Phase Equilibria, Diffusion and Structure in the Epoxypolycaprolactone System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.3. Optical Interferometry
2.4. Refractometry
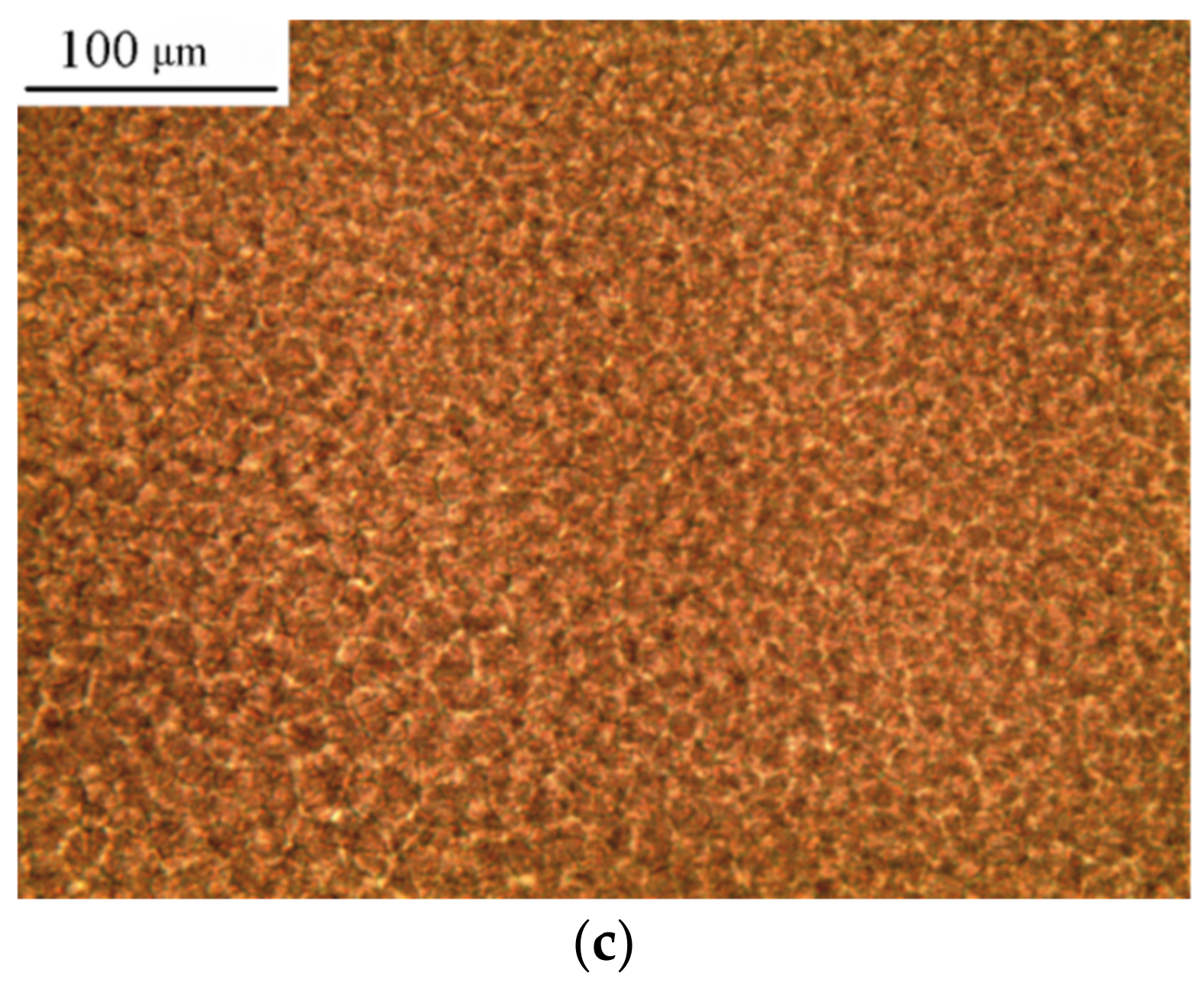
2.5. Optical Microscopy
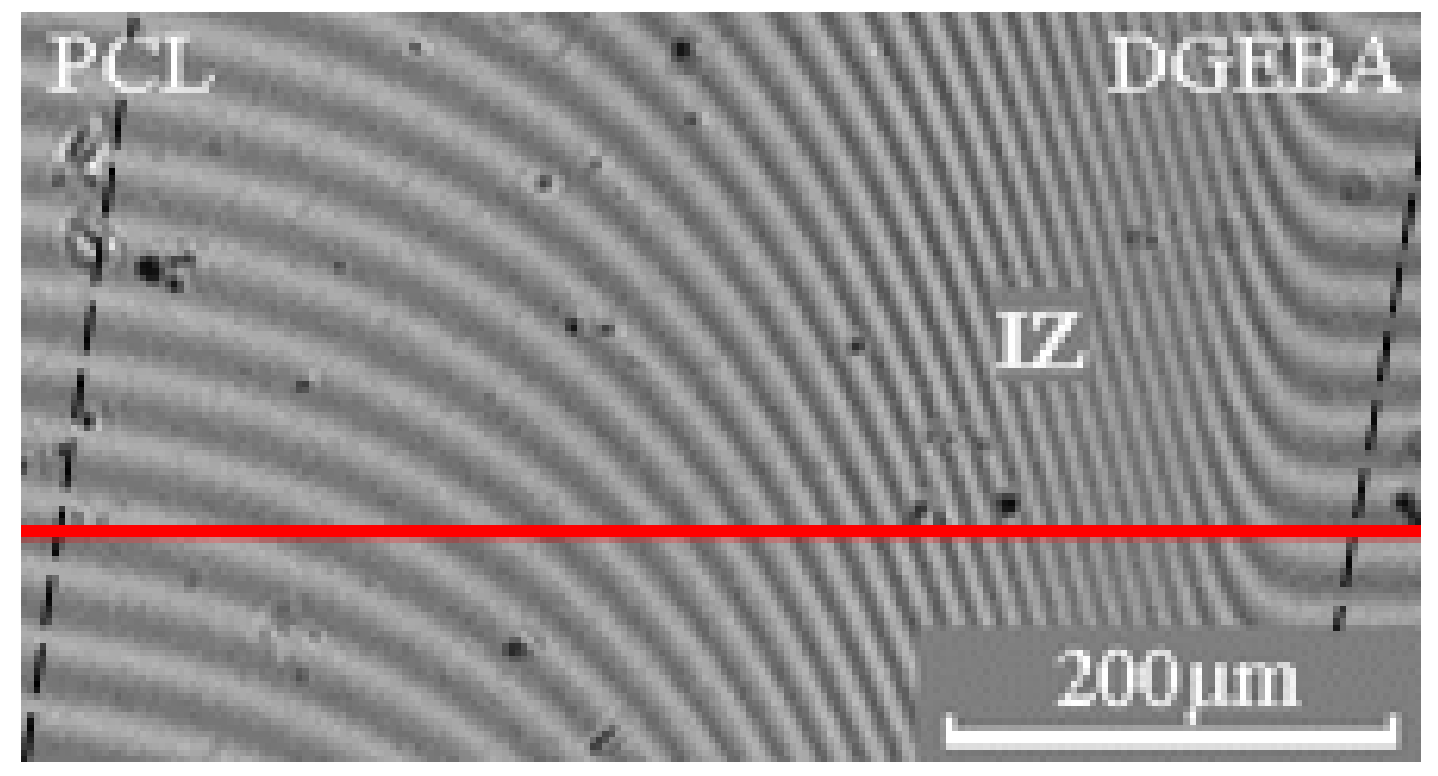
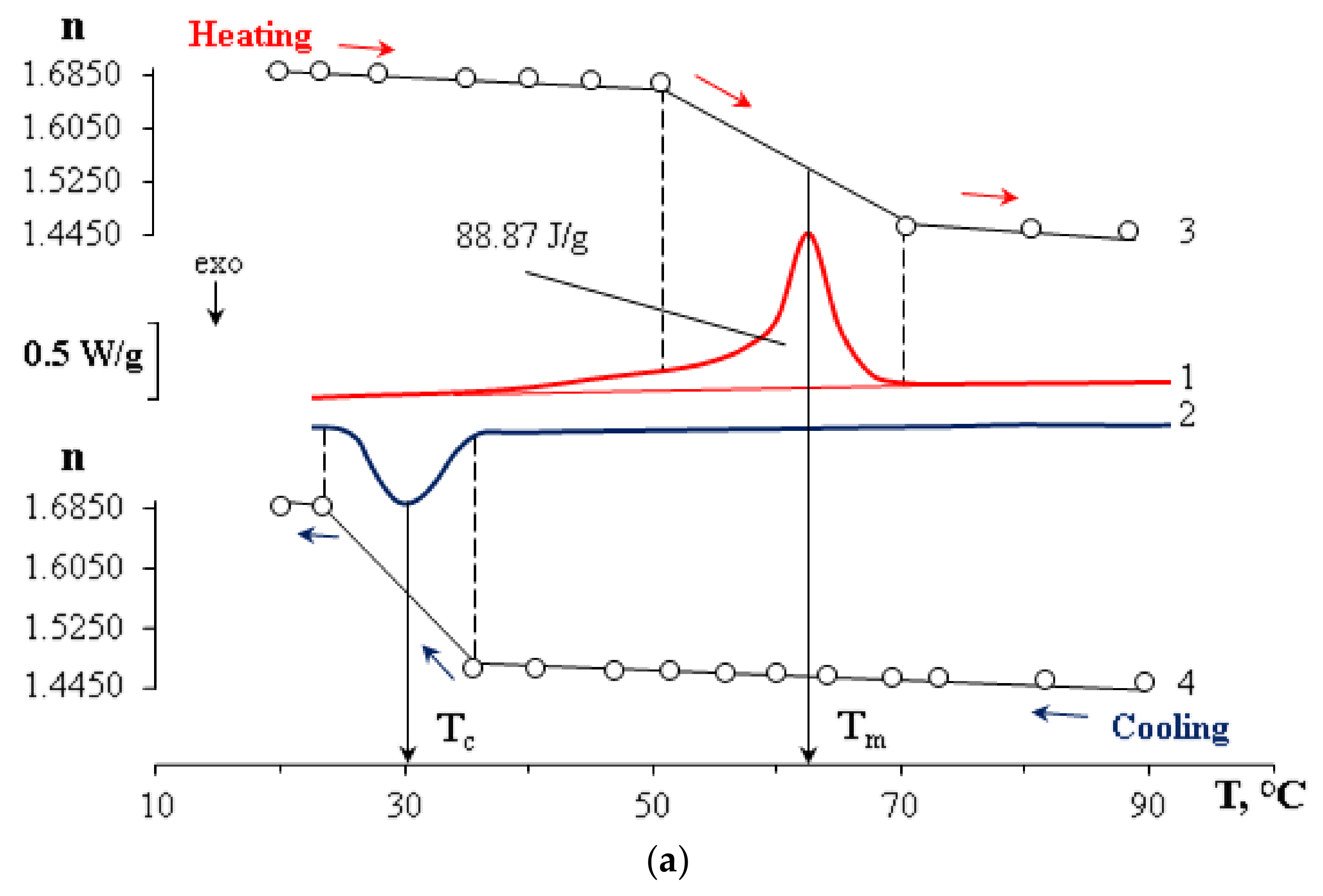
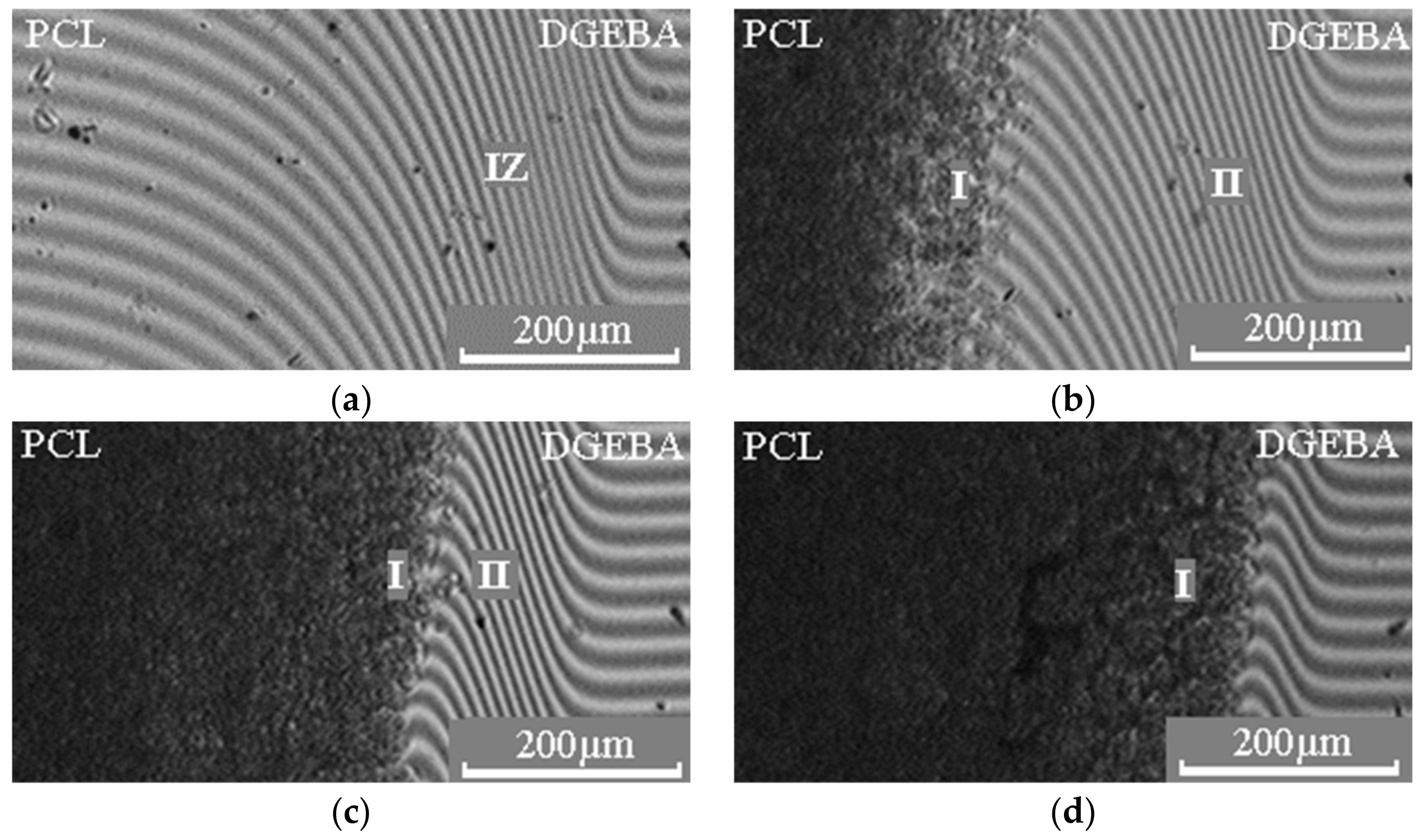
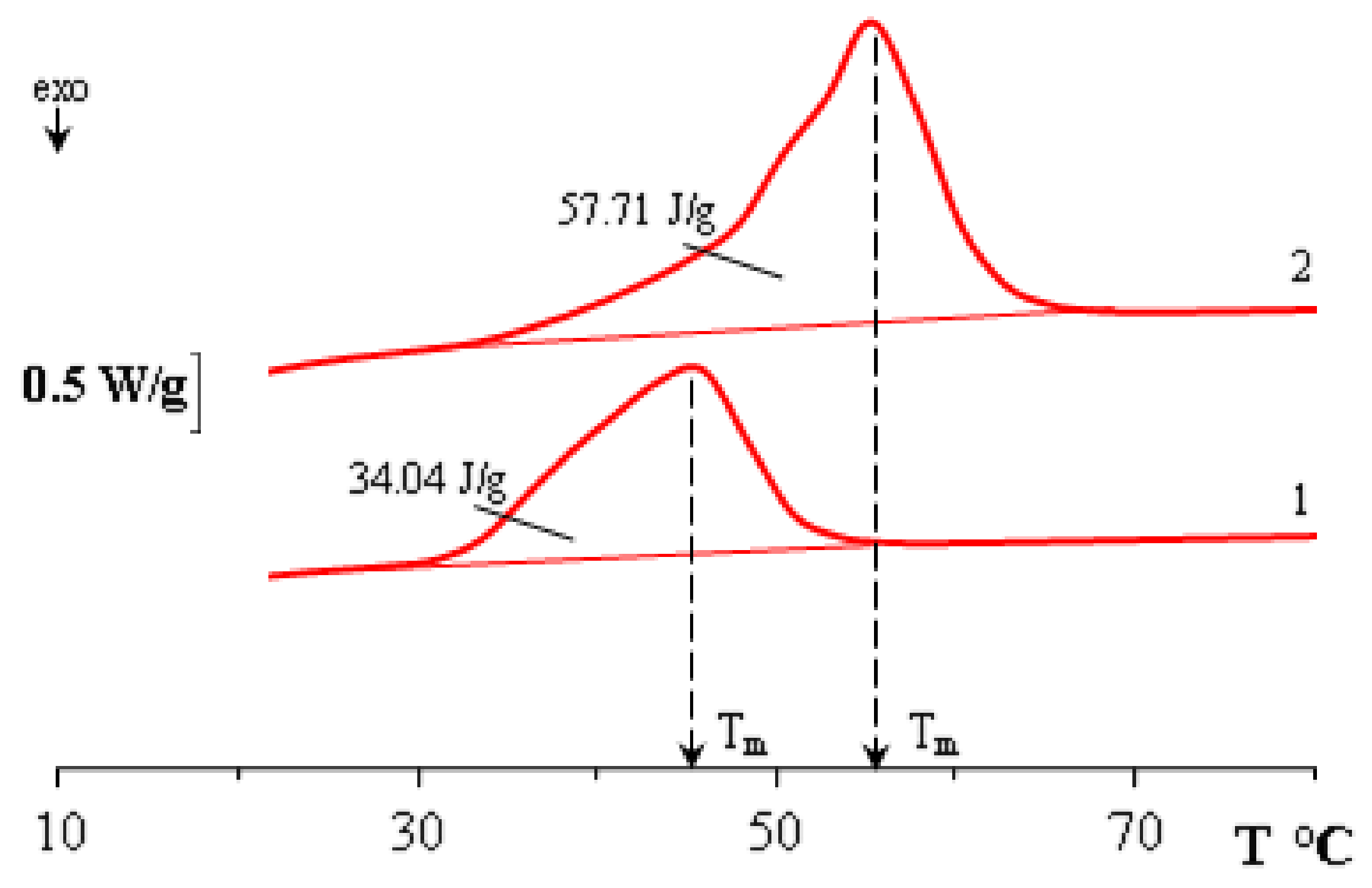
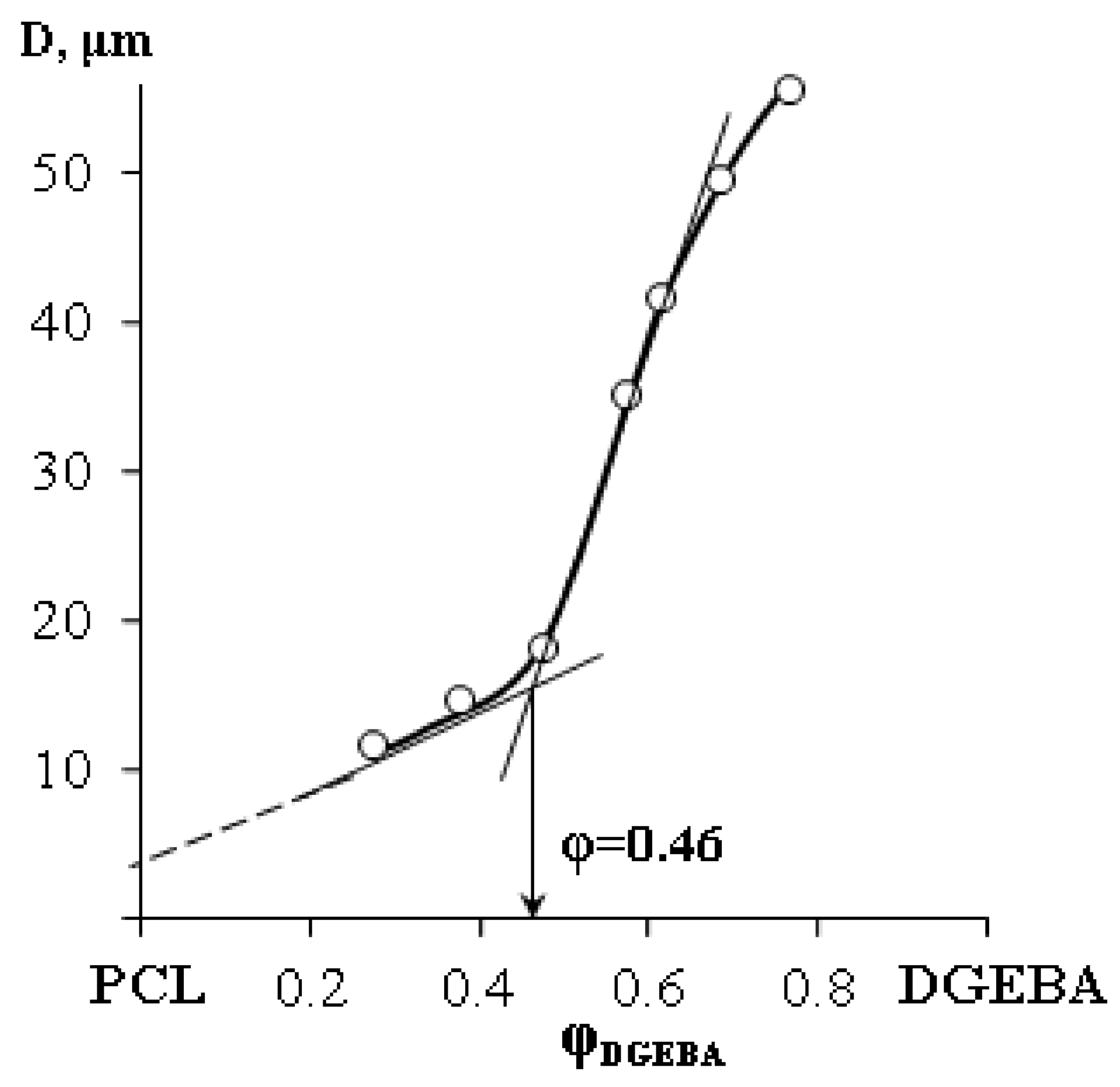
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosetti, Y.; Alcouffe, P.; Pascault, J.-P.; Gérard, J.-F.; Lortie, F. Polyether Sulfone-Based Epoxy Toughening: From Micro-to Nano-Phase Separation via PES End-Chain Modification and Process Engineering. Materials 2018, 11, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Shi, K.; Wang, T.; Harkin-Jones, E. Constructing a Filler Network for Thermal Conductivity Enhancement in Epoxy Composites via Reaction-Induced Phase Separation. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2018, 110, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishi, H.; Tanaka, S.; Nakashima, Y.; Saruwatari, T. Self-Assembled Three-Dimensional Structure of Epoxy/Polyethersulphone/Silver Adhesives with Electrical Conductivity. Polymer 2016, 82, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.; Tognana, S.; Salgueiro, W. Miscibility in Crystalline/Amorphous Blends of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate)/DGEBA. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2013, 51, 680–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elnaiem, A.M.; Hussein, S.I.; Assaedi, H.S.; Mebed, A.M. Fabrication and Evaluation of Structural, Thermal, Mechanical and Optical Behavior of Epoxy–TEOS/MWCNTs Composites for Solar Cell Covering. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 3995–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.I.; Abd-Elnaiem, A.M.; Asafa, T.B.; Jaafar, H.I. Effect of Incorporation of Conductive Fillers on Mechanical Properties and Thermal Conductivity of Epoxy Resin Composite. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toldy, A.; Niedermann, P.; Rapi, Z.; Szolnoki, B. Flame Retardancy of Glucofuranoside Based Bioepoxy and Carbon Fibre Reinforced Composites Made Thereof. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 142, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangermano, M.; Tonin, M.; Yagci, Y. Degradable Epoxy Coatings by Photoinitiated Cationic Copolymerization of Bisepoxide with ε-Caprolactone. Eur. Polym. J. 2010, 46, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venu, G.; Jayan, J.S.; Saritha, A.; Joseph, K. Thermal Decomposition Behavior and Flame Retardancy of Bioepoxies, Their Blends and Composites: A Comprehensive Review. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 162, 110904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-P.; Chuang, C.-M. Thermal and Dielectric Properties of Cyanate Ester Cured Main Chain Rigid-Rod Epoxy Resin. Polymers 2021, 13, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, F.-L.; Park, S.-J. Thermomechanical Behavior of Epoxy Resins Modified with Epoxidized Vegetable Oils. Polym. Int. 2008, 57, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Schuman, T.P. Vegetable Oil-Derived Epoxy Monomers and Polymer Blends: A Comparative Study with Review. Express Polym. Lett. 2013, 7, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.J.; Kim, D.S. Effect of Functionality and Content of Epoxidized Soybean Oil on the Physical Properties of a Modified Diglycidyl Ether of Bisphenol A Resin System. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, app50441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, T.; Jaswal, S.; Gaur, B.; Singha, A.S. Thermo-mechanical Properties of Rosin-modified O-cresol Novolac Epoxy Thermosets Comprising Rosin-based Imidoamine Curing Agents. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021, 61, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosu, L.; Mustata, F.; Rosu, D.; Varganici, C.-D.; Rosca, I.; Rusu, T. Bio-Based Coatings from Epoxy Resins Crosslinked with a Rosin Acid Derivative for Wood Thermal and Anti–Fungal Protection. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 151, 106008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diógenes, O.B.F.; de Oliveira, D.R.; da Silva, L.R.R.; Pereira, Í.G.; Mazzetto, S.E.; Araujo, W.S.; Lomonaco, D. Development of Coal Tar-Free Coatings: Acetylated Lignin as a Bio-Additive for Anticorrosive and UV-Blocking Epoxy Resins. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 161, 106533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.D.S.; Barros, J.J.P.; Jaques, N.G.; Wellen, R.M.R. On the Curing Kinetics of Epoxy/PLA Compounds. J. Mater. Res. 2021, 36, 2973–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Suárez, A.; Del Rosario, G.; Sánchez-Romate, X.X.; Prolongo, S.G. Influence of Morphology on the Healing Mechanism of PCL/Epoxy Blends. Materials 2020, 13, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Bonab, V.S.; Patel, A.; Manas-Zloczower, I. Self-Healing Epoxy Coatings with Enhanced Properties and Facile Processability. Polymer 2018, 147, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J. Self-Healing Properties of Epoxy Resins with Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Healing Agent. Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 3081–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddhamalli, S.K. Toughening of Epoxy/Polycaprolactone Composites via Reaction Induced Phase Separation. Polym. Compos. 2000, 21, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-L.; Chang, F.-C. Phase Separation Process in Poly(ε-Caprolactone)−Epoxy Blends. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 5348–5356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zheng, S. Influence of Intramolecular Specific Interactions on Phase Behavior of Epoxy Resin and Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Blends Cured with Aromatic Amines. Polymer 2005, 46, 5828–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalykh, A.E.; Gerasimov, V.K.; Bukhteev, A.E.; Shapagin, A.V.; Kudryakova, G.K.; Brantseva, T.V.; Gorbatkina, Y.A.; Kerber, M.L. Compatibility and Phase Structure Evolution in Polysulfone-Curable Epoxy Oligomer Blends. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2003, 45, 676–685. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chalykh, A.E.; Shapagin, A.V. Phase Equilibrium and Phase Structure of Cured Polymer Nanocompositions. In Modern Problems of Physical Chemistry of Nanomaterials; Publishing Group “Border”: Moscow, Russia, 2008; pp. 118–140. ISBN 978-5-94691-351-5. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Brantseva, T.V.; Solodilov, V.I.; Antonov, S.V.; Gorbunova, I.Y.; Korohin, R.A.; Shapagin, A.V.; Smirnova, N.M. Epoxy Modification with Poly(Vinyl Acetate) and Poly(Vinyl Butyral). I. Structure, Thermal, and Mechanical Characteristics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 44081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korokhin, R.A.; Shapagin, A.V.; Solodilov, V.I.; Zvereva, U.G.; Solomatin, D.V.; Gorbatkina, Y.A. Epoxy Polymers Modified with Polyetherimide. Part I: Rheological and Thermomechanical Characteristics. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodilov, V.I.; Gorbatkina, Y.A.; Korokhin, R.A.; Kuperman, A.M. Properties of Filament-Wound Organoplastics Based on Epoxy Polysulfone Matrices and Armos and Rusar Aramid Fibers. Polym. Sci. Ser. D 2018, 11, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapagin, A.V.; Budylin, N.Y.; Chalykh, A.E. Regulation of a Phase Structure at the Interface in Epoxy–Polysulfone Systems. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2018, 67, 2172–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, V.A.; Egorov, V.M. Differential Scanning Calorimetry in Physicochemistry of Polymers; Khimia: Leningrad, Russia, 1990. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chalykh, A.E.; Zagaitov, A.L.; Korotchrnko, D.P. Optical Diffusiometer; IFKh RAN: Moscow, Russia, 1996. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Malkin, A.; Ascadsky, A.; Kovriga, V.; Chalykh, A.E. Experimental Methods of Polymer Physics; MIR Publishers: Moscow, Russia, 1983. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Chalykh, A.E.; Gerasimov, V.K.; Mikhailov, Y.M. Phase State Diagrams of Polymer Systems; Yanus-K: Moscow, Russia, 1998. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Nikulova, U.V.; Chalykh, A.E. Phase Equilibrium and Interdiffusion in Poly(Vinyl Methyl Ether)-Water System. Polymers 2020, 12, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remiro, P.M.; Cortazar, M.M.; Calahorra, M.E.; Calafel, M.M. Miscibility and Crystallization of an Amine-Cured Epoxy Resin Modified with Crystalline Poly(ɛ-Caprolactone). Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2001, 202, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, M.F.; Huang, S.J. Biodegradable Blends and Composites of Polycaprolactone and Starch Derivatives. Polymer 1995, 36, 1877–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsah, A.H.; Cartmell, S.H.; Richardson, S.M.; Bosworth, L.A. Material Characterization of PCL:PLLA Electrospun Fibers Following Six Months Degradation In Vitro. Polymers 2020, 12, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicy, K.; Geethamma, V.G.; Kalarikkal, N.; Rouxel, D.; Thomas, S. Poly(ɛ-Caprolactone)/Functionalized-Carbon Nanotube Electrospun Nanocomposites: Crystallization and Thermal Properties. Macromol. Symp. 2018, 381, 1800140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, B. Macromolecular Physics. 3: Crystal Melting; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 63–181. [Google Scholar]
- Kammer, H.W. On Immiscibility-Loop Phase Behaviour of Polymer Blends. Polymer 1999, 40, 5793–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalykh, A.E.; Gerasimov, V.K.; Mironov, A.V.; Kuptsov, S.A.; Kil’deeva, N.R. Phase Equilibria of Poly(ɛ-Caprolactone)-Co-Poly(Acryl Methacrylate)-Methylene Chloride Systems and the Phase Structure of Polymer Binary Mixtures. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2012, 54, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelkern, L. Crystallization of Polymers, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1964; p.359. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, C.A.; Murphy, S.H.; Leeke, G.A.; Howdle, S.M.; Shakesheff, K.M.; Jenkins, M.J. Rheological Studies of Polycaprolactone in Supercritical CO2. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


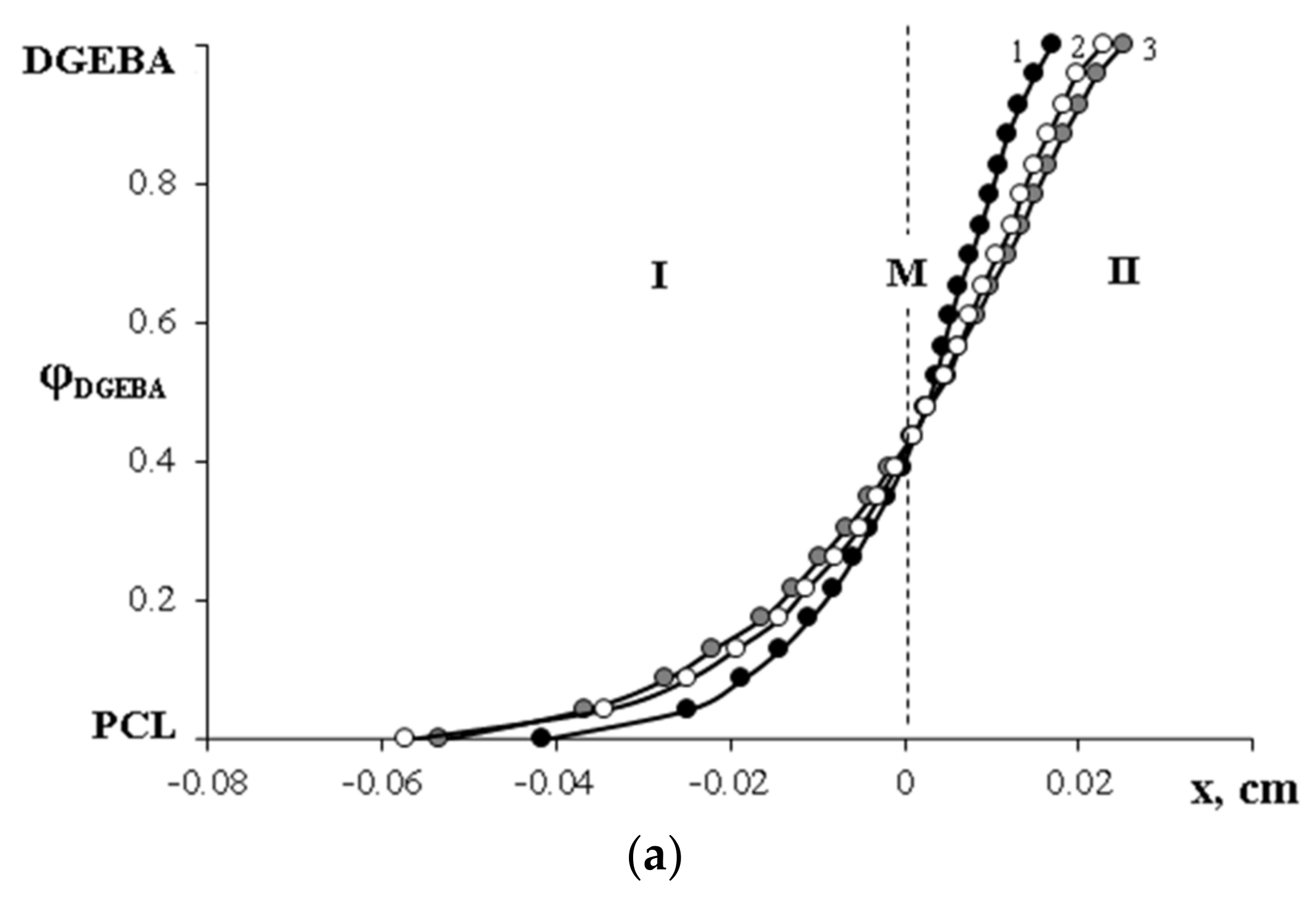
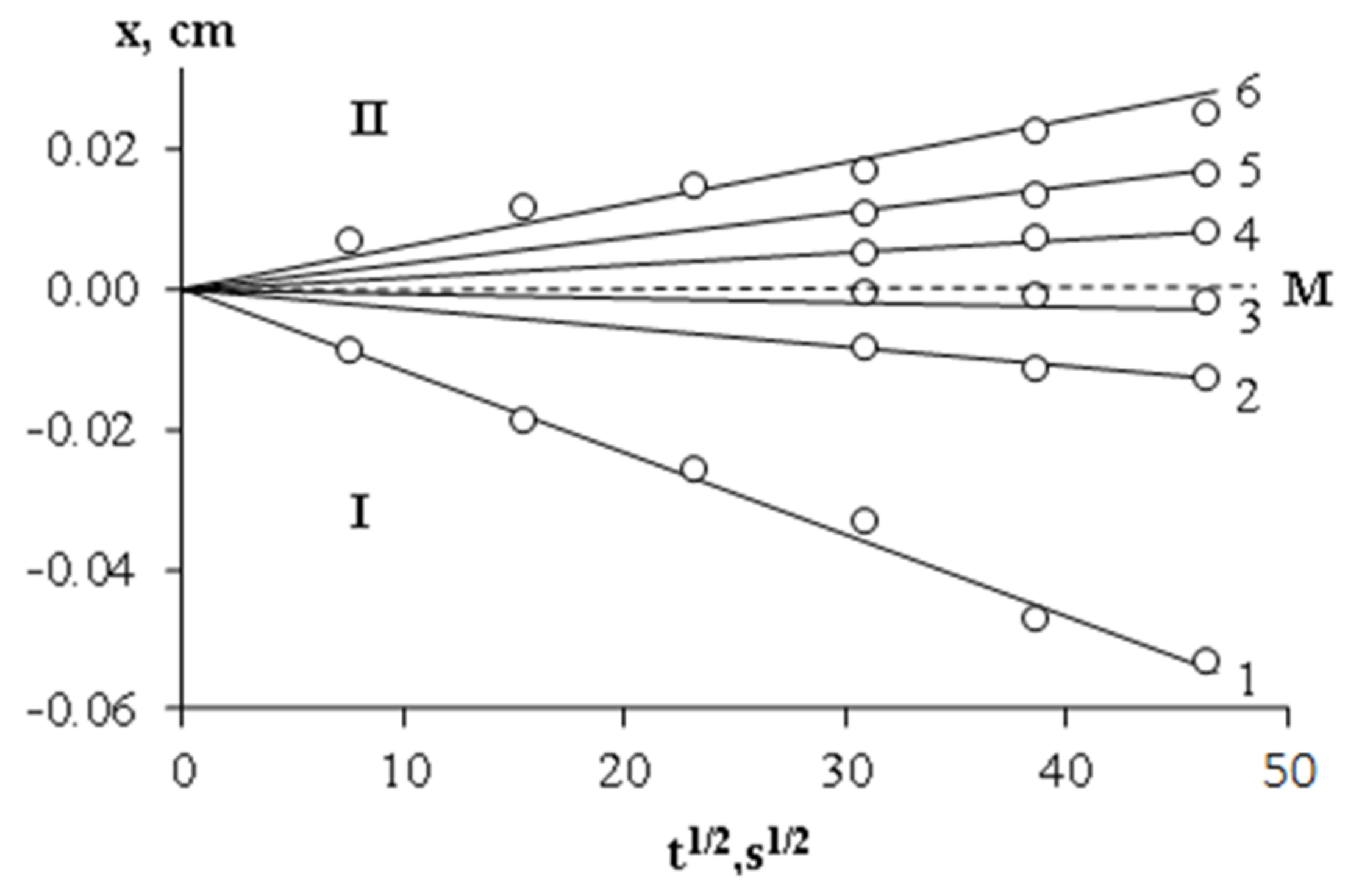
 ,
,  —compositions of coexisting phases for Mn PCL = 80 × 103;
—compositions of coexisting phases for Mn PCL = 80 × 103;  ,
,  —for Mn PCL = 45 × 103.
—for Mn PCL = 45 × 103.  —melting points of the PCL–DGEBA mixture (Mn PCL = 45 × 103) obtained by DSC. I—homogeneous solution; II—heterogeneous solution.
—melting points of the PCL–DGEBA mixture (Mn PCL = 45 × 103) obtained by DSC. I—homogeneous solution; II—heterogeneous solution.
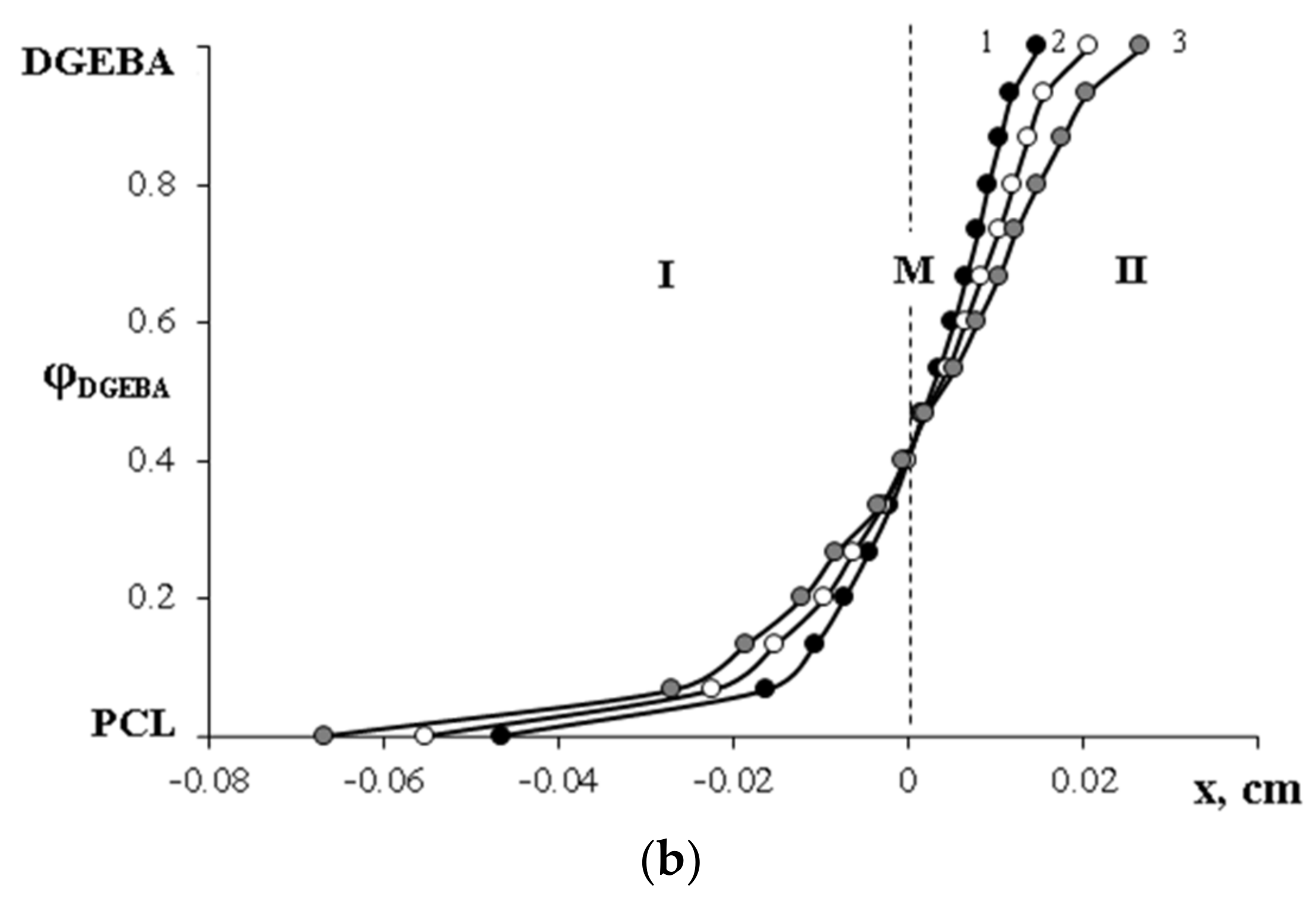
 ,
,  —compositions of coexisting phases for Mn PCL = 80 × 103;
—compositions of coexisting phases for Mn PCL = 80 × 103;  ,
,  —for Mn PCL = 45 × 103.
—for Mn PCL = 45 × 103.  —melting points of the PCL–DGEBA mixture (Mn PCL = 45 × 103) obtained by DSC. I—homogeneous solution; II—heterogeneous solution.
—melting points of the PCL–DGEBA mixture (Mn PCL = 45 × 103) obtained by DSC. I—homogeneous solution; II—heterogeneous solution.


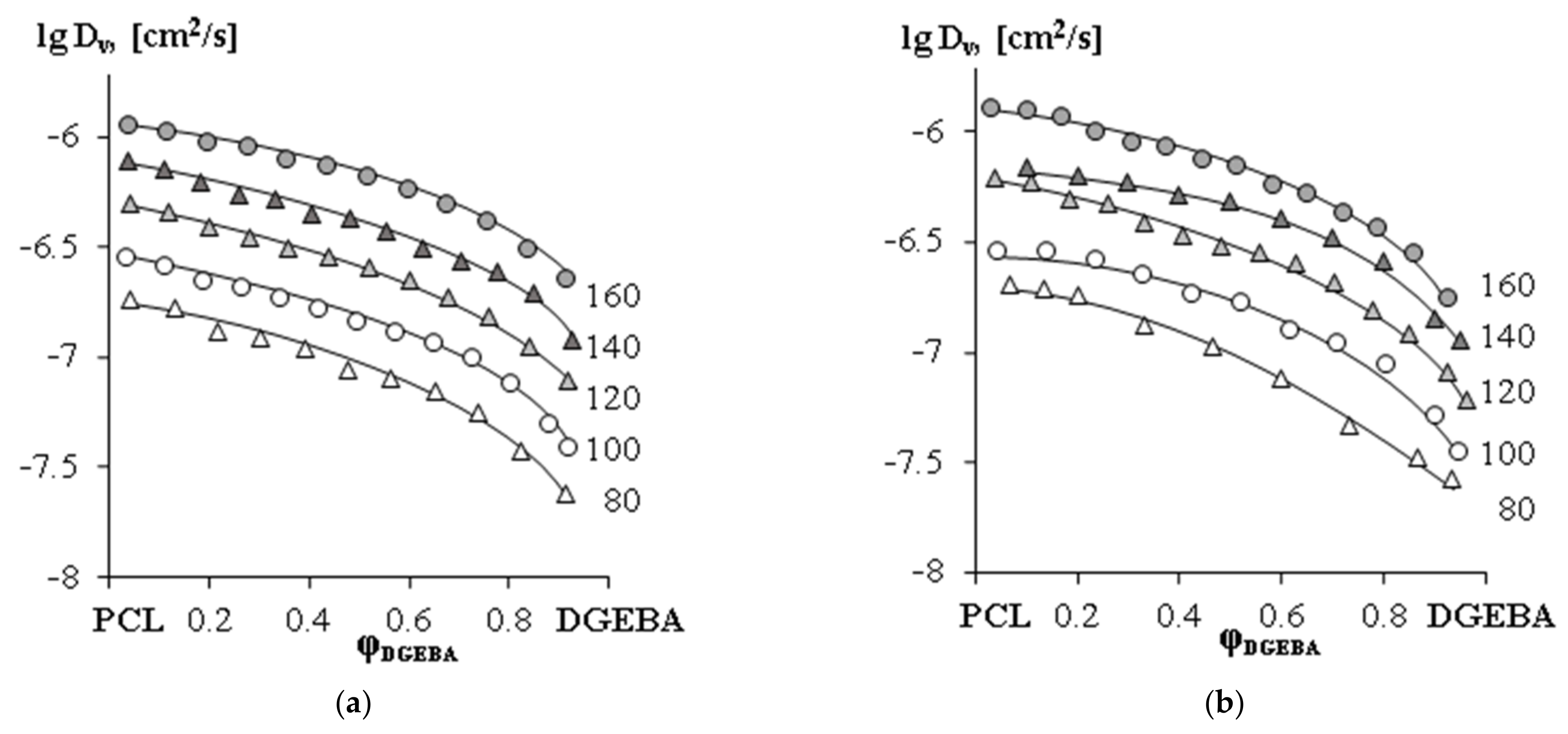
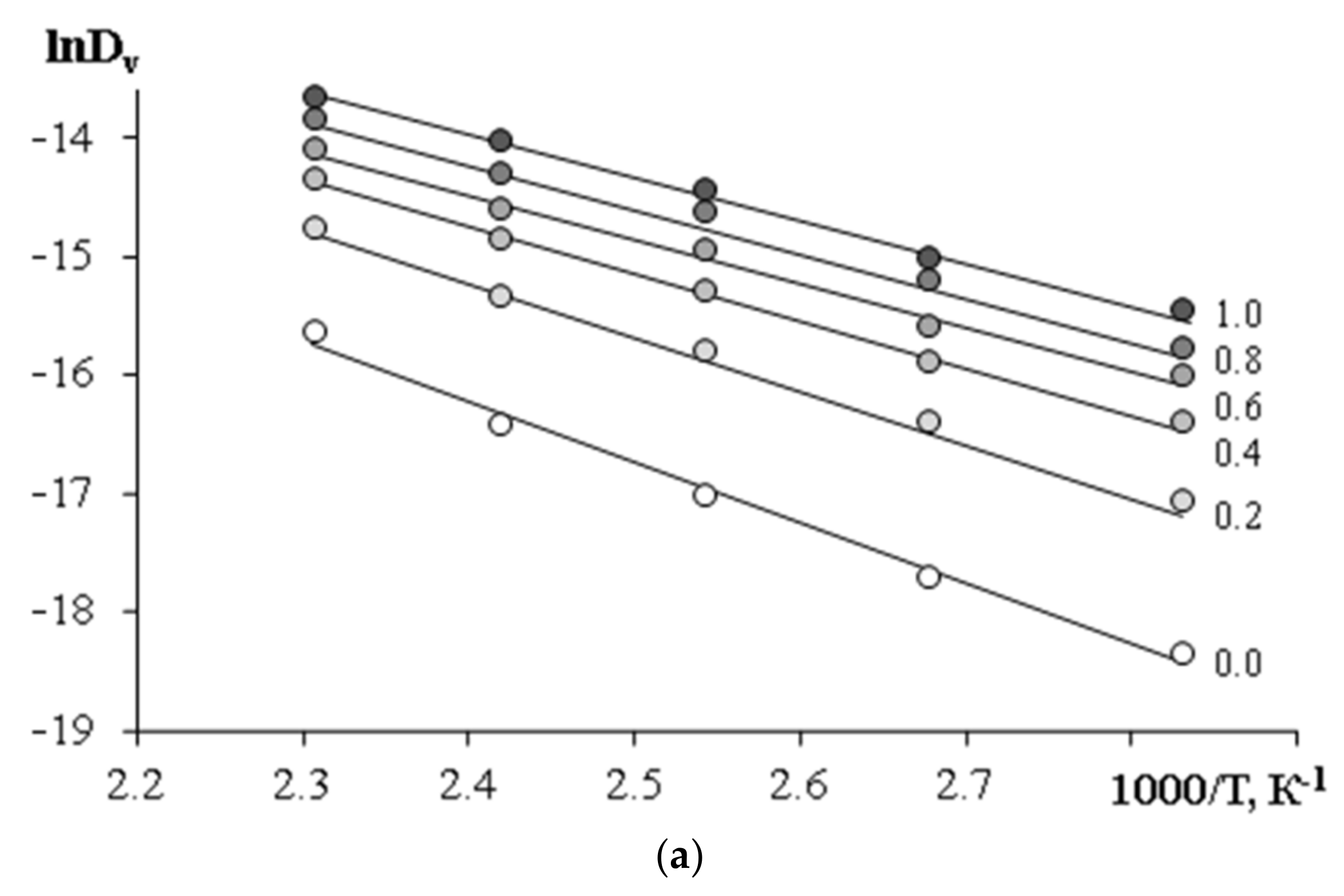

 —PCL with Mn = 45 × 103,
—PCL with Mn = 45 × 103,  —PCL with Mn = 80 × 103.
—PCL with Mn = 80 × 103.
 —PCL with Mn = 45 × 103,
—PCL with Mn = 45 × 103,  —PCL with Mn = 80 × 103.
—PCL with Mn = 80 × 103.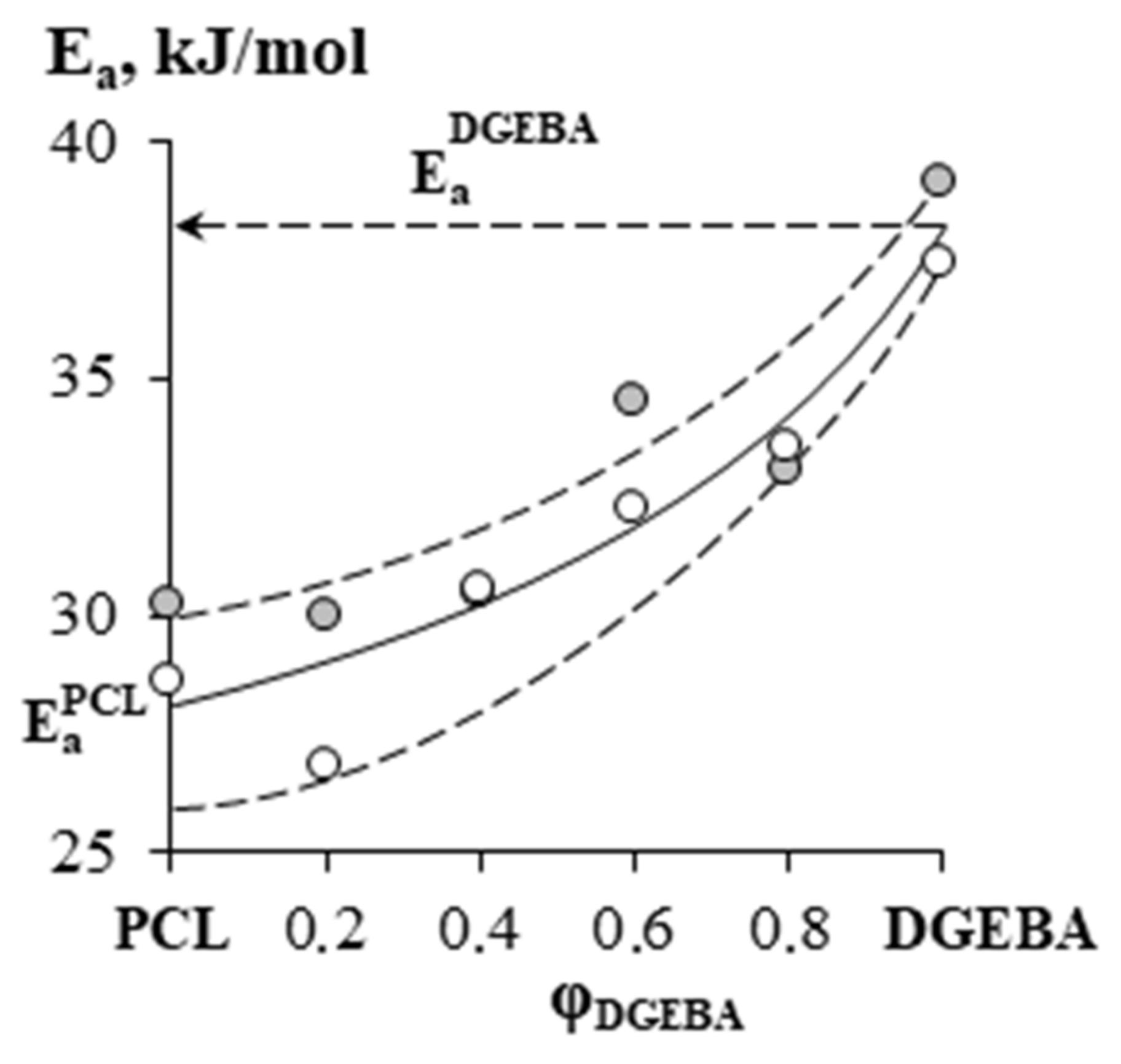
| T−1, K | Χ | |
|---|---|---|
| PCL (Mn = 45 × 103) – DGEBA | PCL (Mn = 80 × 103) – DGEBA | |
| 3.095975 | 0.538435 | 0.836821 |
| 3.194888 | 0.228042 | 0.253214 |
| 3.300330 | 0.093582 | 0.067616 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plyusnina, I.O.; Budylin, N.Y.; Shapagin, A.V. Phase Equilibria, Diffusion and Structure in the Epoxypolycaprolactone System. Polymers 2023, 15, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010117
Plyusnina IO, Budylin NY, Shapagin AV. Phase Equilibria, Diffusion and Structure in the Epoxypolycaprolactone System. Polymers. 2023; 15(1):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010117
Chicago/Turabian StylePlyusnina, Irina O., Nikita Yu. Budylin, and Alexey V. Shapagin. 2023. "Phase Equilibria, Diffusion and Structure in the Epoxypolycaprolactone System" Polymers 15, no. 1: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010117
APA StylePlyusnina, I. O., Budylin, N. Y., & Shapagin, A. V. (2023). Phase Equilibria, Diffusion and Structure in the Epoxypolycaprolactone System. Polymers, 15(1), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15010117







