Analyzing Temperature Distribution Patterns on the Facing and Backside Surface: Investigating Combustion Performance of Flame-Retardant Particle Boards Using Aluminum Hypophosphite, Intumescent, and Magnesium Hydroxide Flame Retardants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Manufacture of Particle Board
2.3. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. LOI Analysis
3.2. Temperature Distribution on the Facing Surface and the Temperature Rise on the Backside Surface
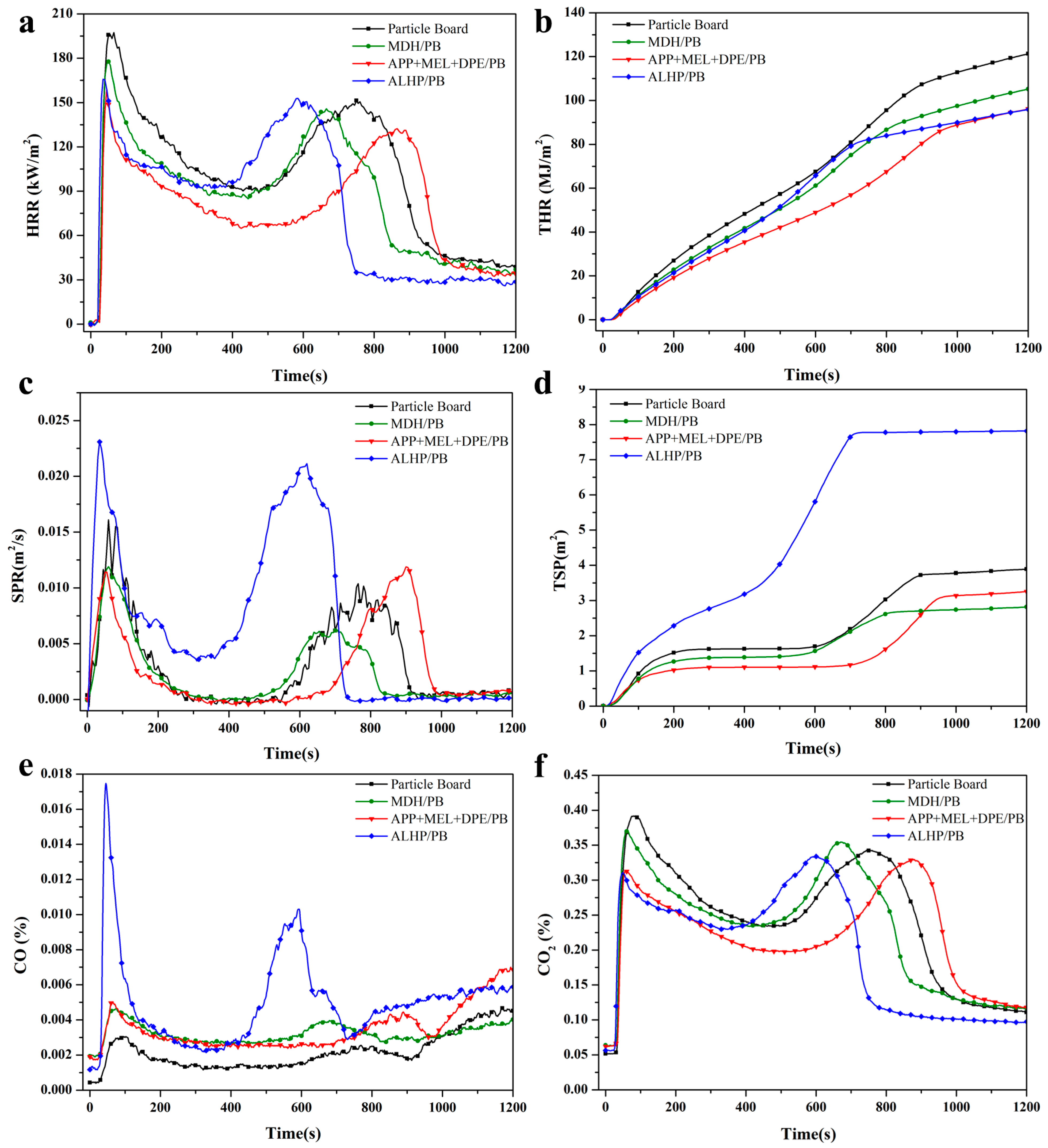
3.3. Cone Calorimeter
3.4. Physical and Mechanical Performance
3.5. Mechanism Analysis
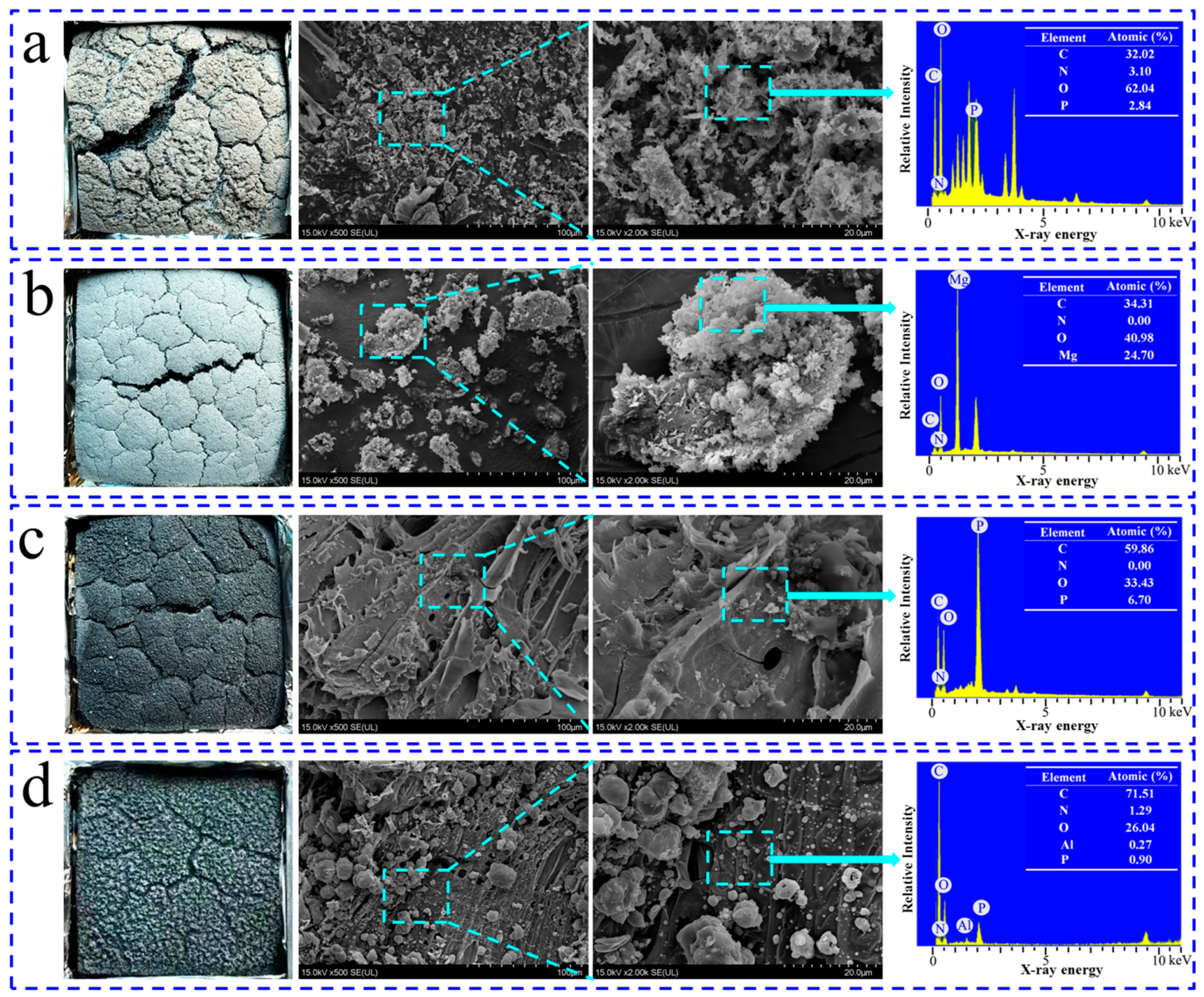
3.5.1. Morphology of Char Residue
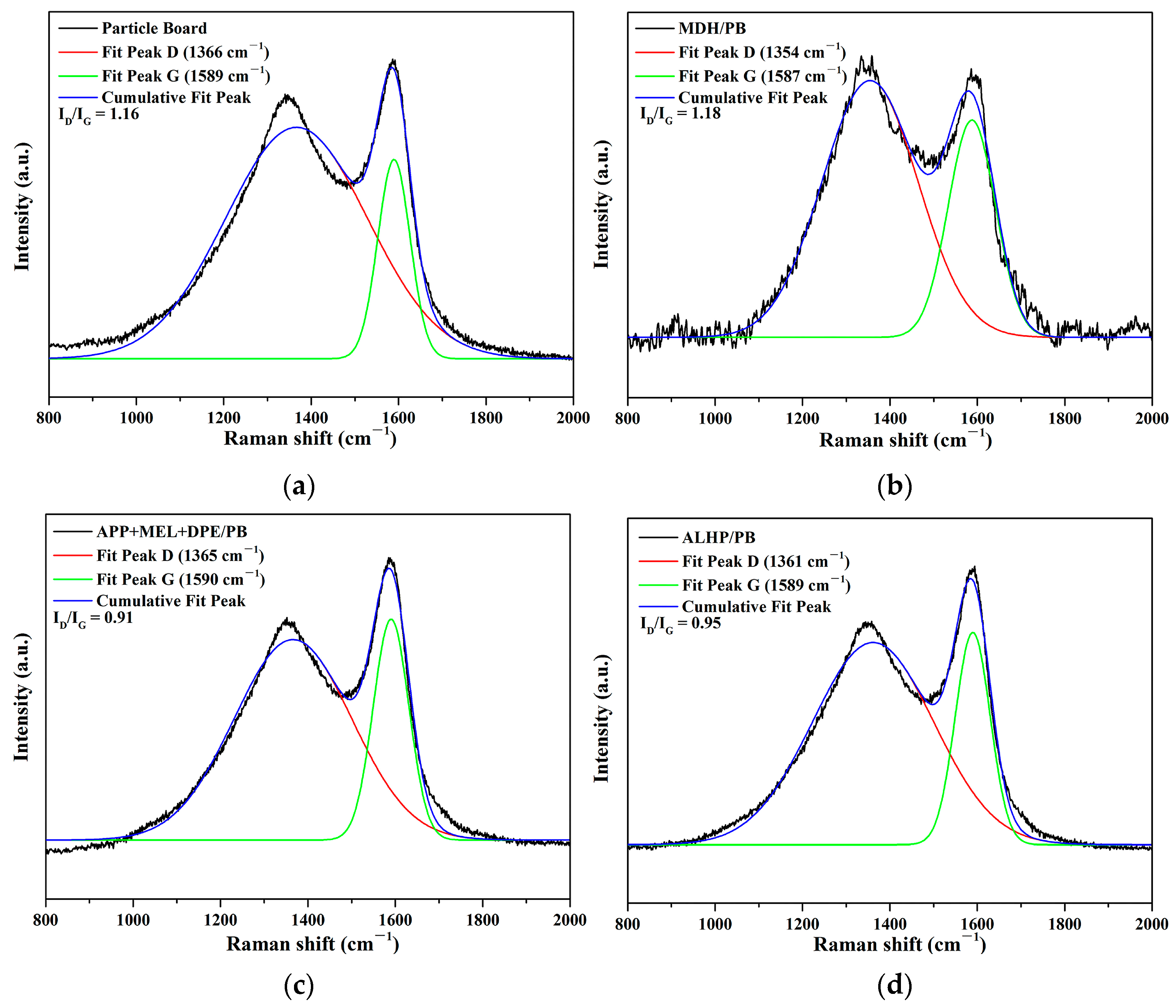
3.5.2. Raman Spectrum of Char Residue
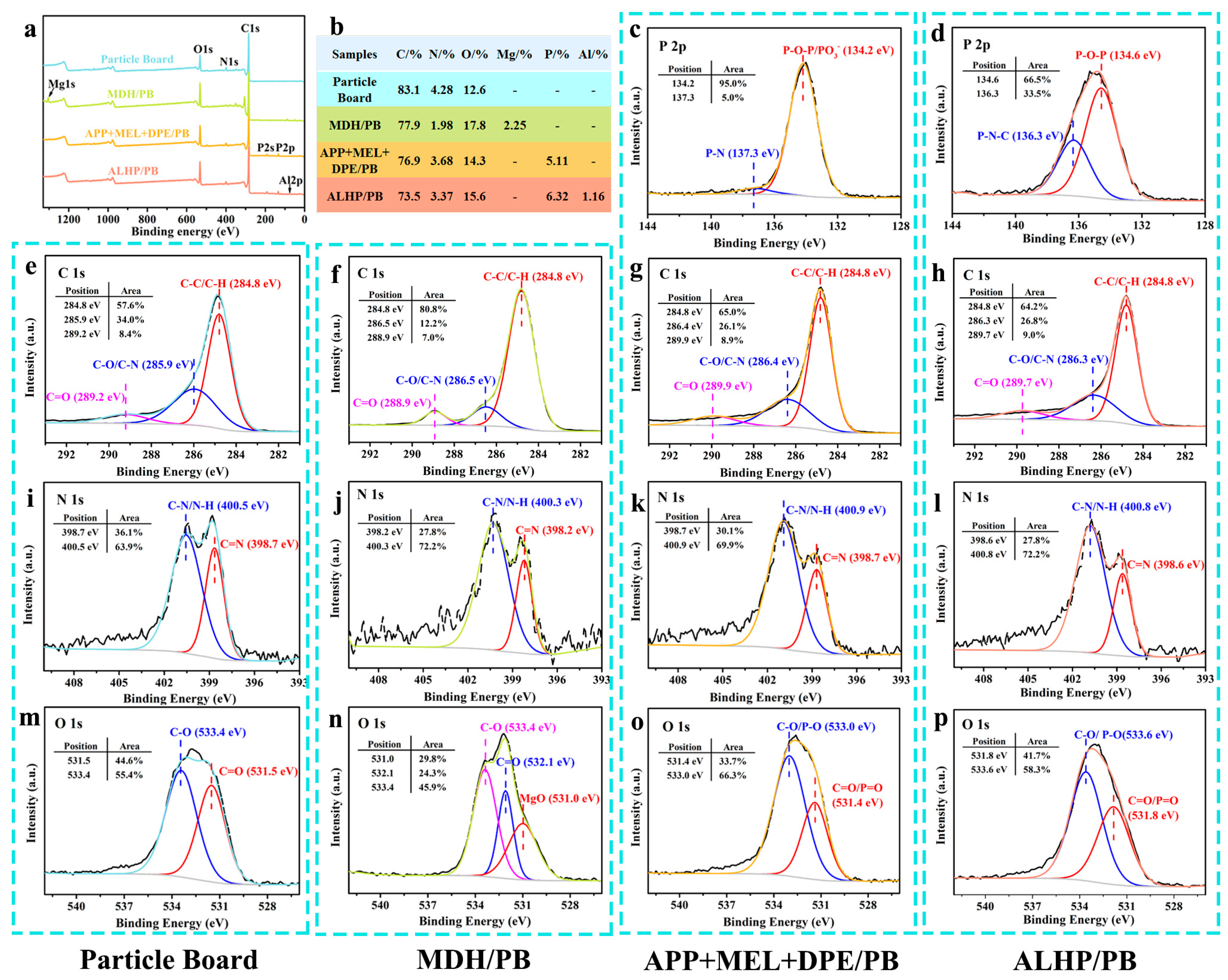
3.5.3. XPS Analysis of Char Residue
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orelma, H.; Tanaka, A.; Vuoriluoto, M.; Khakalo, A.; Korpela, A. Manufacture of all-wood sawdust-based particle board using ionic liquid-facilitated fusion proces. Wood Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badila, M.; Jocham, C.; Zhang, W.B.; Schmidt, T.; Wuzella, G.; Müller, U.; Kandelbauer, A. Powder coating of veneered particle board surfaces by hot pressing. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 1547–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y. Study on the Formaldehyde-Free Flame Retardant Wood Particleboard and Its Adhesive. Master’s Thesis, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.H.; Wang, S.H.; Meng, D.; Chen, D.; Mu, C.Z.; Li, H.F.; Sun, J.; Gu, X.Y.; Zhang, S. A facile preparation of environmentally-benign and flame-retardant coating on wood by comprising polysilicate and boric acid. Cellulose 2021, 28, 11551–11566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.J. Modern Flame Retardant Materials and Technology; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2021; pp. 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, W.L.; Peng, Y.; Wang, W.; Cao, J.Z. Thermal behavior and flame retardancy of poplar wood impregnated with furfuryl alcohol catalyzed by boron/phosphorus compound system. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 176, 114361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Chai, Y.B.; Ni, L.; Lyu, W.H. Flame retardant properties and thermal decomposition kinetics of wood treated with boric acid modified silica sol. Materials 2020, 13, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.M.; Chen, Z.L.; Lu, J.H.; Wei, M.; Huang, Y.X.; Jiang, P. Combustion behavior and thermal degradation properties of wood impregnated with intumescent biomass flame retardants: Phytic acid, hydrolyzed collagen, and glycerol. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 3921–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.B.; Qasem, B.; Hou, J.F.; Wang, Z.M.; Cen, J.J.; Arkin, S.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.G.; Yu, Y.M. Recycling construction wastes to fabricate particle boards with admirable flame retardancy, smoke suppression and mechanical performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 133265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, I.; Butron, A.; Puyadena, M.; González, A.; Irusta, L.; Barrio, A. Bio-Based Phosphate-Containing Polyester for Improvement of Fire Reaction in Wooden Particleboard. Polymers 2023, 15, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, M.; Gulati, K.; Bagoria, R.; Arora, S. Thermal, flammability and iso-conversional multiple heating rate kinetic studies of impregnated poplar wood veneers. J. Indian Acad. Wood Sci. 2022, 19, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, P.F.; Li, P.; Wu, Y.Q.; Li, X.G.; Yuan, G.M.; Zuo, Y.F. Comparative study on the properties of inorganic silicate and organic phenolic prepolymer modified poplar wood by vacuum cycle pressurization. J. Renew. Mater. 2022, 10, 2451–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.T.; Mu, J.; Chu, D.M.; Zhao, Y. Synthesis of N-P fire retardant modified with MH and flame retardance and smoke suppression of poplar impregnated by it. New Chem. Mater. 2015, 43, 126–129. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.D.; Wu, Y.Q.; Tian, C.H.; Yan, Q.; Yao, C.H. Synergistic effect of nanosilica aerogel with phosphorus flame retardants on improving flame retardancy and leaching resistance of wood. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grexa, O.; Lübke, H. Flammability parameters of wood tested on a cone calorimeter. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 74, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürü, M.; Atar, M.; Yildinm, R. Production of polymer matrix composite particleboard from walnut shell and improvement of its requirements. Mater. Des. 2008, 29, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Thole, V. Investigation of modified water glass as adhesive for wood and particleboard: Mechanical, thermal and flame retardant properties. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2018, 76, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, X.G. Preparation of mineral bound particleboards with improved fire retardant and smoke suppression properties based on a mix of inorganic adhesive. Holzforschung 2019, 73, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskaran, M.; Hashim, R.; Leong, J.Y.; Ong, Y.N.; Yhaya, M.F.; Sulaiman, O. Flame retardant properties of oil palm trunk particleboard with addition of epoxy resin as a binder and aluminium hydroxide and magnesium hydroxide as additives. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2019, 42, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grexa, O.; Poutch, F.; Manikova, D.; Martvonova, H.; Bartekov, A. Intumescence in fire retardancy of lignocellulosic panels. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2003, 82, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savas, L.A.; Dogan, M. Flame retardant effect of zinc borate in polyamide 6 containing aluminum hypophosphite. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 165, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, R.; Jiang, J.C. Effects of melamine cyanurate and aluminum hypophosphite on the flame retardancy of high-impact polystyrene. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 17860–17873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.H.; Wu, H.Z.; Sun, M.M.; Su, S.Q.; Yan, B.; Tang, L.S. Fire-retardant synergy of tris(1-methoxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-4-piperidinyl)phosphite and aluminum hypophosphite/melamine hydrobromide in polypropylene. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2021, 27, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.Y.; Sun, M.M.; Wu, H.Z.; Tang, M.; Yan, B.; Tang, L.S. Synergistic flame retardancy of bis(1-methoxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidin-4-yl)sebacate and aluminium hypophosphite/melamine hydrobromide in PP. Fire Mater. 2021, 45, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Huang, C.X.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhou, R.; Jiang, J.C. Multi-element synergistic effects to improve the flame retardancy of high impact polystyrene. Polym. Test. 2022, 115, 107766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savas, L.A.; Hacioglu, F.; Hancer, M.; Dogan, M. Flame retardant effect of aluminum hypophosphite in heteroatom-containing polymers. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSI/ASTM E84-2021; Standard Test Method for Surface Burning Characteristics of Building Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- GB/T 17658-2018; Test of Burning Behavior for Flame Retardant Treated Wood-Method of Test for Fire Propagation. Research Institute of Wood Industry, Chinese Academy of Forestry: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Li, B.; Wang, J.Q. Utilization of cone calorimeter for the appraisal of the flammability and flame retardancy of polymeric materials. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1998, 14, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, A.I.; Hadden, R.M.; Bisby, L.A. A review of factors affecting the burning behaviour of wood for application to tall timber construction. Fire Technol. 2019, 55, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2863-17; Standard Test Method for Measuring the Minimum Oxygen Concentration to Support Candle-Like Combustion of Plastics (Oxygen Index). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- ASTM E1354-17; Standard Test Method for Heat and Visible Smoke Release Rates for Materials and Products Using an Oxygen Consumption Calorimeter. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- GB/T 17657-2013; Test methods of evaluating the properties of wood-based panels and surface decorated wood-based panels. Standardization Administration of the Peopleʹs Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2013.
- Cui, J.Q.; Fen, X.P.; Gu, Y.; Han, S.G.; Cai, Z.W.; Zhu, J.; Dai, X.; Zeng, L. Effect of Feeding Modes of Melamine on Properties of Fiberboard Glued with MUF Adhesive. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2015, 43, 134–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Liao, D.J.; Hu, X.P.; Li, W.X.; Xie, C.Q.; Zhang, H.J.; Yang, W.X. Synergistic fire retardant effect between expandable graphite and ferrocene-based non-phosphorus polymer on polypropylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 178, 109201. [Google Scholar]
- Pachfule, P.; Shinde, D.; Majumder, M.; Xu, Q. Fabrication of carbon nanorods and graphene nanoribbons from a metal–organic framework. Nat. Chem. 2016, 8, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Zhang, H.J.; Hu, X.P.; Yang, W.X.; Cheng, Z.; Xie, C.Q. Highly efficient replacement of traditional intumescent flame retardants in polypropylene by manganese ions doped melamine phytate nanosheets. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 123001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.J.; He, W.T.; Long, L.J.; Yan, W.; He, M.; Qin, S.H.; Yu, J. Highly efficient flame-retardant glass-fiber-reinforced polyamide 6T system based on a novel DOPO-based derivative: Flame retardancy, thermal decomposition, and pyrolysis behavior. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 148, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wu, X.; Ma, W.; Qian, L.J.; Xin, F.; Qiu, Y. Synthesis and characterization of a novel organic-inorganic hybrid char-forming agent and its flame-retardant application in polypropylene composites. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2018, 134, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; Physical Electronics, Inc.: Chanhassen, MN, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.E.; Zhang, J.; Yan, H.; Guo, X.R.; Sun, Q.; Guo, R.J. A novel organic-inorganic hybrid K-HBPE@APP performing excellent flame retardancy and journal pre-proofsmoke suppression for polypropylene. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.H.; Huang, J.Q.; Yang, J.C.; Shao, Z.B.; Wang, Y.Z. An effective way to flame-retard biocomposite with ethanolamine modified ammonium polyphosphate and its flame retardant mechanisms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 3524–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.M.; Liang, M.Y.; Jiang, J.L.; Huang, J.G.; Liu, H.B. Flame retardant properties and mechanism of an efficient intumescent flame retardant PLA composites. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xia, L.; Jian, R.K.; Ai, Y.F.; Zheng, X.L.; Chen, G.L.; Wang, J.S. Flame-retarding epoxy resin with an efficient P/N/S-containing flame retardant: Preparation, thermal stability, and flame retardance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 149, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.S.; Chu, Z.Y.; Yan, L.; Chen, H.G.; Jia, H.Y.; Tang, W.F. Effect of chicken eggshell on the flame-retardant and smoke suppression properties of an epoxy-based traditional APP-PER-MEL system. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 2712–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuggle, J.C. XPS, UPS AND XAES studies of oxygen adsorption on polycrystalline Mg at 100 and 300 K. Surf. Sci. 1977, 69, 581–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, Y.; Yasumori, I. Catalysis by alkaline earth metal oxides. III. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic study of catalytically active MgO, CaO, and BaO surfaces. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1981, 54, 1505–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shul’ga, Y.M.; Bulatov, A.V.; Gould, R.A.T.; Konze, W.V.; Pignolet, L.H. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of a series of heterometallic gold-platinum phosphine cluster compounds. Inorg. Chem. 1992, 31, 4704–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Zhang, L.; Semple, K.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.B.; Dai, C.P. Development of biodegradable flame-retardant bamboo charcoal composites, part ii: Thermal degradation, gas phase, and elemental analyses. Polymers 2020, 12, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

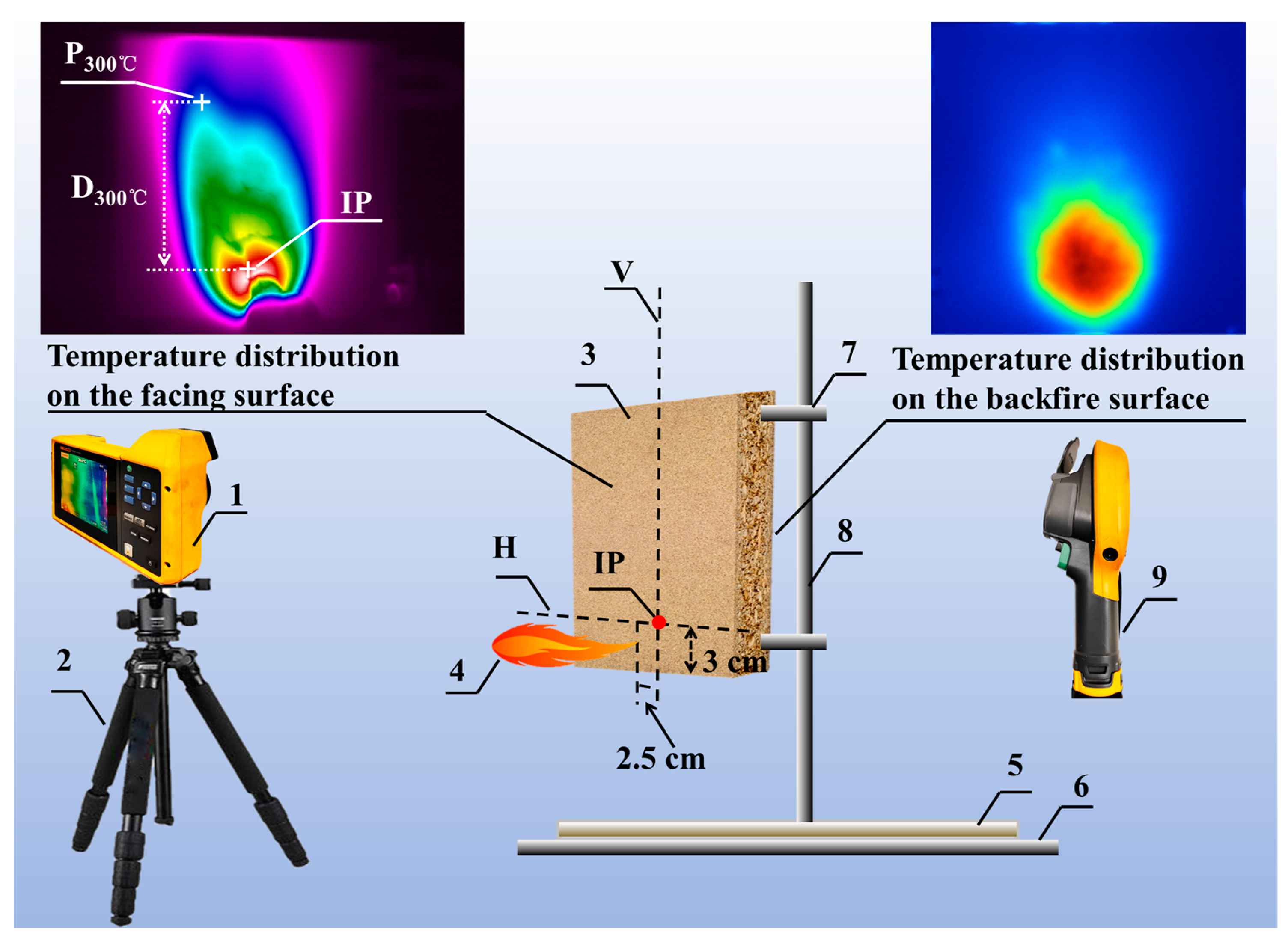


| Samples | Solid Content (%) | Viscosity (Pa·s) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface adhesive | 59.2 | 39.2 | 7.7 |
| Core layer adhesive | 65.0 | 150.0 | 8.0 |
| Samples | Surface Layer (34 wt%) | Core Layer (66 wt%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shavings (wt%) | Resin (wt%) | Flame Retardant (wt%) | Shavings (wt%) | Resin (wt%) | Flame Retardant (wt%) | |
| Particle Board | 100 | 10 | - | 100 | 10.5 | - |
| MDH/PB | 100 | 10 | 10 | 100 | 10.5 | 10 |
| APP + MEL + DPE/PB | 100 | 10 | 10 | 100 | 10.5 | 10 |
| ALHP/PB | 100 | 10 | 10 | 100 | 10.5 | 10 |
| Samples | MDH (wt%) | Intumescent Flame Retardant (IFR) (wt%) | ALHP (wt%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APP (wt%) | MEL (wt%) | DPE (wt%) | |||
| Particle Board | - | - | - | - | - |
| MDH/PB | 10 | - | - | - | - |
| APP + MEL + DPE/PB | - | 5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | |
| ALHP/PB | - | - | - | - | 10 |
| Samples | Particle Board | MDH/PB | APP + MEL + DPE/PB | ALHP/PB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOI/% | 26.4 ± 0.1 d | 29.4 ± 0.2 c | 33.7 ± 0.1 b | 35.8 ± 0.3 a |
| Samples | The First Stage (min) | The Second Stage (min) | The Third Stage (min) | The Fourth Stage (min) | Temperature Rise Rate (°C/min) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The Second Stage | The Fourth Stage | |||||
| Particle Board | 1.30 ± 0.08 b | 3.45 ± 0.23 b | 3.57 ± 0.23 c | 8.48 ± 0.59 b | 27.11 ± 1.89 b | 61.64 ± 5.32 a |
| MDH/PB | 1.43 ± 0.09 ab | 3.95 ± 0.25 a | 5.02 ± 0.32 b | 7.25 ± 0.50 b | 27.98 ± 2.02 b | 60.16 ± 4.21 a |
| APP + MEL + DPE/PB | 1.47 ± 0.08 a | 4.15 ± 0.23 a | 5.73 ± 0.35 a | 12.08 ± 0.80 a | 21.94 ± 1.52 c | 35.45 ± 2.38 b |
| ALHP/PB | 1.55 ± 0.08 a | 2.2 ± 0.13 c | 6.25 ± 0.36 a | 12.13 ± 0.85 a | 38.27 ± 2.87 a | 41.96 ± 2.94 b |
| Samples | tign (s) | tpHRR1 (s) | pHRR1 (kW/m2) | tpHRR2 (s) | pHRR2 (kW/m2) | THR800 (MJ/m2) | Residual Weight (%) | FPI (m2·s/kW) | pSPR (m2/s) | TSP (m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle Board | 21 ± 2 a | 65 ± 5 a | 197.36 ± 13.06 a | 750 ± 31 b | 151.31 ± 9.87 a | 95.48 ± 10.46 a | 22.01 ± 1.54 b | 0.106 ± 0.007 bc | 0.016 ± 0.001 b | 3.89 ± 0.26 b |
| MDH/PB | 21 ± 2 a | 50 ± 3 b | 177.74 ± 11.74 ab | 665 ± 29 c | 145.83 ± 9.63 b | 86.66 ± 9.42 a | 28.19 ± 1.84 a | 0.118 ± 0.007 b | 0.012 ± 0.001 c | 2.82 ± 0.18 c |
| APP + MEL + DPE/PB | 24 ± 2 a | 45 ± 3 b | 159.21 ± 10.25 b | 865 ± 35 a | 132.32 ± 8.66 b | 67.51 ± 7.24 b | 29.59 ± 2.07 a | 0.151 ± 0.009 a | 0.012 ± 0.001 c | 3.26 ± 0.23 c |
| ALHP/PB | 16 ± 1 b | 35 ± 3 c | 165.74 ± 10.85 b | 585 ± 24 d | 152.88 ± 10.09 a | 83.98 ± 9.15 ab | 30.20 ± 2.11 a | 0.097 ± 0.006 c | 0.023 ± 0.002 a | 7.82 ± 0.45 a |
| Samples | Thickness (mm) | Density (kg·m3) | Internal Bonding Strength (MPa) | Surface Bonding Strength (MPa) | MOR (MPa) | MOE (MPa) | Absorption Thickness Expansion Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle Board | 17.72 ± 1.95 a | 669.83 ± 60.21 a | 0.89 ± 0.12 a | 1.10 ± 0.21 a | 15.11 ± 1.43 a | 2489.67 ± 290.56 a | 13.54 ± 1.47 c |
| MDH/PB | 17.77 ± 2.00 a | 657.71 ± 58.13 a | 0.57 ± 0.02 b | 0.64 ± 0.08 bc | 7.39 ± 0.73 b | 1757.00 ± 167.14 b | 62.22 ± 5.38 a |
| APP + MEL + DPE/PB | 17.70 ± 2.12 a | 659.71 ± 58.31 a | 0.47 ± 0.19 b | 0.67 ± 0.18 b | 10.02 ± 3.31 b | 1978.00 ± 401.40 bc | 22.24 ± 3.24 b |
| ALHP/PB | 17.69 ± 1.94 a | 654.61 ± 59.86 a | 0.21 ± 0.02 c | 0.37 ± 0.10 c | 7.47 ± 0.47 b | 1342.00 ± 100.44 c | 22.47 ± 1.74 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, F.; Jia, H.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liang, S.; Jiang, P. Analyzing Temperature Distribution Patterns on the Facing and Backside Surface: Investigating Combustion Performance of Flame-Retardant Particle Boards Using Aluminum Hypophosphite, Intumescent, and Magnesium Hydroxide Flame Retardants. Polymers 2023, 15, 4479. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234479
Pan F, Jia H, Huang Y, Chen Z, Liang S, Jiang P. Analyzing Temperature Distribution Patterns on the Facing and Backside Surface: Investigating Combustion Performance of Flame-Retardant Particle Boards Using Aluminum Hypophosphite, Intumescent, and Magnesium Hydroxide Flame Retardants. Polymers. 2023; 15(23):4479. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234479
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Fangya, Hongyu Jia, Yuxiang Huang, Zhilin Chen, Shanqing Liang, and Peng Jiang. 2023. "Analyzing Temperature Distribution Patterns on the Facing and Backside Surface: Investigating Combustion Performance of Flame-Retardant Particle Boards Using Aluminum Hypophosphite, Intumescent, and Magnesium Hydroxide Flame Retardants" Polymers 15, no. 23: 4479. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234479
APA StylePan, F., Jia, H., Huang, Y., Chen, Z., Liang, S., & Jiang, P. (2023). Analyzing Temperature Distribution Patterns on the Facing and Backside Surface: Investigating Combustion Performance of Flame-Retardant Particle Boards Using Aluminum Hypophosphite, Intumescent, and Magnesium Hydroxide Flame Retardants. Polymers, 15(23), 4479. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15234479








