Sodium Alginate/β-Cyclodextrin Reinforced Carbon Nanotubes Hydrogel as Alternative Adsorbent for Nickel(II) Metal Ion Removal
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. SA-β-CD/CNTs Hydrogel Preparation
2.3. Characterizations of SA-β-CD/CNTs Hydrogel
2.4. Adsorption Experiment of Ni(II) Solution
2.4.1. Adsorption Isotherm and Kinetics
2.4.2. Study of Adsorption Thermodynamic
2.5. Regeneration Studies
2.6. Real Water Sample Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Novel Aspect of This Work
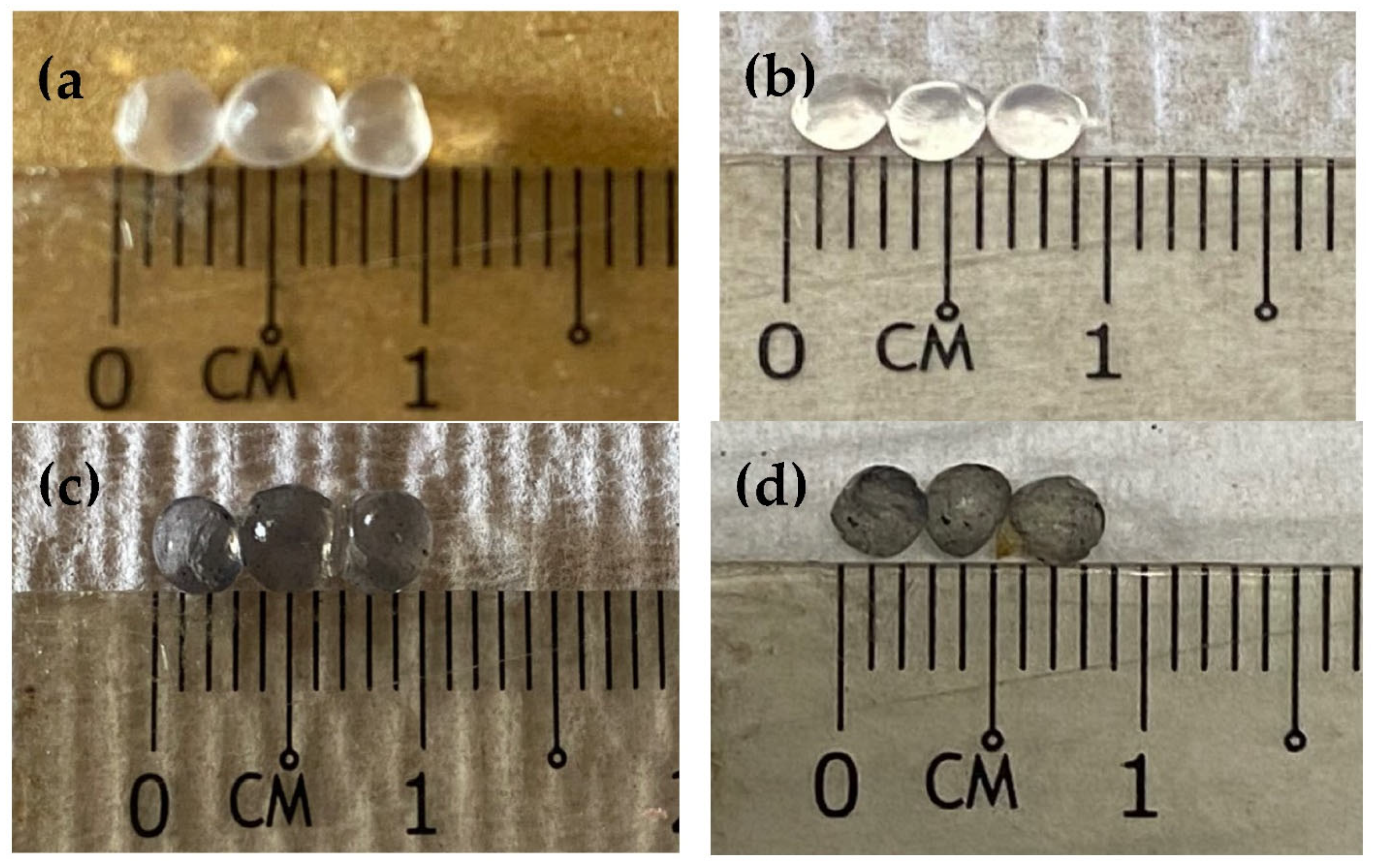
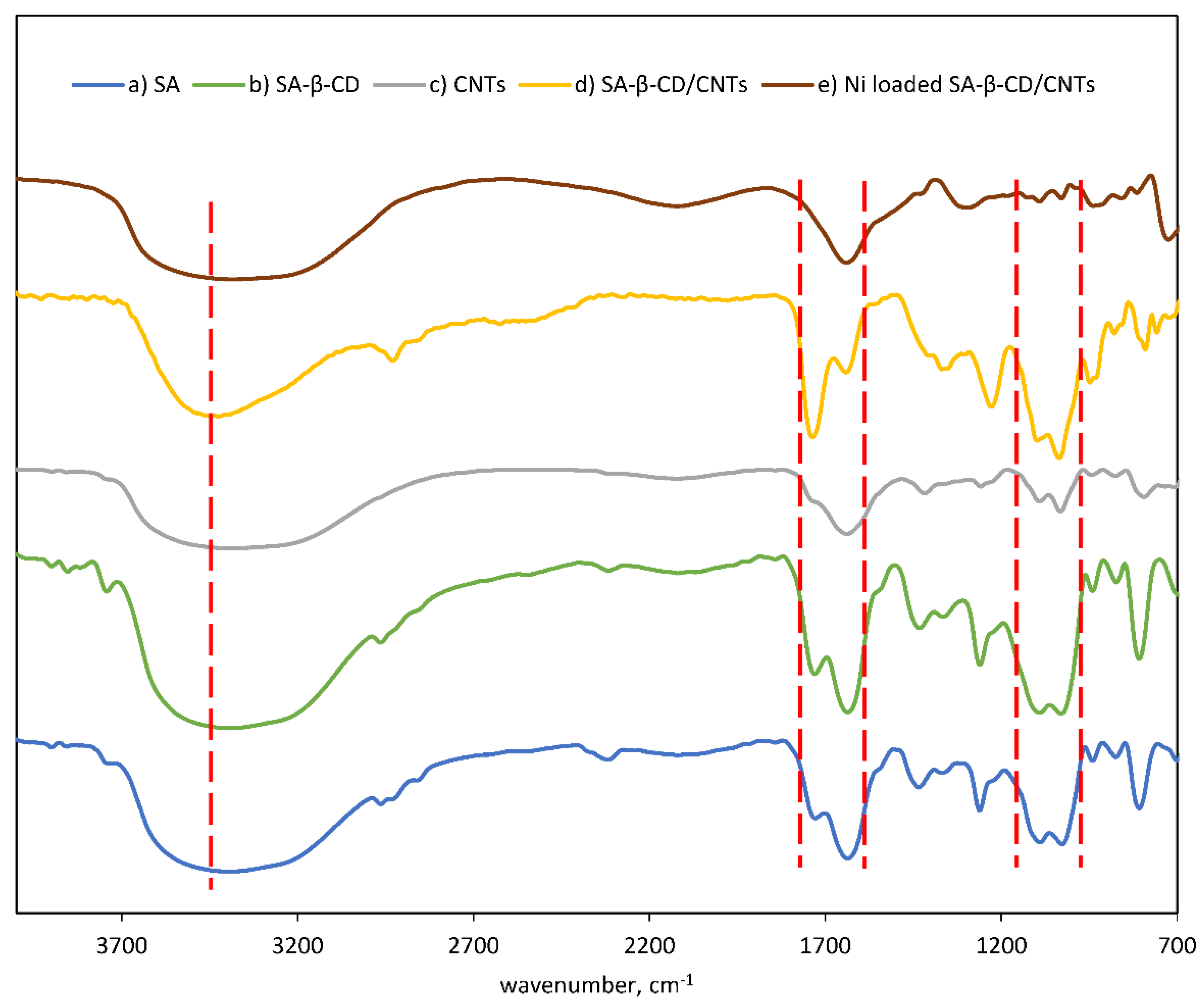
3.2. Spectroscopic Study of SA-β-CD/CNTs Hydrogel Beads
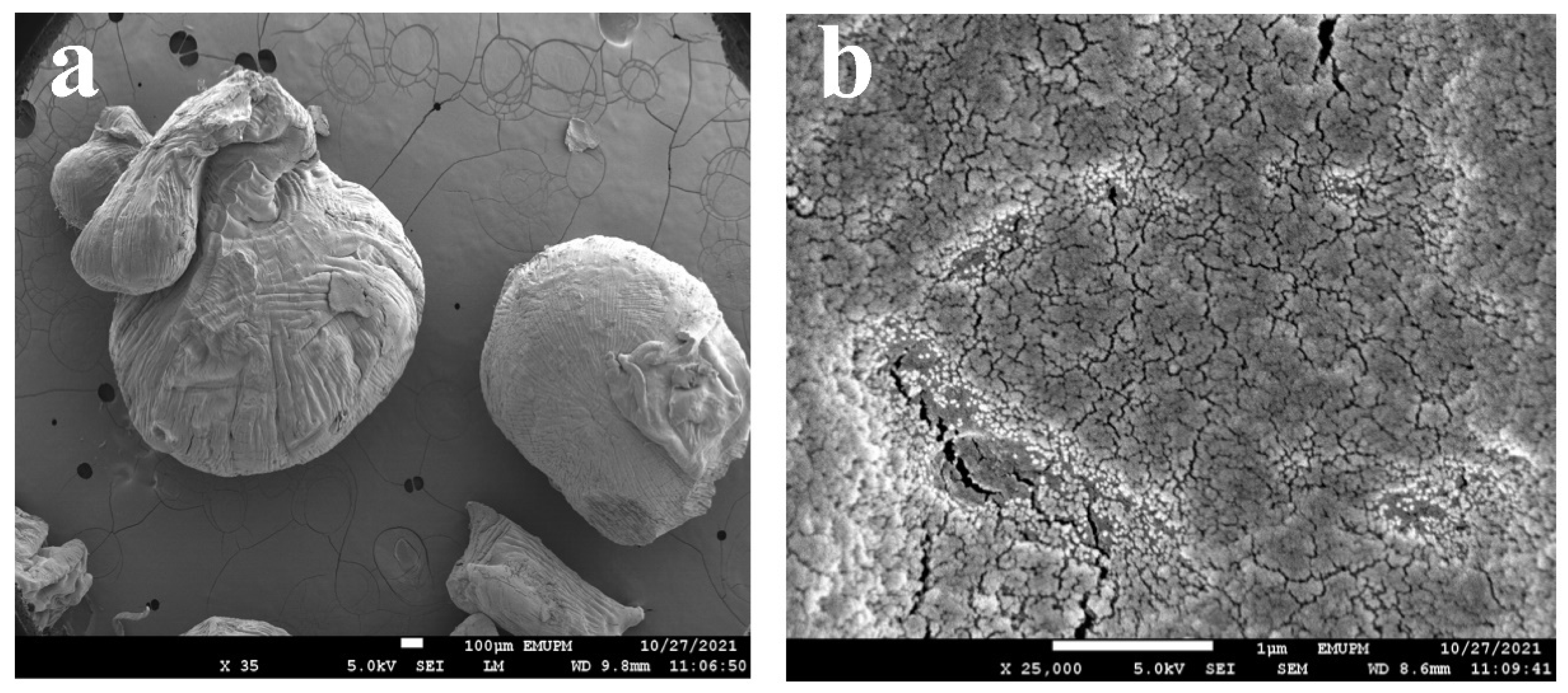
3.3. Morphological Study of SA-β-CD/CNTs
3.4. Elemental Composition of SA-β-CD/CNTs Hydrogel
3.5. Thermal Stability Analysis
3.6. Batch Adsorption Studies
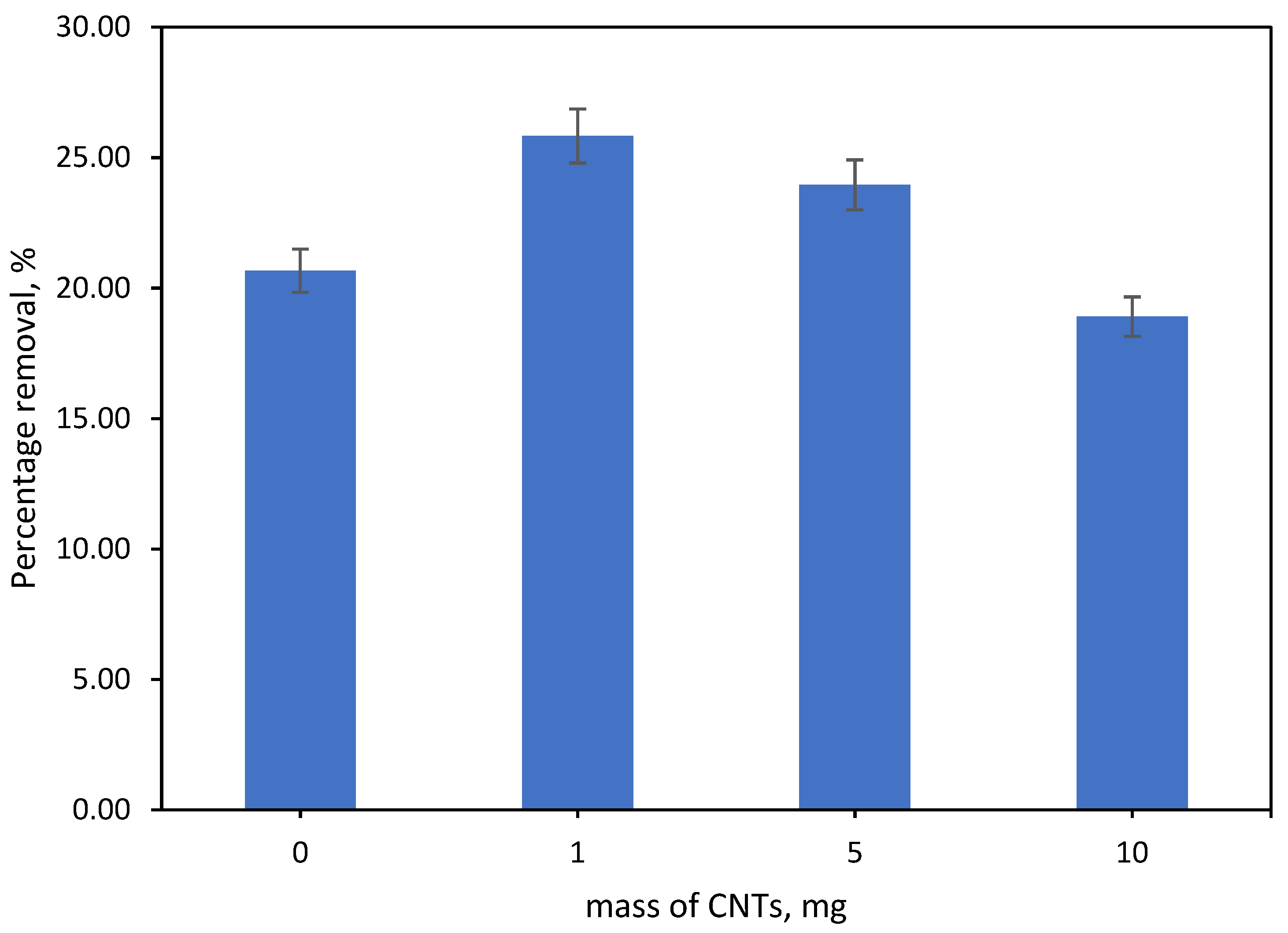
3.6.1. Effect Mass of Incorporated CNTs
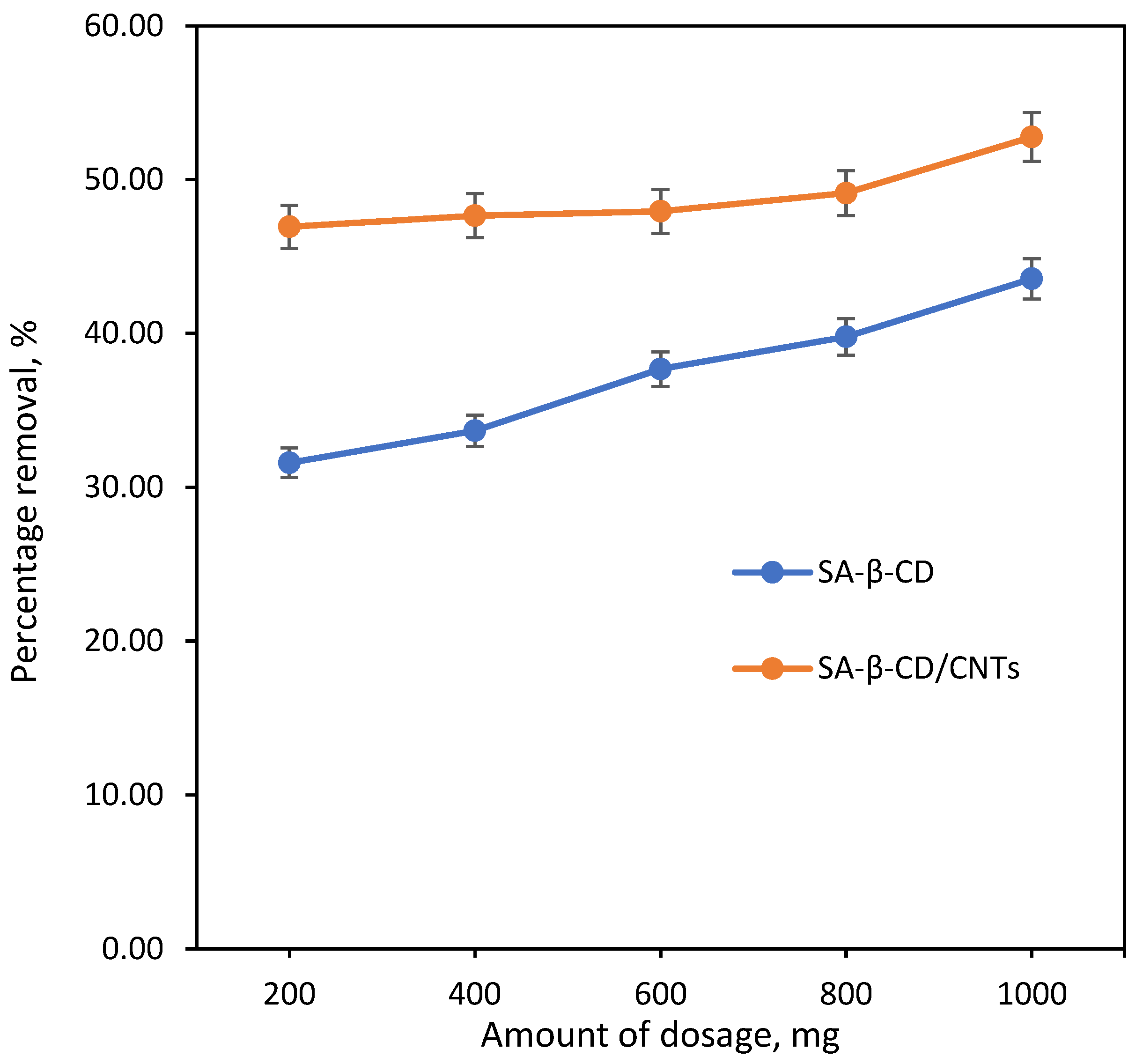
3.6.2. Effect of SA/β-CD/CNT Hydrogel Dosage Effect
3.6.3. Effect of pH
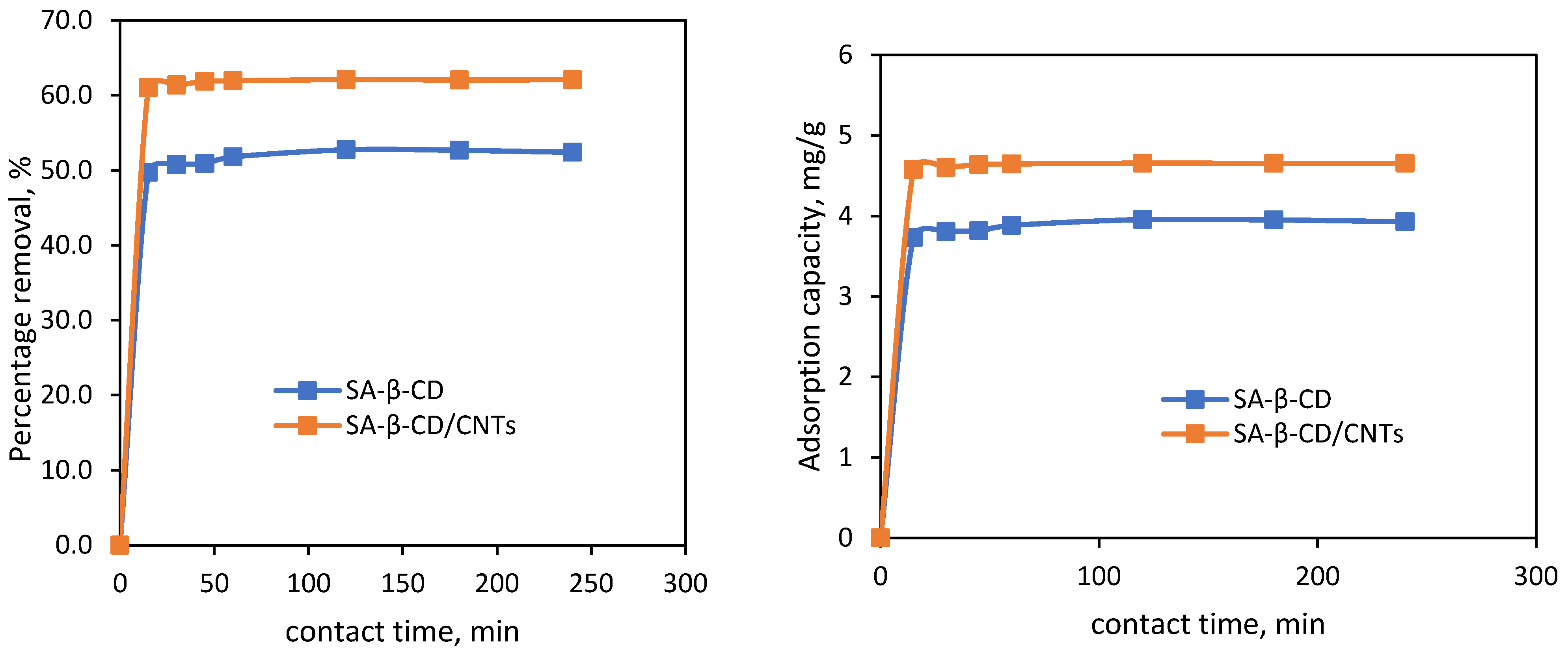
3.6.4. Effect of Contact Time and Kinetic Studies
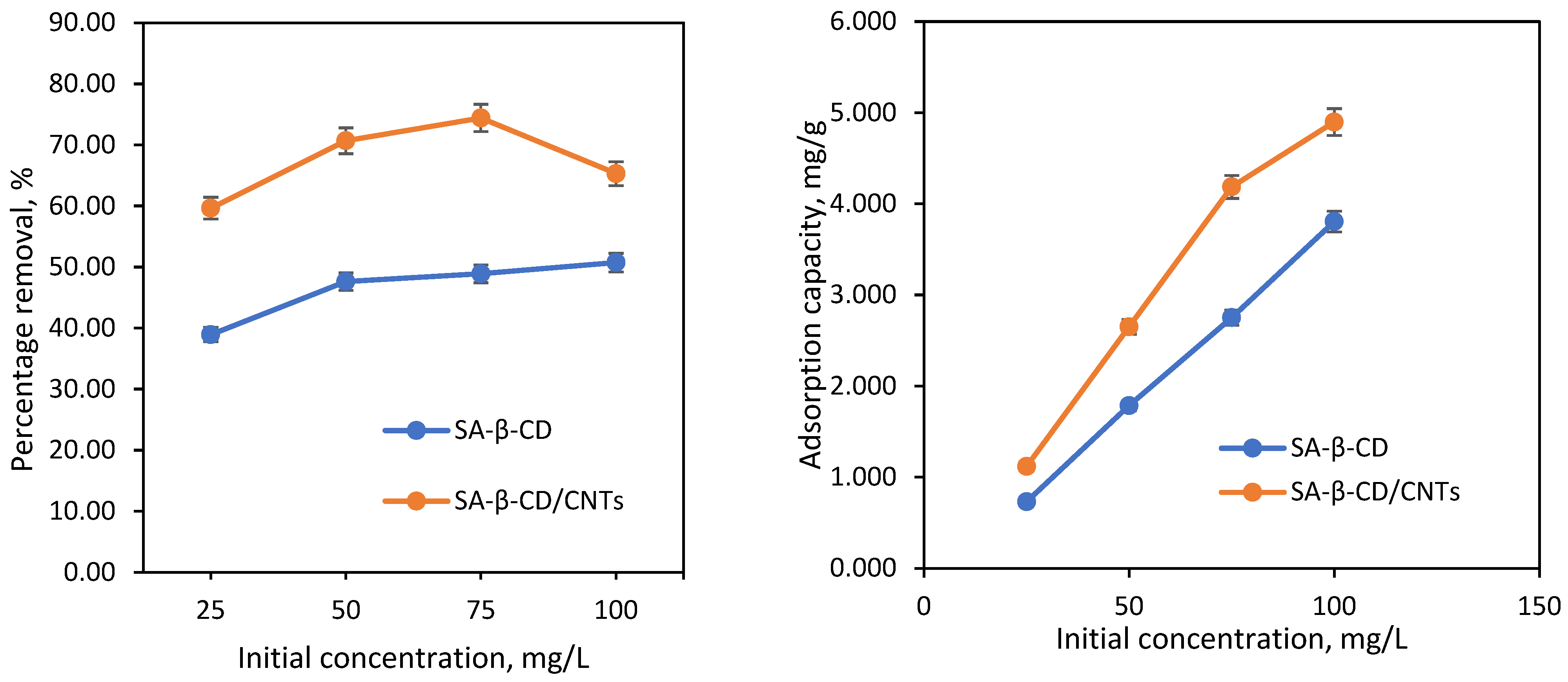
3.6.5. Effect of Initial Concentration and Isotherm Studies
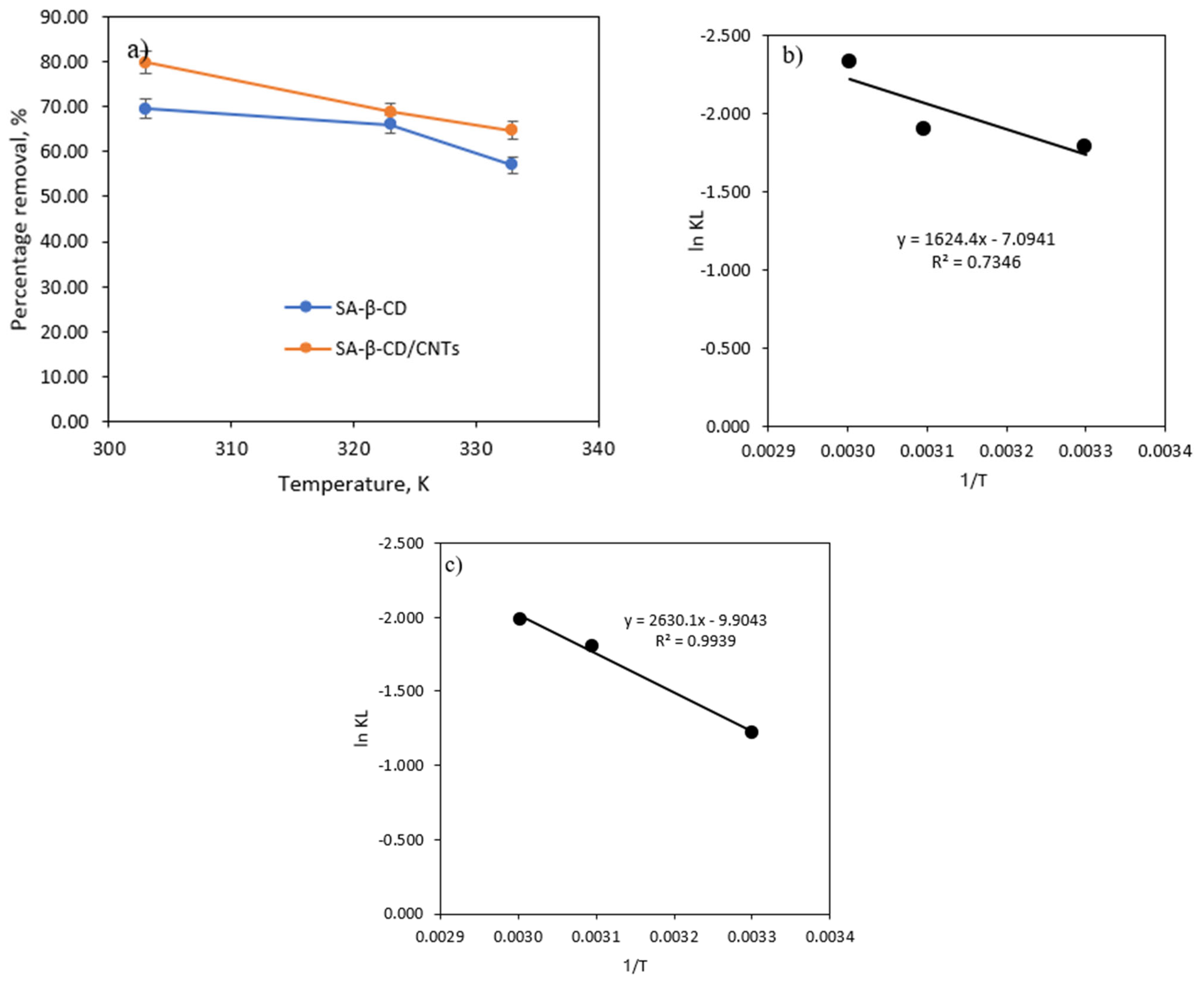
3.6.6. Effect of Temperature and Thermodynamic
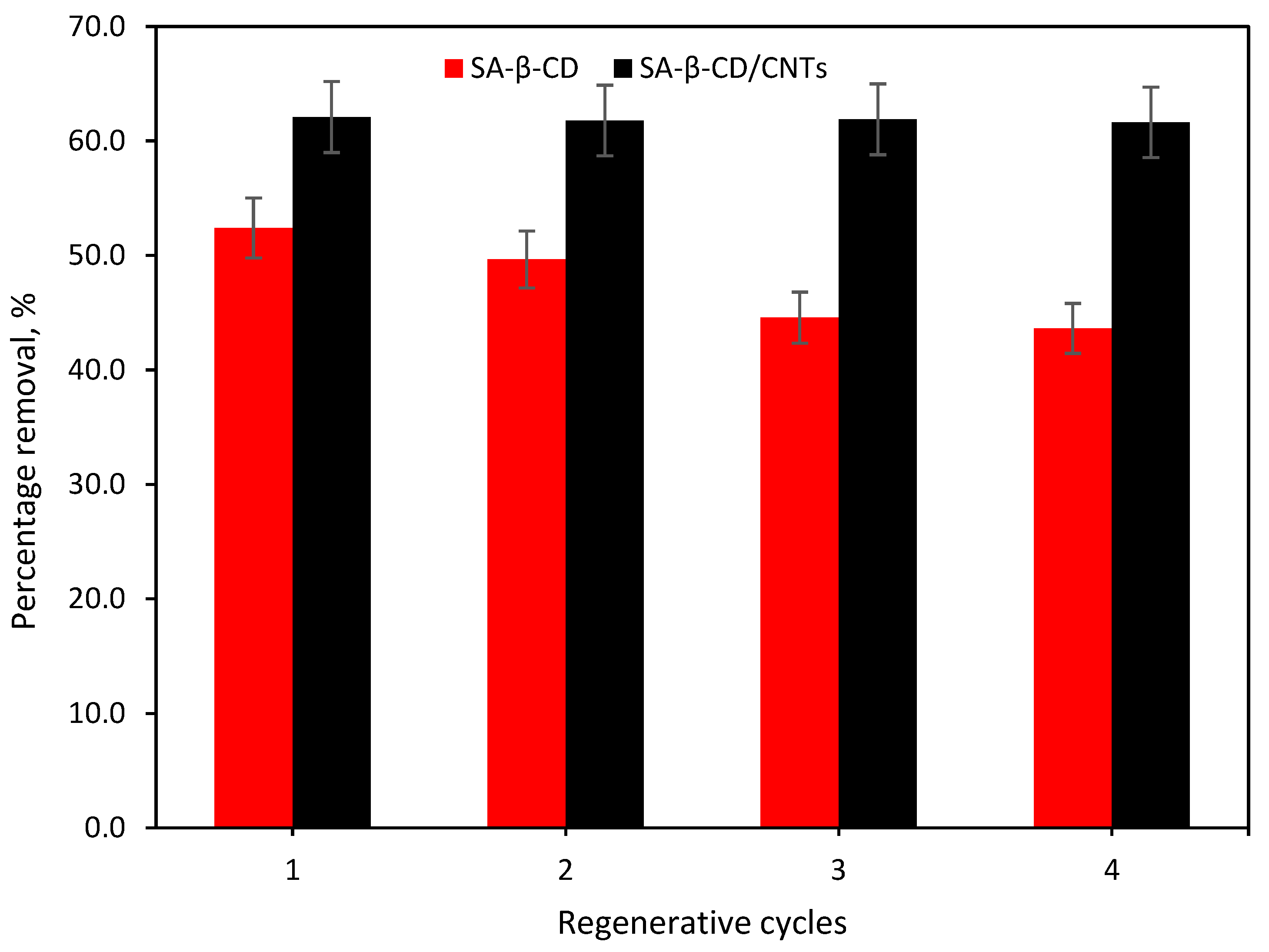
3.7. Regeneration Studies
3.8. Real Water Sample Treatment
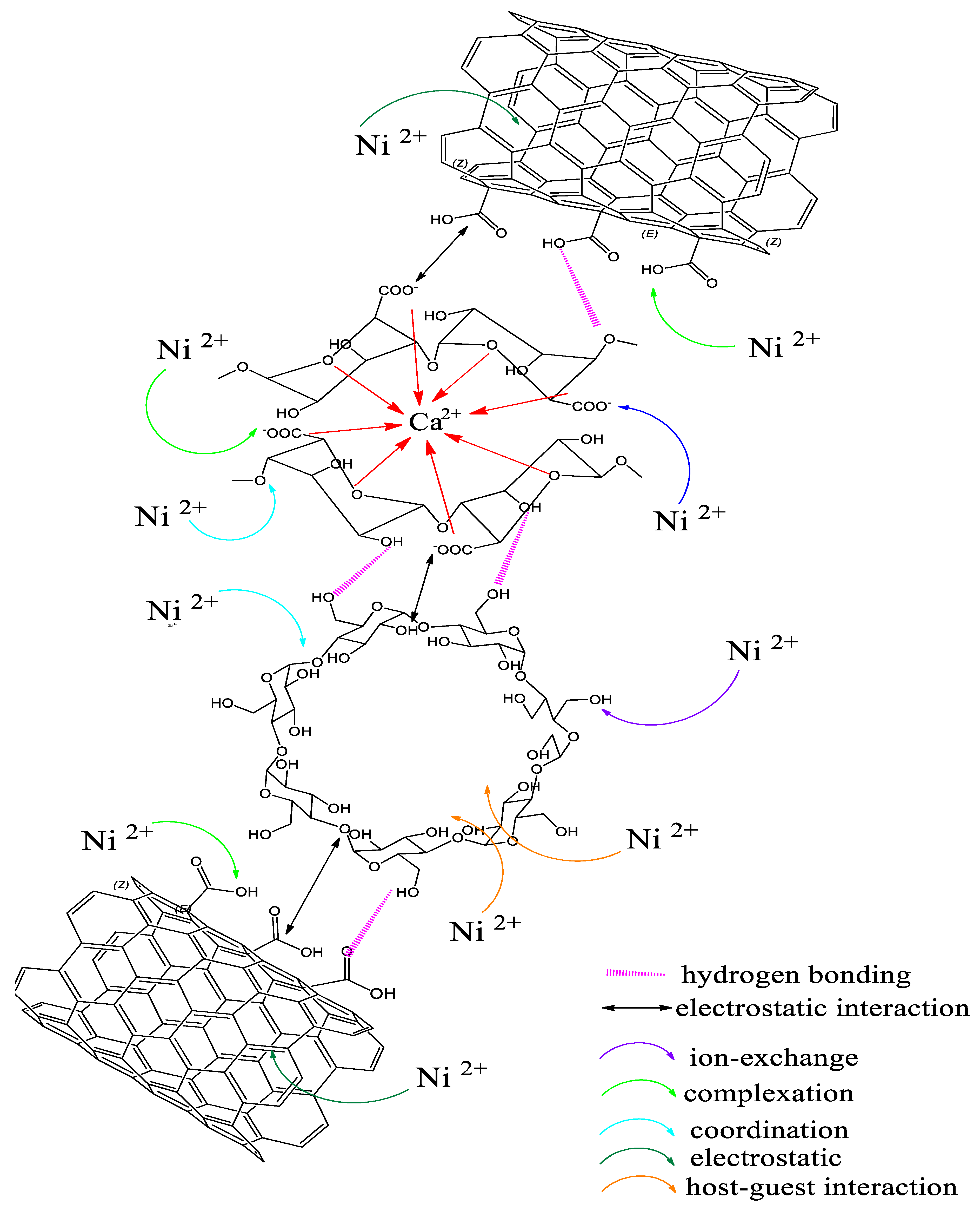
3.9. Possible Chemical Interaction of SA-β-CD/CNTs Hydrogel and Ni(II) Metal
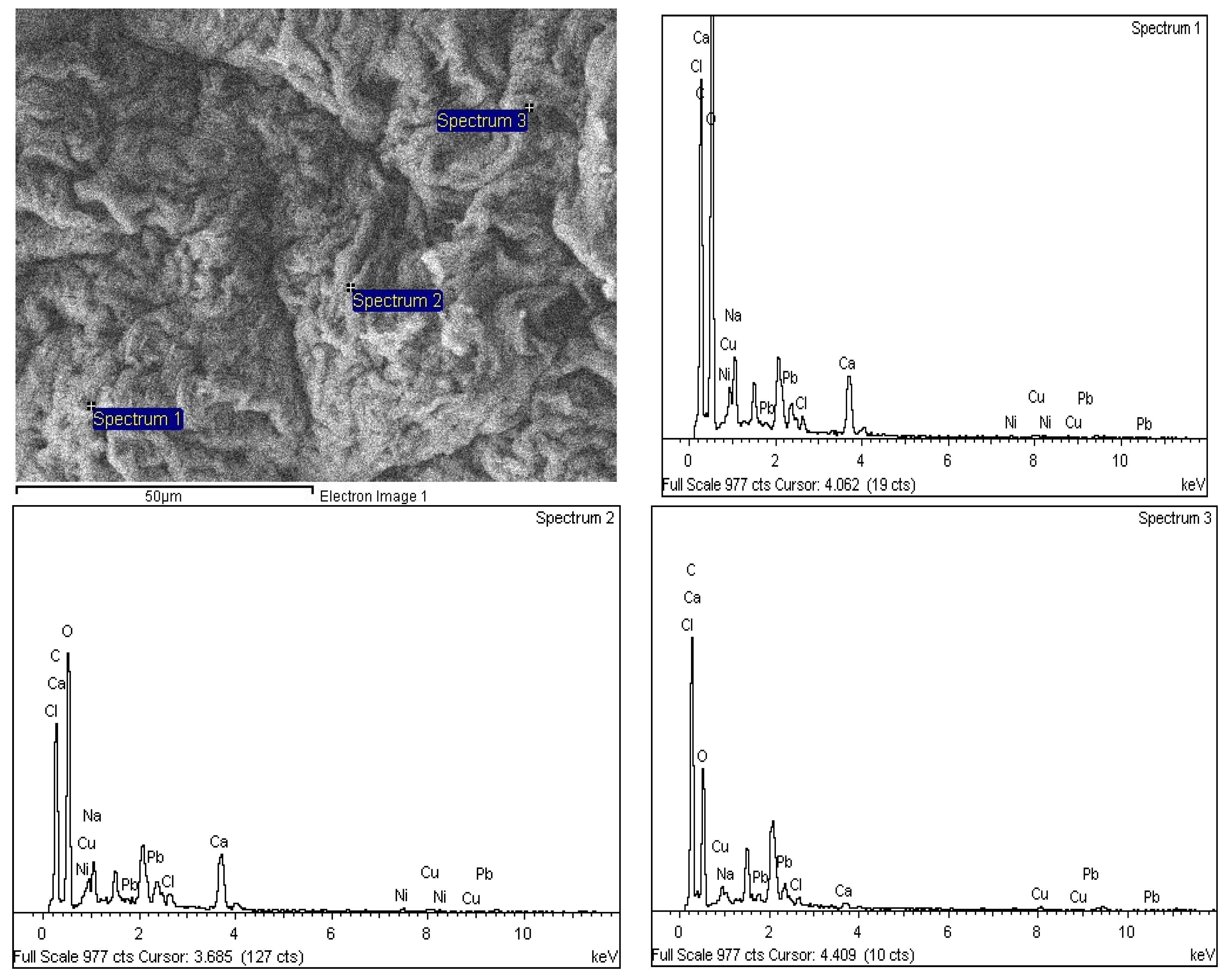
4. Elemental Composition and Distribution on SA-β-CD/CNTs after Ni(II) Adsorption
5. Comparative Evaluation of Other Adsorbents
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mitra, S.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Tareq, A.M.; Bin Emran, T.; Nainu, F.; Khusro, A.; Idris, A.M.; Khandaker, M.U.; Osman, H.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; et al. Impact of heavy metals on the environment and human health: Novel therapeutic insights to counter the toxicity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.; Zeng, S.; Hussain, M.; Tang, P.; Ma, S.; Yi, J.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Wu, G.; et al. Bio-accumulation effects of heavy metals Pb, Zn and Cd on Procecidochares utilis parasitism to Eupatorium adenophorum at Suzu metal mines, Yunnan. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attar, K.; Demey, H.; Bouazza, D.; Sastre, A.M. Sorption and Desorption Studies of Pb(II) and Ni(II) from Aqueous Solutions by a New Composite Based on Alginate and Magadiite Materials. Polymers 2019, 11, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beni, E.; Giurlani, W.; Fabbri, L.; Emanuele, R.; Santini, S.; Sarti, C.; Martellini, T.; Piciollo, E.; Cincinelli, A.; Innocenti, M. Graphene-based nanomaterials in the electroplating industry: A suitable choice for heavy metal removal from wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 292, 133448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.K.; Reddy, R.C.; Bagoji, I.B.; Das, S.; Bagali, S.; Mullur, L.; Khodnapur, J.P.; Biradar, M.S. Primary concept of nickel toxicity—An overview. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2019, 30, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, M.; Abedi, M.A.; Abbasizadeh, S.; Sheshdeh, R.K.; Mousavi, S.E.; Shohani, S. Effect of zeolite hydroxyl active site distribution on adsorption of Pb(II) and Ni(II) pollutants from water system by polymeric nanofibers. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 55, 1994–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; Del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.; Nebbia, C.S.; et al. Update of the risk assessment of nickel in food and drinking water. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claude, N.J.; Shanshan, L.; Khan, J.; Yifeng, W.; Dongxu, H.; Xiangru, L. Waste tea residue adsorption coupled with electrocoagulation for improvement of copper and nickel ions removal from simulated wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Jiang, J.; An, Y.; Jiang, X.; Sun, Q.; Zheng, H.; Li, H. A novel self-floating silica adsorbent for antibiotic ciprofloxacin and nickel (II) ion. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 429, 132227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.; Anbarasu, A.; Pasupuleti, R.R.; Manigandan, S.; Praveenkumar, T.; Kumar, J.A. Treatment of heavy metals containing wastewater using biodegradable adsorbents: A review of mechanism and future trends. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens-Gámez, M.; Serrano-Aroca, A. Low-cost advanced hydrogels of calcium alginate/carbon nanofibers with enhancedwater diffusion and compression properties. Polymers 2018, 10, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Zhou, S. Green synthesis of network nanostructured calcium alginate hydrogel and its removal performance of Cd2+ and Cu2+ ions. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 258, 123931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-P.; Jiang, H.-L.; Hu, Q.-D.; He, F.-A.; Zou, H.-L.; Zhong, Z.-R.; Zhu, Q.-J.; Lv, H.-W.; Yang, Y.-Y. Preparation of the hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene crosslinked sodium alginate polymer/multi-walled carbon nanotubes composite powder for the removal of the cationic dyes. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1262, 133050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şolpan, D.; Torun, M. (Sodium alginate/acrylamide) semi-interpenetrating polymer networks and their usability on removal of lead, cadmium, nickel ions. J. Macromol. Sci.-Pure Appl. Chem. 2005, 42, 1435–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; An, Q.-D.; Xiao, Z.-Y.; Zhai, S.-R.; Hao, J.-A.; Tong, Y. Alginate modified graphitic carbon nitride composite hydrogels for efficient removal of Pb(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 1298–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, Z.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Zinadini, S.; van Loosdrecht, M. β-cyclodextrin functionalized MWCNTs as a promising antifouling agent in fabrication of composite nanofiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 247, 116979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukat, H.; Pervaiz, F.; Rehman, S.; Noreen, S. Development of β-cyclodextrin/chitosan-co-poly (2-acrylamide-2-methylpropane sulphonic acid) cross-linked hybrid IPN-nanogels to enhance the solubility of rosuvastatin: An in vitro and in vivo attributes. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 75, 103696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.-J.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.-R.; Zhang, Y.-C. Development of active packaging films based on liquefied shrimp shell chitin and polyvinyl alcohol containing β-cyclodextrin/cinnamaldehyde inclusion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 214, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izawa, H.; Kawakami, K.; Sumita, M.; Tateyama, Y.; Hill, J.P.; Ariga, K. β-Cyclodextrin-crosslinked alginate gel for patient-controlled drug delivery systems: Regulation of host-guest interactions with mechanical stimuli. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2155–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X. A novel method of synthesizing cyclodextrin grafted multiwall carbon nanotubes/iron oxides and its adsorption of organic pollutant. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 320, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Zou, C.; Liang, H.; Peng, H.; Liao, Y. The effective removal of nickel ions from aqueous solution onto magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified by β-cyclodextrin. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 619, 126544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, O.; Gürkan Polat, T.; Tunç, S. Development of Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Β-Cyclodextrin/P(Mve-Ma) Composite Nanofibers as Effective and Selective Adsorbent and Filtration Material for the Removal and Separation of Cationic Dyes from Water. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 322, 116130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, J.; An, J.M.; Surwase, S.S.; Chakraborty, K.; Sutradhar, S.C.; Hwang, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.-K. Carbon Nanotube and Its Derived Nanomaterials Based High Performance Biosensing Platform. Biosensors 2022, 12, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.K.; Kim, H.-B.; Dutta, S.D.; Ganguly, K.; Lim, K.-T. Carbon nanotubes-based nanomaterials and their agricultural and biotechnological applications. Materials 2020, 13, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, W.; Jie, F.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, K.; Liu, H. The selective adsorption performance and mechanism of multiwall magnetic carbon nanotubes for heavy metals in wastewater. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, Y.A. Fabrication of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/amine modified carbon nanotube composite films for rapid chromate removal. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 138, 50339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Gao, L.; Fu, X.; Siyal, S.H.; Sui, G.; Yang, X. Green synthesis of amino-functionalized carbon nanotube-graphene hybrid aerogels for high performance heavy metal ions removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Zheng, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, H.-M. Swelling and mechanical behaviors of carbon nanotube/poly(vinyl alcohol) hybrid hydrogels. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 1704–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, A.; Bhowmick, R.; Prodhan, C.; Majumder, D.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Ali, M. Synthesis and characterization of biopolymer based hybrid hydrogel nanocomposite and study of their electrochemical efficacy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhado, E.; Hato, M.J. Preparation and Characterization of Sodium Alginate-Based Oxidized Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Hydrogel Nanocomposite and its Adsorption Behaviour for Methylene Blue Dye. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 576913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinezhad, A.; Marandi, G.B.; Farsadrooh, M.; Javadian, H. Synthesis of poly(acrylamide-co-itaconic acid)/MWCNTs superabsorbent hydrogel nanocomposite by ultrasound-assisted technique: Swelling behavior and Pb (II) adsorption capacity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 49, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Asthana, A.; Singh, A.K.; Chakraborty, R.; Vidya, S.S.; Susan, A.B.H.; Carabineiro, S.A. Adsorption of cationic dyes, drugs and metal from aqueous solutions using a polymer composite of magnetic/β-cyclodextrin/activated charcoal/Na alginate: Isotherm, kinetics and regeneration studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.-H.; Liu, S.-C.; Chen, C.-Y. Comparative adsorption of Cu(II), Zn(II), and Pb(II) ions in aqueous solution on the crosslinked chitosan with epichlorohydrin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Mafize, A.A.; Adlin, N.; Abdul, M. Efficient Removal of Pb (II) from Aqueous Solutions by Using Oil Palm Bio-Waste/MWCNTs Reinforced PVA Hydrogel Composites: Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Modeling. Polymers 2020, 12, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gao, B.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Lee, X. Impregnation of multiwall carbon nanotubes in alginate beads dramatically enhances their adsorptive ability to aqueous methylene blue. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 133, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiti, K.; Suwantong, O. Bilayer wound dressing based on sodium alginate incorporated with curcumin-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex/chitosan hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4113–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, A.; Seguin, C.; Brion, A.; Lavalle, P.; Schaaf, P.; Fournel, S.; Bourel-Bonnet, L.; Frisch, B.; De Giorgi, M. β-Cyclodextrin-Functionalized Chitosan/Alginate Compact Polyelectrolyte Complexes (CoPECs) as Functional Biomaterials with Anti-Inflammatory Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 29347–29356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-Y.; Chu, C.-C. Synthesis of photoresponsive hybrid alginate hydrogel with photo-controlled release behavior. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 119, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainao, W.; Shi, Z.; Pang, H.; Feng, H. Alleviative effects of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles on the physiological toxicity of 3-nitrophenol to rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. Open Life Sci. 2022, 17, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, F.; Chen, H.; Noh, K.; Sue, H.-J. Critical challenges and advances in the carbon nanotube–metal interface for next-generation electronics. Nanoscale Adv. 2021, 3, 942–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhijiang, C.; Cong, Z.; Ping, X.; Jie, G.; Kongyin, Z. Calcium alginate-coated electrospun polyhydroxybutyrate/carbon nanotubes composite nanofibers as nanofiltration membrane for dye removal. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 14801–14820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Thakur, S.; Mamba, G.; Gupta, R.K.; Thakur, P.; Thakur, V.K. Graphite modified sodium alginate hydrogel composite for efficient removal of malachite green dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 148, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.; Arotiba, O. Synthesis, characterization and adsorption studies of an acrylic acid-grafted sodium alginate-based TiO2 hydrogel nanocomposite. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2017, 36, 458–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darini, A.; Eslaminejad, T.; Mahani, S.N.N.; Ansari, M. Magnetogel Nanospheres Composed of Cisplatin-Loaded Alginate/BCyclodextrinas Controlled Release Drug Delivery. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Qi, H.; Shi, C.; Ma, R.; Liu, S.; Huang, Z. Preparation and adsorption behaviors of sodium alginate-based adsorbent-immobilized β-cyclodextrin and graphene oxide. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31549–31557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godiya, C.B.; Xiao, Y.; Lu, X. Amine functionalized sodium alginate hydrogel for efficient and rapid removal of methyl blue in water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 144, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-S.; Han, S.-Y.; Yang, L.; Zheng, H.-C. Synthesis of beta-cyclodextrin-grafted-alginate and its application for removing methylene blue from water solution. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 91, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Niu, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, M.; Shang, Z.; Yang, Y. Sodium alginate-grafted β-cyclodextrins as a matrix for immobilized Arthrobacter simplex for cortisone acetate biotransfromation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 444, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jiang, Z.; Cao, J.; Yu, F. Enhanced adsorption for the removal of antibiotics by carbon nanotubes/graphene oxide/sodium alginate triple-network nanocomposite hydrogels in aqueous solutions. Chemosphere 2020, 242, 125188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Ma, Y.; Yan, X. Preparation and characterization of coaxial multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polyaniline tubular nanocomposites for electrochemical energy storage in the presence of sodium alginate. Synth. Met. 2014, 193, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, E.; Rajesh, M.; Prabhakar, S. Removal and recovery of heavy metals from aqueous solution using b-cyclodextrin polymer and optimization of complexation conditions. Desalination Water Treat. 2018, 122, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antić, K.; Onjia, A.; Vasiljević-Radović, D.; Veličković, Z.; Tomić, S.L. Removal of Nickel Ions from Aqueous Solutions by 2-Hydroxyethyl Acrylate/Itaconic Acid Hydrogels Optimized with Response Surface Methodology. Gels 2021, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joddar, B.; Garcia, E.; Casas, A.; Stewart, C. Development of functionalized multi-walled carbon-nanotube-based alginate hydrogels for enabling biomimetic technologies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Guo, C.; Hao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Long, H.; Li, M. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by sodium alginate based adsorbent-a review and new perspectives. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 4423–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, S.; Eris, S.; Azizian, S. Alginate-Based Hydrogel Beads as a Biocompatible and Efficient Adsorbent for Dye Removal from Aqueous Solutions. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 15140–15148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-H.; Omer, A.M.; Ouyang, X.; Yu, D. Fabrication of carboxylated cellulose nanocrystal/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for adsorption of pb(ii) from Aqueous Solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio-Collado, J.; García-San-Martín, N.; Molina-Mateo, J.; Cabanilles, C.T.; Quiles, V.D.; Serrano-Aroca, A.; Serra, R.S.I. Electroactive calcium-alginate/polycaprolactone/reduced graphene oxide nanohybrid hydrogels for skeletal muscle tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 214, 112455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Fan, M.; Ni, J.; Peng, W.; Cao, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Fan, G.; Zhao, Y.; Song, S. Efficient dye removal using fixed-bed process based on porous montmorillonite nanosheet/poly(acrylamide-co-acrylic acid)/sodium alginate hydrogel beads. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 219, 106443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, K.; Gao, X.; Ren, M.; Jia, M.; Yang, Y. Enhanced thermal properties of hydrate salt/poly (acrylate sodium) copolymer hydrogel as form-stable phase change material via incorporation of hydroxyl carbon nanotubes. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2020, 208, 110387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnica-Palafox, I.; Estrella-Monroy, H.; Vázquez-Torres, N.; Álvarez-Camacho, M.; Castell-Rodríguez, A.; Sánchez-Arévalo, F. Influence of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the physico-chemical and biological responses of Chitosan-based hybrid hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 236, 115971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.K.; Sundaram, K.S.; Iyengar, G.A.; Lee, K.-P. A novel chitosan functional gel included with multiwall carbon nanotube and substituted polyaniline as adsorbent for efficient removal of chromium ion. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 267, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Lee, M.W.; Woo, S.H. Adsorption of congo red by chitosan hydrogel beads impregnated with carbon nanotubes. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1800–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseinzadeh, H. Synthesis of carrageenan/multi-walled carbon nanotube hybrid hydrogel nanocomposite for adsorption of crystal violet from aqueous solution. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2015, 17, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafiu, M.; Maje, Y.S. Application of Iron Nanoparticle Coupled with Modified Orange Peel (FeNps/MOP) in Removal of Nickel from Water. Chem. Res. J. 2022, 7, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, X.; Cai, Z. Adsorption of pb(ii), CD(II) and zn(ii) by extracellular polymeric substances extracted from aerobic granular sludge: Efficiency of protein. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, V.; Patkar, M. Removal of nickel from aqueous solution by using corncob as adsorbent. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 61, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Idrissi, A.; El Gharrak, A.; Achagri, G.; Essamlali, Y.; Amadine, O.; Akil, A.; Sair, S.; Zahouily, M. Synthesis of urea-containing sodium alginate-G-poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) superabsorbent-fertilizer hydrogel reinforced with carboxylated cellulose nanocrystals for efficient water and nitrogen utilization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torab-Mostaedi, M.; Asadollahzadeh, M.; Hemmati, A.; Khosravi, A. Equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies for biosorption of cadmium and nickel on Grapefruit Peel. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalak, T.; Marciszewicz, K.; Piepiórka-Stepuk, J. Highly effective adsorption process of ni(Ii) ions with the use of sewage sludge fly ash generated by circulating fluidized bed combustion (cfbc) technology. Materials 2021, 14, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Yu, P.; Shen, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, R.; Fu, X.; Chi, J.; Chen, X.; Feng, Y. Ion imprinted polymer layer modified magnetic nanocomposites for selective recycling of aqueous Ni(II). J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayalvizhi, K.; Alhaji, N.; Saravanakkumar, D.; Mohamed, S.B.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Ayeshamariam, A.; Al-Mohaimeed, A.M.; AbdelGawwad, M.R.; Elshikh, M.S. Adsorption of copper and nickel by using sawdust chitosan nanocomposite beads—A kinetic and thermodynamic study. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Liu, S.; Liu, T.; Zhang, B. A novel biodegradable β-cyclodextrin-based hydrogel for the removal of heavy metal ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 97, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, S.; Din, M.I.; Rasool, A.; Qasim, I.; Mohsin, I.U. Equilibrium, thermodynamics, and kinetic sorption studies for the removal of coomassie brilliant blue on wheat bran as a low-cost adsorbent. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2012, 2012, 405980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.T.; Tran, N.Y.; Tran, Q.N.; Bach, G.L.; Lam, T.V. Kinetics of pilot-scale essential oil extraction from pomelo (citrus maxima) peels: Comparison between linear and nonlinear models. Alex. Eng. J. 2022, 61, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuránek, M.; Melichová, Z.; Kureková, V.; Kljajević, L.; Nenadović, S. Removal of nickel from aqueous solutions by natural bentonites from slovakia. Materials 2021, 14, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mansouri, F.; El Farissi, H.; Cacciola, F.; Talhaoui, A.; El Bachiri, A.; Tahani, A.; da Silva, J.C.G.E.; Brigui, J. Rapid elimination of copper (ii), nickel (ii) and chromium (vi) ions from aqueous solutions by charcoal modified with phosphoric acid used as a green biosorbent. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2022, 33, 2254–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkan, E.; Nadaroğlu, H.; Celebi, N. Use of silica fume as low-cost absorbent material for nickel removal from aqueous solutions. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 6121–6126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyun, T.S.; Mseer, A.H. Comparison of the experimental results with the Langmuir and Freundlich models for copper removal on limestone adsorbent. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, Z.N.; Ugbaga, N.I.; Abdullahi, A.K. Evaluation of optimum adsorption conditions for Ni (II) and Cd (II) removal from aqueous solution by Modified Plantain Peels (MPP). Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Kumar, A. Removal of nickel (II) from aqueous solution by biosorption on A. Barbadensis Miller waste leaves powder. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, B.; Açikel, U. Adsorption isotherms for removal of heavy metal ions (copper and nickel) from aqueous solutions in single and binary adsorption processes. GAZI Univ. J. Sci. 2022, 36, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Khan, M.I.; Khraisheh, M.; Lashari, M.H.; Shahida, S.; Azhar, M.F.; Prapamonthon, P.; Mirza, M.L.; Khalid, N. Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies for adsorption of nickel ions onto husk of Oryza sativa. Desalination Water Treat. 2019, 167, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Qiu, B.; Sun, D. Enhanced naproxen adsorption by a novel β-cyclodextrin immobilized the three-dimensional macrostructure of reduced graphene oxide and multiwall carbon nanotubes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Ding, X.; Fu, J.; Zhao, J. Investigating the zinc ion adsorption capacity of a chitosan/β-cyclodextrin complex in wastewater. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 143, 02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, F.; Zoppas, F.M.; Soomro, M.; Jatoi, A.S.; Noureen, F.; Akhtar, M.N.; Mehreen, F. Carbon-based sorbets for heavy metal removal from aqueous solution, discrepancies, and future prospects: A state-of-the-art review. Biomass-Conv. Biorefinery 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordin, N.A.; Rahman, N.A.; Abdullah, A.H. Effective Removal of Pb(II) Ions by Electrospun PAN/Sago Lignin-Based Activated Carbon Nanofibers. Molecules 2020, 25, 3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdaus, F.; Idris, M.S.F.; Yusoff, S.F.M. Adsorption of Nickel Ion in Aqueous Using Rubber-Based Hydrogel. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volesky, B. Biosorption and me. Water Res. 2007, 41, 4017–4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Liu, Y.; Naidu, R.; Du, J.; Qi, F.; Donne, S.W.; Islam, M. Mesoporous Biopolymer Architecture Enhanced the Adsorption and Selectivity of Aqueous Heavy-Metal Ions. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 15316–15331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Naidu, R.; Du, J.; Qi, F.; Ahsan, A.; Liu, Y. Magnetic responsive mesoporous alginate/β-cyclodextrin polymer beads enhance selectivity and adsorption of heavy metal ions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 826–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelebi, H.; Gök, G.; Gök, O. Adsorption capability of brewed tea waste in waters containing toxic lead(II), cadmium (II), nickel (II), and zinc(II) heavy metal ions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moino, B.P.; Costa, C.S.D.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Removal of nickel ions on residue of alginate extraction from Sargassum f ilipendula seaweed in packed bed. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 95, 2120–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber-Samandari, S.; Saber-Samandari, S.; Joneidi-Yekta, H.; Mohseni, M. Adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution using gelatin-based magnetic nanocomposite beads comprising carboxylic acid functionalized carbon nanotube. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Rahdar, S.; Asadi, Z. The survey of application of the linear and nonlinear kinetic models for the adsorption of nickel(II) by modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurbankova, M.; Volkovova, K.; Hraskova, D.; Wimmerova, S.; Moricova, S. Respiratory toxicity of Fe3O4 nanoparticles: Experimental study. Rev. Environ. Health 2016, 32, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Kinetic Modelling | Parameters | Type of Adsorbent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SA-β-CD | SA-β-CD/CNTs | ||
| Pseudo-first order | k1 (1/min) | 0.00002 | 0.00009 |
| qe (mg/g) | 3.7396 | 2.8933 | |
| R2 | 0.65717 | 0.51638 | |
| Pseudo-second order | k2 (g/mg min) | 0.3883 | 0.1417 |
| qe (mg/g) | 3.9948 | 5.9347 | |
| R2 | 0.9993 | 0.999 | |
| Bangham | Ko | 0.0215 | 0.0062 |
| α | 0.0906 | 0.1162 | |
| R2 | 0.8962 | 0.80782 | |
| Elovich | α | 0.3384 | 0.3244 |
| β | 0.0905 | 0.0347 | |
| R2 | 0.8962 | 0.8086 | |
| Isotherm | Isotherm Parameter | Type of Adsorbent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SA−β−CD | SA−β−CD/CNTs | ||
| Langmuir | qmax | −3.4247 | −18.7970 |
| b (L/mg) | −0.0118 | −0.0082 | |
| R2 | 0.9826 | 0.8591 | |
| Freundlich | Kf | 0.0169 | 0.1016 |
| n | 1.1528 | 0.8675 | |
| R2 | 0.9921 | 0.8165 | |
| Tempkin | Kt | 0.0826 | 1.6040 |
| Bt | 2.5473 | 3.0770 | |
| R2 | 0.9732 | 0.9045 | |
| D–R | B | −0.00006 | −0.00005 |
| qmax | 5.2179 | 5.9960 | |
| R2 | 0.9728 | 0.9861 | |
| Adsorbent | Temperature (K) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (kJ/mol K) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA-β-CD | 303 | 4.4970 | −13.5053 | −0.0590 |
| 323 | 5.0954 | |||
| 333 | 6.4520 | |||
| SA-β-CD/CNTs | 303 | 3.056 | −21.8670 | −0.0823 |
| 323 | 4.826 | |||
| 333 | 5.486 |
| Wastewater Industry | Before Treatment, Ci (mg/L) | After Treatment, Ce (mg/L) | Qe (mg/g) | % Removal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Battery | 100 | 35.94 | 4.8045 | 64.06 |
| Electronic | 100 | 34.28 | 4.9290 | 65.72 |
| Steel | 100 | 33.98 | 4.9515 | 66.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zakaria, A.F.; Kamaruzaman, S.; Abdul Rahman, N.; Yahaya, N. Sodium Alginate/β-Cyclodextrin Reinforced Carbon Nanotubes Hydrogel as Alternative Adsorbent for Nickel(II) Metal Ion Removal. Polymers 2022, 14, 5524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245524
Zakaria AF, Kamaruzaman S, Abdul Rahman N, Yahaya N. Sodium Alginate/β-Cyclodextrin Reinforced Carbon Nanotubes Hydrogel as Alternative Adsorbent for Nickel(II) Metal Ion Removal. Polymers. 2022; 14(24):5524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245524
Chicago/Turabian StyleZakaria, Aiza Farhani, Sazlinda Kamaruzaman, Norizah Abdul Rahman, and Noorfatimah Yahaya. 2022. "Sodium Alginate/β-Cyclodextrin Reinforced Carbon Nanotubes Hydrogel as Alternative Adsorbent for Nickel(II) Metal Ion Removal" Polymers 14, no. 24: 5524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245524
APA StyleZakaria, A. F., Kamaruzaman, S., Abdul Rahman, N., & Yahaya, N. (2022). Sodium Alginate/β-Cyclodextrin Reinforced Carbon Nanotubes Hydrogel as Alternative Adsorbent for Nickel(II) Metal Ion Removal. Polymers, 14(24), 5524. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245524








