Synthesis of Hollow PVP/Ag Nanoparticle Composite Fibers via Electrospinning under a Dense CO2 Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Materials
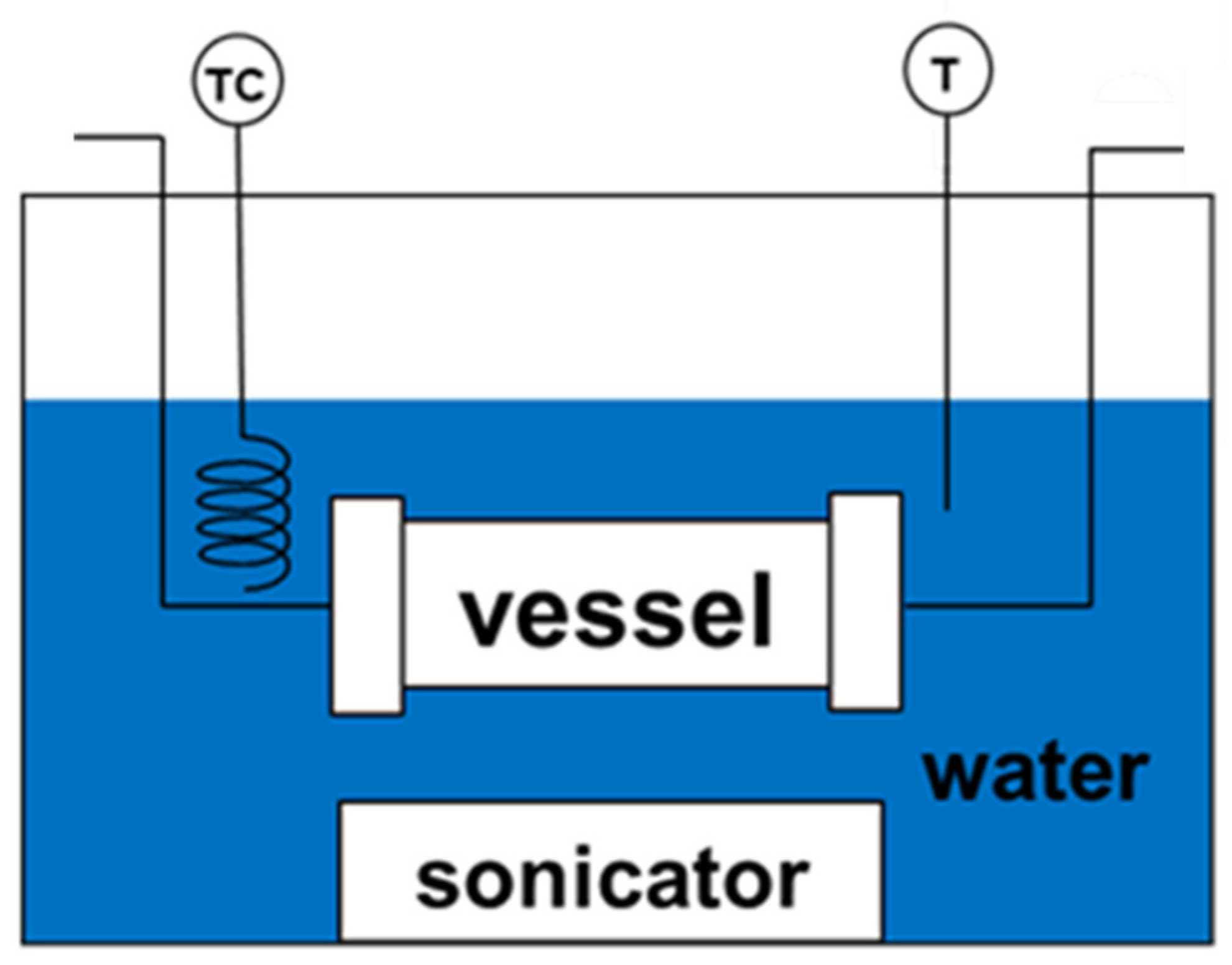
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of Ag NPs
2.3. Feed Solution Preparation for Electrospinning
2.4. Synthesis of the Hollow PVP and PVP/Ag NPs Composite Fibers
2.5. Characterization of the Hollow PVP and PVP/Ag NPs Composite Fibers
3. Results and Discussion
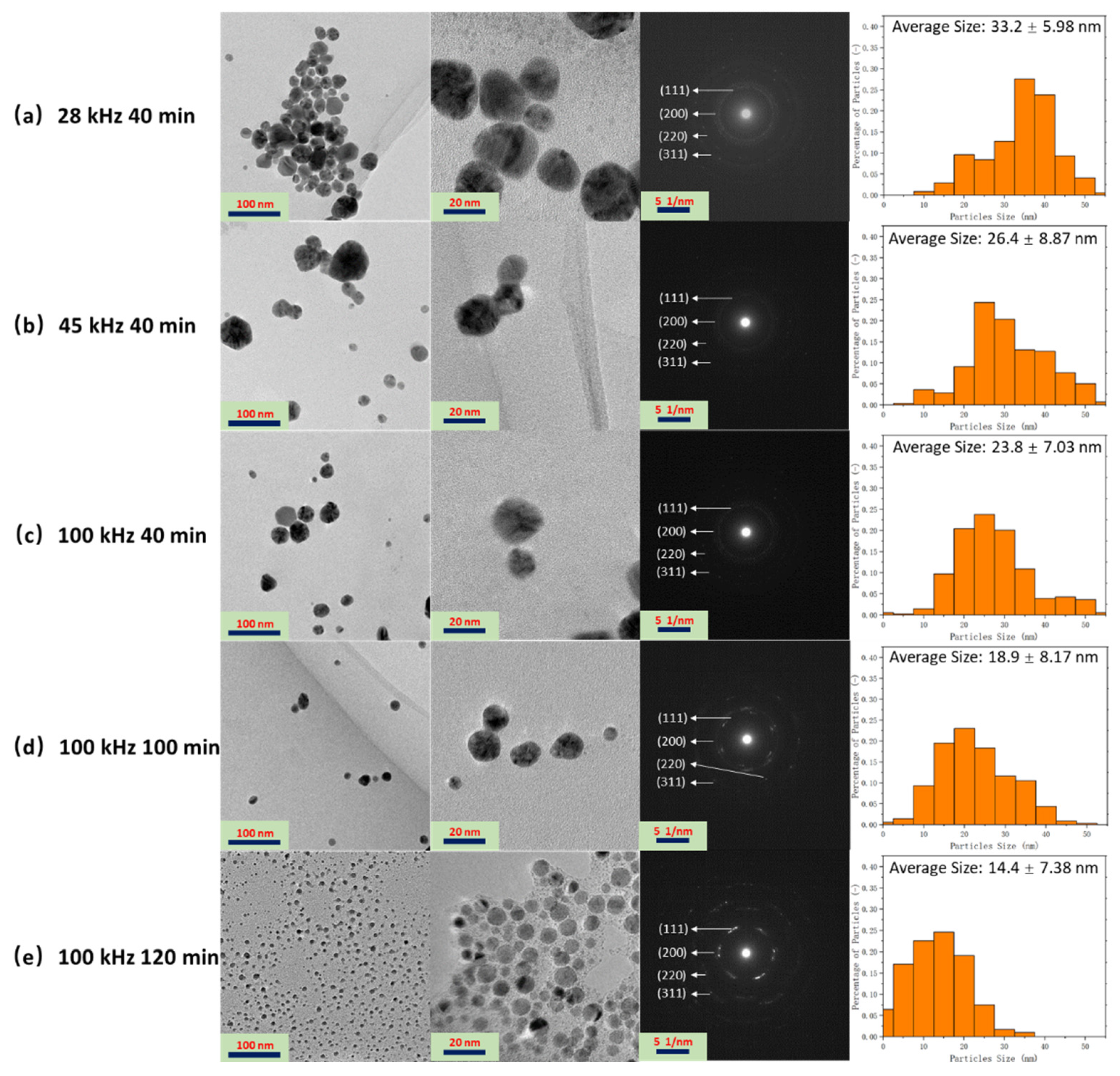
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of the Ag NPs Synthesized by Ultrasonic Irradiation
3.2. Fabrication and Characterization of Electrospun PVP Fibers
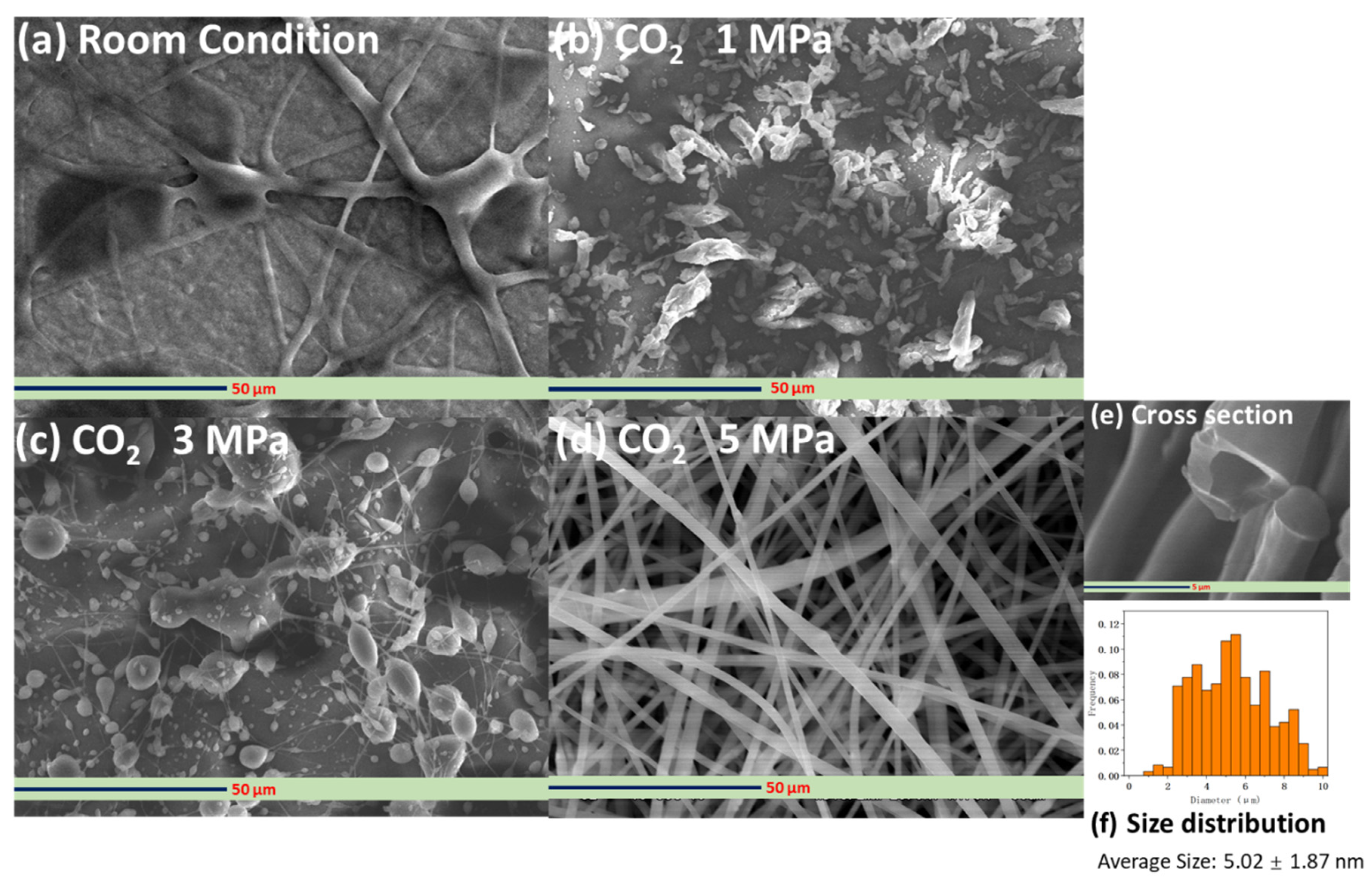
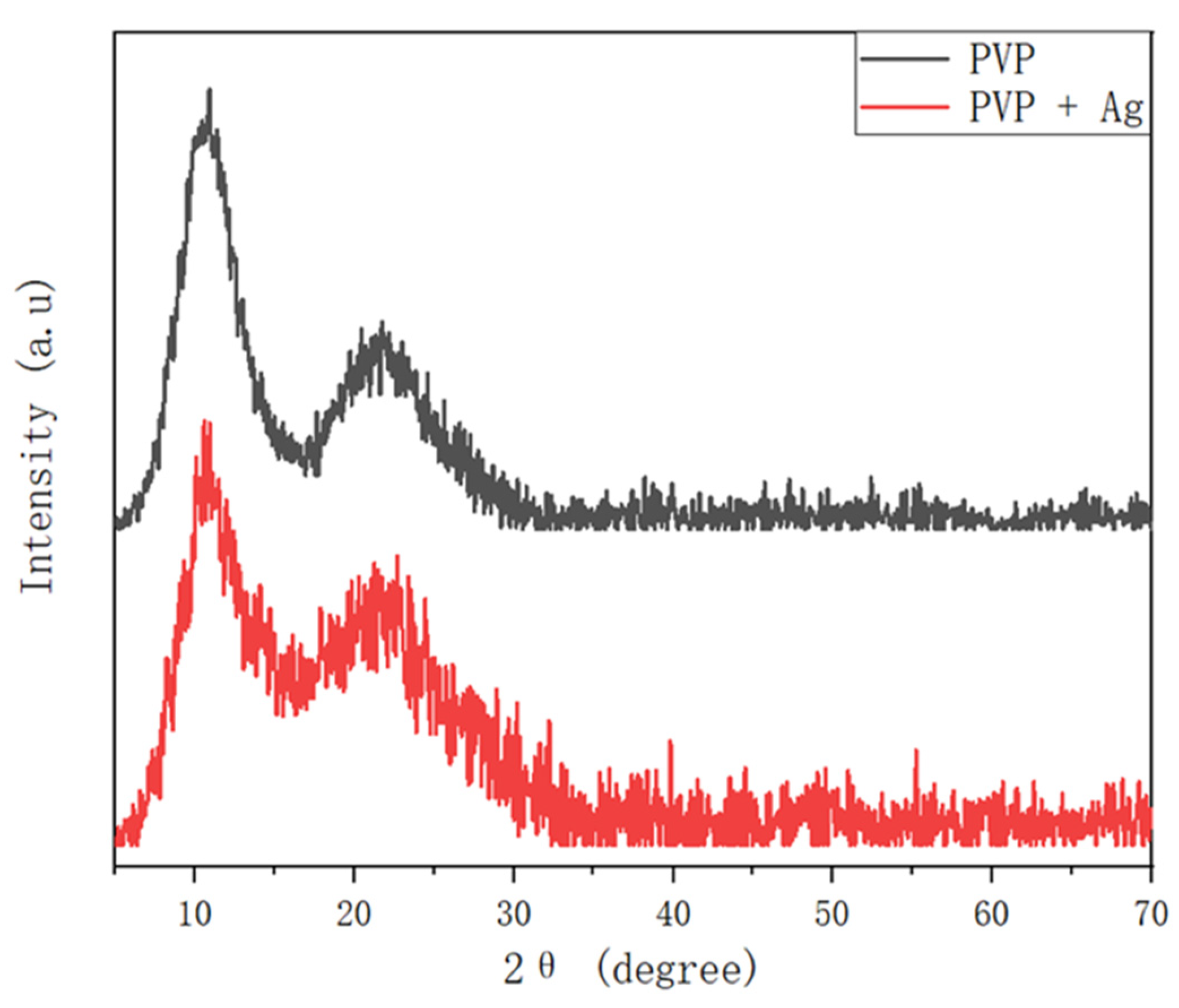
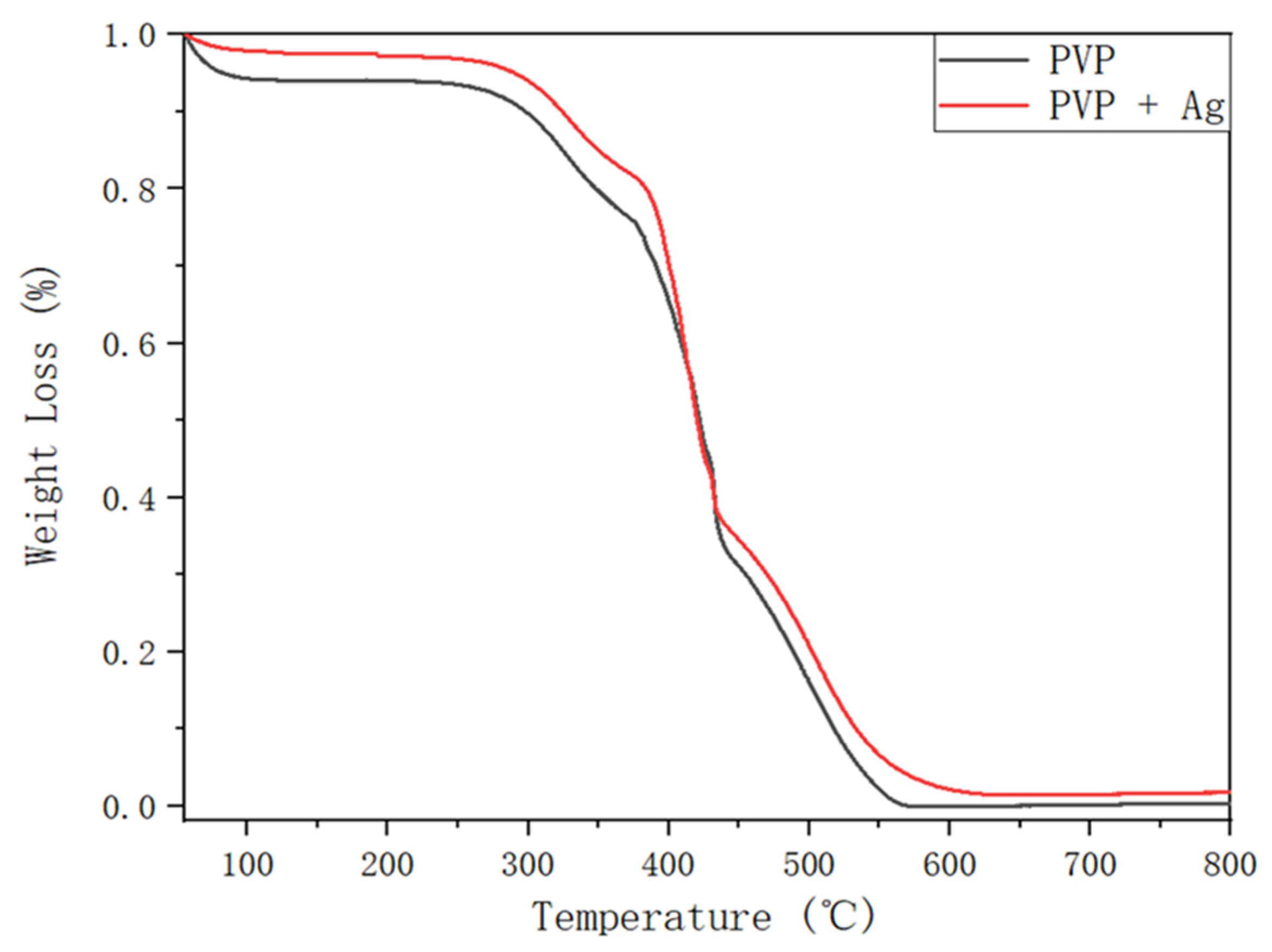
3.3. Fabrication and Characterization of the Hollow PVP/Ag NP Composite Fibers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shrivas, K.; Nirmalkar, N.; Deb, M.K.; Dewangan, K.; Nirmalkar, J.; Kumar, S. Application of functionalized silver nano-particles as a biochemical sensor for selective detection of lysozyme protein in milk sample. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 213, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franci, G.; Falanga, A.; Galdiero, S.; Palomba, L.; Rai, M.; Morelli, G.; Galdiero, M. Silver nanoparticles as potential antibacterial agents. Molecules 2015, 20, 8856–8874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chimentao, R.; Kirm, I.; Medina, F.; Rodriguez, X.; Cesteros, Y.; Salagre, P.; Sueiras, J. Different morphologies of silver nanoparticles as catalysts for the selective oxidation of styrene in the gas phase. Chem. Commun. 2004, 7, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, M.; El Roz, M.; Dong, B.; Retoux, R.; Aad, R.; Cardin, J.; Dufour, C.; Gourbilleau, F.; Gilson, J.-P.; Mintova, S. Photochemical preparation of silver nanoparticles supported on zeolite crystals. Langmuir 2014, 30, 6250–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Takada, N.; Machmudah, S.; Wahyudiono; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Ultrasonic-enhanced fabrication of metal nanoparticles by laser ablation in liquid. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 7512–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qiao, X.; Chen, J.; Ding, S. Preparation of silver nanoparticles by chemical reduction method. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 256, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaydarov, R.A.; Khaydarov, R.R.; Gapurova, O.; Estrin, Y.; Scheper, T. Electrochemical method for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2009, 11, 1193–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Cai, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, G.; Zhang, L. Sonochemical processes and formation of gold nanoparticles within pores of mesoporous silica. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2001, 238, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darroudi, M.; Zak, A.K.; Muhamad, M.; Huang, N.; Hakimi, M. Green synthesis of colloidal silver nanoparticles by sonochemical method. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizukoshi, Y.; Takagi, E.; Okuno, H.; Oshima, R.; Maeda, Y.; Nagata, Y. Preparation of platinum nanoparticles by sonochemical reduction of the Pt (IV) ions: Role of surfactants. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2001, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.S.; Yang, H.J.; Kim, S.B.; Lee, M.S. Mechanism of growth of colloidal silver nanoparticles stabilized by polyvinyl pyrrolidone in γ-irradiated silver nitrate solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 274, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Smita, K.; Cumbal, L.; Debut, A.; Pathak, R.N. Sonochemical synthesis of silver nanoparticles using starch: A comparison. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2014, 2014, 784268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Božanić, D.K.; Djoković, V.; Blanuša, J.; Nair, P.; Georges, M.; Radhakrishnan, T. Preparation and properties of nano-sized Ag and Ag 2 S particles in biopolymer matrix. Eur. Phys. J. E 2007, 22, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, M.; Mills, D.K.; Urbanska, A.M.; Saeb, M.R.; Venugopal, J.R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mozafari, M. Electrospinning for tissue engineering applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-M.; Wutzler, A.; Radusch, H.-J.; Michler, G.H.; Simon, P.; Sperling, R.A.; Parak, W.J. One-dimensional arrangement of gold nanoparticles by electrospinning. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 4949–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, A.; Baskar, C.; Baskar, S.; Ratheesh, G.; Ramakrishna, S. An overview of electrospun nanofibers and their application in energy storage, sensors and wearable/flexible electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 12657–12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, T.W.; Li, L. A review of hollow fibers in application-based learning: From textiles to medical. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 237–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasseuguette, E.; Rouch, J.-C.; Remigy, J.-C. Hollow-fiber coating: Application to preparation of composite hollow-fiber membrane for gas separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 13146–13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, X.; Su, Z.; Wang, P.; Ma, G.; Zhang, S. Tethering of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide inside hollow nanofibers for high-yield synthesis of methanol from carbon dioxide catalyzed by coencapsulated multienzymes. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 4600–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyudiono; Machmudah, S.; Murakami, K.; Okubayashi, S.; Goto, M. Generation of PVP fibers by electrospinning in one-step process under high-pressure CO2. Int. J. Ind. Chem. 2013, 4, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirby, C.F. Phase behavior of polymers in supercritical fluid solvents. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 565–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahyudiono; Machmudah, S.; Kanda, H.; Okubayashi, S.; Goto, M. Formation of PVP hollow fibers by electrospinning in one-step process at sub and supercritical CO2. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2014, 77, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyudiono; Okamoto, K.; Machmudah, S.; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Generation of multihollow structured poly (methyl methacrylate) fibers by electrospinning under pressurized CO2. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2016, 56, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, H.; Machmudah, S.; Wahyudiono; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Electrospinning of poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) fibers containing metal oxide nanoparticles under dense CO2. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 2215–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttiponparnit, K.; Jiang, J.; Sahu, M.; Suvachittanont, S.; Charinpanitkul, T.; Biswas, P. Role of surface area, primary particle size, and crystal phase on titanium dioxide nanoparticle dispersion properties. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vatansever, H.Ç.; Meriçboyu, A.E. Production of antibacterial polyvinylpyrrolidone nanofibers containing silver nanoparticles via electrospinning method. MANAS J. Eng. 2019, 7, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.-G.; Teng, M.-Y.; Chou, W.-L.; Yang, M.-C. Characterization and inhibitory effect of antibacterial PAN-based hollow fiber loaded with silver nitrate. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 225, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.J.; Cathcart, N.; Maly, K.E.; Kitaev, V. Synthesis of silver nanoprisms with variable size and investigation of their optical properties: A first-year undergraduate experiment exploring plasmonic nanoparticles. J. Chem. Educ. 2010, 87, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Nam, J.-S.; Sharma, A.R.; Lee, S.-S. Antimicrobial potential of silver nanoparticles synthesized using medicinal herb coptidis rhizome. Molecules 2018, 23, 2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takada, N.; Fujikawa, A.; Koshizaki, N.; Sasaki, K. Effect of ultrasonic wave on the syntheses of Au and ZnO nanoparticles by laser ablation in water. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 110, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okitsu, K.; Ashokkumar, M.; Grieser, F. Sonochemical synthesis of gold nanoparticles: Effects of ultrasound frequency. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 20673–20675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salkar, R.; Jeevanandam, P.; Aruna, S.; Koltypin, Y.; Gedanken, A. The sonochemical preparation of amorphous silver nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. 1999, 9, 1333–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jasinski, J.B.; Howell, J.L.; Patel, D.; Stephens, D.P.; Gobin, A.M. Tunability and stability of gold nanoparticles obtained from chloroauric acid and sodium thiosulfate reaction. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raffi, M.; Hussain, F.; Bhatti, T.; Akhter, J.; Hameed, A.; Hasan, M. Antibacterial characterization of silver nanoparticles against E. coli ATCC-15224. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2008, 24, 192–196. [Google Scholar]
- Doktycz, S.J.; Suslick, K.S. Interparticle collisions driven by ultrasound. Science 1990, 247, 1067–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prozorov, T.; Prozorov, R.; Suslick, K.S. High velocity interparticle collisions driven by ultrasound. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 13890–13891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahdavi, R.; Talesh, S.S.A. The effect of ultrasonic irradiation on the structure, morphology and photocatalytic performance of ZnO nanoparticles by sol-gel method. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 39, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, A.S.; Vallett, R.; Dion, G.; Schauer, C.L. Effect of electrospinning processing variables on polyacrylonitrile nanoyarns. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyudiono; Ozawa, H.; Machmudah, S.; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Electrospraying technique under pressurized carbon dioxide for hollow particle production. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 142, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beachley, V.; Wen, X. Effect of electrospinning parameters on the nanofiber diameter and length. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Fan, J.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.Y. Effect of applied voltage on diameter and morphology of ultrafine fibers in bubble electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can-Herrera, L.; Oliva, A.; Dzul-Cervantes, M.; Pacheco-Salazar, O.; Cervantes-Uc, J. Morphological and mechanical properties of electrospun polycaprolactone scaffolds: Effect of applied voltage. Polymers 2021, 13, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, M.-C.; Wu, Q.; Kojima, Y.; Zhou, D. Preparation and properties of electrospun poly (vinyl pyrrolidone)/cellulose nanocrystal/silver nanoparticle composite fibers. Materials 2016, 9, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H. Phase behavior of the poly (vinyl pyrrolidone)+ dichloromethane+ supercritical carbon dioxide system. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2008, 272, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyudiono; Okamoto, K.; Machmudah, S.; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Hydrophilic polymer composites synthesized by electrospinning under dense carbon dioxide. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1699, 040010. [Google Scholar]
- El Hotaby, W.; Sherif, H.; Hemdan, B.; Khalil, W.; Khalil, S. Assessment of in situ-prepared polyvinylpyrrolidone-silver nanocomposite for antimicrobial applications. Acta Phys. Pol. Part A 2017, 131, 1554–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-G.; Kresse, I.; Springer, J.; Nissen, J.; Yang, Y.-L. Morphology and gas permselectivity of blend membranes of polyvinylpyridine with ethylcellulose. Polymer 2001, 42, 6859–6869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenillas, A.; Rubiera, F.; Pevida, C.; Pis, J. A comparison of different methods for predicting coal devolatilisation kinetics. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2001, 58, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chrissafis, K.; Bikiaris, D. Can nanoparticles really enhance thermal stability of polymers? Part I: An overview on thermal decomposition of addition polymers. Thermochimica Acta 2011, 523, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xin, Z.; Deng, M.; Wen, Y.; Song, Y. Synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles for ink-jet printed flexible electronics. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 425601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Wavenumber (cm−1) | Functional Groups |
|---|---|
| 3435.47–3415.45 and 1286.37–1284.84 | N–H stretching vibration and C–N stretching vibration from pyrrolidone structure |
| 2950.02–2921.18 | C–H stretching for aliphatic compounds |
| 1651.12–1650.46 | Carbonyl (C–O) stretching of the five-membered cyclic lactam structure |
| 1493.25–1493.16 and 1461.00–1460.82 | C=C aromatic stretching |
| 1422.11–1421.63 and 1372.91–1372.32 | C–H bending vibration from methylene groups (aliphatic compound) |
| 843.82–843.29 | =C–H bending vibrations (unsaturated compounds) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, X.; He, J.; Zhu, L.; Machmudah, S.; Wahyudiono; Kanda, H.; Goto, M. Synthesis of Hollow PVP/Ag Nanoparticle Composite Fibers via Electrospinning under a Dense CO2 Environment. Polymers 2022, 14, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010089
Hu X, He J, Zhu L, Machmudah S, Wahyudiono, Kanda H, Goto M. Synthesis of Hollow PVP/Ag Nanoparticle Composite Fibers via Electrospinning under a Dense CO2 Environment. Polymers. 2022; 14(1):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010089
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Xin, Jiayang He, Li Zhu, Siti Machmudah, Wahyudiono, Hideki Kanda, and Motonobu Goto. 2022. "Synthesis of Hollow PVP/Ag Nanoparticle Composite Fibers via Electrospinning under a Dense CO2 Environment" Polymers 14, no. 1: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010089
APA StyleHu, X., He, J., Zhu, L., Machmudah, S., Wahyudiono, Kanda, H., & Goto, M. (2022). Synthesis of Hollow PVP/Ag Nanoparticle Composite Fibers via Electrospinning under a Dense CO2 Environment. Polymers, 14(1), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010089









