Phosphonate poly(vinylbenzyl chloride)-Modified Sulfonated poly(aryl ether nitrile) for Blend Proton Exchange Membranes: Enhanced Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
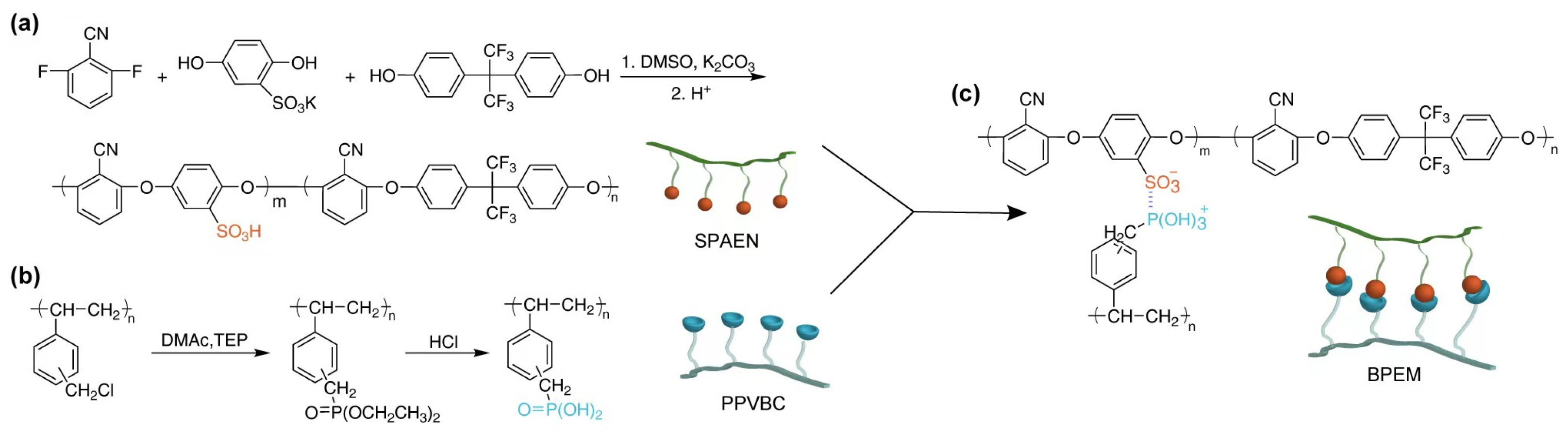
2.2. Synthesis of PA-PVBC
2.3. Synthesis of PPVBC
2.4. Preparation and Acidification of SPM-x% PEMs
2.5. The Measurement for Proton Conductivity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of Polymers
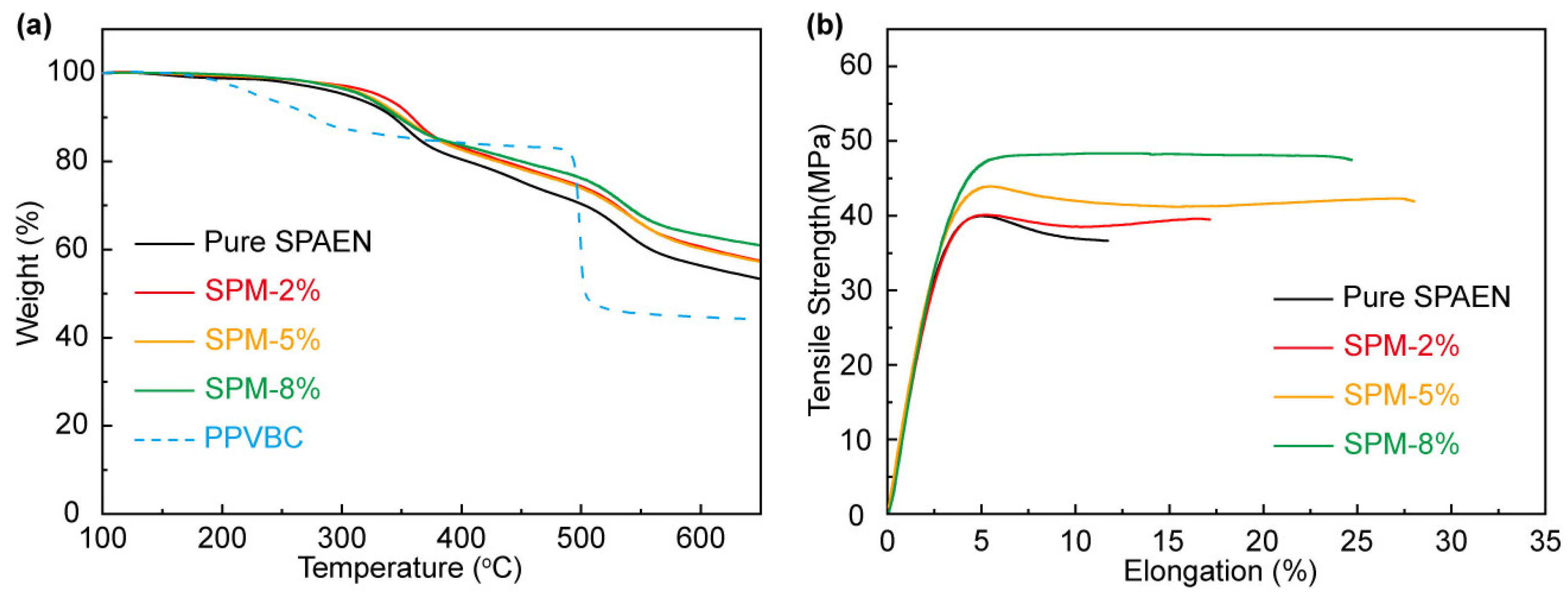
3.2. Physical and Chemical Properties of SPM-x% Membranes
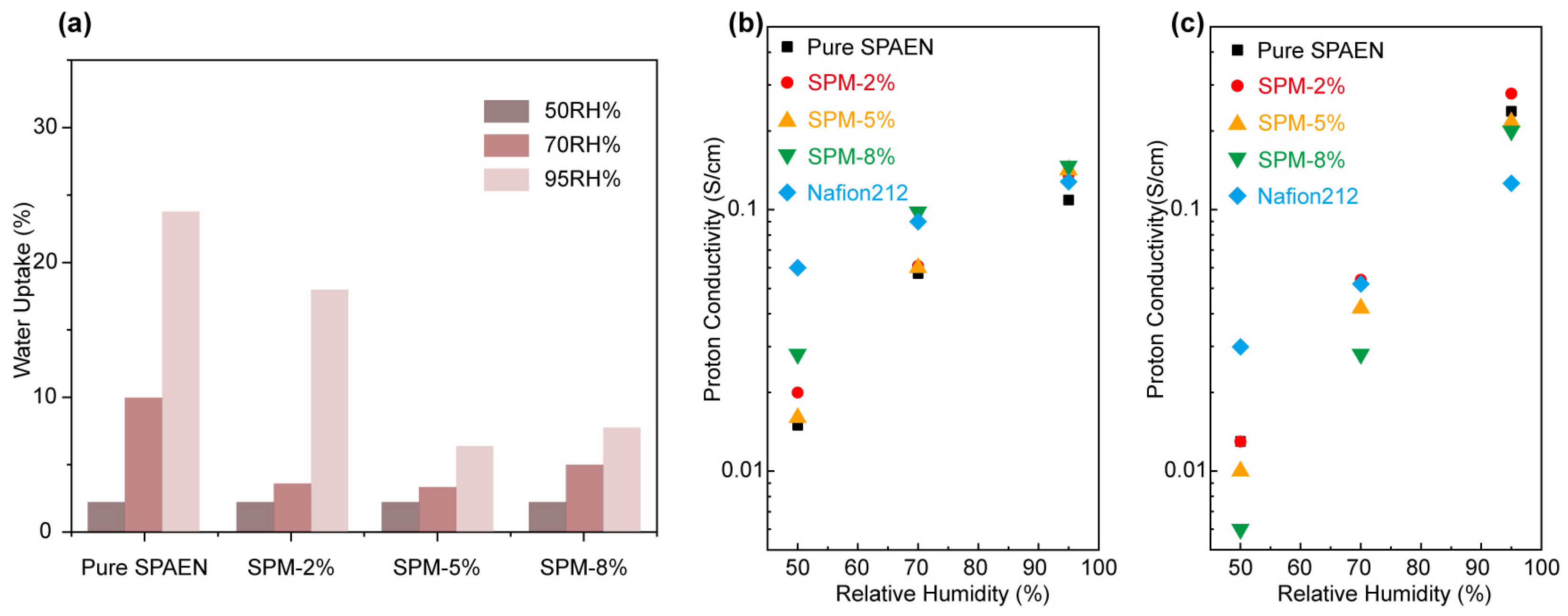
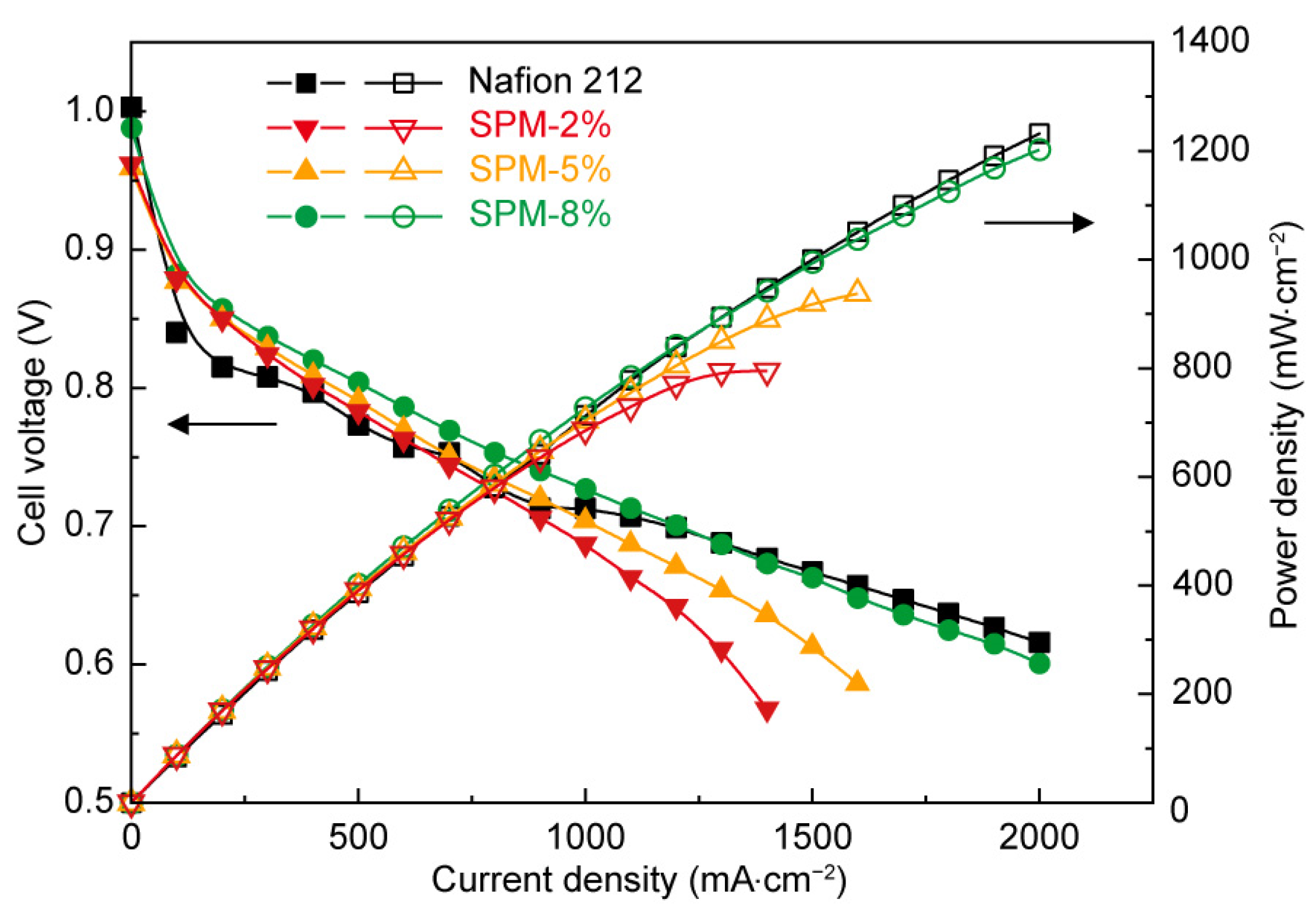
3.3. Water Uptake and Proton Conductivity of SPM-x% Membranes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xie, H.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, T.; Wu, Y.; Lan, C.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Shao, Z. A membrane-based seawater electrolyser for hydrogen generation. Nature 2022, 612, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, M.M.; Sánchez-Ramos, A.; Ureña, N.; Pérez-Prior, M.T.; Levenfeld, B.; García-Salaberri, P.A.; Elsharkawy, M.R. Characterization and Modeling of Free Volume and Ionic Conduction in Multiblock Copolymer Proton Exchange Membranes. Polymers 2022, 14, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, A.; Huang, Y.; Tang, H. Proton-conductive channels engineering of perfluorosulfonic acid membrane via in situ acid–base pair of metal organic framework for fuel cells. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2023, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Qiu, D.; Peng, L.; Lai, X. Numerical and experimental characterization of gas permeation through membranes with consideration of mechanical degradation in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Power Sources 2023, 556, 232489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkannan, M.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Kim, A.R.; Lee, H.-K.; Yoo, D.J. Ceria Stabilized by Titanium Carbide as a Sustainable Filler in the Nafion Matrix Improves the Mechanical Integrity, Electrochemical Durability, and Hydrogen Impermeability of Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells: Effects of the Filler Content. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 5704–5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkannan, M.; Kim, A.R.; Yoo, D.J. Potential carbon nanomaterials as additives for state-of-the-art Nafion electrolyte in proton-exchange membrane fuel cells: A concise review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 18351–18370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, R.; Tang, H. Hydrophilic Channel Volume Behavior on Proton Transport Performance of Proton Exchange Membrane in Fuel Cells. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 2423–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tian, R.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Tian, M.; Ning, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, H. Precise Control of the Preparation of Proton Exchange Membranes via Direct Electrostatic Deposition. Polymers 2022, 14, 3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, R.; Tian, T.; Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, H. Self-Assembly-Cooperating in Situ Construction of MXene–CeO2 as Hybrid Membrane Coating for Durable and High-Performance Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 4269–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Lu, Z.; Ai, Y.; Jia, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Tian, M.; Bian, X.; Lin, J.; He, S. High performance nanocomposite proton exchange membranes based on the nanohybrids formed by chemically bonding phosphotungstic acid with covalent organic frameworks. J. Power Sources 2023, 554, 232332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qu, T.; Ni, J.; Cheng, F.; Hu, F.; Ou, Y.; Gong, C.; Wen, S.; Chen, X.; Liu, H. Composite proton exchange membranes based on inorganic proton conductor boron phosphate functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and chitosan. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 36, 102557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annapragada, R.; Vandavasi, K.R.; Kanuparthy, P.R. Metal-organic framework membranes for proton exchange membrane fuel cells: A mini-review. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2023, 546, 121304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xu, J.; Feng, Q.; Ni, L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, C.; Fan, J.; Li, H.; Wang, H. Poly-hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid (PHEDP) as a highly effective water-retentive and proton-conductive material for low-humidity proton exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 606, 118144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, N.V.; Nguyen, X.L.; Kim, Y.; Yu, S. Characteristics of Water Transport of Membrane Electrolyte over Selected Temperature for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Polymers 2022, 14, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Yin, Y.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Incorporating phosphoric acid-functionalized polydopamine into Nafion polymer by in situ sol-gel method for enhanced proton conductivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 570–571, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, E.; Hao, X.; Xiao, M.; Han, D.; Huang, S.; Huang, Z.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y. Proton exchange membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells: Challenges and perspectives. J. Power Sources 2022, 533, 231386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Z.; Perez-Page, M.; Jia, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Holmes, S.M. Synthesis of phosphonated graphene oxide by electrochemical exfoliation to enhance the performance and durability of high-temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Energy Chem. 2023, 76, 448–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Fu, X.; Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Luo, J.; Peng, X. Constructing proton transport channels in low phosphoric-acid doped polybenzimidazole membrane by introducing metal–organic frameworks containing phosphoric-acid groups. J. Power Sources 2021, 507, 230316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Li, Z.; Xiao, M.; Han, D.; Huang, S.; Xi, G.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y. A phosphonated phenol-formaldehyde-based high-temperature proton exchange membrane with intrinsic protonic conductors and proton transport channels. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 10916–10925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, H.; Peng, X. Synthesis and characterization of phosphonated polybenzimidazole membranes with improved proton conductivity for high-temperature proton exchange membrane applications. High Perform. Polym. 2022, 34, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Shen, C.; Gao, S.; Jin, H.; Cheng, X.; Gong, C. High-temperature proton exchange membrane with dual proton transfer channels by incorporating phosphonic acid functionalized siloxane into poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenyleneoxide) (PPO). Solid State Ion. 2019, 337, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouz Tadavani, K.; Abdolmaleki, A.; Molavian, M.R.; Borandeh, S.; Sorvand, E.; Zhiani, M. Synergistic Behavior of Phosphonated and Sulfonated Groups on Proton Conductivity and Their Performance for High-Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFCs). Energy Fuels 2017, 31, 11460–11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, T.; Shi, B.; Fan, C.; Liu, Y.; Yin, Z.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Porous organic polymer with high-density phosphoric acid groups as filler for hybrid proton exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 666, 121147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lufrano, E.; Simari, C.; Enotiadis, A.; Nicotera, I. Sulfonated Polyether Ether Ketone and Organosilica Layered Nanofiller for Sustainable Proton Exchange Membranes Fuel Cells (PEMFCs). Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Shen, C.; Gao, S.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, M.; Ding, A. Crosslinked Proton Exchange Membranes with a Wider Working Temperature Based on Phosphonic Acid Functionalized Siloxane and PPO. Macromol. Res. 2021, 29, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jin, H.; Shen, C.; Gao, S. Novel proton exchange membranes based on sulfonated poly (ether-ether-ketone)/phosphonic acid-functionalized siloxane. Chem. Phys. 2020, 532, 110594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, V.; Lee, A.S.; Park, E.J.; Maurya, S.; Baca, E.D.; Fujimoto, C.; Hibbs, M.; Matanovic, I.; Kerres, J.; Kim, Y.S. Synergistically integrated phosphonated poly(pentafluorostyrene) for fuel cells. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Geng, K.; Hu, Y.; Li, N. Synthesis and properties of phosphonated polysulfones for durable high-temperature proton exchange membranes fuel cell. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 605, 118107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, S.; Negi, Y.S.; Ramya, K. Studies on new highly phosphonated poly(ether ether ketone) based promising proton conducting membranes for high temperature fuel cell. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 28968–28983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, V.; Annapooranan, R.; Ganapathikrishnan, M.; Sangeetha, D. A synthesis study of phosphonated PSEBS for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elumalai, V.; Rathinavel, S.; Annapooranan, R.; Ganapathikrishnan, M.; Sangeetha, D. Phosphonated mesoporous silica based composite membranes for high temperature proton exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2019, 23, 1837–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingöl, B.; Meyer, W.H.; Wagner, M.; Wegner, G. Synthesis, Microstructure, and Acidity of Poly(vinylphosphonic acid). Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2006, 27, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoun, K.; Ayadi, M.; El Hage, R.; Nakhl, M.; Sonnier, R.; Gardiennet, C.; Le Moigne, N.; Besserer, A.; Brosse, N. Renewable phosphorous-based flame retardant for lignocellulosic fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 186, 115265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Shen, C.; Gao, S.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, J. Proton Exchange Membrane with Enlarged Operating Temperature by Incorporating Phosphonic Acid Functionalized and Crosslinked Siloxane in Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) (SPEEK) Matrix. Macromol. Res. 2018, 26, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Thabit, N.Y.; Ali, S.A.; Zaidi, S.M.J.; Mezghani, K. Novel sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone)/phosphonated polysulfone polymer blends for proton conducting membranes. J. Mater. Res. 2012, 27, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotnaya, U.M.; Privalov, A.F.; Kresse, B.; Vogel, M.; Ponomarev, I.I.; Volkova, Y.A.; Sinitsyn, V.V. Diffusion in Sulfonated Co-Polynaphthoyleneimide Proton Exchange Membranes with Different Ratios of Hydrophylic to Hydrophobic Groups Studied Using SFG NMR. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 8823–8833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Liu, J. Porous Nafion nanofiber composite membrane with vertical pathways for efficient through-plane proton conduction. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 585, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Wu, W.; Lin, J.; Wang, J.; Qu, L.; Zhang, H. Porous nanofiber composite membrane with 3D interpenetrating networks towards ultrafast and isotropic proton conduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 5128–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, C.L.; Anantaraman, A.V. Studies on ion-exchange membranes. II. Measurement of the anisotropic conductance of Nafion®. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1998, 449, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Qin, Y.; Jiao, K.; Du, Q.; Cheng, B.; et al. Magnetic field alignment of stable proton-conducting channels in an electrolyte membrane. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourzare, K.; Mansourpanah, Y.; Farhadi, S.; Hasani Sadrabadi, M.M.; Frost, I.; Ulbricht, M. Improving the efficiency of Nafion-based proton exchange membranes embedded with magnetically aligned silica-coated Co3O4 nanoparticles. Solid State Ion. 2020, 351, 115343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, K.; Xuan, J.; Du, Q.; Bao, Z.; Xie, B.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, L.; Wang, H.; Hou, Z.; et al. Designing the next generation of proton-exchange membrane fuel cells. Nature 2021, 595, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xie, N.; Xue, J.; Li, M.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Yin, Y.; Dekel, D.R.; Guiver, M.D. Magnetic-field-oriented mixed-valence-stabilized ferrocenium anion-exchange membranes for fuel cells. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zhou, S.; Yao, J.; Wang, F.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, S. Novel proton exchange membranes based on sulfonated-phosphonated poly(p-phenylene-co-aryl ether ketone) terpolymers with microblock structures for passive direct methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 594, 117466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Hu, J.; Ueda, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Enhanced proton conductivity of multiblock poly(phenylene ether ketone)s via pendant sulfoalkoxyl side chains with excellent H2/air fuel cell performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 2321–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Code | EW | IEC | WU a | Mechanical Properties b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titr | 50% | 70% | 95% | T | E | Y | ||
| g/mol | equiv g−1 | MPa | % | Gpa | ||||
| Pure SPAEN | 499.70 | 2.00 | 2.5 | 10.0 | 23.8 | 40.0 | 11.7 | 1.50 |
| SPM-2% | 506.24 | 1.98 | 2.3 | 3.8 | 18.0 | 40.1 | 17.1 | 1.50 |
| SPM-5% | 512.92 | 1.95 | 2.3 | 3.5 | 6.6 | 43.9 | 28.1 | 1.53 |
| SPM-8% | 537.35 | 1.86 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 8.0 | 48.4 | 24.7 | 1.57 |
| PPVBC | 220.97 | 4.53 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Nafion 212 | 934.58 | 1.07 | - | - | - | 17.0 c | 320.0 c | 0.04 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Dong, T.; Deng, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, C.; Jia, W.; Meng, Z.; Zhou, M.; Tang, H. Phosphonate poly(vinylbenzyl chloride)-Modified Sulfonated poly(aryl ether nitrile) for Blend Proton Exchange Membranes: Enhanced Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153203
Zhang Z, Liu H, Dong T, Deng Y, Li Y, Lu C, Jia W, Meng Z, Zhou M, Tang H. Phosphonate poly(vinylbenzyl chloride)-Modified Sulfonated poly(aryl ether nitrile) for Blend Proton Exchange Membranes: Enhanced Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153203
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zetian, Hao Liu, Tiandu Dong, Yingjiao Deng, Yunxi Li, Chuanrui Lu, Wendi Jia, Zihan Meng, Mingzheng Zhou, and Haolin Tang. 2023. "Phosphonate poly(vinylbenzyl chloride)-Modified Sulfonated poly(aryl ether nitrile) for Blend Proton Exchange Membranes: Enhanced Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153203
APA StyleZhang, Z., Liu, H., Dong, T., Deng, Y., Li, Y., Lu, C., Jia, W., Meng, Z., Zhou, M., & Tang, H. (2023). Phosphonate poly(vinylbenzyl chloride)-Modified Sulfonated poly(aryl ether nitrile) for Blend Proton Exchange Membranes: Enhanced Mechanical and Electrochemical Properties. Polymers, 15(15), 3203. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153203







