Sequencing Biodegradable and Potentially Biobased Polyesteramide of Sebacic Acid and 3-Amino-1-propanol by MALDI TOF-TOF Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
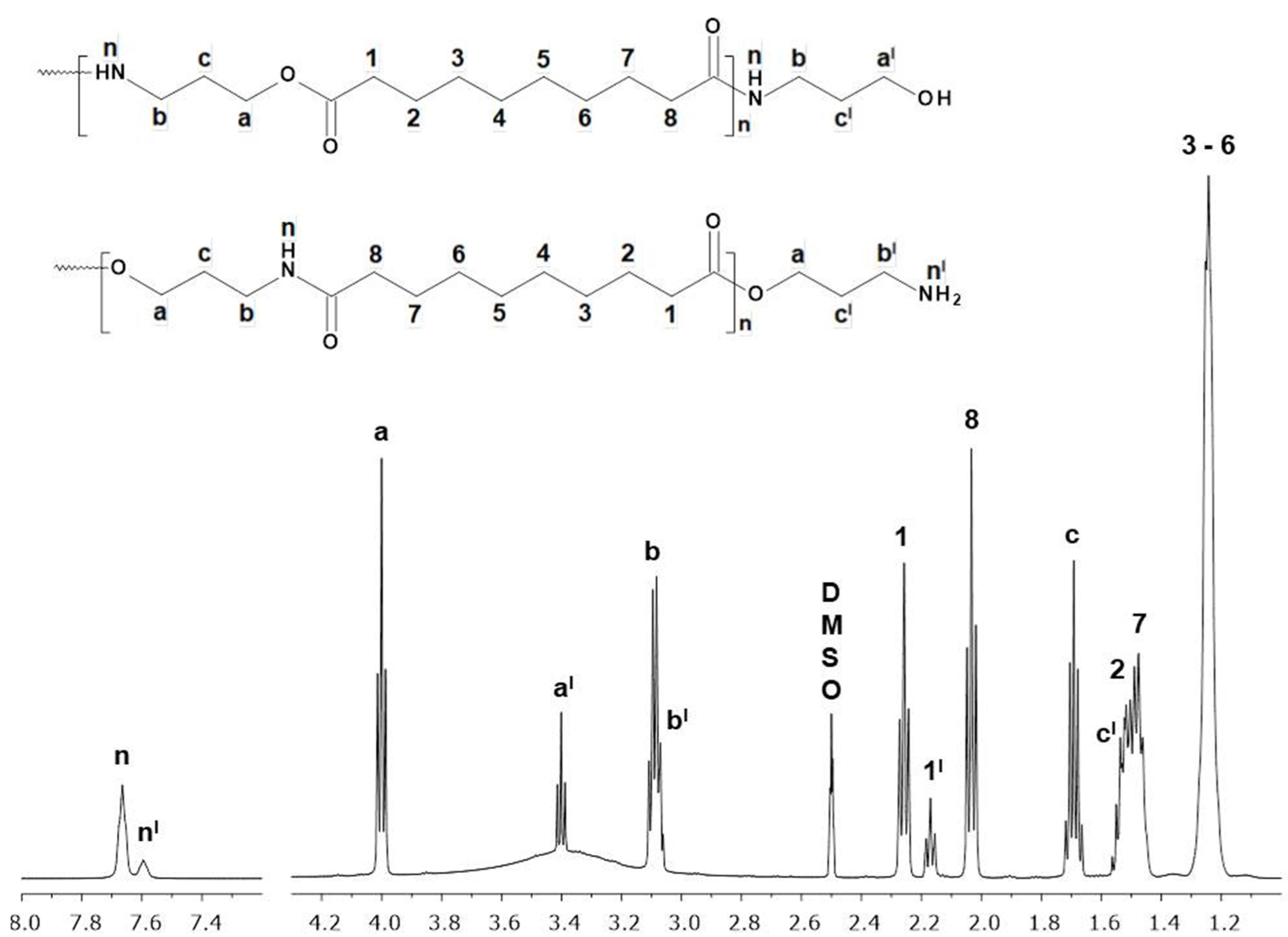
2.2. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
2.3. MALDI Sample Preparation
2.4. MALDI-TOF/MS Analysis
2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.6. Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Analysis (Py-GC/MS)
3. Results
3.1. NMR Analysis
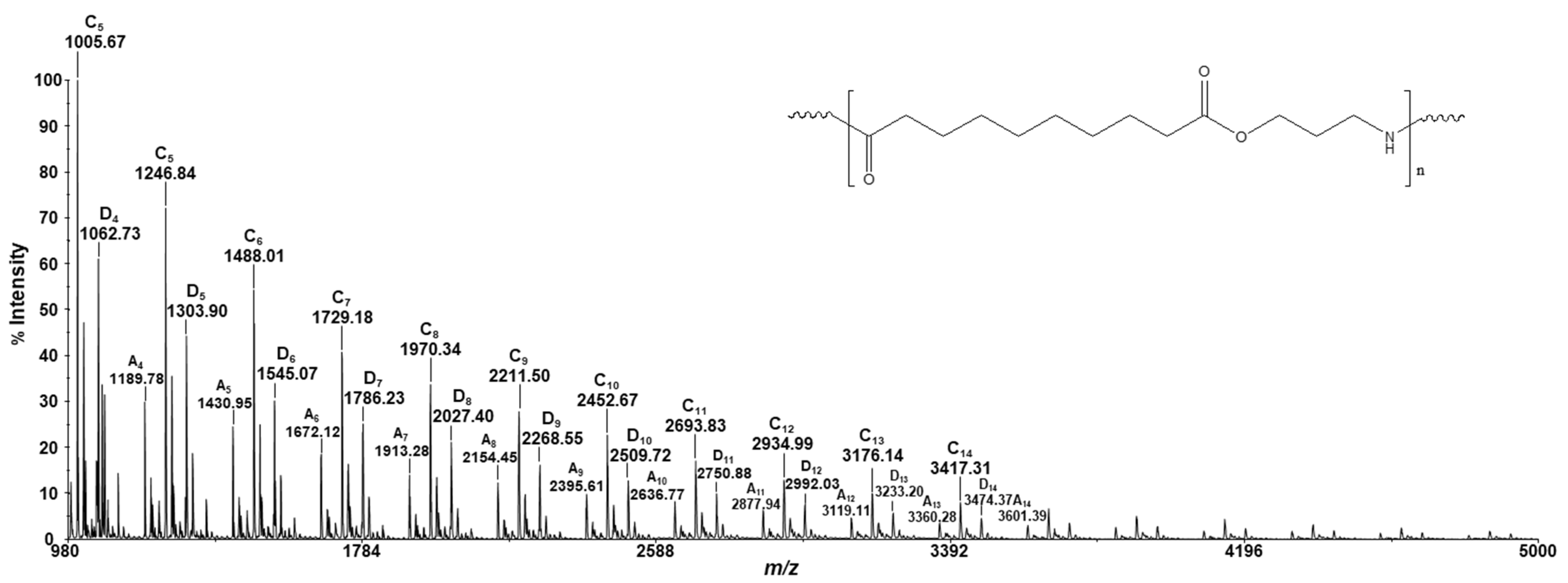
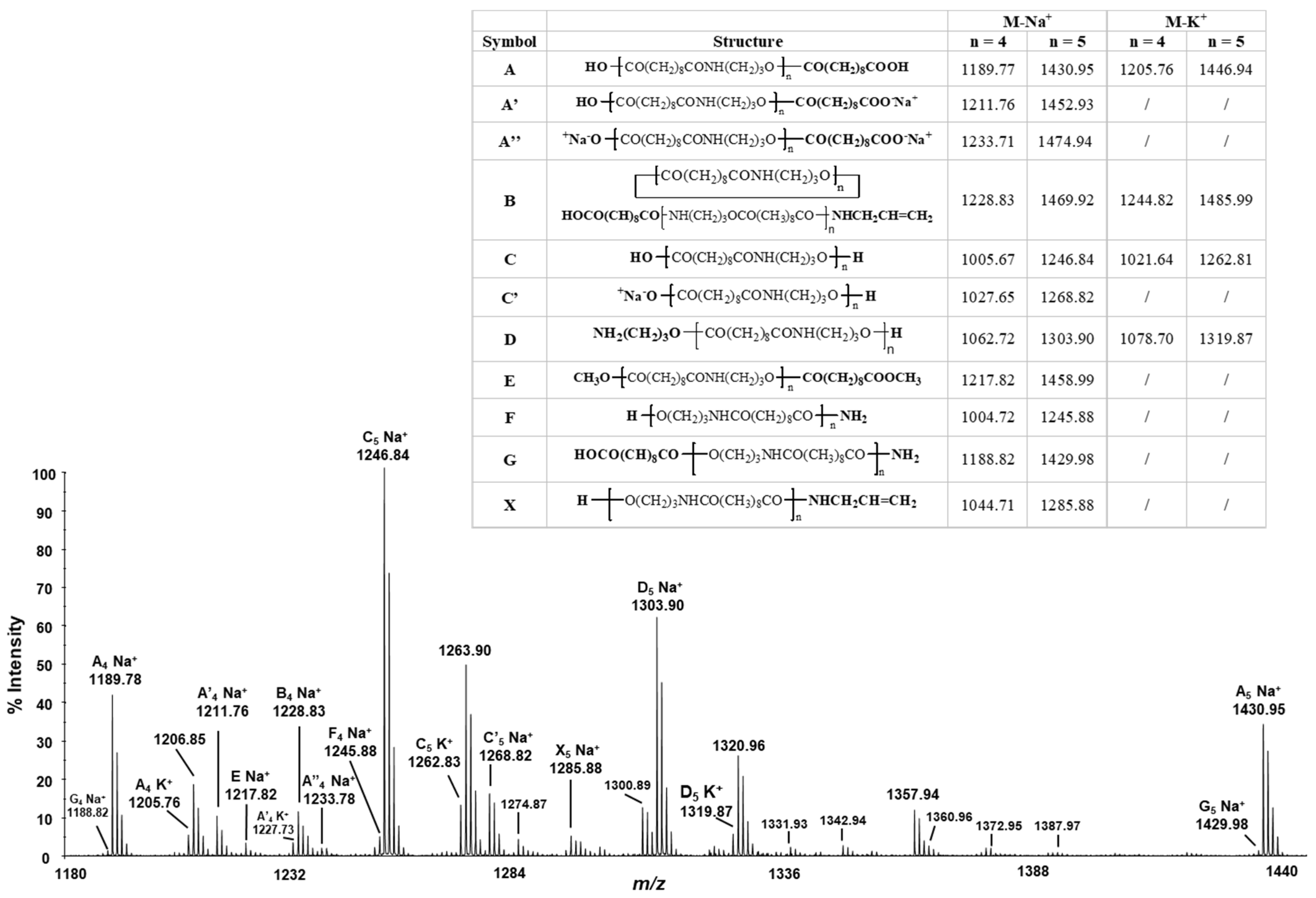
3.2. MALDI-TOF/TOF Analysis
- Sodiated and potassiated linear di-carboxyl terminated chains (species A Na+, m/z 1189.77–1430.95; species A K+, m/z 1205.76–1446.94) and the corresponding sodium salt (A’ Na+, m/z 1211.76–1452.93) and disodium salt of the same species (A’’ Na+, m/z 1233.71–1474.94);
- Sodiated and potassiated cyclic PEA-Pro chains (species B Na+, m/z 1228.83; B K+, m/z 1244.82).
- Sodiated and potassiated linear oligomers terminated with carboxyl at one end and amino-alcohol groups at the other end (species C Na+, m/z 1246.84; species C K+, m/z 1262.81), and the corresponding sodium salt of the same species (C’ Na+, m/z 1268.82);
- Sodiated and potassiated linear di-amino-alcohol terminated oligomers (species D Na+ m/z 1303.90, species D K+, m/z 1319.87);
- Sodiated linear oligomers terminated with dimethyl ester of sebacic acid at both the ends (species E Na+ m/z 1217.82);
- Sodiated linear oligomers terminated with amino-alcohol at one end and –NH2 group at the other end (species F Na+ m/z 1245.88);
- Sodiated linear oligomers terminated with sebacic acid at one end and –NH2 group at the other end (species G Na+ m/z 1429.98);
- Sodiated linear oligomers terminated with amino alcohol at one end and olefin derived by amino alcohol at the other end (species X Na+ m/z 1285.88).
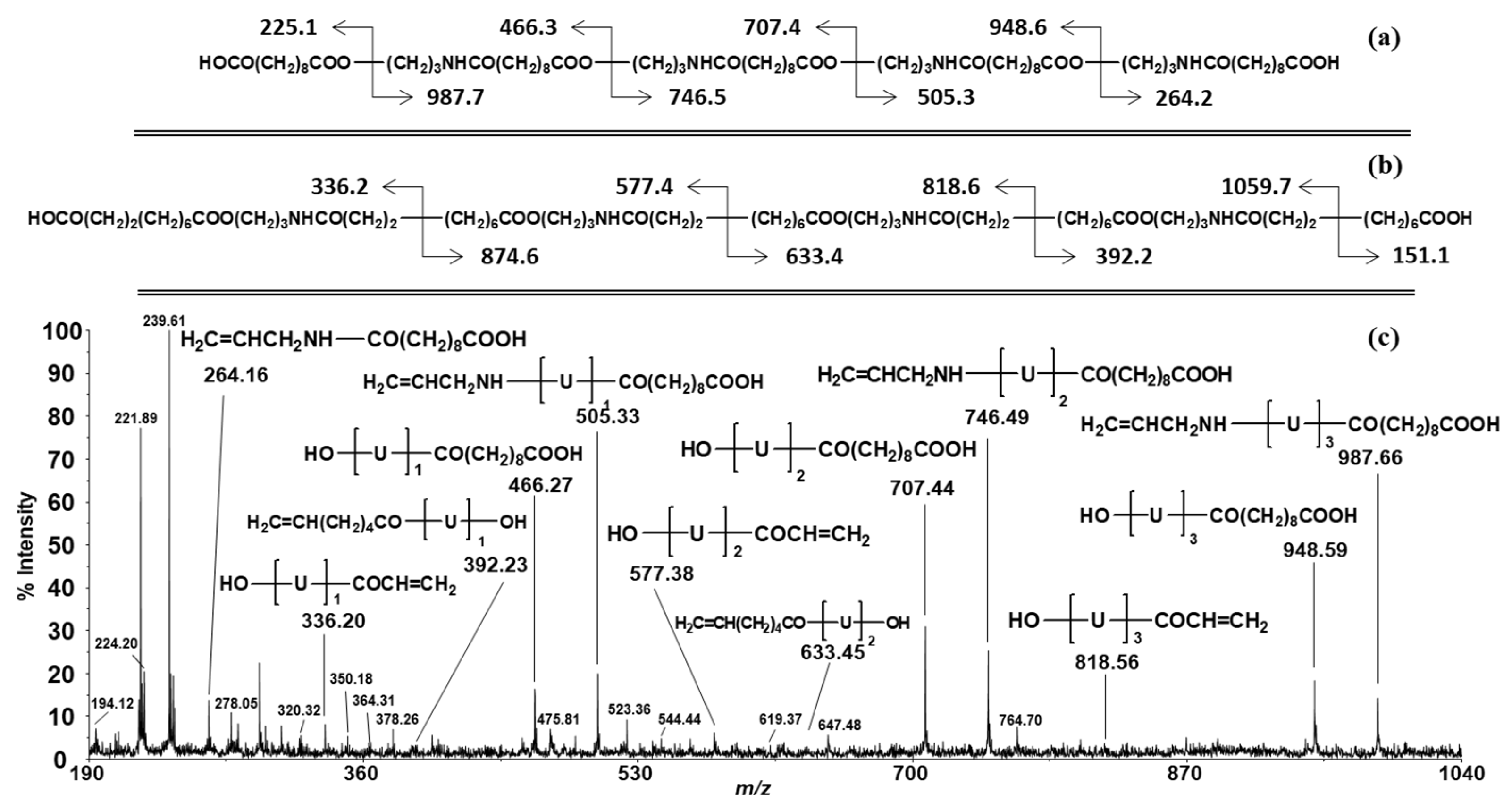
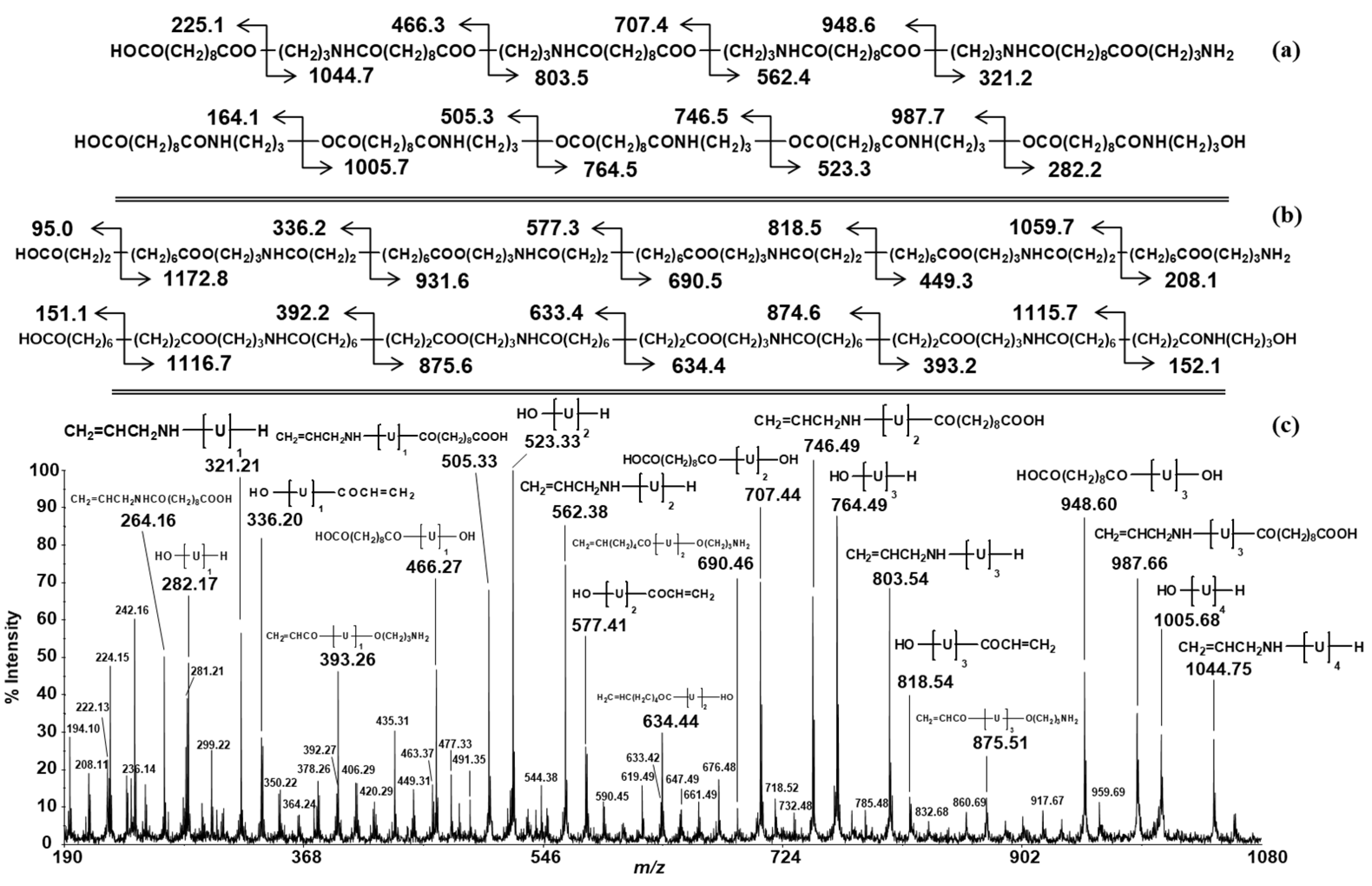
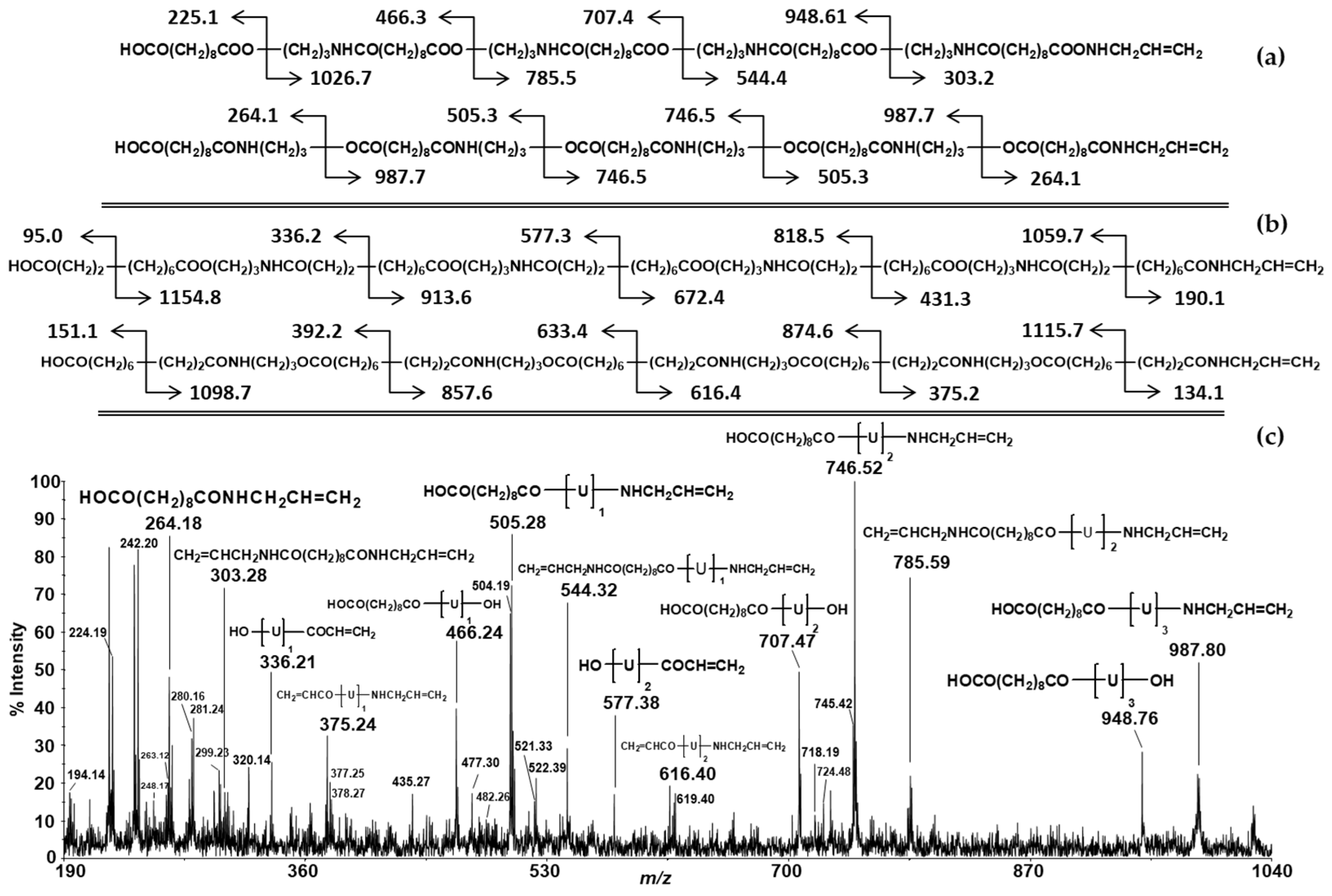
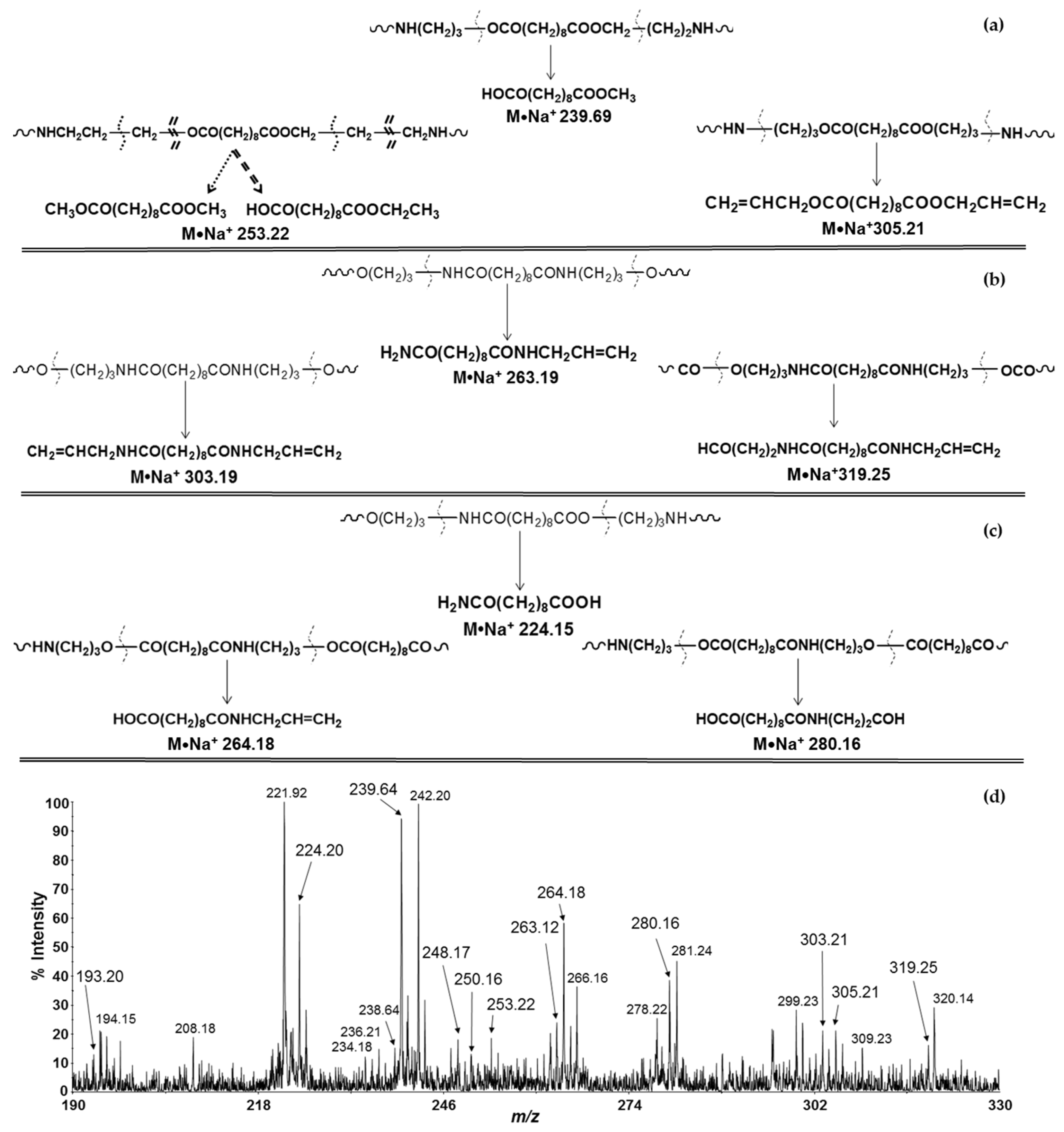
3.3. MALDI-TOF/TOF-MS/MS Analysis
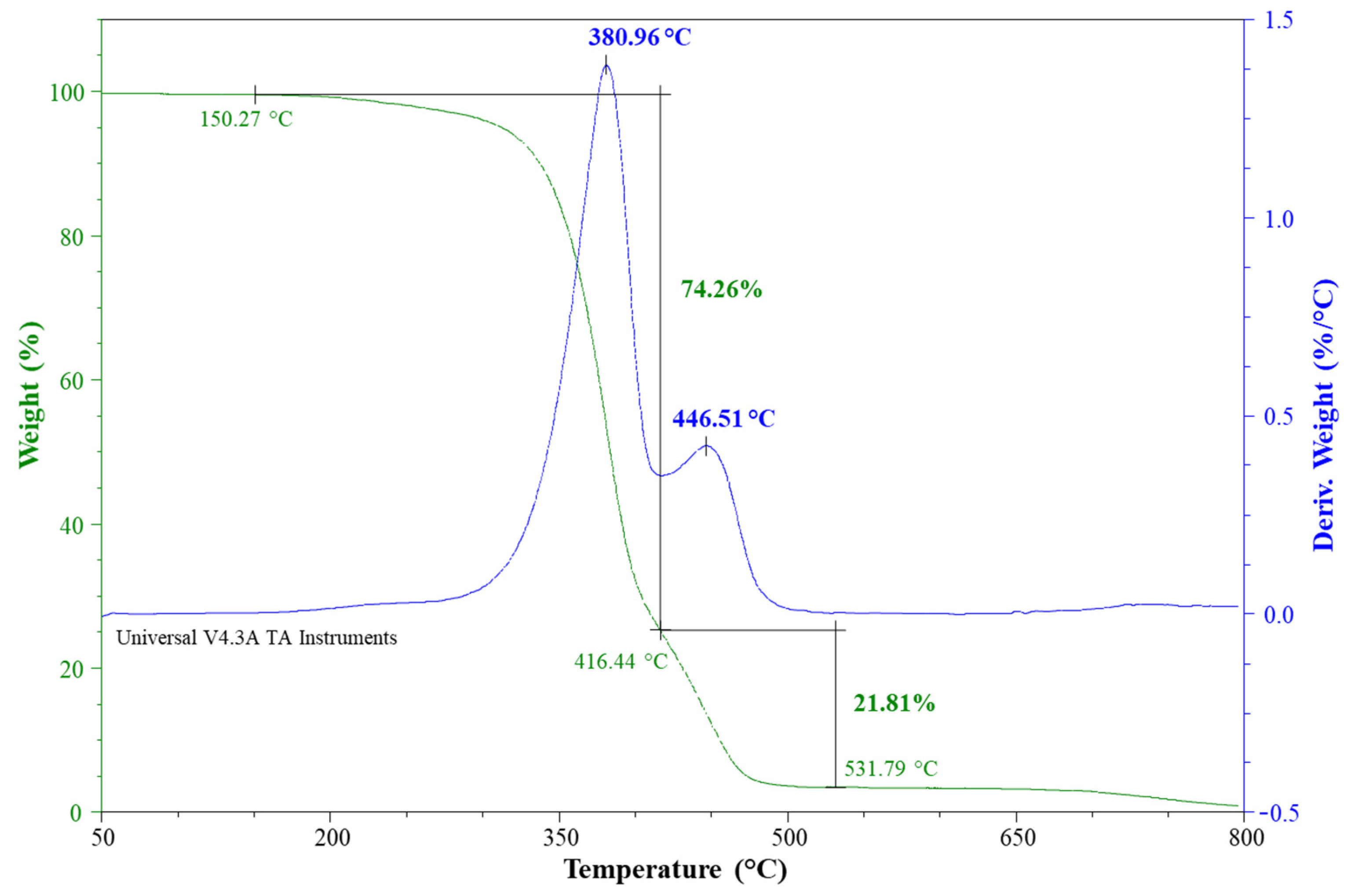
3.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
3.5. Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry Analysis (Py-GC/MS)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodriguez, R.; Franco, M.; Puiggali, J. Biodegradable Poly(Ester Amide)s: Synthesis and Applications. In Biodegradable Polymers: Processing, Degradation and Applications; Felton, G.P., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 207–272. ISBN 978-1-61209-534-9. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2117/13036 (accessed on 11 March 2022).
- Li, L. (Ed.) MALDI Mass Spectrometry for Synthetic Polymer Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; Volume 175, ISBN 978-0-470-56722-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, H.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Shin, D.; Oh, Y.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, Y.-J.; Lee, K.-S.; Kim, Y.; Cho, K. Recent developments in pre-treatment and analytical techniques for synthetic polymers by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 5767–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, H.C.M.; McEwen, C.N. The Limitations of MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry in the Analysis of Wide Polydisperse Polymers. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 4568–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielen, M.W.F. Maldi time-of-flight mass spectrometry of synthetic polymers. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 1999, 18, 309–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medzihradszky, K.F.; Campbell, J.M.; Baldwin, M.A.; Falick, A.M.; Juhasz, P.; Vestal, M.L.; Burlingame, A.L. The Characteristics of Peptide Collision-Induced Dissociation Using a High-Performance MALDI-TOF/TOF Tandem Mass Spectrometer. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yol, A.M.; Dabney, D.E.; Wang, S.-F.; Laurent, B.A.; Foster, M.D.; Quirk, R.P.; Grayson, S.M.; Wesdemiotis, C. Differentiation of linear and cyclic polymer architectures by MALDI tandem mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS2). J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom 2013, 24, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crotty, S.; Gerişlioğlu, S.; Endres, K.J.; Wesdemiotis, C.; Schubert, U.S. Polymer architectures via mass spectrometry and hyphenated techniques: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 932, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wesdemiotis, C.; Solak, N.; Polce, M.J.; Dabney, D.E.; Chaicharoen, K.; Katzenmeyer, B.C. Fragmentation pathways of polymer ions. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2011, 30, 523–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Rapisarda, M.; Valenti, G. Mass spectrometry in bioresorbable polymer development, degradation and drug-release tracking. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 34, e8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Rapisarda, M. Tandem Mass Spectrometry in the Analysis of Biodegradable Polymers. In Mass Spectrometry: Theory and Applications; Nichols, W.O., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 127–181. ISBN 978-1-53619-790-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Puglisi, C.; Montaudo, G. Sequence determination in aliphatic poly(ester amide)s by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight and time-of-flight/time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Puglisi, C. Structural characterization of synthetic poly(ester amide)from sebacic acid and 4-amino-1-butanol by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight/time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 739–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Puglisi, C.; Montaudo, G. Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight/time-of-flight tandem mass spectra of poly(butylene adipate). Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 1683–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzarelli, P. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight/time-of-flight tandem mass spectra of biodegradable polybutylenesuccinate. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Carroccio, S. Role of Mass Spectrometry in the Elucidation of Thermal Degradation Mechanisms in Polymeric Materials. In Reactions and Mechanisms in Thermal Analysis of Advanced Materials; Tiwari, A., Raj, B., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 221–258. ISBN 978-1-119-11771-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuge, S.; Ohtani, H. Structural characterization of polymeric materials by pyrolysis-GC/MS. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1997, 58, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Rapisarda, M.; Perna, S.; Mirabella, E.F.; La Carta, S.; Puglisi, C.; Valenti, G. Determination of polyethylene in biodegradable polymer blends and in compostable carrier bags by Py-GC/MS and TGA. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2016, 117, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Cirica, M.; Pastorelli, G.; Puglisi, C.; Valenti, G. Aliphatic poly(ester amide)s from sebacic acid and aminoalcohols of different chain lengths: Synthesis, characterization and soil burial degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 121, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levchik, S.V.; Weil, E.D.; Lewin, M. Thermal decomposition of aliphatic nylons. Polym. Int. 1999, 48, 532–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Carroccio, S. Modern mass spectrometry in the characterization and degradation of biodegradable polymers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 808, 18–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzarelli, P.; Piredda, G.; La Carta, S.; Mirabella, E.F.; Valenti, G.; Bernet, R.; Impallomeni, G. Characterization and laser-induced degradation of a medical grade polylactide. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 169, 108991–109004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, L.; Klonos, P.A.; Kluge, K.; Zamboulis, A.; Terzopoulou, Z.; Kourtidou, D.; Magaziotis, A.; Chrissafis, K.; Kyritsis, A.; Bikiaris, D.N.; et al. Unlocking the potential of furan-based poly(ester amide)s: An investigation of crystallization, molecular dynamics and degradation kinetics of novel poly(ester amide)s based on renewable poly(propylene furanoate). Polym. Chem. 2021, 12, 5518–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuge, S.; Ohtani, H.; Watanabe, C. Pyrolysis-GC/MS Data Book of Synthetic Polymers: Pyrograms, Thermograms and MS of Pyrolyzates, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2012; ISBN 9780444538932. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizzarelli, P.; La Carta, S.; Mirabella, E.F.; Rapisarda, M.; Impallomeni, G. Sequencing Biodegradable and Potentially Biobased Polyesteramide of Sebacic Acid and 3-Amino-1-propanol by MALDI TOF-TOF Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Polymers 2022, 14, 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081500
Rizzarelli P, La Carta S, Mirabella EF, Rapisarda M, Impallomeni G. Sequencing Biodegradable and Potentially Biobased Polyesteramide of Sebacic Acid and 3-Amino-1-propanol by MALDI TOF-TOF Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Polymers. 2022; 14(8):1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081500
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizzarelli, Paola, Stefania La Carta, Emanuele Francesco Mirabella, Marco Rapisarda, and Giuseppe Impallomeni. 2022. "Sequencing Biodegradable and Potentially Biobased Polyesteramide of Sebacic Acid and 3-Amino-1-propanol by MALDI TOF-TOF Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Polymers 14, no. 8: 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081500
APA StyleRizzarelli, P., La Carta, S., Mirabella, E. F., Rapisarda, M., & Impallomeni, G. (2022). Sequencing Biodegradable and Potentially Biobased Polyesteramide of Sebacic Acid and 3-Amino-1-propanol by MALDI TOF-TOF Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Polymers, 14(8), 1500. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14081500






