Adhesive and Rheological Features of Ecofriendly Coatings with Antifouling Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Antifouling Filler Preparation and Characterization
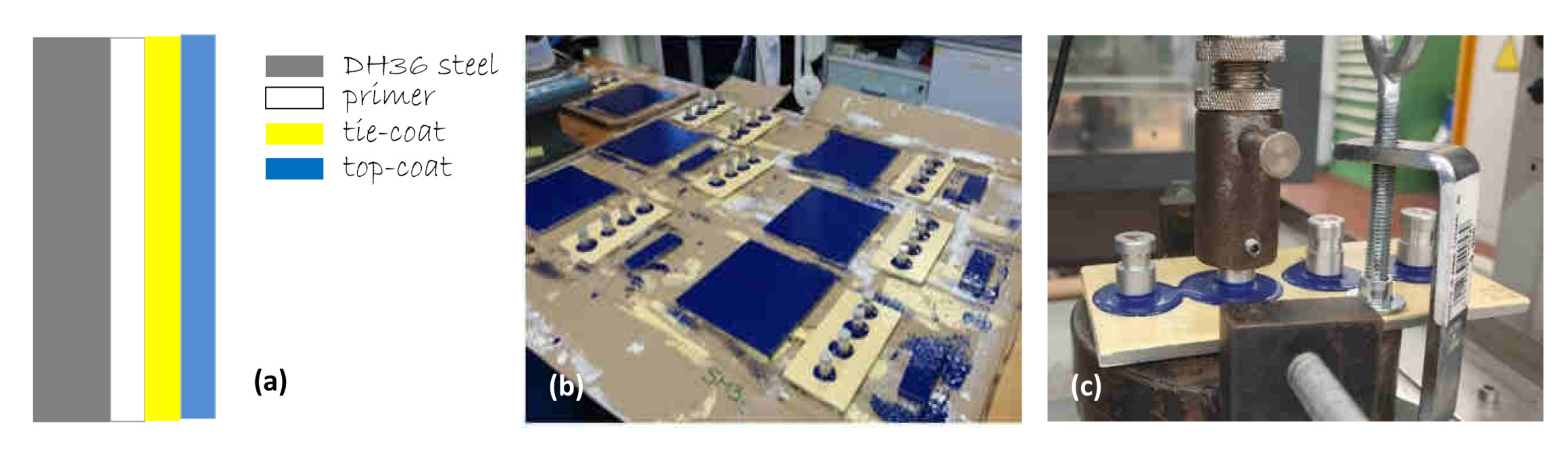
2.2. Antifouling Coating Preparation
2.3. Coatings Characterization
3. Results
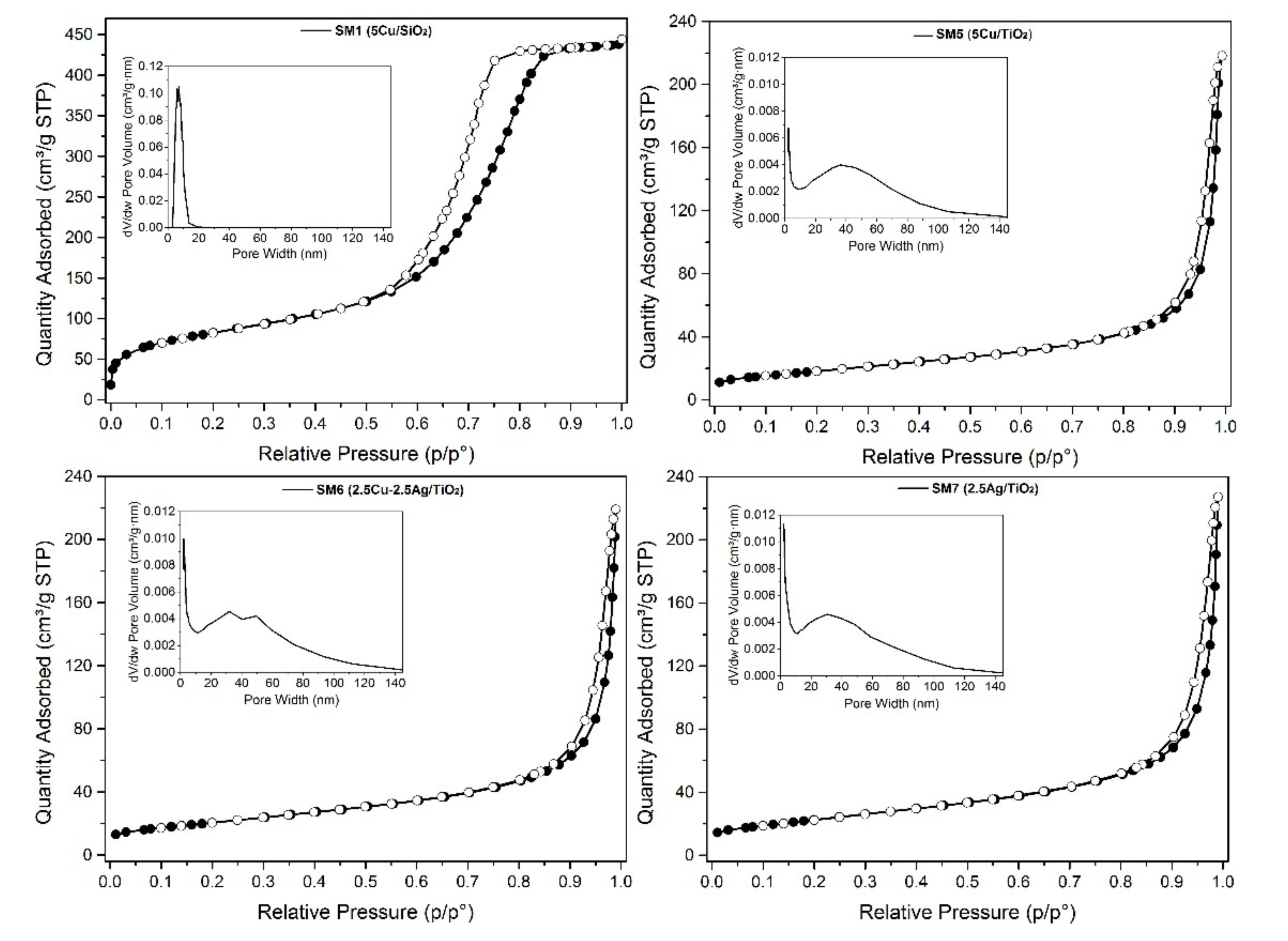
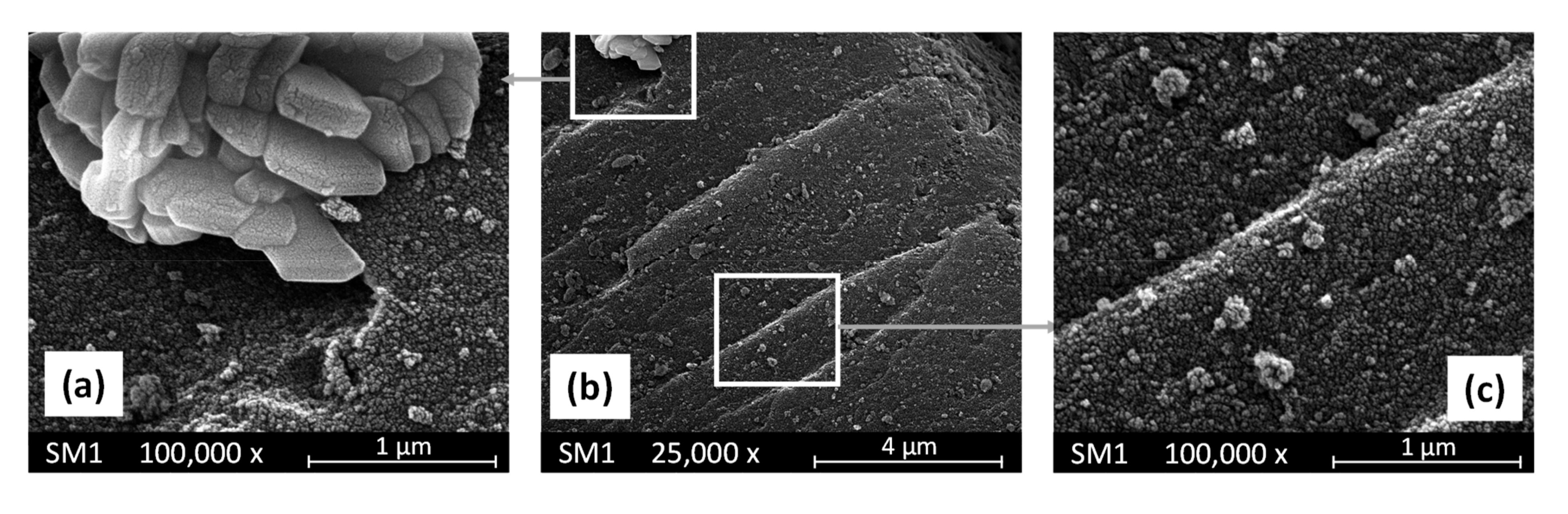
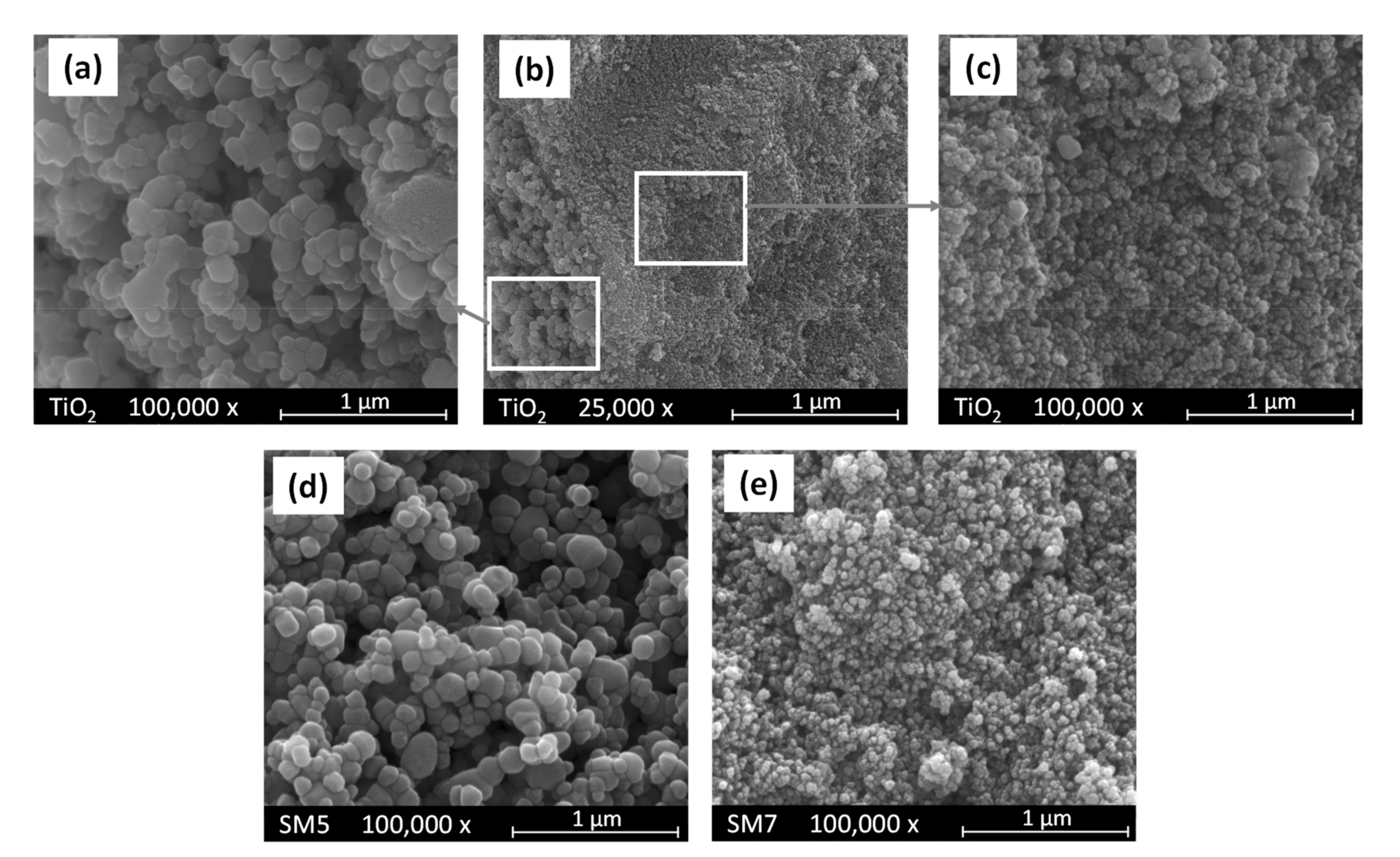
3.1. Evaluation of the Morphological Properties of the SM Powders
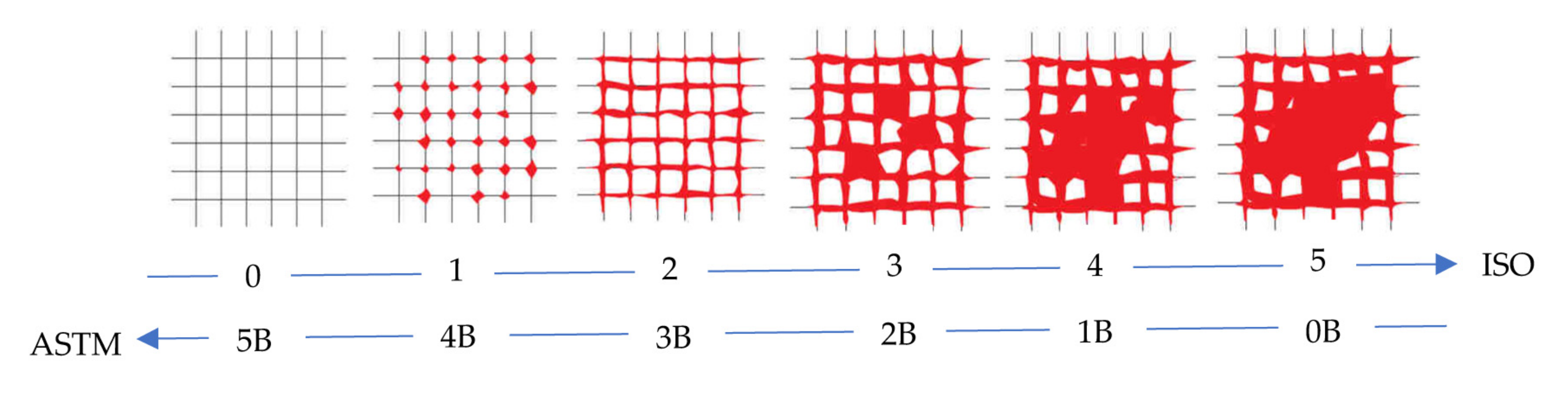
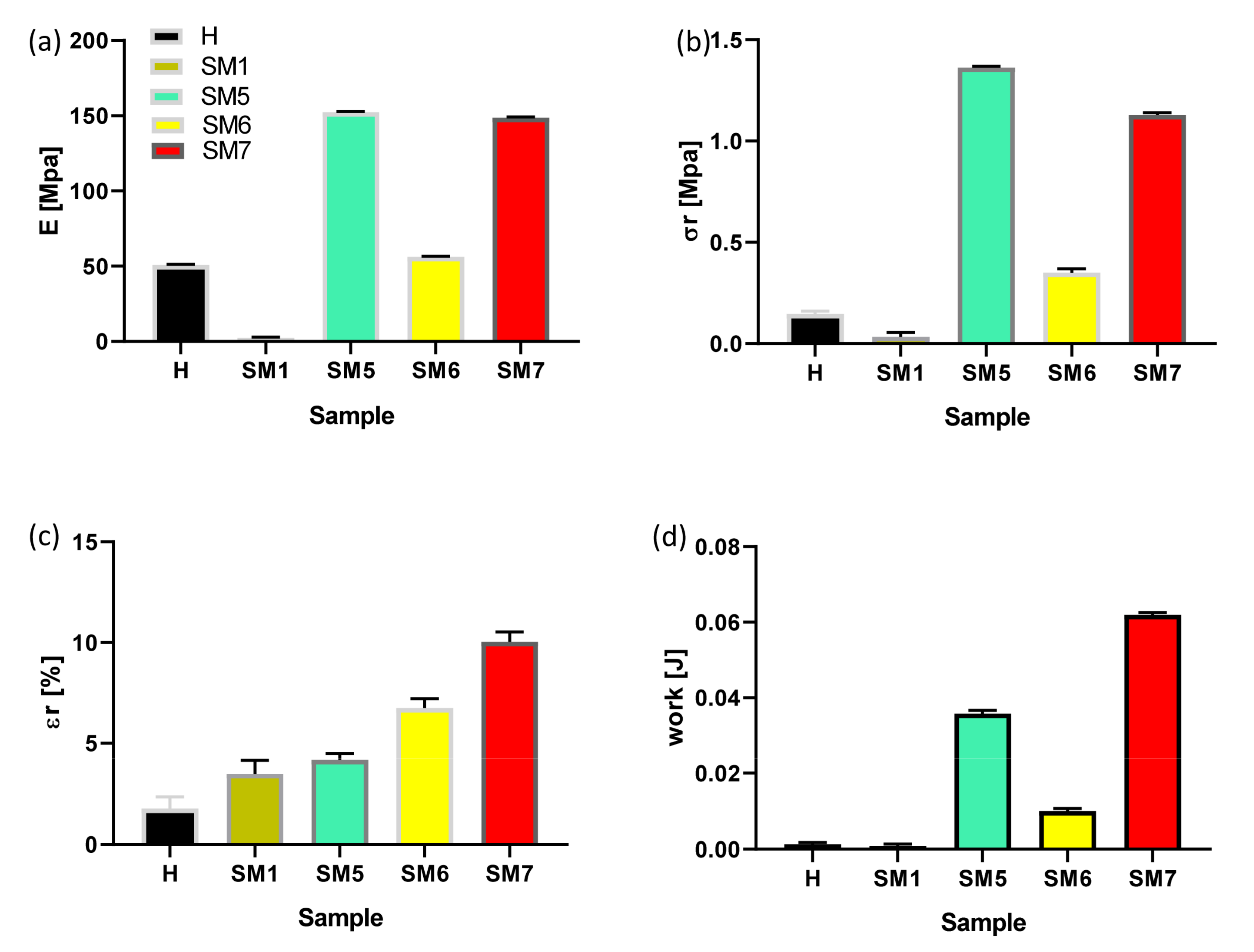
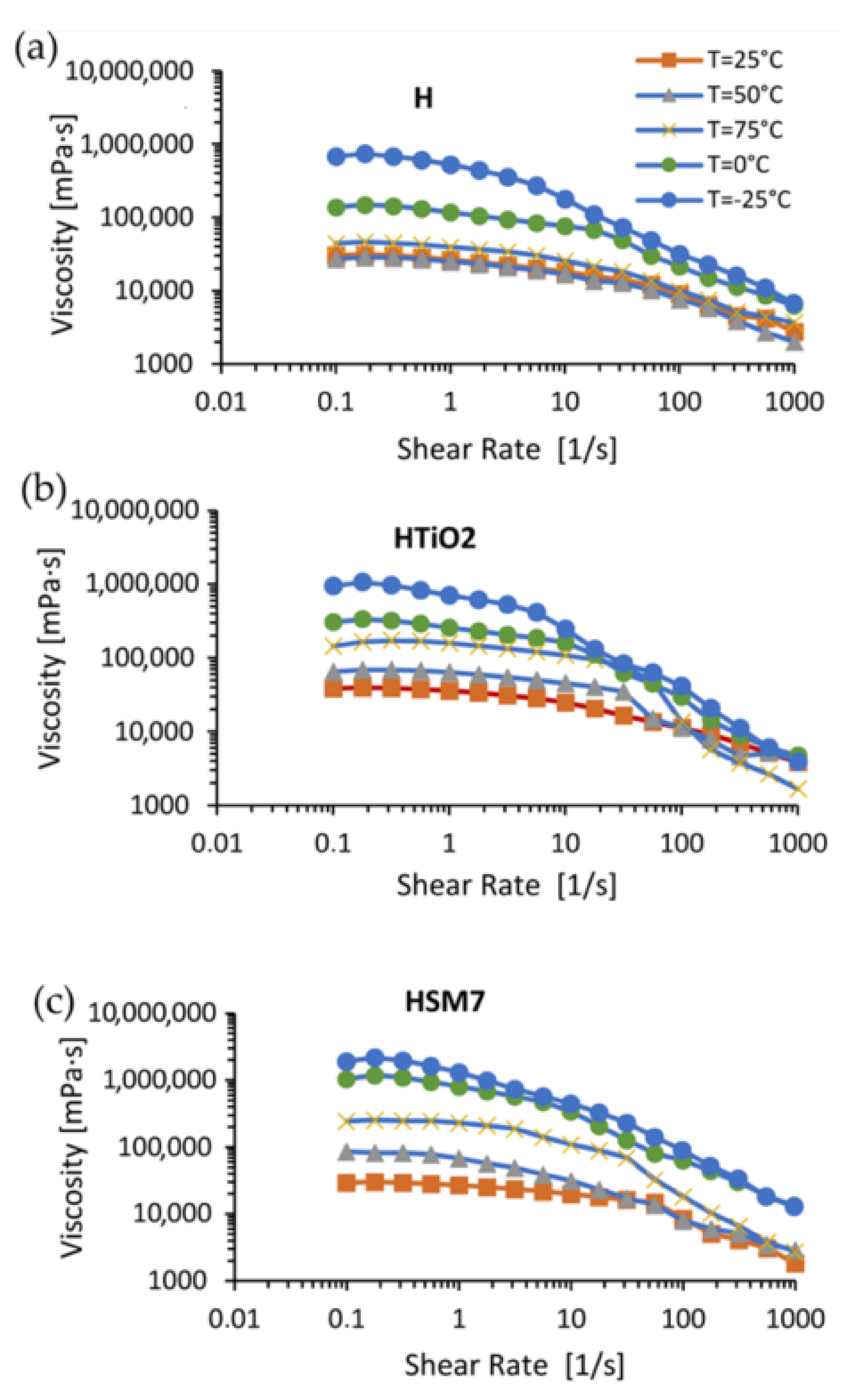
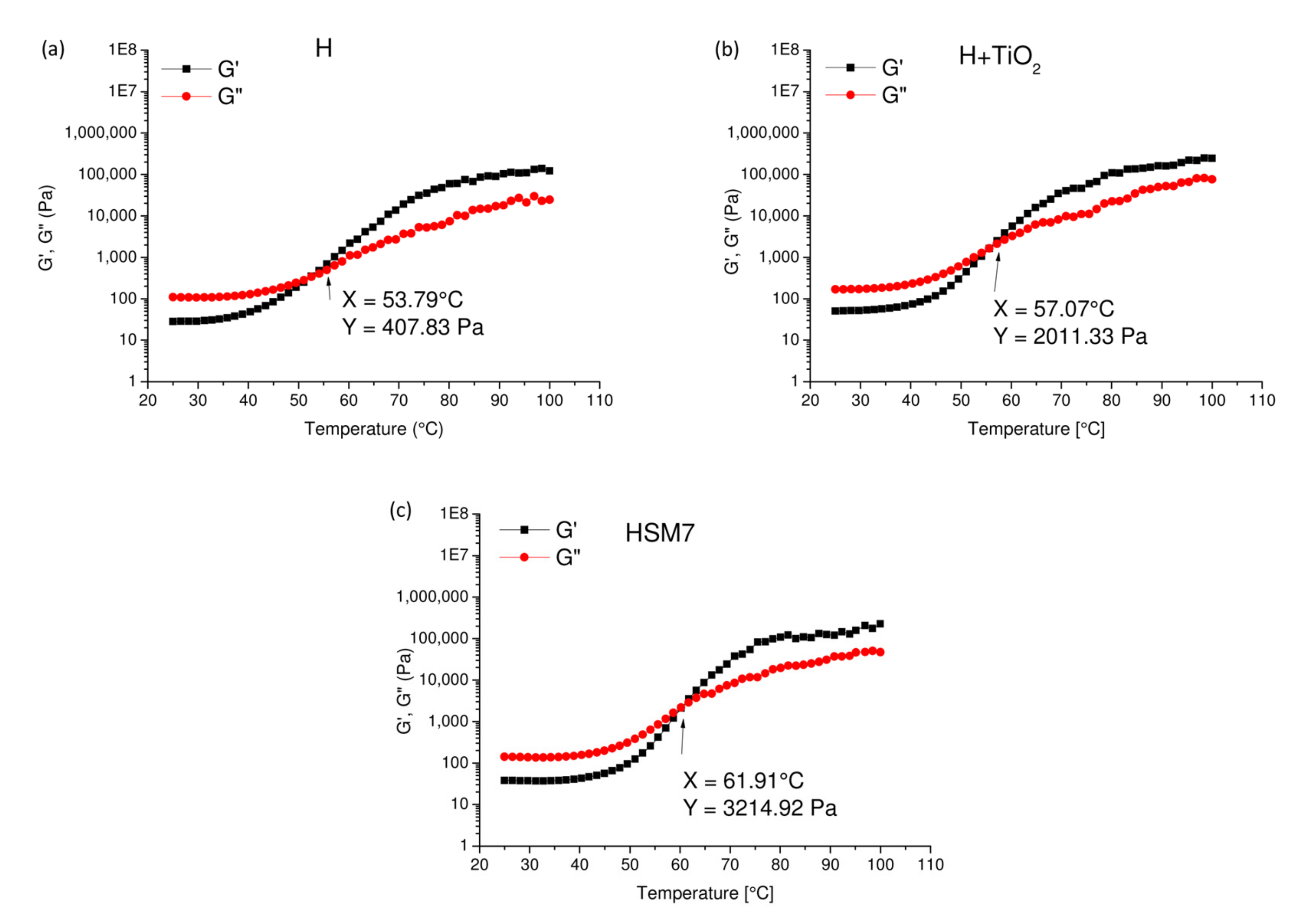
3.2. Evaluation of the Adhesion Power and Rheological Features of the Coatings
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Callow, J.A.; Callow, M.E. Trends in the development of environmentally friendly fouling-resistant marine coatings. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistone, A.; Scolaro, C.; Visco, A. Mechanical properties of protective coatings against marine fouling: A review. Polymers 2021, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurioglu, A.G.; Esteves, A.C.C.; De With, G. Non-toxic, non-biocide-release antifouling coatings based on molecular structure design for marine applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6547–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, S.; Sarode, S.; Sargunaraj, F.; Chandrasekhar, K. Bacterial-Mediated Biofouling: Fundamentals and Control Techniques, In Biotechnological Applications of Quorum Sensing Inhibitors; Kalia, V., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.J.; Tyler, C.R.; Galloway, T.S. Impacts of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles on marine organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champ, M.A. Economic and environmental impacts on ports and harbors from the convention to ban harmful marine anti-fouling systems. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 46, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jägerbrand, A.K.; Brutemark, A.; Barthel Svedén, J.; Gren, I.-M. A review on the environmental impacts of shipping on aquatic and nearshore ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, J. Comparative toxicity of alternative antifouling biocides on embryos and larvae of marine invertebrates. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 367, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.Y.; Lau, S.C.K.; Dahms, H.U.; Lewin, R. Microbial adhesion is a sticky problem. Science 1984, 224, 375–378. [Google Scholar]
- Dobretsov, S.; Thomason, J.C. The development of marine biofilms on two commercial non-biocidal coatings: A comparison between silicone and fluoropolymer technologies. J. Bioadhesion Biofilm Res. 2011, 27, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Chen, R.; Gao, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Liu, P.; Takahashi, K.; Wang, J. Fabrication of epoxy modified polysiloxane with enhanced mechanical properties for marine antifouling application. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 117, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Xie, Q.; Ma, C.; Zhang, G. Silicone-based fouling-release coatings for marine antifouling. Langmuir 2020, 36, 2170–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistone, A.; Visco, A.M.; Galtieri, G.; Iannazzo, D.; Marino-Merlo, F.; Urzì, C.; De Leo, F. Polyester resin and carbon nanotubes based nanocomposite as new-generation coating to prevent biofilm formation. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2016, 21, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yebra, D.M.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Antifouling technology—Past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMO—International Marine Organization: BIOFOULING. Available online: https://www.imo.org/en/OurWork/Environment/Pages/Biofouling.aspx (accessed on 20 May 2023).
- Uc-Peraza, R.G.; Castro, B.; Fillmann, G. An absurd scenario in 2021: Banned TBT-based antifouling products still available on the market. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Villarraga, C.A.; Castro, Í.B.; Fillmann, G. Biocides in antifouling paint formulations currently registered for use. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 30090–30101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannazzo, D.; Pistone, A.; Visco, A.; Galtieri, G.; Giofre, S.; Romeo, R.; Romeo, G.; Cappello, S.; Bonsignore, M.; Denaro, R.; et al. 1,2,3-Triazole/MWCNT Conjugates as filler for gelcoat nanocomposites: New active antibiofouling coatings for marine application. Mater. Res. Express 2015, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistone, A.; Scolaro, C.; Celesti, C.; Visco, A. Study of Protective Layers Based on Crosslinked Glutaraldehyde/3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. Polymers 2022, 14, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurria, A.; Scolaro, C.; Sfameni, S.; Di Carlo, G.; Pagliaro, M.; Visco, A.; Ciriminna, R. Towards AquaSun practical utilization: Strong adhesion and lack of ecotoxicity of solar-driven antifouling sol-gel coating. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 165, 106771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfameni, S.; Rando, G.; Marchetta, A.; Scolaro, C.; Cappello, S.; Urzì, C.; Visco, A.; Plutino, M.R. Development of Eco-Friendly Hydrophobic and Fouling-Release Coatings for Blue-Growth Environmental Applications: Synthesis, Mechanical Characterization and Biological Activity. Gels 2022, 8, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfameni, S.; Rando, G.; Galletta, M.; Ielo, I.; Brucale, M.; De Leo, F.; Cardiano, P.; Cappello, S.; Visco, A.; Trovato, V.; et al. Design and Development of Fluorinated and Biocide-Free Sol–Gel Based Hybrid Functional Coatings for Anti-Biofouling/Foul-Release Activity. Gels 2022, 8, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, C.; La Parola, V.; Cappello, S.; Visco, A.; Scolaro, C.; Liotta, L.F. Antifouling Systems Based on Copper and Silver Nanoparticles Supported on Silica, Titania, and Silica/Titania Mixed Oxides. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascariu, P.; Cojocaru, C.; Samoila, P.; Airinei, A.; Olaru, N.; Rotaru, A.; Romanitan, C.; Tudoran, L.B.; Suche, M. Cu/TiO2 composite nanofibers with improved photocatalytic performance under UV and UV–visible light irradiation. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 28, 101644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L.; Shi, D.C.; Jia, C.C. Robust nanoporous Cu/TiO2 ceramic filter membrane with promoted bactericidal function. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2022, 65, 2687–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffolo, S.A.; Macchia, A.; La Russa, M.F.; Mazza, L.; Urzì, C.; De Leo, F.; Barberio, M.; Crisci, G.M. Marine Antifouling for Underwater Archaeological Sites: TiO2 and Ag-Doped TiO2. Hindawi Publ. Corp. Int. J. Photoenergy 2013, 23, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presentato, A.; La Greca, E.; Consentino, L.; Alduina, R.; Liotta, L.F.; Gruttadauria, M. Antifouling Systems Based on a Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane-Based Hexyl Imidazolium Salt Adsorbed on Copper Nanoparticles Supported on Titania. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Pan, G.; Fang, L.; Liu, Y.; Rui, Z. Z-Scheme CuOx/Ag/TiO2 Heterojunction as Promising Photoinduced Anticorrosion and Antifouling Integrated Coating in Seawater. Molecules 2023, 28, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, C.; La Parola, V.; Testa, M.L.; Liotta, L.F. Antifouling and antimicrobial activity of Ag, Cu and Fe nanoparticles supported on silica and titania. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2022, 529, 120636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel’s Silic One. Available online: https://www.hempel.com/products/hempels-silic-one-77450 (accessed on 11 June 2022).
- ASTM D3359-09e2, Standard Test Methods for Measuring Adhesion by Tape Test. Available online: https://www.astm.org/d3359-09e02.html (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- ISO 2409:2007, Paints and Varnishes—Cross-Cut Test. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/37487.html (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Arabpour, A.; Shockravi, A.; Rezania, H.; Farahati, R. Investigation of anticorrosive properties of novel silane-functionalized polyamide/GO nanocomposite as steel coatings. Surf. Interfaces 2020, 18, 100453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Carroccio, S.C.; Mendichi, R.; Gioiella, L.; Dintcheva, N.T.; Gambarotti, C. Time-resolved rheology as a tool to probe polymer degradation in the melt state—Part I: Thermal and thermo-oxidative degradation of polyamide 11. Polymer 2015, 72, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Carroccio, S.C.; Curcuruto, G.; Passaglia, E.; Gambarotti, C.; Dintcheva, N.T. Time-resolved rheology as a tool to probe polymer degradation in the melt state—Part II: Thermal and thermo-oxidative degradation of polyamide 11/organo-clay nanocompo-site. Polymer 2015, 73, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wu, M.; Ao, Z.; Lai, B.; Zhou, Y.; An, T.; Wang, S. Metal–organic frameworks derived C/TiO2 for visible light photocatalysis: Simple synthesis and contribution of carbon species. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 124048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Metcalfe, I.S. Investigation of the generation of hydroxyl radicals and their oxidative role in the presence of heterogeneous copper catalysts. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckner, S.; Allegra, G.; Pegoraro, M.; La Mantia, F.P. Scienza e Tecnologia dei Materiali Polimerici. Edises Ed.: Napoli, Italy, 2020; ISBN ISBN-10 8879599194. [Google Scholar]


| Chemical Composition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample | (Code) | Nominal (wt%) | Nominal (at%) | * Actual (at%) |
| Cu/SiO2 | (SM1) | Cu (5.0) | 4.7 | 6.4 |
| Cu/TiO2 | (SM5) | Cu (5.0) | 6.2 | 10 |
| Cu-Ag/TiO2 | (SM6) | Cu (2.5)-Ag (2.5) | Cu (3.1)-Ag (1.9) | Cu (3.6)-Ag (1.6) |
| Ag/TiO2 | (SM7) | Ag (2.5) | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Sample | (Code) | SSA (BET Method) | Pore Volume (BJH Method) | Pore Width (BJH Method) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| m2/g | cm3/g | nm | ||
| Cu/SiO2 | (SM1) | 300 | 0.68 | 6.9 |
| Cu/TiO2 | (SM5) | 45 | 0.45 | 35 |
| Cu-Ag/TiO2 | (SM6) | 46 | 0.47 | 40 |
| Ag/TiO2 | (SM7) | 47 | 0.48 | 35 |
| Sample | H | H + TiO2 | H + TiO2 + Ag (HSM7) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T (°C) | η (mPa·s) × 105 | ||
| −25 | 6.86 | 9.42 | 19.1 |
| 0 | 1.38 | 3.05 | 10.4 |
| 25 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.39 |
| 50 | 0.27 | 0.65 | 0.86 |
| 75 | 0.44 | 1.44 | 2.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scolaro, C.; Liotta, L.F.; Calabrese, C.; Marcì, G.; Visco, A. Adhesive and Rheological Features of Ecofriendly Coatings with Antifouling Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112456
Scolaro C, Liotta LF, Calabrese C, Marcì G, Visco A. Adhesive and Rheological Features of Ecofriendly Coatings with Antifouling Properties. Polymers. 2023; 15(11):2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112456
Chicago/Turabian StyleScolaro, Cristina, Leonarda Francesca Liotta, Carla Calabrese, Giuseppe Marcì, and Annamaria Visco. 2023. "Adhesive and Rheological Features of Ecofriendly Coatings with Antifouling Properties" Polymers 15, no. 11: 2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112456
APA StyleScolaro, C., Liotta, L. F., Calabrese, C., Marcì, G., & Visco, A. (2023). Adhesive and Rheological Features of Ecofriendly Coatings with Antifouling Properties. Polymers, 15(11), 2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15112456










