Evaporation Driven Hydrovoltaic Generator Based on Nano-Alumina-Coated Polyethylene Terephthalate Film
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Production of the Hydrovoltaic Generator
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Preparation of the Hydrovoltaic Generator
3.2. Electricity Generation from Evaporation
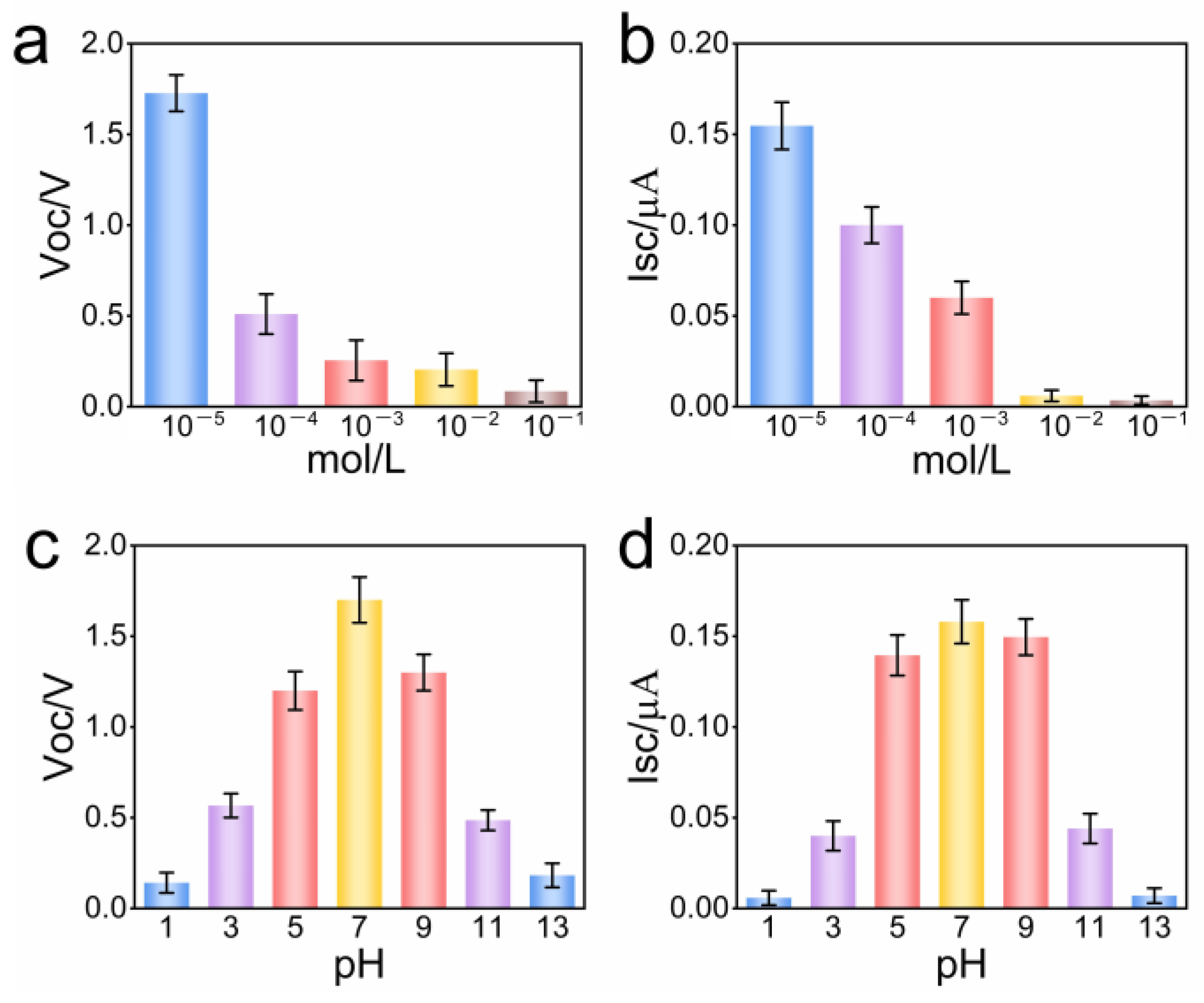
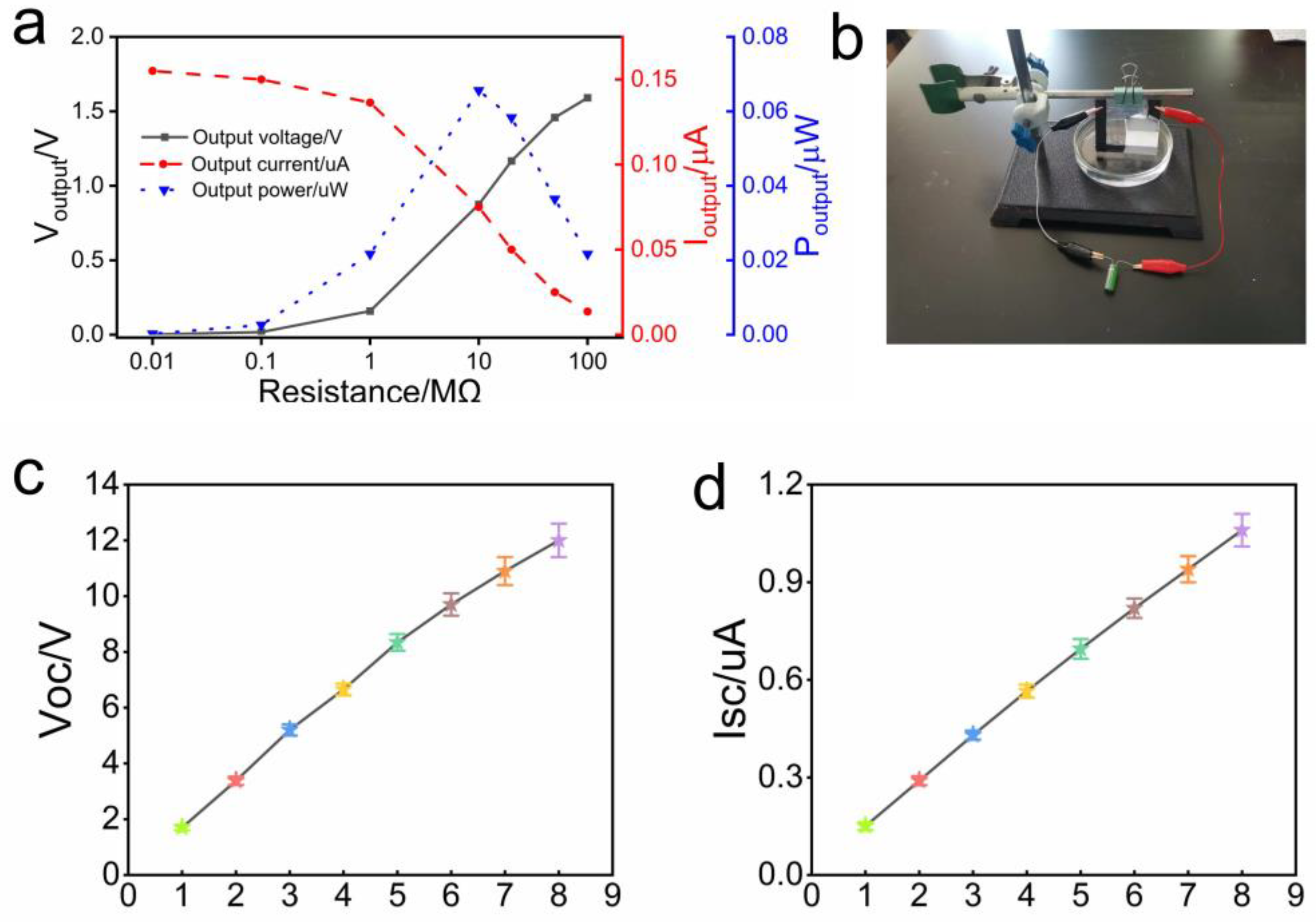
3.3. Influence Factors
3.4. Application of the Device
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- D’Odorico, P.; Davis, K.F.; Rosa, L.; Carr, J.A.; Chiarelli, D.; Dell’Angelo, J.; Gephart, J.; MacDonald, G.K.; Seekell, D.A.; Suweis, S.; et al. The Global Food-Energy-Water Nexus. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 456–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddeland, I.; Heinke, J.; Biemans, H.; Eisner, S.; Floerke, M.; Hanasaki, N.; Konzmann, M.; Ludwig, F.; Masaki, Y.; Schewe, J.; et al. Global water resources affected by human interventions and climate change. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3251–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Fakhreddine, S.; Rateb, A.; de Graaf, I.; Famiglietti, J.; Gleeson, T.; Grafton, R.Q.; Jobbagy, E.; Kebede, S.; Kolusu, S.R.; et al. Global water resources and the role of groundwater in a resilient water future. Nat. Rev. Earth Env. 2023, 4, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, V.-D.; Vu, N.H.; Dang, H.-L.T.; Yun, S. Recent advances and challenges for water evaporation-induced electricity toward applications. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 105979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Abrha, H.; Liu, M.; Cui, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Liu, X. Graphene oxide as a versatile platform for emerging hydrovoltaic technology. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 18451–18469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Abrha, H.; Wang, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, J.; Kang, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Emerging hydrovoltaic technology based on carbon black and porous carbon materials: A mini review. Carbon 2022, 193, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Kim, M.S.; Cho, Y.; Ahn, J.; Ahn, S.; Nam, J.S.; Bae, J.; Yun, T.G.; Kim, I.-D. Hydrovoltaic Electricity Generator with Hygroscopic Materials: A Review and New Perspective. Adv. Mater. 2023, e2301080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Yin, J.; Xu, Y.; Fei, W.; Xue, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Guo, W. Emerging hydrovoltaic technology. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2018, 13, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, F.; Wang, X.; Fang, S.; Tan, J.; Chu, W.; Rong, R.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Hydrovoltaic technology: From mechanism to applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 4902–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zheng, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.; Song, Y.; Deng, X.; Leung, M.; Yang, Z.; Xu, R.X.; et al. A droplet-based electricity generator with high instantaneous power density. Nature 2020, 578, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Mendel, N.; van Der Ham, S.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G.; Mugele, F. Charge Trapping-Based Electricity Generator (CTEG): An Ultrarobust and High Efficiency Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting from Water Droplets. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wall, S. The history of electrokinetic phenomena. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Sood, A.K.; Kumar, N. Carbon nanotube flow sensors. Science 2003, 299, 1042–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, G.; Xu, Y.; Ding, T.; Li, J.; Yin, J.; Fei, W.; Cao, Y.; Yu, J.; Yuan, L.; Gong, L.; et al. Water-evaporation-induced electricity with nanostructured carbon materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.; Liao, Q.; Yao, H.; Shi, G.; Qu, L. Interface-mediated hygroelectric generator with an output voltage approaching 1.5 volts. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, D.; Xiao, M.; Zou, G.; Liu, L.; Duley, W.W.; Zhou, Y.N. Self-Powered Wearable Electronics Based on Moisture Enabled Electricity Generation. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Gao, H.; Ward, J.E.; Liu, X.; Yin, B.; Fu, T.; Chen, J.; Lovley, D.R.; Yao, J. Power generation from ambient humidity using protein nanowires. Nature 2020, 578, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.J. Simultaneous solar-driven seawater desalination and spontaneous power generation using polyvalent crosslinked polypyrrole/alginate hydrogels. Desalination 2021, 500, 114900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Ma, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, S. Water evaporation-induced electricity with Geobacter sulfurreducens biofilms. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shen, D.; Duley, W.W.; Tan, C.; Zhou, Y.N. Water-Enabled Electricity Generation: A Perspective. Adv. Energ. Sust. Res. 2022, 3, 2100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, I.; Brandon, D. Metastable alumina polymorphs: Crystal structures and transition sequences. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1998, 81, 1995–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-F.V.; Kurma, T. Transport properties of alumina nanofluids. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 345702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Huang, A.; Gu, H.; Ni, H. Properties and microstructures of lightweight alumina containing different types of nano-alumina. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 17885–17894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ding, Z.; Tan, Q.; Qi, H.; He, Y. Preparation of nano alpha-alumina powder and wear resistance of nanoparticles reinforced composite coating. Powder Technol. 2014, 257, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yan, Y.; Liu, B.; Chen, W.; Chen, S. Studies of surface functional modification of nanosized alpha-alumina. Powder Technol. 2007, 178, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimazaki, Y.; Hojo, F.; Takezawa, Y. Highly Thermoconductive Polymer Nanocomposite with a Nanoporous alpha-Alumina Sheet. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.R.; Borah, J.M.; Kunz, W.; Ninham, B.W.; Mahiuddin, S. Ion specificity of the zeta potential of alpha-alumina, and of the adsorption of p-hydroxybenzoate at the alpha-alumina-water interface. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2010, 344, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Chemistry of alumina, reactions in aqueous solution and its application in water treatment. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2004, 110, 19–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Clavijo, A.; Caballero-Calero, O.; Martin-Gonzalez, M. Revisiting anodic alumina templates: From fabrication to applications. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 2227–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, N.; Ola, O.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, Y. Porous ceramics: Light in weight but heavy in energy and environment technologies. Mat. Sci. Eng. R 2021, 143, 100589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez-Alvarez, C.; Zilkova, N.; Perez-Pariente, J.; Cejka, J. Synthesis, characterization and catalytic applications of organized mesoporous aluminas. Catal. Rev. 2008, 50, 222–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Ji, B.; Xu, T.; Gao, J.; Gao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, N.; Jiang, L.; Qu, L. Large-Scale Production of Flexible, High-Voltage Hydroelectric Films Based on Solid Oxides. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 30927–30935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Feng, S.; Bai, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, M.; Hao, M.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Sun, F.; Liu, Z.; et al. Enhancing hydrovoltaic power generation through heat conduction effects. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hao, M.; Yang, X.; Sun, F.; Bai, Y.; Ding, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, T. Sustainable and flexible hydrovoltaic power generator for wearable sensing electronics. Nano Energy 2020, 72, 104663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Li, J.; Xu, Y.; Shen, C.; Guo, W. Evaporating potential. Joule 2022, 6, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Chen, N.; Shao, C.; Liu, Q.; Gao, J.; Xu, T.; Cheng, H.; Qu, L. Intelligent multiple-liquid evaporation power generation platform using distinctive Jaboticaba-like carbon nanosphere@TiO2 nanowires. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 6766–6772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Maryam, B.; Xu, S.; Liu, W.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X. Evaporation Driven Hydrovoltaic Generator Based on Nano-Alumina-Coated Polyethylene Terephthalate Film. Polymers 2023, 15, 4079. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204079
Jiao S, Zhang Y, Li Y, Maryam B, Xu S, Liu W, Liu M, Li J, Zhang X, Liu X. Evaporation Driven Hydrovoltaic Generator Based on Nano-Alumina-Coated Polyethylene Terephthalate Film. Polymers. 2023; 15(20):4079. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204079
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Shipu, Yihao Zhang, Yang Li, Bushra Maryam, Shuo Xu, Wanxin Liu, Miao Liu, Jiaxuan Li, Xu Zhang, and Xianhua Liu. 2023. "Evaporation Driven Hydrovoltaic Generator Based on Nano-Alumina-Coated Polyethylene Terephthalate Film" Polymers 15, no. 20: 4079. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204079
APA StyleJiao, S., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Maryam, B., Xu, S., Liu, W., Liu, M., Li, J., Zhang, X., & Liu, X. (2023). Evaporation Driven Hydrovoltaic Generator Based on Nano-Alumina-Coated Polyethylene Terephthalate Film. Polymers, 15(20), 4079. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15204079






