Effect of Rice Husk and Wood Flour on the Structural, Mechanical, and Fire-Retardant Characteristics of Recycled High-Density Polyethylene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Materials
2.2. Fabrication of Composites
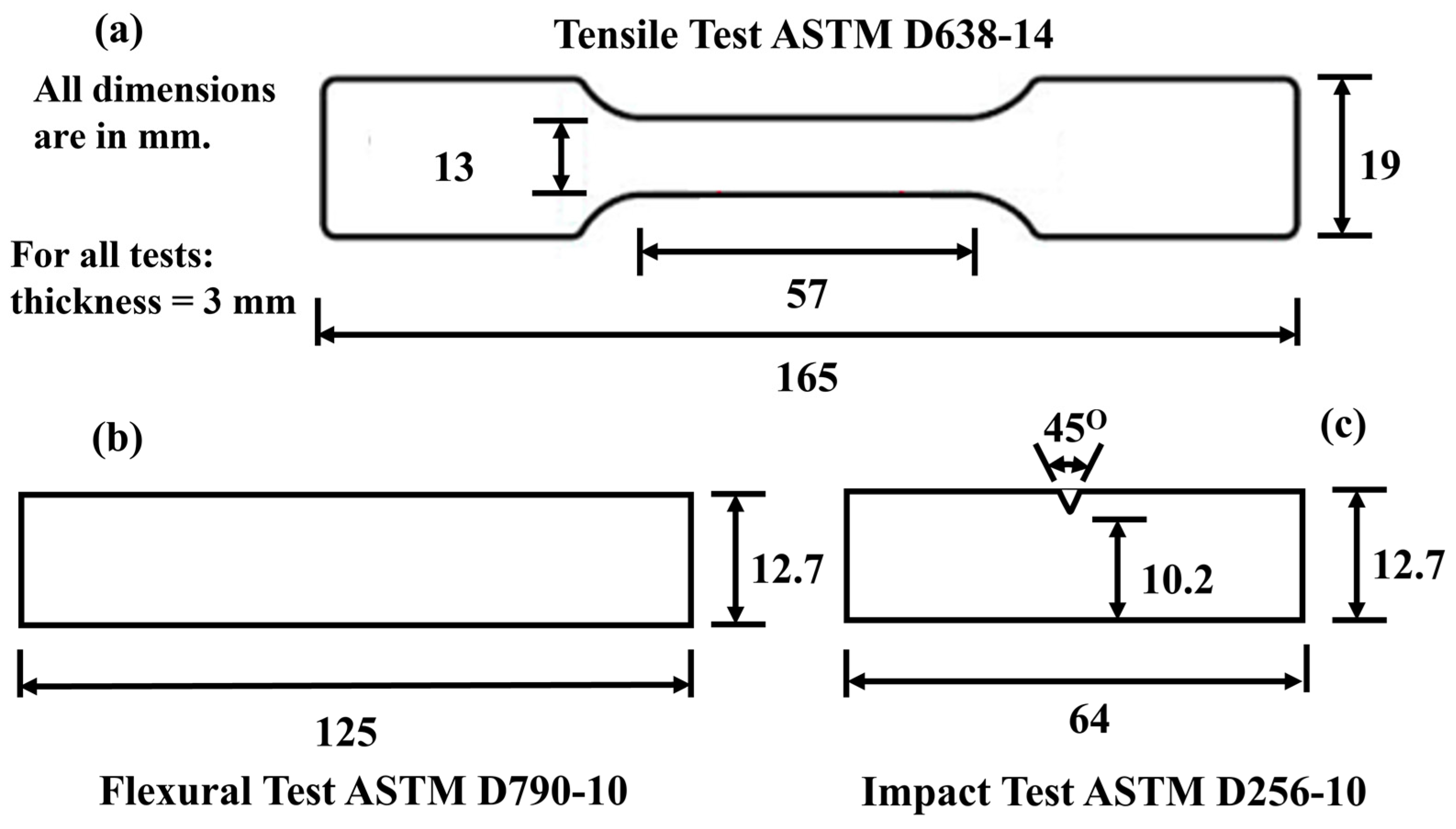
2.3. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
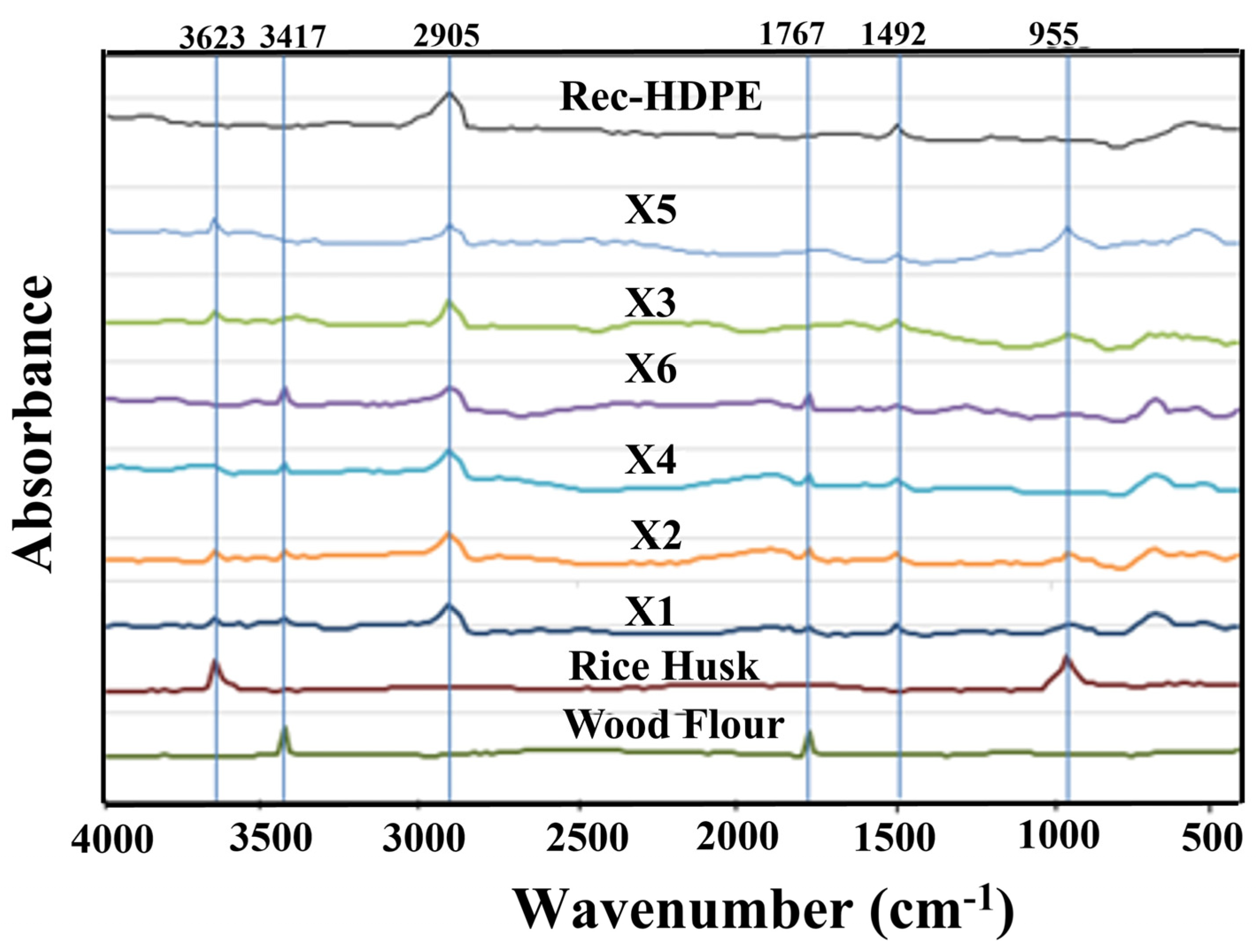
3.1. FTIR
3.2. Tensile Properties
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
3.4. Flexural Properties
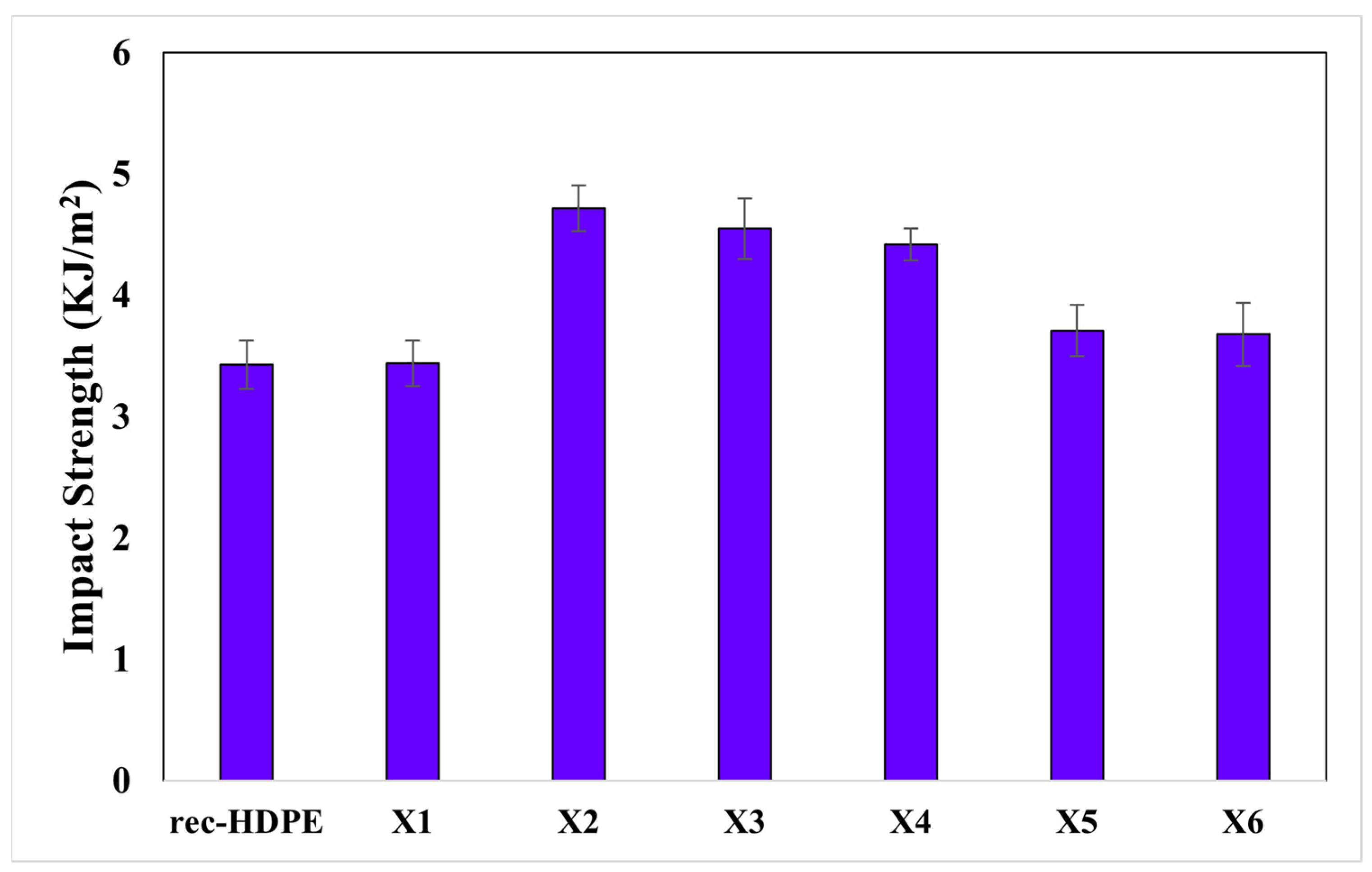
3.5. Charpy Impact Test
3.6. Horizontal and Vertical Burning Tests
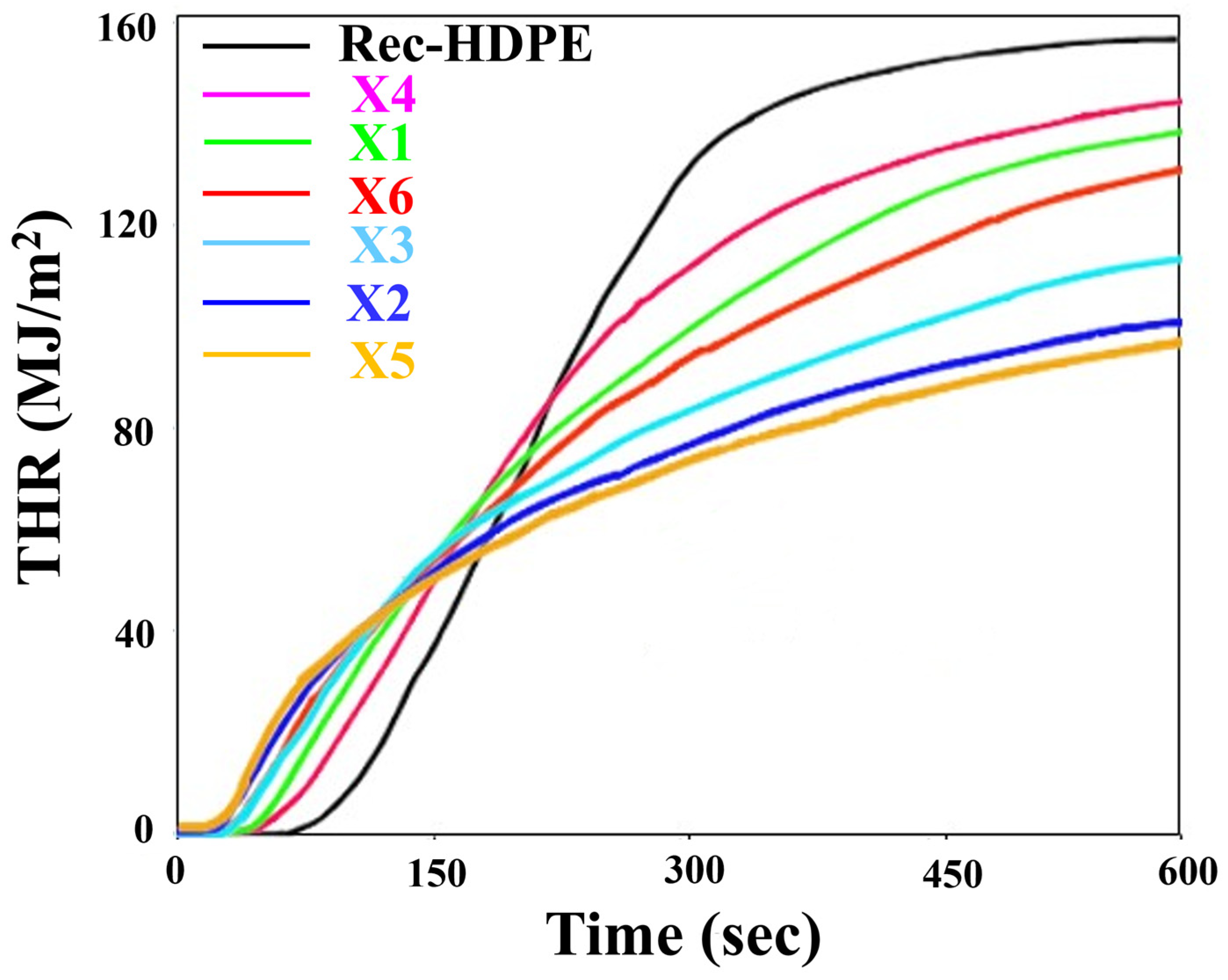
3.7. Cone Calorimeter Test
3.8. Limited Oxygen Index Test (LOI Test)
3.9. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abd-Elhady, A.A.; Sallam, H.E.D.M.; Alarifi, I.M.; Malik, R.A.; El-Bagory, T.M. Investigation of fatigue crack propagation in steel pipeline repaired by glass fiber reinforced polymer. Compos. Struct. 2020, 242, 11218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabeel, M.; Nasir, M.A.; Sattar, M.; Malik, R.A.; Alzaid, M.; Butt, M.S.; Saleem, M.; Alrobei, H. Numerical and experimental evaluation of the mechanical behavior of Kevlar/glass fiber reinforced epoxy hybrid composites. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2020, 34, 4613–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, Z.; Nasir, M.A.; Baig, Y.; Zeeshan, M.; Malik, R.A.; Shaker, K.; Hussain, A.; Latif, M.; Sattar, M.; Alrobei, H. Drop weight impact and tension-tension loading fatigue behaviour of jute/carbon fibers reinforced epoxy- based hybrid composites. Polymers 2020, 44, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-H.; Liu, B.-W.; Zeng, F.-R.; Lin, X.-C.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Zhao, H.-B. Fully recyclable multifunctional adhesive with high durability, transparency, flame retardancy, and harsh environment resistance. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eadd8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.-R.; Liu, B.-W.; Wang, Z.-H.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Chen, X.-L.; Zhao, H.-B.; Wang, Y.-Z. Recyclable Biophenolic Nanospheres for Sustainable and Durable Multifunctional Applications in Thermosets. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 1692–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, Y. Recent progress on preparation and properties of nanocomposites from recycled polymers: A review. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Koubaa, A.; Xing, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.M.; Wang, Q. Flammability, thermal stability, and mechanical properties of wood flour/polycarbonate/polyethylene bio-based composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 169, 113638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.S.; Ab Ghani, M.H.; Ahmad, S.; Salleh, M.N.; Tarawneh, M.A.A. Rice husk flour biocomposites based on recycled high-density polyethylene/polyethylene terephthalate blend: Effect of high filler loading on physical, mechanical and thermal properties. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjmandi, R.; Hassan, A.; Majeed, K.; Zakaria, Z. Rice husk filled polymer composites. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2015, 2015, 501471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Saini, M.S.; Kanungo, B.K.; Sinha, S. Study of Thermal Properties of Rice Husk Polypropylene (RHPP) Composites. Adv. Compos. Lett. 2013, 22, 096369351302200601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orjuela, D.; Munar, D.A.; Solano, J.K.; Becerra, A.P. Assessment of the Thermal Properties of a Rice Husk Mixture with Recovered Polypropylene and High Density Polyethylene, Using Sulfur-silane as a Coupling Agent. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2021, 87, 565–570. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, B.; Quan, H.; Yam, R.C.; Yuen, R.K.; Li, R.K. Flame retardancy of rice husk-filled high-density polyethylene ecocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 2675–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Salazar, M.A.; Salinas, E. Mechanical, thermal, viscoelastic performance and product application of PP-rice husk Colombian biocomposites. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 176, 107135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord, B. Nanofiller reinforcement effects on the thermal, dynamic mechanical, and morphological behavior of HDPE/rice husk flour composites. BioResources 2011, 6, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Telang, A.; Rana, R. Mechanical characterization of bio-char made hybrid composite. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2016, 6, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ketabchi, M.R.; Khalid, M.; Walvekar, R. Effect of oil palm EFB-biochar on properties of PP/EVA composites. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2017, 12, 797–808. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, M.D.; Govindaraju, H.K.; Jayaraju, T.; Kumar, N. Effect of fillers on mechanical properties of polymer matrix composites. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 22421–22424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundie, F.; Azhari, C.H.; Muchtar, A.; Ahmad, Z.A. Effects of filler size on the mechanical properties of polymer-filled dental composites: A review of recent developments. J. Phys. Sci. 2018, 29, 141–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiyad, M.; Devashrayee, N.M.; Mevada, R.K. Study the effect of dispersion of filler in polymer composite for radiation shielding. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, N.; Yamunadevi, V.; Mohanavel, V.; Chinnaiyan, V.K.; Bharani, M.; Ganeshan, P.; Karthick, A. Effects of the interfacial bonding behavior on the mechanical properties of E-glass fiber/nanographite reinforced hybrid composites. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2021, 2021, 6651896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.K.; Mandal, A.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Short jute fiber reinforced polypropylene composites: Effect of compatibiliser, impact modifier and fiber loading. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Matuana, L.M. Effectiveness of maleated and acrylic acid-functionalized polyolefin coupling agents for HDPE-wood-flour composites. J. Thermoplast. Compos. Mater. 2003, 16, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Pang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xia, R.; Li, Y.; Guo, H. Improvement of rice husk/HDPE bio- composites interfacial properties by silane coupling agent and compatibilizer complementary modification. Polymers 2019, 11, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.R.; Imdad, A.; Sadiq, A.; Malik, R.A.; Alrobei, H.; Badruddin, I.A. Mechanical, Thermal, and Fire Retardant Properties of Rice Husk Biochar Reinforced Recycled High-Density Polyethylene Composite Material. Polymers 2023, 15, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulana, F.; Mariana, M.; Hadman, M.N.; Hanipah, S.H. The study on composites formation from HDPE and sawdust/rice husk as raw materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 523, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xie, Y.; Ou, R.; Wang, Q. Grafting effects of polypropylene/polyethylene blends with maleic anhydride on the properties of the resulting wood–plastic composites. Compos. A Appl. 2012, 43, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Khan, M.U.; Lin, X.; Cai, H.; Lei, H. Temperature varied biochar as a reinforcing filler for high-density polyethylene composites. Compos. B Eng. 2019, 175, 107151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Cai, H.; Lin, X.; Yi, W.; Zhang, J. Properties comparison of high density polyethylene composites filled with three kinds of shell fibers. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 1542–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.; Gerdts, G.; Völker, C.; Niebühr, V. Using FTIRS as pre-screening method for detection of microplastic in bulk sediment samples. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 689, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Koubaa, A.; Xing, D.; Liu, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Improving lignocellulose thermal stability by chemical modification with boric acid for incorporating into polyamide. Mater. Des. 2020, 191, 108589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, L.K.; Zimmermann, M.V.G.; Perondi, D.; Zampieri, V.B.; Zattera, A.J.; Santana, R.M.C. Production of carbon foams from rice husk. Mater. Res. 2019, 22 (Suppl. S1), e20190427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffalla, S.B.; Mukhtar, H.; Shaharun, M.S. Preparation and characterization of rice husk adsorbents for phenol removal from aqueous systems. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmiyati, H.; Suci, R.P. Nanocomposite of cellulose-ZnO/SiO2 as catalyst biodiesel methyl ester from virgin coconut oil. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing: Melville, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 2168, p. 020063. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, B.; Hakkarainen, M. Green plasticizers from liquefied wood. Waste Biomass Valorization 2014, 5, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Son, J.; Park, H.J.; Lee, B.J.; Hwang, T.S. Rice-husk flour filled polypropylene composites; mechanical and morphological study. Compos. Struct. 2004, 63, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, S.; Sreekala, M.S.; Oommen, Z.; Koshy, P.; Thomas, S. A comparison of the mechanical properties of phenol formaldehyde composites reinforced with banana fibres and glass fibres. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2002, 62, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, S.M.; Del, T.J.; Rocha, G.J.M.; Gonçalves, A.R.; Del’Arco, A.P., Jr. Cellulose and cellulignin from sugarcane bagasse reinforced polypropylene composites: Effect of acetylation on mechanical and thermal properties. Compos. A Appl. 2008, 39, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.Y.; Royan, N.R.R.; Ng, Y.C.; Ab Ghani, M.H.; Ahmad, S. Study of the mechanical and morphology properties of recycled HDPE composite using rice husk filler. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 938961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, H.J.; Lee, B.J.; Hwang, T.S. Effect of compatibilizing agents on rice-husk flour reinforced polypropylene composites. Compos. Struct. 2007, 77, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.A.; Peng, W.; Zare, Y.; Rhee, K.Y. Effects of size and aggregation/agglomeration of nanoparticles on the interfacial/interphase properties and tensile strength of polymer nanocomposites. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Islam, M.N.; Huque, M.M.; Hamdan, S.; Ahmed, A.S. Effect of chemical treatment on rice husk (RH) reinforced polyethylene (PE) composites. BioResources 2010, 5, 854–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.C.; Chang, L.C.; Nien, M.H.; Ho, H.L. Mechanical behavior of various nanoparticle filled composites at low-velocity impact. Compos. Struct. 2006, 74, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, M.; Azad, M.M.; Shah, A.R.; Afaq, S.K.; Song, J.I. Synergistic effect of aluminum trihydrate and zirconium hydroxide nanoparticles on mechanical properties, flammability, and thermal degradation of polyester/jute fiber composite. Cellulose 2022, 29, 1775–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Nayak, R.K.; Panigrahi, I. Effect of nano-fillers on low-velocity impact properties of synthetic and natural fibre reinforced polymer composites—A review. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 8, 2963–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Ni, A.; Chen, H.; Shen, P. Synthesis of a novel phosphorous-nitrogen based charring agent and its application in flame-retardant HDPE/IFR composites. Polymers 2019, 11, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-W.; Zhao, H.-B.; Wang, Y.-Z. Advanced Flame-Retardant Methods for Polymeric Materials. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Gilman, J.W.; Butler, K.M.; Harris, R.H.; Shields, J.R.; Asano, A. Flame retardant mechanism of silica gel/silica. Fire Mater. 2000, 24, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwagi, T.; Shields, J.R.; Harris Jr, R.H.; Davis, R.D. Flame-retardant mechanism of silica: Effects of resin molecular weight. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 87, 1541–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Eom, Y.G. Thermogravimetric analysis of rice husk flour for a new raw material of lignocellulosic fiber-thermoplastic polymer composites. J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2001, 29, 59–67. [Google Scholar]





| Sr. No | Recycled HDPE Pellets wt. % | Rice Husk Powder wt. % | Wood Flour Powder wt. % | Compatibilizer (MAPE) wt. % | Nomenclature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | rec-HDPE |
| 2 | 87 | 5 | 5 | 3 | X1 |
| 3 | 77 | 10 | 10 | 3 | X2 |
| 4 | 87 | 10 | 0 | 3 | X3 |
| 5 | 87 | 0 | 10 | 3 | X4 |
| 6 | 77 | 20 | 0 | 3 | X5 |
| 7 | 77 | 0 | 20 | 3 | X6 |
| Samples | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Tensile Modulus (GPa) | Flexural Strength (MPa) | Flexural Modulus (GPa) | Impact Strength (kJ/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rec-HDPE | 14.99 | 1.01 | 20.12 | 0.77 | 3.43 |
| X1 | 15.01 | 1.01 | 20.14 | 0.79 | 3.44 |
| X2 | 15.52 | 1.06 | 20.44 | 0.87 | 4.72 |
| X3 | 16.77 | 1.17 | 21.59 | 1.17 | 4.55 |
| X4 | 15.41 | 1.1 | 20.67 | 0.02 | 4.42 |
| X5 | 15.25 | 1.07 | 20.44 | 0.9 | 3.71 |
| X6 | 14.15 | 0.98 | 19.56 | 0.78 | 3.68 |
| Cone Calorimetric Test | Horizontal Burning Test | Vertical Burning Test | LOI Test | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Types | TTI (sec) | TPHRR (sec) | PHRR (kW/m2) | THR (MJ/m2) | Avg. Burning Time (Min) | Avg. Burning Rate (mm/Min) | Rating | Max. after Flame Time (sec) | Total after Flame Time (sec) | Max after Flame + after Glow Time (sec) | Flame up to the Holding Clamp | Cotton Ignited by Flaming Drops | Rating | LOI (%) |
| Rec-HDPE | 59 | 210 | 548.66 | 155.40 | 1.66 | 45.10 | Nil | 61 | 281 | - | Yes | Yes | Nil | 16.97 |
| X1 | 46 | 130 | 475.76 | 137.31 | 1.77 | 42.22 | Nil | 53 | 261 | - | Yes | Yes | Nil | 17.97 |
| X2 | 36 | 96 | 389.25 | 100.22 | 1.83 | 40.84 | Nil | 50 | 252 | - | Yes | Yes | Nil | 20.58 |
| X3 | 36 | 123 | 418.91 | 112.49 | 1.82 | 41.06 | Nil | 52 | 257 | - | Yes | Yes | Nil | 19.41 |
| X4 | 51 | 138 | 494.29 | 143.14 | 1.70 | 44.04 | Nil | 55 | 271 | - | Yes | Yes | Nil | 17.63 |
| X5 | 33 | 104 | 363.3 | 96.24 | 2.01 | 37.25 | HB | 24 | 237 | 56 | Yes | No | V-2 | 21.06 |
| X6 | 45 | 127 | 446.10 | 129.65 | 1.86 | 40.18 | Nil | 48 | 235 | - | Yes | Yes | Nil | 18.52 |
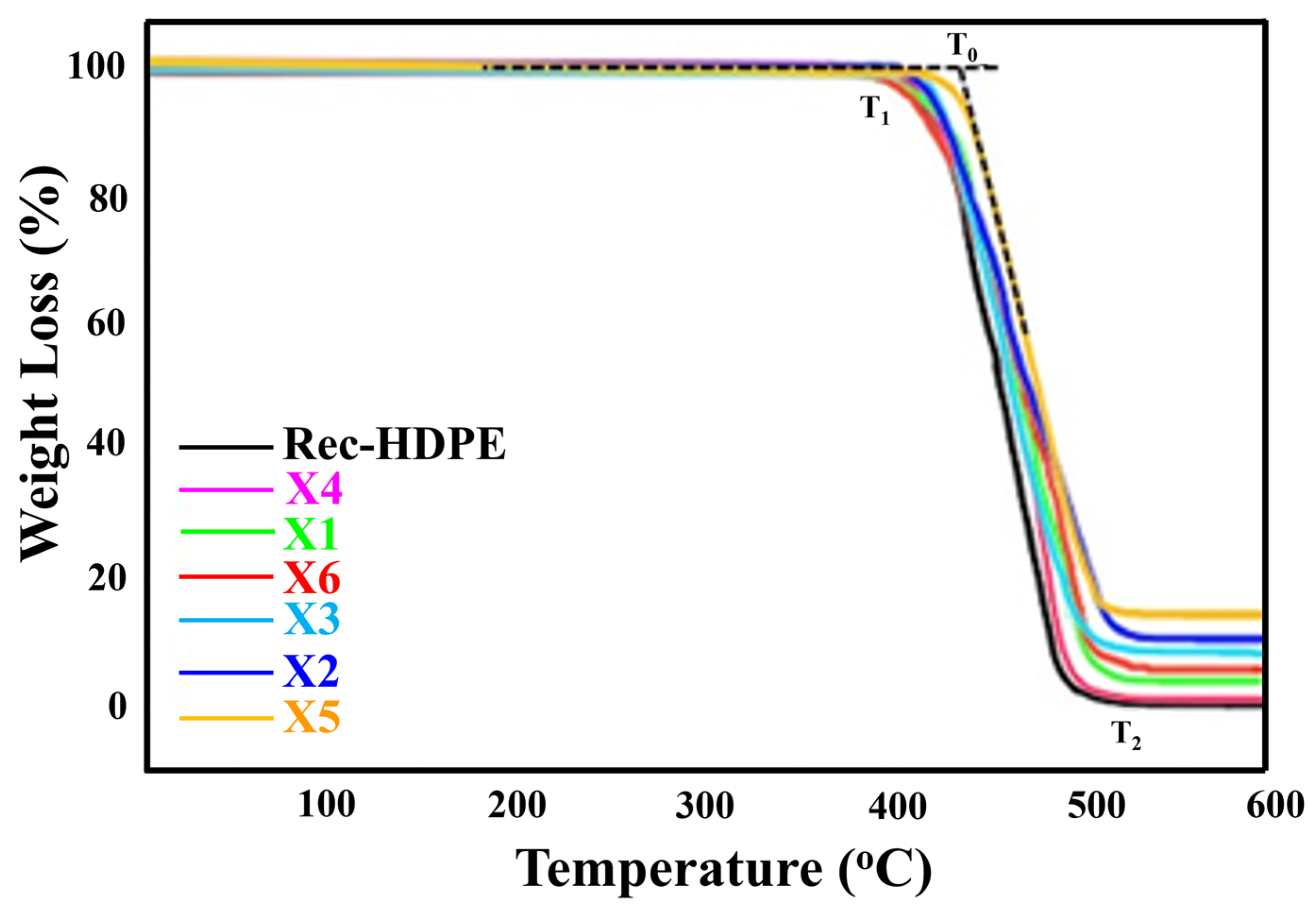
| Sample | To (Onset Degradation Temperature) (°C) | T1 (Starting Degradation Temperature) (°C) | T2 (Final Degradation Temperature) (°C) | Residue % at 600 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| REC-HDPE | 426.55 | 402.34 | 522.12 | 0.39% |
| X1 | 431.38 | 404.97 | 525.95 | 3.93% |
| X2 | 429.94 | 409.29 | 533.08 | 10.66% |
| X3 | 427.84 | 407.64 | 531.32 | 8.91% |
| X4 | 426.74 | 402.92 | 525.88 | 0.95% |
| X5 | 436.13 | 413.11 | 535.19 | 14.73% |
| X6 | 432.86 | 403.55 | 536.74 | 6.81% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shah, A.U.R.; Jalil, A.; Sadiq, A.; Alzaid, M.; Naseem, M.S.; Alanazi, R.; Alanazi, S.; Alanzy, A.O.; Alsohaimi, I.H.; Malik, R.A. Effect of Rice Husk and Wood Flour on the Structural, Mechanical, and Fire-Retardant Characteristics of Recycled High-Density Polyethylene. Polymers 2023, 15, 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15194031
Shah AUR, Jalil A, Sadiq A, Alzaid M, Naseem MS, Alanazi R, Alanazi S, Alanzy AO, Alsohaimi IH, Malik RA. Effect of Rice Husk and Wood Flour on the Structural, Mechanical, and Fire-Retardant Characteristics of Recycled High-Density Polyethylene. Polymers. 2023; 15(19):4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15194031
Chicago/Turabian StyleShah, Atta Ur Rehman, Abdul Jalil, Atiya Sadiq, Meshal Alzaid, Muhammad Shoaib Naseem, Rakan Alanazi, Sultan Alanazi, Abdullatyf Obaid Alanzy, Ibrahim Hotan Alsohaimi, and Rizwan Ahmed Malik. 2023. "Effect of Rice Husk and Wood Flour on the Structural, Mechanical, and Fire-Retardant Characteristics of Recycled High-Density Polyethylene" Polymers 15, no. 19: 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15194031
APA StyleShah, A. U. R., Jalil, A., Sadiq, A., Alzaid, M., Naseem, M. S., Alanazi, R., Alanazi, S., Alanzy, A. O., Alsohaimi, I. H., & Malik, R. A. (2023). Effect of Rice Husk and Wood Flour on the Structural, Mechanical, and Fire-Retardant Characteristics of Recycled High-Density Polyethylene. Polymers, 15(19), 4031. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15194031








