Stimuli-Responsive Protein Hydrogels: Their Design, Properties, and Biomedical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
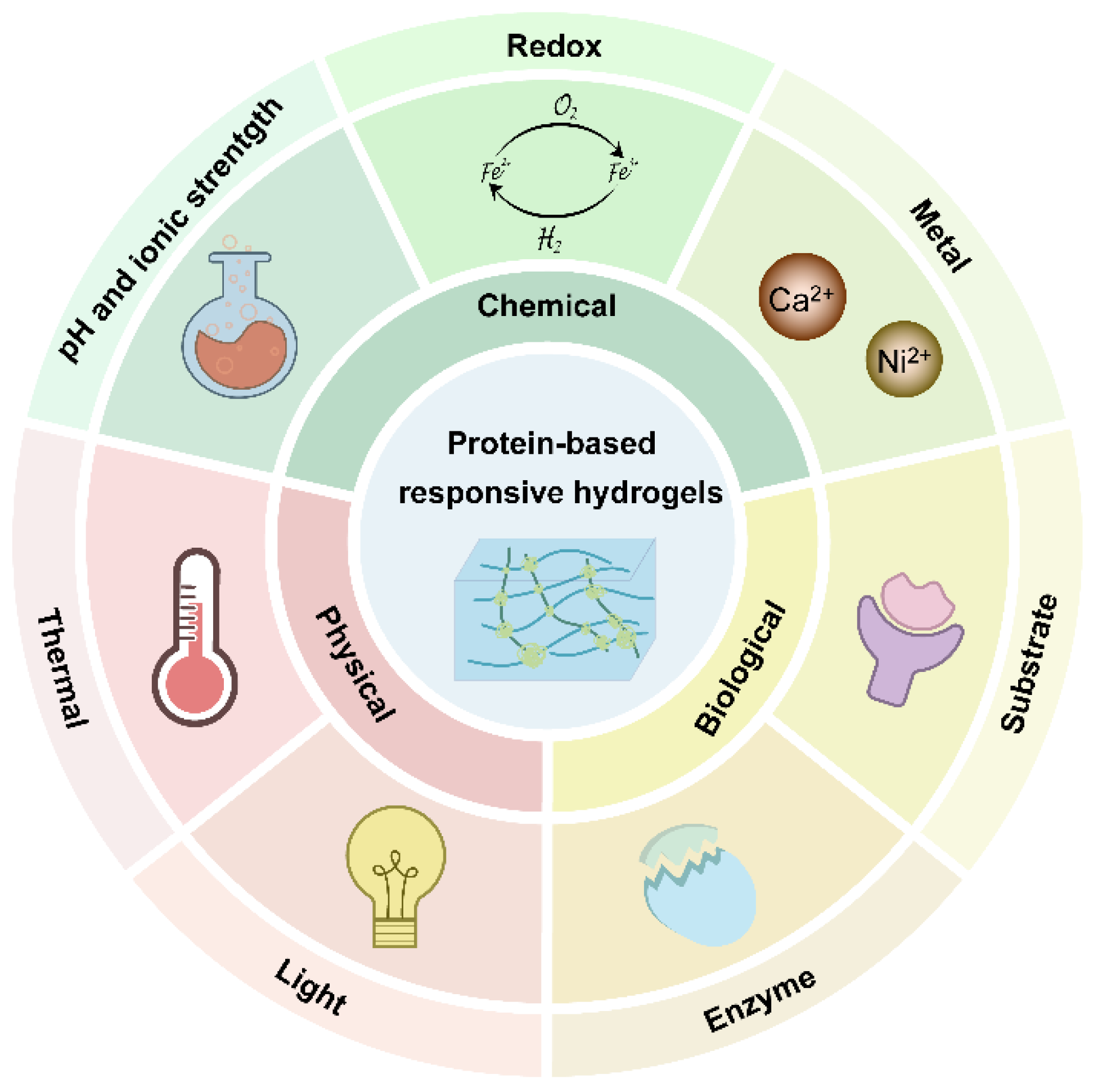
2. The Current Development of Responsive Protein Hydrogels
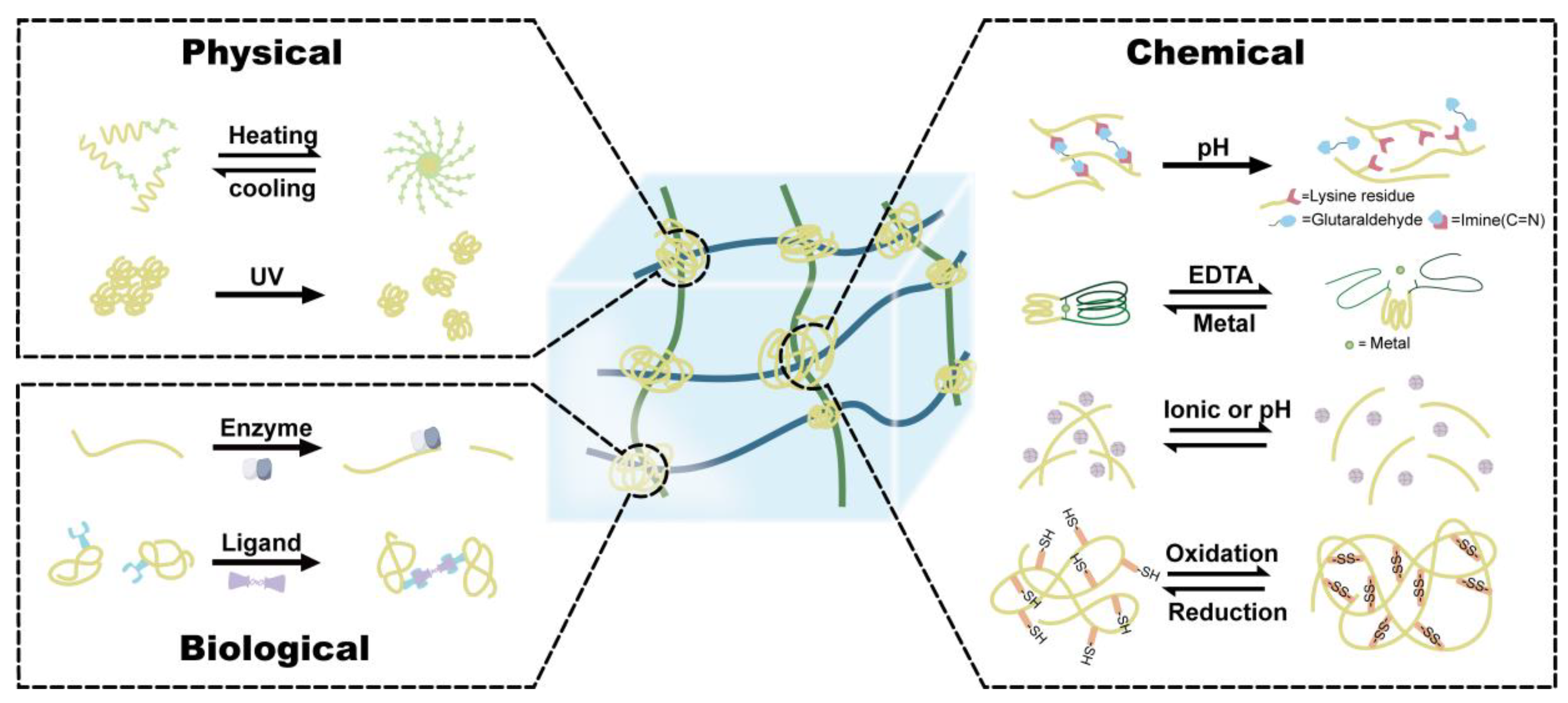
2.1. Physical-Responsive Hydrogel
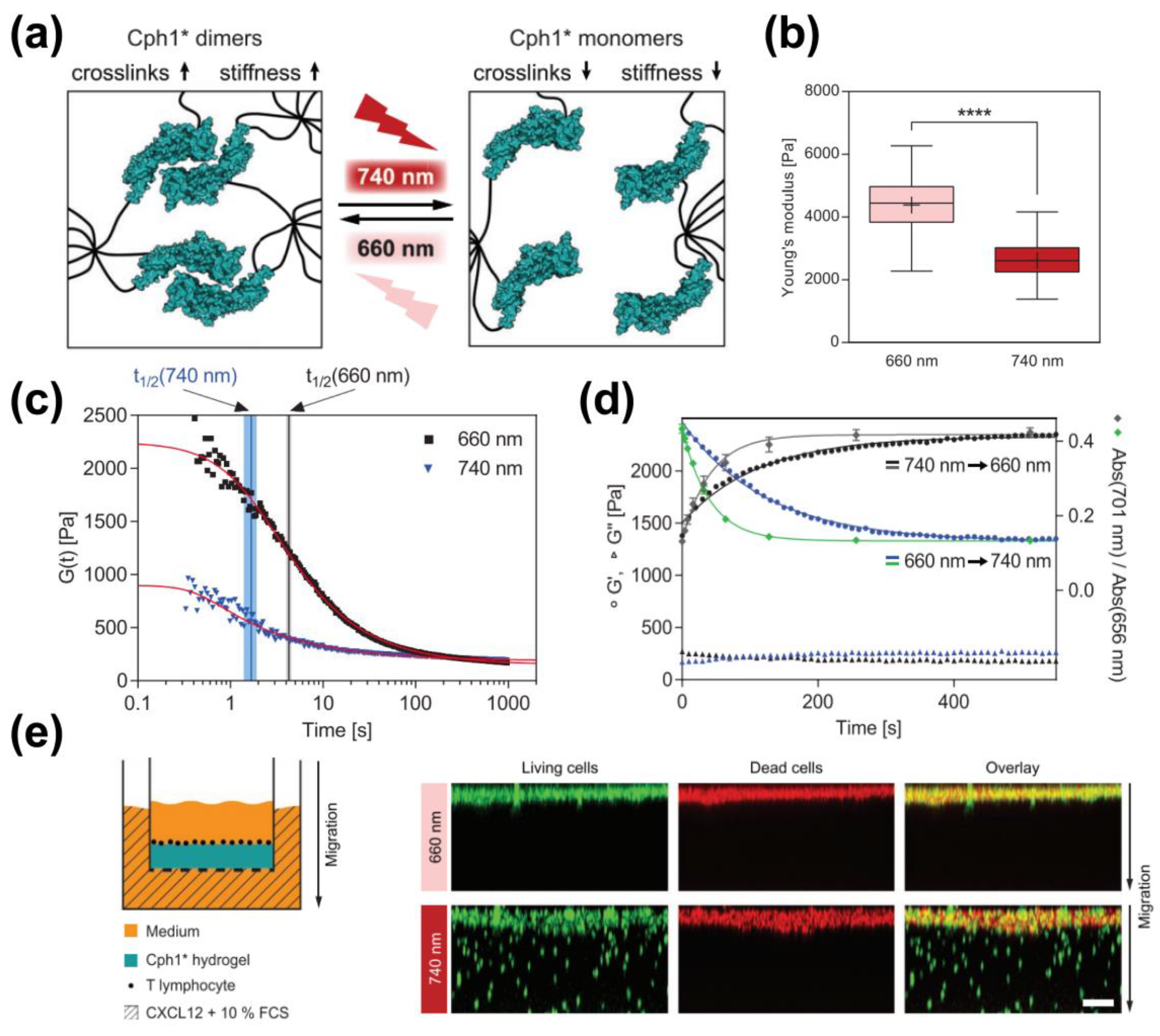
2.1.1. Photo-Responsive Hydrogel
2.1.2. Thermal-Responsive Hydrogel
2.2. Chemical-Responsive Hydrogel
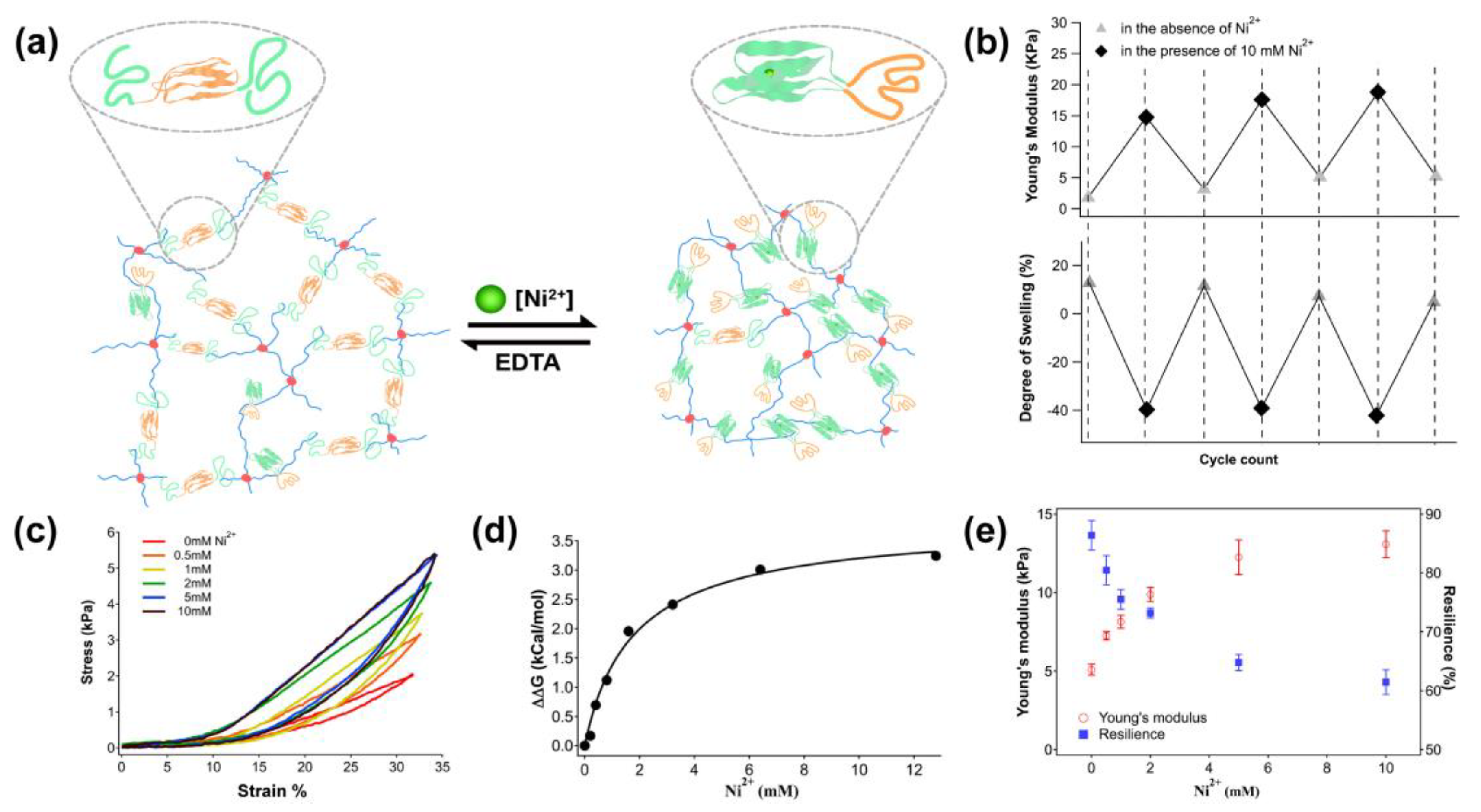
2.2.1. Metal Ion-Responsive Hydrogel
2.2.2. Redox-Responsive Hydrogel
2.2.3. pH- and Ionic Strength-Responsive Hydrogel
2.3. Biologically Responsive Hydrogel
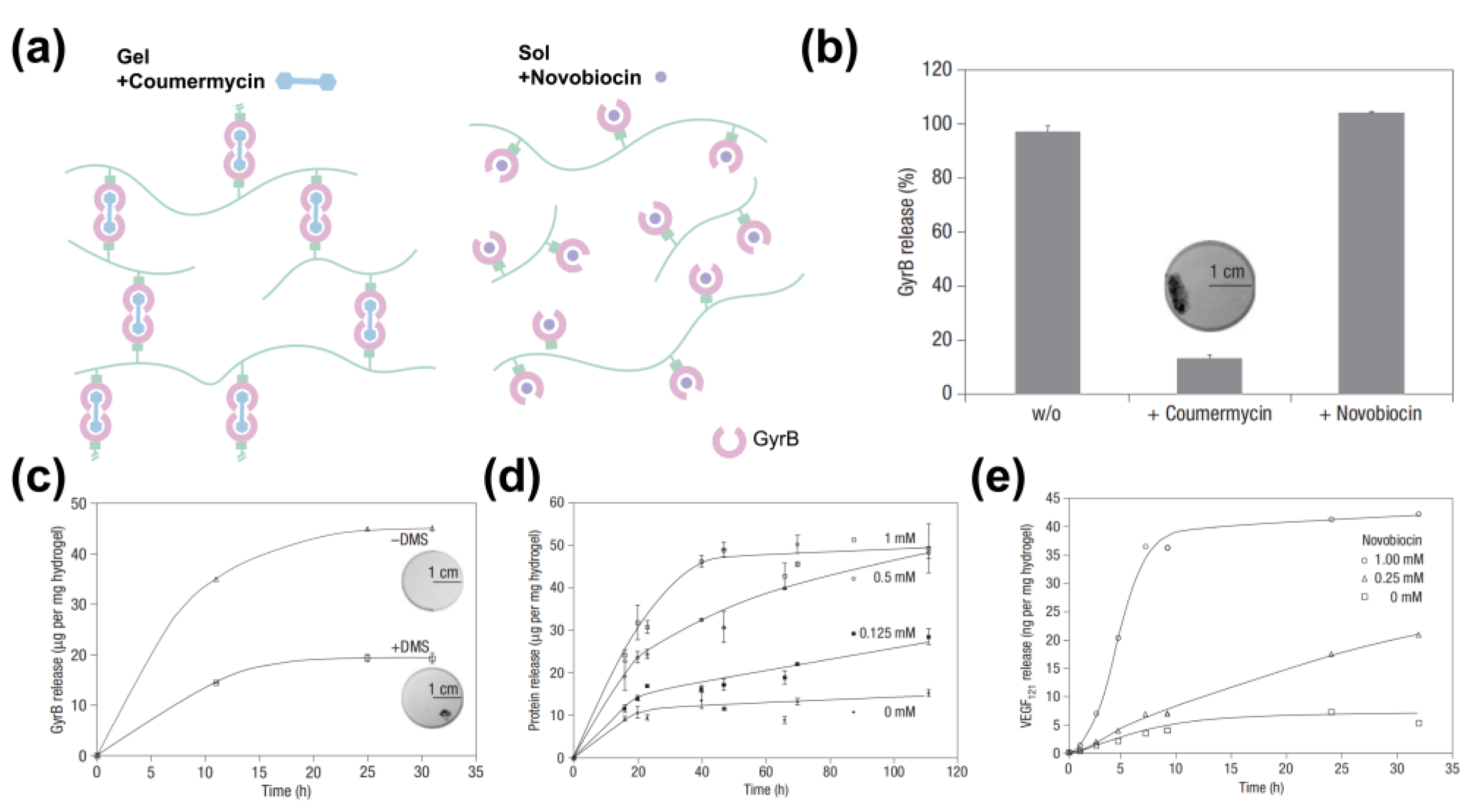
2.3.1. Ligand-Responsive Protein Hydrogel
2.3.2. Enzyme-Responsive Protein Hydrogel
3. General Principles for the Design and Fabrication of Responsive-Protein Hydrogels
3.1. Photo-Responsive Crosslinks
3.2. Temperature-Induced Reversible Phase Transition
3.3. Reversible Covalent Crosslinks
3.4. Reversible Non-Covalent Crosslinks
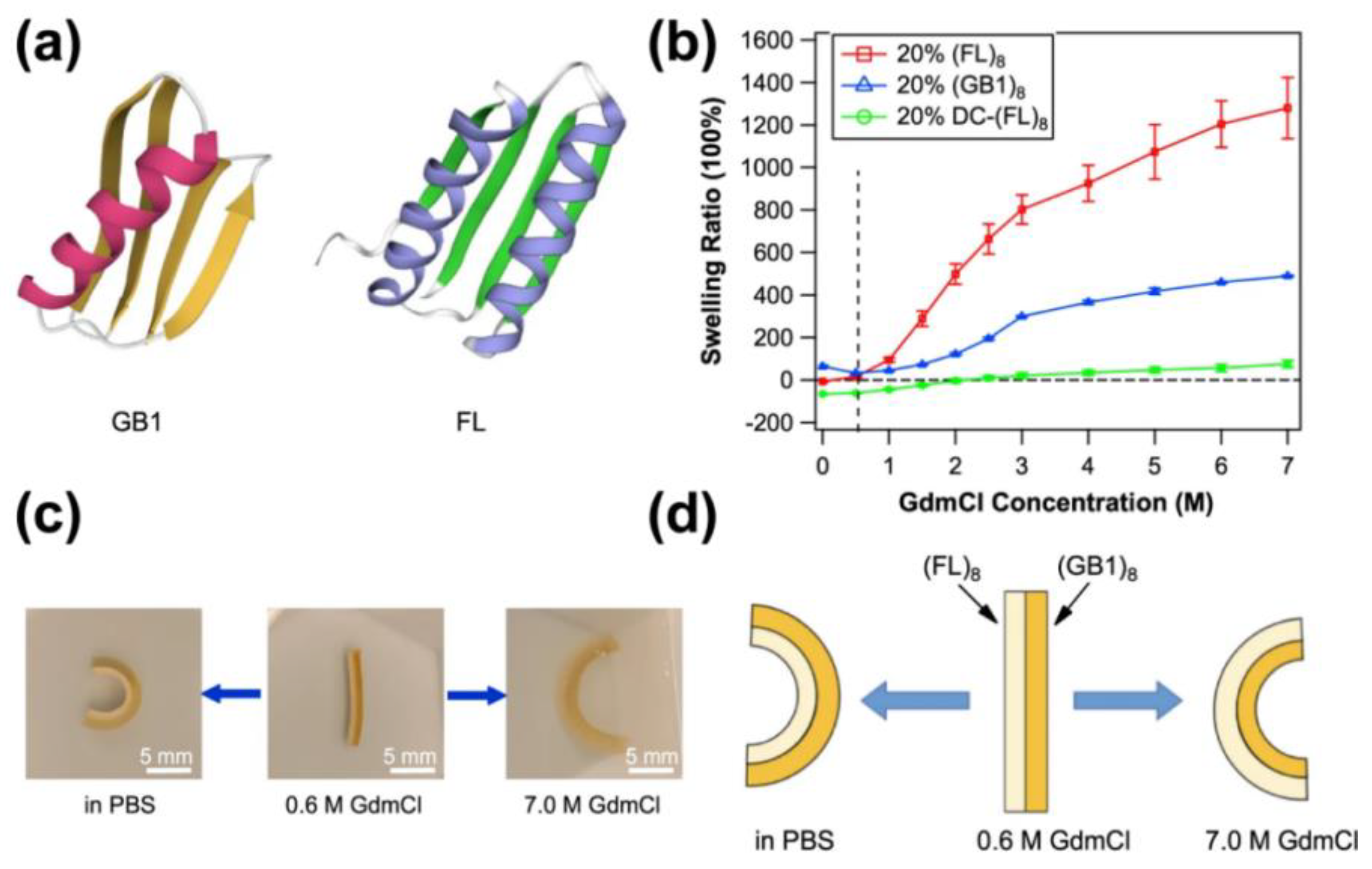
3.5. Folding/Unfolding
4. Discussion
4.1. Precise Control over Responsiveness
4.2. Expanding the Responsive Scope
4.3. Multi-Responsive Protein Hydrogel
4.4. AI-Assisted Responsive Protein Hydrogel
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vashist, A.; Kaushik, A.; Vashist, A.; Sagar, V.; Ghosal, A.; Gupta, Y.K.; Ahmad, S.; Nair, M. Advances in Carbon Nano-tubes-Hydrogel Hybrids in Nanomedicine for Therapeutics. Adv. Healthc. Mater 2018, 7, e1701213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.-W.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S. Recent Advances in Polymer Additive Engineering for Diagnostic and Therapeutic Hydrogels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, N.; Chauhan, M.K.; Chauhan, V.S. Short to Ultrashort Peptide-Based Hydrogels as a Platform for Biomedical Appli-cations. Biomater. Sci. 2020, 8, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davari, N.; Bakhtiary, N.; Khajehmohammadi, M.; Sarkari, S.; Tolabi, H.; Ghorbani, F.; Ghalandari, B. Protein-Based Hydrogels: Promising Materials for Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2022, 14, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chander, S.; Kulkarni, G.T.; Dhiman, N.; Kharkwal, H. Protein-Based Nanohydrogels for Bioactive Delivery. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 573748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zhang, K. Current Hydrogel Advances in Physicochemical and Biological Re-sponse-Driven Biomedical Application Diversity. Signal Transduct Tar. 2021, 6, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deptuch, T.; Penderecka, K.; Kaczmarek, M.; Molenda, S.; Dams-Kozlowska, H. In vivo study of the immune response to bioengineered spider silk spheres. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xue, B.; Cao, Y. 100th Anniversary of Macromolecular Science Viewpoint: Synthetic Protein Hydrogels. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 9, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörner, M.; Raute, K.; Hummel, B.; Madl, J.; Creusen, G.; Thomas, O.S.; Christen, E.H.; Hotz, N.; Gübeli, R.J.; Engesser, R.; et al. Phytochrome-Based Extracellular Matrix with Reversibly Tunable Mechanical Properties. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, e1806727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.K.; Meleties, M.; Katyal, P.; Xie, X.; Delgado-Fukushima, E.; Jihad, T.; Liu, C.-F.; O’neill, S.; Tu, R.S.; Renfrew, P.D.; et al. Thermoresponsive Protein-Engineered Coiled-Coil Hydrogel for Sustained Small Molecule Release. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3340–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, G.; Rivkin, A.; Lapidot, S.; Hu, X.; Preis, I.; Arinus, S.B.; Dgany, O.; Shoseyov, O.; Kaplan, D.L. Recombinant exon-encoded resilins for elastomeric biomaterials. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 9231–9243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.D.G.; Cussons, S.; Mahmoudi, N.; Brockwell, D.J.; Dougan, L. Tuning Protein Hydrogel Mechanics through Mod-ulation of Nanoscale Unfolding and Entanglement in Postgelation Relaxation. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 10667–10678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Goudounet, G.; Zhao, H.; Garbay, B.; Garanger, E.; Pecastaings, G.; Schultze, X.; Lecommandoux, S. Thermosensitive Hybrid Elastin-like Polypeptide-Based ABC Triblock Hydrogel. Macromolecules 2020, 54, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, H.M.; Thomas, O.S.; Riegel, N.; Zurbriggen, M.D.; Weber, W.; Hörner, M. Generic and reversible opto-trapping of biomolecules. Acta Biomater. 2018, 79, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Bian, Q.; Li, H. Light-Responsive Dynamic Protein Hydrogels Based on LOVTRAP. Langmuir 2021, 37, 10214–10222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Yang, Z.; Luo, J.; Hsing, I.-M.; Sun, F. B12–dependent photoresponsive protein hydrogels for controlled stem cell/protein release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5912–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, O.P.; Mu, X.; Hasturk, O.; Kaplan, D.L. Dynamically tunable light responsive silk-elastin-like proteins. Acta Biomater. 2020, 121, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, C.; Huang, W.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Ding, D.; Zhou, H.; Long, J.; Wang, T.; Yang, Z. Rational design of a photo-responsive UVR8-derived protein and a self-assembling peptide–protein conjugate for responsive hydrogel formation. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16666–16670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Fang, J.; Duan, T.; Fu, L.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Optically controlled reversible protein hydrogels based on photoswitchable fluorescent protein Dronpa. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 13375–13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Huang, W.; Wu, W.-H.; Xue, B.; Xiang, D.; Li, Y.; Qin, M.; Sun, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.-B.; et al. Reversible hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties for optically controlling cell migration. Nano Res. 2017, 11, 5556–5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadish, J.A.; Strange, A.C.; DeForest, C.A. Genetically Encoded Photocleavable Linkers for Patterned Protein Release from Biomaterials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 15619–15625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, D.; Wu, X.; Cao, W.; Xue, B.; Qin, M.; Cao, Y.; Wang, W. Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Properties Based on Photocleavable Proteins. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Sun, W.; Tong, Z. Ultrafast and Programmable Shape Memory Hydrogel of Gelatin Soaked in Tannic Acid Solution. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 46701–46709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, R.N.; Cairns, D.M.; Wu, W.A.; Jordan, K.; Guo, C.; Huang, W.; Martin-Moldes, Z.; Kaplan, D.L. Smart Material Hy-drogel Transfer Devices Fabricated with Stimuli-Responsive Silk-Elastin-Like Proteins. Adv. Healthc. Mater 2020, 9, e2000266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.; Li, H. In Situ Phase Transition of Elastin-Like Polypeptide Chains Regulates Thermoresponsive Properties of Elas-tomeric Protein-Based Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2258–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.-W.; Qian, Z.-G.; Liu, H.; Chen, H.-F.; Kaplan, D.L.; Xia, X.-X. On-Demand Regulation of Dual Thermosensitive Protein Hydrogels. ACS Macro Lett. 2021, 10, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, S.-H.; Kim, A.; Shin, W.; Heo, M.B.; Noh, H.J.; Hong, K.S.; Cho, J.-H.; Lim, Y.T. Photothermal-modulated drug delivery and magnetic relaxation based on collagen/poly(γ-glutamic acid) hydrogel. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2607–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.-G.; Zhou, M.-L.; Song, W.-W.; Xia, X.-X. Dual Thermosensitive Hydrogels Assembled from the Conserved C-Terminal Domain of Spider Dragline Silk. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3704–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.; Li, H. Rationally Designed Dynamic Protein Hydrogels with Reversibly Tunable Mechanical Properties. Biophys. J. 2016, 110, 40a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Montclare, J.K. Effect of Divalent Metal Cations on the Conformation, Elastic Behavior, and Controlled Release of a Photocrosslinked Protein Engineered Hydrogel. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 3587–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, N.; Fu, L.; Peng, Q.; Li, H. Metal Chelation Dynamically Regulates the Mechanical Properties of Engineered Protein Hydrogels. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 3, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.; Yang, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Wegner, S.V.; Sun, F. Cobalt-Cross-Linked, Redox-Responsive Spy Network Protein Hy-drogels. ACS Macro Lett. 2019, 8, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, B.; Liu, X.; Yang, C.; Yang, Z.; Luo, J.; Kou, S.; Liu, K.; Sun, F. Injectable, photoresponsive hydrogels for delivering neuroprotective proteins enabled by metal-directed protein assembly. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tan, B.; Wang, S.; Tang, R.; Bao, Z.; Chen, G.; Chen, S.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.; Long, C.; et al. Rationally designed protein cross-linked hydrogel for bone regeneration via synergistic release of magnesium and zinc ions. Biomaterials 2021, 274, 120895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Sun, F. Calcium-responsive hydrogels enabled by inducible protein–protein interactions. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 4973–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallivan, J.P.; Topp, S. Engineering of Stimuli-Sensitive Biomaterials That Respond to Calcium Ions. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. S 2004, 227, U430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, M.-L.; Qian, Z.-G.; Chen, L.; Kaplan, D.L.; Xia, X.-X. Rationally Designed Redox-Sensitive Protein Hydrogels with Tunable Mechanical Properties. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 3508–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikfarjam, S.; Gibbons, R.; Burni, F.; Raghavan, S.R.; Anisimov, M.A.; Woehl, T.J. Chemically Fueled Dissipative Cross-Linking of Protein Hydrogels Mediated by Protein Unfolding. Biomacromolecules 2023, 24, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.; Obst, F.; Geisler, M.; Che, Y.; Richter, A.; Appelhans, D.; Gaitzsch, J.; Voit, B. Reversible Protein Capture and Release by Redox-Responsive Hydrogel in Microfluidics. Polymers 2022, 14, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Cao, Z.; Yang, G. Tunable keratin hydrogel based on disulfide shuffling strategy for drug delivery and tissue engineering. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 544, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, T.R.; Lee, R.T.; Han, S.; Haque, S.; Vodovotz, Y.; Gu, J.; Burnett, L.R.; Tomblyn, S.; Saul, J.M. Tunable Keratin Hydrogels for Controlled Erosion and Growth Factor Delivery. Biomacromolecules 2015, 17, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcgill, M.; Grant, J.M.; Kaplan, D.L. Enzyme-Mediated Conjugation of Peptides to Silk Fibroin for Facile Hydrogel Function-alization. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 48, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Man, S.; Guo, Z.; et al. Genetically encoded in situ gelation redox-responsive collagen-like protein hydrogel for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2023, 11, 7748–7758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, D.; Xu, D.; Liu, W.; Quiroz, F.G.; Callahan, D.J.; Zalutsky, M.R.; Craig, S.L.; Chilkoti, A. Protein polymer hydrogels by in situ, rapid and reversible self-gelation. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5451–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Liu, J.; Li, H. Engineering protein polymers of ultrahigh molecular weight via supramolecular polymerization: Towards mimicking the giant muscle protein titin. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 9277–9284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Shang, L.; Gu, Z.; Zhao, Y. Bio-inspired self-healing structural color hydrogel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5900–5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Fei, J.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, J. Stimuli-Responsive Dipeptide–Protein Hydrogels through Schiff Base Coassembly. Macromol. Rapid Comm. 2017, 38, 1700408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Q.; Fu, L.; Li, H. Engineering shape memory and morphing protein hydrogels based on protein unfolding and folding. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, L.R.; Popa, I. Chemical unfolding of protein domains induces shape change in programmed protein hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perovic, I.; Davidyants, A.; Evans, J.S. Aragonite-Associated Mollusk Shell Protein Aggregates To Form Mesoscale “Smart” Hydrogels. ACS Omega 2016, 1, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, P.A.; St-Pierre, J.-P.; Chow, L.W.; Spicer, C.D.; Stoichevska, V.; Peng, Y.Y.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Ramshaw, J.A.; Stevens, M.M. Enhanced articular cartilage by human mesenchymal stem cells in enzymatically mediated transiently RGDS-functionalized collagen-mimetic hydrogels. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, P.A.; Skaalure, S.C.; Chow, L.W.; St-Pierre, J.-P.; Stoichevska, V.; Peng, Y.Y.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Ramshaw, J.A.; Stevens, M.M. Temporally degradable collagen–mimetic hydrogels tuned to chondrogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2016, 99, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, P.A.; Chow, L.W.; St-Pierre, J.P.; Horejs, C.M.; Peng, Y.Y.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Ramshaw, J.A.; Stevens, M.M. Colla-gen-Mimetic Peptide-Modifiable Hydrogels for Articular Cartilage Regeneration. Biomaterials 2015, 54, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.-R.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Syue, M.-H.; Wang, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-Y.; Huang, T.-W.; Young, T.-H. Controlled Decomposable Hydrogel Triggered with a Specific Enzyme. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 3254–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Yang, J.; Kopeckova, P.; Kopecek, J. Smart Hydrogels Containing Adenylate Kinase: Translating Substrate Recog-nition into Macroscopic Motion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 15760–15761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrbar, M.; Schoenmakers, R.; Christen, E.H.; Fussenegger, M.; Weber, W. Drug-sensing hydrogels for the inducible release of biopharmaceuticals. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, W.J.; Pytel, N.J.; Ng, K.; Murphy, W.L. Triggered Drug Release from Dynamic Microspheres via a Protein Conformational Change. Macromol. Biosci. 2010, 10, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, M.D.G.; Cussons, S.; Mahmoudi, N.; Brockwell, D.J.; Dougan, L. Single molecule protein stabilisation translates to macromolecular mechanics of a protein network. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 6389–6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.X.; Chung, H.K.; Lam, A.J.; Lin, M.Z. Optical Control of Protein Activity by Fluorescent Protein Domains. Science 2012, 338, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Hu, Q.; Yan, Z.; Chen, W.; Yan, C.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, P.; Deng, H.; Wang, J.; et al. Structural Basis of Ultra-violet-B Perception by Uvr8. Nature 2012, 484, 214–219. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, J.A.; Ruta, A.; West, J.L. Using Tools from Optogenetics to Create Light-Responsive Biomaterials: Lovtrap-Peg Hy-drogels for Dynamic Peptide Immobilization. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 48, 1885–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Lohman, A.W.; Zhuravlova, Y.; Lu, X.; Wiens, M.D.; Hoi, H.; Yaganoglu, S.; A Mohr, M.; Kitova, E.N.; Klassen, J.S.; et al. Optogenetic control with a photocleavable protein, PhoCl. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerlund, A.M.; Delemotte, L. Effect of Ca2+ on the promiscuous target-protein binding of calmodulin. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, S.; Yan, T.; Fan, X.; Li, F.; Yang, X.; Ren, B.; Xu, J.; Liu, J. Injectable and fast self-healing protein hydrogels. Soft Matter 2019, 15, 7583–7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, R.S.; Galas, R.J.; Lin, C.; Liu, J.C. Redox-Responsive Resilin-Like Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering and Drug Delivery Applications. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, e1900122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, G.S.; Pérez-Chávez, N.A.; Szleifer, I. How Protonation Modulates the Interaction between Proteins and Ph-Responsive Hydrogel Films. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 41, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, S.; Komiyama, T.; Masuzawa, T.; Yokoya, M.; Oyoshi, T.; Yamanaka, M. Bovine Serum Albumin Hydrogel Formation: pH Dependence and Rheological Analyses. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2023, 71, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, D.; Xue, X. Fabrication of Ph-Responsive Ta-Keratin Bio-Composited Hydrogels Encapsulated with Photoluminescent Go Quantum Dots for Improved Bacterial Inhibition and Healing Efficacy in Wound Care Management: In Vivo Wound Evaluations. J. Photoch. Photobio B 2020, 202, 111676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Tian, Y.; Pang, L.; Xu, T.; Yu, B.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y. Wound Microenvironment-Responsive Protein Hydrogel Drug-Loaded System with Accelerating Healing and Antibacterial Property. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 10187–10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce, C.B.; Evans, J.S. Polymorph Crystal Selection by n16, an Intrinsically Disordered Nacre Framework Protein. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 4690–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S. Hofmeister Effect-Assisted One Step Fabrication of Ductile and Strong Gelatin Hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Su, D.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, F.; Ding, W.; Zhang, S.; Dong, J. Salt-Assisted Toughening of Protein Hydrogel with Controlled Degradation for Bone Regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Long, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Dual-Crosslinked Mussel-Inspired Smart Hydrogels with Enhanced Antibacterial and Angiogenic Properties for Chronic Infected Diabetic Wound Treatment Via Ph-Responsive Quick Cargo Release. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yang, Z. Benzoic-Imine-Based Physiological-Ph-Responsive Materials for Biomedical Applications. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 2633–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.G.; Lin, P.; Schmidt, C.E. Biodegradable Hydrogels Composed of Oxime Crosslinked Poly(Ethylene Glycol), Hyaluronic Acid and Collagen: A Tunable Platform for Soft Tissue Engineering. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed 2015, 26, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Mehlich, A.; Koga, N.; Huang, J.; Koga, R.; Gao, X.; Hu, C.; Jin, C.; Rief, M.; Kast, J.; et al. Forced protein unfolding leads to highly elastic and tough protein hydrogels. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, Z.; King, W.J.; Murphy, W.L. Dynamic Materials Based on a Protein Conformational Change. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3377–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, B.; Fierer, J.O.; Celik, E.; Chittock, E.C.; Schwarz-Linek, U.; Moy, V.T.; Howarth, M. Peptide tag forming a rapid covalent bond to a protein, through engineering a bacterial adhesin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E690–E697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkenberg, M.R.; Moore, D.M.; Lin, C.C. Dynamic Control of Hydrogel Crosslinking Via Sortase-Mediated Reversible Trans-peptidation. Acta Biomater. 2019, 83, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadish, J.A.; Benuska, G.M.; DeForest, C.A. Bioactive site-specifically modified proteins for 4D patterning of gel biomaterials. Nat. Mater. 2019, 18, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.; Hart, S.A.; Schink, A.; Pollok, B.A. Sortase-Mediated Protein Ligation: A New Method for Protein Engineering. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 2670–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.A.; Chen, Z. Split-Intein Triggered Protein Hydrogels. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1495, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Andresen, M.; Stiel, A.C.; Trowitzsch, S.; Weber, G.; Eggeling, C.; Wahl, M.C.; Hell, S.W.; Jakobs, S. Structural Basis for Re-versible Photoswitching in Dronpa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13005–13009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Vilela, M.; Winkler, A.; Tarnawski, M.; Schlichting, I.; Yumerefendi, H.; Kuhlman, B.; Liu, R.; Danuser, G.; Hahn, K.M. LOVTRAP: An optogenetic system for photoinduced protein dissociation. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijenhuis, K.T. On the nature of crosslinks in thermoreversible gels. Polym. Bull. 2006, 58, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Liu, X.; Xiong, J.; Feng, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, H.; Xiao, K. Ph-Responsive Hyperbranched Polypeptides Based on Schiff Bases as Drug Carriers for Reducing Toxicity of Chemotherapy. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13889–13899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, A.; Li, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, X.; Cao, Z.; Nie, H.; Yang, G. Injectable keratin hydrogels as hemostatic and wound dressing materials. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 4169–4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.-C.; Martin-Martinez, F.J.; Qin, Z.; Dennis, P.B.; Gupta, M.K.; Naik, R.R.; Buehler, M.J. Ion Effect and Met-al-Coordinated Cross-Linking for Multiscale Design of Nereis Jaw Inspired Mechanomutable Materials. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 1858–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahajpal, K.; Shekhar, S.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, B.; Meena, M.K.; Bhagi, A.K.; Sharma, S. Dynamic protein and polypeptide hydrogels based on Schiff base co-assembly for biomedicine. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 3173–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shymborska, Y.; Budkowski, A.; Raczkowska, J.; Donchak, V.; Melnyk, Y.; Vasiichuk, V.; Stetsyshyn, Y. Switching it Up: The Promise of Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Systems in Biomedical Science. Chem. Rec. 2023, e202300217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.-H.; Liu, T.-Y.; Liu, D.-M.; Chen, S.-Y. Nano-ferrosponges for controlled drug release. J. Control. Release 2007, 121, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Jeon, J.; Zhu, Y.; Hoppe, E.D.; Jun, Y.-S.; Genin, G.M.; Zhang, F. A Biosynthetic Hybrid Spidroin-Amyloid-Mussel Foot Protein for Underwater Adhesion on Diverse Surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48457–48468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Type of Stimuli | Stimuli-Response Mode | Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Light | Oligomerization switch of photoreceptors induced by light | Cph1 [9], PhyB-PIF6 [14], LOV2-zdk1 [15], CarHc [16,17], UVR8 [18], Dronpa145N [19,20] |
| Photo cleavage | PhoCl [21,22] | |
| Temperature | Temperature-induced phase transition | Tannic-gelatin [23], Q protein [10], ELPs and ELP-derived peptides [13,24,25,26], γ-glutamic-collagen [27], |
| Non-covalent protein assembly | CTD [28] | |
| Metal ion | Metal coordination with histidine residues | His-tag coordinate with Ni2+ [29,30,31], Co2+ [32], Zn2+ [33,34] |
| Ca2+-induced protein self-assembly | Ca2+-dependent CaM-ligand M13-peptide binding [35,36] | |
| Redox | Inter-and-intra cysteine-disulfide transition | Disulfide bonds in Resilin [11], SELPs [37], BSA [38,39], keratin [40,41], SF [42], CLP [43], ELP [44] |
| Disulfide bond mediated assembly of split protein | Split GN/GC [45] | |
| pH and Ionic strength | Reversible Schiff base dynamic change | Schiff base reactions between aldehyde and amine groups in proteins [46,47] |
| The protein domain fold and unfold | (GB1)8 and (FL)8 [48] | |
| Coiled-coil interactions | BSA [49] | |
| β-Sheet Assembly | Shell nacre protein (r-n 16.3) [50] | |
| Enzyme | Enzyme catalyzed crosslinker cleavage | MMP7 [51,52,53], TP [54] |
| Ligand | Ligands binding with receptor | Aktm/ATP [55] Novobiocin/coumermycin-GyrB [56] CaM/Phenothiazine or trifluowere [57] Maltose-MBP [12,58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Ren, K.; Lu, Z.; Li, J.; Hao, Z. Stimuli-Responsive Protein Hydrogels: Their Design, Properties, and Biomedical Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 4652. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244652
Lu Y, Chen Y, Zhu Y, Zhao J, Ren K, Lu Z, Li J, Hao Z. Stimuli-Responsive Protein Hydrogels: Their Design, Properties, and Biomedical Applications. Polymers. 2023; 15(24):4652. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244652
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yuxuan, Yuhe Chen, Yuhan Zhu, Jingyi Zhao, Ketong Ren, Zhao Lu, Jun Li, and Ziyang Hao. 2023. "Stimuli-Responsive Protein Hydrogels: Their Design, Properties, and Biomedical Applications" Polymers 15, no. 24: 4652. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244652
APA StyleLu, Y., Chen, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhao, J., Ren, K., Lu, Z., Li, J., & Hao, Z. (2023). Stimuli-Responsive Protein Hydrogels: Their Design, Properties, and Biomedical Applications. Polymers, 15(24), 4652. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15244652






