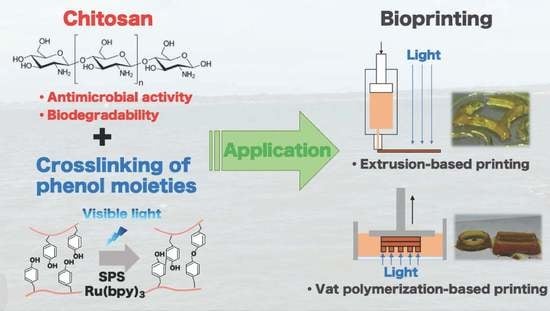
Visible Light-Curable Chitosan Ink for Extrusion-Based and Vat Polymerization-Based 3D Bioprintings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
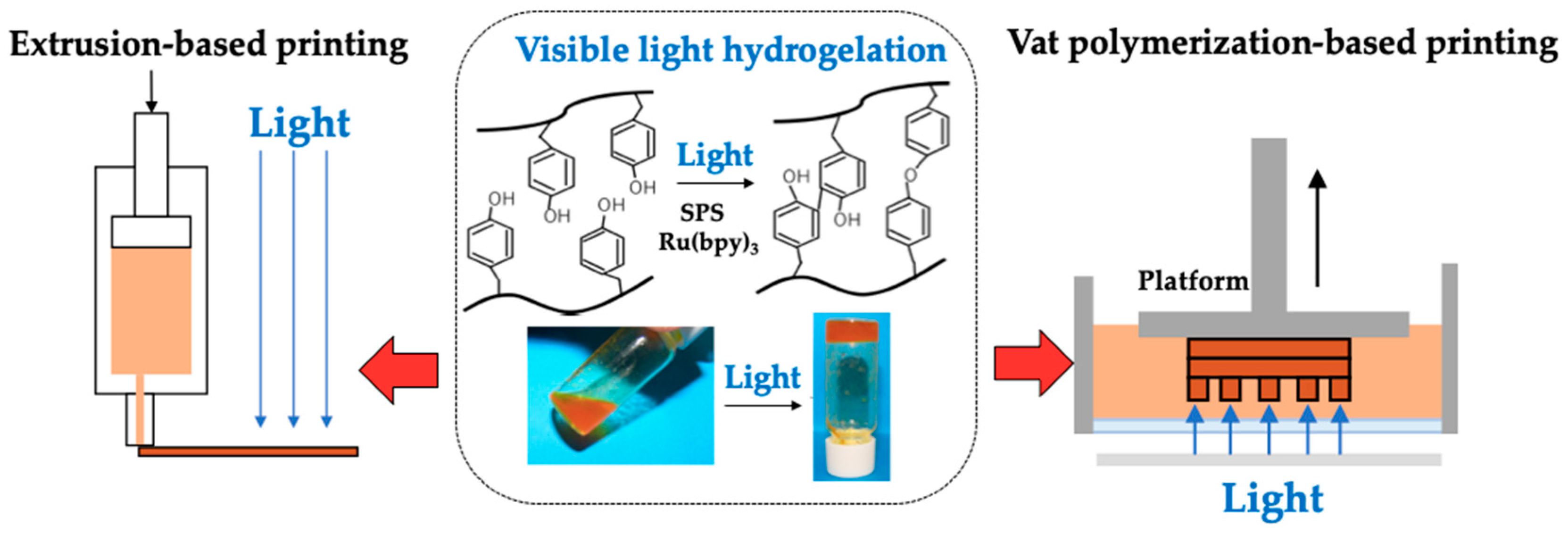
2.2. Synthesis of Chitosan-Ph
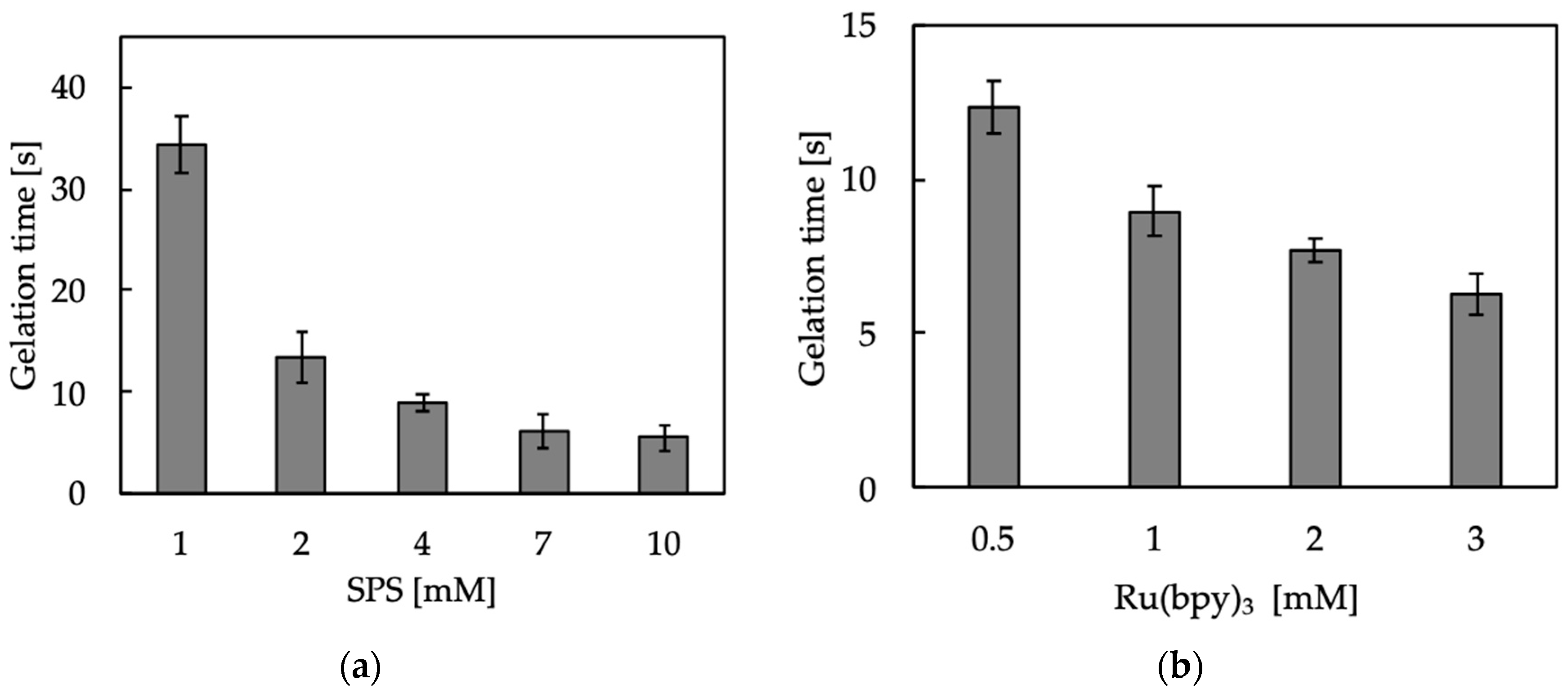
2.3. Gelation Time
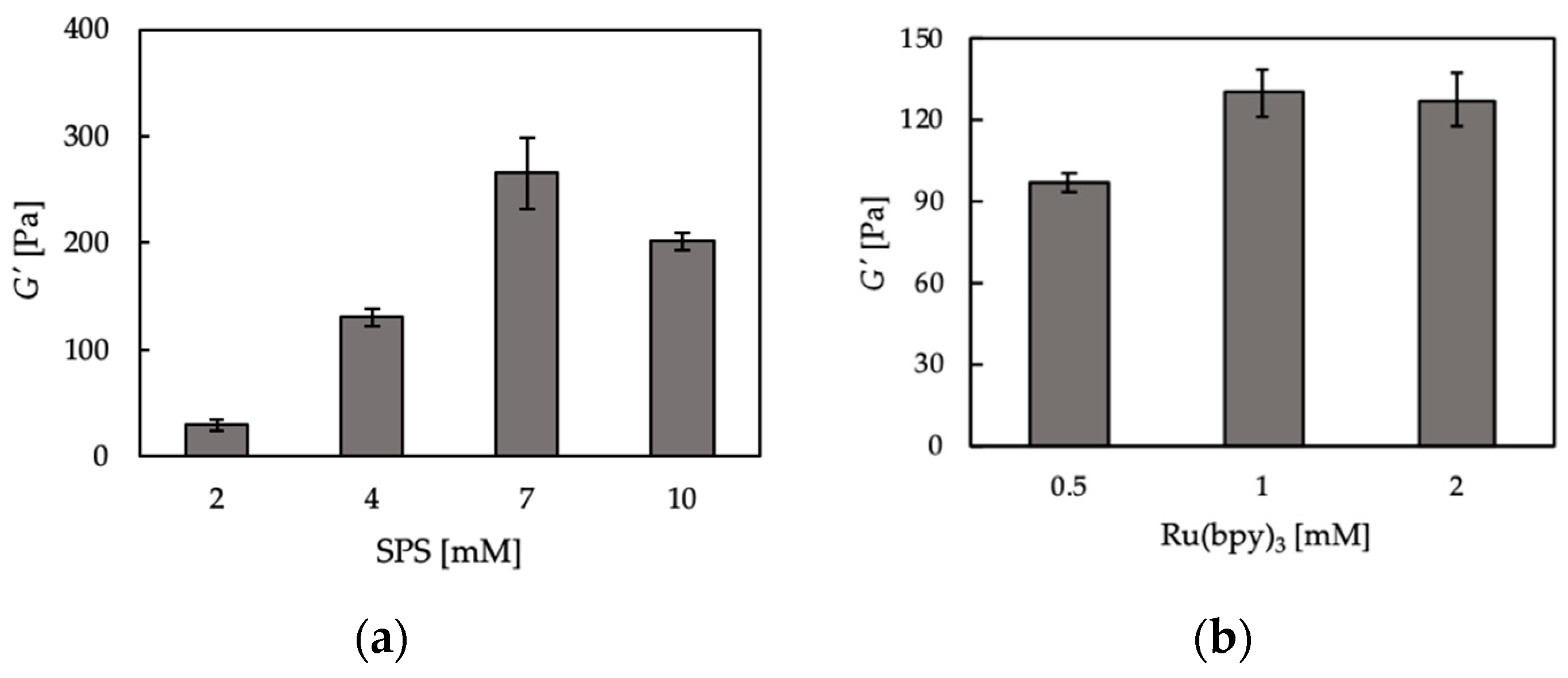
2.4. Viscoelastic Property of Hydrogels
2.5. Extrusion-Based Bioprinting
2.6. Vat Polymerization-Based Bioprinting
2.7. Chitosan-Ph Hydrogel Swelling
2.8. Chitosan-Ph Hydrogel Biodegradability
2.9. Chitosan-Ph Antimicrobial Activity
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Hydrogelation and Hydrogel Properties
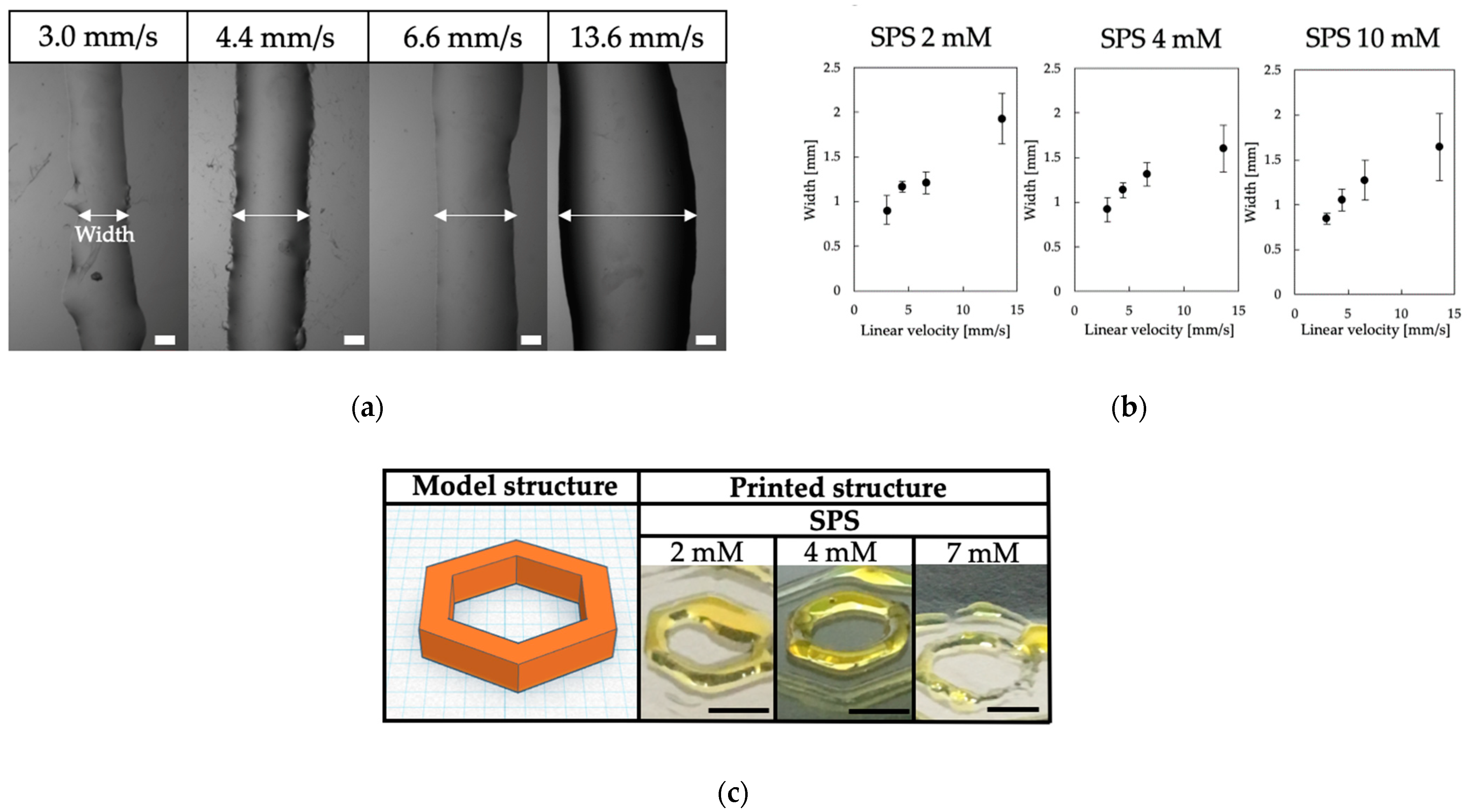
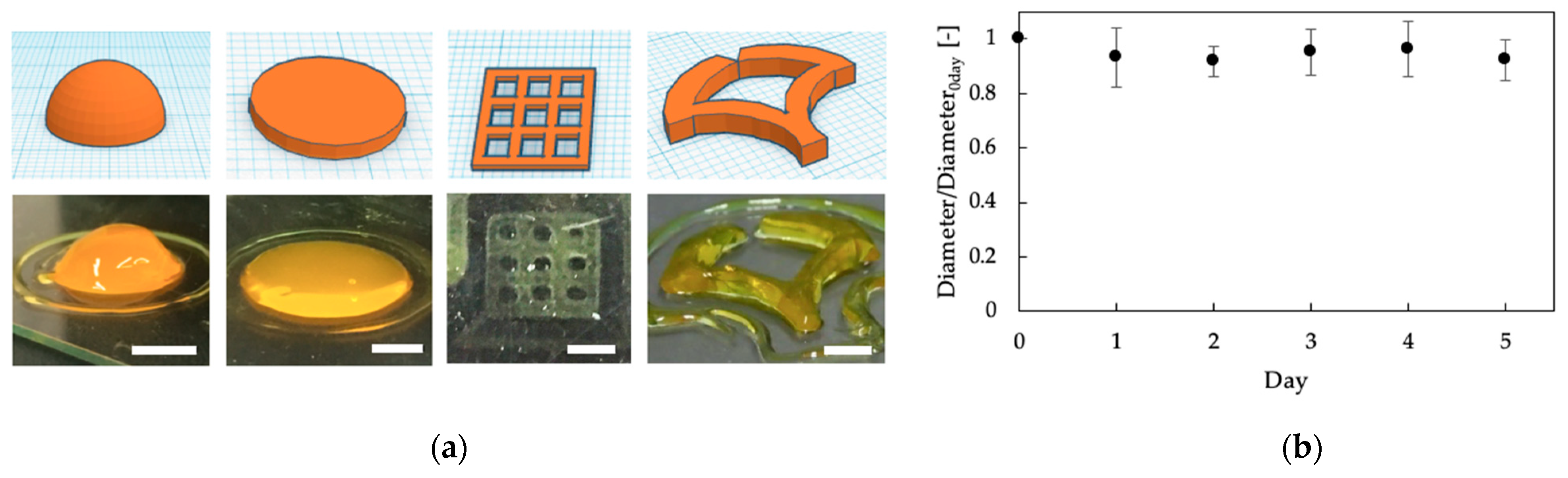
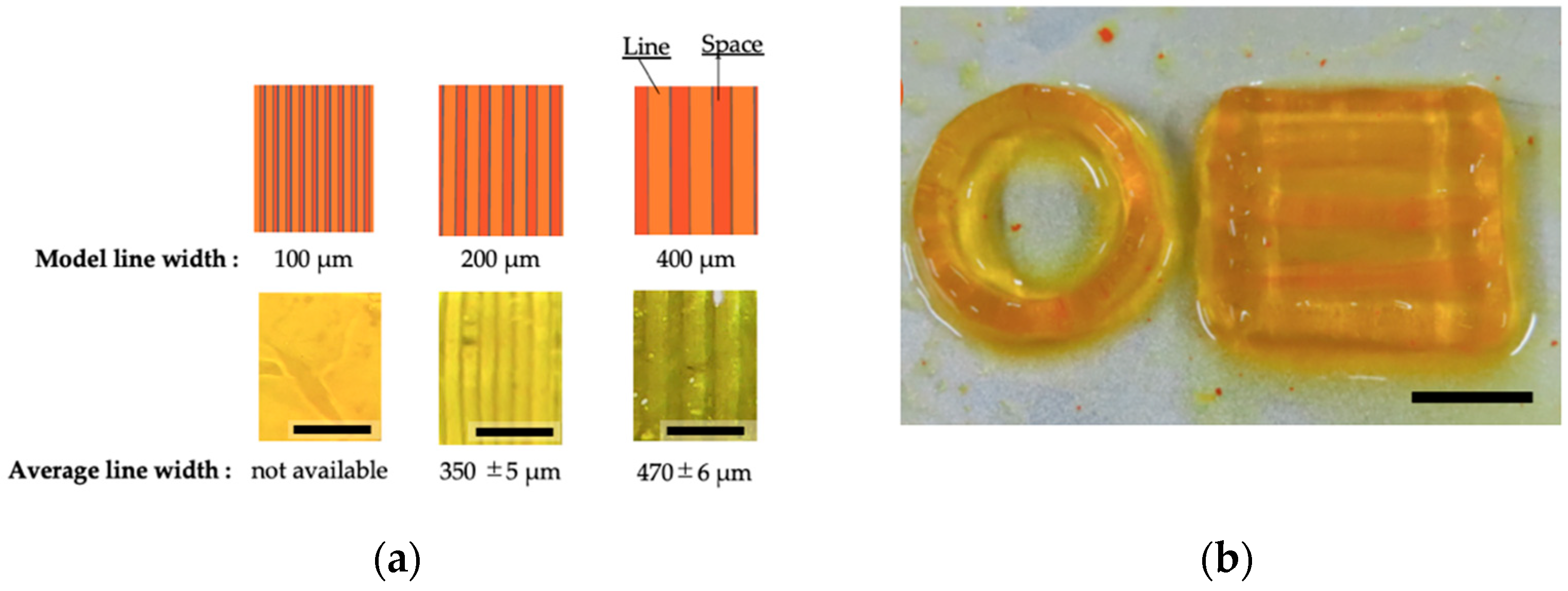
3.2. Printability of Chitosan-Ph Inks
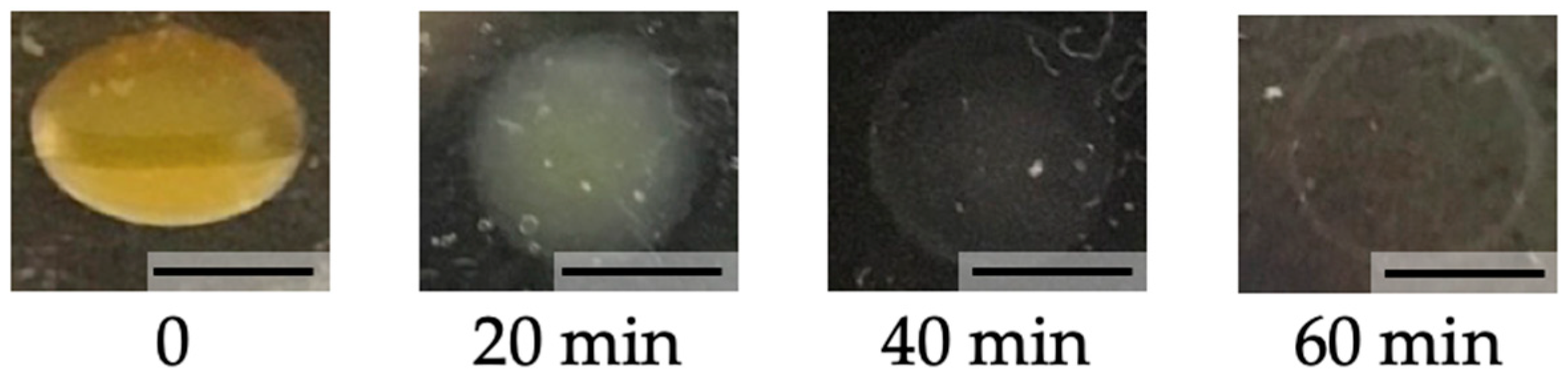
3.3. Biodegradability
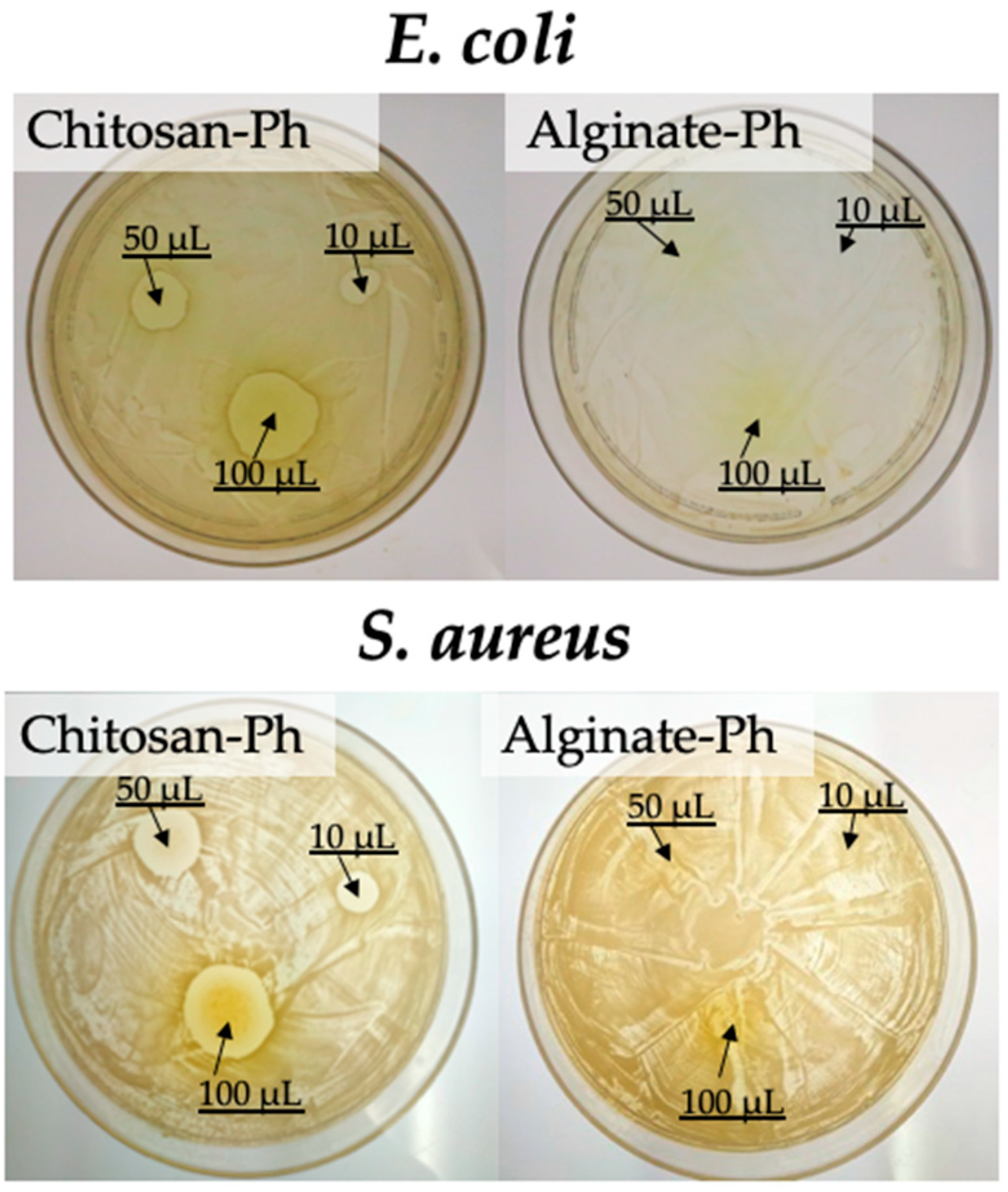
3.4. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Derakhshanfar, S.; Mbeleck, R.; Xu, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, W.; Xing, M. 3D bioprinting for biomedical devices and tissue engineering: A review of recent trends and advances. Bioact. Mater. 2018, 3, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor-Ozkerim, P.S.; Inci, I.; Zhang, Y.S.; Khademhosseini, A.; Dokmeci, M.R. Bioinks for 3D bioprinting: An overview. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 915–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.V.; Atala, A. 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, C.; Bouissil, S.; Gantumur, E.; Carranza, M.S.; Yoshii, A.; Sakai, S.; Pierre, G.; Michaud, P.; Delattre, C. Use of anionic polysaccharides in the development of 3D bioprinting technology. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillispie, G.; Prim, P.; Copus, J.; Fisher, J.; Mikos, A.G.; Yoo, J.J.; Atala, A.; Lee, S.J. Assessment methodologies for extrusion-based bioink printability. Biofabrication 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Pei, B.; Chen, J.; Zhou, D.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; Jia, W.; Xu, T. Inkjet Bioprinting of Biomaterials. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 10793–10833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.L.; Lee, J.M.; Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.W.; Lee, K.X.A.; Yeong, W.Y.; Shen, Y.F. Vat polymerization-based bioprinting-process, materials, applications and regulatory challenges. Biofabrication 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimene, D.; Kaunas, R.; Gaharwar, A.K. Hydrogel Bioink Reinforcement for Additive Manufacturing: A Focused Review of Emerging Strategies. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, B. State-of-the-Art Review of 3D Bioprinting for Cardiovascular Tissue Engineering. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Molino, B.Z.; Cheng, F.; Molino, P.J.; Yue, Z.; Su, D.; Wang, X.; Willför, S.; Xu, C.; Wallace, G.G. On Low-Concentration Inks Formulated by Nanocellulose Assisted with Gelatin Methacrylate (GelMA) for 3D Printing toward Wound Healing Application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 8838–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessop, Z.M.; Al-Sabah, A.; Gao, N.; Kyle, S.; Thomas, B.; Badiei, N.; Hawkins, K.; Whitaker, I.S. Printability of pulp derived crystal, fibril and blend nanocellulose-alginate bioinks for extrusion 3D bioprinting. Biofabrication 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, S.; Sun, W. Bioprinting endothelial cells with alginate for 3D tissue constructs. J. Biomech. Eng. 2009, 131, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goy, R.C.; De Britto, D.; Assis, O.B.G. A review of the antimicrobial activity of chitosan. Polimeros 2009, 19, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elieh Ali Komi, D.; Sharma, L.; Dela Cruz, C.S. Chitin and Its Effects on Inflammatory and Immune Responses. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 54, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, H. Topical formulations and wound healing applications of chitosan 2. Topical findings of healing with chitosan at early phase of experimental open skin wound. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 52, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.L.; Chua, C.K.; Shen, Y.F. Print Me An Organ! Why We Are Not There Yet. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 97, 101145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Allardyce, B.J.; Rajkhowa, R.; Zhao, Y.; Dilley, R.J.; Redmond, S.L.; Wang, X.; Liu, X. 3D Printing of Silk Particle-Reinforced Chitosan Hydrogel Structures and Their Properties. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Fu, H.; Wang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Z. BMSCs-laden gelatin/sodium alginate/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel for 3D bioprinting. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 108423–108430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, K.; Zhou, X.; Li, T.; Xu, Y.; Qiang, L.; Peng, M.; Xu, Y.; Xie, L.; He, C.; et al. Controllable fabrication of hydroxybutyl chitosan/oxidized chondroitin sulfate hydrogels by 3D bioprinting technique for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wong, C.; Chang, S.; Hsu, S. An injectable, self-healing phenol-functionalized chitosan hydrogel with fast gelling property and visible light-crosslinking capability for 3D printing Institute of Polymer Science and Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Institute of Cel. Acta Biomater. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchels, F.P.W.; Feijen, J.; Grijpma, D.W. A review on stereolithography and its applications in biomedical engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6121–6130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.S.; Schon, B.S.; Mekhileri, N.V.; Brown, G.C.J.; Chia, C.M.; Prabakar, S.; Hooper, G.J.; Woodfield, T.B.F. New Visible-Light Photoinitiating System for Improved Print Fidelity in Gelatin-Based Bioinks. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1752–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Ohi, H.; Taya, M. Gelatin/hyaluronic acid content in hydrogels obtained through blue light-induced gelation affects hydrogel properties and adipose stem cell behaviors. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Kamei, H.; Mori, T.; Hotta, T.; Ohi, H.; Nakahata, M.; Taya, M. Visible Light-Induced Hydrogelation of an Alginate Derivative and Application to Stereolithographic Bioprinting Using a Visible Light Projector and Acid Red. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Cui, S.; Zhou, L.; He, K.; Song, L.; Liang, H.; He, C. Effect of cosmetic chemical preservatives on resident flora isolated from healthy facial skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Yamada, Y.; Zenke, T.; Kawakami, K. Novel chitosan derivative soluble at neutral pH and in-situ gellable via peroxidase-catalyzed enzymatic reaction. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Khanmohammadi, M.; Khoshfetrat, A.B.; Taya, M. Horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed formation of hydrogels from chitosan and poly(vinyl alcohol) derivatives both possessing phenolic hydroxyl groups. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 111, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Hirose, K.; Taguchi, K.; Ogushi, Y.; Kawakami, K. An injectable, in situ enzymatically gellable, gelatin derivative for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3371–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, S.; Mochizuki, K.; Qu, Y.; Mail, M.; Nakahata, M.; Taya, M. Peroxidase-catalyzed microextrusion bioprinting of cell-laden hydrogel constructs in vaporized ppm-level hydrogen peroxide. Biofabrication 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.S.; Ramaswamy, Y.; Roberts, J.J.; Alves, M.H.; Poole-Warren, L.A.; Martens, P.J. Promoting Cell Survival and Proliferation in Degradable Poly(vinyl alcohol)-Tyramine Hydrogels. Macromol. Biosci. 2015, 15, 1423–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.M.; Park, S.A.; Park, W.H. Effect of photoinitiator on chain degradation of hyaluronic acid. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oropallo, W.; Piegl, L.A. Ten challenges in 3D printing. Eng. Comput. 2016, 32, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, H.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Luo, S.; Nie, J.; Zhu, X. Photo-curing 3D printing technique and its challenges. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, H.; Tokiwa, Y. Effects of higher-order structure of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) on its biodegradation. II. Effects of crystal structure on microbial degradation. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 1993, 1, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Wang, X. Biodegradable polymers and stem cells for bioprinting. Molecules 2016, 21, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Xiao, S.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, F.; Qin, C. Chitosan-acorn starch-eugenol edible film: Physico-chemical, barrier, antimicrobial, antioxidant and structural properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altiok, D.; Altiok, E.; Tihminlioglu, F. Physical, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of chitosan films incorporated with thyme oil for potential wound healing applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2010, 21, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Chi, F.; Tan, Z.; Liu, L. Development and characterization of novel active chitosan films containing fennel and peppermint essential oils. Coatings 2020, 10, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qian, J.; Ding, F. Emerging Chitosan-Based Films for Food Packaging Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 395–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, R.R.; Ullah, M.W.; Pei, E.; Yang, G. Antimicrobial Inks: The Anti-Infective Applications of Bioprinted Bacterial Polysaccharides. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1155–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, A.; Kuss, M.A.; Duan, B.; Kielian, T. 3D Bioprinted Scaffolds Containing Viable Macrophages and Antibiotics Promote Clearance of Staphylococcus aureus Craniotomy-Associated Biofilm Infection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 12298–12307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hidaka, M.; Kojima, M.; Nakahata, M.; Sakai, S. Visible Light-Curable Chitosan Ink for Extrusion-Based and Vat Polymerization-Based 3D Bioprintings. Polymers 2021, 13, 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091382
Hidaka M, Kojima M, Nakahata M, Sakai S. Visible Light-Curable Chitosan Ink for Extrusion-Based and Vat Polymerization-Based 3D Bioprintings. Polymers. 2021; 13(9):1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091382
Chicago/Turabian StyleHidaka, Mitsuyuki, Masaru Kojima, Masaki Nakahata, and Shinji Sakai. 2021. "Visible Light-Curable Chitosan Ink for Extrusion-Based and Vat Polymerization-Based 3D Bioprintings" Polymers 13, no. 9: 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091382
APA StyleHidaka, M., Kojima, M., Nakahata, M., & Sakai, S. (2021). Visible Light-Curable Chitosan Ink for Extrusion-Based and Vat Polymerization-Based 3D Bioprintings. Polymers, 13(9), 1382. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13091382