Characterization, Properties and Mixing Mechanism of Rubber Asphalt Colloid for Sustainable Infrastructure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Tire Rubber and Its Degradation Behavior
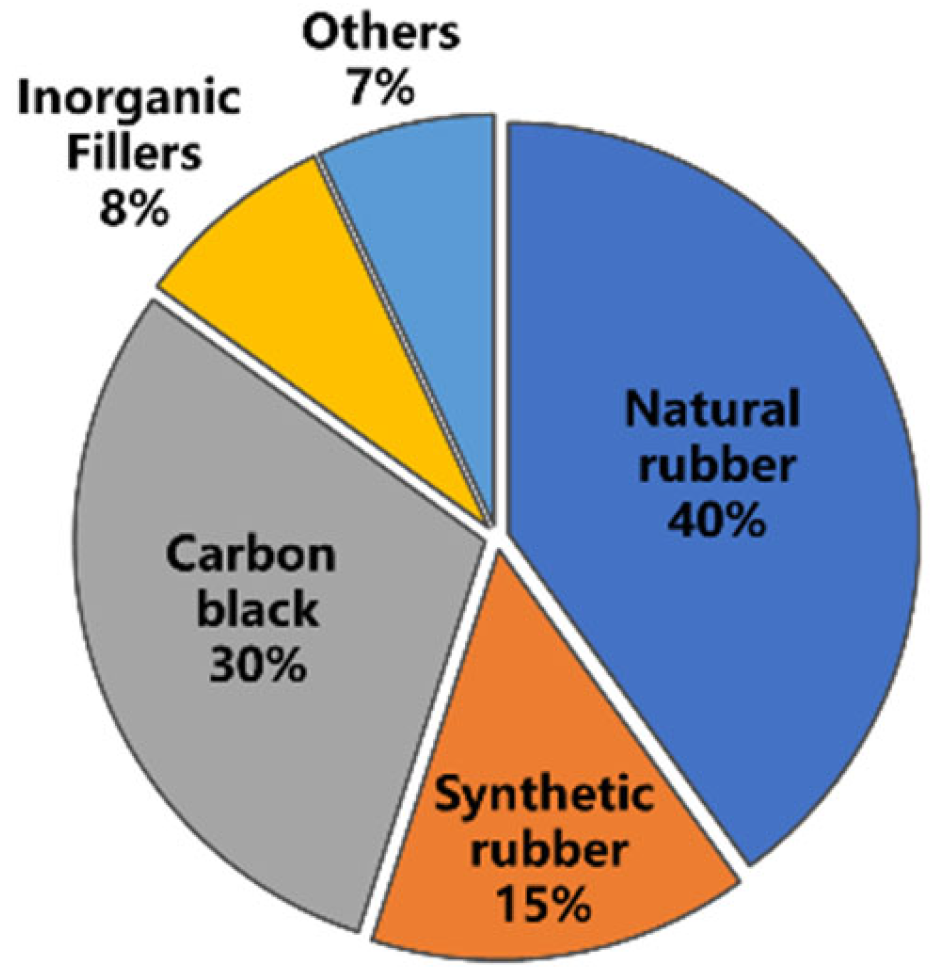
2.1. Chemical Composition of Tire Rubber
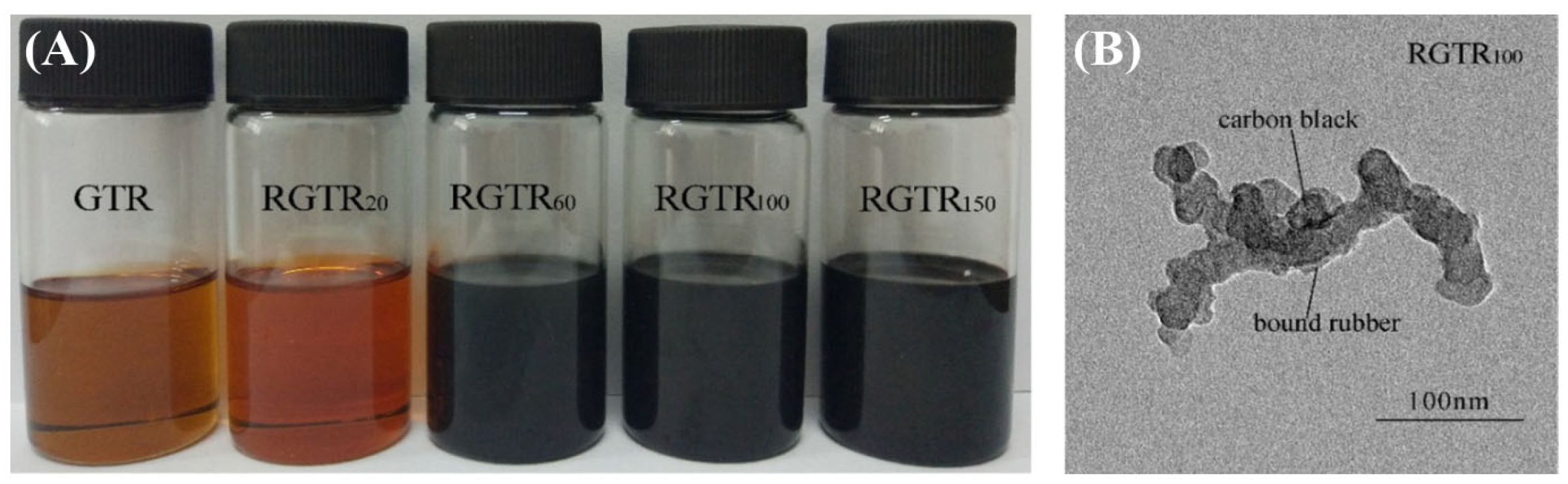
2.2. Degradation Behavior of Tire Rubber
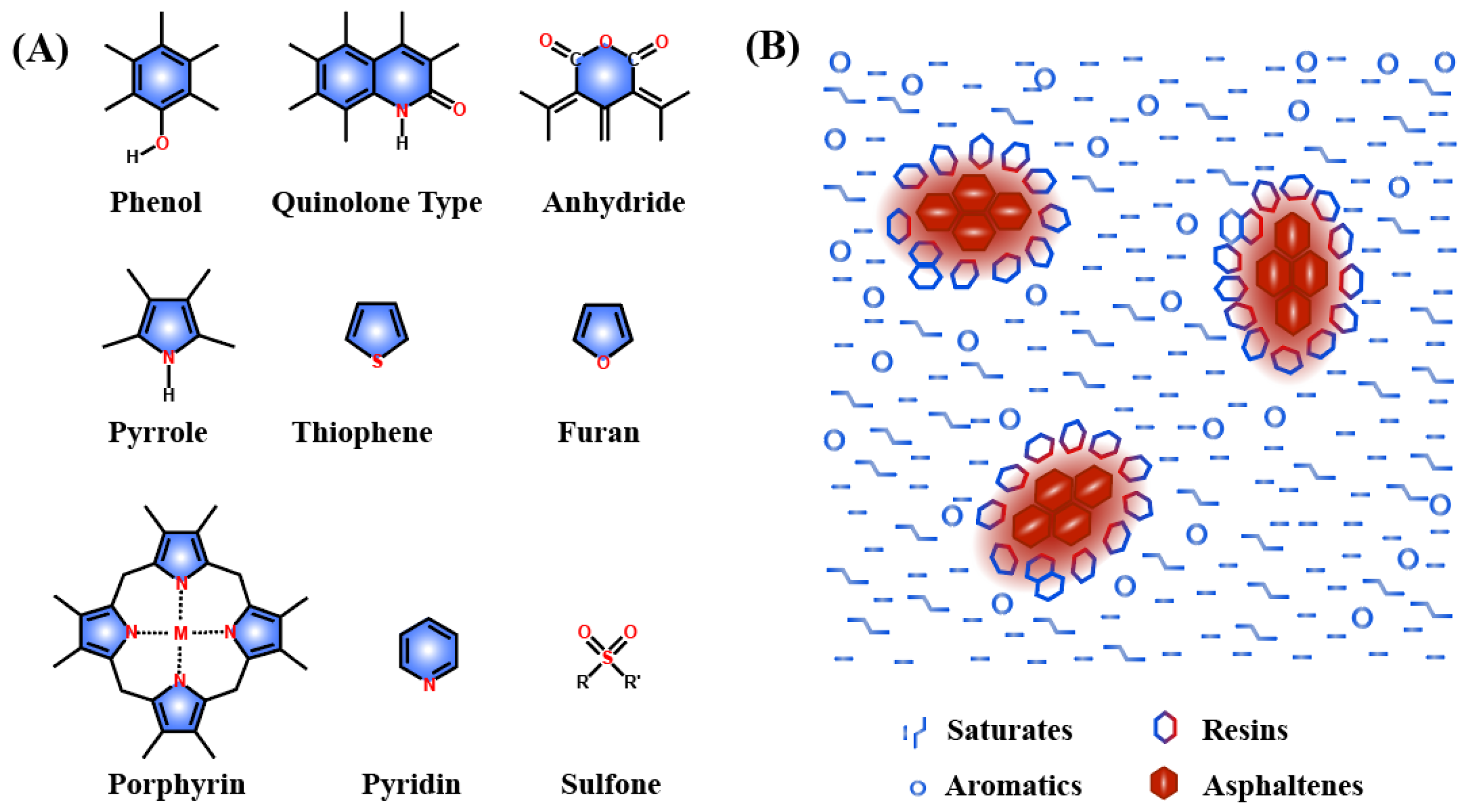
3. Colloidal Structure of Asphalt
4. Mixing Mechanism of DR with Asphalt
4.1. Distribution of Typical Elements and Functional Groups
4.2. Interactions between DR and Asphalt
4.3. Compatibility of DR and Asphalt
4.4. Colloidal Structure of DRMA
5. Sustainability of Rubberized Asphalt
5.1. Performance for Rubber Asphalt Pavement
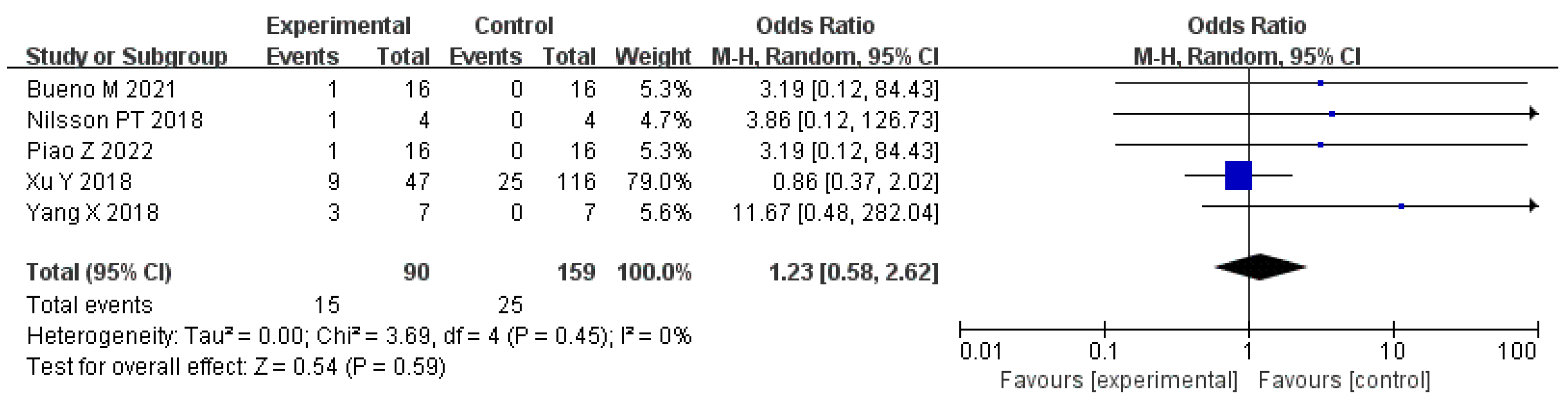
5.2. Emissions and Environmental Effects
5.3. Economic Effects
5.4. Applications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Czajczyńska, D.; Krzyyńska, R.; Jouhara, H.; Spencer, N. Use of pyrolytic gas from waste tire as a fuel: A review. Energy 2017, 134, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joulazadeh, M.H. Environmental friendly consumption of scrap tires in eaf’s to save power and carbon. Metall. Foundry Eng. 2008, 34, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Turner, A.; Rice, L. Toxicity of tire wear particle leachate to the marine macroalga, Ulva lactuca. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3650–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Occurrence and effects of tire wear particles in the environment–A critical review and an initial risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.-T. Use of ground tire rubber in asphalt pavements: Field trial and evaluation in Taiwan. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2008, 52, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; You, Z.; Mills-Beale, J.; Hao, P. Laboratory evaluation on high temperature viscosity and low temperature stiffness of asphalt binder with high percent scrap tire rubber. Construct. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; You, Z.; Wu, G.; Kong, L.; Liu, C.; Gao, J. Measurement and modeling of skid resistance of asphalt pavement: A review. Construct. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dang, Z.; Li, L.; You, Z. Analysis on fatigue crack growth laws for crumb rubber modified (CRM) asphalt mixture. Construct. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanasom, N.; Saowapark, T.; Deeprasertkul, C. Reinforcement of natural rubber with silica/carbon black hybrid filler. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wan, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y. Separation of core-shell structured carbon black nanoparticles from waste tires by light pyrolysis. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 135, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Dong, R. Lightly pyrolyzed tire rubber used as potential asphalt alternative. Construct. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Zhou, S.; Wang, S. Structural evolution of recycled tire rubber in asphalt. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 42954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, R.; Zhu, H.; Huang, W. Emission behavior of crumb rubber modified asphalt in the production process. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Dong, R.; Shi, C.; Yang, J.; Leng, Z. The influence of the mass ratio of crumb rubber and waste cooking oil on the properties of rubberised bio-rejuvenator and rejuvenated asphalt. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Mikhailenko, P.; Piao, Z.; Fini, E.H.; Pei, J.; Poulikakos, L.D. Unraveling the modification mechanisms of waste bio-oils and crumb rubber on asphalt binder based on microscopy and chemo-rheology. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 185, 106447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Li, S.; Wang, S. Interfacial interaction between degraded ground tire rubber and polyethylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 143, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaro, L.; Gratton, M.; Seghar, S.; Hocine, N.A. Recycling of rubber wastes by devulcanization. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2018, 133, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akca, E.; Gursel, A.; Sen, N. A review on devulcanization of waste tire rubber. Period. Eng. Nat. Sci. (PEN) 2018, 6, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopi, J.A.; Patel, S.K.; Chandra, A.K.; Tripathy, D.K. SBR-clay-carbon black hybrid nanocomposites for tire tread application. J. Polym. Res. 2011, 18, 1625–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angellier, H.; Molina-Boisseau, S.; Lebrun, L.; Dufresne, A. Processing and structural properties of waxy maize starch nanocrystals reinforced natural rubber. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 3783–3792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockelhuber, K.; Svistkov, A.; Pelevin, A.; Heinrich, G. Impact of filler surface modification on large scale mechanics of styrene butadiene/silica rubber composites. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4366–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrus, S.S.; Ismail, H.; Palaniandy, S. Study of the effect of different shapes of ultrafine silica as fillers in natural rubber compounds. Polym. Test. 2011, 30, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.B. Rubber Basics; iSmithers Rapra Publishing: Shropshire, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Franta, I. Elastomers and Rubber Compounding Materials, Manufacture, Properties and Application; Elvevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Song, P.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, S.; Wang, S. Recycling the nanostructured carbon from waste tires. Compos. Commun. 2018, 7, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wan, C.; Xie, Y.; Formela, K.; Wang, S. Vegetable derived-oil facilitating carbon black migration from waste tire rubbers and its reinforcement effect. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seghar, S.; Asaro, L.; Rolland-Monnet, M.; Hocine, N.A. Thermo-mechanical devulcanization and recycling of rubber industry waste. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 144, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.C.; Liao, X.X.; Liao, S.Q.; Zhao, Y.F. Review on the Broken Three-Dimensional Network Modification Methods of Waste Rubber Powder, Advanced Materials Research; Trans Tech Publication: Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 181–186. [Google Scholar]
- Markl, E.; Lackner, M. Devulcanization technologies for recycling of tire-derived rubber: A review. Materials 2020, 13, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wemyss, A.M.; Wan, C.; Liu, Y.; Song, P.; Wang, S. Effective thermal-oxidative reclamation of waste tire rubbers for producing high-performance rubber composites. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 9079–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, J.L. Rubber–filler interactions and rheological properties in filled compounds. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2002, 27, 627–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Abbas, A.; Rasheed, T.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.; Wang, S. Development, influencing parameters and interactions of bioplasticizers: An environmentally friendlier alternative to petro industry-based sources. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 682, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tur Rasool, R.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Improving the aging resistance of SBS modified asphalt with the addition of highly reclaimed rubber. Construct. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesueur, D. The colloidal structure of bitumen: Consequences on the rheology and on the mechanisms of bitumen modification. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 42–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, L.W. Composition of asphalt based on generic fractionation, using solvent deasphaltening, elution-adsorption chromatography, and densimetric characterization. Anal. Chem. 1969, 41, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.; Abdollahi, T.; Pahlavan, F.; Fini, E.H. The influence of asphaltene-resin molecular interactions on the colloidal stability of crude oil. Fuel 2016, 183, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, W.; Tang, N.; Hu, J.; Lin, P.; Guan, W.; Xiao, F.; Shan, Z. Evolution of components distribution and its effect on low temperature properties of terminal blend rubberized asphalt binder. Construct. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Lin, P.; Tang, N.; Hu, J.; Xiao, F. Effect of crumb rubber degradation on components distribution and rheological properties of Terminal Blend rubberized asphalt binder. Construct. Build. Mater. 2017, 151, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, W.; Lin, P. Low-Temperature and Fatigue Characteristics of Degraded Crumb Rubber–Modified Bitumen Before and After Aging. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 04021493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Xiao, F.; Wang, J.; Amirkhanian, S. Identification of asphalt aging characterization by spectrophotometry technique. Fuel 2018, 226, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Pei, J.; Li, R.; Li, P.; Zhou, B. The preparation and characterization of a novel self-healing based on the dynamic translocation of disulfide bonds. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 105301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Xin, X.; Fan, W.; Sun, H.; Yao, Y.; Xing, B. Viscous properties, storage stability and their relationships with microstructure of tire scrap rubber modified asphalt. Construct. Build. Mater. 2015, 74, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Internal de-crosslinking of scrap tire crumb rubber to improve compatibility of rubberized asphalt. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 32, e00417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Tang, B.; He, L.; Yang, F.; Wang, H.; Ling, J. Compatibility of cured phase-inversion waterborne epoxy resin emulsified asphalt. Construct. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ji, J.; You, Z.; Zhang, Y. A review on compatibility between crumb rubber and asphalt binder. Construct. Build. Mater. 2021, 297, 123820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Lv, Q.; Huang, W.; Lin, P.; Yan, C. Chemical and rheological evaluation of aging characteristics of terminal blend rubberized asphalt binder. Construct. Build. Mater. 2019, 205, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Ouyang, C. Weather aging resistance of different rubber modified asphalts. Construct. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiao, F.; Zhu, X.; Huang, B.; Wang, J.; Amirkhanian, S. Energy consumption and environmental impact of rubberized asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 180, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Deng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Gong, M.; Oeser, M. Workability of rubberized asphalt from a perspective of particle effect. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2021, 91, 102712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, O.; Rangaraju, P.R.; Wang, S.; Xiao, F. Comparison of rheological properties and hot storage characteristics of asphalt binders modified with devulcanized ground tire rubber and other modifiers. Construct. Build. Mater. 2017, 154, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dong, B.; Zhao, D.; Guo, P.; Zhang, J. Physical, rheological and stability properties of desulfurized rubber asphalt and crumb rubber asphalt. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 5043–5056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, S.; Kutay, M.E. Effect of devulcanized rubber modification on the performance grade, fatigue cracking resistance, and rutting resistance of asphalt binders. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, L.; Formela, K.; Wang, S. Impact and stretching standardized tests as useful tools for assessment of viscoelastic behavior for highly rubberized asphalt binder. Construct. Build. Mater. 2022, 348, 128650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. Swelling process of rubber in asphalt and its effect on the structure and properties of rubber and asphalt. Construct. Build. Mater. 2012, 29, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, T.; Pei, J.; Amirkhanian, S.; Xiao, F.; Ye, Q.; Fan, Z. Low temperature and fatigue characteristics of treated crumb rubber modified asphalt after a long term aging procedure. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Pei, J.; Hu, D.; Fini, E.H. Durability of rubberized asphalt binders containing waste cooking oil under thermal and ultraviolet aging. Construct. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 124282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, G.; Chen, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, H. Evaluation of aging resistance for high-performance crumb tire rubber compound modified asphalt. Construct. Build. Mater. 2019, 218, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, A.; Li, M.; Fini, E.H. Effects of Elemental Sulfur on the Aging Trajectory and Adhesion Characteristics of Rubber-Modified Bitumen. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 16918–16925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Rahmani, Z.; Zahedi, M.; Nasrollahi, M. Technical, economic, and environmental investigation of the effects of rubber powder additive on asphalt mixtures. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2020, 146, 04019039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picado-Santos, L.G.; Capitão, S.D.; Neves, J.M. Crumb rubber asphalt mixtures: A literature review. Construct. Build. Mater. 2020, 247, 118577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-Z.; Wang, N.-N.; Tseng, M.-L.; Huang, Y.-M.; Li, N.-L. Waste tire recycling assessment: Road application potential and carbon emissions reduction analysis of crumb rubber modified asphalt in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 249, 119411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Sun, C.; Yao, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Ren, S. Utilization of wax residue as compatibilizer for asphalt with ground tire rubber/recycled polyethylene blends. Construct. Build. Mater. 2020, 230, 116966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Zanetti, M.C.; Santagata, E.; Blengini, G.A. Life cycle assessment applied to bituminous mixtures containing recycled materials: Crumb rubber and reclaimed asphalt pavement. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 117, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukvar, M.; Tatari, O. Ecologically based hybrid life cycle analysis of continuously reinforced concrete and hot-mix asphalt pavements. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2012, 17, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boom, Y.J.; Enfrin, M.; Grist, S.; Giustozzi, F. Recycled plastic modified bitumen: Evaluation of VOCs and PAHs from laboratory generated fumes. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 832, 155037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borinelli, J.B.; Blom, J.; Portillo-Estrada, M.; Maeijer, P.K.D.; den Bergh, W.V.; Vuye, C. VOC Emission Analysis of Bitumen Using Proton-Transfer Reaction Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Materials 2020, 13, 3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, P.T.; Bergendorf, U.; Tinnerberg, H.; Nordin, E.; Gustavsson, M.; Strandberg, B.; Albin, M.; Gudmundsson, A. Emissions into the Air from Bitumen and Rubber Bitumen-Implications for Asphalt Workers’ Exposure. Ann. Work Expo. Health 2018, 62, 828–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; You, Z.; Perram, D.; Hand, D.; Ahmed, Z.; Wei, W.; Luo, S. Emission analysis of recycled tire rubber modified asphalt in hot and warm mix conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, M.; Haag, R.; Heeb, N.; Mikhailenko, P.; Boesiger, L.; Poulikakos, L.D. Functional and environmental performance of plant-produced crumb rubber asphalt mixtures using the dry process. Mater. Struct. 2021, 54, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Karedal, M.; Nielsen, J.; Adlercreutz, M.; Bergendorf, U.; Strandberg, B.; Antonsson, A.B.; Tinnerberg, H.; Albin, M. Exposure, respiratory symptoms, lung function and inflammation response of road-paving asphalt workers. Occup. Environ. Med. 2018, 75, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, Z.; Bueno, M.; Poulikakos, L.D.; Hellweg, S. Life cycle assessment of rubberized semi-dense asphalt pavements; A hybrid comparative approach. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 176, 105950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, M.F.; Nelson, P.O.; Thayumanavan, P.; Williamson, K.J. Environmental impact of highway construction and repair materials on surface and ground waters. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Temperature/°C | (104 g/mol) | (104 g/mol) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 220 | 1.19 | 6.12 | 5.12 |
| 240 | 1.25 | 6.01 | 4.79 |
| 260 | 1.42 | 6.89 | 4.84 |
| 280 | 1.34 | 6.29 | 4.70 |
| 300 | 0.41 | 2.28 | 5.57 |
| Fractions | H/C | C (%) | H (%) | O (%) | N (%) | S (%) | Mn (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asphalt | 1.5 | 80–88 | 8–12 | 0–2 | 0–2 | 0–9 | 600–1500 |
| Saturates | 1.9 | 78–84 | 12–14 | <0.1 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 470–880 |
| Aromatics | 1.5 | 80–86 | 9–13 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0–4 | 570–980 |
| Resins | 1.4 | 67–88 | 9–12 | 0.3–2 | 0.2–1 | 0.4–5 | 780–1400 |
| Asphaltenes | 1.1 | 78–88 | 7–9 | 0.3–5 | 0.6–4 | 0.3–11 | 800–3500 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, S. Characterization, Properties and Mixing Mechanism of Rubber Asphalt Colloid for Sustainable Infrastructure. Polymers 2022, 14, 4429. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204429
Zhang L, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Wang H, Wang S. Characterization, Properties and Mixing Mechanism of Rubber Asphalt Colloid for Sustainable Infrastructure. Polymers. 2022; 14(20):4429. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204429
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lu, Chuanping Zhang, Zhen Zhang, Hanbing Wang, and Shifeng Wang. 2022. "Characterization, Properties and Mixing Mechanism of Rubber Asphalt Colloid for Sustainable Infrastructure" Polymers 14, no. 20: 4429. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204429
APA StyleZhang, L., Zhang, C., Zhang, Z., Wang, H., & Wang, S. (2022). Characterization, Properties and Mixing Mechanism of Rubber Asphalt Colloid for Sustainable Infrastructure. Polymers, 14(20), 4429. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14204429





