Properties of Basalt Fiber Core Rods and Their Application in Composite Cross Arms of a Power Distribution Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
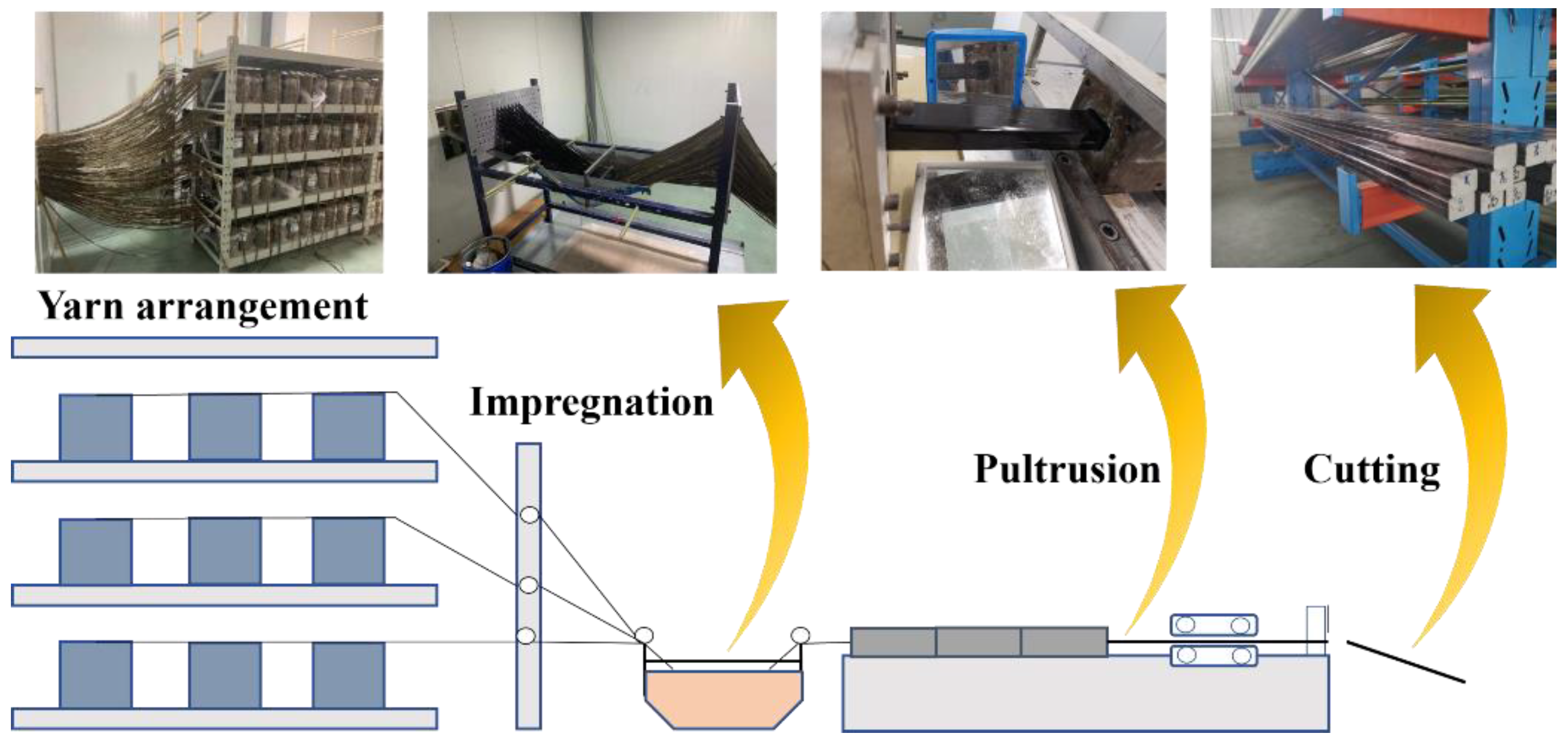
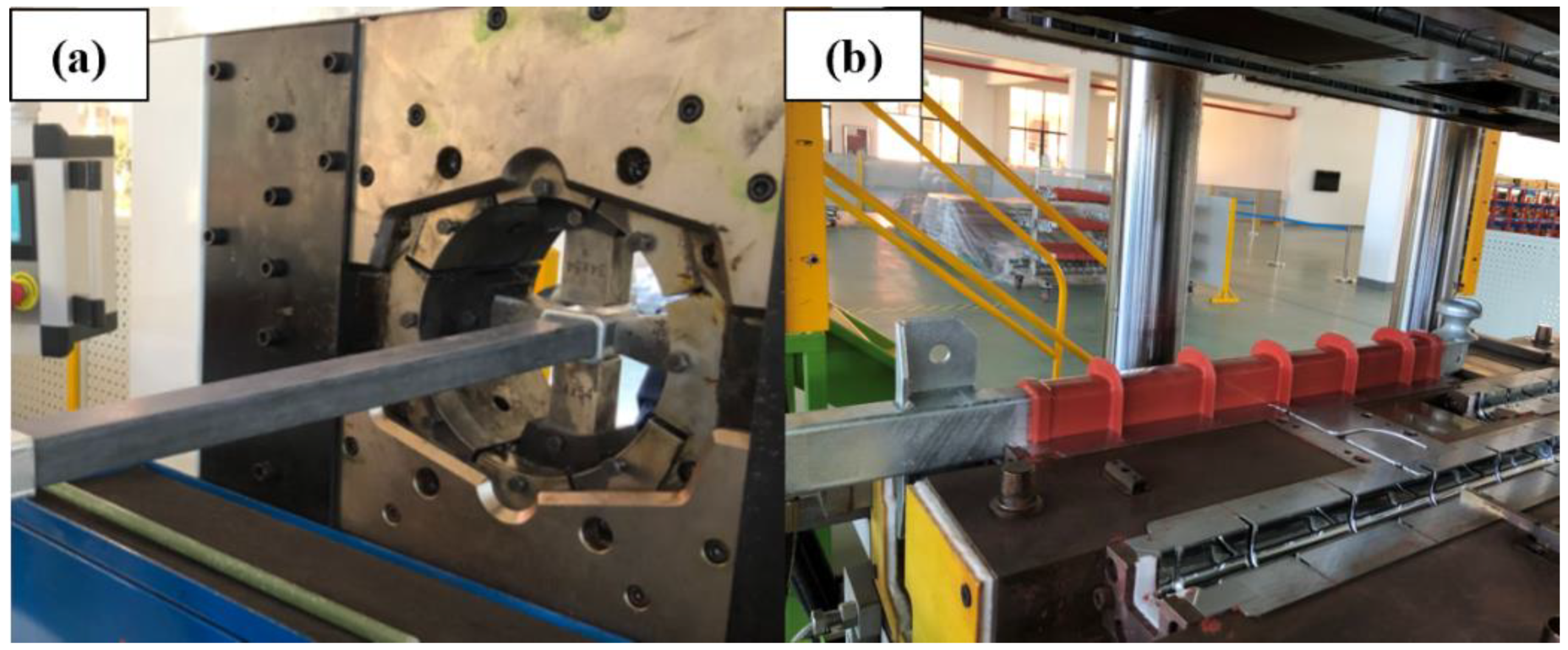
2.2. Fabrication of Core Rods and Composite Cross Arms
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Fiber Properties
2.3.2. Interface Characteristics
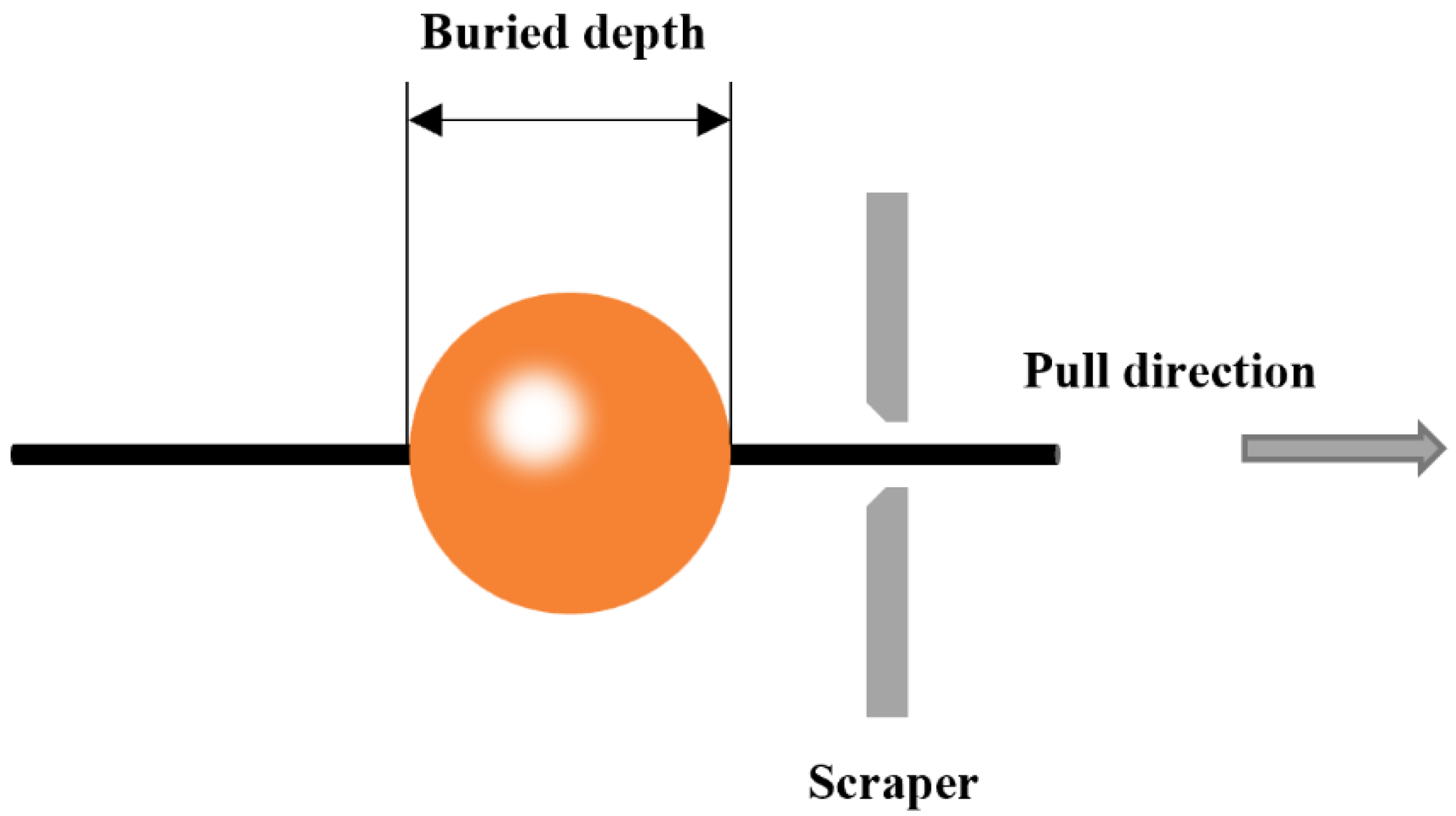
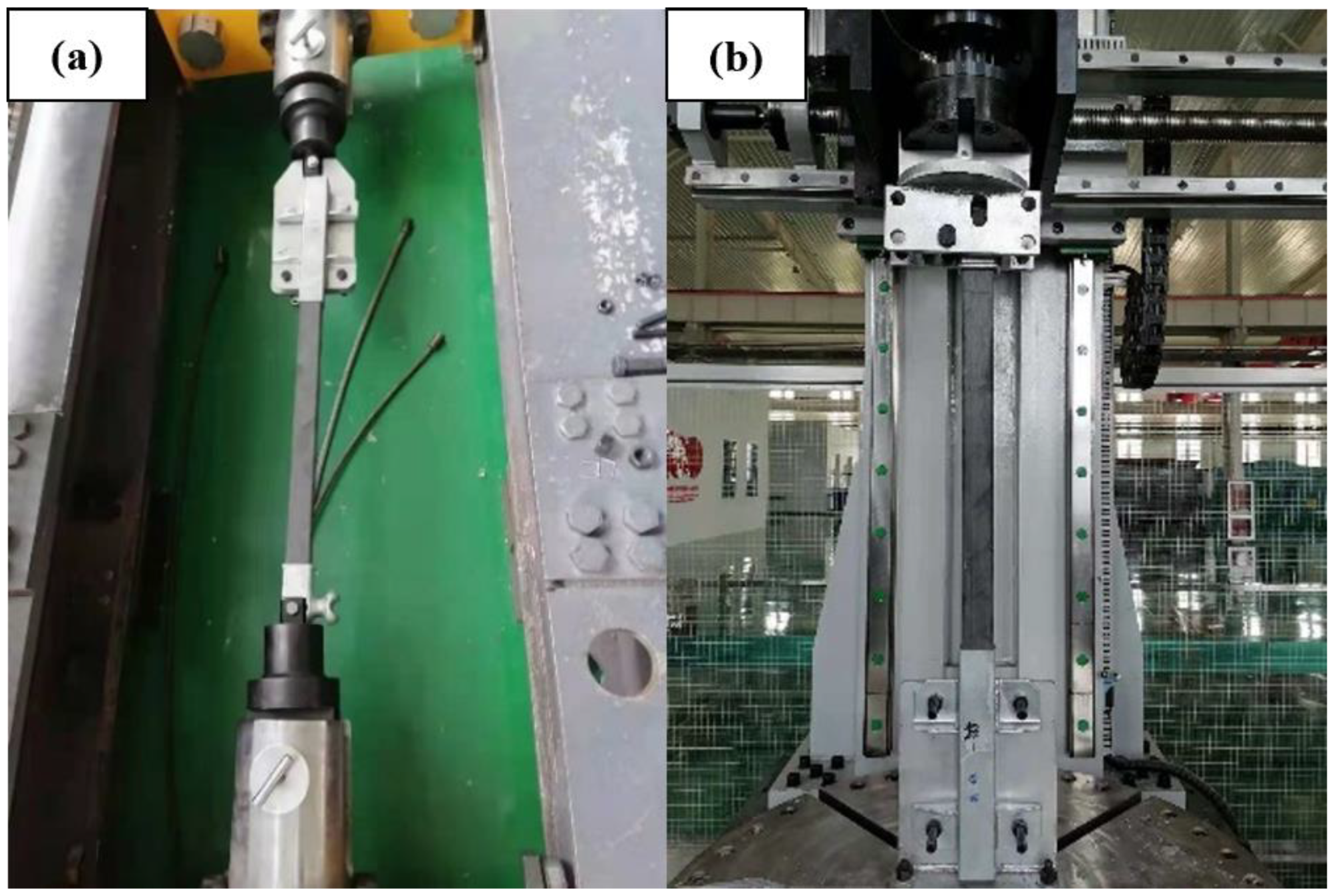
2.3.3. Mechanical Properties
2.3.4. Insulation Properties
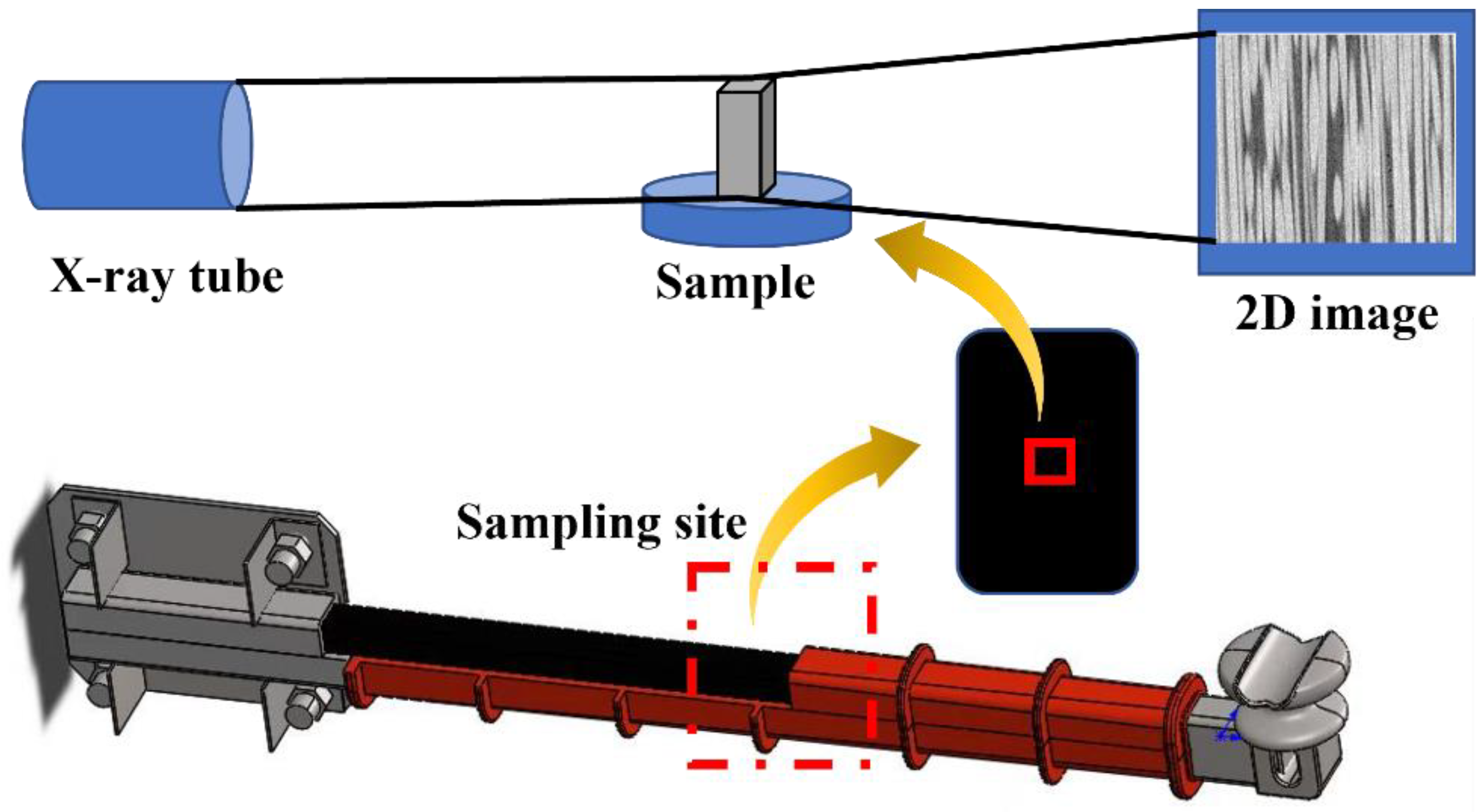
2.3.5. Microtopographic Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Fiber Properties
3.2. Interface Properties
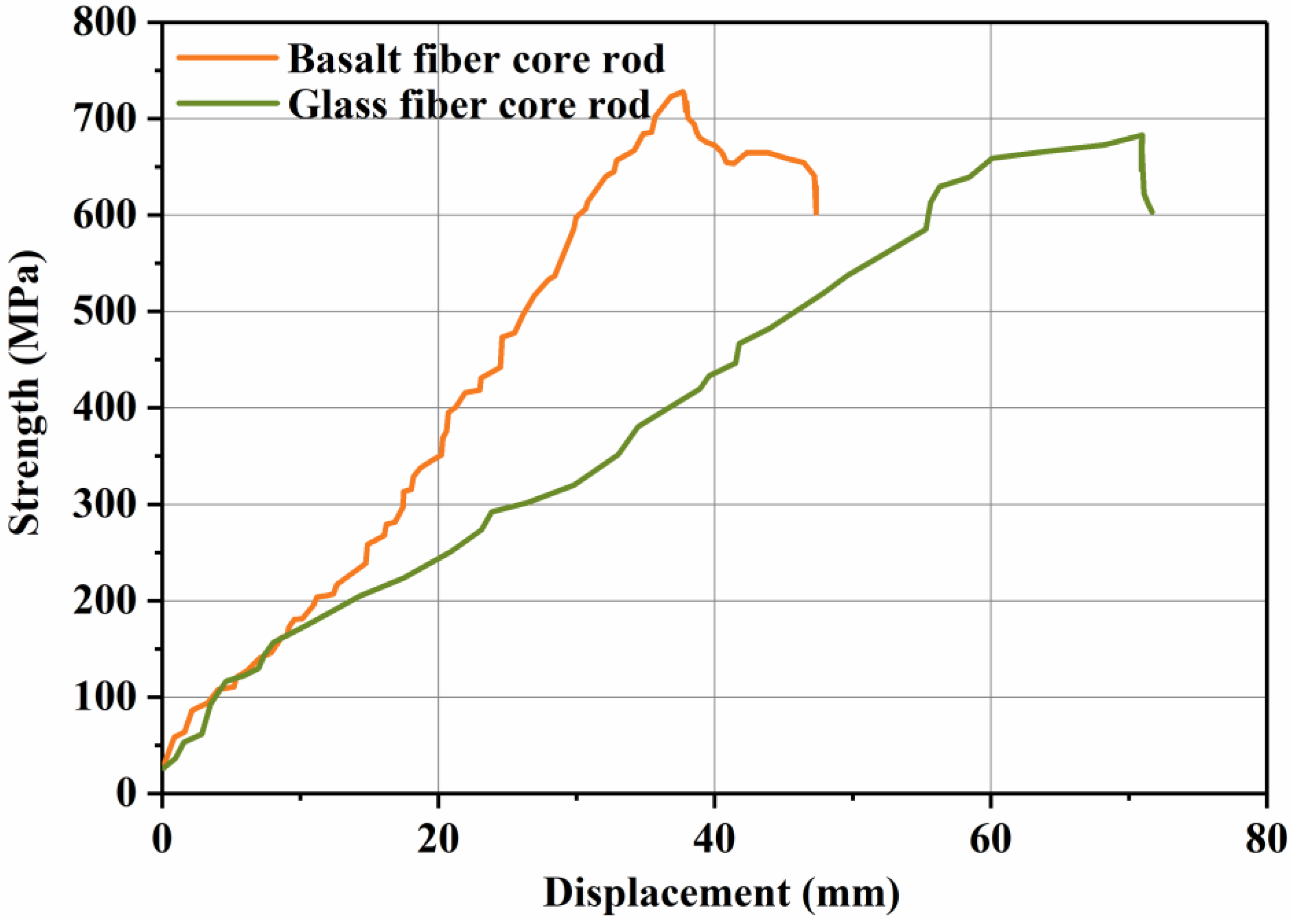
3.3. Mechanical Properties
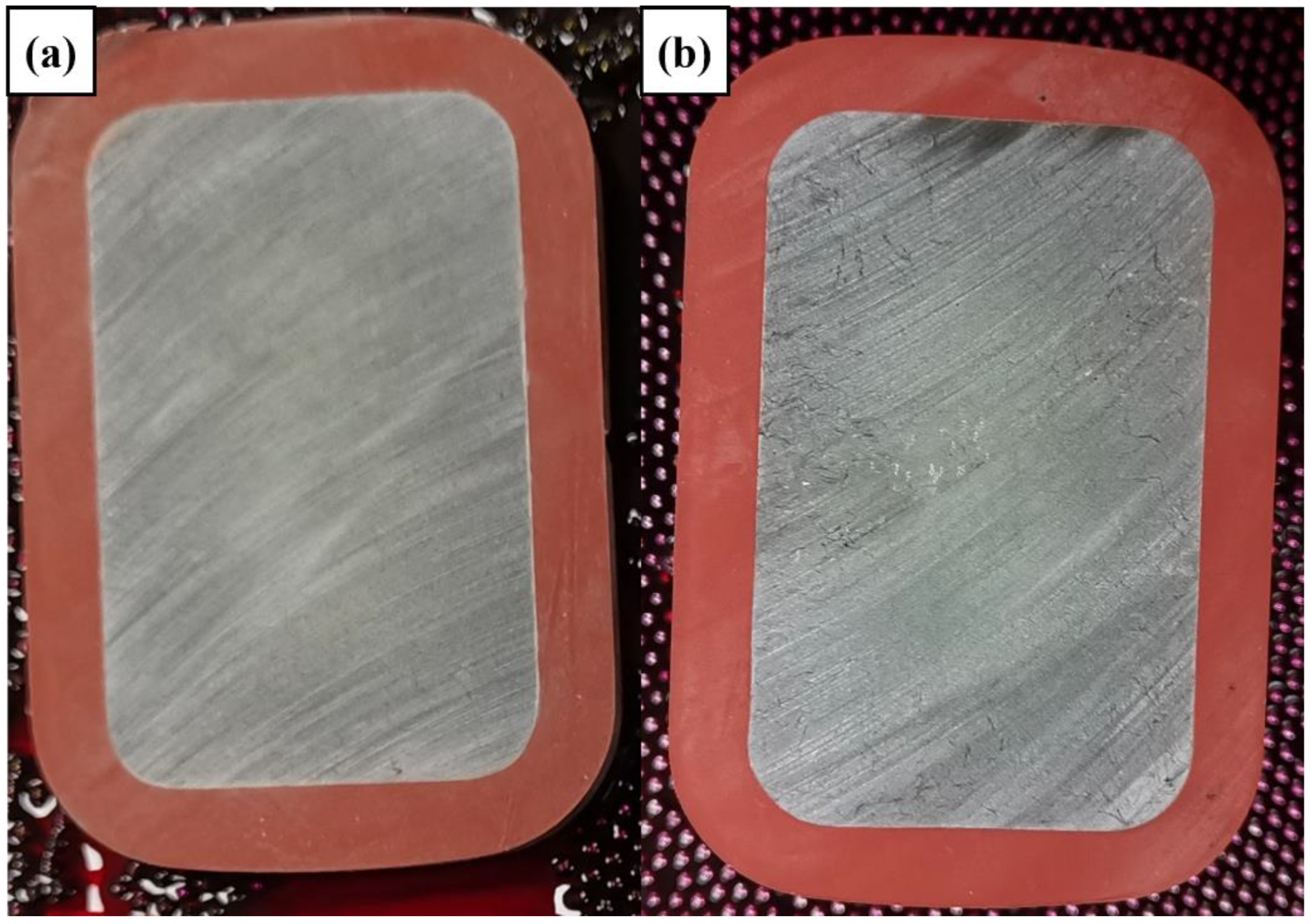
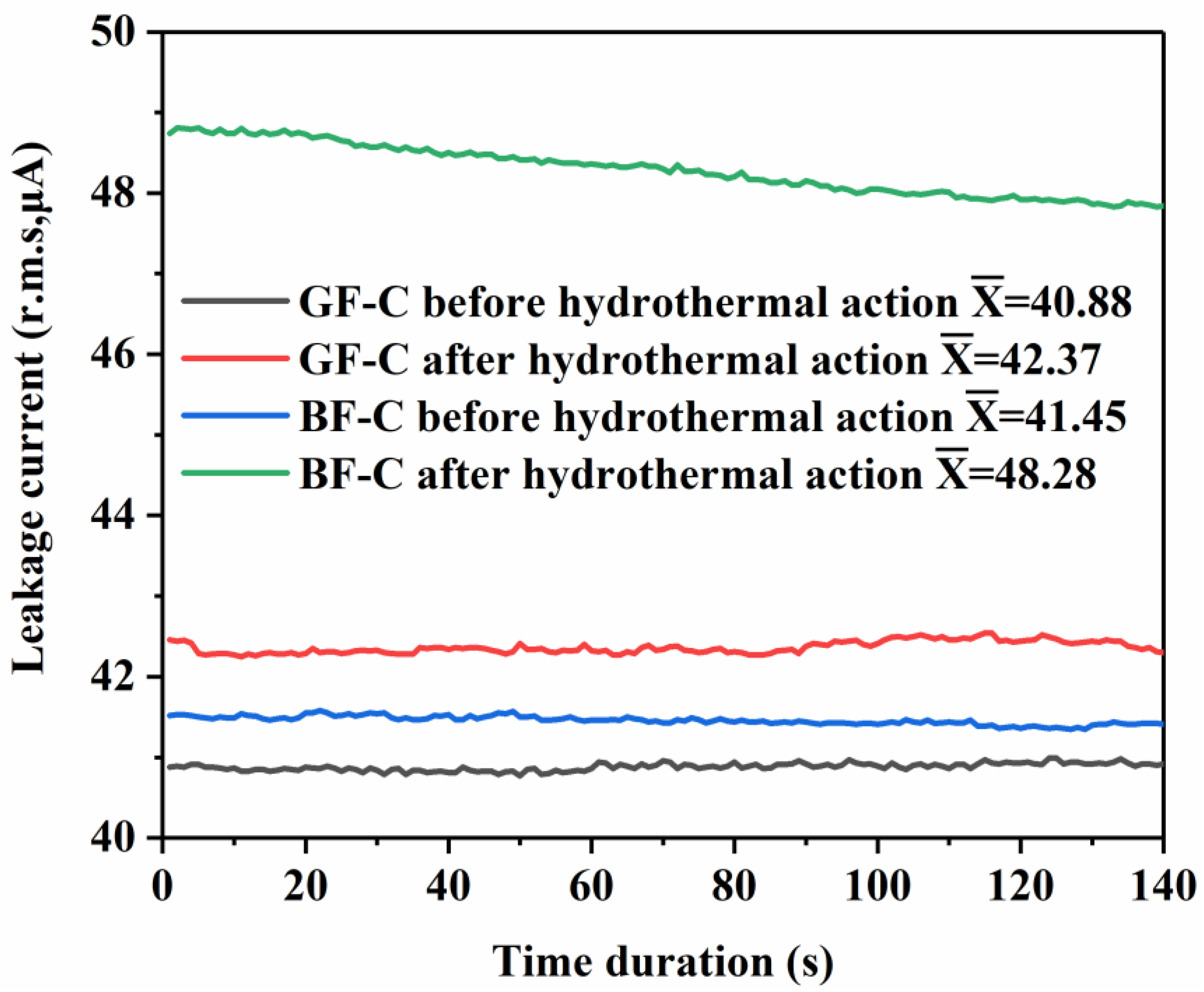
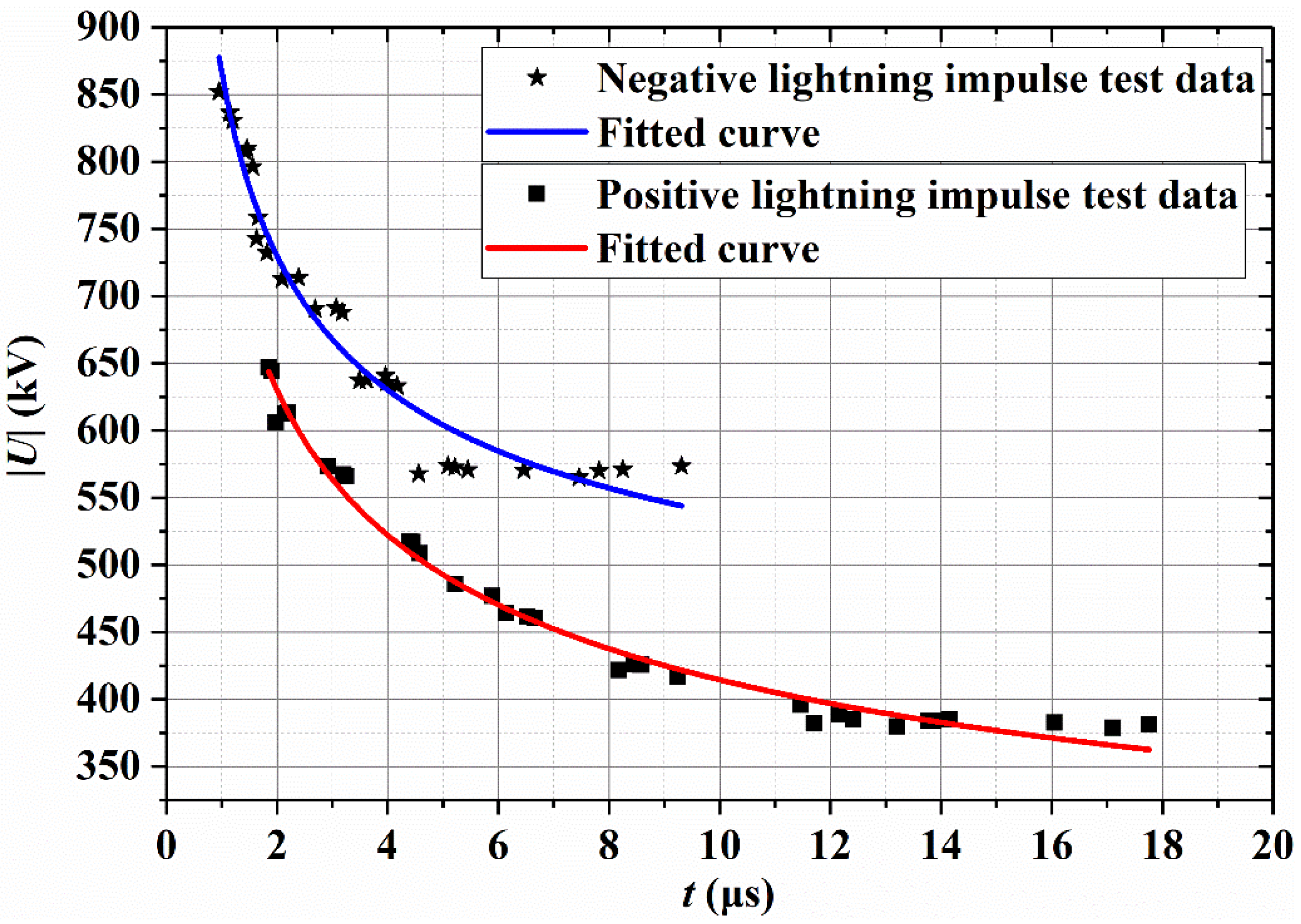
3.4. Insulation Properties
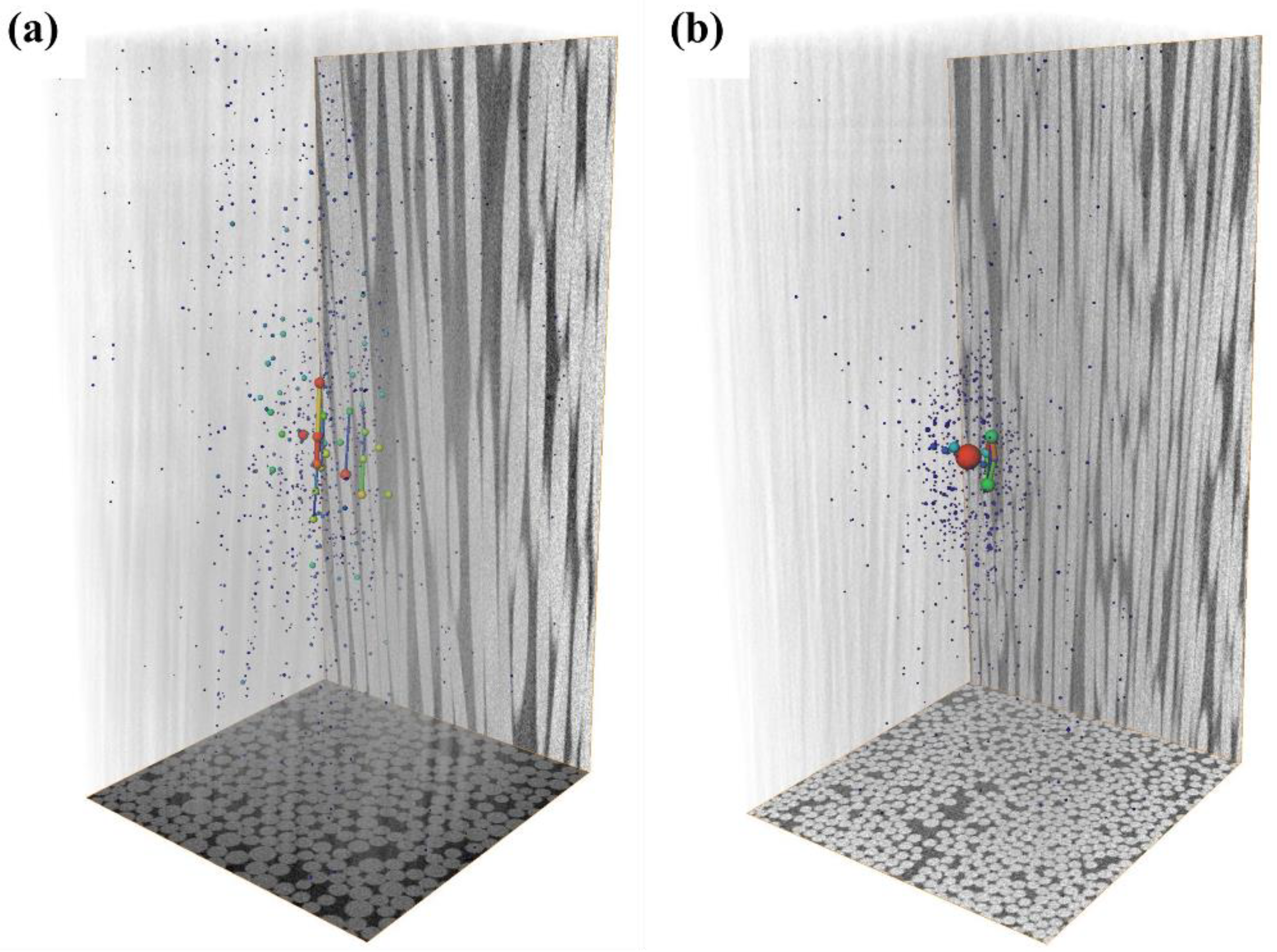
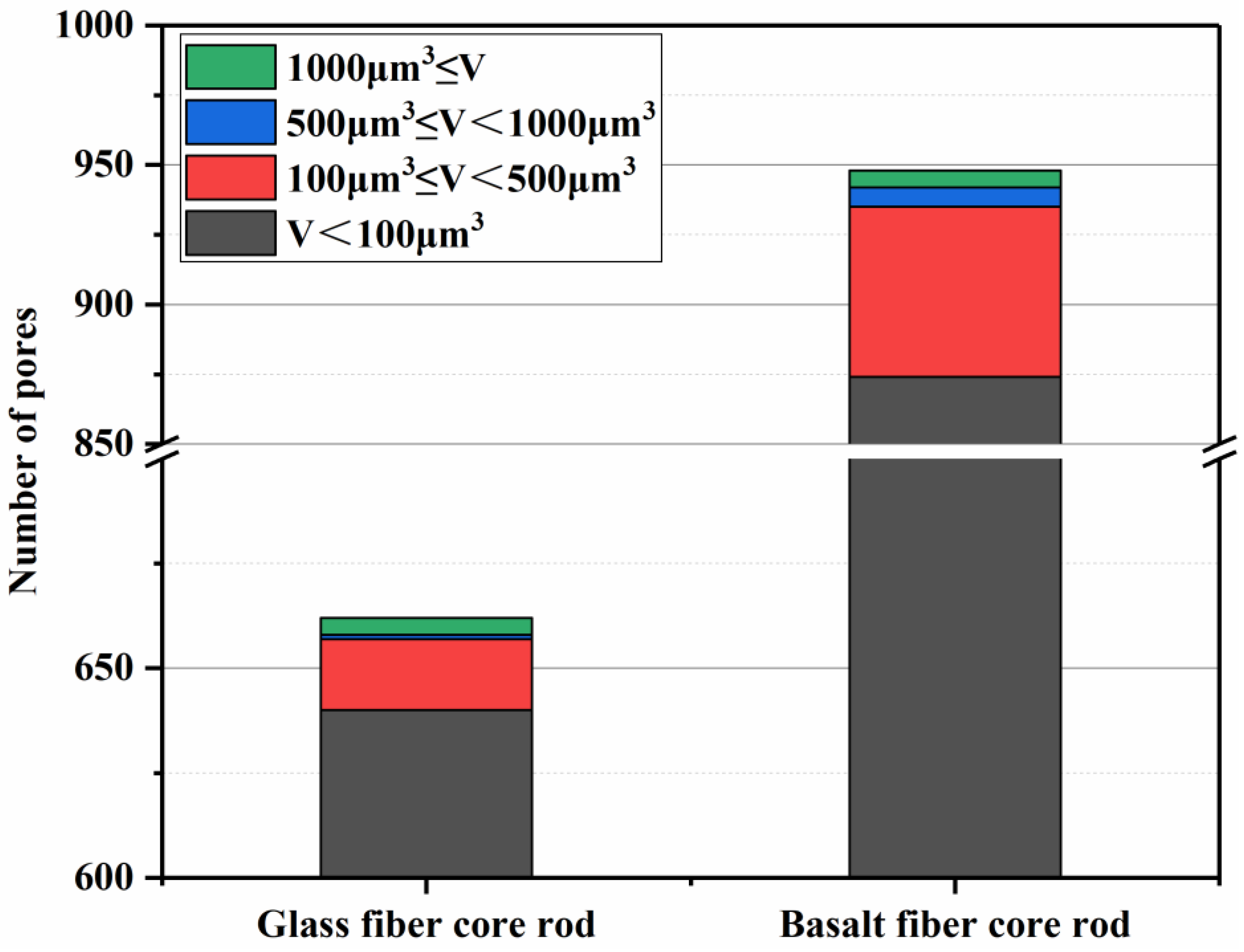
3.5. Microtopography
4. Conclusions
- Due to the good mechanical properties of basalt fiber, basalt fiber core rods are superior to glass fiber core rods in terms of flexural modulus and failure deflection. Basalt fiber core rods are better load-bearing members than glass fiber rods.
- The breakdown field strength of basalt fiber core rods is only slightly different from that of commonly used glass fiber core rods, so they can be used as a reliable insulating medium for composite cross arms. In addition, the positive- and negative-polarity U50% values of composite cross arms made of basalt fiber core rods are much higher than 350 kV.
- The prepared basalt fiber composite cross arms can pass the dye penetrant test, hydrothermal test, core rod-fitting tensile test and lightning strike surface flashover test, meeting the strict requirements of transmission lines in terms of quality and reliability of composite cross arms.
- SEM and the microcomputed tomography show that there are differences in the interface bonding of basalt fiber core rods and glass fiber core rods, with the former being slightly weaker than the latter. Through 3D reconstruction, the number and size of internal pores of the basalt fiber core sample were found to far exceed those of the glass fiber core rod sample.
- At present, the conventional impregnating compounds for glass fiber are mostly used for basalt fiber processing, which cannot generate satisfactory treatment effects on basalt fiber due to the difference in surface properties. The development of basalt fiber impregnating compounds suitable for the power generation sector can further improve the excellent properties of basalt fiber.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Qi, J.W.; Liu, H.C.; Wang, W.X.; Zhang, M.J.; Wu, X. Research on external insulation characteristics of composite cross-arm of 10 kV distribution network based on multi-factor aging. Polymers 2022, 14, 1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syamsir, A.; Nadhirah, A.; Mohamad, D.; Beddu, S.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Itam, Z.; Anggraini, V. Performance Analysis of Full Assembly Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polymer Composite Cross-Arm in Transmission Tower. Polymers 2022, 14, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segovia, F.; Salvador, M.D.; Sahuquillo, O.; Vicente, A. Effects of long-term exposure on E-glass composite material subjected to stress corrosion in a saline medium. J. Compos. Mater. 2007, 41, 2119–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asyraf, M.R.M.; Ishak, M.R.; Sapuan, S.M.; Yidris, N. Utilization of bracing arms as additional reinforcement in pultruded glass fiber-reinforced polymer composite cross-arms: Creep experimental and numerical analyses. Polymers 2021, 13, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhayek, A.; Syamsir, A.; Supian, A.M.; Usman, F.; Asyraf, M.R.M.; Atiqah, M.A. Flexural Creep Behaviour of Pultruded GFRP Composites Cross-Arm: A Comparative Study on the Effects of Stacking Sequence. Polymers 2022, 14, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Liu, X.; Feng, P. A comprehensive review on mechanical properties of pultruded FRP composites subjected to long-term environmental effects. Compos. B. Eng. 2020, 191, 107958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiore, V.; Scalici, T.; Di Bella, G.; Valenza, A. A review on basalt fibre and its composites. Compos. B. Eng. 2015, 74, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.Y.; Hoo, M.S.; Cheah, Y.W.; Tran, L.Q.N. Processing and Mechanical Properties of Basalt Fibre-Reinforced Thermoplastic Composites. Polymers 2022, 14, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanks, J.; Naito, K.; Ueda, H. Characterization of the Static, Creep, and Fatigue Tensile Behavior of Basalt Fiber/Polypropylene Composite Rods for Passive Concrete Reinforcement. Polymers 2021, 13, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Cao, H.L.; Song, S.H. Tensile behavior contrast of basalt and glass fibers after chemical treatment. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 4244–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin, P.; Hassan, M.; Vijay, P.V.; Robert, M.; Benmokrane, B. Chemical resistance of carbon, basalt, and glass fibers used in FRP reinforcing bars. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 3651–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopresto, V.; Leone, C.; De Iorio, I. Mechanical characterisation of basalt fibre reinforced plastic. Compos. B. Eng. 2011, 42, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigato, A.; Pegoretti, A. Fatigue resistance of basalt fibers-reinforced laminates. J. Compos. Mater. 2012, 46, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.H.; Li, Y.B.; Zhang, Z.G.; Sun, Z.J. Impact damage modes and residual flexural properties of composites beam. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 2008, 27, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Cao, H.L.; Song, S.H. Degradation of basalt fibre and glass fibre/epoxy resin composites in seawater. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, O.; Shaw, M.T.; Parnas, R.S.; McDonnell, A.M. Investigation of basalt fiber composite aging behavior for applications in transportation. Polym. Compos. 2006, 27, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Zhang, M.J.; Liu, H.C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.X.; Liu, J. The influences of silane coupling agents on the heat and moisture resistance of basalt fibre-reinforced composites. High Volt. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracz, W.; Janowski, G.; Pruchniak, M.; Walek, L. The Use of Computed Tomography in the Study of Microstructure of Molded Pieces Made of Poly(3-hydroxybutyric-co-3-hydroxyvaleric acid) (PHBV) Biocomposites with Natural Fiber. Polymers 2021, 13, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.S.; Liu, J.X.; Chen, X.F. Continuous Basalt Fiber Technology, 1st ed.; Chemical Industry Press: Beijing, China; p. 195.
- Zhang, S.D.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.F.; Liao, R.J.; Wang, T.T.; Huang, H. Study on the detection method of holes in composite insulator rods. High Volt. 2021, 6, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.J.; Liu, L.; Tang, L.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, H.C. Research status of interface detection for composite cross-arm. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2020, 35, 408–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; Ishak, M.R.; Yidris, N.; Zuhri, M.Y.M.; Asyraf, M.R.M. Potential of honeycomb-filled composite structure in composite cross-arm component: A review on recent progress and its mechanical properties. Polymers 2021, 13, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.H.; Jiang, B.Y.; Chen, C.; Drummer, D.; Zhai, Z.Y. The Effect of Temperature and Strain Rate on the Interfacial Behavior of Glass Fiber Reinforced Polypropylene Composites: A Molecular Dynamics Study. Polymers 2019, 11, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramesh, T.; Anthony, M.W. Concepts and definitions related to mechanical behavior of fiber reinforced composite materials. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 217, 109081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Cai, H.F.; Chen, X.; Zheng, C.; Guo, W.H. Study of UHMWPE Fiber Surface Modification and the Properties of UHMWPE/Epoxy Composite. Polymers 2020, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Glass Fiber Core Rod | Basalt Fiber Core Rod | |
|---|---|---|
| Bending modulus (GPa) | 63.29 | 114.07 |
| Bending strength (MPa) | 682.67 | 727.97 |
| Displacement (mm) | 70.96 | 37.68 |
| Polarity | Dry Arc Distance (m) | U50% test (kV) | U50% (kV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | 0.65 | 380.11 | 399.40 |
| − | 0.65 | 569.98 | 564.22 |
| Basalt Fiber Core Rod | Glass Fiber Core Rod | |
|---|---|---|
| Total number of throats | 9 | 6 |
| Average throat area (μm2) | 23.46 | 46.27 |
| Average throat radius (μm) | 2.57 | 3.76 |
| Average throat length (μm) | 40.51 | 28.94 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Tian, L.; Liu, J.; Fu, C.; Fu, X. Properties of Basalt Fiber Core Rods and Their Application in Composite Cross Arms of a Power Distribution Network. Polymers 2022, 14, 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122443
Liu Y, Zhang M, Liu H, Tian L, Liu J, Fu C, Fu X. Properties of Basalt Fiber Core Rods and Their Application in Composite Cross Arms of a Power Distribution Network. Polymers. 2022; 14(12):2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122443
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yunpeng, Mingjia Zhang, Hechen Liu, Lin Tian, Jie Liu, Chuanfu Fu, and Xiaotao Fu. 2022. "Properties of Basalt Fiber Core Rods and Their Application in Composite Cross Arms of a Power Distribution Network" Polymers 14, no. 12: 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122443
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhang, M., Liu, H., Tian, L., Liu, J., Fu, C., & Fu, X. (2022). Properties of Basalt Fiber Core Rods and Their Application in Composite Cross Arms of a Power Distribution Network. Polymers, 14(12), 2443. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14122443






