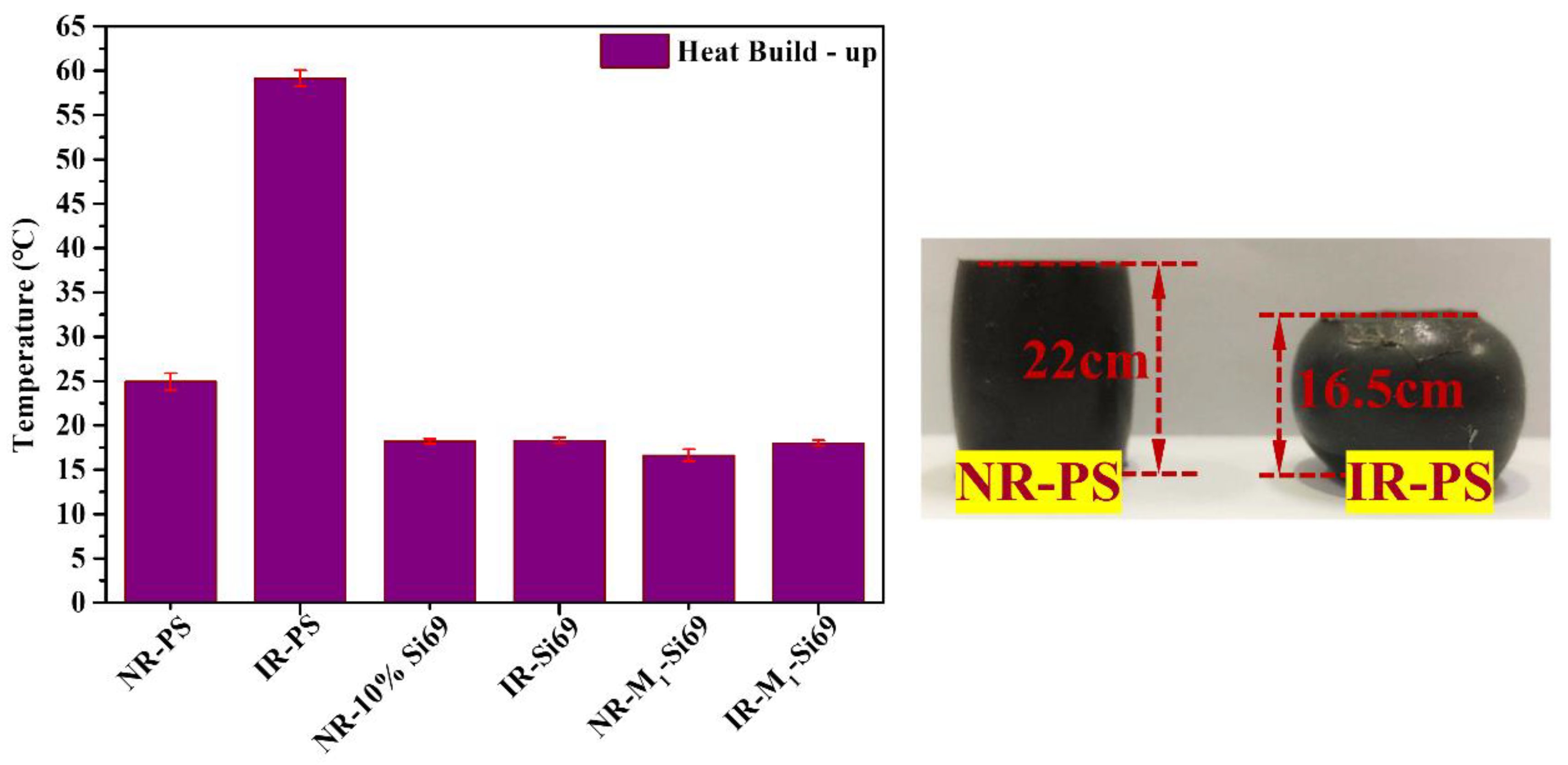
3.2.4. Rolling Resistance of the Silica/NR Nanocomposites
3.2.5. Wet-Skid Resistance of the Silica/NR Nanocomposites
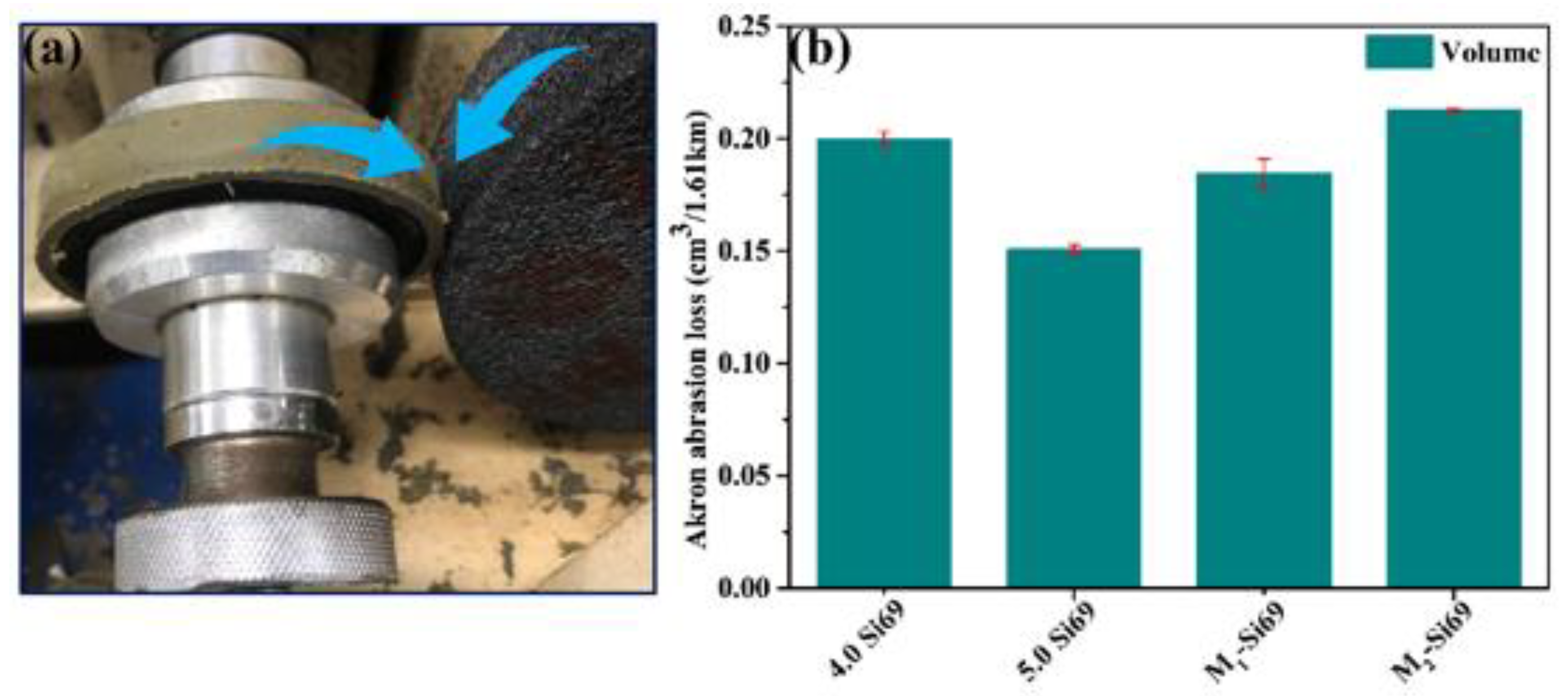
3.2.6. Akron Abrasion Loss of the Silica/NR Nanocomposites
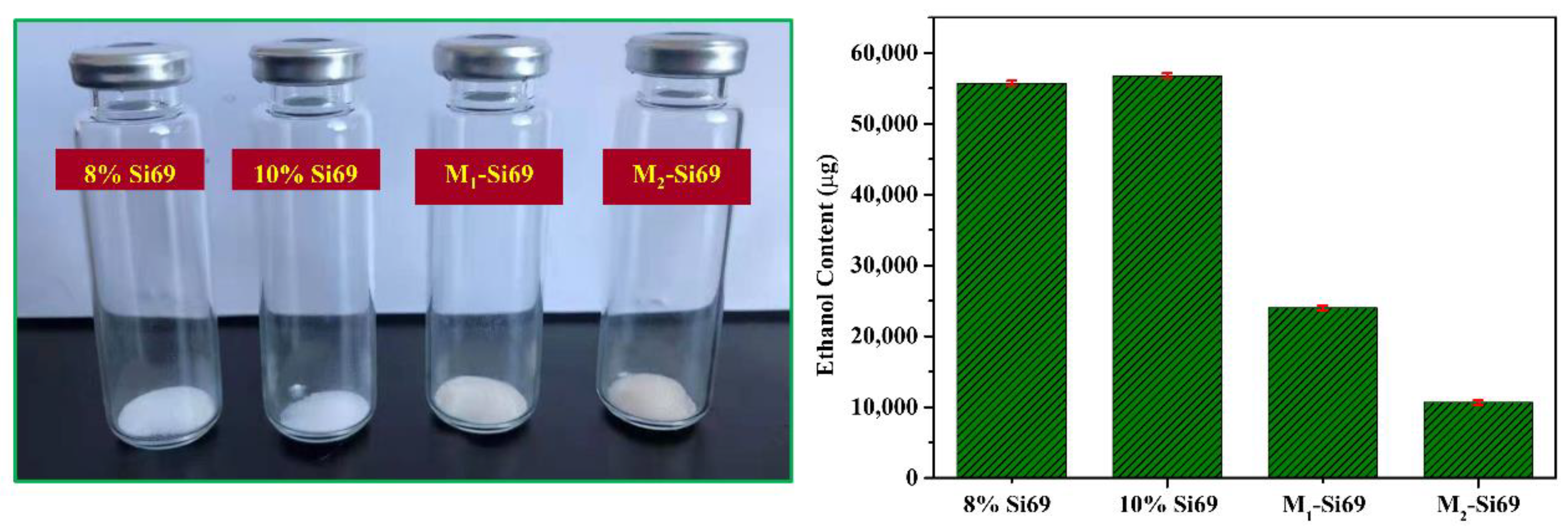
3.2.7. VOC Contents of Different Coupling Agents Reacted with Silica
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akutagawa, K. Technology for Reducing Tire Rolling Resistance. Tribol. Online 2017, 12, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanorkar, R.J.; Mohanty, S.; Gupta, V.K. Synthesis of Functionalized Styrene Butadiene Rubber and Its Applications in SBR–Silica Composites for High Performance Tire Applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 4517–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Morris, M.; Doshi, D. Materials development for lowering rolling resistance of tires. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2016, 89, 79–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrana, C.; Eisele, U.; Kelbch, S. Measurement and molecular modeling of rolling resistance in tire treads. Kautsch. Gummi Kunstst. 2000, 53, 126–128. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Han, B.; Wen, S.; Lu, Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L. Effect of the temperature on surface modification of silica and properties of modified silica filled rubber composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 62, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Lu, J.; Song, W.; Hu, J.; Han, B. Solution Mechanochemical Approach for Preparing High-Dispersion SiO2-g-SSBR and the Performance of Modified Silica/SSBR Composites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 7146–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.J.; Brown, P.; Chapman, A.V.; Cook, S. Silica-reinforced epoxidized natural rubber tire treads—Performance and durability. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2015, 88, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, P.; Tang, Z.; Guo, B. Solving “magic triangle” of tread rubber composites with phosphonium-modified petroleum resin. Polymer 2020, 190, 122244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, A. Cryptocurrency Market Analysis from the Open Innovation Perspective. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylov, A. Development of Friedrich von Hayek’s theory of private money and economic implications for digital currencies. Terra Econ. 2021, 19, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Zhou, X.; Russell, T.P.; Hua, K.-C.; Yang, X.; Qiao, H.; Wang, W.; Li, F.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L. High performance bio-based elastomers: Energy efficient and sustainable materials for tires. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13058–13062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L. Structure and Performance of Silica-Grafted Epoxidized Solution-Polymerized Styrene–Butadiene Nanocomposites. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2022, 61, 3031–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, P.E. History of Natural Rubber. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A—Chem. 2006, 15, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guo, X.; Luo, Y.; Jia, Z.; Bai, J.; Chen, Y.; Jia, D. Effect of novel supported vulcanizing agent on the interfacial interaction and strain-induced crystallization properties of natural rubber nanocomposites. Polymer 2018, 148, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.business-biodiversity.eu/en/natural-rubber (accessed on 3 October 2022).
- Poompradub, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Kokubo, Y.; Shiono, T. Cuttlebone as reinforcing filler for natural rubber. Eur. Polym. J. 2008, 44, 4157–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arayapranee, W.; Rempel, G.L. A comparative study of the cure characteristics, processability, mechanical properties, ageing, and morphology of rice husk ash, silica and carbon black filled 75: 25 NR/EPDM blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 932–941. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkawi, S.S.; Kaewsakul, W.; Sahakaro, K.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W. A review on reinforcement of natural rubber by silica fillers for use in low-rolling resistance tires. J. Rubber Res. 2015, 18, 203–233. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.C.; Adhikari, J.; Kim, J.K.; Saha, P. Preparation of novel bio-elastomers with enhanced interaction with silica filler for low rolling resistance and improved wet grip. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 208, 1622–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Han, D.; Ye, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Chemical and physical interaction between silane coupling agent with long arms and silica and its effect on silica/natural rubber composites. Polymer 2018, 135, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Ye, X.; Han, D.; Zhao, S.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Dong, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L. Silica Modified by Alcohol Polyoxyethylene Ether and Silane Coupling Agent Together to Achieve High Performance Rubber Composites Using the Latex Compounding Method. Polymers 2017, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Han, D.; Zhang, G.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Ye, X.; Zhang, L. A novel VOC free bio-based coupling agent and its using strategy facing green tires with excellent dynamic performances. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 223, 109413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zheng, J.; Han, B.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; Ye, X. Designing novel epoxy-terminated polybutadiene to construct chemical interface between nanosilica and rubbers with green nature. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 178, 107451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, N.; Zheng, J.; Ye, X.; Xue, J.; Han, D.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L. Performance enhancement of rubber composites using VOC-Free interfacial silica coupling agent. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 202, 108301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Chen, Y.; Han, D.; Zheng, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Ye, X.; Zhang, L. New designed coupling agents for silica used in green tires with low VOCs and low rolling resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 558, 149819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkawi, S.S. Silica-Reinforced Deproteinized Natural Rubber. In Silicon Materials; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Jia, Z.; Wu, L.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D.; Peng, Z. Influence of acetone extract from natural rubber on the structure and interface interaction in NR/silica composites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkawi, S.S.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W. Natural rubber-silica combinations for low rolling resistance truck tyre treads. Rubber World 2012, 2012, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin, V.V.; Ecker, E.; Stepanov, G.V.; Shamonin, M.; Monkman, G.J.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R. Experimental study of the magnetic field enhanced Payne effect in magnetorheological elastomers. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8765–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdov, A.D.; Dorfmann, A. The payne effect for particle-reinforced elastomers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2002, 42, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luginsland, H.-D.; Röben, C. The Development of Sulphur-Functional Silanes as Coupling Agents in Silica-Reinforced Rubber Compounds. Their Historical Development over Several Decades. Int. Polym. Sci. Technol. 2016, 43, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zou, H.; Zhang, L.; Ye, X.; Han, D. Surface modification of silica nanoparticles by a polyoxyethylene sorbitan and silane coupling agent to prepare high-performance rubber composites. Polym. Test. 2019, 81, 106195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L. Novel percolation phenomena and mechanism of strengthening elastomers by nanofillers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2010, 12, 3014–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Huang, Q.; Gao, H.; Zhao, S. Development of raw materials for green tire. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2016, 61, 3348–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, D.; Liu, B.; Wu, S.; Tang, Z.; Guo, B. Rubber-reinforced rubbers toward the combination of high reinforcement and low energy loss. Nano Energy 2021, 83, 105822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.; Wu, Y.-P.; Li, W.-J.; Zhang, L.-Q. Influence of filler type on wet skid resistance of SSBR/BR composites: Effects from roughness and micro-hardness of rubber surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 2058–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takino, H.; Nakayama, R.; Yamada, Y.; Kohjiya, S.; Matsuo, T. Viscoelastic Properties of Elastomers and Tire Wet Skid Resistance. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1997, 70, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassim, D.H.A.I.; Abraham, F.; Summerscales, J.; Brown, P. The effect of interface morphology in waste tyre rubber powder filled elastomeric matrices on the tear and abrasion resistance. Express Polym. Lett. 2019, 13, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sare, I.R. Abrasion resistance and fracture toughness of white cast irons. Met. Technol. 1979, 6, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutton, P.; Watson, J. Some effects of microstructure on the abrasion resistance of metals. Wear 1978, 48, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Materials/Phr a | NR–PS | IR–PS | NR–8% Si69 | NR–10% Si69 | IR–Si69 | NR–Mx–Si69 | IR–Mx–Si69 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | 100 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| IR | 100 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | |
| silica | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Mx–Si69 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| Si69 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| other additives b | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 | 14 |
| Sample | Mn a/(g/mol) | Mw b/(g/mol) | Ð c |
|---|---|---|---|
| NR | 488,346 | 1,269,122 | 2.60 |
| IR | 484,641 | 1,157,461 | 2.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhai, X.; Chen, X.; Zheng, F.; Han, D.; Zheng, J.; Ye, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Designing a Coupling Agent with Aliphatic Polyether Chain and Exploring Its Effect on Silica/Natural Rubber Nanocomposites under the Action of Non-Rubber Contents. Polymers 2023, 15, 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030674
Zhai X, Chen X, Zheng F, Han D, Zheng J, Ye X, Li X, Zhang L. Designing a Coupling Agent with Aliphatic Polyether Chain and Exploring Its Effect on Silica/Natural Rubber Nanocomposites under the Action of Non-Rubber Contents. Polymers. 2023; 15(3):674. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030674
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhai, Xiaobo, Xin Chen, Fangyuan Zheng, Dongli Han, Junchi Zheng, Xin Ye, Xiaolin Li, and Liqun Zhang. 2023. "Designing a Coupling Agent with Aliphatic Polyether Chain and Exploring Its Effect on Silica/Natural Rubber Nanocomposites under the Action of Non-Rubber Contents" Polymers 15, no. 3: 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030674
APA StyleZhai, X., Chen, X., Zheng, F., Han, D., Zheng, J., Ye, X., Li, X., & Zhang, L. (2023). Designing a Coupling Agent with Aliphatic Polyether Chain and Exploring Its Effect on Silica/Natural Rubber Nanocomposites under the Action of Non-Rubber Contents. Polymers, 15(3), 674. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15030674






