Removal of the Water Pollutant Ciprofloxacin Using Biodegradable Sorbent Polymers Obtained from Polysaccharides
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
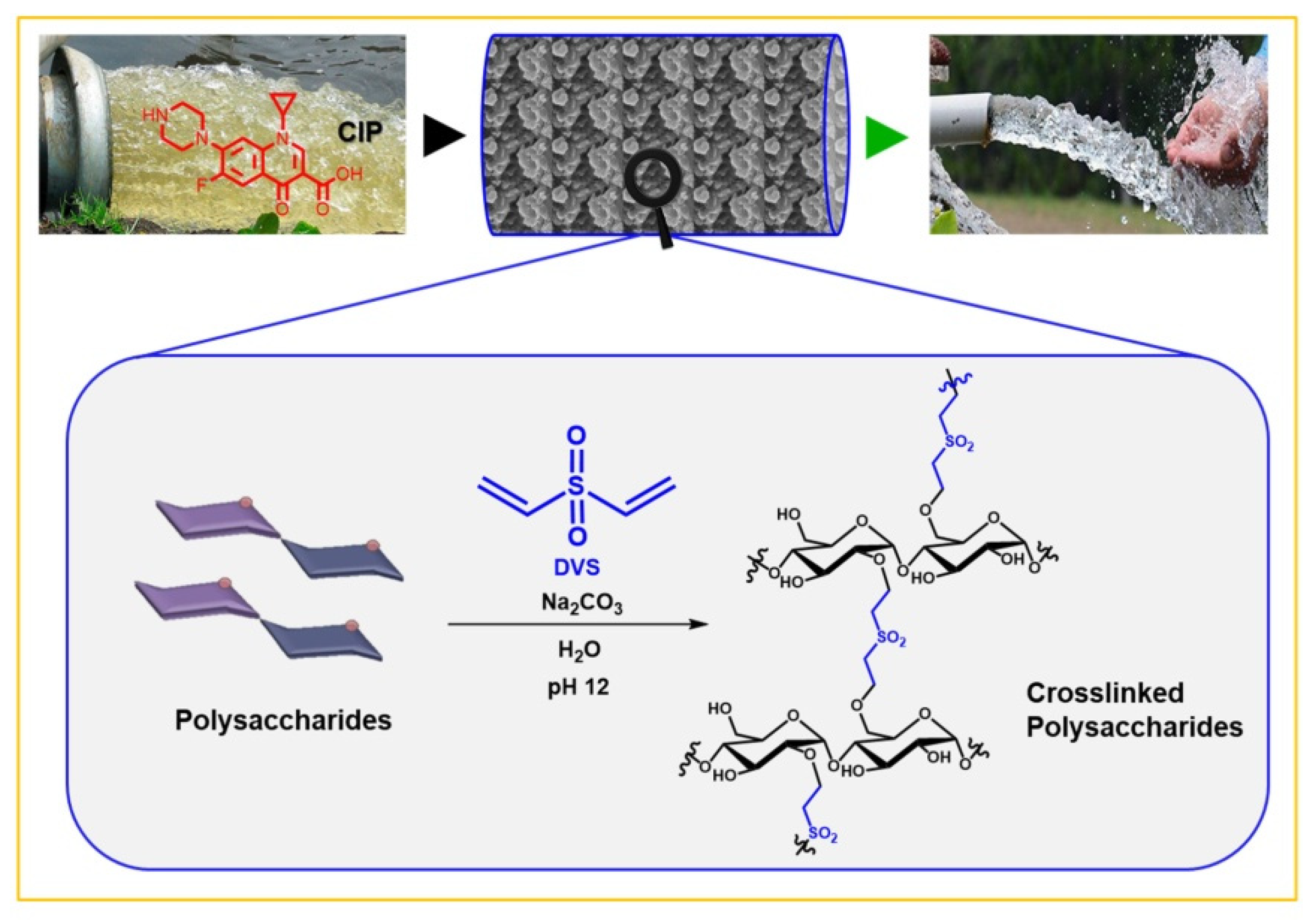
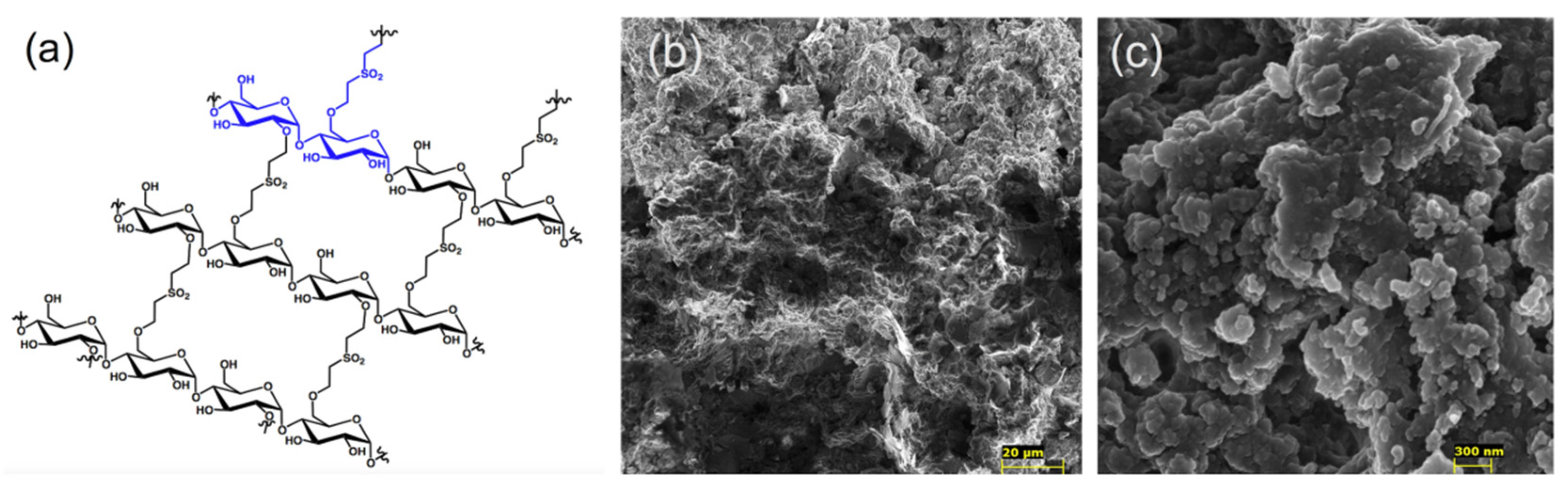
2.2. Synthesis of Cross-Linked Polymers
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Sorption Studies
2.5. Modeling of Sorption Experiments
2.6. Effect of the Ionic Strength and pH on the Sorption of CIP onto pSt
2.7. Fixed Bed Studies with pSt
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
3.2. Characterization of the Polymers as Sorbents for CIP and OFL
3.3. Study of the CIP and OFL Sorption on pSt
3.4. Factors Affecting the Sorption of CIP and OFL on pSt
3.5. Fixed Bed Studies with pSt
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNESCO. UN Water The United Nations World Water Development Report 2023: Partnerships and Cooperation for Water; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2023; ISBN 978-92-3-100576-3. [Google Scholar]
- González-Alonso, S.; Merino, L.M.; Esteban, S.; López de Alda, M.; Barceló, D.; Durán, J.J.; López-Martínez, J.; Aceña, J.; Pérez, S.; Mastroianni, N.; et al. Occurrence of Pharmaceutical, Recreational and Psychotropic Drug Residues in Surface Water on the Northern Antarctic Peninsula Region. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 229, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, J.L.; Boxall, A.B.A.; Kolpin, D.W.; Leung, K.M.Y.; Lai, R.W.S.; Galbán-Malagón, C.; Adell, A.D.; Mondon, J.; Metian, M.; Marchant, R.A.; et al. Pharmaceutical Pollution of the World’s Rivers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2113947119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallat, G.A.; Salameh, E.; Shteiwi, M.; Bardaweel, S. Pharmaceuticals as Emerging Pollutants in the Reclaimed Wastewater Used in Irrigation and Their Effects on Plants, Soils, and Groundwater. Water 2022, 14, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Kumar, R.; Kishor, K.; Mlsna, T.; Pittman, C.U.; Mohan, D. Pharmaceuticals of Emerging Concern in Aquatic Sys-tems: Chemistry, Occurrence, Effects, and Removal Methods. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 3510–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, S.; Chang, C. Emerging pollutants—Part II: Treatment. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1603–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariente, N. The Antimicrobial Resistance Crisis Needs Action Now. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millanao, A.R.; Mora, A.Y.; Villagra, N.A.; Bucarey, S.A.; Hidalgo, A.A. Biological Effects of Quinolones: A Family of Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Agents. Molecules 2021, 26, 7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, A.; Hancu, G.; Uivaroşi, V. Fluoroquinolone Pollution of Food, Water and Soil, and Bacterial Resistance. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2015, 13, 21–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, G.; Junza, A.; Segarra, D.; Barbosa, J.; Barrón, D. Wildlife Contamination with Fluoroquinolones from Livestock: Widespread Occurrence of Enrofloxacin and Marbofloxacin in Vultures. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczala, F.; Blum, S.E. The Occurrence of Veterinary Pharmaceuticals in the Environment: A Review. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2016, 12, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, D.G.J. Pollution from Drug Manufacturing: Review and Perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, F.; Akar, S.T.; Akar, T. From Green Biowaste to Water Treatment Applications: Utilization of Modified New Biochar for the Efficient Removal of Ciprofloxacin. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 24, 100522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Bai, Y.; Guan, Y. Facile Assembled N, S-Codoped Corn Straw Biochar Loaded Bi2WO6 with the Enhanced Electron-Rich Feature for the Efficient Photocatalytic Removal of Ciprofloxacin and Cr(VI). Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velusamy, K.; Periyasamy, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Jayaraj, T.; Krishnasamy, R.; Sindhu, J.; Sneka, D.; Subhashini, B.; Vo, D.-V.N. Analysis on the Removal of Emerging Contaminant from Aqueous Solution Using Biochar Derived from Soap Nut Seeds. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 287, 117632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolić, K.; Mutavdžić Pavlović, D.; Stankir, N.; Runje, M. Biosorbents from Tomato, Tangerine, and Maple Leaves for the Re-moval of Ciprofloxacin from Aqueous Media. Water. Air. Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrosa, M.; Ribeiro, R.S.; Guerra-Rodríguez, S.; Rodríguez-Chueca, J.; Rodríguez, E.; Silva, A.M.T.; Ðolic, M.; Rita Lado Ri-beiro, A. Spirulina-Based Carbon Bio-Sorbent for the Efficient Removal of Metoprolol, Diclofenac and Other Micropollutants from Wastewater. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2022, 18, 100720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahnaz, T.; Vishnu Priyan, V.; Pandian, S.; Narayanasamy, S. Use of Nanocellulose Extracted from Grass for Adsorption Abatement of Ciprofloxacin and Diclofenac Removal with Phyto, and Fish Toxicity Studies. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Chang, Q.; Yang, H. Selective Adsorption of Ofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin from a Binary System Using Lignin-Based Adsorbents: Quantitative Analysis, Adsorption Mechanisms, and Structure-Activity Relationship. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nie, Q.; Huang, B.; Cheng, H.; Wang, L.; He, Q. Removal of Ciprofloxacin as an Emerging Pollutant: A Novel Application for Bauxite Residue Reuse. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 120049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Han, X.; Xing, B. Adsorption of Antibiotic Ciprofloxacin on Carbon Nanotubes: pH Dependence and Thermodynamics. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Tong, X.; Pan, W.; Zeng, Q.; You, S.; Shen, J. Recent Advances in Polysaccharide-Based Adsorbents for Wastewater Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cova, T.F.; Murtinho, D.; Aguado, R.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Valente, A.J.M. Cyclodextrin Polymers and Cyclodextrin-Containing Polysaccharides for Water Remediation. Polysaccharides 2021, 2, 16–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero-Oñate, C.; Martínez-Francés, E. A Review of Chitosan-Based Materials for the Removal of Organic Pollution from Water and Bioaugmentation. In Chitin-Chitosan—Myriad Functionalities in Science and Technology; Dongre, R.S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78923-406-0. [Google Scholar]
- Bayatloo, M.R.; Salehpour, N.; Alavi, A.; Nojavan, S. Introduction of Maltodextrin Nanosponges as Green Extraction Phases: Magnetic Solid Phase Extraction of Fluoroquinolones. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 297, 119992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, S.F.; Nogueira, J.; Trindade, T.; Daniel-da-Silva, A.L. Towards Efficient Ciprofloxacin Adsorption Using Magnetic Hybrid Nanoparticles Prepared with κ-, ι-, and λ-Carrageenan. J. Nanostructure Chem. 2023, 13, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Shi, Y.; Sun, C.; Niu, M.; Wang, R.; Hu, F.; Xiao, D.; He, H. Determination of Quinolones in Wastewater by Porous β-Cyclodextrin Polymer Based Solid-Phase Extraction Coupled with HPLC. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1068, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Sanfrutos, J.; Lopez-Jaramillo, F.; Elremaily, M.; Hernández-Mateo, F.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. Divinyl Sulfone Cross-Linked Cyclodextrin-Based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis and Applications as Sorbents and Encapsulating Agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 3565–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Jaramillo, F.; Giron-Gonzalez, M.; Salto-Gonzalez, R.; Hernandez-Mateo, F.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Novel Cross-Linked Saccharide Based Polymers as Bile Acid Sequestrants. Molecules 2015, 20, 3716–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.D. Xpowder Software. Available online: https://www.xpowder.com/ (accessed on 24 July 2023).
- Beltrán, J.L.; Pignatello, J.J.; Teixidó, M. ISOT_Calc: A Versatile Tool for Parameter Estimation in Sorption Isotherms. Comput. Geosci. 2016, 94, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunsona, E.; Ojogbo, E.; Mekonnen, T. Advanced Material Applications of Starch and Its Derivatives. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 108, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamage, A.; Punniamoorthy, T.; Madhujith, T. Starch-Based Hybrid Nanomaterials for Environmental Remediation. In Bio-chemistry; Ochubiojo Emeje, M., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; Volume 33, ISBN 978-1-83969-890-3. [Google Scholar]
- Olmstead, S.; Zheng, J. Water Pollution Control in Developing Countries: Policy Instruments and Empirical Evidence. Rev. Environ. Econ. Policy 2021, 15, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, K.C. Infrared Spectra of Sulfones and Related Compounds. Anal. Chem. 1949, 21, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermal Analysis of Polymers: Fundamentals and Applications; Menczel, J.D., Prime, R.B., Eds.; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; Chapter 3; ISBN 978-0-471-76917-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ternes, T.A.; Herrmann, N.; Bonerz, M.; Knacker, T.; Siegrist, H.; Joss, A. A Rapid Method to Measure the Solid–water Dis-tribution Coefficient (Kd) for Pharmaceuticals and Musk Fragrances in Sewage Sludge. Water Res. 2004, 38, 4075–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limousin, G.; Gaudet, J.-P.; Charlet, L.; Szenknect, S.; Barthès, V.; Krimissa, M. Sorption Isotherms: A Review on Physical Bases, Modeling and Measurement. Appl. Geochem. 2007, 22, 249–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, K.H. Revisiting the Temkin Isotherm: Dimensional Inconsistency and Approximate Forms. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 13140–13147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voudrias, E.; Fytianos, K.; Bozani, E. Sorption-Desorption Isotherms of Dyes from Aqueous Solutions and Wastewaters with Different Sorbent Meterials. Glob. NEST J. 2002, 4, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Kumar, A.; Dhodapkar, R.; Pal, S. Adsorption of Five Emerging Contaminants on Activated Carbon from Aqueous Medium: Kinetic Characteristics and Computational Modeling for Plausible Mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 21347–21358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorival-García, N.; Zafra-Gómez, A.; Navalón, A.; González, J.; Vílchez, J.L. Removal of Quinolone Antibiotics from Was-tewaters by Sorption and Biological Degradation in Laboratory-Scale Membrane Bioreactors. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, M.M.; Kordzadeh-Kermani, V.; Ghalandari, V.; Askari, A.; Sillanpää, M. Adsorption Isotherm Models: A Comprehensive and Systematic Review (2010−2020). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 151334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Isotherm | CIP-pSt | OFL-pSt |
|---|---|---|
| Freundlich | KF = 1.533 × 104 | KF = 7.977 × 102 |
| r.s.d. (%) = 41 | r.s.d. (%) = 14 | |
| N = 1.5303 | N = 1.193 | |
| r.s.d. (%) = 5.3 | r.s.d. (%) = 2.8 | |
| MWSE = 6.76 × 10−3 | MWSE = 2.45 × 10−3 | |
| Temkin | K1 = 9.425 × 100 | K1 = 5.692 × 10−1 |
| r.s.d. (%) = 7.3 | r.s.d. (%) = 9.8 | |
| K2 = 5.664 × 101 | K2 = 3.139 × 101 | |
| r.s.d. (%) = 6.5 | r.s.d. (%) = 8.2 | |
| MWSE = 2.12 × 10−2 | MWSE = 4.56 × 10−2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alvarado, S.; Megia-Fernandez, A.; Ortega-Muñoz, M.; Hernandez-Mateo, F.; Lopez-Jaramillo, F.J.; Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. Removal of the Water Pollutant Ciprofloxacin Using Biodegradable Sorbent Polymers Obtained from Polysaccharides. Polymers 2023, 15, 3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153188
Alvarado S, Megia-Fernandez A, Ortega-Muñoz M, Hernandez-Mateo F, Lopez-Jaramillo FJ, Santoyo-Gonzalez F. Removal of the Water Pollutant Ciprofloxacin Using Biodegradable Sorbent Polymers Obtained from Polysaccharides. Polymers. 2023; 15(15):3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153188
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlvarado, Sarah, Alicia Megia-Fernandez, Mariano Ortega-Muñoz, Fernando Hernandez-Mateo, F. Javier Lopez-Jaramillo, and Francisco Santoyo-Gonzalez. 2023. "Removal of the Water Pollutant Ciprofloxacin Using Biodegradable Sorbent Polymers Obtained from Polysaccharides" Polymers 15, no. 15: 3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153188
APA StyleAlvarado, S., Megia-Fernandez, A., Ortega-Muñoz, M., Hernandez-Mateo, F., Lopez-Jaramillo, F. J., & Santoyo-Gonzalez, F. (2023). Removal of the Water Pollutant Ciprofloxacin Using Biodegradable Sorbent Polymers Obtained from Polysaccharides. Polymers, 15(15), 3188. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15153188