A Relation between Exopolysaccharide from Lactic Acid Bacteria and Properties of Fermentation Induced Soybean Protein Gels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains
2.2. Preparation of Fermentation Induced Gel (FG) and EPS Isolation
2.3. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA) and Water Distribution
2.4. Rheological Analysis
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.6. Raman Spectroscopy
2.7. Chemical Forces of Gel
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
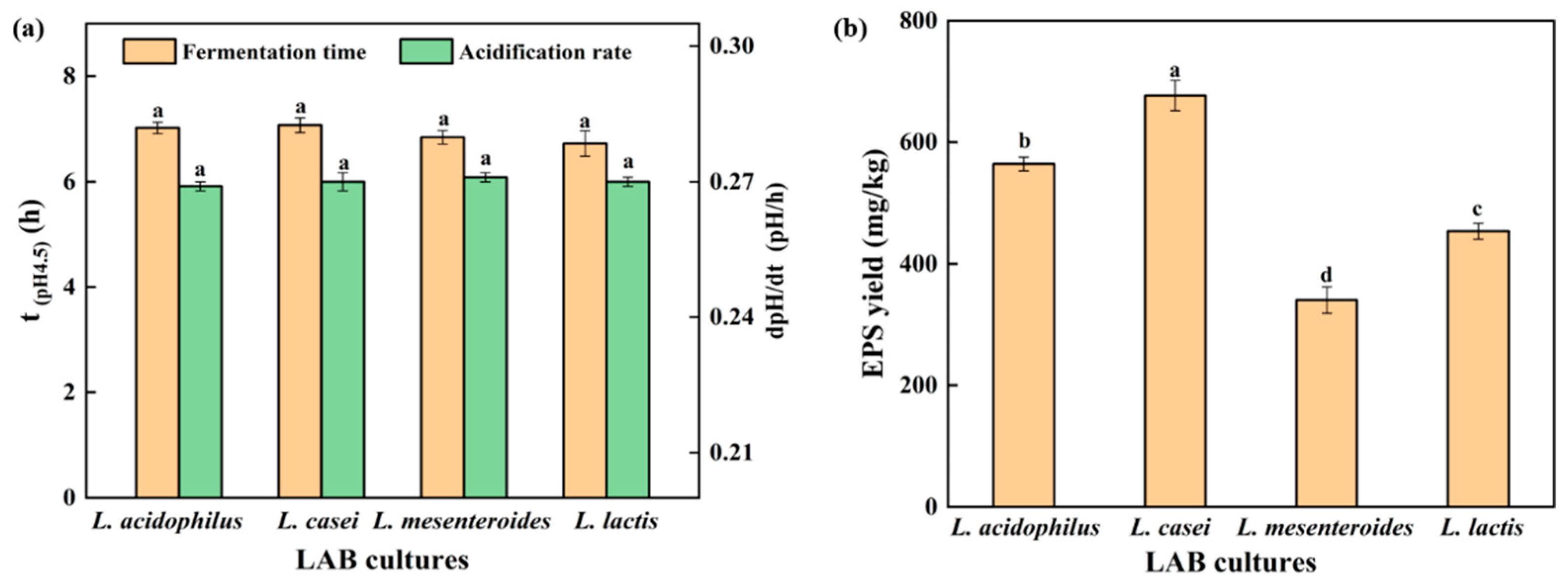
3.1. Acidification and EPS Yield
3.2. Texture Characteristics
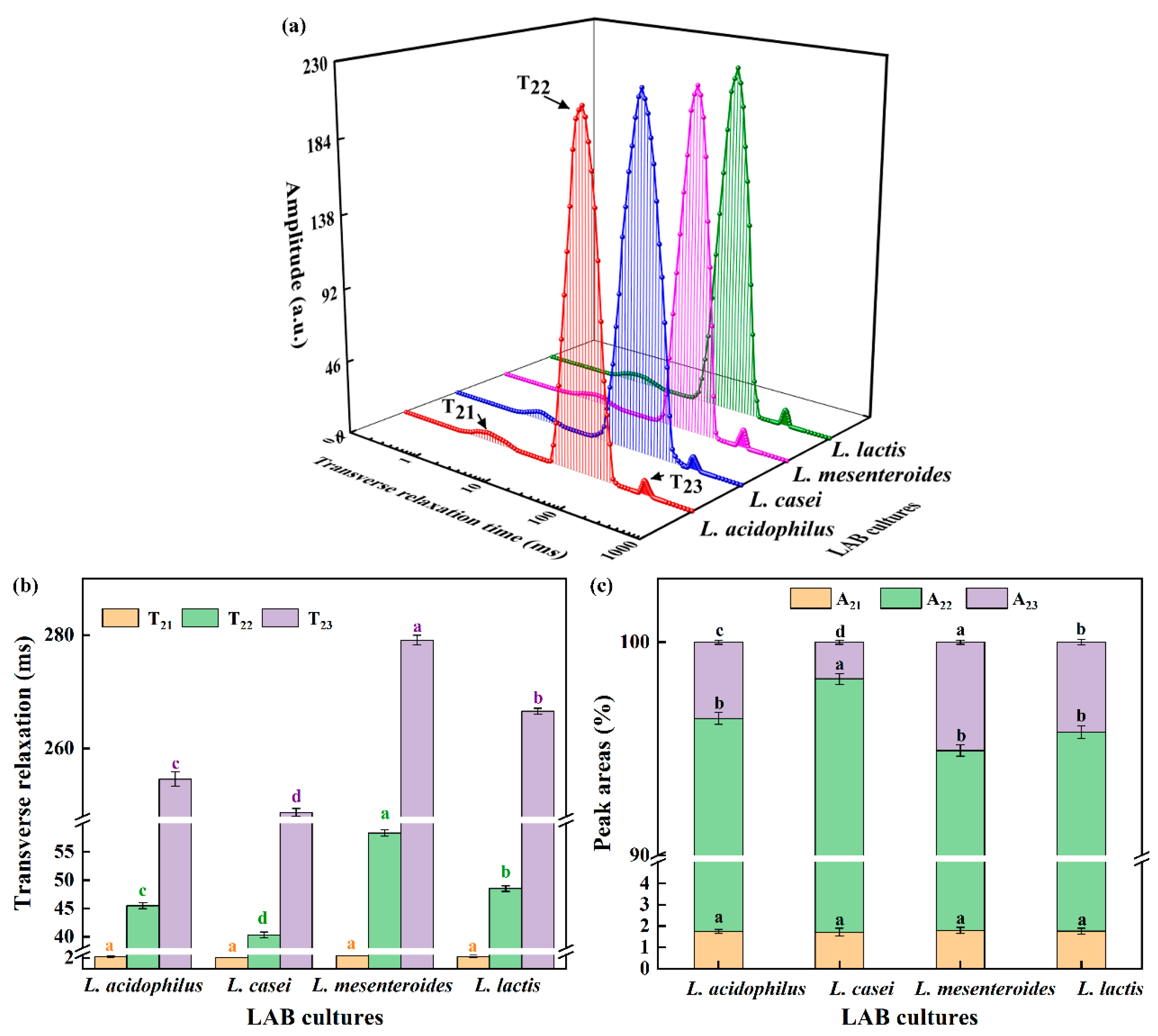
3.3. WHC and LF-NMR
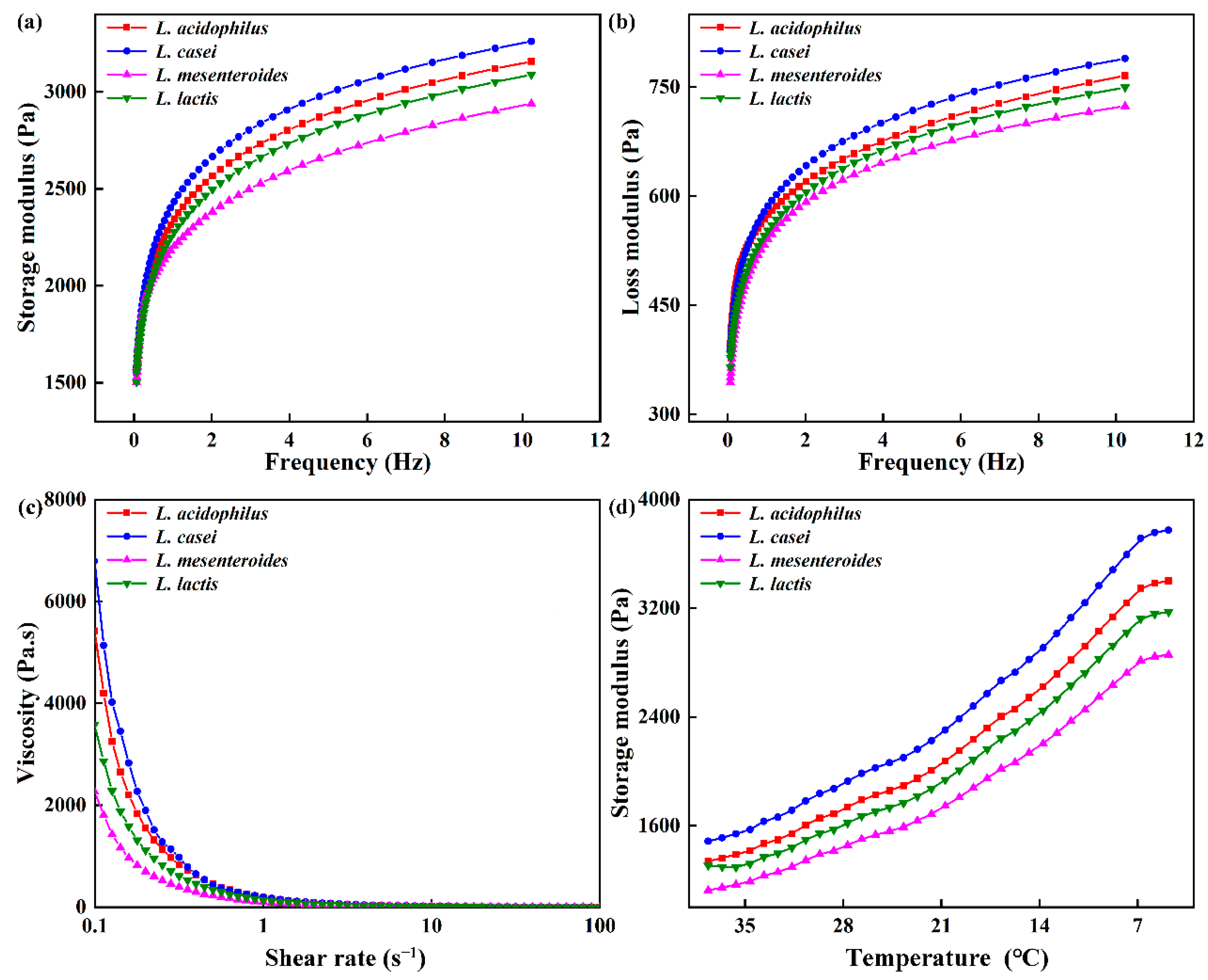
3.4. Rheological Properties
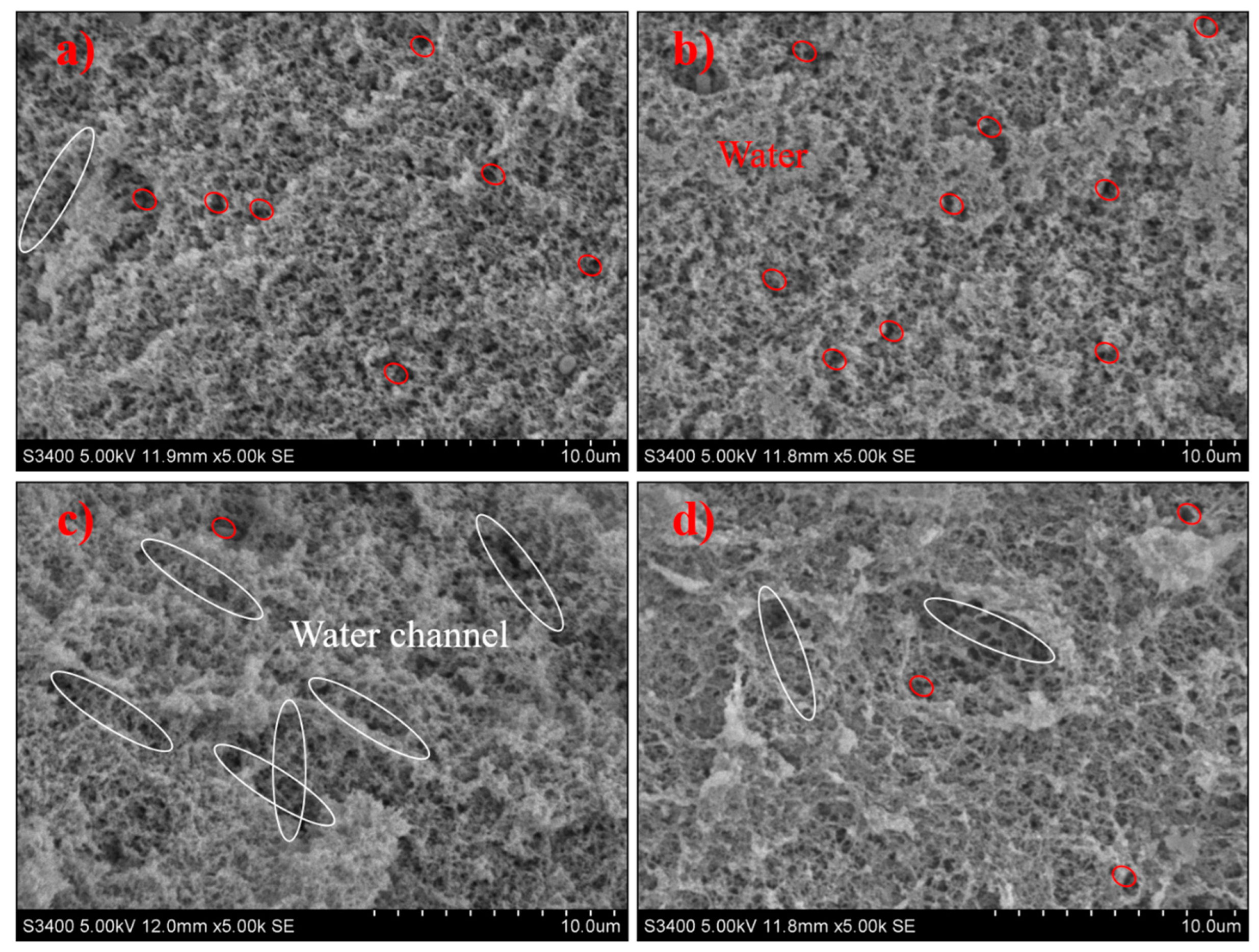
3.5. Microstructure
3.6. Raman Spectral Analysis
3.7. Chemical Force Analysis
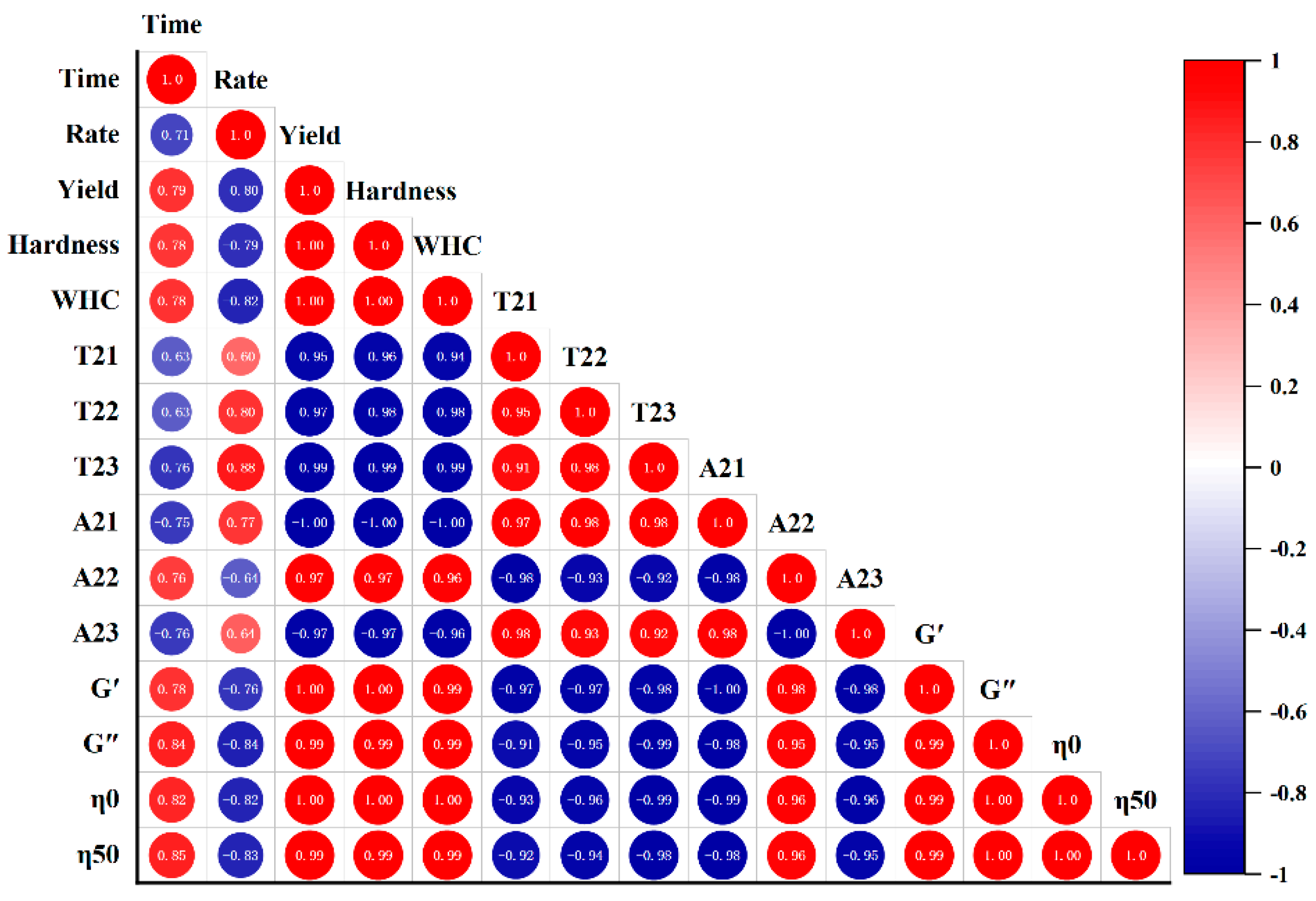
3.8. Correlation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Chen, L.; Hua, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kong, X.; Zhang, C. Effect of preheating-induced denaturation during protein production on the structure and gelling properties of soybean proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, E.A.; Massoud, M.I.; Ragaee, S. Food wastes as natural sources of lactic acid bacterial exopolysaccharides for the functional food industry: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 189, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Kavitake, D.; Devi, P.B.; Shetty, P.H. Bacterial exopolysaccharides for improvement of technological, functional and rheological properties of yoghurt. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Feng, M.; Rui, X.; Jiang, M.; Dong, M. Microbiological, physicochemical and rheological properties of fermented soymilk produced with exopolysaccharide (EPS) producing lactic acid bacteria strains. LWT 2014, 57, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surber, G.; Spiegel, T.; Dang, B.P.; Pombo, A.W.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Cream cheese made with exopolysaccharide-producing Lactococcus lactis: Impact of strain and curd homogenization pressure on texture and syneresis. J. Food Eng. 2021, 308, 110664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, C.-H. Comparative analysis of 3D printability and rheological properties of surimi gels via LF-NMR and dielectric characteristics. J. Food Eng. 2021, 292, 110278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.J.; Vicente, A.A.; Cunha, R.L.; Cerqueira, M.A. Edible oleogels: An opportunity for fat replacement in foods. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 758–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, K.F.; Barrera-Arellano, D.; Ribeiro, A.P.B. Potential application of lipid organogels for food industry. Food Res. Int. 2018, 105, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raut, S.; Bhadoriya, S.S.; Uplanchiwar, V.; Mishra, V.; Gahane, A.; Jain, S.K. Lecithin organogel: A unique micellar system for the delivery of bioactive agents in the treatment of skin aging. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2012, 2, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marangoni, A.G. Organogels: An Alternative Edible Oil-Structuring Method. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 749–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, G.; Grasselli, S.; Malchiodi, A.; Bayer, I.S. Antiseptic povidone-iodine encapsulating edible phospholipid gels. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 619 (Suppl. 2), 126537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramiotis, S.; Papadimitriou, V.; Hatzara, E.; Bekiari, V.; Lianos, P.; Xenakis, A. Lecithin organogels used as bioactive compounds carriers. A microdomain properties investigation. Langumir 2007, 23, 4438–4447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Yang, P.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ma, J. Double-network hydrogel adsorbents for environmental applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ke, C.; Li, L. Physicochemical, rheological and digestive characteristics of soy protein isolate gel induced by lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Eng. 2021, 292, 110243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surber, G.; Mende, S.; Jaros, D.; Rohm, H. Clustering of Streptococcus thermophilus Strains to Establish a Relation between Exopolysaccharide Characteristics and Gel Properties of Acidified Milk. Foods 2019, 8, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, L. Structural characteristics and antioxidant properties of exopolysaccharides isolated from soybean protein gel induced by lactic acid bacteria. LWT 2021, 150, 111811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Ren, F.; Zhao, H.; Cui, B.; Liu, P. Effects of native starch and modified starches on the textural, rheological and microstructural characteristics of soybean protein gel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuldt, S.; Raak, N.; Jaros, D.; Rohm, H. Acid-induced formation of soy protein gels in the presence of NaCl. LWT 2014, 57, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ren, Y.; Li, L. The relationship between charge intensity and bioactivities/processing characteristics of exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria. LWT 2022, 153, 112345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.; Xu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Bansal, N.; Liu, X. Comparison of rheological, tribological, and microstructural properties of soymilk gels acidified with glucono-δ-lactone or culture. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.; Abu-Jdayil, B.; Hamed, F.; Shaker, R. Rheological, textural, microstructural and sensory impact of exopolysaccharide-producing Lactobacillus plantarum isolated from camel milk on low-fat akawi cheese. LWT 2018, 87, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín, D.; Alemán, A.; Montero, P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Protein aggregation, water binding and thermal gelation of salt-ground hake muscle in the presence of wet and dried soy phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Food Hydrocolloid 2018, 82, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Gong, Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Yu, D.; Pan, M. Emulsion gels stabilized by soybean protein isolate and pectin: Effects of high intensity ultrasound on the gel properties, stability and β-carotene digestive characteristics. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 79, 105756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Sun, W. Low frequency magnetic field plus high pH promote the quality of pork myofibrillar protein gel: A novel study combined with low field NMR and Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klost, M.; Brzeski, C.; Drusch, S. Effect of protein aggregation on rheological properties of pea protein gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wu, K.; Wang, F.; Liang, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, G.; Li, Q. Effect of exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria on the texture and microstructure of buffalo yoghurt. Int. Dairy J. 2014, 34, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhou, K.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, B. Insight into the mechanism of textural deterioration of myofibrillar protein gels at high temperature conditions. Food Chem. 2020, 330, 127186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, Y.; Joulak, I.; Amara, C.B.; Casillo, A.; Attia, H.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Azabou, S. Study of interactions between anionic exopolysaccharides produced by newly isolated probiotic bacteria and sodium caseinate. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2018, 167, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Frank, J.; Elsoda, M. Observation of bacterial exopolysaccharide in dairy products using cryo-scanning electron microscopy. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G. Insight into the mechanism of myofibrillar protein gel influenced by konjac glucomannan: Moisture stability and phase separation behavior. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Wang, L.; Ma, J.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, W. The direct current magnetic field improved the water retention of low-salt myofibrillar protein gel under low temperature condition. LWT 2021, 151, 112034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhou, T.; Wang, X.; Zou, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, W. Effects of the structure and gel properties of myofibrillar protein on chicken breast quality treated with ultrasound-assisted potassium alginate. Food Chem. 2021, 358, 129873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, M.; Jiang, L.; Song, Q.; Liu, S.; Xie, J. Influence of Mesona blumes polysaccharide on the gel properties and microstructure of acid-induced soy protein isolate gels. Food Chem 2020, 313, 126125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purohit, D.; Hassan, A.; Bhatia, E.; Zhang, X.; Dwivedi, C. Rheological, sensorial, and chemopreventive properties of milk fermented with exopolysaccharide-producing lactic cultures. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hassan, A.; Ipsen, R.; Janzen, T.; Qvist, K. Microstructure and Rheology of Yogurt Made with Cultures Differing Only in Their Ability to Produce Exopolysaccharides. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, W.; Lei, Z.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J. Effect of polysaccharides on the gel characteristics of “Yu Dong” formed with fish (Cyprinus carpio L.) scale aqueous extract. Food Chem 2021, 338, 127792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A. ADSA Foundation Scholar Award: Possibilities and Challenges of Exopolysaccharide-Producing Lactic Cultures in Dairy Foods. J. Dairy Sci. 2008, 91, 1282–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mende, S.; Peter, M.; Bartels, K.; Dong, T.; Rohm, H.; Jaros, D. Concentration dependent effects of dextran on the physical properties of acid milk gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, S.R.; Lopes-Da-Silva, J.A. Effect of the molecular weight of a neutral polysaccharide on soy protein gelation. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Hugenholtz, J.; Zoon, P. An overview of the functionality of exopolysaccharides produced by lactic acid bacteria. Int. Dairy J. 2002, 12, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, M.; Schaffer-Lequart, C. Gelation of skim milk containing anionic exopolysaccharides and recovery of texture after shearing. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Z.; Liu, W.; McClements, D.; Zou, L. Rheological, structural, and microstructural properties of ethanol induced cold-set whey protein emulsion gels: Effect of oil content. Food Chem. 2019, 291, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuhongsung, P.; Zhang, M.; Devahastin, S. Investigation on 3D printing ability of soybean protein isolate gels and correlations with their rheological and textural properties via LF-NMR spectroscopic characteristics. LWT 2020, 122, 109019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| L. acidophilus | L. casei | L. mesenteroides | L. lactis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (g) | 278.60 ± 8.93 b | 319.74 ± 9.98 a | 200.99 ± 6.41 d | 242.29 ± 8.74 c |
| Springiness | 0.76 ± 0.03 ab | 0.80 ± 0.01 a | 0.65 ± 0.02 c | 0.74 ± 0.01 b |
| Cohesiveness | 0.46 ± 0.02 a | 0.48 ± 0.02 a | 0.47 ± 0.03 a | 0.48 ± 0.02 a |
| Gumminess | 114.15 ± 12.34 b | 108.45 ± 2.20 b | 66.41 ± 5.59 c | 140.87 ± 7.90 a |
| Chewiness | 89.58 ± 12.52 b | 77.07 ± 3.88 b | 46.85 ± 13.62 c | 116.35 ± 6.31 a |
| WHC (%) | 79.26 ± 3.75 b | 87.74 ± 2.00 a | 58.99 ± 0.81 d | 69.29 ± 1.88 c |
| L. acidophilus | L. casei | L. mesenteroides | L. lactis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G′, at 1 Hz | 2344.97 ± 18.06 b | 2434.22 ± 14.33 a | 2205.23 ± 17.74 d | 2278.50 ± 25.43 c |
| G″, at 1 Hz | 574.28 ± 15.05 ab | 586.24 ± 11.64 a | 540.40 ± 10.41 c | 552.92 ± 13.12 bc |
| Tan δ, at 1 Hz | 0.250 ± 0.015 a | 0.240 ± 0.013 a | 0.265 ± 0.013 a | 0.256 ± 0.005 a |
| Slope of log (G′) vs. log (f) | 0.130 ± 0.004 a | 0.160 ± 0.008 a | 0.124 ± 0.005 b | 0.139 ± 0.005 a |
| Slope of log (G″) vs. log (f) | 0.139 ± 0.009 ab | 0.146 ± 0.007 a | 0.110 ± 0.005 b | 0.139 ± 0.003 ab |
| K′ | 2316.02 ± 8.74 b | 2487.70 ± 15.43 a | 2197.95 ± 10.08 d | 2257.28 ± 19.49 c |
| n′ | 0.138 ± 0.012 a | 0.142 ± 0.011 a | 0.123 ± 0.009 a | 0.138 ± 0.002 a |
| R′2 | 0.999 | 0.996 | 0.996 | 0.999 |
| K″ | 118.32 ± 1.31 b | 129.34 ± 1.19 a | 90.81 ± 0.95 d | 99.73 ± 0.62 c |
| n″ | 0.224 ± 0.023 ab | 0.25 ± 0.009 a | 0.198 ± 0.007 b | 0.216 ± 0.015 ab |
| R″2 | 0.995 | 0.997 | 0.974 | 0.997 |
| η0 (mPa s) | 5419.14 ± 73.19 b | 6793.57 ± 35.49 a | 2265.62 ± 57.63 d | 3577.73 ± 67.86 c |
| η50 (mPa s) | 1.66 ± 0.10 b | 2.00 ± 0.08 a | 0.80 ± 0.01 d | 1.10 ± 0.00 c |
| (mg/mL) | L. acidophilus | L. casei | L. mesenteroides | L. lactis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S2–S1 Ionic bond | 8.48 ± 0.14 Bb | 9.50 ± 0.18 Ba | 7.08 ± 0.11 Bd | 7.69 ± 0.17 Bc |
| S3–S2 Hydrogen bonds | 3.12 ± 0.03 Cb | 3.23 ± 0.04 Da | 2.93 ± 0.03 Cc | 3.08 ± 0.05 Cb |
| S4–S3 Hydrophobic interactions | 24.57 ± 1.94 Ab | 29.83 ± 1.74 Aa | 20.58 ± 1.25 Abc | 22.10 ± 1.30 Ac |
| S5–S4 Disulfide bonds | 6.56 ± 0.10 Bb | 6.97 ± 0.10 Ca | 6.01 ± 0.12 Bc | 6.23 ± 0.11 Bc |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Feng, J.; Zhu, Q.; Hong, R.; Li, L. A Relation between Exopolysaccharide from Lactic Acid Bacteria and Properties of Fermentation Induced Soybean Protein Gels. Polymers 2022, 14, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010090
Yang X, Feng J, Zhu Q, Hong R, Li L. A Relation between Exopolysaccharide from Lactic Acid Bacteria and Properties of Fermentation Induced Soybean Protein Gels. Polymers. 2022; 14(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xiaoyu, Jiao Feng, Qianqian Zhu, Rui Hong, and Liang Li. 2022. "A Relation between Exopolysaccharide from Lactic Acid Bacteria and Properties of Fermentation Induced Soybean Protein Gels" Polymers 14, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010090
APA StyleYang, X., Feng, J., Zhu, Q., Hong, R., & Li, L. (2022). A Relation between Exopolysaccharide from Lactic Acid Bacteria and Properties of Fermentation Induced Soybean Protein Gels. Polymers, 14(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14010090





