Preparation, Characterization, and Performance Evaluation of Petroleum Asphalt Modified with Bio-Asphalt Containing Furfural Residue and Waste Cooking Oil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Analysis of the Raw Materials
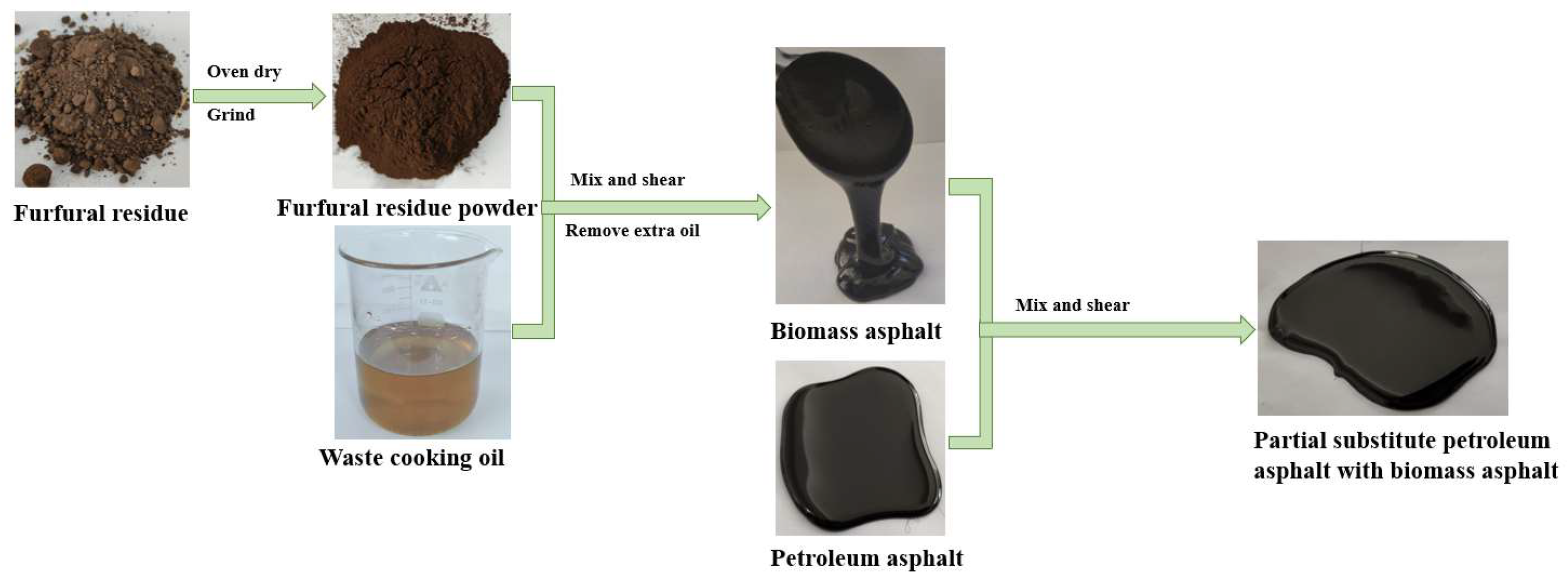
2.2.2. Preparation of the Bio-Asphalt
2.2.3. Substitution of the Petroleum Asphalt with Bio-Asphalt
2.2.4. Characterization of the Bio-Asphalt
2.2.5. Asphalt Performance
2.2.6. Road Performance of the Substituted Asphalt
2.2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Raw Materials Analysis
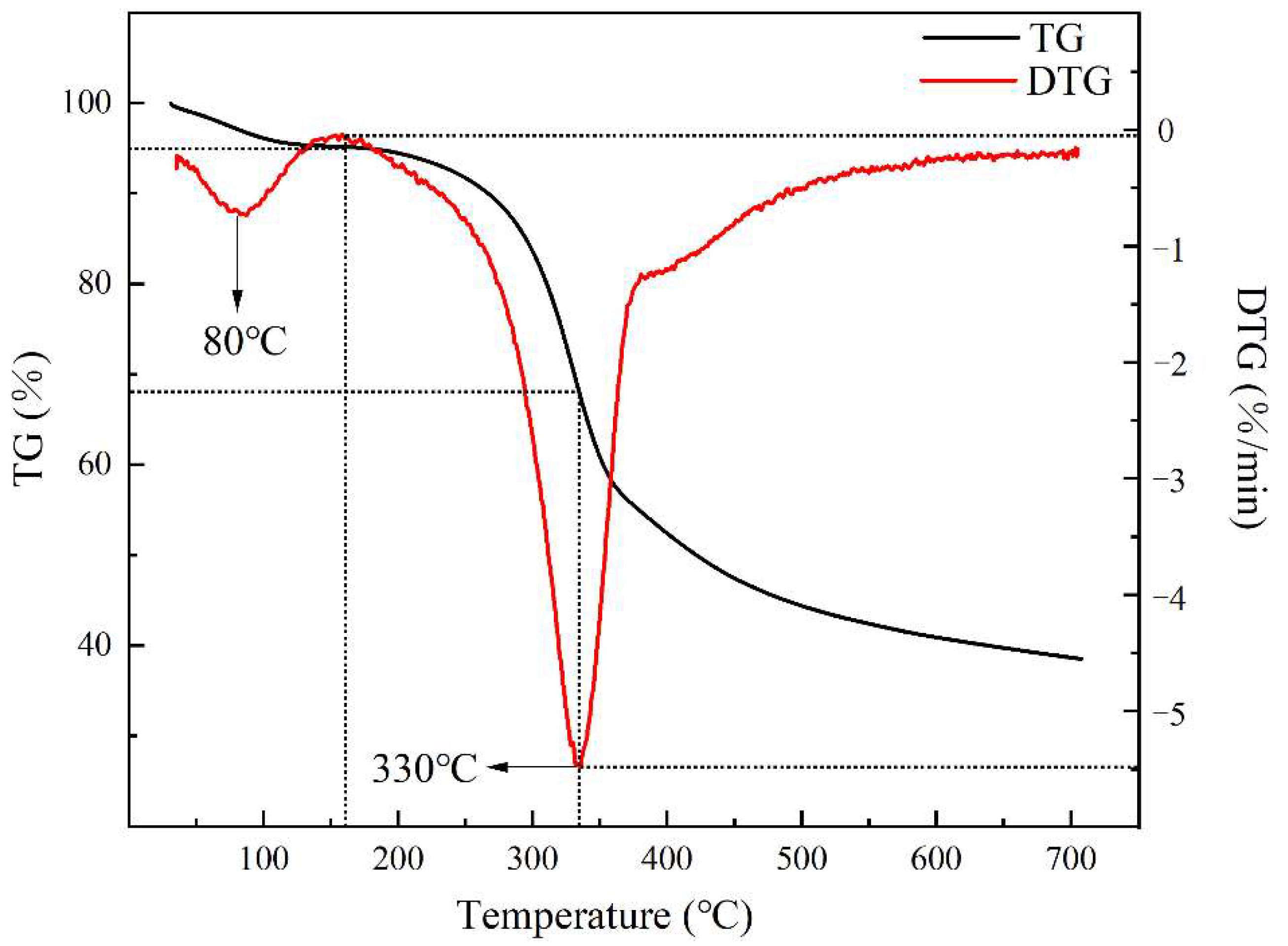
3.1.1. Furfural Residue Analysis
3.1.2. Waste Cooking Oil Analysis
3.1.3. 90# Petroleum Asphalt Analysis
3.2. Characterization
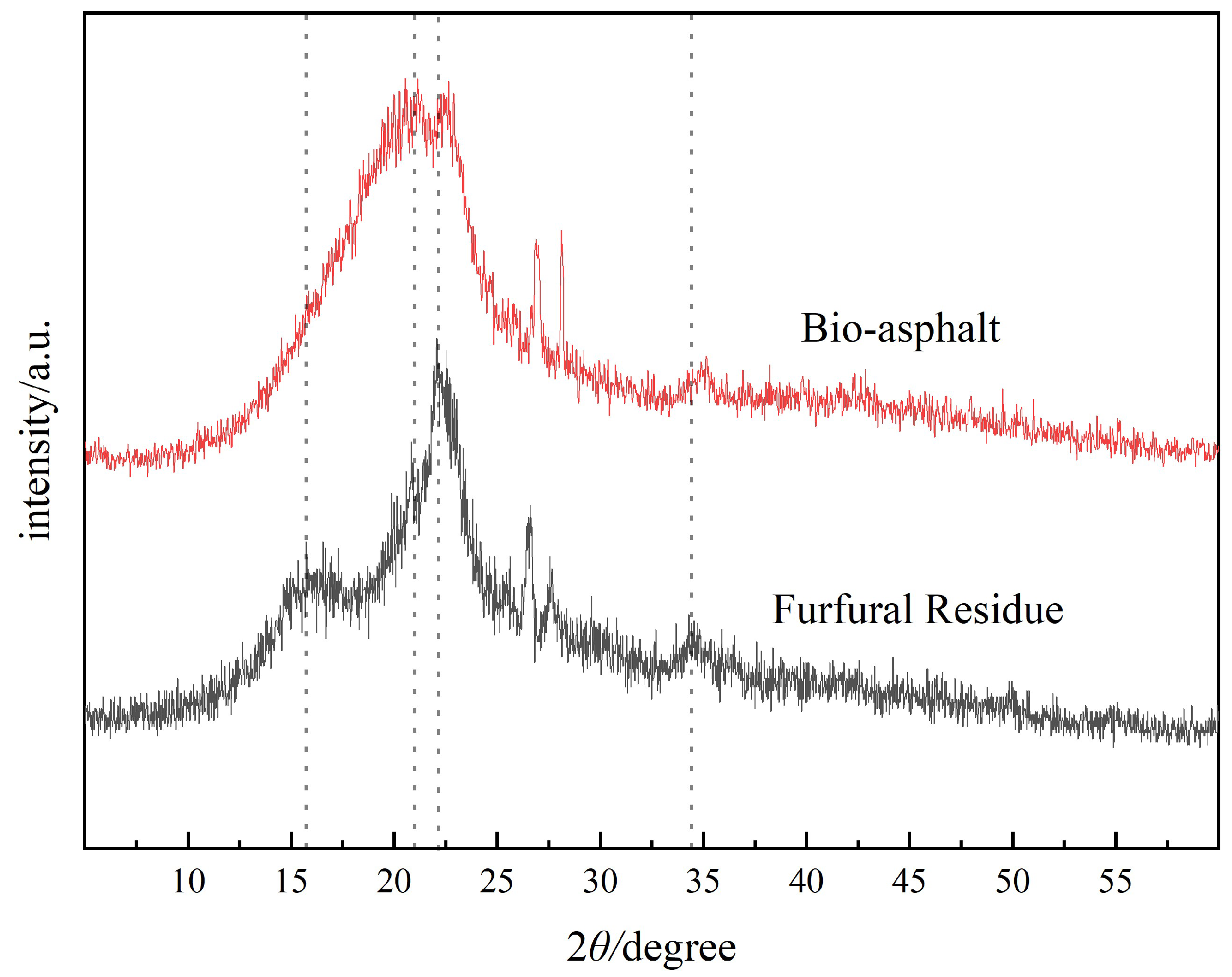
3.2.1. X-ray Diffraction Analysis of the Bio-Asphalt
3.2.2. Water Contact Angle of the Bio-Asphalt
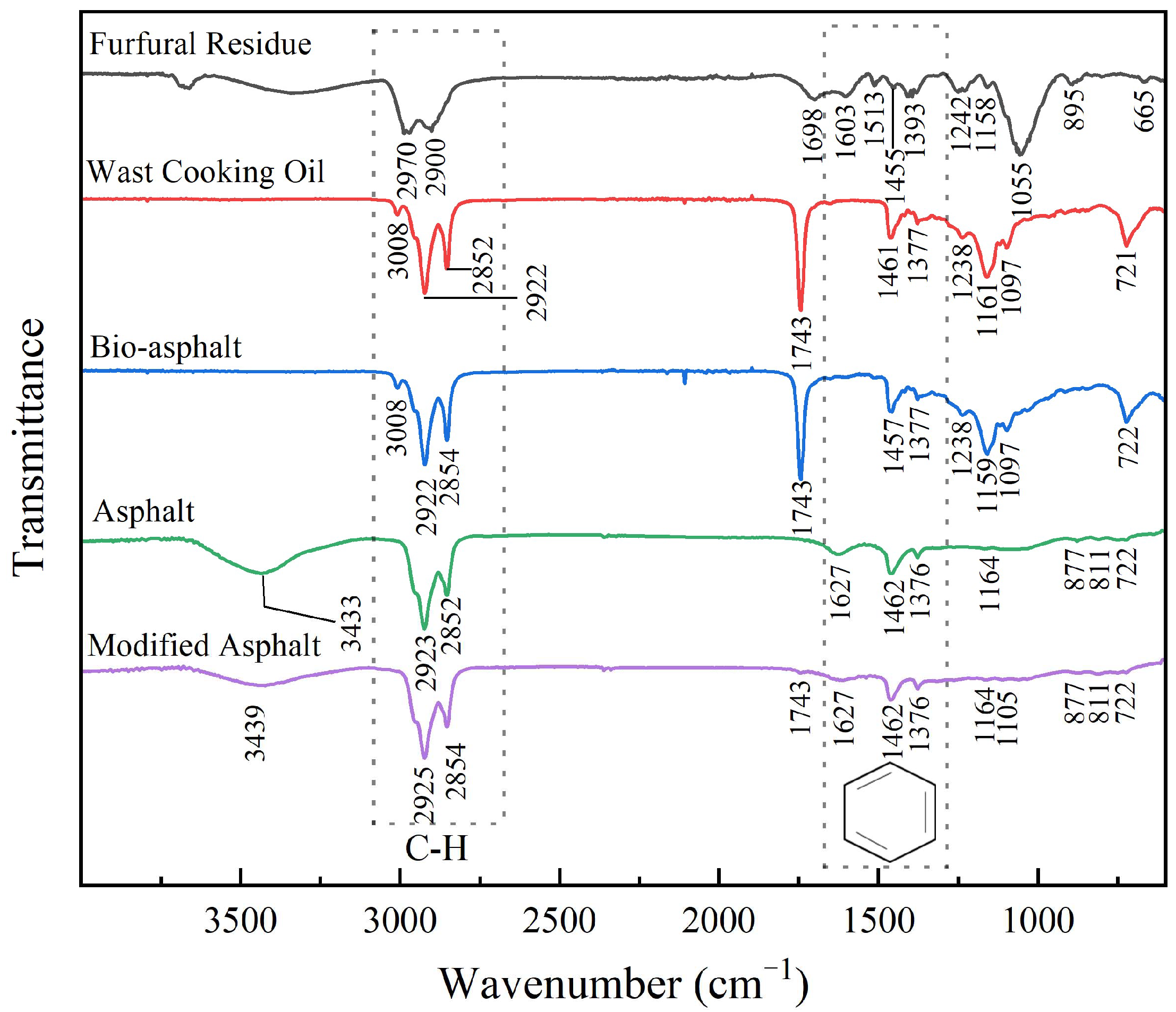
3.2.3. FTIR Analysis
3.2.4. Morphology Analysis
3.3. Mechanical Performance of the Asphalt Mixtures
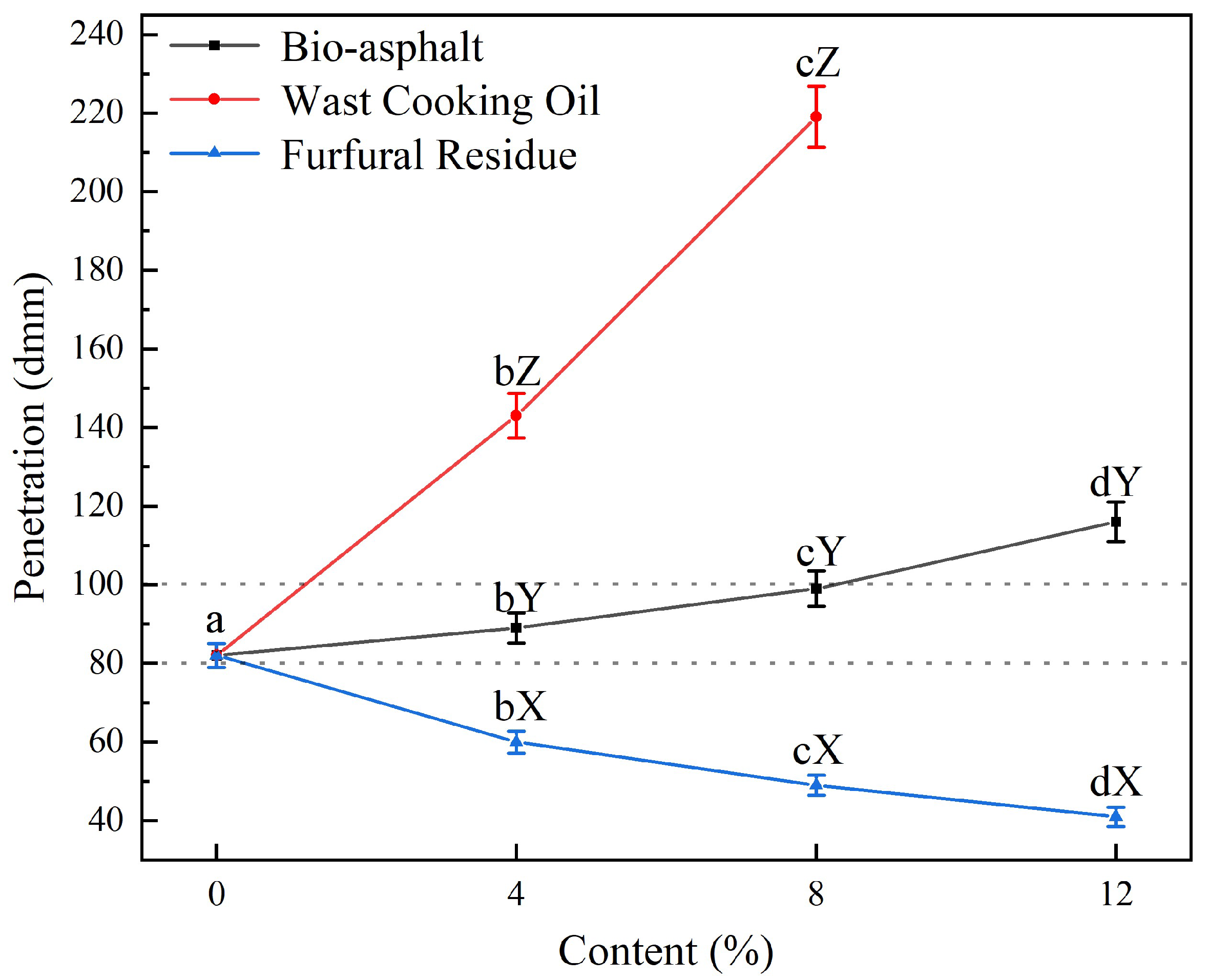
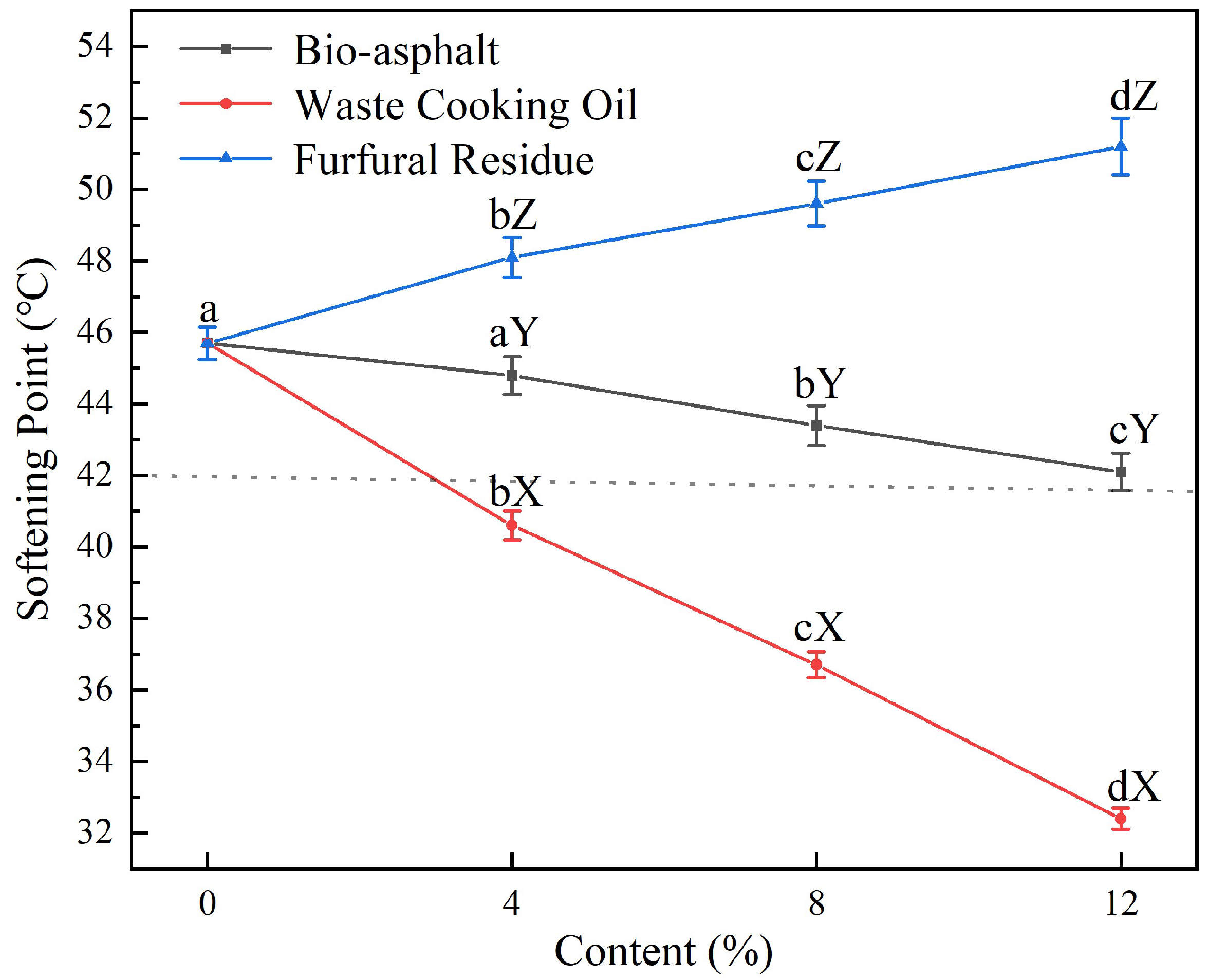
3.3.1. Penetration, Softening Point, and Ductility
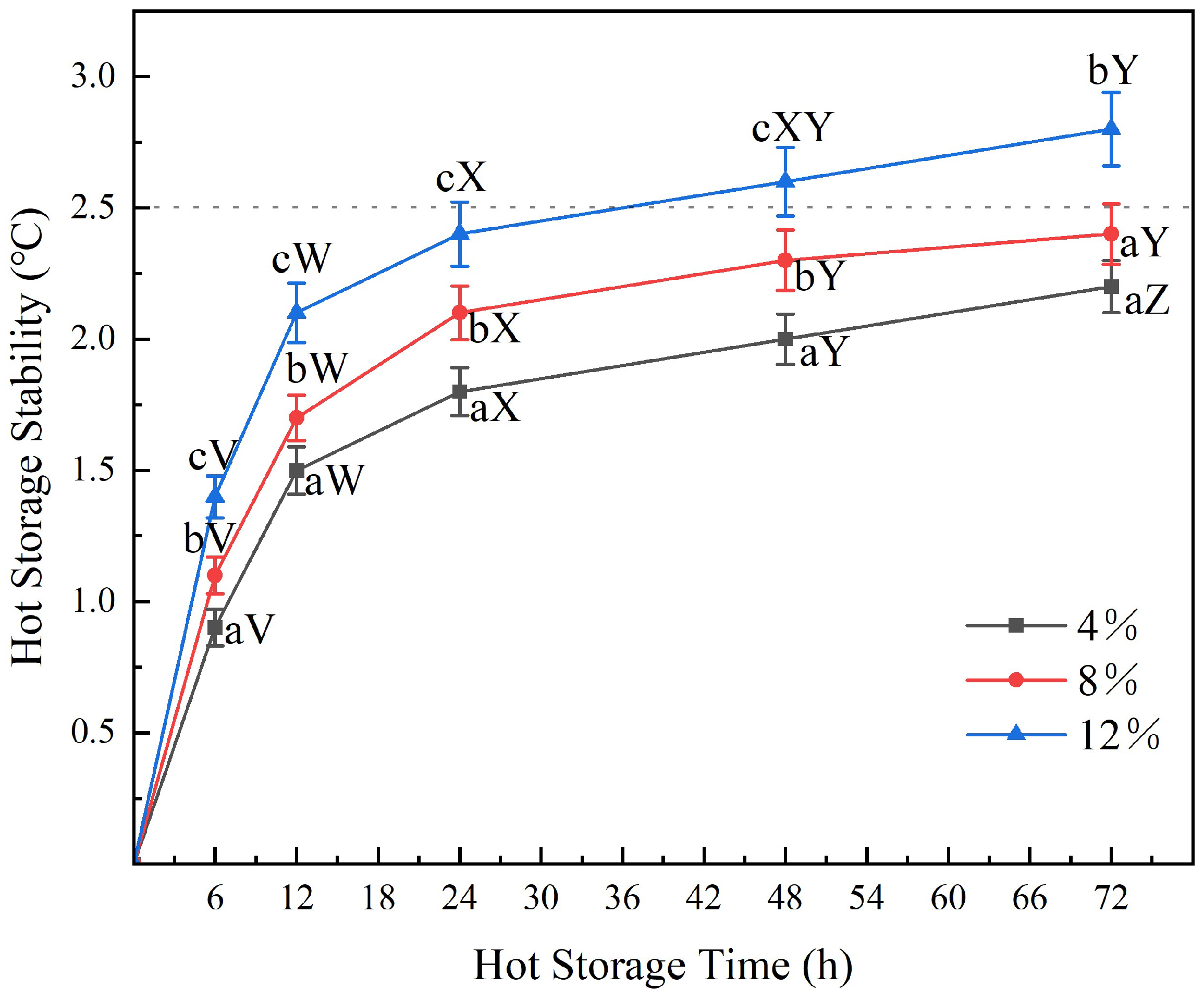
3.3.2. Thermal Storage Stability
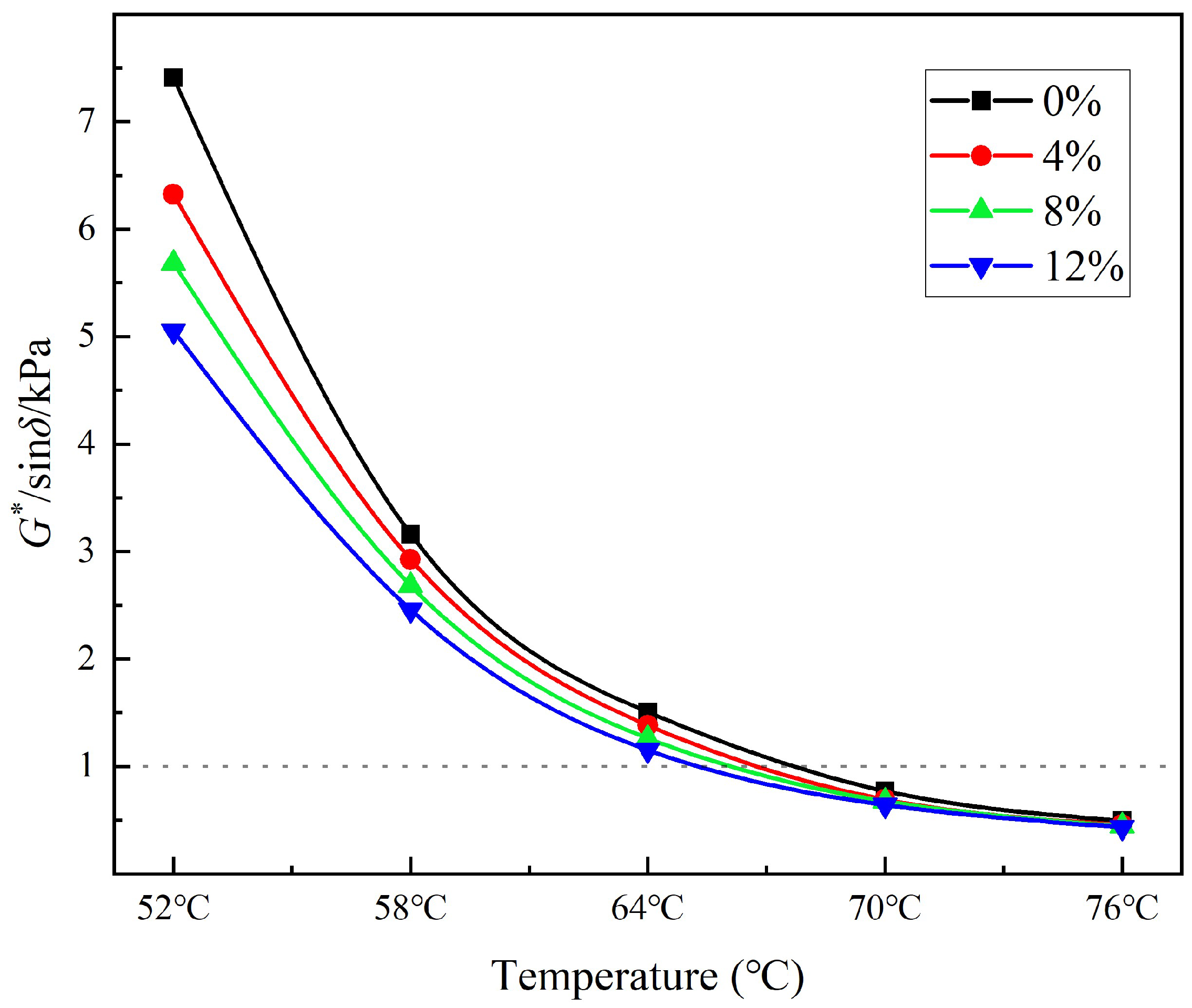
3.3.3. High Temperature Rheological Properties
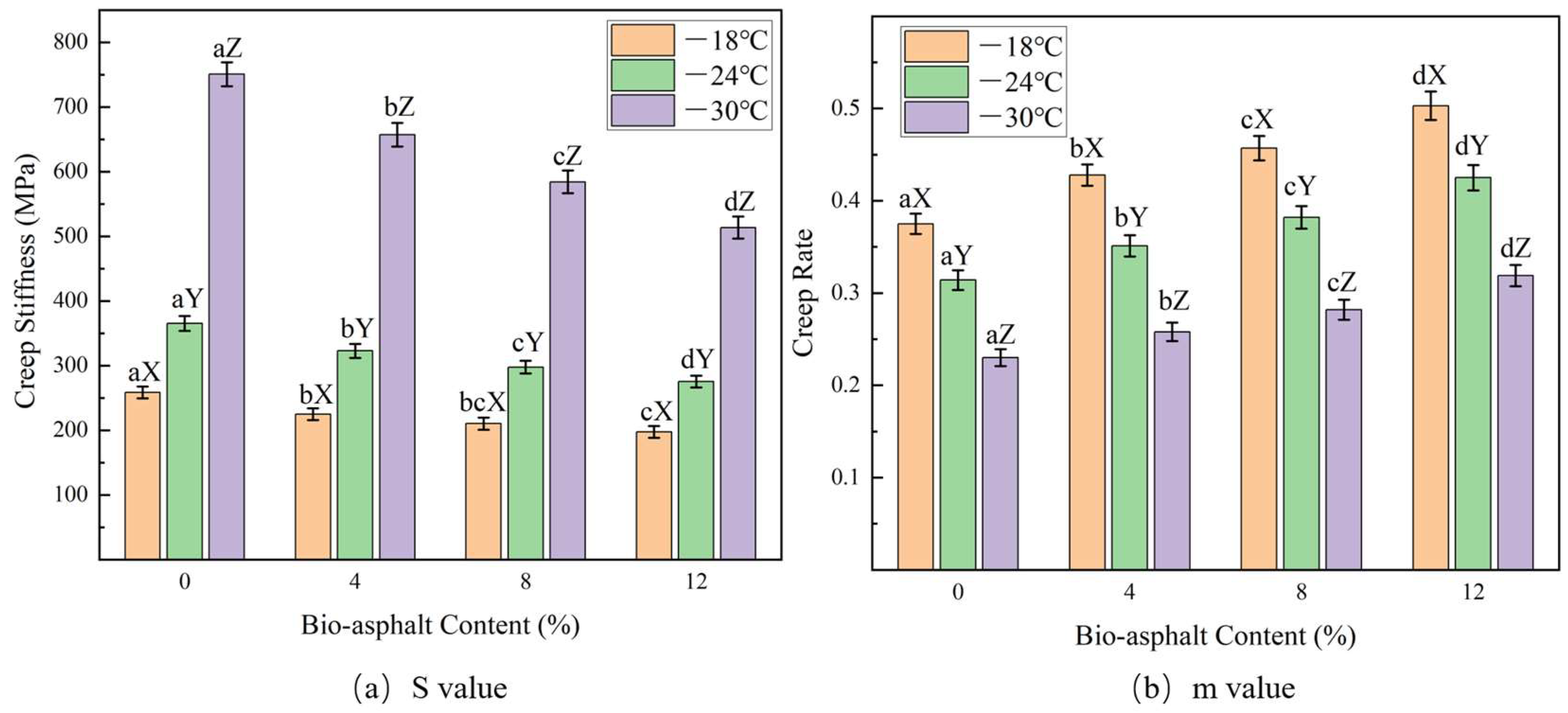
3.3.4. Low-Temperature Bending Creep Stiffness
3.4. Road Performance
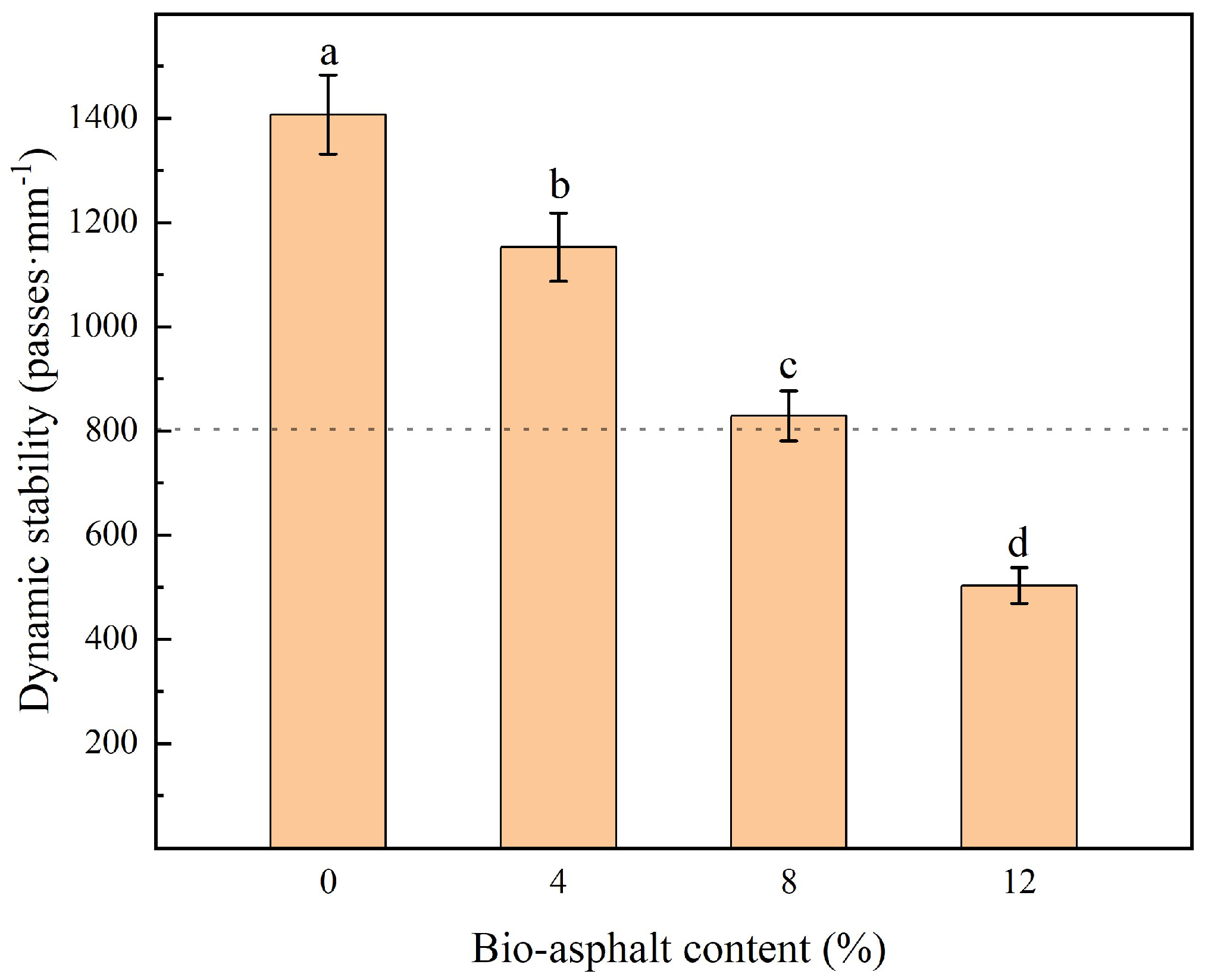
3.4.1. High-Temperature Stability
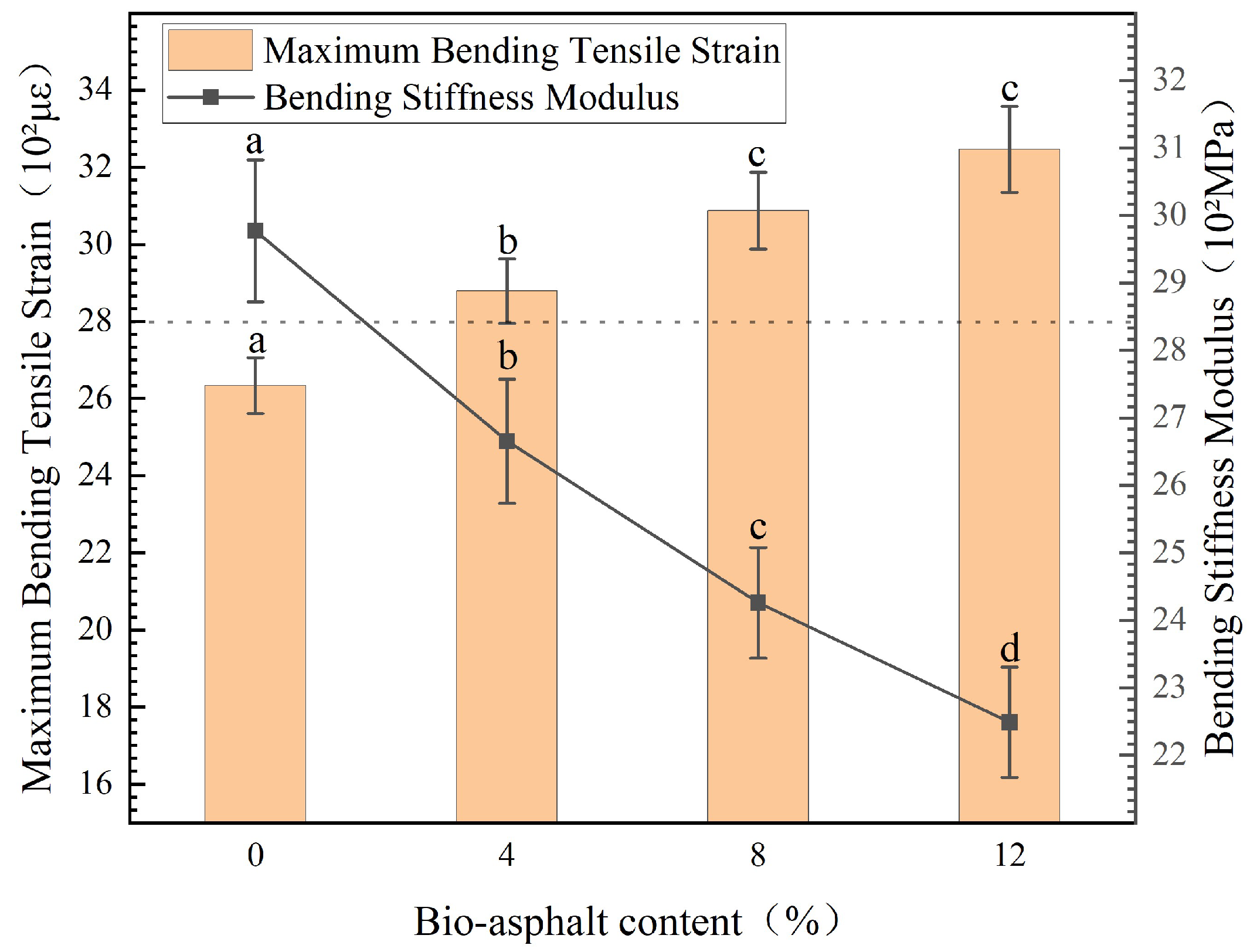
3.4.2. Low Temperature Crack Resistance
3.4.3. Water Stability
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The addition of bio-asphalt increased the penetration of asphalt and reduced its softening point, and its ductility value increased at first and then decreased with the increase of substitution amount.
- (2)
- The bio-asphalt exhibited excellent compatibility with 90# asphalt, when the bio-asphalt substitution amount was 8 wt.%, its 72 h hot storage stability met the standard requirements of 90# petroleum asphalt.
- (3)
- Substitution of petroleum asphalt with bio-asphalt had an adverse effect on the high-temperature rutting resistance performance and water stability of the resulting asphalt.
- (4)
- The low-temperature stress relaxation performance and low-temperature crack resistance increased as the bio-asphalt content increased.
- (5)
- When the bio-asphalt content was no more than 8 wt.%, the road performance indices of the biomass-modified asphalt met the standard requirements of 90# petroleum asphalt. The asphalt modified with the bio-asphalt was more suitable for use in low-temperature conditions than for use in high-temperature conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wan Azahar, W.N.A.; Bujang, M.; Jaya, R.P.; Hainin, M.R.; Mohamed, A.; Ngad, N.; Jayanti, D.S. The potential of waste cooking oil as bio-asphalt for alternative binder—An overview. J. Teknol. 2016, 78, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, W.; Xu, T.; Wang, H. Thermal behaviors and harmful volatile constituents released from asphalt components at high temperature. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peralta, J.; Raouf, M.A.; Sheng, T.; Williams, R.C. Bio-Renewable Asphalt Modifiers and Asphalt Substitutes; Springer: London, UK, 2011; pp. 89–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Miranda, S.M.; Belo, I. Microbial valorization of waste cooking oils for valuable compounds production—A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 2583–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadoran, A.; Ramakrishna, S.; Oryani, B.; Ahmed Al-Keridis, L.; Rashidi Nodeh, H.; Rezania, S. Biodiesel production from waste cooking oil using heterogeneous nanocatalyst-based magnetic polyaniline decorated with cobalt oxide. Fuel 2022, 319, 123858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonic, B.; Dordevic, D.; Jancikova, S.; Tremlova, B.; Nejezchlebova, M.; Goldová, K.; Treml, J. Reused Plant Fried Oil: A Case Study with Home-Made Soaps. Processes 2021, 9, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha, H.; Li, C.; Chen, X.; Peng, W.; Aghbashlo, M.; Lam, S.S.; Tabatabaei, M. Managing the hazardous waste cooking oil by conversion into bioenergy through the application of waste-derived green catalysts: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, M.; Ahmadinia, E.; Asli, H.; Karim, M.R. Investigation of the possibility of using waste cooking oil as a rejuvenating agent for aged bitumen. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 233–234, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Serji, A. Analysis of the Relationships between Waste Cooking Oil Qualities and Rejuvenated Asphalt Properties. Materials 2017, 10, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; You, Z. High temperature performance evaluation of bio-oil modified asphalt binders using the DSR and MSCR tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 76, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Mills-Beale, J.; You, Z. Chemical characterization and oxidative aging of bio-asphalt and its compatibility with petroleum asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 1837–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Leng, B.; Wu, S.; Yang, S. Physical, chemical and rheological properties of waste edible vegetable oil rejuvenated asphalt binders—ScienceDirect. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oishi, Y.; Nakaya, M.; Matsui, E.; Hotta, A. Structural and mechanical properties of cellulose composites made of isolated cellulose nanofibers and poly(vinyl alcohol). Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 73, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, W.G.; Akin, M.; You, Z.; Shi, X. Effect of deicing solutions on the tensile strength of micro- or nano-modified asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghabchi, R.; Castro, M. Effect of laboratory-produced cellulose nanofiber as an additive on performance of asphalt binders and mixes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 286, 122922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Vaidya, M.; Su, G.; Adhikari, S.; Shekhovtsova, S. Experimental study of soda lignin powder as an asphalt modifier for a sustainable pavement material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 298, 123884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, K.B.; Padilha, R.; Castro, T.O.; Silva, C.; Araújo, M.; Leite, L.; Pasa, V.; Lins, V. High-temperature, low-temperature and weathering aging performance of lignin modified asphalt binders. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 111, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norgbey, E.; Huang, J.; Hirsch, V.; Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Ripke, O.; Li, Y.; Anann, G.E.T.; Mensah-Ewusi, D.; Wang, X.; et al. Unravelling the efficient use of waste lignin as a bitumen modifier for sustainable roads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 230, 116957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Derewecki, K. Rheological Properties of Asphalt Binder Partially Substituted with Wood Lignin. In Proceedings of the Airfield & Highway Pavement Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 June 2013; pp. 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, W.; Han, W. Investigation of lignin as an alternative extender of bitumen for asphalt pavements—ScienceDirect. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 283, 124663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.D.; Xie, Y.; Cheng, X.S.; Jin, Y.Q.; Xu, M.Y. Research on Enzymatic Hydrolysis Lignin Modified Petroleum Asphalt. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 306–307, 1080–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, X.; Kuga, S.; Wu, M.; Huang, Y. Influence of solvent polarity on surface-fluorination of cellulose nanofiber by ball milling. Cellulose 2015, 22, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Robles, J.; Tamminen, T.; Liitiä, T.; Peresin, M.S.; Rodríguez, A.; Jääskeläinen, A.-S. Aqueous acetone fractionation of kraft, organosolv and soda lignins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. Struct. Funct. Interact. 2018, 106, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Li, J. Metabolites and chemical group changes in the wood-forming tissue of pinus koraiensis under inclined conditions. Bioresources 2012, 7, 3463–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, H.; Li, H.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C. Application of Raman spectroscopy in the rapid detection of waste cooking oil. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaronzaman, M.; Kahar, H.; Hassan, N.; Hanafi, M.F.; Sapawe, N. Analysis of biodiesel product derived from waste cooking oil using fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Pei, J.; Hu, D.; Fini, E.H. Durability of rubberized asphalt binders containing waste cooking oil under thermal and ultraviolet aging. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 124282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, S.; Kumar, N.; Wasiuddin, N.M.; Owhe, E.O.; Lynam, J.G. Sustainable lignin to enhance asphalt binder oxidative aging properties and mix properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sieve Pore Size/mm | Passing Percentage | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Limit of Gradation | Aggregate Gradation | Lower Limit of Gradation | |
| 19 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 16 | 100 | 98.5 | 90 |
| 13.2 | 92 | 86 | 76 |
| 9.5 | 80 | 68 | 60 |
| 4.75 | 62 | 47 | 34 |
| 2.36 | 48 | 31 | 20 |
| 1.18 | 36 | 21 | 13 |
| 0.6 | 26 | 14 | 9 |
| 0.3 | 18 | 9.5 | 7 |
| 0.15 | 14 | 7.2 | 5 |
| 0.075 | 8 | 5 | 4 |
| Test Project | Measured Value | Standard Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration degree (25 °C, 5 s,100 g) | 83 dmm | 80~100 dmm |
| Softening point | 45.7 °C | ≥42 °C |
| Ductility (10 °C) | 103 cm | ≥15 cm |
| Ductility (15 °C) | >150 cm | ≥50 cm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lai, S.-R.; Li, S.-J.; Xu, Y.-L.; Xu, W.-Y.; Zhang, X.-Q. Preparation, Characterization, and Performance Evaluation of Petroleum Asphalt Modified with Bio-Asphalt Containing Furfural Residue and Waste Cooking Oil. Polymers 2022, 14, 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091683
Lai S-R, Li S-J, Xu Y-L, Xu W-Y, Zhang X-Q. Preparation, Characterization, and Performance Evaluation of Petroleum Asphalt Modified with Bio-Asphalt Containing Furfural Residue and Waste Cooking Oil. Polymers. 2022; 14(9):1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091683
Chicago/Turabian StyleLai, Shuo-Rong, Shu-Jun Li, Yong-Li Xu, Wen-Yuan Xu, and Xian-Quan Zhang. 2022. "Preparation, Characterization, and Performance Evaluation of Petroleum Asphalt Modified with Bio-Asphalt Containing Furfural Residue and Waste Cooking Oil" Polymers 14, no. 9: 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091683
APA StyleLai, S.-R., Li, S.-J., Xu, Y.-L., Xu, W.-Y., & Zhang, X.-Q. (2022). Preparation, Characterization, and Performance Evaluation of Petroleum Asphalt Modified with Bio-Asphalt Containing Furfural Residue and Waste Cooking Oil. Polymers, 14(9), 1683. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14091683






