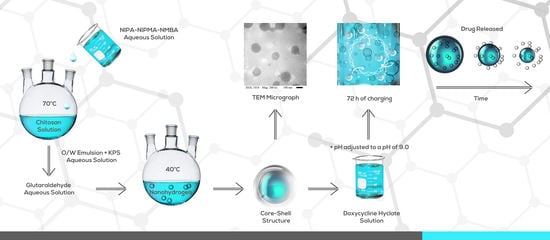
Drug Delivery from Stimuli-Responsive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-isopropylmethacrylamide)/Chitosan Core/Shell Nanohydrogels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuckling, D.; Doering, A.; Krahl, F.; Arndt, K.-F. Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Systems. Polym. Sci. Compr. Ref. 2012, 8, 377–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, S.A.; Gholve, S.B.; Savalsure, S.M.; Ghodake, K.B.; Bhusnure, O.G.; Thakare, V.M. Smart polymer and their applications: A review. Int. J. Curr. Pharm. Rev. Res. 2017, 8, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmaljohann, D. Thermo-and pH-responsive polymers in drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Javadi, A.; Ghaffari, M.; Shaoquin, G. A pH-sensitive molecularly imprinted nanospheres/hydrogel composite as coating for implantable biosensors. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4944–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terefe, N.S.; Glagovskaia, O.; de Silva, K.; Stockmann, R. Applications of stimuli responsive polymers for sustainable ion exchange chromatography. Food Bioprod. Process. 2014, 92, 208–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Barbero, A.; Suárez, I.J.; Sierra-Martín, B.; Fernández-Nieves, A.; de las Nieves, F.J.; Marquez, M.; Rubio-Retama, J.; López-Cabarcos, E. Gels and microgels for nanotechnological applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 88–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Bautista, A.; Duarte, C.M.M.; Mendizábal, E.; Katime, I. Controlled delivery of drugs through smart pH-sensitive nanohydrogels for anti-cancer therapies: Synthesis, drug release and cellular studies. Des. Monomers Polym. 2016, 19, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, J.T.; Hutchinson, S.S.; Lizana, N.; Verma, I.; Peppas, N.A. Synthesis and characterization of poly(N-isopropyl methacrylamide) sore/shell nanogels for controlled release of chemotherapeutics. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 340, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, A.K.; Shukla, S.K.; Bhanu, S.; Kankane, S. Responsive polymers in controlled drug delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 1088–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, R.; Dey, A.; Chakrabarty, D. Synthesis, characterization, and drug release study of acrylamide-co-itaconic acid based smart hydrogel. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, F.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. Stimuli-responsive polydopamine-based smart materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8319–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; MacConaghy, K.I.; Kaar, J.L.; Stoykovich, M.P. Enhance Optical Sensitivity in Thermoresponsive Photonic Crystal Hydrogels by Operating Near the Phase Transition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 27927–27935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekhar, A.; Gimi, B.; Hu, W. Applications of semiconductor fabrication methods to nanomedicine: A review of recent inventions and techniques. Recent Pat. Nanomed. 2013, 3, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Du, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhai, G. Internal stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery: Design strategies and applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 1267–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuggino, J.C.; Alvarez, I.C.I.; Strumia, M.C.; Welker, P.; Licha, K.; Steinhilbert, D.; Mutihac, R.-C.; Calderón, M. Thermosensitive nanogels based on dendritic polyglycerol and N-isopropylacrylamide for biomedical applications. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 11259–11266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, H.S.; Herron, C.C.; Hastings, C.L.; Deckers, R.; López-Noriega, A.; Kelly, H.M.; Hennink, W.E.; McDonnell, C.O.; O’Brien, F.J.; Ruiz-Hernández, E.; et al. A stimuli responsive liposome loaded hydrogel provides flexible on-demand release of therapeutic agents. Acta Biomater. 2016, 48, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiantore, O.; Guaita, M.; Trossarelli, L. Solution properties of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide). Die Makromol. Chem. 1979, 180, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkert, T.; Oberreich, J.; Meewes, M.; Nyffenegger, R.; Ricka, J. Coil-globule transition of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide): A study of segment mobility fluorescence depolarization. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 5806–5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, K.; Hamano, K.; Kuwahara, N.; Fujishige, S.; Ando, I. Characterization of poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide) in wáter. Polym. J. 1990, 22, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokpé, E.; Vogt, W. N-isopropylacrylamide and N-isopropylmethacryl-amide: Cloud points of mixtures and copolymers. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2001, 202, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmerón Sánchez, M.; Hanyková, L.; Ilavský, M.; Monleón Pradas, M. Thermal transitions of poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide) in aqueous solutions. Polymer 2004, 45, 4087–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokufuta, M.K.; Sato, S.; Kokufuta, E. LCST behavior of copolymers of N-isopropylacrylamide and N-isopropylmethacrylamide in water. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2012, 290, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-León, T.; Carvalho, E.L.S.; Seijo, B.; Ortega-Vinuesa, J.L.; Bastos-González, D. Physicochemical characterization of chitosan nanoparticles: Electrokinetic and stability behavior. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 283, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, M.R.; Elvira, C.; Gallardo, A.; Vázquez, B.; Román, J.S. Smart polymer and their applications as biomaterials. In Topics in Tissue Engineering; Ashammakhi, N., Reis, R., Chiellini, E., Eds.; University of Oulu: Oulu, Finland, 2007; Volume 3, pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.-H.; Wang, C.-F.; Don, T.-M.; Chiu, W.-Y. Preparation of pH- and thermo-sensitive chitosan-PNIPAAm core-shell nanoparticles and evaluation as drug carriers. Cellulose 2013, 20, 1791–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A.G.; Ortega, A.; Pérez-Carrillo, L.A.; Ceja, I.; Arellano, M.; López, R.G.; Puig, J.E. Synthesis, characterization, and drug delivery from pH- and thermoresponsive poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)/chitosan core/shell nanocomposites made by semicontinuous heterophase polymerization. J. Nanomater. 2017, 2017, 6796412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, T.G. Influence of diluent and copolymer composition on the glass temperature of a polymer system. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. 1956, 1, 123–125. [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein, R.M.; Webster, F.X.; Kiemle, D.J.; Bryce, D.L. Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds, 8th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ríos-Donato, N.; Peña-Flores, A.M.; Katime, I.; Leyva-Ramos, R.; Mendizábal, E. Kinetics and thermodynamics of adsorption of red dye 40 from acidic aqueous solutions onto a novel chitosan sulfate. Afinidad LXXIV 2017, 74, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Singhvi, G.; Singh, M. Review: In-vitro drug release characterization models. Int. J. Pharm. Stud. Res. 2011, 2, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Korsmeyer, R.W.; Gurny, R.; Doelker, E.; Buri, P.; Peppas, N.A. Mechanism of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 1983, 15, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, R.; Baishya, H.; Qing, Z. Applications of mathematical models in drug release kinetics of carbidopa and levodopa ER tablets. J. Dev. Drugs 2017, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, W.D.; Lippold, B.C. Drug release from hydrocolloid embeddings with high or low susceptibility to hydrodynamics stress. Pharm. Res. 1995, 12, 1781–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, F.O.; Sousa, J.J.S.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Formosinho, S.J. Comparison of dissolution profiles of ibuprofen pellets. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramteke, K.H.; Dighe, P.A.; Kharat, A.R.; Patil, S.V. Mathematical models of drug dissolution: A review. Sch. Acad. J. Pharm. 2014, 3, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balleño, J.A.; Mendizábal-Ruiz, A.P.; Saade, H.; Díaz de León-Gómez, R.; Mendizábal, E.; Rios-Donato, N.; López, R.G. Ibuprofen release from poly(ethyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles prepared by semicontinuous heterophase polymerization. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 2018, 4527203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serrano-Medina, A.; Cornejo-Bravo, J.M.; Licea-Claveríe, A. Synthesis of pH and temperature sensitive, core-shell nano/microgels, by one pot, soap-free emulsion polymerization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 369, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundueanu, G.; Constantin, M.; Bucatariu, S.; Ascenzi, P. Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-isopropylmethacrylamide) thermo-responsive microgels as self-regulated drug delivery system. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2016, 271, 2525–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
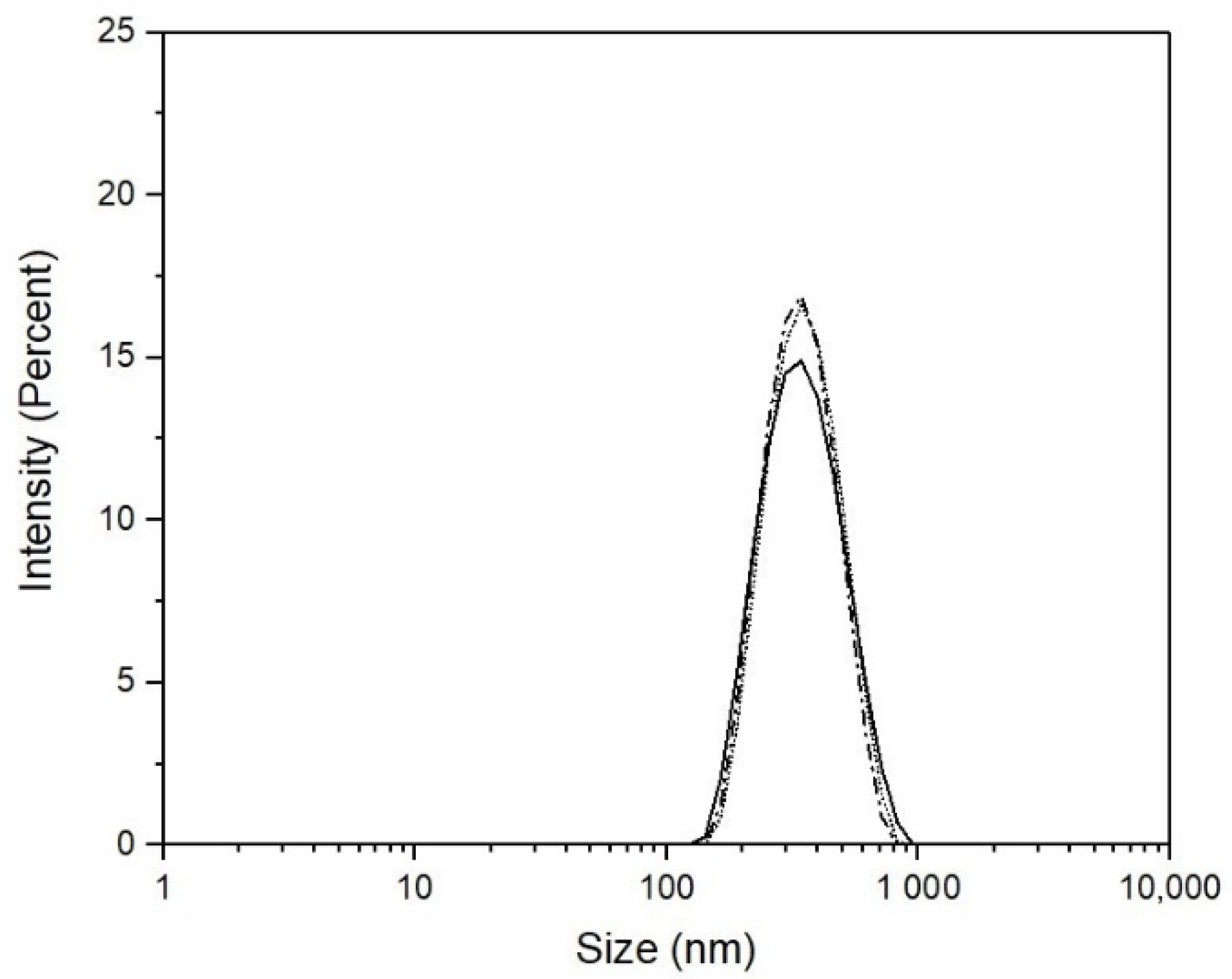
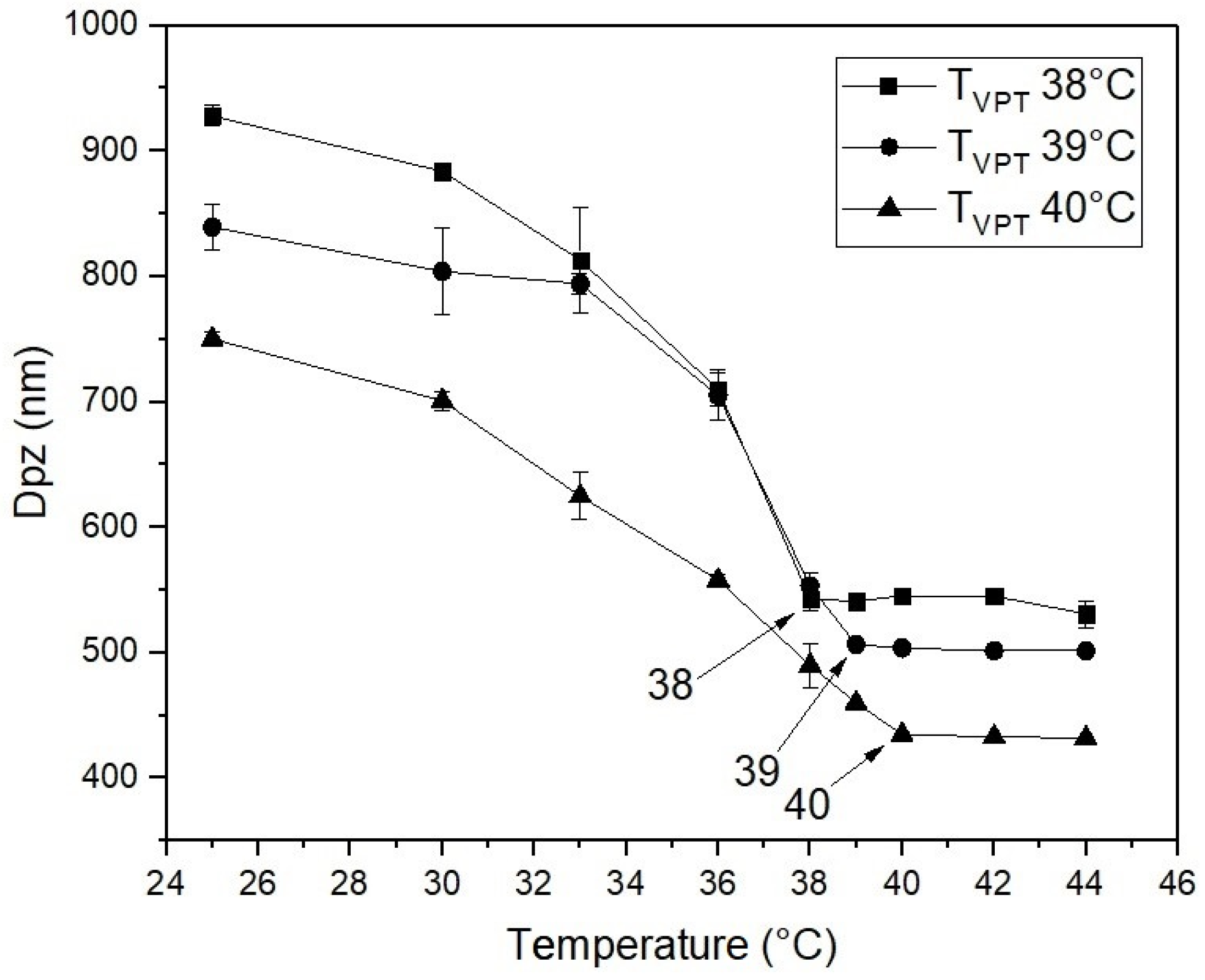
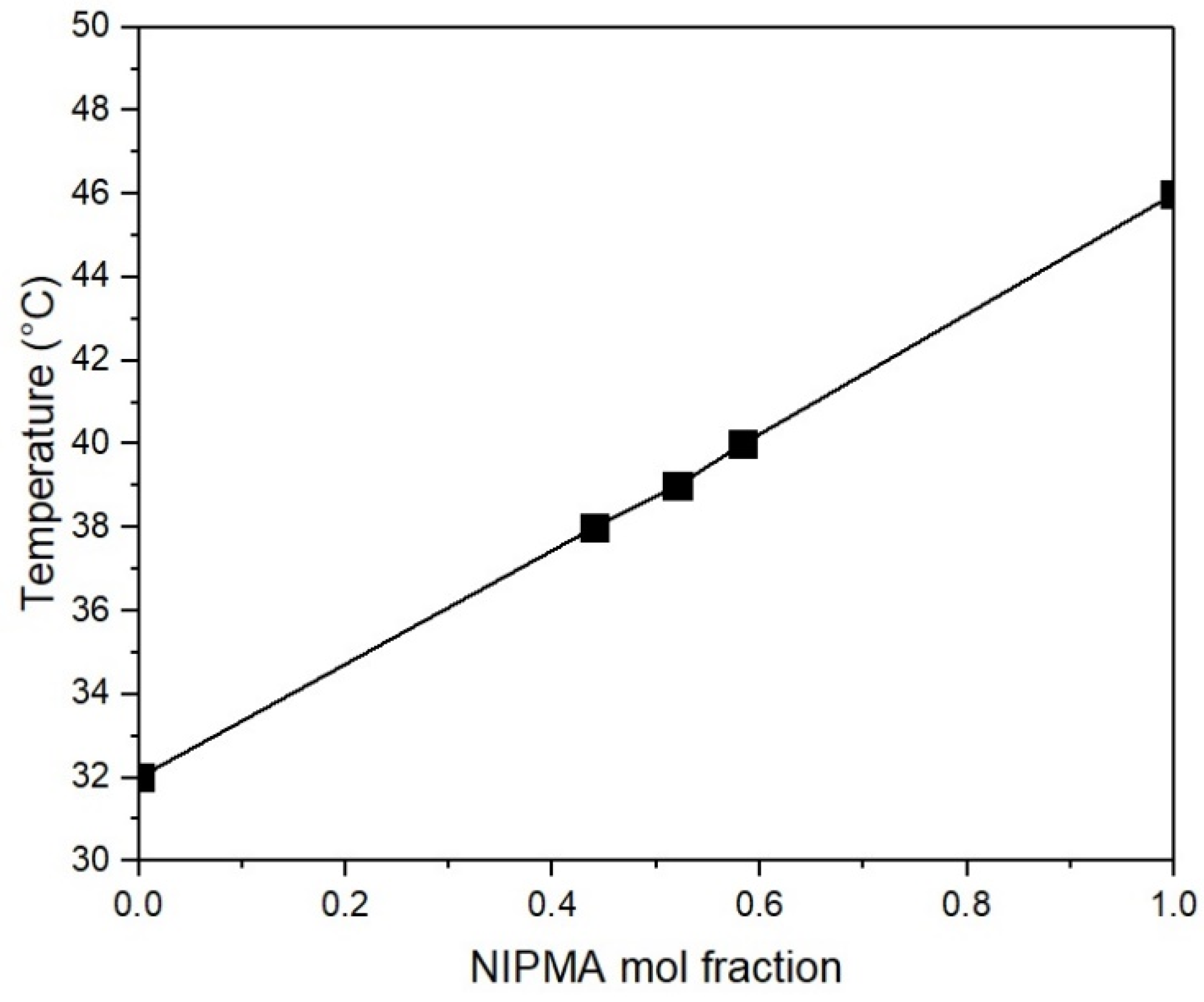


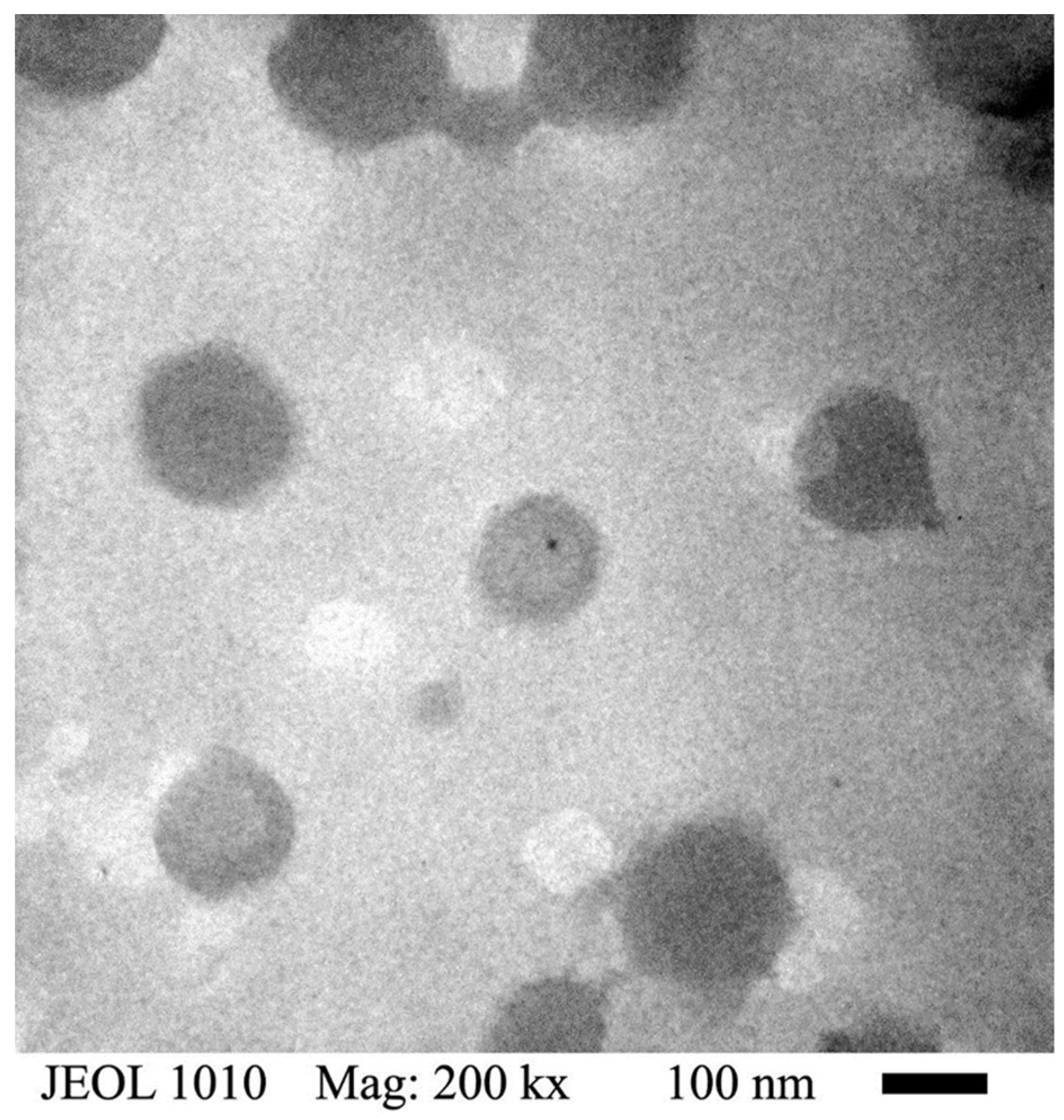

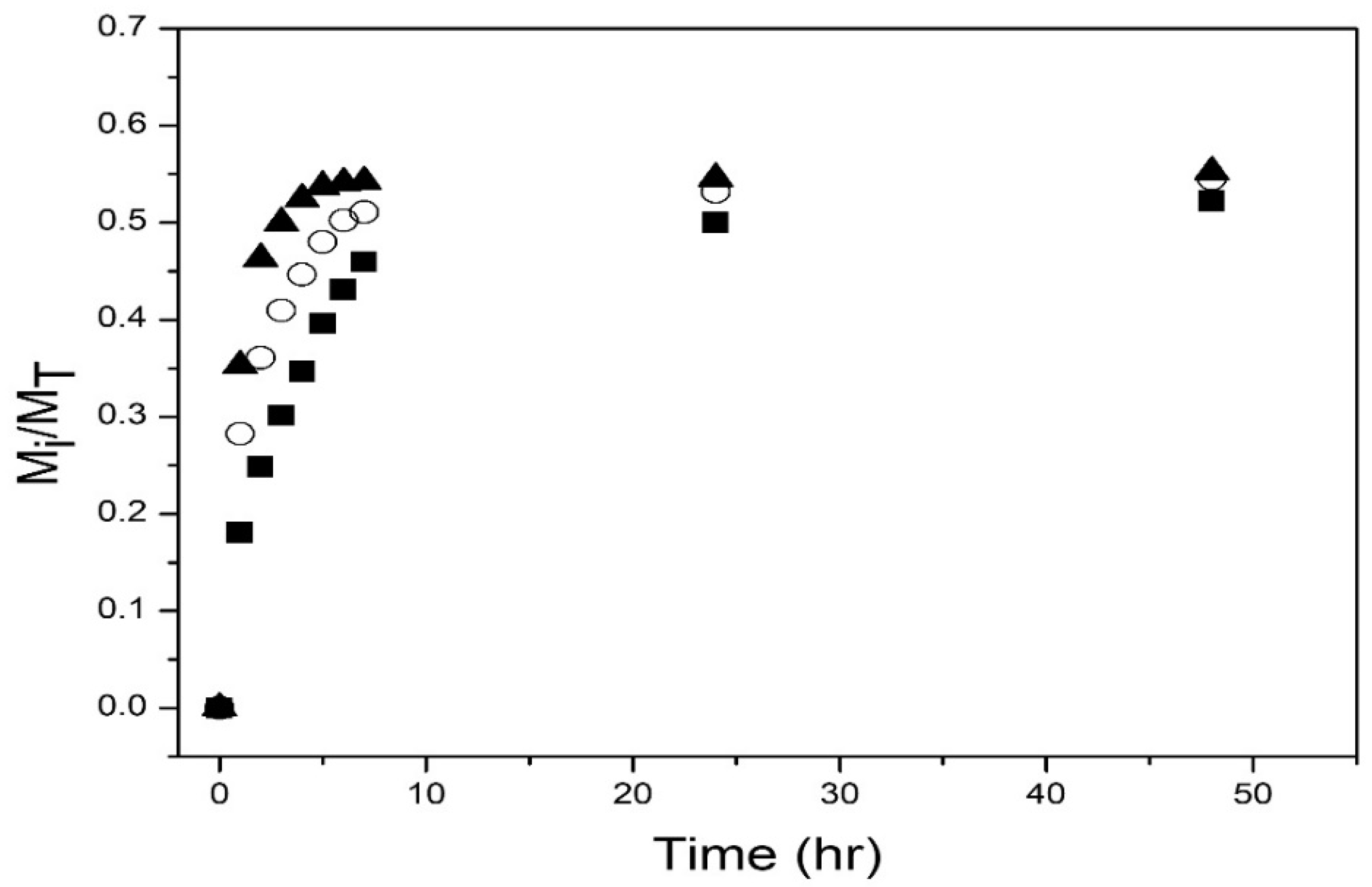


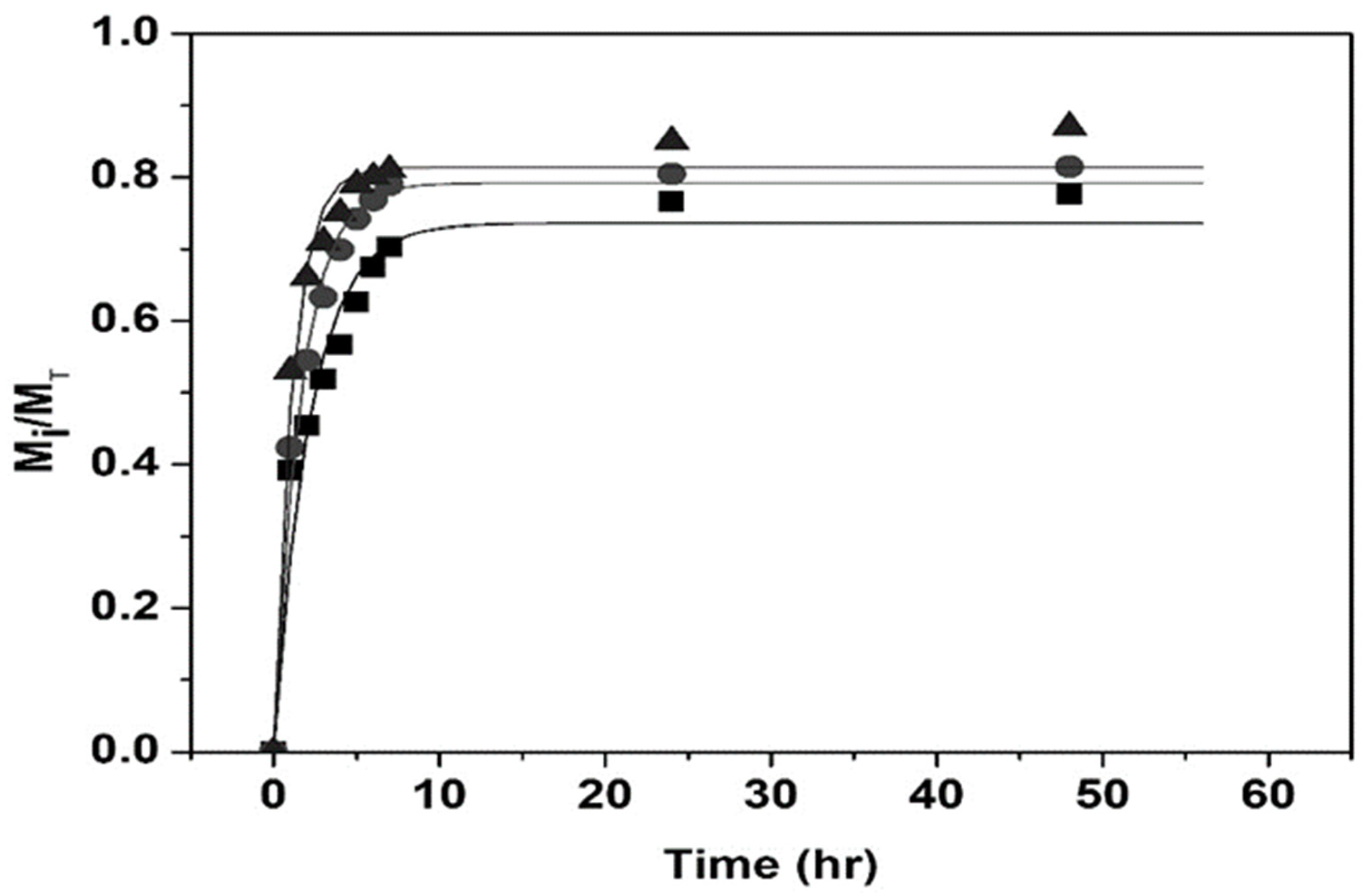

| TVPTc (°C) | NIPA Moles | NIPMA Moles | NIPMA/NIPA Ratio | NMBA Moles |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 38 | 0.014 | 0.011 | 0.785 | 0.12 |
| 39 | 0.012 | 0.013 | 1.083 | 0.12 |
| 40 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 1.400 | 0.12 |
| TVPT (°C) | Sample | Average Size (nm) | Conversion |
|---|---|---|---|
| 38 | 1 | 296.5 | 96.1 |
| 2 | 312.9 | ||
| 39 | 1 | 300.8 | 97.7 |
| 2 | 315.3 | ||
| 40 | 1 | 300.1 | 96.4 |
| 2 | 316.2 |
| TVPT of the Nanohydrogels (°C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| TVPT | 38 | 39 | 40 |
| % of drug content | 5.00 | 5.20 | 5.41 |
| pH = 2.0 | pH = 7.4 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | K | n | R2 | b | k | n | R2 |
| 0.632 | 0.098 | 0.9647 | 0.444 | 0.0742 | 0.943 | ||
| 0.632 | 0.098 | 0.9647 | −0.001 | 0.445 | 0.7407 | 0.943 | |
| 16.9 | 7.009 | 0.7872 | 26.16 | 4.242 | 0.00 | ||
| 0.814 | 0.887 | 0.9801 | 0.541 | 0.998 | 0.988 | ||
| 0.028 | 0.005 | 0.033 | 0.008 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortega-García, A.; Martínez-Bernal, B.G.; Ceja, I.; Mendizábal, E.; Puig-Arévalo, J.E.; Pérez-Carrillo, L.A. Drug Delivery from Stimuli-Responsive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-isopropylmethacrylamide)/Chitosan Core/Shell Nanohydrogels. Polymers 2022, 14, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030522
Ortega-García A, Martínez-Bernal BG, Ceja I, Mendizábal E, Puig-Arévalo JE, Pérez-Carrillo LA. Drug Delivery from Stimuli-Responsive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-isopropylmethacrylamide)/Chitosan Core/Shell Nanohydrogels. Polymers. 2022; 14(3):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030522
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtega-García, Andrés, Bryan Giovanny Martínez-Bernal, Israel Ceja, Eduardo Mendizábal, Jorge Emilio Puig-Arévalo, and Lourdes Adriana Pérez-Carrillo. 2022. "Drug Delivery from Stimuli-Responsive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-isopropylmethacrylamide)/Chitosan Core/Shell Nanohydrogels" Polymers 14, no. 3: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030522
APA StyleOrtega-García, A., Martínez-Bernal, B. G., Ceja, I., Mendizábal, E., Puig-Arévalo, J. E., & Pérez-Carrillo, L. A. (2022). Drug Delivery from Stimuli-Responsive Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-N-isopropylmethacrylamide)/Chitosan Core/Shell Nanohydrogels. Polymers, 14(3), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14030522