Abstract
Lignin is a natural biopolymer. A vibrant and rapid process in the synthesis of silica nanoparticles by consuming the lignin as a soft template was carefully studied. The extracted biopolymer from coir pith was employed as capping and stabilizing agents to fabricate the silica nanoparticles (nSi). The synthesized silica nanoparticles (nSi) were characterized by ultraviolet–visible (UV–Vis) spectrophotometry, X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDAX), Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). All the results obtained jointly and independently verified the formation of silica nanoparticles. In addition, EDAX analysis confirmed the high purity of the nSi composed only of Si and O, with no other impurities. XRD spectroscopy showed the characteristic diffraction peaks for nSi and confirmed the formation of an amorphous nature. The average size of nSi obtained is 18 nm. The surface charge and stability of nSi were analyzed by using the dynamic light scattering (DLS) and thus revealed that the nSi samples have a negative charge (−20.3 mV). In addition, the seed germination and the shoot and root formation on Vigna unguiculata were investigated by using the nSi. The results revealed that the application of nSi enhanced the germination in V. unguiculata. However, further research studies must be performed in order to determine the toxic effect of biogenic nSi before mass production and use of agricultural applications.
1. Introduction
There is a broad consensus that the nanoparticle is a material with at least one dimension less than 100 nm. Nanoparticles can be distinguished into nanopowders, nanoclusters, nanocrystals and many other groups which can be further subdivided [1]. At the end of the 20th century, nanotechnology was perceived as the next game-changer [2]. Based on the laboratory experiments, as more and more nanomaterials of different compositions, sizes and shapes became available [3], dramatic changes were predicted to improve human lives [4]. Nanomaterials showed varied optical, catalytic, magnetic and other chemical–physical characteristics, including distinct biological properties, such as antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory activities [5]. Most of these excellent properties have been repeatedly and independently confirmed in the chemical industry [6], metal production [7], agriculture [8] and energetics [9] (Mardoyan and Braun 2015), to name a few. However, as fast as the nano industry grew initially, it hit its upper limit about a decade ago, and a price ceiling has been slowing down its further development since then [10]. A plethora of methods have been developed to synthesize various nanomaterials of different characteristics. The two most important production directions are A/electrochemical and chemical reduction [11] and B/photochemical and physical vapor condensation [12]. Carbon nanotubes, quantum dots, nanorods, nano capsules, nano emulsions, fullerenes, metallic nanoparticles, ceramic nanoparticles and polymer nanoparticles hold the largest market share [13,14], whereas usual wholesale prices range from 4 to 18 €g−1 [15]. Although these conventional production processes make it possible to achieve nanoparticles with perfect shapes and a purity higher than 99.995%, it is the high production costs (about 90% of the market price) that block further industry development [16,17]. To make matters worse, all of these various combinations of chemical and physical methods are energy demanding and require hazardous reagents (mostly stabilizing and reducing agents) during almost all production phases [18], not to mention various biological risks to the environment [19]. Hence, there is a wide demand for the definition of less demanding production technologies that would improve the competitiveness of the entire nanotechnology industry [20].
Si and SiO2 nanomaterials have drawn more attention by various entrepreneurs due to their widespread application in the advance of new technologies in various areas [21,22]. They have a wide range of applications in industries such as agriculture, pharmacy, pigments, catalysis, electronics and cosmetics [23,24]. There are numerous types of nSi, including non-porous, mesoporous, hollow mesoporous and core–shell, all of which can be modified on the surface [25,26]. Mesoporous nSi have few flexible and desirable properties, such as biocompatibility, tenable pore size and volume for delivery of targeted drugs [27]. Using Tetra ethyl ortho silicate [Si(OC2H5)4,TEOS] as a precursor is the most straightforward and cost-effective method for producing spherical, monodispersed and nanosized nSi [28]. In plants, silica is important for inducing resistance against the biotic and abiotic stresses [29]. The recent advances in nanotechnology and its use in agriculture fields are astonishingly increasing to improve crop production [30].
There are various methods, namely Sol-Gel, reverse microemulsion and flame-synthesis methods employed in extracting silica from waste materials. The Sol-Gel method is the most common approach for research purposes. The original method of Stöber et al. [31] has largely altered and modified the synthesis of silica via hydrolysis–condensation reaction. The polymeric networks of gels were formed from silicon alkoxide/halide gels, and polymeric gel is otherwise known as as xerogel [32]. Many silica-based nanomaterials and derivatives are produced by using the Sol-Gel method. The acids HCl, H2SO4, carboxylic acid, citric acid and nitric acid have been utilized for the production of highly pure amorphous silica from rice husks and oil palm ash [33,34,35]. TEOS is a Sol-Gel precursor for the production of silica-based nanomaterials, because it is able to bond with polymers via the creation of a link between the hydroxyl group of polymers and silanol groups through covalent and hydrogen bonds [36]. This research motivated us to use alternative sources of production of silica nanoparticles.
Coir pith is a by-product of padding that is employed in mattress factories. It is a lignocellulosic biomass that is produced during the extraction of coir fiber from coconut husk [37]. It has a huge amount of lignin. It accumulates near coir processing industries as a waste product and caused environmental and disposal complications. The raw coir pith comprises 30% lignin, 26.5% cellulose, 26% carbon and 17.5% others [38]. Hence, this investigation focused on the usage of coir pith in the production of nanosilica.
Following the abovementioned, our hypothesis addressed whether it might be environmentally and techno-economically reasonable to produce nSi via the acidic Sol-Gel method (biopolymer and TEOS as Si precursor) as a tool to improve seed germination (shoot and root formation, in particular).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction of Lignin Form Coir Pith
Raw coir pith was obtained from the coir-processing industry. It was cut 2 cm, and the biomass obtained was immediately washed under running tap water for about 5 min and then with 20 L of distilled water until no impurities remained. A total of 20 g of powdered coir pith was treated with 200 mL of toluene–ethanol (2:1 ratio (v/v)) for dewaxing process. Then lignin was extracted from dewaxed coir pith through the alkali extraction method. After that, a dark brownish solution was attained and separated via filtration. Next, the filtrate was concentrated by using a hot-air oven at 60 °C. The ethanol and HCl were mixed to remove the soluble cellulose. The extracted lignin was kept at −4 °C for production of nanomaterials. The amount of lignin (24.5 ± 2.5 g/kg) from the coir pith was assessed by using the protocols of Periakaruppan et al. [39].
2.2. nSi Synthesis
A total of 100% of coir pith mediated lignin (obtained according to Section 2.1) was mixed with 12.5 mL of Tetraethyl orthosilicate (99% purity, CAS 78-10-4, MERCK Inc., Darmstadt, Germany) as a precursor and ethanol (95%, MERCK Inc., Darmstadt, Germany) and continuously stirred for 10 min at room temperature. Then 1 M HCl (99% purity, CAS 30827-99-7, MERCK Inc., Darmstadt, Germany) was added to the mixture and slowly stirred for 15 min at room temperature. At the end, the jelly-like precipitation was formed. The precipitate was kept for 10 h in an EKOCELL drier (MMM Group, Planegg, Germany) at 90 °C for drying. The white-color powder was obtained at the last, and it was stored in an airtight plastic container for further studies [19] (Al-Azawi et al., 2019). Here, lignin and its monomers acted as reducing and capping agents for the formation of silica nanoparticles. Lignin and TEOS were reacted and formed as silica nanoparticles through polymerization. Lignin was an effective chelating agent.
2.3. nSi Characterization
Lignin-mediated nSi was slowly dissolved (1:10) in distilled water of analytical purity and sonicated (five 20 kHz cycles) via UP100H ultrasonic homogenizer (Hielscher Ultrasonics, Teltow, Germany) via the at room temperature. The absorption maxima of nSi solution were determined by the C10082MD (Hamamatsu, Japan) UV–Visible spectrophotometer from 200 to 800 nm. Then nSi was placed on the quartz slide, and then the IFS 66v/S vacuum FTIR spectrometer (Bruker optics, Woodlands, TX, USA) was employed to observe the FTIR spectra of materials in the range of 4000–400 cm−1. An X-ray diffractometer (XRD) was used to analyze the nature of nSi. The sizes of the nSi samples were calculated by the Scherrer’s formula. The surface morphology of synthesized silica nanoparticles was observed by using the JSM–7610F Schottky field emission scanning electron microscope (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan). Epsilon Xflow (Malvern P Analytical, Ltd., Malvern, United Kingdom) energy-dispersive X–ray analyzer (EDAX) was used to find out the elemental composition (atomic weight percentage of elements) of the nSi. The zeta potential of the nSi was determined by the measurement of the electrophoretic mobility, using the LS 13 320 XR (Beckman Coulter, Inc., Pasadena, CA, USA) particle-size analyzer. The thermal stability of synthesized silica nanoparticle was assessed by TGA/DSC 3+ (Mettler Toledo, Columbus, OH, USA) thermogravimetric analyzer with a small furnace.
2.4. Agricultural Application
Seeds of V. unguiculata were obtained from a local botany garden. The collected seeds were surface sterilized with Savo Original (Unilever, Prague, Czech Republic) liquid disinfectant and washed three times with distilled water. Four different concentrations (25%, 50%, 75% and 100%) of nSi were prepared by using distilled water and denoted as T1, T2, T3 and T4, respectfully. The control (distilled water) was maintained and referred to as T5. Then, sterile Petri dishes were taken, and 10 seeds were placed on them. The 5 mL of respective concentration of nSi was poured on the corresponding Petri plates. Next, all of the plates were placed at room temperature in dark condition for 3 days. Three independent replications were made for this study. Seeds with a root tip of 1 cm and higher were considered as the germinated seeds. Lengths of roots and shoots (in cm) were observed after 3 days of incubation. After germination, the lengths of roots and shoots of V. unguiculata were measured.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Physiochemical Characterization
3.1.1. Analysis of Optical Properties
The UV–visible absorption spectra of nSi were recorded as depicted in Figure 1. The absorption spectra of nSi were found to be 280–350 nm. The bandgap vibration of electronic transition was found at the broad value of 305 nm for soluble silica suspension. In line with this, Patil et al. [40] concluded that the UV–visible spectrum of nSi displayed the maximum absorption band edge of 310 nm. The optical property of silica nanomaterials is related to the occurrence of various defects caused by the partial formation of a Si-O-Si tetrahedral network at the surface, namely silicon and oxygen vacancies.
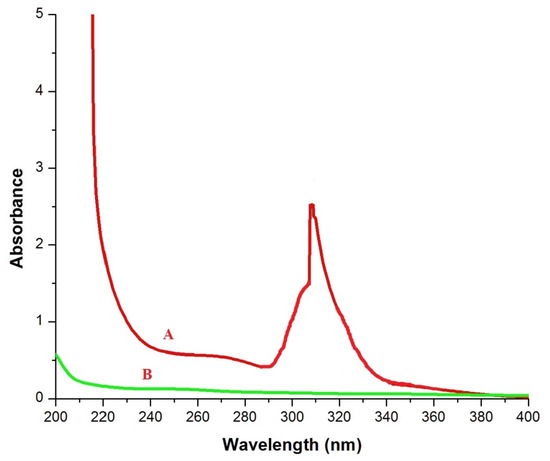
Figure 1.
UV spectra, where A = nSi and B = extracted lignin from coir pith. (Optical property was assessed).
3.1.2. Analysis of Functional Groups
FTIR characterization is routinely used to identify the molecules and their functional group present in the synthesized nSi. As shown in Figure 2, the FTIR spectra of lignin displayed different peaks at 3363, 2137, 1643, 1388, 678 and 555 cm−1, whereas the FTIR spectrum of the nSi produced successive absorption peaks at 1064, 948, 794, 555 and 424 cm−1. The oxide group of nSi was observed at 794, 555 and 424 cm−1, respectively. The FTIR analysis concludes that the formation of silica nanoparticles through the presence of asymmetric stretching vibration of Si-O-Si at 3363 cm−1 and another peak at 948 cm−1 refers to Si-OH bond. A peak at 424 cm−1 corresponds to Si-O-Si bending (Figure 2). Shoulder (Si-O-Si) asymmetric stretch was observed at a peak of 1064 cm−1. The bands at 794 and 948 cm1 are connected with the complex Si-O-Si symmetric bond stretching vibration. A peak of 2978 cm−1 denotes the C=O vibrations. An absorption peak at 1643 cm−1 corresponding to the amide I bond of proteins formed due to carbonyl stretch (Figure 2B). Yadav et al. [41] and Imoisili et al. [42] reported similar FTIR signals for their nSi.
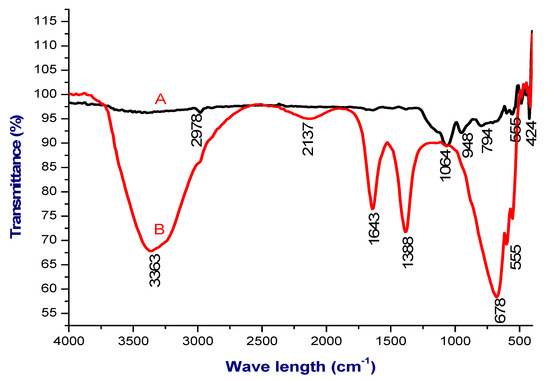
Figure 2.
FTIR spectra, where A = nSi and B = extracted lignin from coir pith. (Metal oxide group of the nSi was observed).
3.1.3. XRD Analysis
XRD was used to determine the structure of nanoparticles. Figure 3 shows the XRD analysis of chemically synthesized nSi. The XRD pattern of nSi displays a strong narrow and sharp peak, indicating that the nSi samples obtained are of high quality and have an amorphous nature. The XRD of the nSi revealed the characteristic peaks at 101 planes and the amorphous nature at a diffraction angle of 2ϴ = 20°. The average size was calculated by using the Scherrer equation (D = KλβCosθ−1), where D is the size, λ is the wavelength of X-ray, θ is the Braggs angle (in radians) and β is the full width at half maximum of the peak (in radians). The average size of synthesized nSi is 18 nm. Similarly, Rojas et al. [43] reported that their Si synthesized from rice husk exhibited a most prominent peak at 2θ = 22.01°, corresponding to the (101) plane. The silica nanoparticles produced by Ghani et al. [44] had an amorphous nature and It was confirmed through XRD analysis. Silica nanoparticles were synthesized by using the raw materials of rice hulls in a simple and inexpensive method, and synthesized silica nanomaterials had an amorphous structure [45]. The amorphous structure of nano-SiO2 was predicated by using the XRD technique [46].
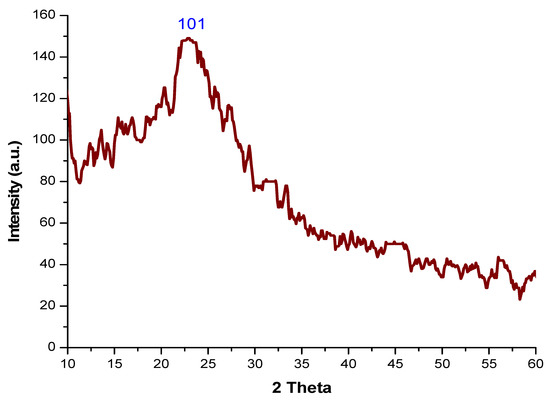
Figure 3.
XRD analysis of nSi.
3.1.4. SEM Analysis
The SEM image of nSi synthesized by using extracted lignin from coir pith is presented in Figure 4. The newly proposed method revealed the monodispersed distribution of particle sizes in the surface morphology, as well as the size of nSi. The images display the spherical nature of nSi. It depicts mostly spherical nSi specimens, as well as the number of aggregates, and some of them represent nanoparticles with an undefined shape. The results presented are corroborated with Verma et al. [47], who synthesized the spherical-shaped nSi, and the morphology was indirectly confirmed by using SEM analysis.
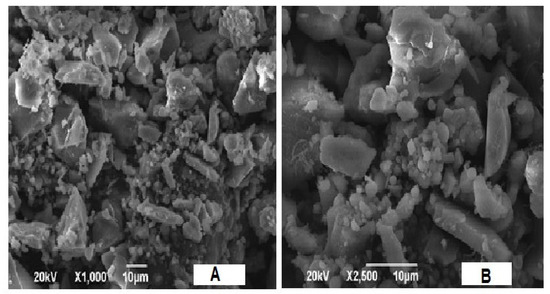
Figure 4.
SEM images of nSi. (Spherical-shaped nSi was observed.) (A = X1000 and B = X2500).
3.1.5. EDAX Analysis
EDAX analysis confirms the purity of the nSi formed by extracted lignin from coir pith. Figure 5 displays the spectra of nSi, using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDAX). Only the signal peaks corresponding to Si (25.58%), O (41.58%), Na (12.12%) and Cl (20.72%) (Table 1) were visible in the spectra. The EDX spectrum obtained shows that the peaks refer to silica and oxygen, indicating that the prepared nanoparticles are silica. From the results, it was confirmed that impurity elements, such as sodium and chloride, are present in the samples. Na and Cl were derived from partially purified lignin because lignin from coir pith was purified and concentrated by HCl and NaOH. In the same manner, Kao et al. [48] observed a closely related result of nSi synthesized from chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) steel substrate and reported that the nanoparticles that resulted were clearly composed of Si and O elements.
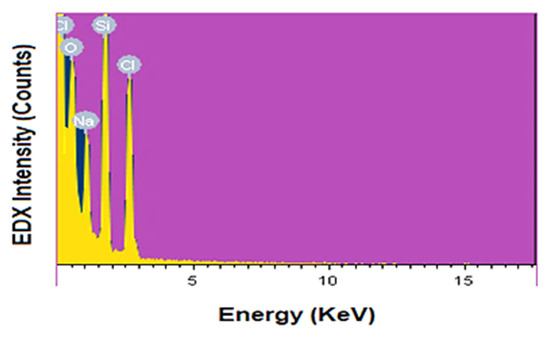
Figure 5.
EDX spectra of nSi. (Purity and weight of elements were assessed).

Table 1.
Elemental composition for nSi.
3.1.6. Analysis of Zeta Potential and Thermal Stability
Zeta potential analysis is used to assess the electrophoretic mobility of nanomaterials. The zeta potential of synthesized nSi was –20.3 mV (Figure 6). The synthesized nanomaterials have a negative charge and are highly stable. Babu et al. [49] demonstrated the green approach for the synthesis of nSi from Cynodondactylon. They performed the zeta potential studies and reported a zeta potential value of nSi(−23.3 mV). Figure 7 refers to the spectrum of thermal stability for the synthesized nSi obtained. A 35% weight loss occurred at 150 °C, and gradually the weight reduced up to 45% at 1000 °C. It shows that totally 45% of weight loss appeared between 100 and 1000 °C in nSi. The weight loss was attributed to the loss of organic solvents and hydroxyl groups from nSi (it was investigated by the exothermic peak in the DTA curve), where the silanol groups were dehydrated at the end. Ethanol was employed during the synthesis of nSi. The hydroxyl group were fabricated with nSi, and the loss occurred between 50 to 150 °C. The weight of nSi was stable at the range of 200–1000 °C. The result clearly determined that the reduction of weight loss occurs at increased heat treatment. The weight loss occurred as a result of the decomposition and evaporation of the organic content of the modified silica nanoparticles [50]. The loss of residual organic solvent and physisorbed water from lignin-mediated silica nanoparticles occurred at 150 °C. These results clearly reveal that the degree increase resulted from the reduction of the amount of the modified nanosilica [50].
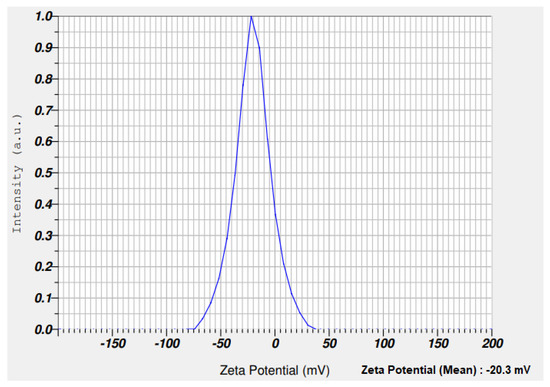
Figure 6.
Zeta potential analysis of nSi. (Stability of nSi was assessed, and nSi has a negative charge).
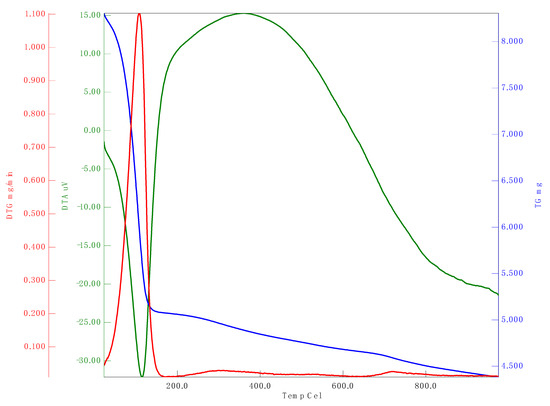
Figure 7.
TGA analysis of nSi. (Weight loss at different temperatures was observed.) Red line, DTG; blue line, TG; green line, DTA.
3.1.7. Market Analysis
The market analysis shows that wholesale pricing of nSi of similar characteristics is somewhere in the range of 2.4 up to 3.3 € g−1. The cost breakdown (Table 2) shows that the production cost of the nSi obtained by this technology might be expected to be around 1.3 €g−1, from which a high degree of cost competitiveness can be expected [51].

Table 2.
Cost breakdown of the nSi production.
3.2. Agricultural Application
With regard to the industrial application, it is evident that the seed germination and shoot and root length of V. unguiculata were improved by the lowest concentration of nSi (Table 3). The maximum seed germination was obtained after 72 h. The root and shoot lengths of the seedling were significantly higher in the T1 treatment (25% of nSi), whereas the minimum seed germination was observed for the T3 treatment (75% of nSi). The shoot and root lengths were minimized at a high concentration of nSi-treated V. unguiculata. The lowest concentration of silica nanoparticles stimulated the biochemical metabolism for better seed germination and root and shoot formation. The highest concentration of nanoparticles inhibited the seed germination through the blocking of the biochemical metabolism. Similarly, the elongation of the root and shoot, the relative water content (RWC) and the activity of photosynthetic pigments were enhanced in Zea mays by the treatment of silica nanoparticles [52].

Table 3.
Seed-germination analysis.
4. Conclusions
A method to synthesize nSi without using harmful chemicals was demonstrated. The nSi were synthesized by using lignin and TEOS as silica precursors. Lignin acts as a capping, stabilizing and reducing agent for the synthesis of nSi.
The amorphous nature of nSi was confirmed by XRD analysis, and no crystalline phase was observed. The fabrication of nSi occurred due to crosslinking of lignin.
FTIR analysis of nSi revealed the formation of a Si-O-Si symmetric bond. A 45% of weight loss was observed by TGA analysis, due to the evaporation of the organic content of the modified nSi.
Characteristics by UV–visible spectroscopy, XRD, SEM, EDAX, FTIR and zeta potential analysis confirmed that the nSi specimens obtained meet all of the established commercial standards (average nanoparticle size obtained is 18 nm).
In addition, the low concentration of nSi was found to enhance the germination of seedling. Taking into account that the production costs are also lower than the conventional chemical and physical methods, it can be assumed that the presented technology hides an interesting commercial potential. This synthesis condition is so fascinating from the economical point of view for mass production of nSi in industrial scales.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization & funding acquisition, J.M.; validation, A.M.; supervision & writing—review and editing, R.P.; investigation & writing—original draft preparation G.M.G.; data curation, A.A.; project administration, A.B.; visualization, P.K.; resources, J.B.; data curation, P.Č.; data curation, formal analysis, P.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to restrictions eg privacy or ethical.
Acknowledgments
The authors thankfully acknowledge the Karpagam Academy of Higher Education for providing the laboratory facilities to conduct the experiments, and also the authors acknowledge the DST–FIST fund for infrastructure facility (SR/FST/LS–1/2018/187).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sriram, T.; Pandidurai, V. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles from leaf extract of Psidium guajava and its antibacterial activity against pathogens. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2014, 3, 146–152. [Google Scholar]
- Skapa, S. Investment characteristics of natural monopoly companies. J. Compet. 2012, 4, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Saini, S.; Sharma, S. Nanotechnology: The future medicine. J. Cutan. Aesthetic Surg. 2010, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungerman, O.; Dedkova, J.; Gurinova, K. The impact of marketing innovation on the competitiveness of enterprises in the context of industry 4. J. Compet. 2018, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saranya, S.; Vijayarani, K.; Pavithra, S. Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using aqueous extract of Musa ornata flower sheath against pathogenic bacteria. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 79, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliestik, T.; Nica, E.; Musa, H.; Poliak, M.; Mihai, E.A. Networked, Smart, and Responsive Devices in Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Systems. Econ. Manag. Financ. Mark. 2020, 15, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hadzima, B.; Janeček, M.; Estrin, Y.; Kim, H.S. Microstructure and corrosion properties of ultrafine–grained interstitial free steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 462, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stávková, J.; Maroušek, J. Novel sorbent shows promising financial results on P recovery from sludge water. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardoyan, A.; Braun, P. Analysis of Czech subsidies for solid biofuels. Int. J. Green Energy 2015, 12, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.; Kliestik, T.; Musa, H.; Durana, P. Product decision–Making information systems, real–time big data analytics, and deep learning–enabled smart process planning in sustainable industry 4. J. Self–Gov. Manag. Econ. 2020, 8, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, P. Biosynthesis of nanoparticles using eco–friendly factories and their role in plant pathogenicity: A review. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2018, 2, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Snehal, S.; Lohani, P. Silica nanoparticles: Its green synthesis and importance in agriculture. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 3383–3393. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Henríquez, L.; Alfaro-Aguilar, K.; Ugalde-Álvarez, J.; Vega-Fernández, L.; Montes de Oca-Vásquez, G.; Vega-Baudrit, J.R. Green Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles from Plant Extracts and Their Possible Applications as Antimicrobial Agents in the Agricultural Area. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroušek, J.; Maroušková, A.; Kůs, T. Shower cooler reduces pollutants release in production of competitive cement substitute at low cost. Energy Sources Part. A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2020, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwaiwu, F. Review and comparison of conceptual frameworks on digital business transformation. J. Compet. 2018, 10, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbancova, H. Competitive advantage achievement through innovation and knowledge. J. Compet. 2013, 5, 82–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muo, I.; Azeez, A.A. Green Entrepreneurship: Literature Review and Agenda for Future Research. Int. J. Entrep. Knowl. 2019, 7, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.K.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U.C. Synthesis of metallic nanoparticles using plant extracts. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Azawi, M.T.; Hadi, S.M.; Mohammed, C.H. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles via green approach by using hot aqueous extract of Thujaorientalis leaf and their effect on biofilm formation. Iraqi J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 50, 245–255. [Google Scholar]
- Blazkova, I.; Dvoulety, O. Sectoral and firm–level determinants of profitability: A multilevel approach. Int. J. Entrep. Knowl. 2018, 6, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Munir, S.; Zeb, N.; Ullah, A.; Khan, B.; Ali, J.; Bilal, M.; Omer, M.; Alamzeb, M.; Salman, S.M.; et al. Green nanotechnology: A review on green synthesis of silver nanoparticles—An ecofriendly approach. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopchuk, O.; Prokopchuk, I.; Mentel, G. Index Insurance as an Innovative Tool for Managing Weather Risks in the Agrarian Sector of Economics. J. Compet. 2018, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.P.; Agarwal, S.K.; Bhattacharyya, S.K.; Sharma, U.; Ahalawat, S. Preparation of silica nanoparticles and its beneficial role in cementitious materials. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2011, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedina, D.; Sanova, P. Creating a competitive advantage by developing an innovative tool to assess suppliers in agri–food complex. J. Compet. 2013, 5, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mushtaq, A.; Jamil, N.; Riaz, M.; Hornyak, G.L.; Ahmed, N.; Ahmed, S.S.; Shahwani, M.N.; Malghani, M.N.K. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles and their effect on priming of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under salinity stress. Biol. Forum 2017, 9, 150–157. [Google Scholar]
- Kasaai, M.R. Nanosized particles of silica and its derivatives for applications in various branches of food and nutrition sectors. J. Nanotechnol. 2015, 2015, 852394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, V.; Obuobi, S.; Ee, P.L.R. Silica Nanoparticles—A Versatile Tool for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.A. and Padavettan, V. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles by Sol-Gel: Size–dependent properties, surface modification, and applications in silica–polymer nanocomposites—A review. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 132424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Serafy, R.S. Silica nanoparticles enhances physio–biochemical characters and postharvest quality of Rosa hybrida L. cut flowers. J. Hortic. Res. 2019, 27, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judit, O.; Péter, L.; Péter, B.; Mónika, H.R.; József, P. The role of biofuels in food commodity prices volatility and land use. J. Compet. 2017, 9, 81–93. [Google Scholar]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, N.S.; Sapawe, N. Optimization of silica (SiO2) synthesis from acid leached oil palm frond ash (OPFA) through sol-gel method. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 31, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, J.; Kondoh, K. High-purity amorphous silica originated in rice husks via carboxylic acid leaching process. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 7084–7090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, F.; Appaturi, J.N.; Thankappan, R.; Nawi, M.A.M. Silica–tin nanotubes prepared from rice husk ash by Sol-Gel method: Characterization and its photocatalytic activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizul, C.P.; Abdullah, C.; Fazlul, B. Extraction of silica from palm ash using citric acid leaching treatment: Preliminary result. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 795, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; De Sarkar, M.; Bhowmick, A.K. Poly (vinyl alcohol)/silica hybrid nanocomposites by sol-gel technique: Synthesis and properties. J. Mater. Sci. 2005, 40, 5233–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksabye, P.; Thiravetyan, P.; Nakbanpote, W. Column study of chromium (VI) adsorption from electroplating industry by coconut coir pith. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 160, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, V.; Kavitha, J.R.; Kamaleshwaran, R.; Prabharan, P.; Alagendran, S. Effect of coir pith compost in agriculture. J. Med. Plants 2021, 9, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Periakaruppan, R.; Li, J.; Mei, H.; Yu, Y.; Hu, S.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Guo, G. Agro–waste mediated biopolymer for production of biogenic nano iron oxide with superparamagnetic power and antioxidant strength. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, N.B.; Sharanagouda, H.; Doddagoudar, S.R.; Ramachandra, C.T.; Ramappa, K.T. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Silica Nanoparticles from Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Husk. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, 7, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.K.; Fulekar, M.H. Green synthesis and characterization of amorphous silica nanoparticles from fly ash. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 18, 4351–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoisili, P.E.; Ukoba, K.O.; Jen, T.C. Green technology extraction and characterisation of silica nanoparticles from palm kernel shell ash via Sol-Gel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 9, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, D.F.H.; Gómez, P.P.; Rivera, A.R. Production and characterization of silica nanoparticles from rice husk. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2019, 10, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, N.N.A.; Saeed, M.A.; Hashim, I.H. Thermoluminescence (TL) response of silica nanoparticles subjected to 50 Gy gamma irradiation. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2017, 13, 178–180. [Google Scholar]
- Nallathambi, G.; Ramachandran, T.; Rajendran, V.; Palanivelu, R. Effect of silica nanoparticles and BTCA on physical properties of cotton fabrics. Mater. Res. 2011, 14, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Xu, Z.; Li, W.; Shen, X. Effect of nano-SiO2 on the early hydration of alite-sulphoaluminate cement. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Bhattacharya, A. Analysis on synthesis of silica nanoparticles and its effect on growth of T. Harzianum & Rhizoctonia species. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 10, 7890–7897. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, M.J.; Hsu, F.C.; Peng, D.X. Synthesis and characterization of SiO2 nanoparticles and their efficacy in chemical mechanical polishing steel substrate. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 691967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, R.H.; Yugandhar, P.; Savithramma, N. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial studies of bio silica nanoparticles prepared from Cynodondactylon, L.: A green approach. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2018, 41, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Guo, J.; Zang, L.; Luo, J. In situ synthesis of poly (methyl methacrylate)/SiO2 hybrid nanocomposites via “grafting onto” strategy based on UV irradiation in the presence of iron aqueous solution. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 217412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vochozka, M.; Rowland, Z.; Suler, P.; Marousek, J. The influence of the international price of oil on the value of the EUR/USD exchange rate. J. Compet. 2020, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi Rad, J.; Karimi, J.; Mohsenzadeh, S.; Sharifi Rad, M.; Moradgholi, J. Evaluating SiO2 nanoparticles effects on developmental characteristic and photosynthetic pigment contents of Zea mays L. Bull. Environ. Pharm. Life Sci. 2020, 3, 194–201. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).