Highly Flame-Retardant and Low Heat/Smoke-Release Wood Materials: Fabrication and Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
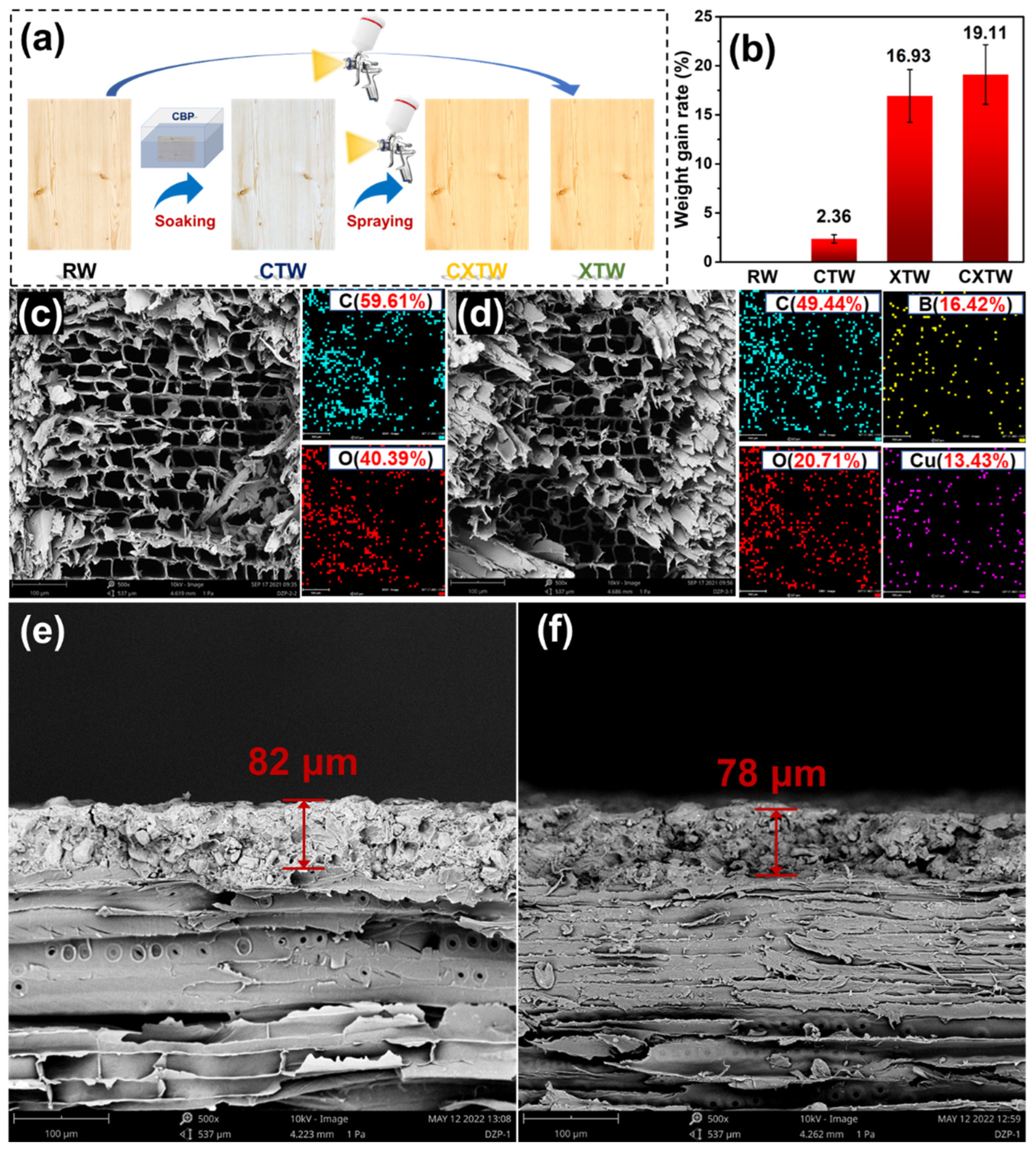
2.2. Preparation of Fireproof and Preservative Wood
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology Characterization and Menchanical Preoperties
3.2. Thermal Decomposition Behavior
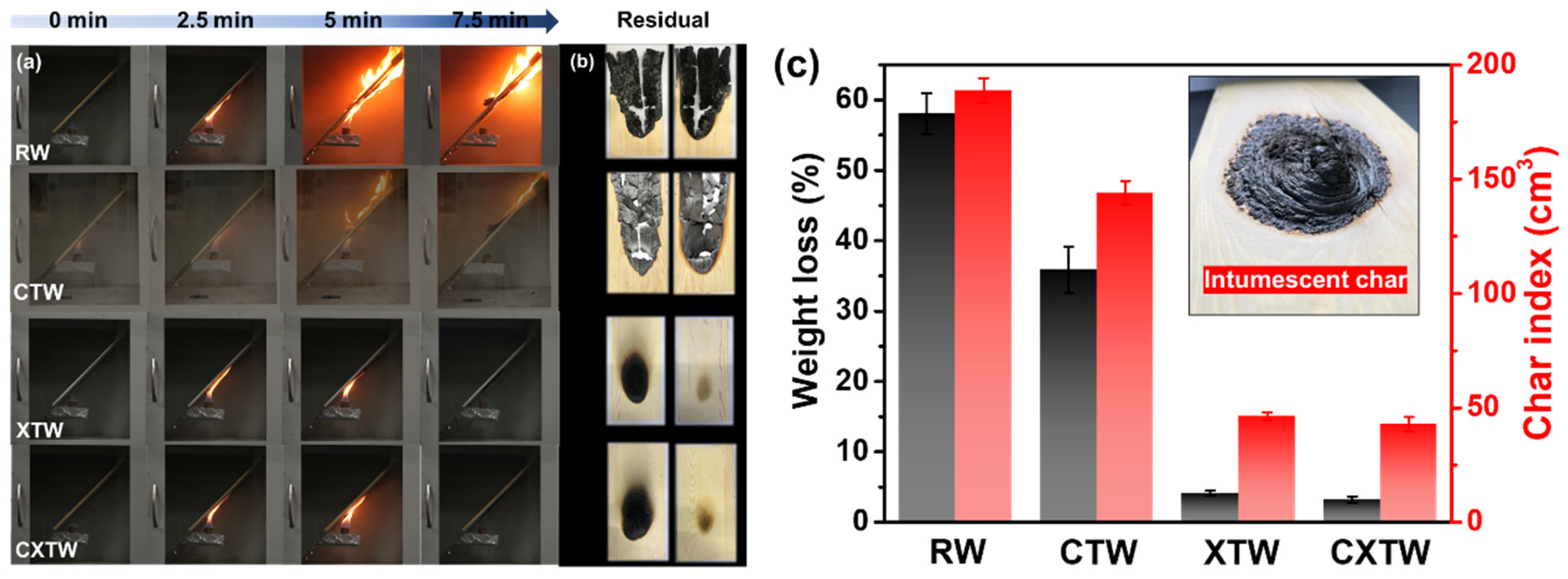
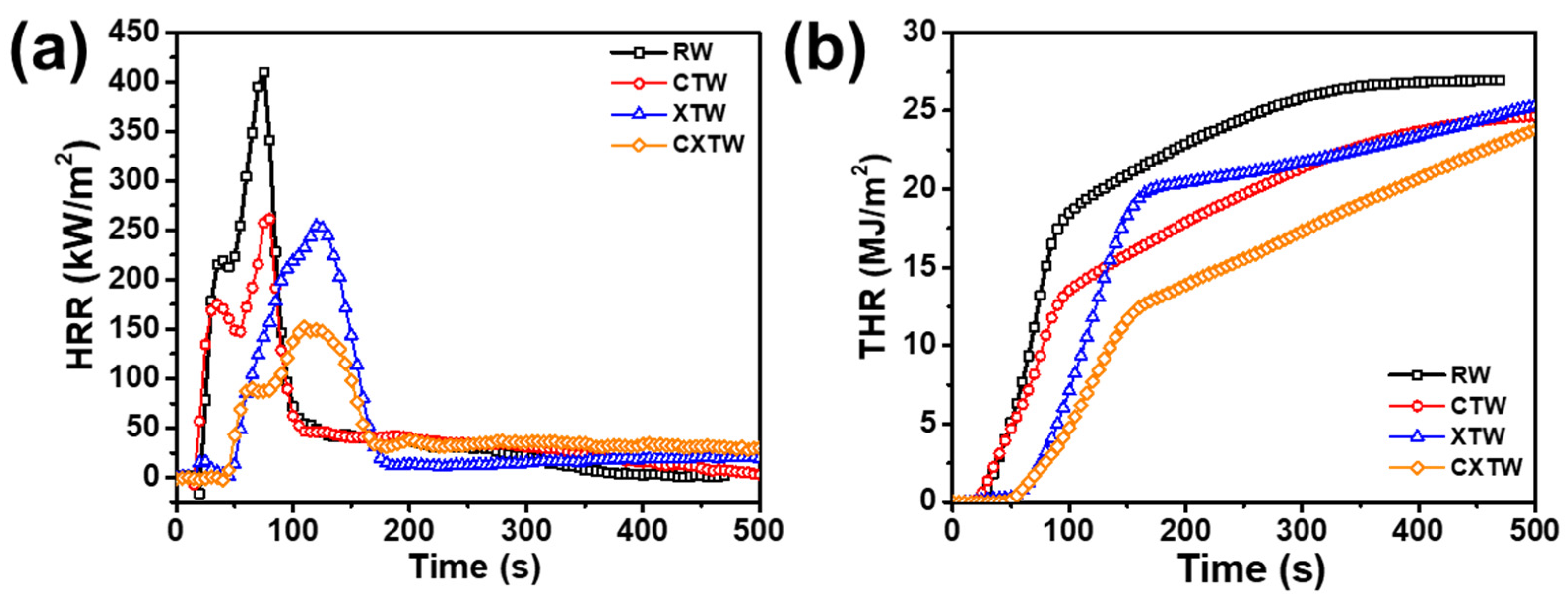
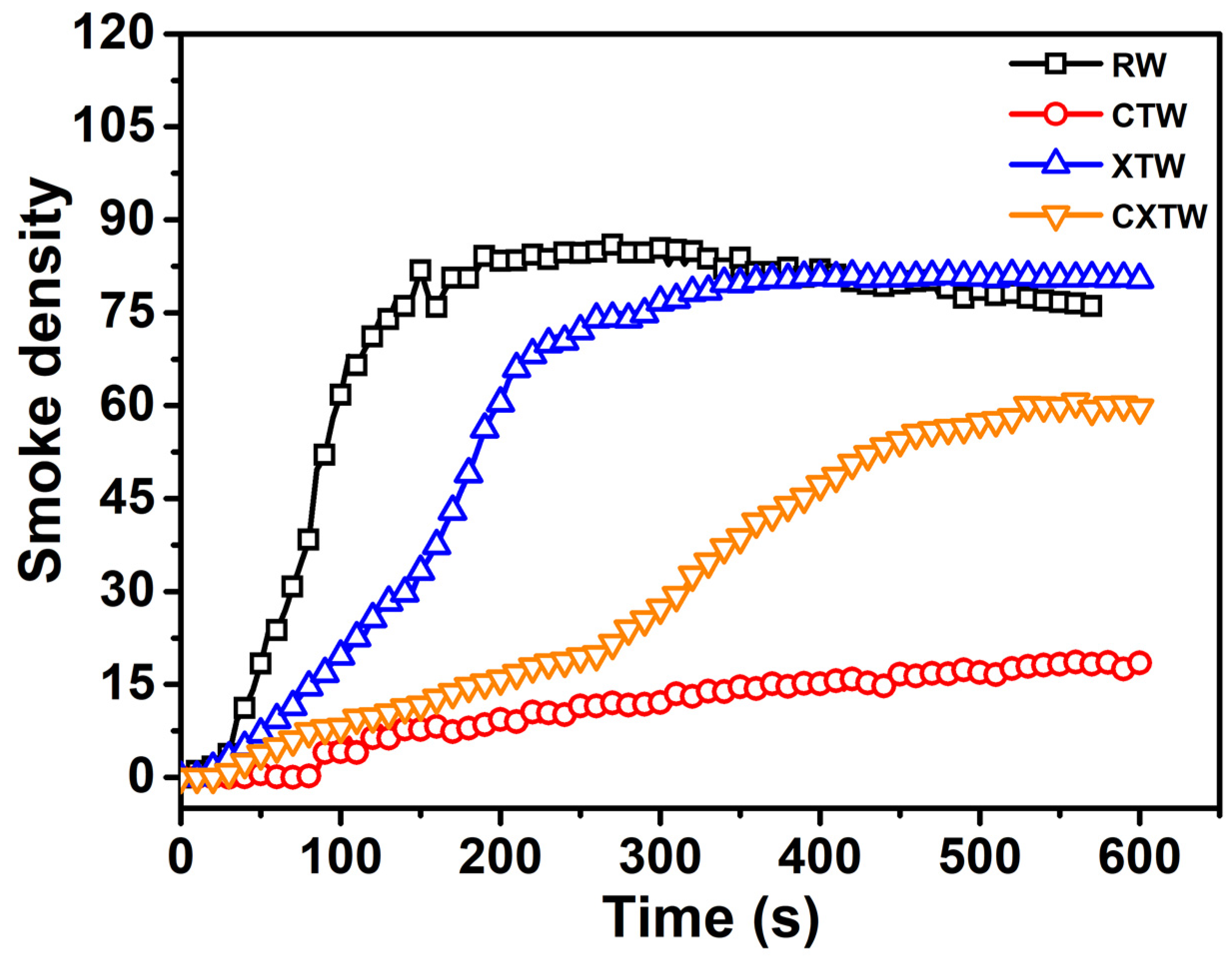
3.3. Flam- Retardant Properties
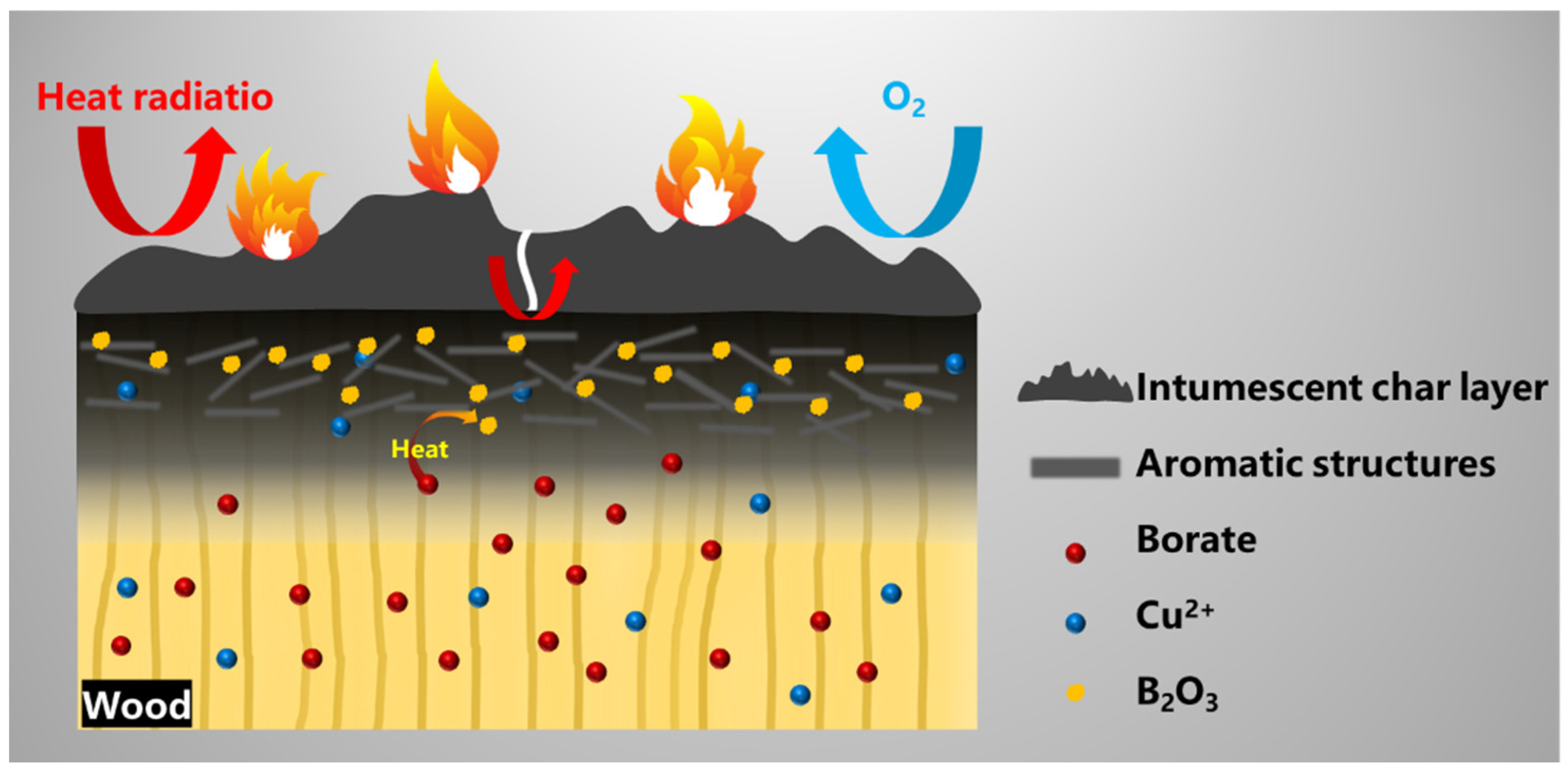
3.4. Char Residue Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gan, W.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Song, J.; Kuang, Y.; He, S.; Mi, R.; Sunderland, P.B.; Hu, L. Dense, Self-Formed Char Layer Enables a Fire retardant Wood Structural Material. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1807444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, M.; Yang, Z.; Song, J.; Dai, J.; Yao, Y.; Luo, W.; Pastel, G.; Yang, B.; Hu, L. Wood Composite as an Energy Efficient Building Material: Guided Sunlight Transmittance and Effective Thermal Insulation. Adv. Energy. Mater. 2016, 6, 1601122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmers, G. Wood: A construction material for tall buildings. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 17051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pondelak, A.; Škapin, A.S.; Knez, N.; Knez, F.; Pazlar, T. Improving the flame retardancy of wood using an eco-friendly mineralisation process. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocco, V.F.; Paes, J.B.; Costa, L.G.D.; Brazolin, S.; Arantes, M.D.C. Potential of teak heartwood extracts as a natural wood preservative. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2093–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soula, M.; Samyn, F.; Duquesne, S.; Landry, V. Innovative polyelectrolyte treatment to flame-retard wood. Polymers 2021, 13, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Meng, D.; Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S. Impregnation of phytic acid into the delignified wood to realize excellent flame retardant. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2022, 176, 114364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Landry, V.; Blanchet, P.; Hoang, D.-T.; Dagenais, C. Fire Performance of Intumescent Waterborne Coatings with Encapsulated APP for Wood Constructions. Coatings 2021, 11, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xu, Z.; Liu, D. Synthesis and application of novel magnesium phosphate ester flame retardants for transparent intumescent fire-retardant coatings applied on wood substrates. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 129, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.C.; Fu, J.H.; Peng, Y.X.; Jiao, X.M.; Liu, H.; Du, F.P.; Zhang, Y.F. Dual-functional intumescent fire-retardant/self-healing water-based plywood coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 154, 106187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, C.-L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.-S.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.-Z. An efficiently halogen-free flame-retardant long-glass-fiber-reinforced polypropylene system. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popescu, C.-M.; Pfriem, A. Treatments and modification to improve the reaction to fire of wood and wood based products—An overview. Fire Mater. 2020, 44, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingston, J.A.; Collins, C.D.; Murphy, R.J.; Lester, J.N. Leaching of chromated copper arsenate wood preservatives: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 111, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.H.; Oh, S.C.; Choi, I.-G.; Han, G.-S.; Jeong, H.-S.; Kim, K.-W.; Yoon, Y.-H.; Yang, I. Environmentally friendly wood preservatives formulated with enzymatic-hydrolyzed okara, copper and/or boron salts. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Yuan, H.; Huhetaoli; Qi, Y.; Lv, P.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, Y. Characterization of the decomposition behaviors of catalytic pyrolysis of wood using copper and potassium over thermogravimetric and Py-GC/MS analysis. Energy 2016, 114, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowski, P. Catalytic effects of copper(II) chloride and aluminum chloride on the pyrolytic behavior of cellulose. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2012, 98, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, H. Efficient Flame-Retardant and Smoke-Suppression Properties of Mg–Al-Layered Double-Hydroxide Nanostructures on Wood Substrate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 23039–23047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poletto, M.; Zattera, A.J.; Forte, M.M.C.; Santana, R.M.C. Thermal decomposition of wood: Influence of wood components and cellulose crystallite size. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 109, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-J.; Yang, H.-S. Thermal properties of bio-flour-filled polyolefin composites with different compatibilizing agent type and content. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 451, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cao, M.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Chao, X.; Mai, B.; Li, Y.; Cao, J. Borate-Modified, Flame-Retardant Paper Packaging Materials for Archive Conservation. J. Renew. Mater. 2022, 10, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, M. Thermal stability and flame retardancy of guanidinium and imidazolium borate finished cotton fabrics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2014, 118, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowden, L.A.; Hull, T.R. Flammability behaviour of wood and a review of the methods for its reduction. Fire Sci. Rev. 2013, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Wu, W.; Wu, H.; Xie, J.; Xu, J. Study on the effects of flame retardants on the thermal decomposition of wood by TG–MS. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 103, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X. Influence of nano-silica on the flame retardancy and smoke suppression properties of transparent intumescent fire retardant coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 112, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, K.-C. Orientation effect on cone calorimeter test results to assess fire hazard of materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babrauskas, V.; Peacock, R.D. Heat release rate: The single most important variable in fire hazard. Fire Saf. J. 1992, 18, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grześkowiak, W.Ł. Evaluation of the effectiveness of the fire retardant mixture containing potassium carbonate using a cone calorimeter. Fire Mater. 2012, 36, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-F.; Karlsson, O.; Kim, I.; Myronycheva, O.; Mensah, R.A.; Försth, M.; Das, O.; Mantanis, G.I.; Jones, D.; Sandberg, D. Fire Retardancy and Leaching Resistance of Furfurylated Pine Wood (Pinus sylvestris L.) Treated with Guanyl-Urea Phosphate. Polymers 2022, 14, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Liu, T.; Fan, Q.; Li, D.; Ou, R.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q. Sustainable, high-performance, flame-retardant waterborne wood coatings via phytic acid based green curing agent for melamine-urea-formaldehyde resin. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 162, 106597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zeng, S.; Xu, Y.; Nie, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, P. Epoxy-modified silicone resin based N/P/Si synergistic flame-retardant coating for wood surface. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 170, 106953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Jiang, H.; Hou, B.; Du, Y.; Jin, C.; Yan, Y. High efficient fire-retardant coatings on wood fabricated by divalent metal ion cross-linked multilayer polyethyleneimine and ammonium polyphosphate polyelectrolytes. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2022, 204, 110112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, S.; Meng, D.; Chen, D.; Mu, C.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Gu, X.; Zhang, S. A facile preparation of environmentally-benign and flame-retardant coating on wood by comprising polysilicate and boric acid. Cellulose 2021, 28, 11551–11566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Nabipour, H.; Kan, Y.C.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. A fully bio-based, anti-flammable and non-toxic epoxy thermosetting network for flame-retardant coating applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2022, 172, 107095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ran, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wang, W.; Cao, J. Combustion behavior of furfurylated wood in the presence of montmorillonite and its char characteristics. Wood Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 623–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.-K.; Wang, X.-S.; Guo, D.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhai, F.-Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.-Z. The high-temperature self-crosslinking contribution of azobenzene groups to the flame retardance and anti-dripping of copolyesters. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 9264–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Deng, Z.-P.; Li, C.-B.; Song, F.; Wang, X.-L.; Chen, L.; Guo, D.-M.; Wang, Y.-Z. A bio-based epoxy resin derived from p-hydroxycinnamic acid with high mechanical properties and flame retardancy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 33, 4912–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wei, P.; Qian, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, J. Effect of talc on thermal stability and flame retardancy of polycarbonate/PSBPBP composite. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 3167–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Xing, W.; Feng, X.; Yu, B.; Mu, X.; Yuen, R.K.K.; Hu, Y. Self-standing cuprous oxide nanoparticles on silica@ polyphosphazene nanospheres: 3D nanostructure for enhancing the flame retardancy and toxic effluents elimination of epoxy resins via synergistic catalytic effect. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wu, L.; Dai, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sui, X.; Xu, H.; Mao, Z. Application of self-templated PHMA sub-microtubes in enhancing flame-retardance and anti-dripping of PET. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 154, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


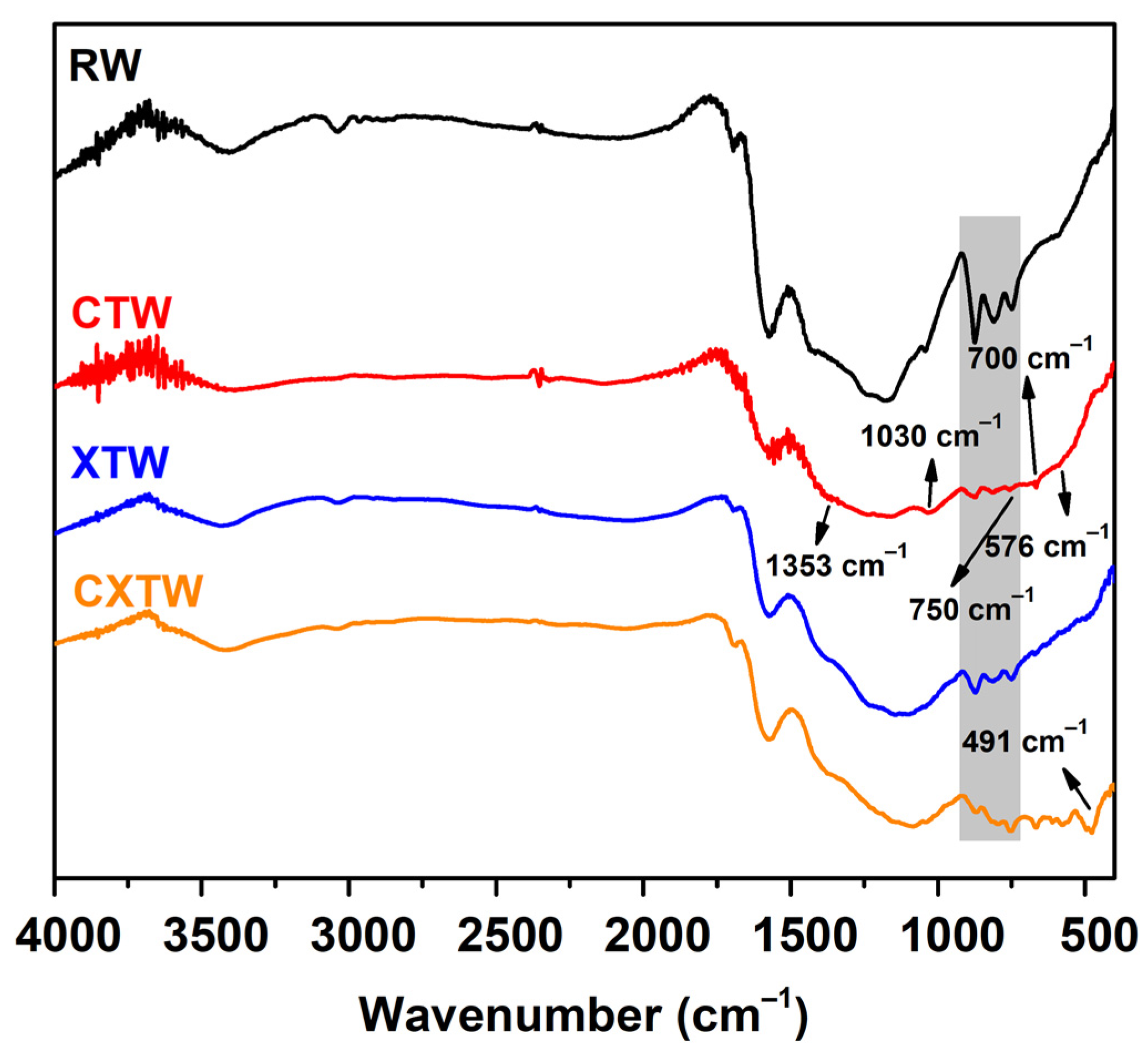
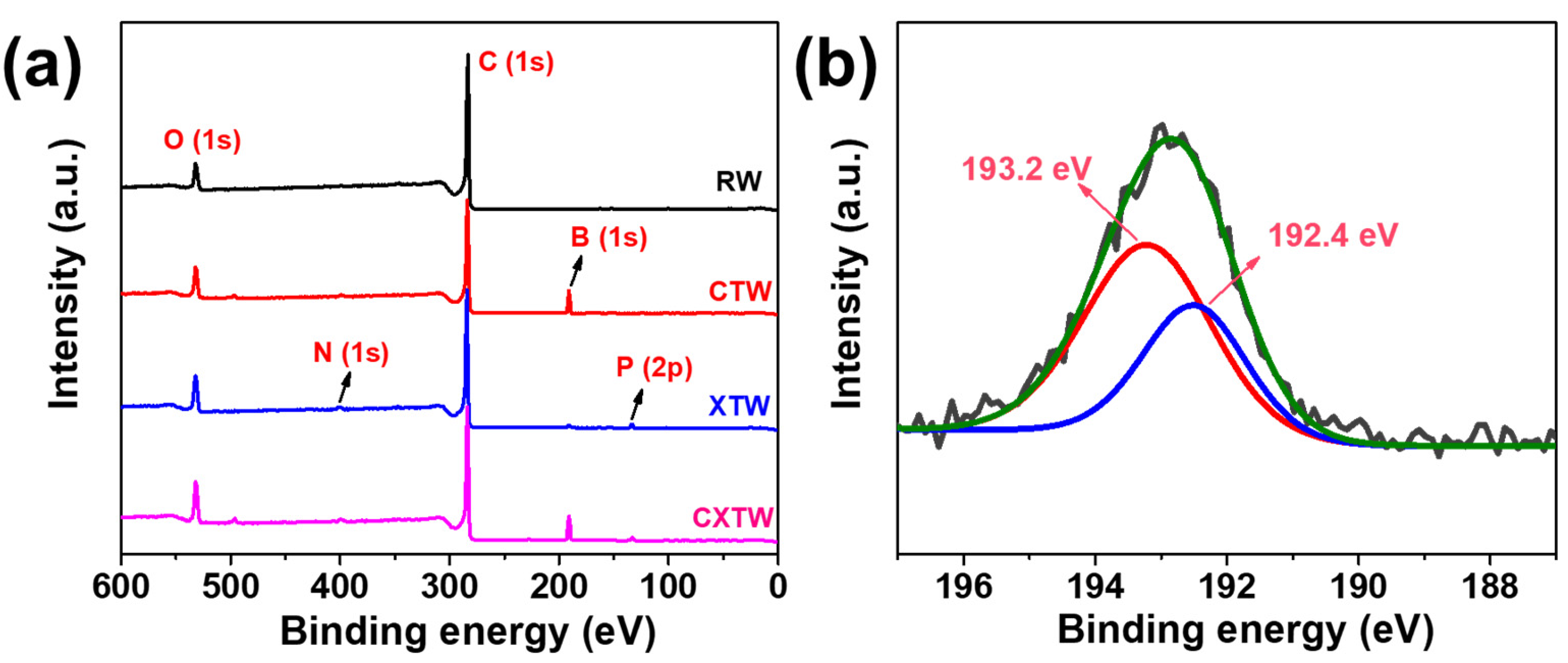

| Sample | T5% (°C) | Tmax (°C) | Vmax (%/min) | Residue (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RW | 281 | 387 | −12.6 | 16.7 |
| CTW | 243 | 295 | −5.0 | 33.2 |
| XTW | 247 | 380 | −9.6 | 23.6 |
| CXTW | 236 | 331 | −9.4 | 33.6 |
| Samples | TTI (s) | THR (MJ m−2) | PHRR (kW m−2) | Residue (wt%) | FIGRA (kW/(m2 s)) | Dsmax |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RW | 10 | 26 | 410 | 15.72 | 5.46 | 86.0 |
| CTW | 8 | 24 | 262 | 18.38 | 3.27 | 18.4 |
| XTW | 35 | 25 | 254 | 30.17 | 2.12 | 80.4 |
| CXTW | 32 | 23 | 152 | 36.22 | 1.39 | 60.6 |
| Samples | C1s (%) | O1s (%) | B1s (%) | N1s (%) | P2p (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RW | 91.50 | 8.50 | - | - | - |
| CTW | 74.85 | 14.75 | 10.40 | - | - |
| XTW | 82.79 | 12.40 | - | 2.32 | 2.49 |
| CXTW | 70.80 | 15.79 | 9.75 | 2.20 | 1.46 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Z.-P.; Fu, T.; Song, X.; Wang, Z.-L.; Guo, D.-M.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Song, F. Highly Flame-Retardant and Low Heat/Smoke-Release Wood Materials: Fabrication and Properties. Polymers 2022, 14, 3944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193944
Deng Z-P, Fu T, Song X, Wang Z-L, Guo D-M, Wang Y-Z, Song F. Highly Flame-Retardant and Low Heat/Smoke-Release Wood Materials: Fabrication and Properties. Polymers. 2022; 14(19):3944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193944
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Ze-Peng, Teng Fu, Xin Song, Zi-Li Wang, De-Ming Guo, Yu-Zhong Wang, and Fei Song. 2022. "Highly Flame-Retardant and Low Heat/Smoke-Release Wood Materials: Fabrication and Properties" Polymers 14, no. 19: 3944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193944
APA StyleDeng, Z.-P., Fu, T., Song, X., Wang, Z.-L., Guo, D.-M., Wang, Y.-Z., & Song, F. (2022). Highly Flame-Retardant and Low Heat/Smoke-Release Wood Materials: Fabrication and Properties. Polymers, 14(19), 3944. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14193944






