Evaluation of the Effect of Recycled Polypropylene as Fine Aggregate Replacement on the Strength Performance and Chloride Penetration of Mortars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
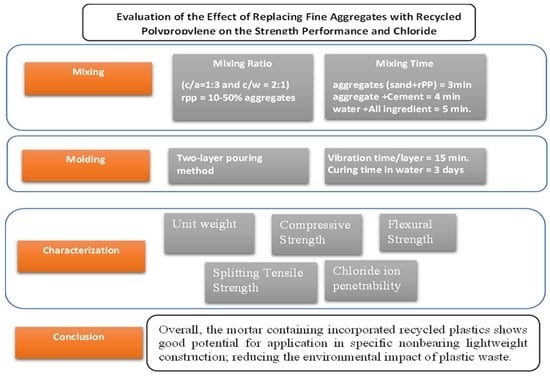
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
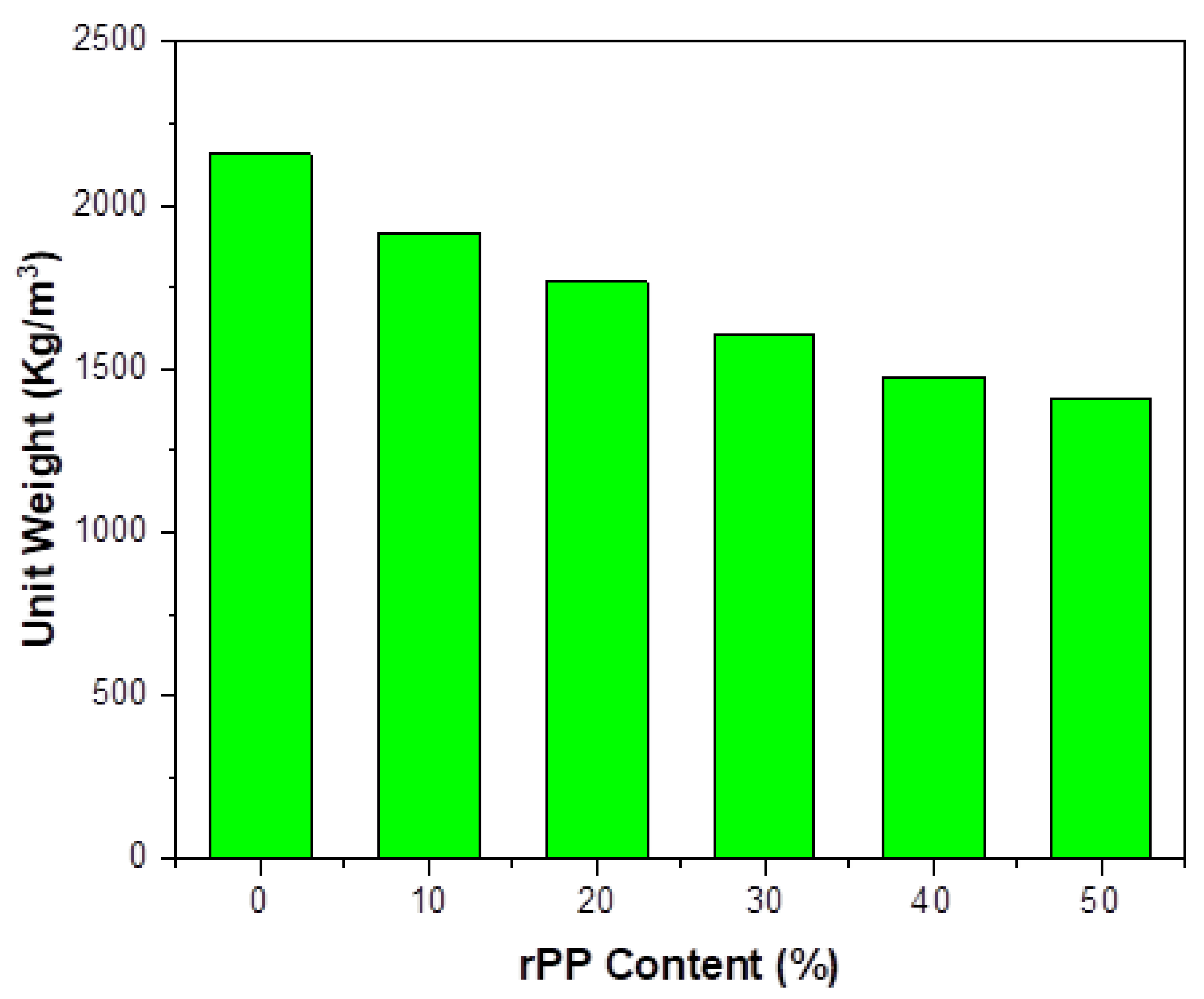
3.1. Fresh Unit Weight
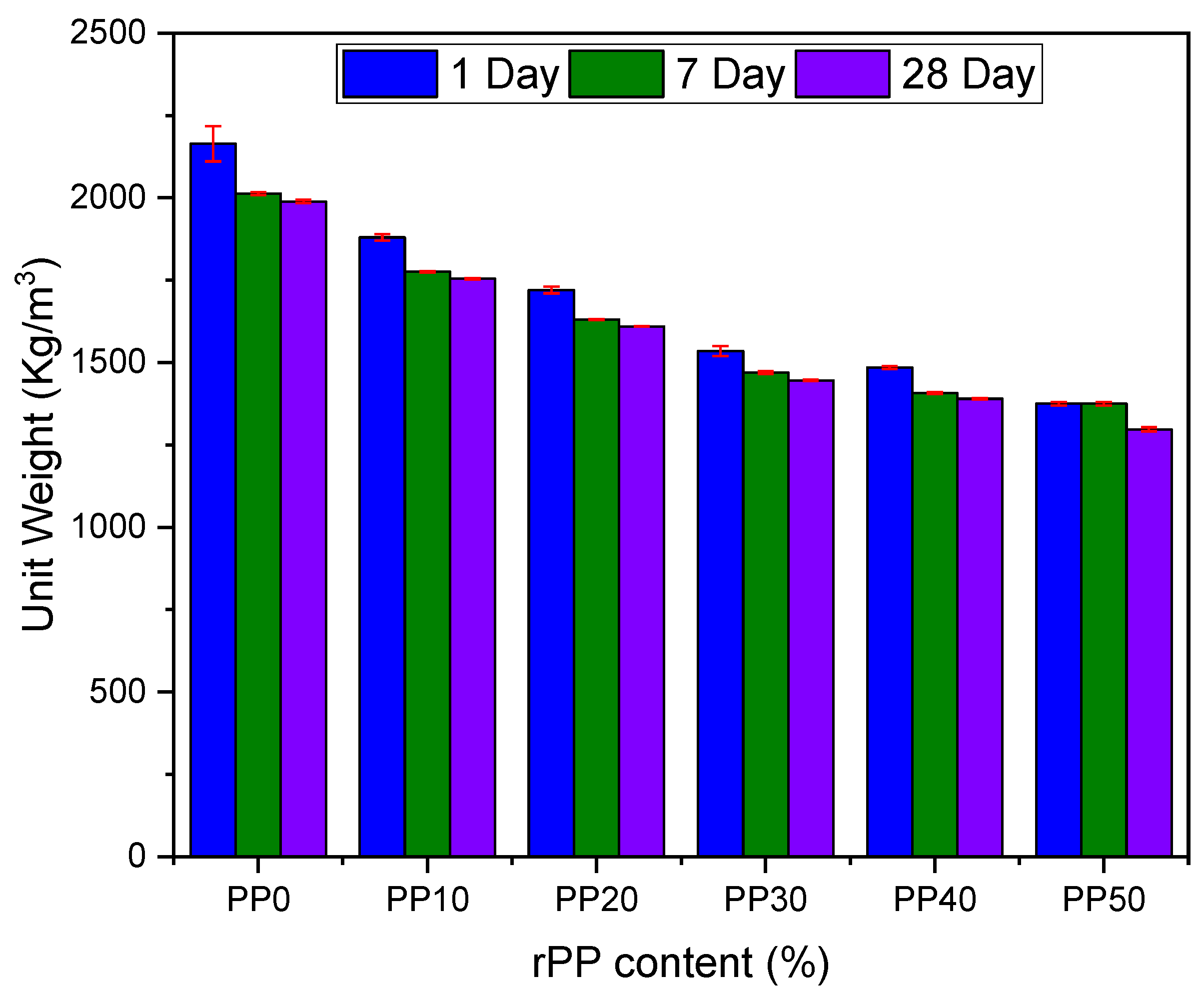
3.2. Dry Unit Weight
3.3. Compressive Strength
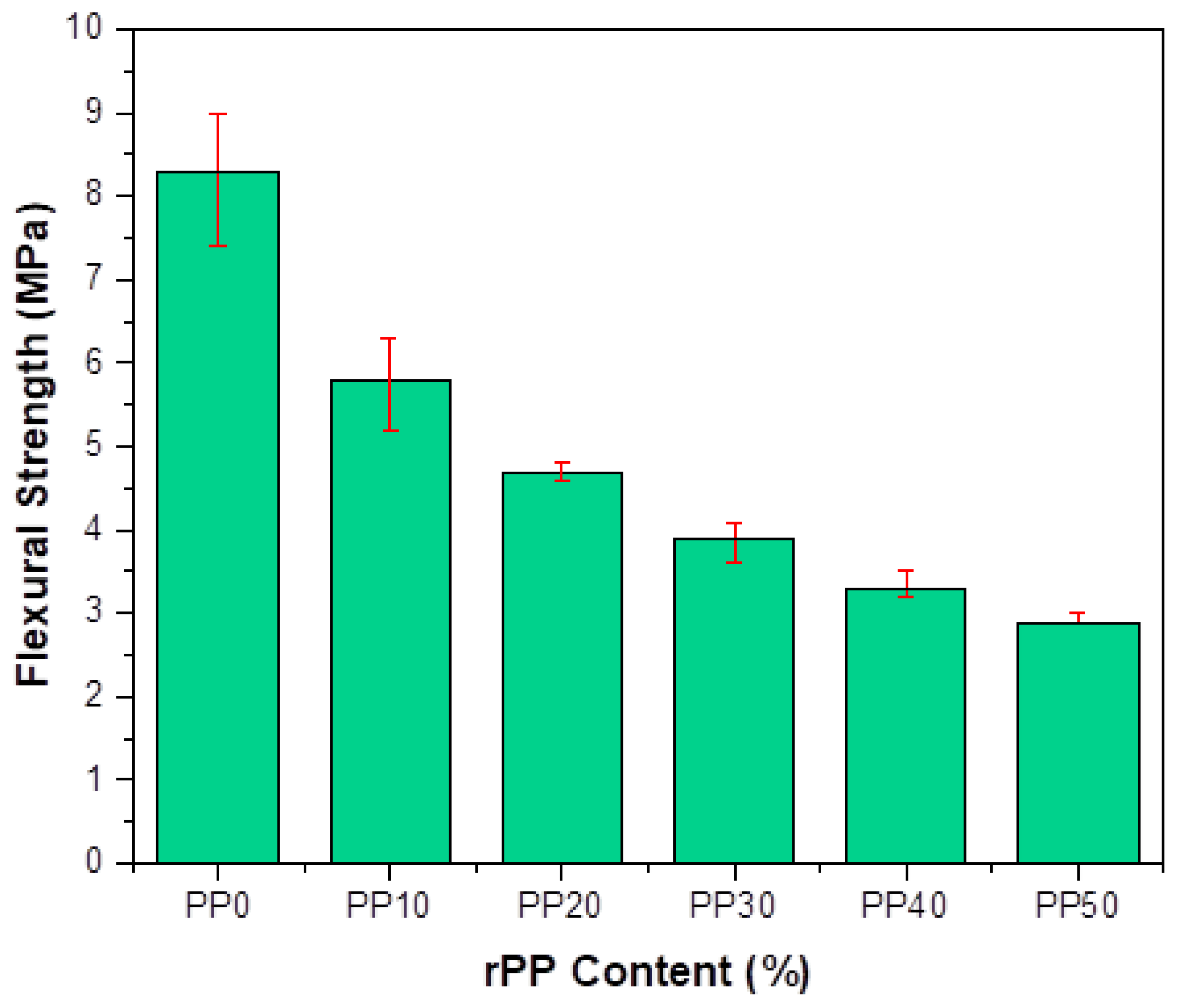
3.4. Flexural Strength
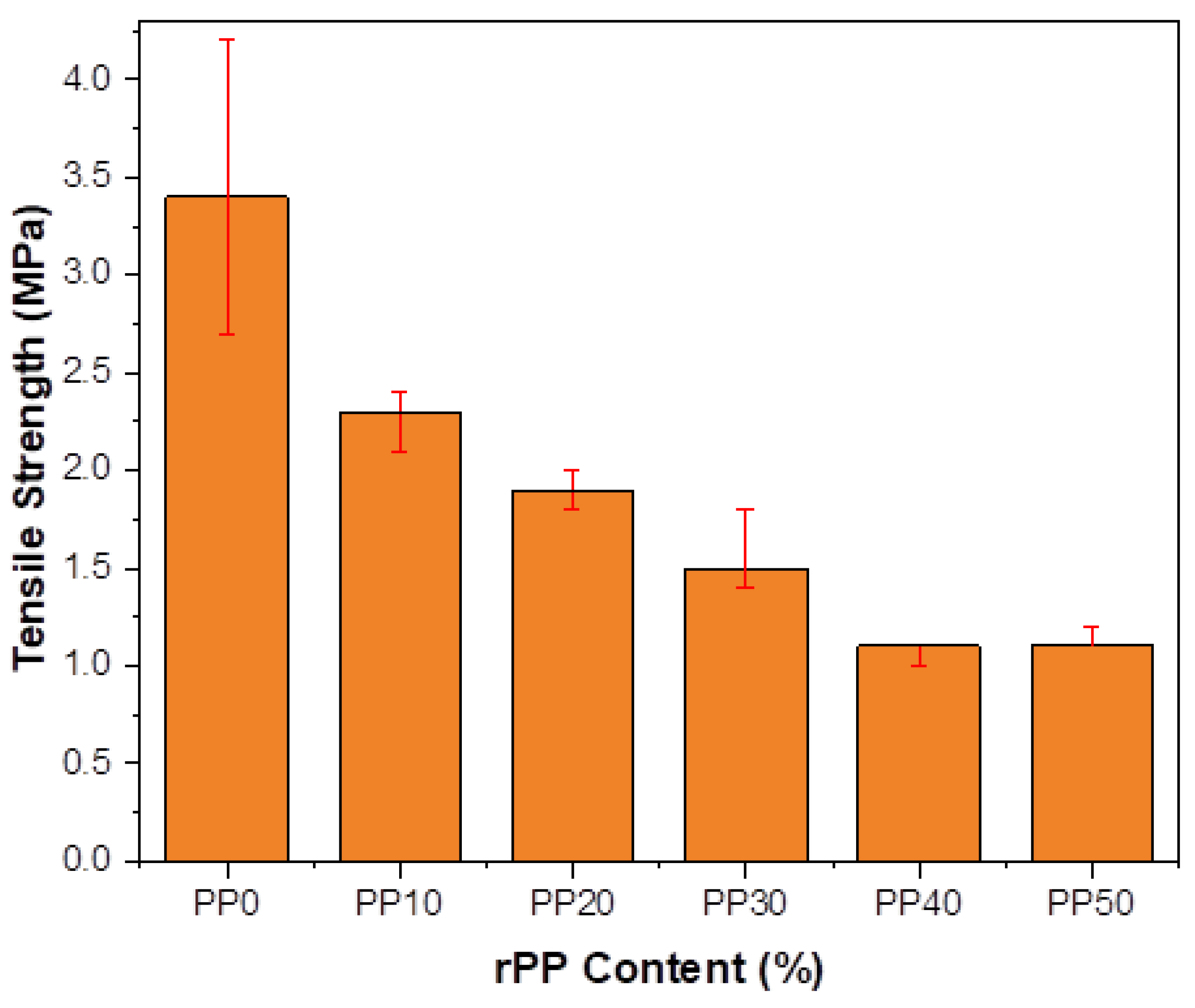
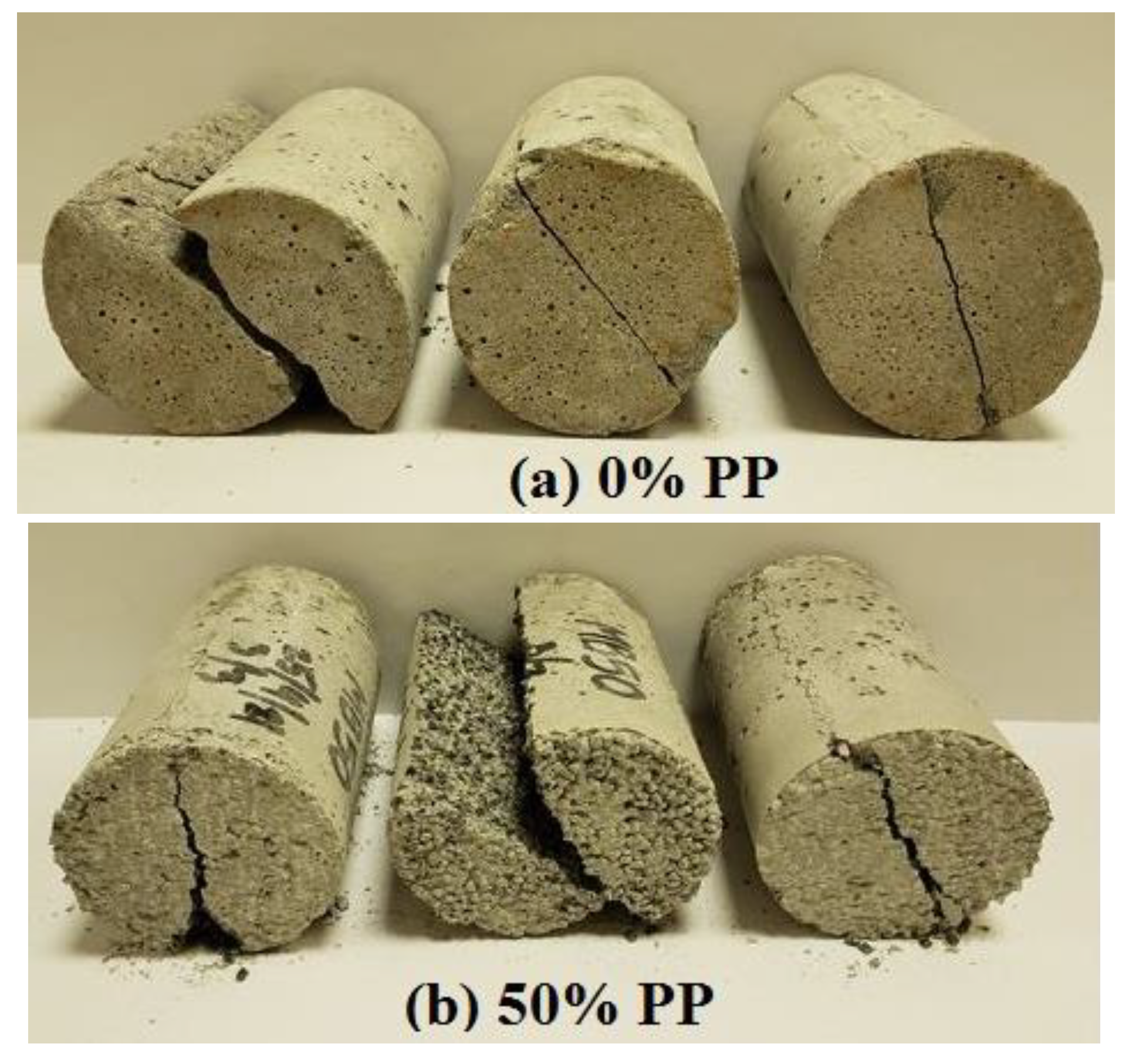
3.5. Splitting Tensile Strength
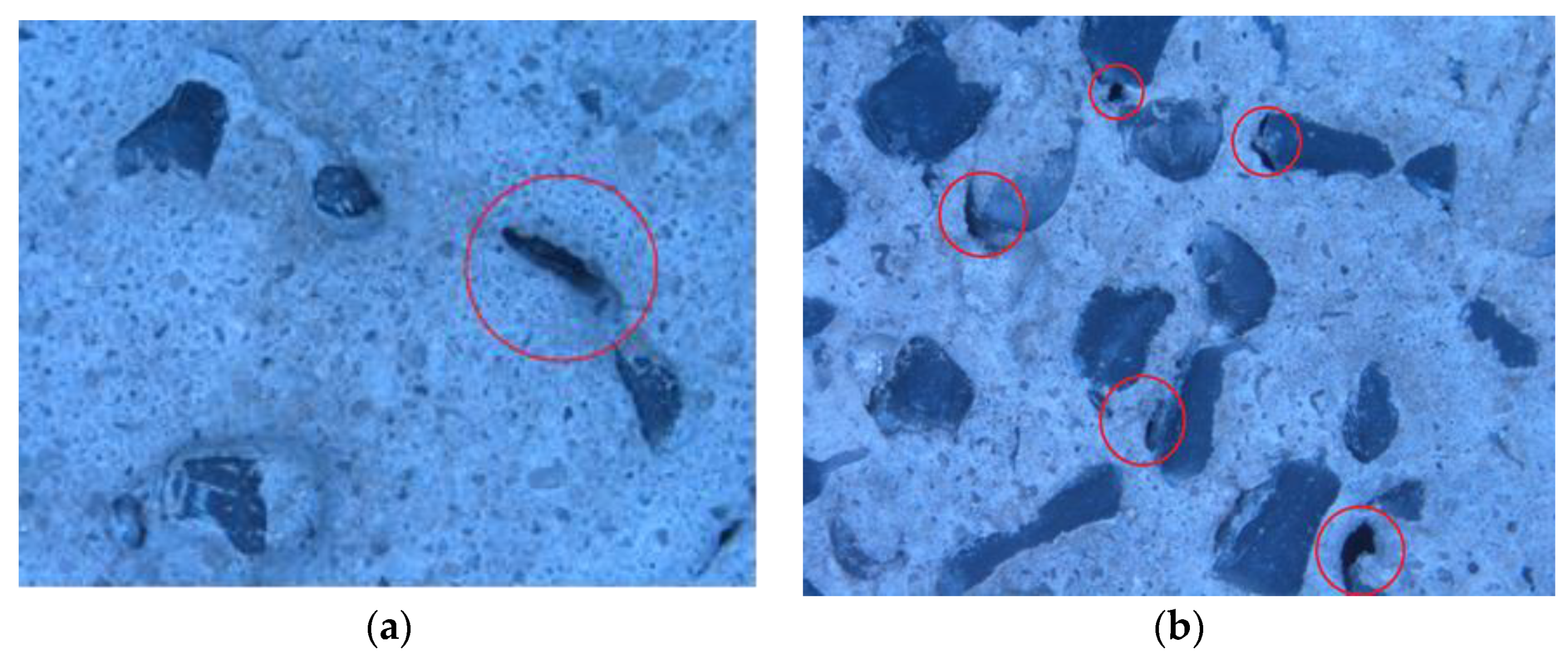
3.6. Optical Microscopy
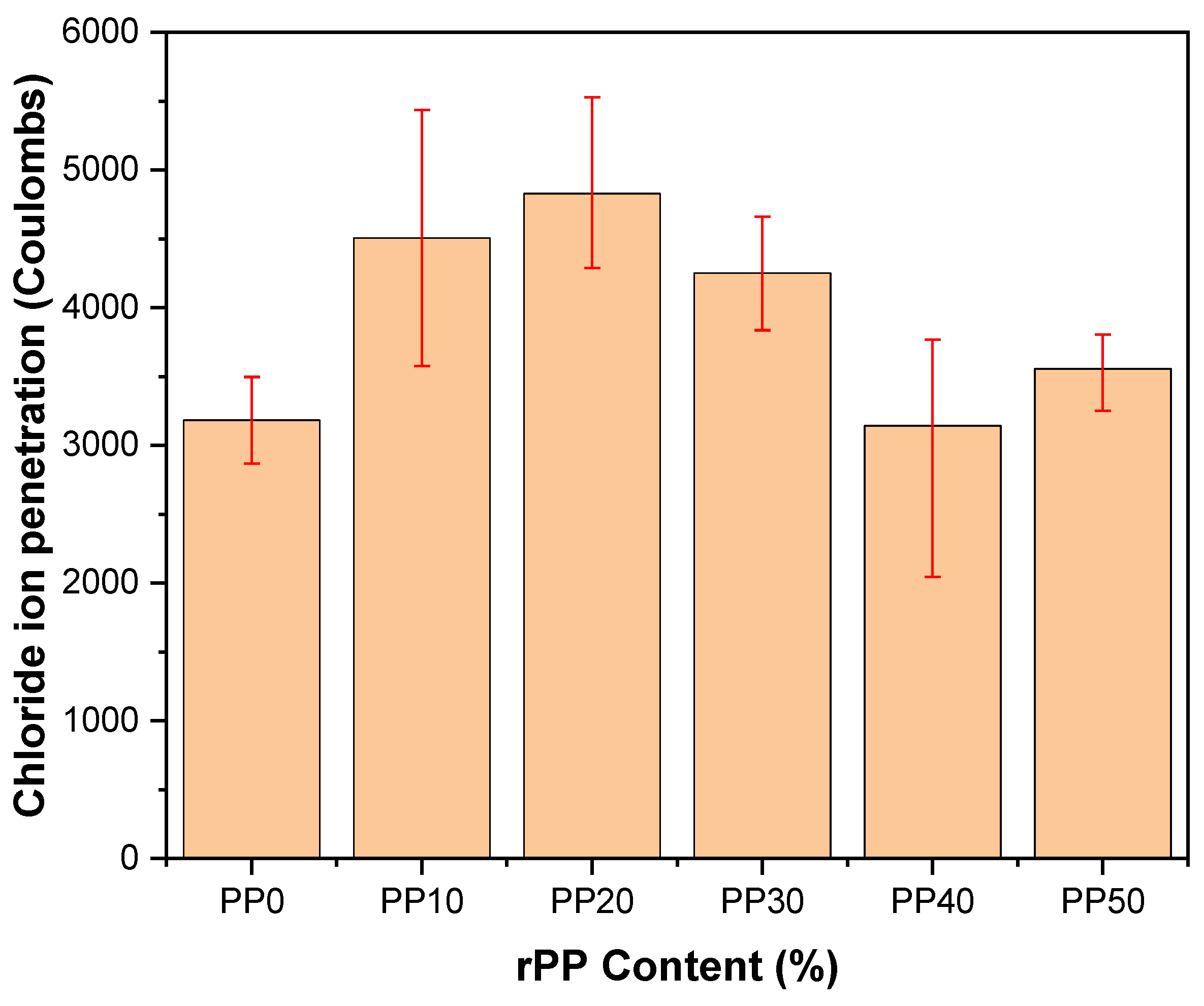
3.7. Chloride Ion Penetrability
4. Conclusions
- The replacement of natural fine aggregates with rPP led to a reduction in the workability of the prepared mortars.
- The fresh and hard unit weight of the proposed mortars tended to decrease with an increasing rPP content in the mortar matrix as a fine aggregate replacement. At a 50% replacement, the loss in the unit weight was approximately 35%.
- Compressive strength of the prepared mortar was negatively influenced by the rPP content. The results showed that the mortar prepared with 50% of rPP aggregates lost 75% of its strength. However, the specimens containing 10% rPP showed acceptable compressive strength for the construction industry.
- The reduction in the flexural strength was up to 65% at a 50% replacement.
- A similar trend of results was observed for flexural and splitting tensile strengths, and the strength values tended to decrease with an increasing rPP content. Due to a 50% of replacement, the reduction in the tensile strength was 67.6%.
- The durability of the mortar was significantly influenced by the rPP content. The chloride ion penetration value tended to increase with an increasing rPP content.
- Overall, the recycled-plastic-incorporated mortars showed a good potential for specific non-bearing lightweight construction applications while reducing the environmental impacts of plastic wastes. For example, they could be used in pavements and non-bearing loading walls.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiseo, I. Production of Plastics Worldwide from 1950 to 2020. 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/282732/global-production-of-plastics-since-1950/ (accessed on 13 May 2022).
- PlasticsEurope. Plastics—The Facts 2020: An Analysis of European Plastics Production, Demand and Waste Data; PlasticsEurope: Brussels, Belgium, 2020; pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Jambeck, J.R.; Geyer, R.; Wilcox, C.; Siegler, T.R.; Perryman, M.; Andrady, A.; Narayan, R.; Law, K.L. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 2015, 347, 768–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebreton, L.; Egger, M.; Slat, B. A global mass budget for positively buoyant macroplastic debris in the ocean. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, P.K.; Lee, J.; Brown, R.J.; Kim, K.-H. Micro- and nano-plastic pollution: Behavior, microbial ecology, and remediation technologies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 291, 125240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeshal, I.; Tayeh, B.A.; Alyousef, R.; Alabduljabbar, H.; Mustafa Mohamed, A.; Alaskar, A. Use of recycled plastic as fine aggregate in cementitious composites: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 253, 119146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, C.; Camacho, N.; Hernández, M.; Matheus, A.; Gutiérrez, A. Influence of content and particle size of waste pet bottles on concrete behavior at different w/c ratios. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 2707–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.W.; Moon, D.-J.; Chung, J.-S.; Cho, S.-K. Effects of waste PET bottles aggregate on the properties of concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.J.; Meherier, M.S.; Islam, A.K.M.R. Effects of waste PET as coarse aggregate on the fresh and harden properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhdarpour, A.M.; Nikoudel, M.R.; Taheri, M. The effect of using polyethylene terephthalate particles on physical and strength-related properties of concrete; a laboratory evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 109, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juki, M.I.; Awang, M.; Annas, M.M.K.; Boon, K.H.; Othman, N.; Roslan, M.A.; Khalid, F.S. Relationship between compressive, splitting tensile and flexural strength of concrete containing granulated waste Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) bottles as fine aggregate. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 795, 356–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araghi, H.J.; Nikbin, I.; Reskati, S.R.; Rahmani, E.; Allahyari, H. An experimental investigation on the erosion resistance of concrete containing various PET particles percentages against sulfuric acid attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 77, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, W.C.; Lo, Y.; Nadeem, A. Mechanical and drying shrinkage properties of structural-graded polystyrene aggregate concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2008, 30, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Meyer, C. Performance of cement mortar made with recycled high impact polystyrene. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.C.; Lee, G.; Poon, C.S.; Lai, W.-L. Properties of lightweight aggregate concrete prepared with PVC granules derived from scraped PVC pipes. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlo, A.; Lavagna, L.; Suarez-Riera, D.; Pavese, M. Mechanical properties of mortar containing waste plastic (PVC) as aggregate partial replacement. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 13, e00467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Mohammed, I.I.; Mohammed, S.A. Some properties of concrete with plastic aggregate derived from shredded PVC sheets. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senhadji, Y.; Escadeillas, G.; Benosman, A.S.; Mouli, M.; Khelafi, H.; Kaci, S.O. Effect of incorporating PVC waste as aggregate on the physical, mechanical, and chloride ion penetration behavior of concrete. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2015, 29, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aciu, C.; Ilutiu-Varvara, D.-A.; Manea, D.-L.; Orban, Y.-A.; Babota, F. Recycling of plastic waste materials in the composition of ecological mortars. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 22, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suganthy, P.; Chandrasekar, D.; Kumar, S. Utilization of Pulverized Plastic in Cement Concrete as Fine Aggregate. Int. J. Res. Eng. Technol. 2013, 2, 1015–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Badache, A.; Benosman, A.S.; Senhadji, Y.; Mouli, M. Thermo-physical and mechanical characteristics of sand-based lightweight composite mortars with recycled high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 163, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamrin; Nurdiana, J. The Effect of Recycled HDPE Plastic Additions on Concrete Performance. Recycling 2021, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugapriya, M.; Santhi, H. Strength and chloride permeable properties of concrete with high density polyethylene waste. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2017, 15, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, M.; Srivastava, V.; Agarwal, V. Effect of waste low density polyethylene on mechanical properties of concrete. J. Acad. Ind. Res. 2014, 3, 123–126. [Google Scholar]
- Ohemeng, E.A.; Ekolu, S.O. Strength prediction model for cement mortar made with waste LDPE plastic as fine aggregate. J. Sustain. Cem.-Based Mater. 2019, 8, 228–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İpek, S.; Diri, A.; Mermerdaş, K. Recycling the low-density polyethylene pellets in the pervious concrete production. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Ali, T.K.M.; Rajab, N.; Hilal, N. Mechanical properties of concrete and mortar containing low density polyethylene waste particles as fine aggregate. J. Mater. Eng. Struct. 2020, 7, 57–72. [Google Scholar]
- Thiam, M.; Fall, M.; Diarra, M.S. Mechanical properties of a mortar with melted plastic waste as the only binder: Influence of material composition and curing regime, and application in Bamako. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, P.A.; Galvín, A.P.; Ayuso, J.; Barbudo, A.; López-Uceda, A. Mechanical performance of concrete made with the addition of recycled macro plastic fibres. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Herrero, J.L.; Nieto, D.V.; Lopez-Gil, A.; Arranz, A.; Fernández, A.; Lorenzana, A.; Merino, S.; De Saja, J.A.; Perez, M.A.R. Mechanical and thermal performance of concrete and mortar cellular materials containing plastic waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 104, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; de Brito, J.; Saikia, N. Influence of curing conditions on the mechanical performance of concrete containing recycled plastic aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 36, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.N.; Khan, K.; Saleem, M.U.; Khurram, N.; Niazi, M.U.K. Aging and curing temperature effects on compressive strength of mortar containing lime stone quarry dust and industrial granite sludge. Materials 2017, 10, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ismail, Z.Z.; AL-Hashmi, E.A. Use of waste plastic in concrete mixture as aggregate replacement. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.A.-T.; Hanafi, I.; Mahmoud, R.; Tayeh, B. Effect of partial replacement of sand by plastic waste on impact resistance of concrete: Experiment and simulation. Structures 2019, 20, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, B.; Rushad, S.T.; Kr, B.; Duggal, S.K. Study of waste plastic mix concrete with plasticizer. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 469272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghernouti, Y.; Rabehi, B.; Safi, B.; Chaid, R. Use of recycled plastic bag waste in the concrete. J. Int. Sci. Publ. Mater. Methods Technol. 2011, 8, 480–487. [Google Scholar]
- Akinyele, J.O.; Ajede, A. The use of granulated plastic waste in structural concrete. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. Dev. 2018, 10, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Siddique, S.; Gupta, T.; Sharma, R.K.; Chaudhary, S. Impact resistance and energy absorption capacity of concrete containing plastic waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 176, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Manalo, A.; Ferdous, W.; Abousnina, R.; Salih, C.; Heyer, T.; Schubel, P. Investigation on the physical, mechanical and microstructural properties of epoxy polymer matrix with crumb rubber and short fibres for composite railway sleepers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, A.; Hajimohammadi, A.; Ferdous, W.; Sahajwalla, V. Roles of waste glass and the effect of process parameters on the properties of sustainable cement and geopolymer concrete—A state-of-the-art review. Polymers 2021, 13, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abousnina, R.; Alsalmi, H.I.; Manalo, A.; Allister, R.L.; Alajarmeh, O.; Ferdous, W.; Jlassi, K. Effect of short fibres in the mechanical properties of geopolymer mortar containing oil-contaminated sand. Polymers 2021, 13, 3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkvanklom, A.; Posi, P.; Homwuttiwong, S.; Sata, V.; Wongsa, A.; Tanangteerapong, D.; Chindaprasirt, P. Lightweight geopolymer concrete containing recycled plastic beads. Key Eng. Mater. 2019, 801, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, F.K.; Ghataora, G.; Dirar, S.; Khan, M.I.; Zafar, I. Experimental study to investigate the engineering and durability performance of concrete using synthetic aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 173, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob-Vaillancourt, C.; Sorelli, L. Characterization of concrete composites with recycled plastic aggregates from postconsumer material streams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 182, 561–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldahdooh, M.; Jamrah, A.; Alnuaimi, A.; Martini, M.; Ahmed, M. Influence of various plastics-waste aggregates on properties of normal concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 17, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Mix | Fine Aggregates | rPP w% in Aggregates | |
|---|---|---|---|
| River Sand | PP Fine Aggregates | ||
| PP0 | 3.0 | 0.0 | 0 |
| PP10 | 2.70 | 0.30 | 10 |
| PP20 | 2.40 | 0.60 | 20 |
| PP30 | 2.10 | 0.90 | 30 |
| PP40 | 1.80 | 1.20 | 40 |
| PP50 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alrshoudi, F.; Abdus Samad, U.; Alothman, O.Y. Evaluation of the Effect of Recycled Polypropylene as Fine Aggregate Replacement on the Strength Performance and Chloride Penetration of Mortars. Polymers 2022, 14, 2806. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142806
Alrshoudi F, Abdus Samad U, Alothman OY. Evaluation of the Effect of Recycled Polypropylene as Fine Aggregate Replacement on the Strength Performance and Chloride Penetration of Mortars. Polymers. 2022; 14(14):2806. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142806
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlrshoudi, Fahed, Ubair Abdus Samad, and Othman Y. Alothman. 2022. "Evaluation of the Effect of Recycled Polypropylene as Fine Aggregate Replacement on the Strength Performance and Chloride Penetration of Mortars" Polymers 14, no. 14: 2806. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142806
APA StyleAlrshoudi, F., Abdus Samad, U., & Alothman, O. Y. (2022). Evaluation of the Effect of Recycled Polypropylene as Fine Aggregate Replacement on the Strength Performance and Chloride Penetration of Mortars. Polymers, 14(14), 2806. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14142806