Tuning the Morphology of HDPE/PP/PET Ternary Blends by Nanoparticles: A Simple Way to Improve the Performance of Mixed Recycled Plastics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Blend Preparation
2.3. Experimental
3. Results
3.1. Morphology Prediction by Thermodynamic Calculations
3.2. Morphological Analyses
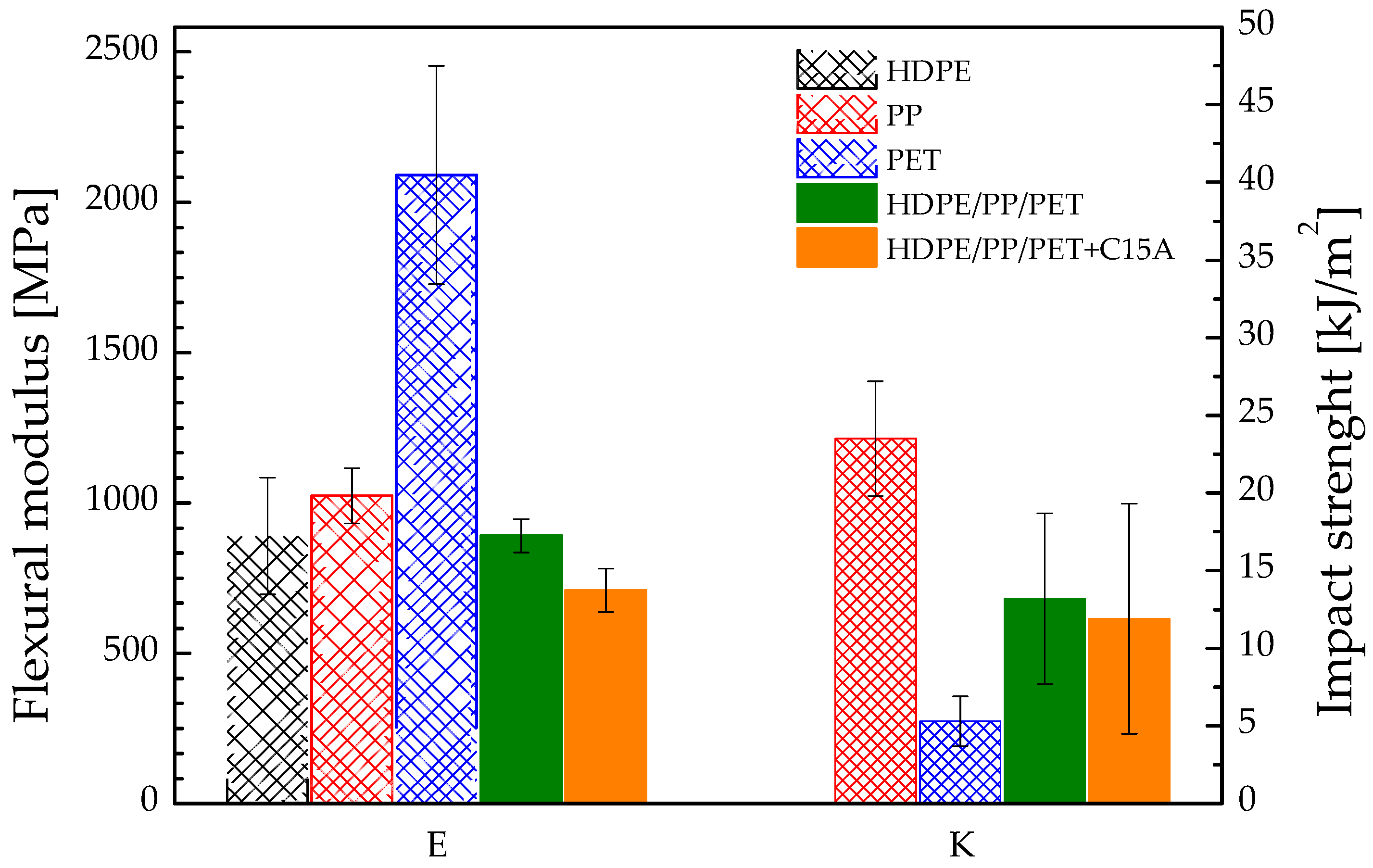
3.3. Mechanical Behavior at High Temperature: Flexural and Impact Strength
3.4. Mechanical Behavior at High Temperature: DMA Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- -
- The number–average drop radius
- -
- The volume–average drop radius
- -
- The circularity of a drop of radius Ri, area Ai and perimeter Pi
- -
- The Rv/Rn ratio, called polydispersity, which is an index of the amplitude of the drop size distribution.
References
- Okan, M.; Aydin, H.M.; Barsbay, M. Current approaches to waste polymer utilization and minimization: A review. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUR-Lex–32019L0904—EN. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2019/904/oj (accessed on 13 November 2022).
- Hundertmark, T.; Mayer, M.; McNally, C.; Simons, T.J.; Witte, C. How plastics waste recycling could transform the chemical industry. McKinsey Co. 2018, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Vollmer, I.; Jenks, M.J.F.; Roelands, M.C.P.; White, R.J.; van Harmelen, T.; de Wild, P.; van der Laan, G.P.; Meirer, F.; Keurentjes, J.T.F.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Beyond mechanical recycling: Giving new life to plastic waste. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 15402–15423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics recycling: Challenges and opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schyns, Z.O.; Shaver, M.P. Mechanical recycling of packaging plastics: A review. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2000415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.K.; Christiansen, J.D.; Daugaard, A.E.; Astrup, T.F. Closing the loop for PET, PE and PP waste from households: Influence of material properties and product design for plastic recycling. Waste Manage. 2019, 96, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, R.S. Polymer recycling: Opportunities and limitations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maris, J.; Bourdon, S.; Brossard, J.M.; Cauret, L.; Fontaine, L.; Montembault, V. Mechanical recycling: Compatibilization of mixed thermoplastic wastes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 147, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utracki, L.A. Compatibilization of polymer blends. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2002, 80, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WM2 Cleaning up the Waste Stream—Recycling Plastics | University of Missouri. Available online: https://extension.missouri.edu/publications/wm2 (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Zander, N.E.; Gillan, M.; Burckhard, Z.; Gardea, F. Recycled polypropylene blends as novel 3D printing materials. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 25, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kets, K.; Delva, L.; Ragaert, K. Structural stabilizing effect of SEBSgMAH on a PP-PET blend for multiple mechanical recycling. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2019, 166, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, G.; Pu, S. Core/shell morphologies in recycled poly (ethylene terephthalate)/linear low-density polyethylene/poly (styrene-b-(ethylene-co-butylene)-b-styrene) ternary blends. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 4223–4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Y.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Lund, A.; Xu, X.; Gkourmpis, T.; Hagstrand, P.O.; Müller, C. High-temperature creep resistant ternary blends based on polyethylene and polypropylene for thermoplastic power cable insulation. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 59, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pracella, M.; Chionna, D.; Pawlak, A.; Galeski, A. Reactive mixing of PET and PET/PP blends with glycidyl methacrylate–modified styrene-b-(ethylene-co-olefin) block copolymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pracella, M.; Pazzagli, F.; Galeski, A. Reactive compatibilization and properties of recycled poly (ethylene terephthalate)/polyethylene blends. Polym. Bull. 2002, 48, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghavi, S.K.; Shahrajabian, H.; Hosseini, H.M. Detailed comparison of compatibilizers MAPE and SEBS-g-MA on the mechanical/thermal properties, and morphology in ternary blend of recycled PET/HDPE/MAPE and recycled PET/HDPE/SEBS-g-MA. J. Elastomers Plast. 2018, 50, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagli, S.S.; Kamdar, K.M. Effects of component addition protocol on the reactive compatibilization of HDPE/PET blends. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1994, 34, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguet, A.; Cassagnau, P.; Lopez-Cuesta, J.M. Structuration, selective dispersion and compatibilizing effect of (nano) fillers in polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1526–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Salzano de Luna, M.; Acierno, D.; Russo, P. Elasticity and structure of weak graphite nanoplatelet (GNP) networks in polymer matrices through viscoelastic analyses. Polymer 2012, 53, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acierno, D.; Filippone, G.; Romeo, G.; Russo, P. Rheological aspects of PP-TiO2 micro and nanocomposites: A preliminary investigation. Macromol. Symp. 2007, 247, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzano de Luna, M.; Filippone, G. Effects of nanoparticles on the morphology of immiscible polymer blends–challenges and opportunities. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 79, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Causa, A.; de Luna, M.S.; Sanguigno, L.; Acierno, D. Assembly of plate-like nanoparticles in immiscible polymer blends–effect of the presence of a preferred liquid–liquid interface. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippone, G.; Romeo, G.; Acierno, D. Role of Interface Rheology in Altering the Onset of Co-Continuity in Nanoparticle-Filled Polymer Blends. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2011, 296, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roosen, M.; Mys, N.; Kusenberg, M.; Billen, P.; Dumoulin, A.; Dewulf, J.; Van Geem, K.M.; Ragaert, K.; De Meester, S. Detailed analysis of the composition of selected plastic packaging waste products and its implications for mechanical and thermochemical recycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 13282–13293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S. Calculation of interfacial tension in polymer systems. J. Polym. Sci. C Polym. Symp. 1971, 34, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reignier, J.; Favis, B.D. Core–shell structure and segregation effects in composite droplet polymer blends. AIChE J. 2003, 49, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemirovski, N.; Siegmann, A.; Narkis, M. Morphology of ternary immiscible polymer blends. J. Macromol. Sci. B 1995, 34, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reignier, J.; Favis, B.D. Control of the subinclusion microstructure in HDPE/PS/PMMA ternary blends. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 6998–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, S.Y.; Dekkers, M.E.J.; Watkins, V.H. Effect of interfacial forces on polymer blend morphologies. Polymer 1988, 29, 1598–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkins, W.D.; Feldman, A. Films. The spreading of liquids and the spreading coefficient. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1922, 44, 2665–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Corroller, P.; Favis, B.D. Droplet-in-Droplet Polymer Blend Microstructures: A Potential Route toward the Recycling of Co-mingled Plastics. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2012, 213, 2062–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostofi, N.; Nazockdast, H.; Mohammadigoushki, H. Study on morphology and viscoelastic properties of PP/PET/SEBS ternary blend and their fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 3737–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolhasani, M.M.; Arefazar, A.; Mozdianfard, M. Effect of dispersed phase composition on morphological and mechanical properties of PET/EVA/PP ternary blends. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.R.; Calderon, J.U.; Lennox, B.R. Surface energy of modified nanoclays and its effect on polymer/clay nanocomposites. J. Adhes Sci. Technol. 2009, 23, 663–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglietto, M.; Coltelli, M.B.; Savi, S.; Lochiatto, F.; Ciardelli, F.; Giani, M. Postconsumer polyethylene terephthalate (PET)/polyolefin blends through reactive processing. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2004, 6, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Altobelli, R.; Salzano De Luna, M.; Filippone, G. Interfacial crowding of nanoplatelets in co-continuous polymer blends: Assembly, elasticity and structure of the interfacial nanoparticle network. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 6465–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippone, G.; Dintcheva, N.T.; La Mantia, F.P.; Acierno, D. Selective localization of organoclay and effects on the morphology and mechanical properties of LDPE/PA11 blends with distributed and co-continuous morphology. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, M.L. Spherulite growth rates in binary polymer blends. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2003, 28, 663–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nor Arman, N.S.; Chen, R.S.; Ahmad, S.; Shahdan, D. Mechanical and physical characterizations of compatibilizer-free recycled plastics blend composites modified with carbon nanotube and clay nanofiller. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pötschke, P.; Paul, D.R. Formation of co-continuous structures in melt-mixed immiscible polymer blends. J. Macromol. Sci. Polym. Rev. 2003, 43, 87–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
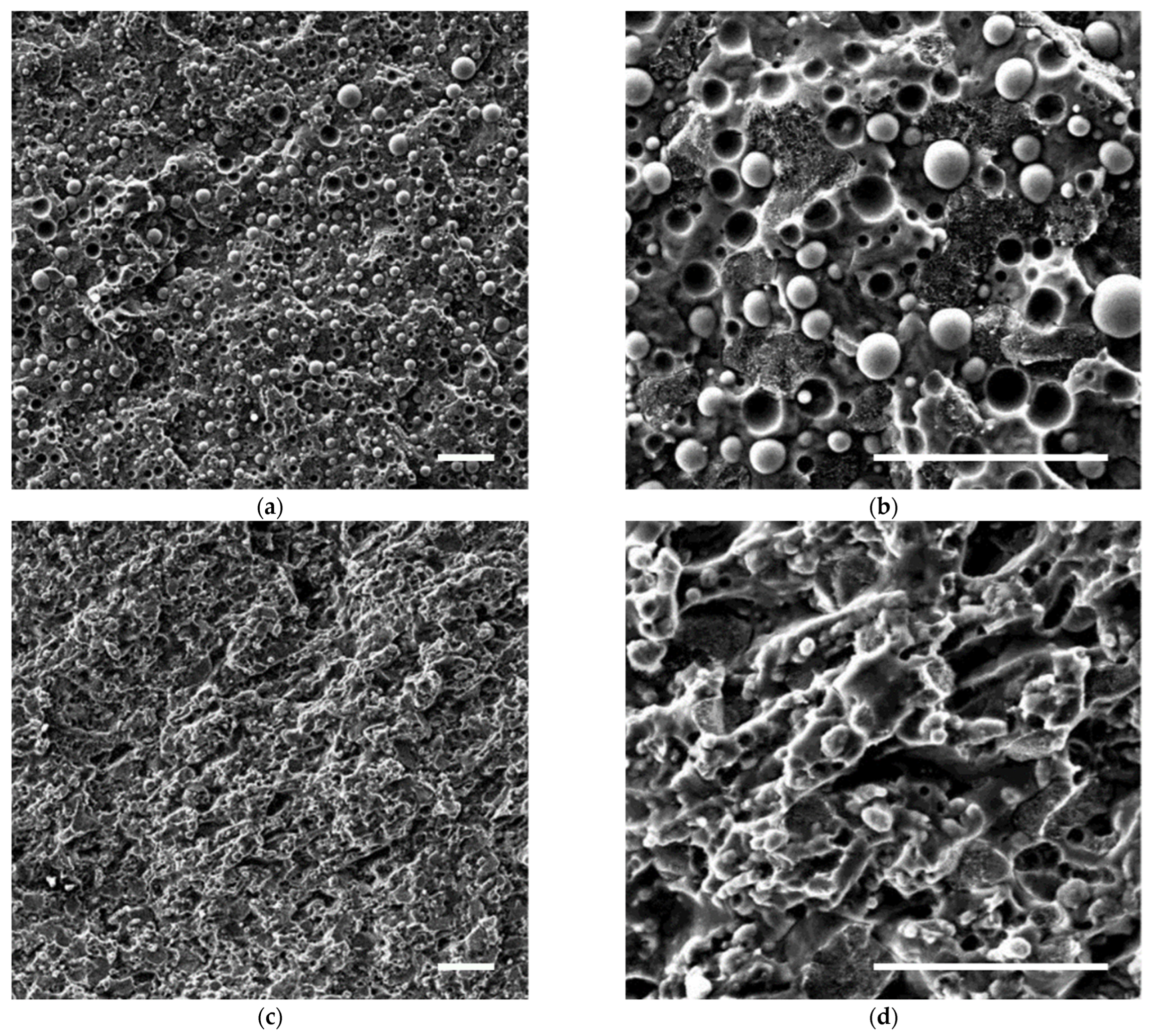


| Sample | HDPE [wt.%] | PP [wt.%] | PET [wt.%] | C15A [phr] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE/PP/PET | 37.5 | 37.5 | 25 | 0 |
| HDPE/PP/PET | 37.5 | 37.5 | 25 | 2 |
| −1.09 | |
| −10.20 | |
| −0.68 |
| −2.85 | |
| 1.08 | |
| −10.40 | |
| −10.61 | |
| −2.63 | |
| −0.27 | |
| −8.85 | |
| −0.47 | |
| −2.43 |
| −2.22 | |
| −0.60 | |
| −0.90 |
| Sample | Phase in the Blend | Tm [°C] | Tc [°C] | χ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDPE | 134.4 ± 1.2 | 117.1 ± 0.7 | 65.8 ± 1.8 | |
| PP | 164.4 ± 0. 9 | 117.9 ± 1.3 | 40.3 ± 2.4 | |
| PET | 250.9 ± 0.4 | 202.5 ± 5.0 | 28.9 ± 3.1 | |
| HDPE/PP/PET | HDPE | 133.4 ± 0.7 | 117.7 ± 1.2 | 66.1 ± 2.0 |
| PP | 162.9 ± 0.9 | 30.7 ± 1.1 | ||
| PET | 244.9 ± 1.5 | 202.4 ± 2.7 | 18.2 ± 1.8 | |
| HDPE/PP/PET+C15A | HDPE | 132.6 ± 0.5 | 114.6 ± 1.0 | 58.3 ± 3.9 |
| PP | 165.0 ± 1.0 | 29.0 ± 2.7 | ||
| PET | 252.1 ± 0.2 | 196.6 ± 1.2 | 21.2 ± 3.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marotta, A.; Causa, A.; Salzano de Luna, M.; Ambrogi, V.; Filippone, G. Tuning the Morphology of HDPE/PP/PET Ternary Blends by Nanoparticles: A Simple Way to Improve the Performance of Mixed Recycled Plastics. Polymers 2022, 14, 5390. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245390
Marotta A, Causa A, Salzano de Luna M, Ambrogi V, Filippone G. Tuning the Morphology of HDPE/PP/PET Ternary Blends by Nanoparticles: A Simple Way to Improve the Performance of Mixed Recycled Plastics. Polymers. 2022; 14(24):5390. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245390
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarotta, Angela, Andrea Causa, Martina Salzano de Luna, Veronica Ambrogi, and Giovanni Filippone. 2022. "Tuning the Morphology of HDPE/PP/PET Ternary Blends by Nanoparticles: A Simple Way to Improve the Performance of Mixed Recycled Plastics" Polymers 14, no. 24: 5390. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245390
APA StyleMarotta, A., Causa, A., Salzano de Luna, M., Ambrogi, V., & Filippone, G. (2022). Tuning the Morphology of HDPE/PP/PET Ternary Blends by Nanoparticles: A Simple Way to Improve the Performance of Mixed Recycled Plastics. Polymers, 14(24), 5390. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14245390








