Optimization the Stab Resistance and Flexibility of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Knitted Structure Fabric with Response Surface Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Test Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Shear Resistant Force and Breaking Strength of UHMWPE
3.2. Analysis of Single-Factor
3.3. Response Surface Method Optimization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panneke, N.; Ehrmann, A. Stab-Resistant Polymers—Recent Developments in Materials and Structures. Polymers 2023, 15, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Crouch, I.; Kanesalingam, S.; Ding, J.; Tan, P.; Lee, B.; Miao, M.H.; Ganga, D.; Wang, L.J. Body armor for stab and spike protection, Part 1: Scientific literature review. Text. Res. J. 2018, 88, 812–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Sun, B.; Gu, B. An analytical model for predicting stab resistance of flexible woven composites. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2013, 20, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mawkhlieng, U.; Majumdar, A.; Laha, A. A review of fibrous materials for soft body armour applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 1066–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tien, D.T.; Kim, J.S.; Huh, Y. Evaluation of anti-stabbing performance of fabric layers woven with various hybrid yarns under different fabric conditions. Fiber. Polym. 2011, 12, 808–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, X. Polyacrylate and Carboxylic Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotube-Strengthened Aramid Fabrics as Flexible Puncture-Resistant Composites for Anti-Stabbing Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 6334–6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, R.; Guan, F.; Zhu, Y.J.; You, F.F. Enhancement of the quasi-static stab resistance of Kevlar fabrics impregnated with shear thickening fluid. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 3673–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Z.S. Stabbing resistance of body armour panels impregnated with shear thickening fluid. Compos. Struct. 2017, 163, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, T.T.; Peng, H.K.; Lou, C.W.; Lin, J.H. Enhanced sandwich structure composite with shear thickening fluid and thermoplastic polyurethanes for High-performance stab resistance. Compos. Struct. 2022, 280, 114930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadow, R.; Niessen, K.V. Lightweight ballistic with additional stab protection made of thermally sprayed ceramic and cermet coatings on aramide fabrics. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Tec. 2006, 3, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.R.; Lin, T.A.; Lin, M.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Lou, C.W.; Lin, J.H. Impact resistance of fiber reinforced sandwich-structured nonwoven composites: Reinforcing effect of different fiber length. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.Z.; Zhou, M.J.; Yao, L.; Yu, H.; Yan, X.F.; Shen, Y.; Chen, W.S.; Ma, P.B.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, S.L.; et al. Crocodile Skin-Inspired Protective Composite Textiles with Pattern-Controllable Soft-Rigid Unified Structures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.V.S.; Midha, V.; Kumar, N. Studies on the stab resistance and ergonomic comfort behaviour of multilayer STF-treated tri-component woven fabric and HPPE laminate composite material. J. Text. Inst. 2023, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürgen, S.; Kuşhan, M.C. The stab resistance of fabrics impregnated with shear thickening fluids including various particle size of additives. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2017, 94, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilisik, K. Two-dimensional (2D) fabrics and three-dimensional (3D) preforms for ballistic and stabbing protection: A review. Text. Res. J. 2017, 87, 2275–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.J.; Hong, K.H.; Yoo, M.R. Preparation and properties of fumed silica/Kevlar composite fabrics for application of stab resistant material. Fiber. Polym. 2010, 11, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, W.; Ahn, H.; Han, S.J.; Harrison, P.; Park, J.K.; Jeong, E.; Yu, W.R. Shear behavior of a shear thickening fluid-impregnated aramid fabrics at high shear rate. Compos. Part B Eng. 2016, 97, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, T.T.; Wang, Y.X.; Shiu, B.C.; Peng, H.K.; Lou, C.W.; Lin, J.H. Hydrogel with high toughness and strength for fabricating high performance stab-resistant aramid composite fabric. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 1630–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Q.; Fu, K.K.; Cui, X.Y.; Zhu, H.X.; Yang, B. Shear Thickening Fluid and Its Application in Impact Protection: A Review. Polymers 2023, 15, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradović, V.; Stojanović, D.B.; Jokić, B.; Zrilić, M.; Radojević, V.; Uskoković, P.S.; Aleksić, R. Nanomechanical and anti-stabbing properties of Kolon fabric composites reinforced with hybrid nanoparticles. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 108, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khuyen, N.Q.; Han, P.V.D.; Nguyen, N.T.; Le, Q.B.; Harjo, M.; Anbarjafari, G.; Kiefer, R.; Tamm, T. The Use of Laminates of Commercially Available Fabrics for Anti-Stab Body-Armor. Polymers 2021, 13, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.B.; Dong, B.; Zhai, W.; Li, H. Stab-Resistant Performance of the Well-Engineered Soft Body Armor Materials Using Shear Thickening Fluid. Molecules 2022, 27, 6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, M.M.; Quan, Z.Z.; Wang, X.L.; Yu, J.Y. Preparation and characterization of B4C particle coated composites for stab-resistance. Compos. Struct. 2019, 228, 111370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharvandi, H.R.; Alebooyeh, M.; Alizadeh, M.; Khaksari, P.; Kordani, N. Effect of silica weight fraction on rheological and quasi-static puncture characteristics of shear thickening fluid-treated Twaron® composite. J. Ind. Text. 2016, 46, 473–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.T.; Wang, R.; Lou, C.W.; Lin, J.Y.; Lin, J.H. Static and dynamic puncture failure behaviors of 3D needle-punched compound fabric based on Weibull distribution. Text. Res. J. 2014, 84, 1903–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauledaitė, J.; Ancutienė, K.; Urbelis, V.; Krauledas, S.; Sacevičienė, V. Development and evaluation of 3D knitted fabrics to protect against mechanical risk. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 49, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, A.A.; Peerzada, M.H.; Sahito, I.A.; Abbassi, S.; Jeong, S.H. Facile fabrication and comparative exploration of high cut resistant woven and knitted composite fabrics using Kevlar and polyethylene. Fash. Text. 2018, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, P.J.; Sokolow, A.C.; Jian, H.Y.; Long, L.L.; Wetzel, E.D. Finite element simulation of ballistic impact on single jersey knit fabric. Compos. Struct. 2017, 162, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, L.L.; Luo, M.; Wu, Q.; Kang, Y.; Ma, P.B. Stab resistance of flexible composite reinforced with warp-knitted fabric like scale structure at quasi-static loading. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 7983S–7998S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Zhao, S.Q.; Liu, Q.; Wu, G.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Ma, P.B. Analyzing the output performance of the knitted triboelectric nanogenerator based on the fish-scale shape using fast Fourier transform. Text. Res. J. 2022, 92, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Mao, H.W.; Niu, L.; Chen, F.X.; Ma, P.B. Excellent flexibility and stab-resistance on pangolin-inspired scale-like structure composite for versatile protection. Compos. Commun. 2022, 35, 101266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.S.; Pang, H.M.; Zhao, C.Y.; Xuan, S.H.; Gong, X.L. The CNT/PSt-EA/Kevlar composite with excellent ballistic performance. Compos. Part B Eng. 2020, 185, 107793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Dong, C.; Yang, Z.; Kang, Y.; Huang, X.C.; Li, M.H.; Chen, Y.C.; Cao, W.J.; Huang, C.G.; Guo, Y.C.; et al. Protective performance and dynamic behavior of composite body armor with shear stiffening gel as buffer material under ballistic impact. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 218, 109190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.M.; Wang, Y.L.; Baba, T.; Fukuda, Y.; Wakatsuki, K.; Morikawa, H. Development of a high-density nonwoven structure to improve the stab resistance of protective clothing material. Ind. Health 2017, 55, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, T.T.; Fang, J.; Huang, C.H.; Lou, C.W.; Lin, J.Y.; Lin, M.C.; Chen, Y.S.; Lin, J.H. Numerical simulation of dynamic puncture behaviors of woven fabrics based on the Finite Element Method. Text. Res. J. 2017, 87, 1308–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Majumdar, A.; Butola, B.S. Structure induced effectiveness of shear thickening fluid for modulating impact resistance of UHMWPE fabrics. Compos. Struct. 2019, 210, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaker, J.; Rim, C.; Nihed, B. Evaluating the effectiveness of coating knitted fabrics with silica nanoparticles for protection from needle-stick injuries. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 3372S–3392S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.J.; Yu, K.J.; Zhang, D.T.; Qian, K. Cut resistant property of weft knitting structure: A review. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 109, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 7690. 3-2013; Reinforcements. Test Method for Yarns. Part 3: Determination of Breaking Force and Breaking Elongation for Glass Fibre. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- ASTM D 3787:2016: R2020; Standard Test Method for Bursting Strength of Textiles—Constant-Rate-of-Traverse (CRT) Ball Burst Test. American Society for Testing and Materials: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- GA 68-2019; Police Stab Proof Clothing. National Technical Committee on Police Equipment: Beijing, China, 2019.
- GB/T 18318-2009; Textiles—Determination of Bending Behavior. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2009.
- Komorek, A.; Przybyłek, P.; Szczepaniak, R.; Godzimirski, J.; Rośkowicz, M.; Imiłowski, S. The influence of low-energy impact loads on the properties of the sandwich composite with a foam core. Polymers 2022, 14, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.R.; Boussu, F.; Soulat, D.; Luo, J.; Wang, P. Impact resistance of pre-deformed stab of multi-ply three-dimensional interlock polymeric fabrics. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 51, 4818S–4841S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
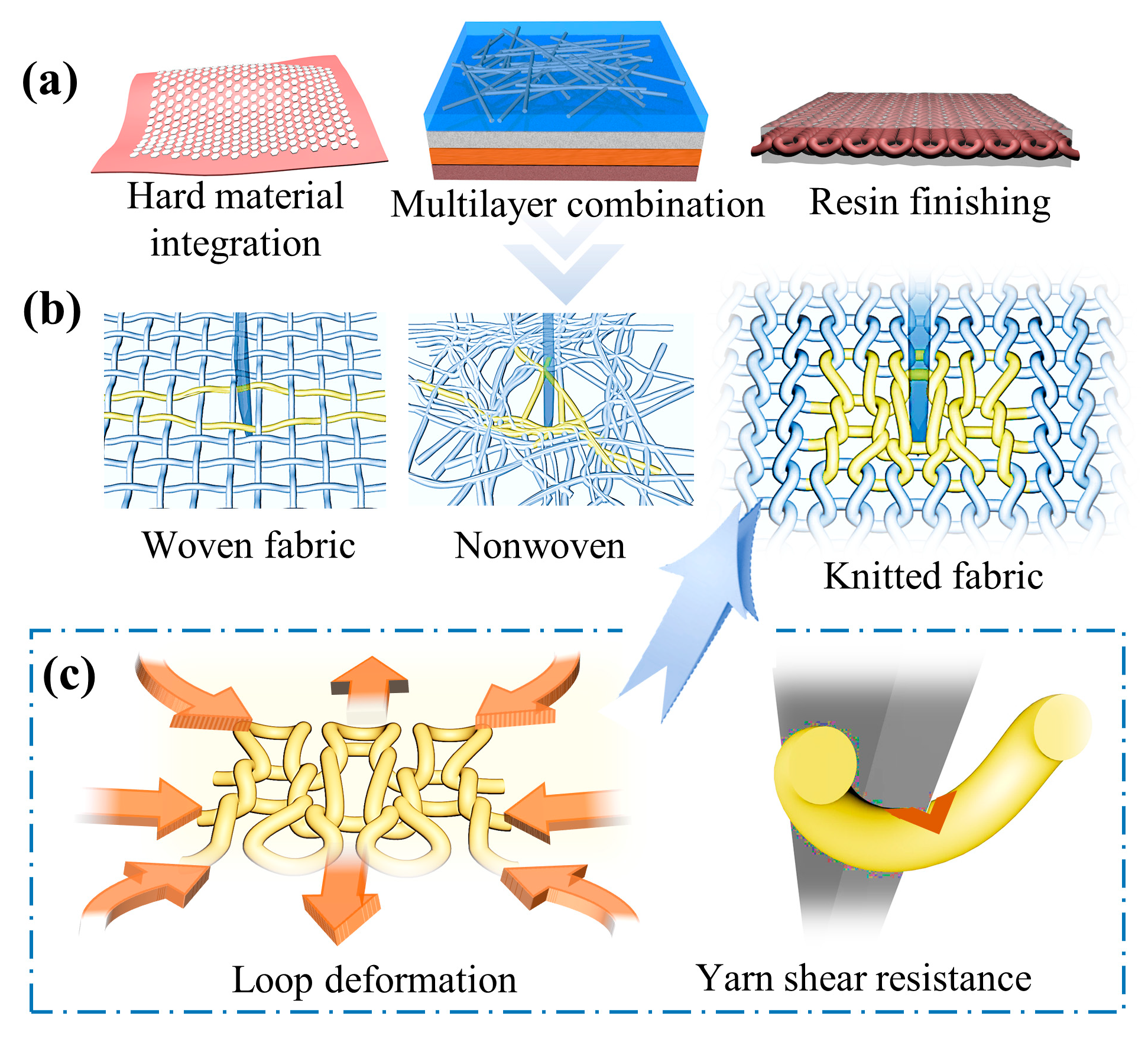

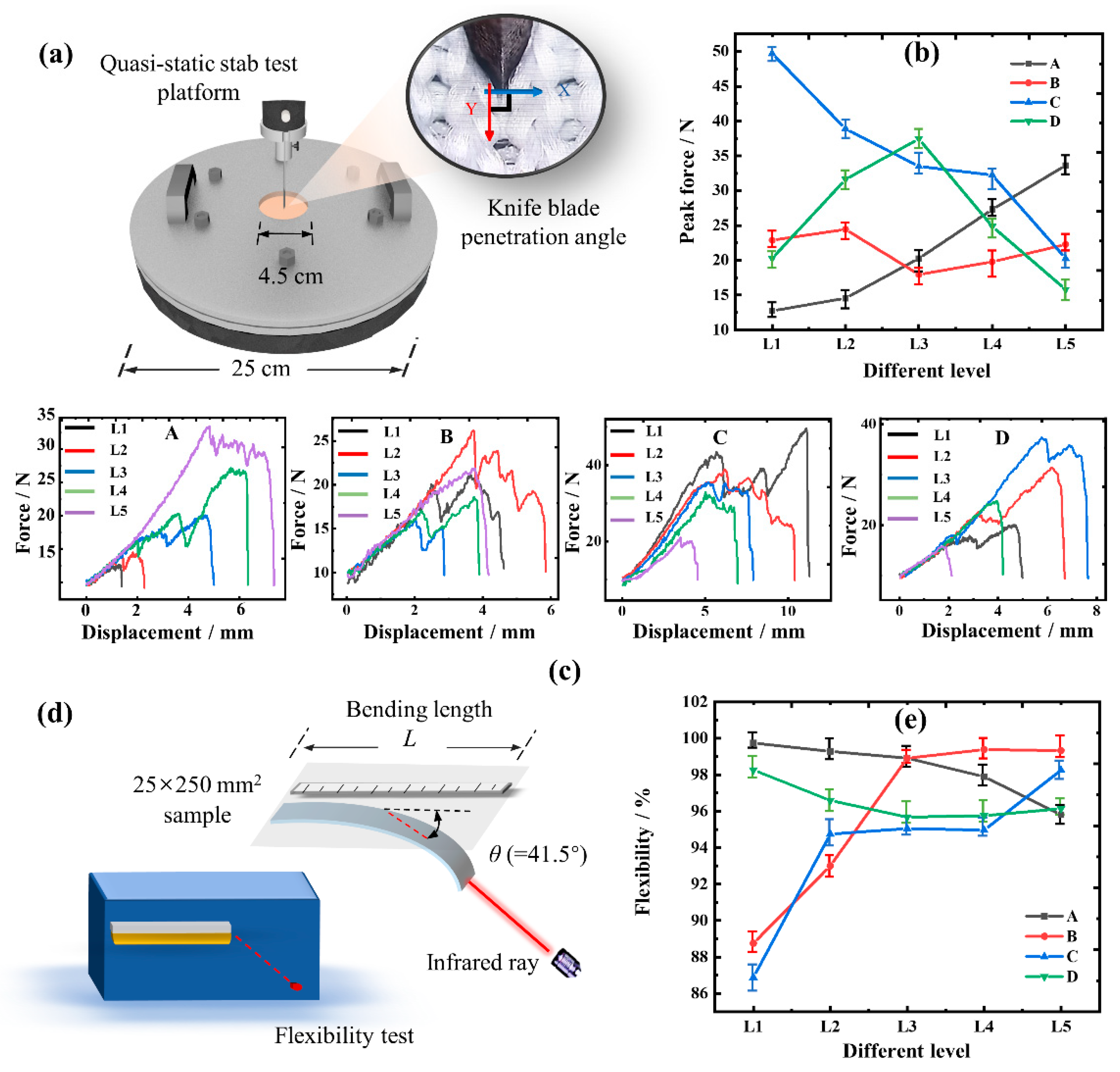


| Factors | A: Yarn Specifications/(D) | B: Stitch Density | C: Fabric Structure | D: Blending Ratio/(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Levels | L1 | 200 | −10 | 1 × 3 | 100 |
| L2 | 400 | −5 | 1 × 5 | 75 | |
| L3 | 600 | 0 | 1 × 7 | 50 | |
| L4 | 800 | 5 | 1 × 9 | 25 | |
| L5 | 1000 | 10 | 1 × 11 | 0 | |
| Normality | p (L1) | 0.666 | 0.381 | 0.993 | 0.439 |
| p (L2) | 0.761 | 0.176 | 0.630 | 0.209 | |
| p (L3) | 0.876 | 0.215 | 0.796 | 0.265 | |
| p (L4) | 0.676 | 0.263 | 0.867 | 0.672 | |
| p (L5) | 0.084 | 0.210 | 0.247 | 0.338 | |
| Homogeneity | p | 0.287 | 0.986 | 0.547 | 0.932 |
| ANOVA | F | 14.930 | 2.052 | 8.894 | 6.008 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.142 | <0.001 | 0.016 | |
| No. | Levels | Thickness/(mm) | Areal Density/(g·m−2) | Stitch Density /(Wales/5 cm × Courses/5 cm) | No. | Levels | Thickness/(mm) | Areal Density/(g·m−2) | Stitch Density /(Wales/5 cm × Courses/5 cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | L1 | 0.69 | 168 | 70 × 118 | C | L1 | 1.95 | 920 | 76 × 138 |
| L2 | 1.16 | 422 | 70 × 112 | L2 | 1.87 | 777 | 70 × 124 | ||
| L3 | 1.47 | 504 | 64 × 106 | L3 | 1.86 | 747 | 68 × 118 | ||
| L4 | 1.75 | 659 | 64 × 102 | L4 | 1.87 | 733 | 68 × 115 | ||
| L5 | 1.97 | 771 | 60 × 100 | L5 | 1.47 | 504 | 64 × 106 | ||
| B | L1 | 1.41 | 677 | 74 × 192 | D | L1 | 1.47 | 504 | 64 × 106 |
| L2 | 1.46 | 571 | 70 × 156 | L2 | 1.51 | 528 | 64 × 118 | ||
| L3 | 1.47 | 463 | 68 × 140 | L3 | 1.64 | 641 | 66 × 130 | ||
| L4 | 1.46 | 424 | 64 × 122 | L4 | 1.65 | 711 | 66 × 136 | ||
| L5 | 1.49 | 367 | 64 × 106 | L5 | 1.75 | 739 | 70 × 148 |
| β0 | β1 | β2 | β3 | β12 | β13 | β23 | β11 | β22 | β33 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stab resistance | +49.9 | +5.10 | −6.32 | +4.32 | +1.10 | +1.73 | −0.6753 | −3.72 | −2.56 | −5.00 |
| Flexibility | +0.935 | −0.027 | +0.030 | +0.0155 | +0.0013 | −0.0039 | +0.0006 | −0.0016 | −0.026 | +0.001 |
| Experiment No. | A: Yarn Specifications/(D) | C: Fabric Structure | D: Blending Ratio/(%) | Peak Force/(N) | Flexibility/(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 400 | 1 × 9 | 25 | 23.6227 | 94.1363 |
| 2 | 600 | 1 × 7 | 50 | 50.622 | 92.7015 |
| 3 | 600 | 1 × 7 | 100 | 39.6543 | 96.8728 |
| 4 | 600 | 1 × 7 | 50 | 53.01 | 92.4698 |
| 5 | 400 | 1 × 9 | 75 | 28.282 | 97.7589 |
| 6 | 600 | 1 × 3 | 50 | 58.306 | 74.4592 |
| 7 | 400 | 1 × 5 | 75 | 40.679 | 94.8173 |
| 8 | 1000 | 1 × 7 | 50 | 47.308 | 88.703 |
| 9 | 200 | 1 × 7 | 50 | 26.9573 | 96.9847 |
| 10 | 600 | 1 × 7 | 50 | 48.389 | 94.6545 |
| 11 | 600 | 1 × 7 | 0 | 24.303 | 90.907 |
| 12 | 400 | 1 × 5 | 25 | 33.054 | 90.4713 |
| 13 | 800 | 1 × 5 | 75 | 52.025 | 86.529 |
| 14 | 800 | 1 × 5 | 25 | 37.748 | 84.7117 |
| 15 | 600 | 1 × 7 | 50 | 46.025 | 95.7696 |
| 16 | 600 | 1 × 11 | 50 | 25.202 | 91.6756 |
| 17 | 800 | 1 × 9 | 25 | 32.4462 | 87.9252 |
| 18 | 600 | 1 × 7 | 50 | 49.763 | 93.5647 |
| 19 | 600 | 1 × 7 | 50 | 55.763 | 91.8816 |
| 20 | 800 | 1 × 9 | 75 | 44.2864 | 90.9779 |
| Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F Value | p Value | Significant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 2232.10 | 9 | 248.01 | 13.14 | 0.0002 | ** |
| A | 415.85 | 1 | 415.85 | 22.04 | 0.0008 | ** |
| C | 638.53 | 1 | 638.53 | 33.84 | 0.0002 | ** |
| D | 298.46 | 1 | 298.46 | 15.82 | 0.0026 | ** |
| AC | 9.65 | 1 | 9.65 | 0.5116 | 0.4908 | |
| AD | 23.92 | 1 | 23.92 | 1.27 | 0.2865 | |
| DC | 3.65 | 1 | 3.65 | 0.1933 | 0.6695 | |
| A2 | 347.08 | 1 | 347.08 | 18.39 | 0.0016 | ** |
| C2 | 164.79 | 1 | 164.79 | 8.73 | 0.0144 | * |
| D2 | 629.56 | 1 | 629.56 | 33.36 | 0.0002 | ** |
| Residual | 188.70 | 10 | 18.87 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 129.71 | 5 | 25.94 | 2.20 | 0.2037 | |
| Pure Error | 58.98 | 5 | 11.80 |
| Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F Value | p Value | Significant | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.0491 | 9 | 0.0055 | 12.49 | 0.0002 | ** |
| A | 0.0119 | 1 | 0.0119 | 27.23 | 0.0004 | ** |
| C | 0.0148 | 1 | 0.0148 | 33.97 | 0.0002 | ** |
| D | 0.0038 | 1 | 0.0038 | 8.79 | 0.0142 | * |
| AC | 0.0000 | 1 | 0.0000 | 0.0319 | 0.8618 | |
| AD | 0.0001 | 1 | 0.0001 | 0.2750 | 0.6114 | |
| DC | 3.277 × 10−6 | 1 | 3.277 × 10−6 | 0.0075 | 0.9327 | |
| A2 | 0.0001 | 1 | 0.0001 | 0.1433 | 0.7130 | |
| C2 | 0.0170 | 1 | 0.0170 | 39.00 | < 0.0001 | ** |
| D2 | 0.0000 | 1 | 0.0000 | 0.0621 | 0.8083 | |
| Residual | 0.0044 | 10 | 0.0004 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 0.0033 | 5 | 0.0007 | 3.04 | 0.1240 | |
| Pure Error | 0.0011 | 5 | 0.0002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, X.; Su, T.; Liang, X.; Cong, H. Optimization the Stab Resistance and Flexibility of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Knitted Structure Fabric with Response Surface Method. Polymers 2023, 15, 4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234509
Yu X, Su T, Liang X, Cong H. Optimization the Stab Resistance and Flexibility of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Knitted Structure Fabric with Response Surface Method. Polymers. 2023; 15(23):4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234509
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Xuliang, Ting Su, Xinhua Liang, and Honglian Cong. 2023. "Optimization the Stab Resistance and Flexibility of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Knitted Structure Fabric with Response Surface Method" Polymers 15, no. 23: 4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234509
APA StyleYu, X., Su, T., Liang, X., & Cong, H. (2023). Optimization the Stab Resistance and Flexibility of Ultra-High Molecular Weight Polyethylene Knitted Structure Fabric with Response Surface Method. Polymers, 15(23), 4509. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234509








