Self-Oscillating Liquid Crystal Elastomer Helical Spring Oscillator with Combined Tension and Torsion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model and Formulation
2.1. Dynamics of the Helical Spring Oscillator
2.2. Helical Spring Model
2.3. Dynamic LCE Model of the Wire
2.4. Nondimensionalization
3. Two Motion Regimes and Mechanism of Self-Oscillation
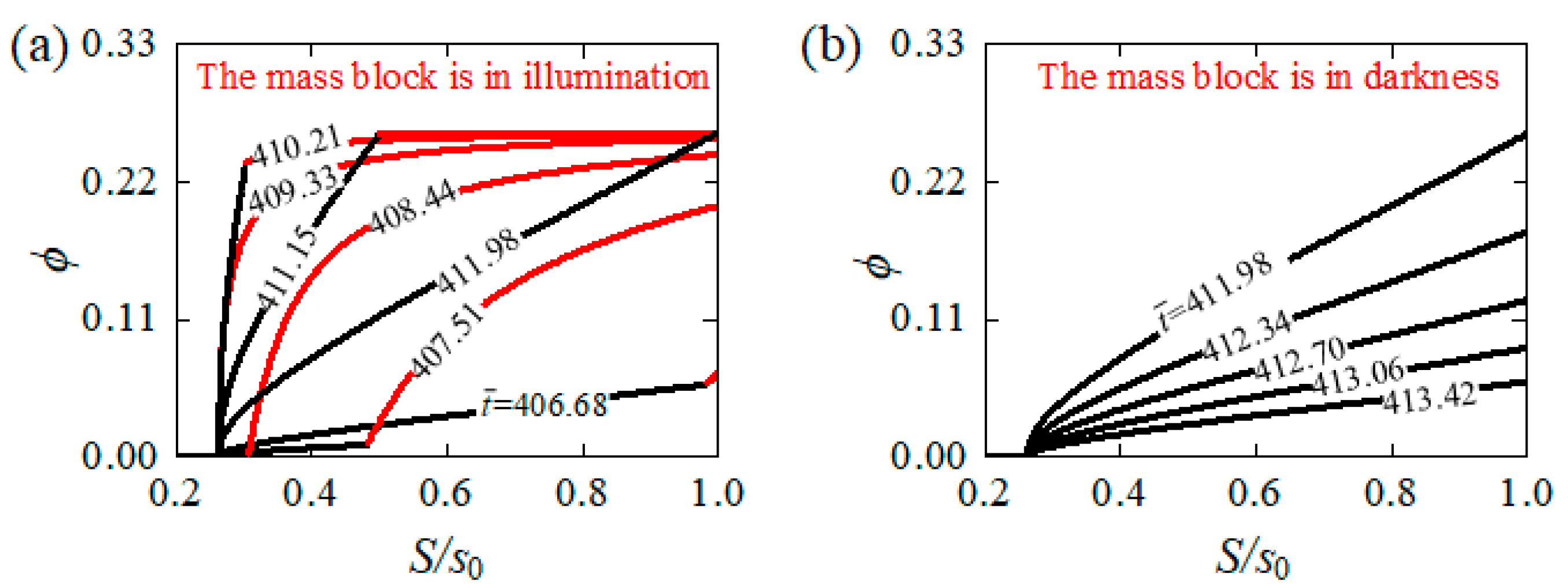
3.1. Two Motion Regimes
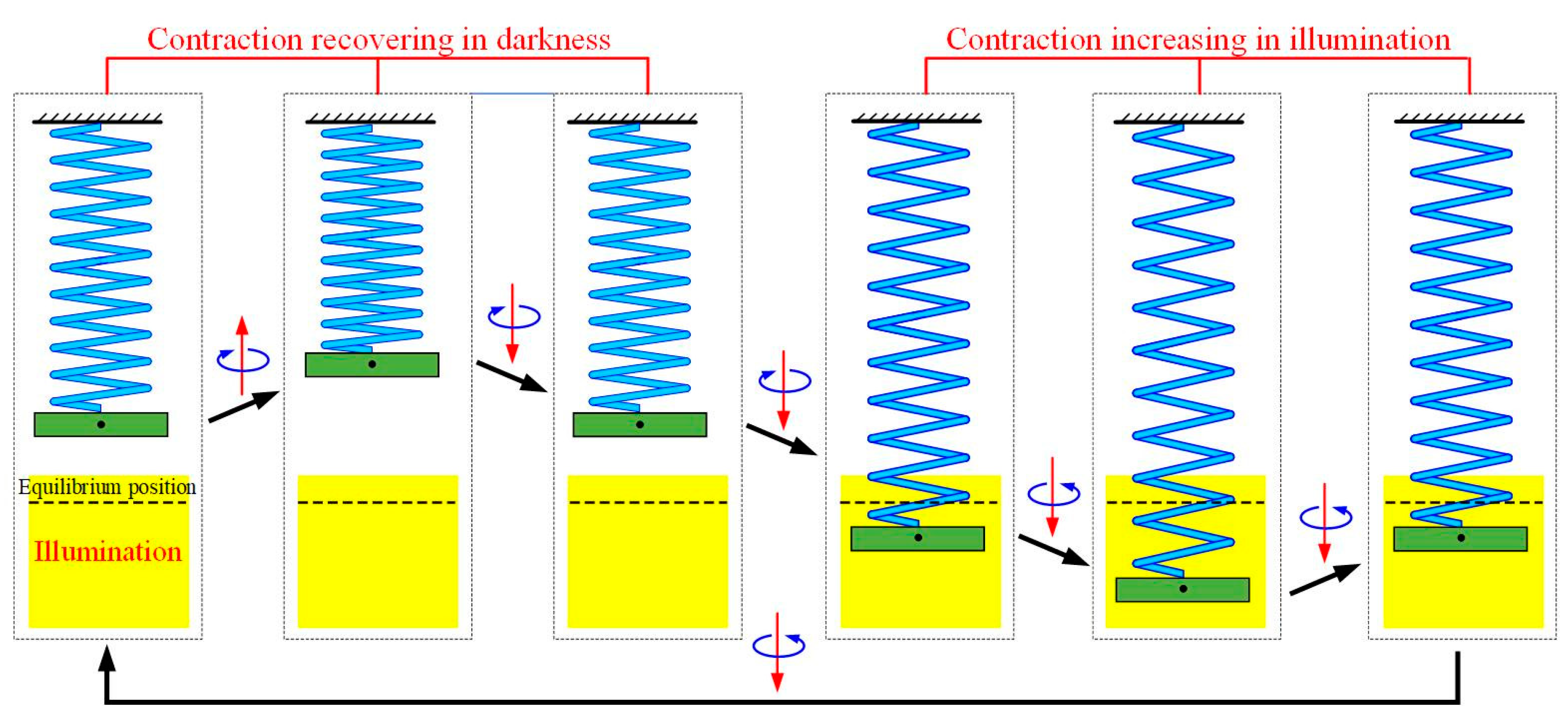
3.2. Mechanisms of the Self-Tension–Torsion
4. Effects of System Parameters on the Self-Tension–Torsion
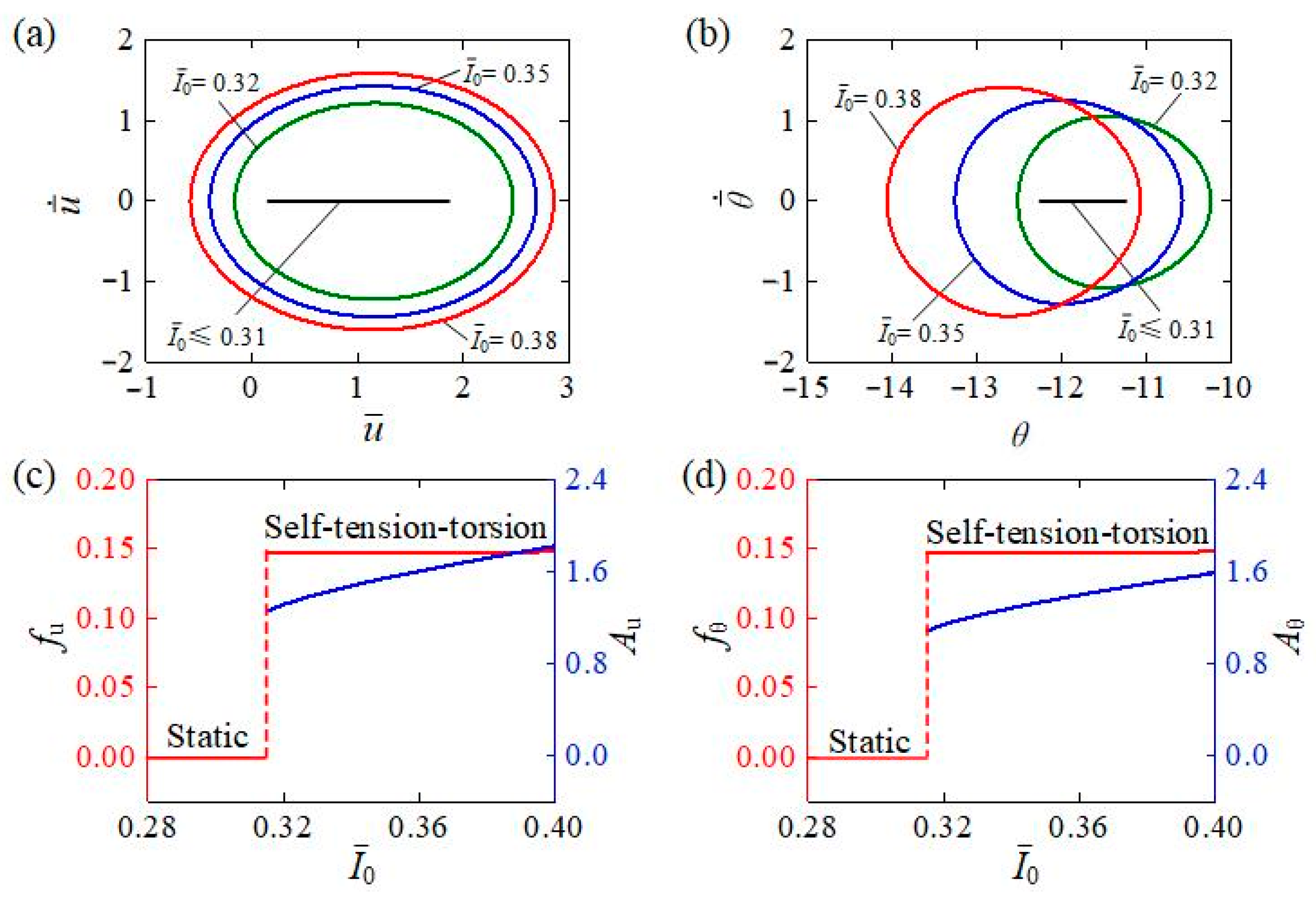
4.1. Influence of the Light Intensity
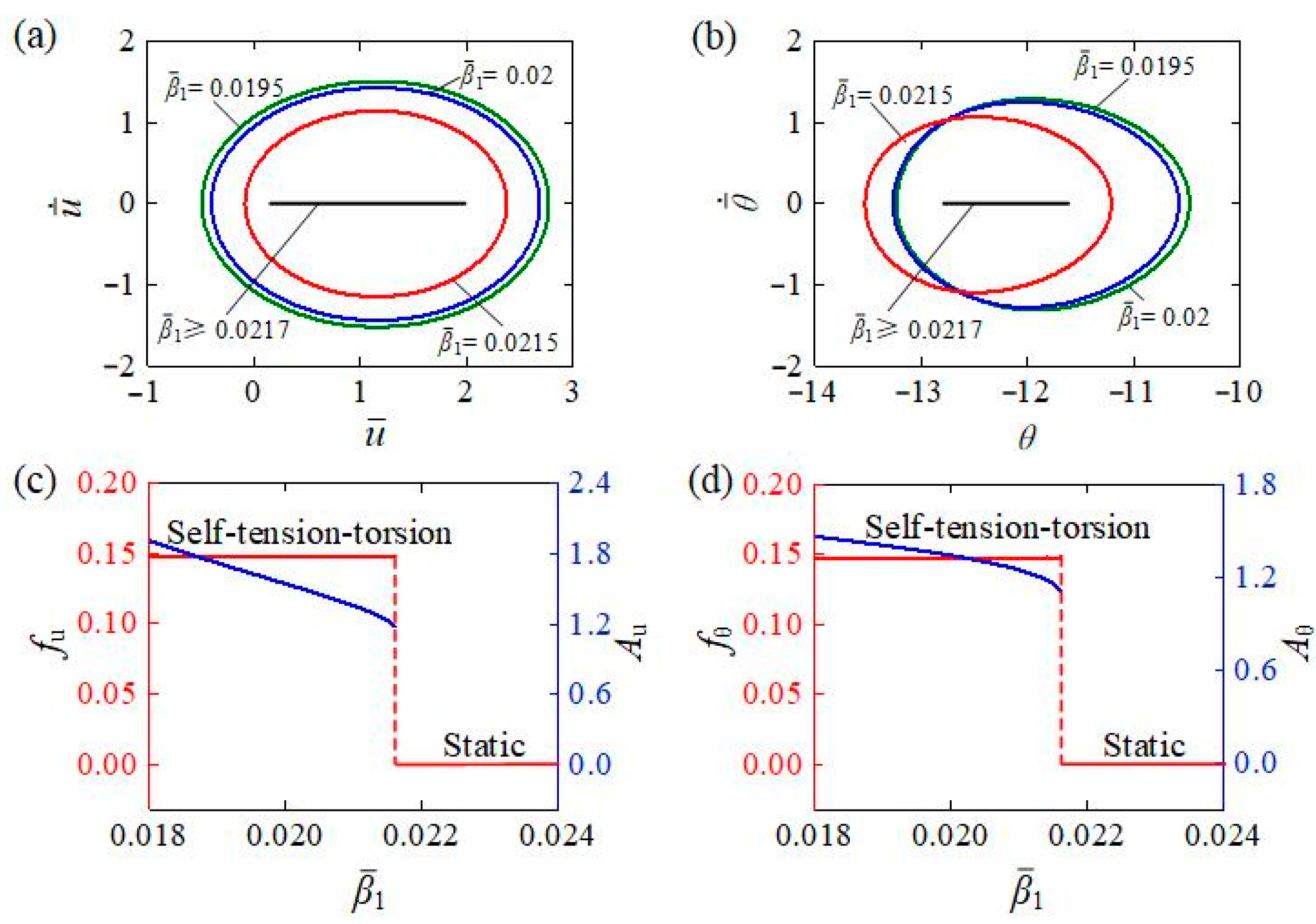
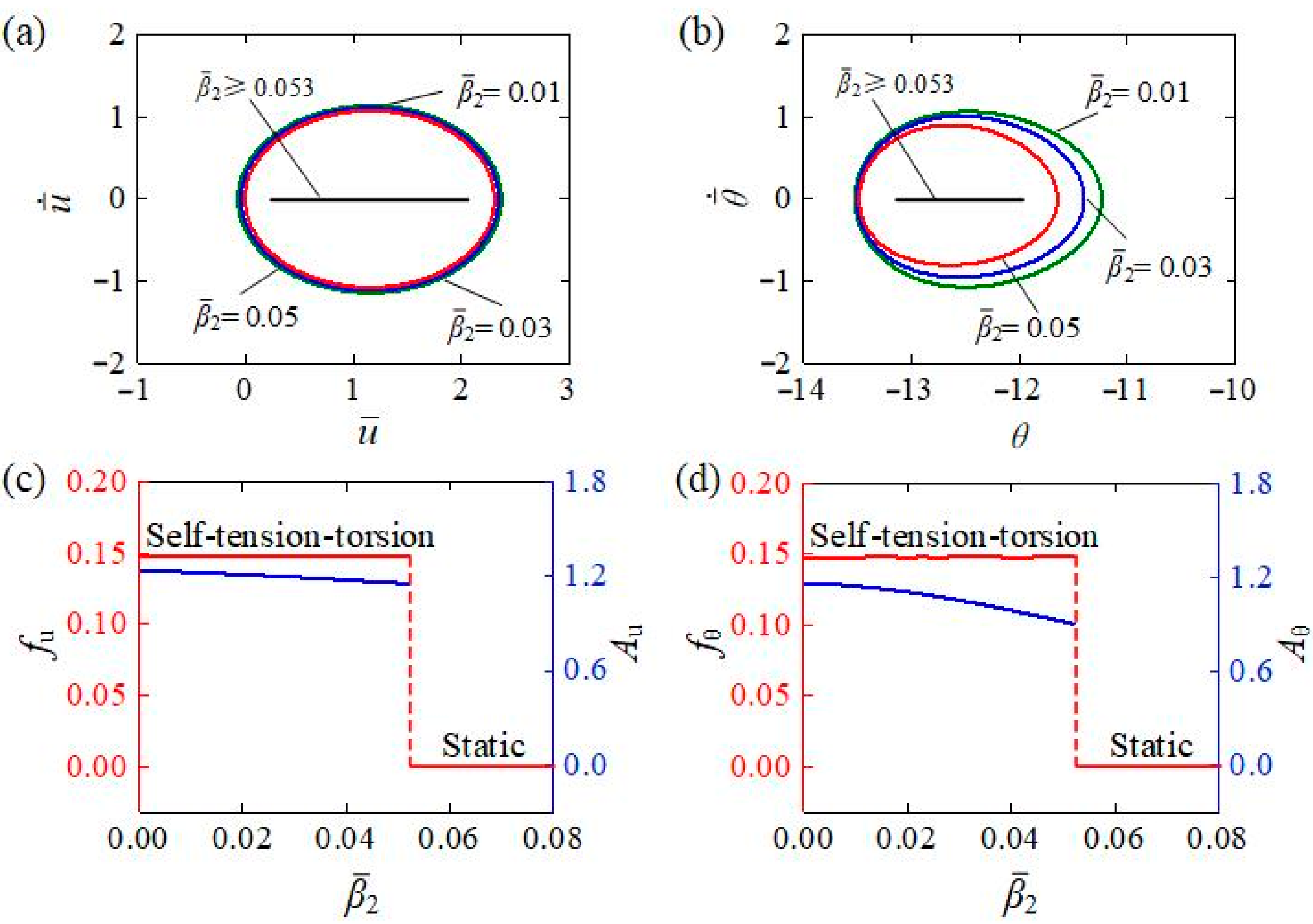
4.2. Influence of the Contraction Coefficient
4.3. Influence of the Translational Damping Coefficient
4.4. Influence of the Rotational Damping Coefficient
4.5. Influence of the Coil Radius
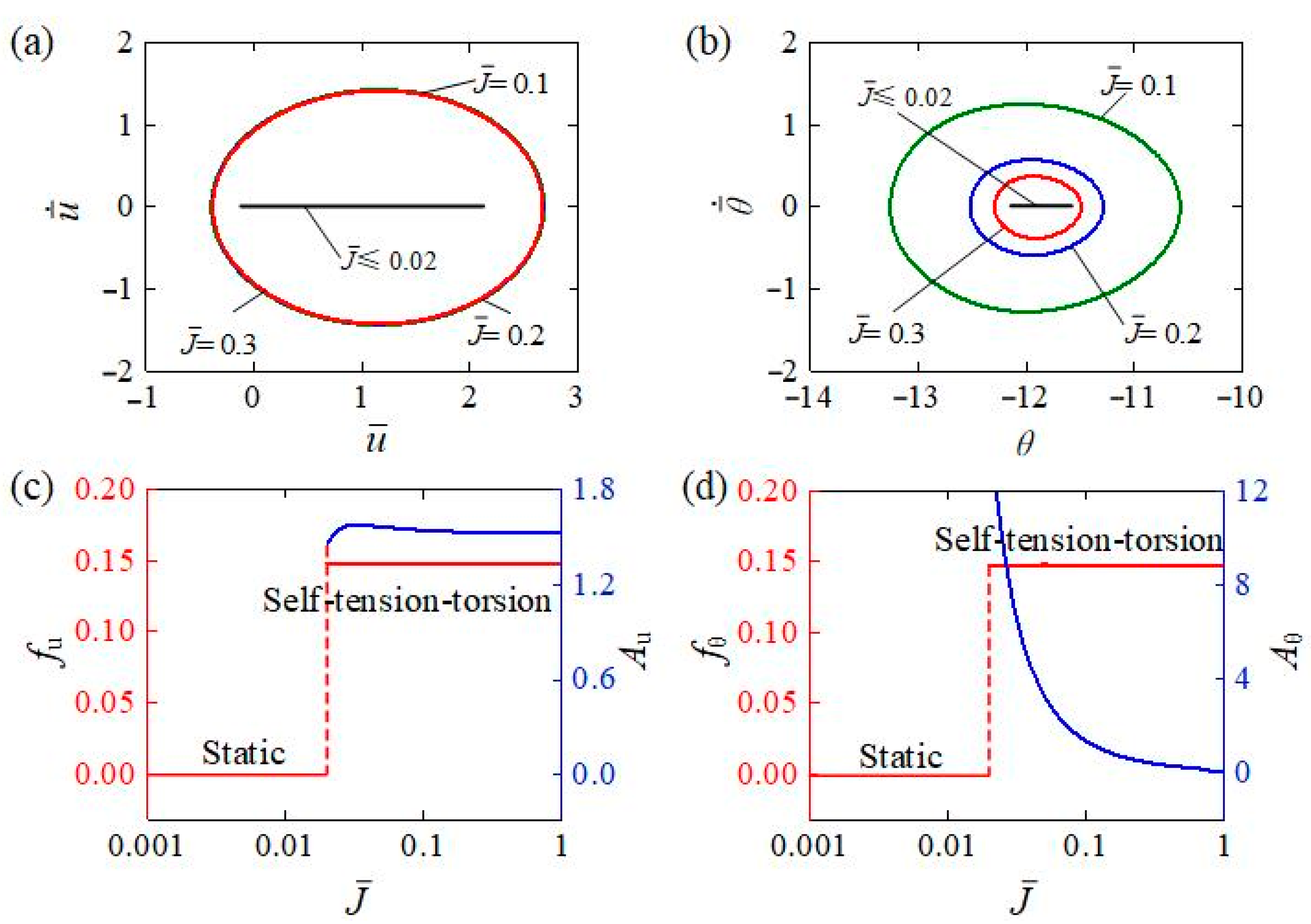
4.6. Influence of the Bending Stiffness
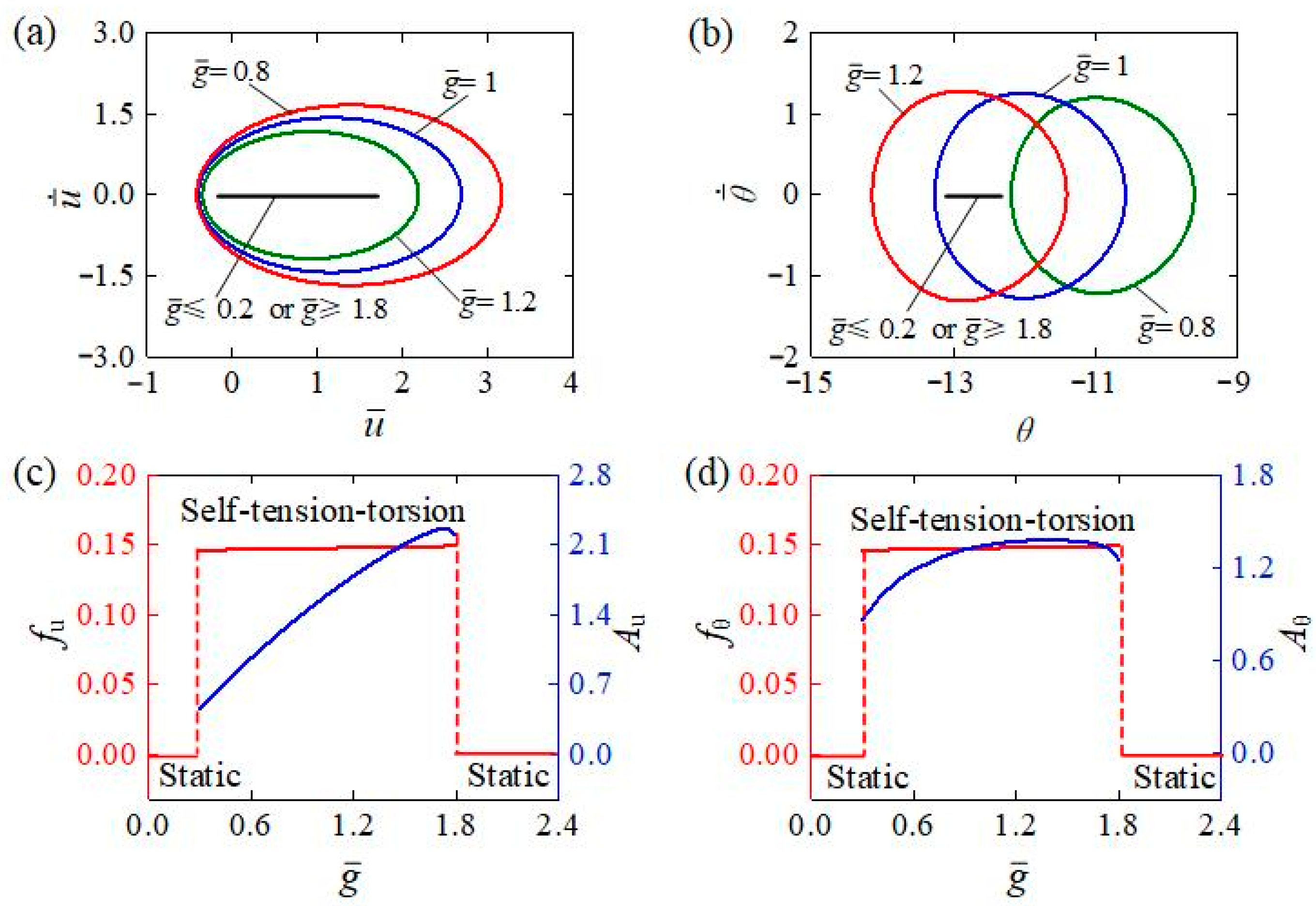
4.7. Influence of the Gravitational Acceleration
4.8. Influence of the Inertia Moment of Mass Block
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Korner, K.; Kuenstler, A.S.; Hayward, R.C.; Audoly, B.; Bhattacharya, K. A nonlinear beam model of photomotile structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9762–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zibaei, R.; Zakerhamidi, M.S.; Korramab, S.; Ranjkeshd, A. Effects of polarized light on the optical and self-oscillation behaviors of liquid crystal network polymers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 14908–14915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Du, C.; Li, K.; Cai, S. Controllable and versatile self-motivated motion of a fiber on a hot surface. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2022, 57, 101918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemati, Y.; Deng, Z.; Pi, H.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Priimagi, A.; Zeng, H. A Scalable, Incoherent-Light-Powered, Omnidirectional Self-Oscillator. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 2300054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ho, G.W. Design of untethered soft material micromachine for life-like locomotion. Mater. Today 2022, 53, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.C.; Lu, H.C.; Lee, X.; Zeng, H.; Priimagi, A. Kirigami-based light-induced shape-morphing and locomotion. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, C.; Ren, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Tang, D.; Hu, W.; Sitti, M. Magnetically actuated gearbox for the wireless control of millimeter-scale robots. Soft. Robot. 2022, 7, eabo4401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, M.F.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, W.; Norris, S.L.; Lee, S.; Miskin, M.Z.; Molnar, A.C.; Cohen, I.; Mceuen, P.L. Microscopic robots with onboard digital control. Soft Robot. 2022, 7, abq2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, Z.; Xu, P. Light-propelled self-sustained swimming of a liquid crystal elastomer torus at low Reynolds number. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 219, 107128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, Y. A prototype for light-electric harvester based on light sensitive liquid crystal elastomer cantilever. Energy 2020, 198, 117351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, S.; Pang, C.; Cho, S.B. A micropillar-assisted versatile strategy for highly sensitive and efficient triboelectric energy generation under in-plane stimuli. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1905539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wie, J.J.; Shankar, M.R.; White, T.J. Photomotility of polymers. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Miao, J.; Li, G.; Ren, R.; Zhang, T.; Guo, D.; Tang, Y.; Shang, W.; Shen, Y. Soft tunable gelatin robot with insect-like claw for grasping, transportation and delivery. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 5431–5440. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, T.; Dong, X.; Hu, W.; Sitti, M. Wireless miniature magnetic phase-change soft actuators. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2204185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Yao, S.; Zhang, H.; Man, W.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Fang, D.; Zhang, Y. Liquid crystal elastomer metamaterials with giant biaxial thermal shrinkage for enhancing skin regeneration. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2170356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shi, W.; Chen, Z.; Du, M.; Xiao, S.; Qu, S.; Li, C. Light-fueled nonequilibrium and adaptable hydrogels for highly tunable autonomous self-oscillating functions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 202214394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, M.; Kim, C.; Du, Y.; Wu, D.; Bai, R.; He, X. Swaying gel: Chemo-mechanical self-oscillation based on dynamic buckling. Matter 2021, 4, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissonade, J.; Kepper, P.D. Multiple types of spatio-temporal oscillations induced by differential diffusion in the Landolt reaction. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 4132–4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Trabia, S.; Stalbaum, T.; Palmre, V.; Kim, K.; Oh, I. A multiple-shape memory polymer-metal composite actuator capable of programmable control, creating complex 3D motion of bending, twisting, and oscillation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, S. Multi-functional liquid crystal elastomer composites. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2022, 9, 011301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; Lahikainen, M.; Liu, L.; Ahmed, Z.; Wani, O.M.; Wang, M.; Yang, H.; Priimagi, A. Light-fuelled freestyle self-oscillators. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Ji, Q.; Huang, M.; Chang, L.; Zhang, C.; Wu, G.; Zi, B.; Bao, N.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y. Light-driven self-oscillating actuators with pototactic locomotion based on black phosphorus heterostructure. Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2021, 60, 20511–20517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serak, S.; Tabiryan, N.; Vergara, R.; White, T.J.; Vaiab, R.A.; Bunning, T.J. Liquid crystalline polymer cantilever oscillators fueled by light. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, R.K.; Shklyaev, O.E.; Balazs, A.C. Chemical pumps and flexible sheets spontaneously form self-regulating oscillators in solution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022987118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Bai, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Wiesner, L.W.; Silberstein, M.; Shepherd, R.F. Digital light processing of liquid crystal elastomers for self-sensing artificial muscles. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, D.; Li, K. Self-oscillating buckling and postbuckling of a liquid crystal elastomer disk under steady illumination. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 221, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelebart, G.A.; Mulder, D.J.; Varga, M.; Konya, A.; Vantomme, G.; Meijer, E.W.; Selinger, R.L.B.; Broer, D.J. Making waves in a photoactive polymer film. Nature 2017, 546, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, D.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Self-sustained Euler buckling of an optically responsive rod with different boundary constraints. Polymers 2023, 15, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Fan, Y.; Lv, J. Photomorphogenesis of diverse autonomous traveling waves in a monolithic soft artificial muscle. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2022, 14, 23839–23849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, A.; Sánchez-Ferrer, A.; Jacomine, L.; Martinoty, P.; Houerou, V.; Ziebert, F.; Kulić, I.M. Motorizing fibers with geometric zero-energy modes. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Zhou, L.; Du, C.; Li, K. A light-fueled self-oscillating liquid crystal elastomer balloon with self-shading effect. Chaos Soliton Fract. 2022, 115, 111646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Cheng, W.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Self-oscillating floating of a spherical liquid crystal elastomer balloon under steady illumination. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 241, 107985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Wu, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Self-sustained chaotic floating of a liquid crystal elastomer balloon under steady illumination. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, G.; Regulagadda, K.; Hodel, P.; Küttel, C.; Landolf, D.; Schutzius, T.M.; Poulikakos, D. Leidenfrost droplet trampolining. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Nie, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, Z.; Huang, S.; Yang, H. Springtail-inspired Light-driven Soft Jumping Robots Based on Liquid Crystal Elastomers with Monolithic Three-leaf Panel Fold Structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202218227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, D.; Jin, J.; Dai, Y.; Xu, P.; Li, K. Self-jumping of a liquid crystal elastomer balloon under steady illumination. Polymers 2022, 14, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, C.; Li, K.; Cai, S. Light or thermally-powered autonomous rolling of an elastomer rod. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2018, 10, 25689–25696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazir, A.; Baumann, A.; Ziebert, F.; Kulić, I.M. Dynamics of fiberboids. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 5210–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Ch, Y.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Yin, J. Twisting for soft intelligent autonomous robot in unstructured environments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2200265119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, J.; Wu, H.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Self-oscillating curling of a Liquid crystal elastomer beam under steady light. Polymers 2023, 15, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Yu, M.; Wang, W.; Yu, H. Photothermal pneumatic wheel with high loadbearing capacity. Compos. Commun. 2021, 24, 100651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Li, K.; Dai, Y.; Zhao, J. Self-oscillation and self-rotation of an optically-responsive liquid crystal elastomer pendulum. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 227, 107439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Light-powered self-spinning of a button spinner. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 238, 107824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Myung, N.V.; Yin, Y. Light-powered soft steam engines for self-adaptive oscillation and biomimetic swimming. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabi4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Xu, P.; Li, K. Self-sustained oscillation of a photothermal-responsive pendulum under steady illumination. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5531530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Li, K. Light-powered self-excited oscillation of a liquid crystal elastomer pendulum. Mech. Syst. Signal. Pro. 2021, 163, 108140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Annapooranan, R.; Zeng, J.; Chen, R.; Cai, S. Electrospun liquid crystal elastomer microfiber actuator. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabi9704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Dai, Y.; Fang, J.; Li, K. Light-powered self-oscillation in liquid crystal elastomer auxetic metamaterials with large volume change. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2023, 254, 108423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Li, K. Pulsating self-snapping of a liquid crystal elastomer bilayer spherical shell under steady illumination. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 233, 107646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Hong, Y.; Qi, F.; Chi, Y.; Hao, S.; Yin, J. Self-sustained snapping drives autonomous dancing and motion in free-standing wavy rings. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lv, J. Phototunable self-oscillating system driven by a self-winding fiber actuator. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Pei, D.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X.; Yi, M.; Li, C. Design of MXene composites with biomimetic rapid and self-oscillating actuation under ambient circumstances. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2021, 13, 31978–31985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, M.P.D.; Peeketi, A.R.; Ramgopal, A.; Annabattula, R.K.; Schenning, A.P.H.J. Light-driven continual oscillatory rocking of a polymer film. ChemistryOpen 2020, 9, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vantomme, G.; Elands, L.C.M.; Gelebart, A.H.; Meijer, E.W.; Pogromsky, A.Y.; Nijmeijer, H.; Broer, D.J. Coupled liquid crystalline oscillators in Huygens’ synchrony. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, B.; Cheng, Q.; Dai, Y.; Yu, Y. Light-Fueled Synchronization of Two Coupled Liquid Crystal Elastomer Self-Oscillators. Polymers 2023, 15, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mou, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y. Oscillating light engine realized by photothermal solvent evaporation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Sundaram, S.; Kang, J.; Tanjeem, N.; Emrick, T.; Hayward, R.C. Coupled oscillation and spinning of photothermal particles in Marangoni optical traps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024581118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, K.M.; Fowler, H.E.; McCracken, J.M.; Schlafmann, K.R.; Koch, J.A.; White, T.J. Synthesis and alignment of liquid crystalline elastomers. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Cheng, Z.; Zuo, B.; Chen, X.; Huang, S.; Yang, H. Liquid crystal elastomer electric locomotives. ACS Macro. Lett. 2020, 9, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Y.; Hu, W.; Soon, R.H.; Davidson, Z.S.; Sitti, M. Liquid crystal elastomer-based magnetic composite films for reconfigurable shape-morphing soft miniature machines. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrany, M. Nonlinear light-induced vibration behavior of liquid crystal elastomer beam. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 136, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, Y. Photomechanical vibration energy harvesting based on liquid crystal elastomer cantilever. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 075017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Kan, Q.; Kang, G. Thermo-mechanically coupled deformation of pseudoelastic NiTi SMA helical spring. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 236, 107767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, B.; Gu, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W. Actuation performance of machined helical springs from NiTi shape memory alloy. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2022, 236, 107744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniasadi, M.; Foyouzat, A.; Baghani, M. Multiple shape memory effect for smart helical springs with variable stiffness over time and temperature. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2020, 182, 105742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottershead, J.E. The large displacements and dynamic stability of springs using helical finite elements. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1982, 24, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, V. On the linearized disturbance dynamic equations for buckling and free vibration of cylindrical helical coil springs under combined compression and torsion. Meccanica 2012, 47, 1015–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, A.M. Mechanical Springs; M. McGraw-Hill: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Chassie, G.G.; Becker, L.E.; Cleghorn, W.L. On the buckling of helical springs under combined compression and torsion. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 1997, 39, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkelmann, H.; Nishikawa, E.; Pereira, G.G.; Warner, M. A new opto-mechanical effect in solids. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 015501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Nakano, M.; Ikeda, T. Photomechanics: Directed bending of a polymer film by light-miniaturizing a simple photomechanical system could expand its range of applications. Nature 2003, 425, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagele, T.; Hoche, R.; Zinth, W.; Wachtveitl, J. Femtosecond photoisomerization of cis-azobenzene. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1997, 272, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, L.B.; Hessberger, T.; Pütz, E.; Müller, C.; Giesselmann, F.; Serra, C.A.; Zentel, R. Actuating thermo- and photo-responsive tubes from liquid crystalline elastomers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 9093–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Lopez, M.; Finkelmann, H.; Palffy-Muhoray, P.; Shelley, M. Fast liquid-crystal elastomer swims into the dark. Nat. Mater. 2004, 3, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
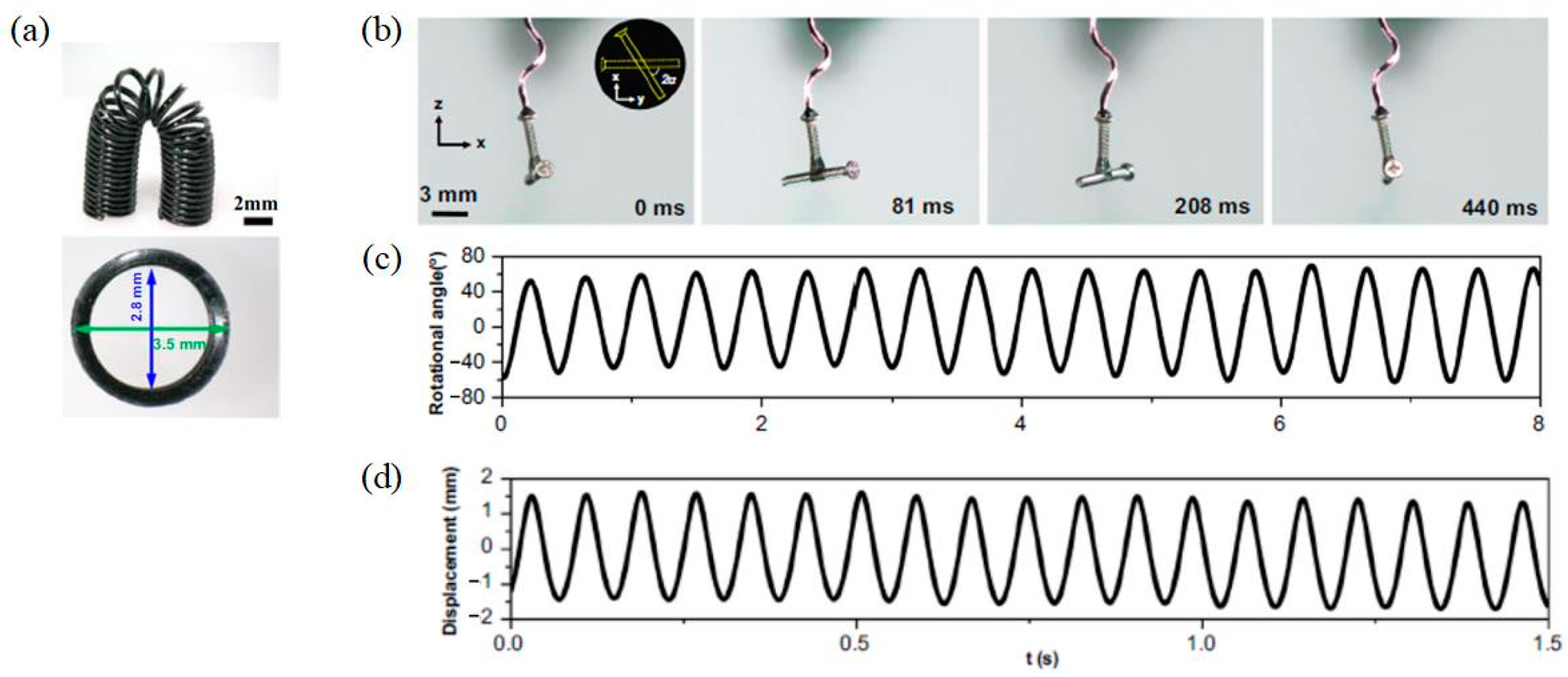
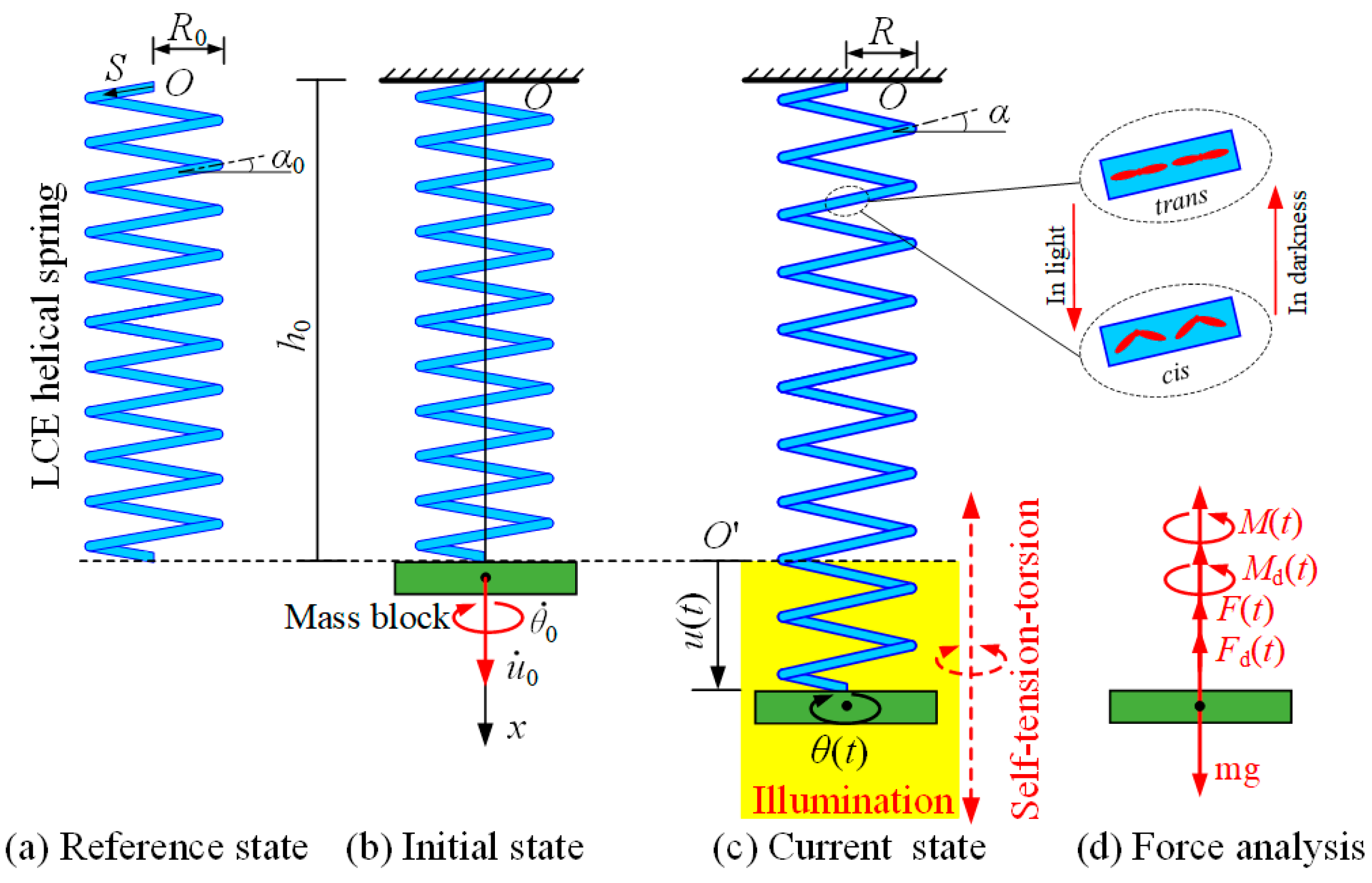
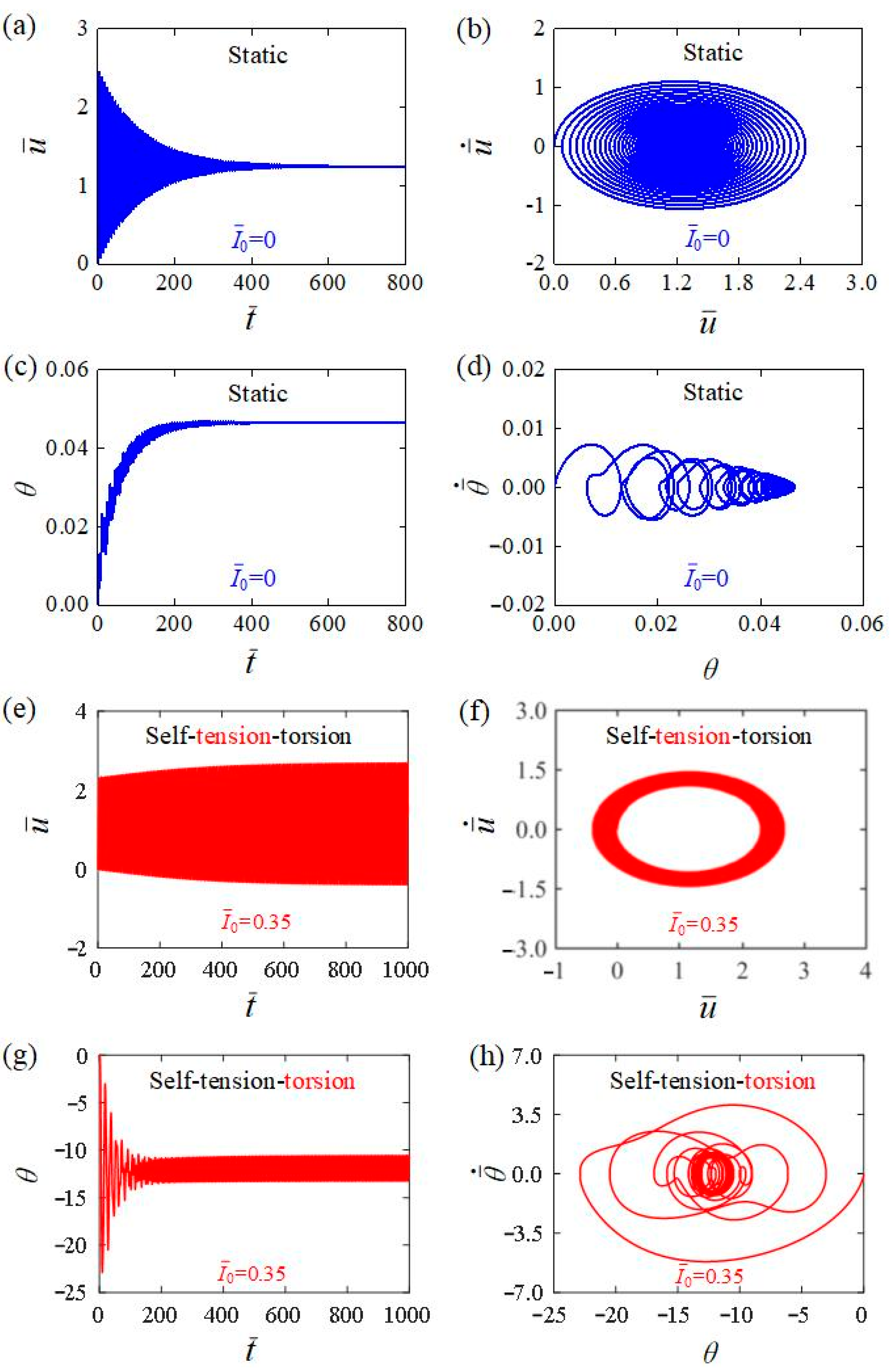
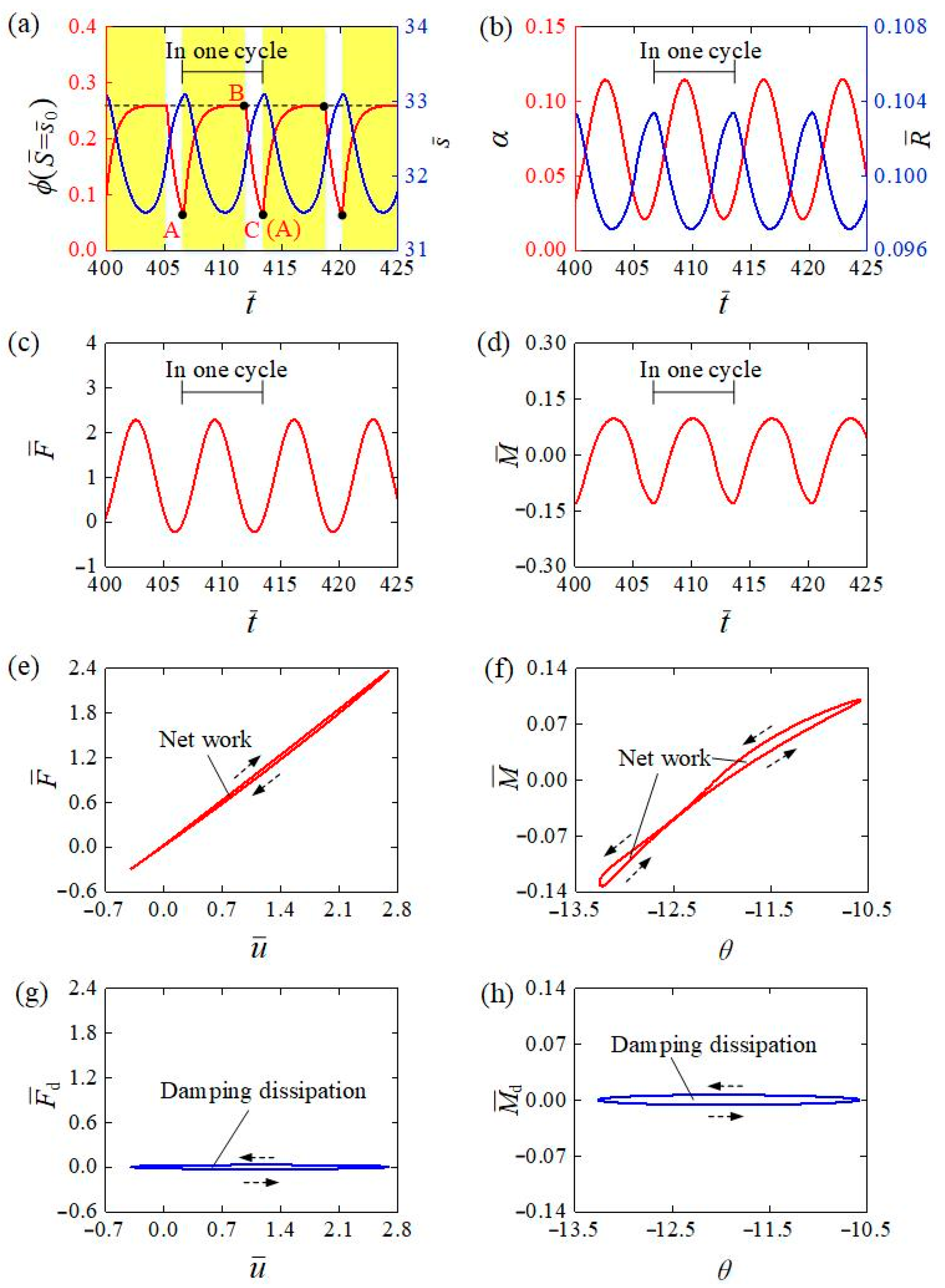



| Parameter | Definition | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contraction coefficient | 0~0.5 | / | |
| trans-to-cis thermal relaxation time | 1~100 | ms | |
| Light intensity | 0~20 | kW/m2 | |
| Light absorption constant | 0.0003 | m2/(s∙W) | |
| Helix angle at stress-free | 0~0.1 | / | |
| Coil radius of the LCE helical spring | 0~5 | mm | |
| Height of the LCE helical spring | 0~50 | mm | |
| Cross-sectional inertia moment of LCE wire | (1~5) × 10−3 | mm4 | |
| Elastic modulus of LCE wire | 1~10 | MPa | |
| Poisson′s ratio | 0.38~0.5 | / | |
| Mass of mass block | 0~100 | g | |
| Inertia moment of mass block | (0~2.5) × 105 | g∙mm2 | |
| Translational damping coefficient | 0~0.001 | mg∙mm/s | |
| Rotational damping coefficient | 0~0.001 | mg∙mm2/s |
| Parameter | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 0~0.5 | 0~0.03 | 0~0.01 | 0.1~0.5 | 0.09~0.11 | 0~1 | 1~3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, D.; Dai, Y.; Li, K. Self-Oscillating Liquid Crystal Elastomer Helical Spring Oscillator with Combined Tension and Torsion. Polymers 2023, 15, 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153294
Ge D, Dai Y, Li K. Self-Oscillating Liquid Crystal Elastomer Helical Spring Oscillator with Combined Tension and Torsion. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153294
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Dali, Yuntong Dai, and Kai Li. 2023. "Self-Oscillating Liquid Crystal Elastomer Helical Spring Oscillator with Combined Tension and Torsion" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153294
APA StyleGe, D., Dai, Y., & Li, K. (2023). Self-Oscillating Liquid Crystal Elastomer Helical Spring Oscillator with Combined Tension and Torsion. Polymers, 15(15), 3294. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153294







