Kinked Bisamides as Efficient Supramolecular Foam Cell Nucleating Agents for Low-Density Polystyrene Foams with Homogeneous Microcellular Morphology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Self-Assembly of Kinked Bisamides and Nano-Object Characterization
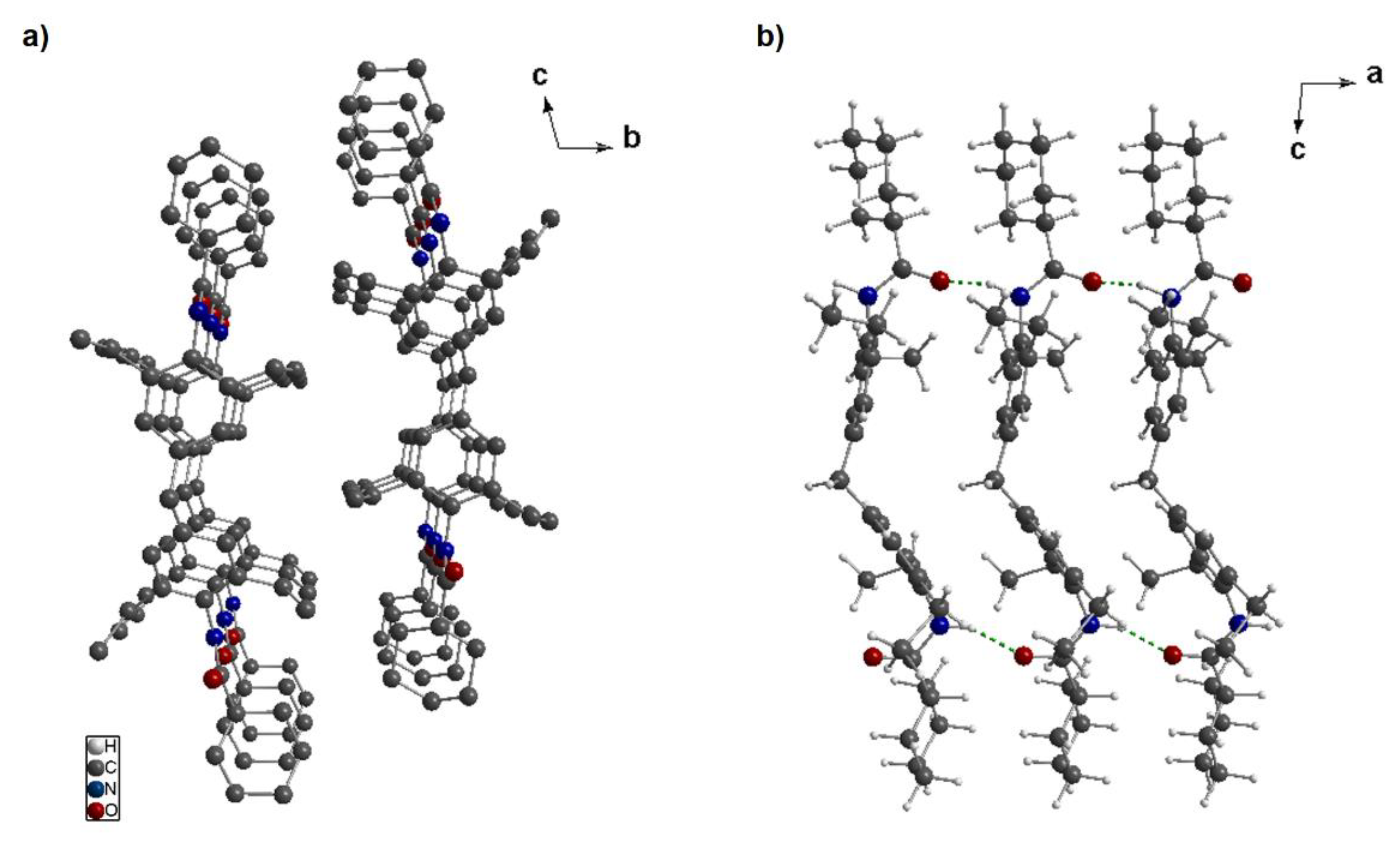
2.3. Structural Studies of Kinked Bisamide 3a
2.4. Polymer Processing and Foaming
2.4.1. Masterbatch Preparation
2.4.2. Compounding and Preparation of Injection-Molded Specimen for Batch Foaming
2.4.3. Batch Foaming
2.4.4. Extrusion Foaming
2.5. Foam Characterization
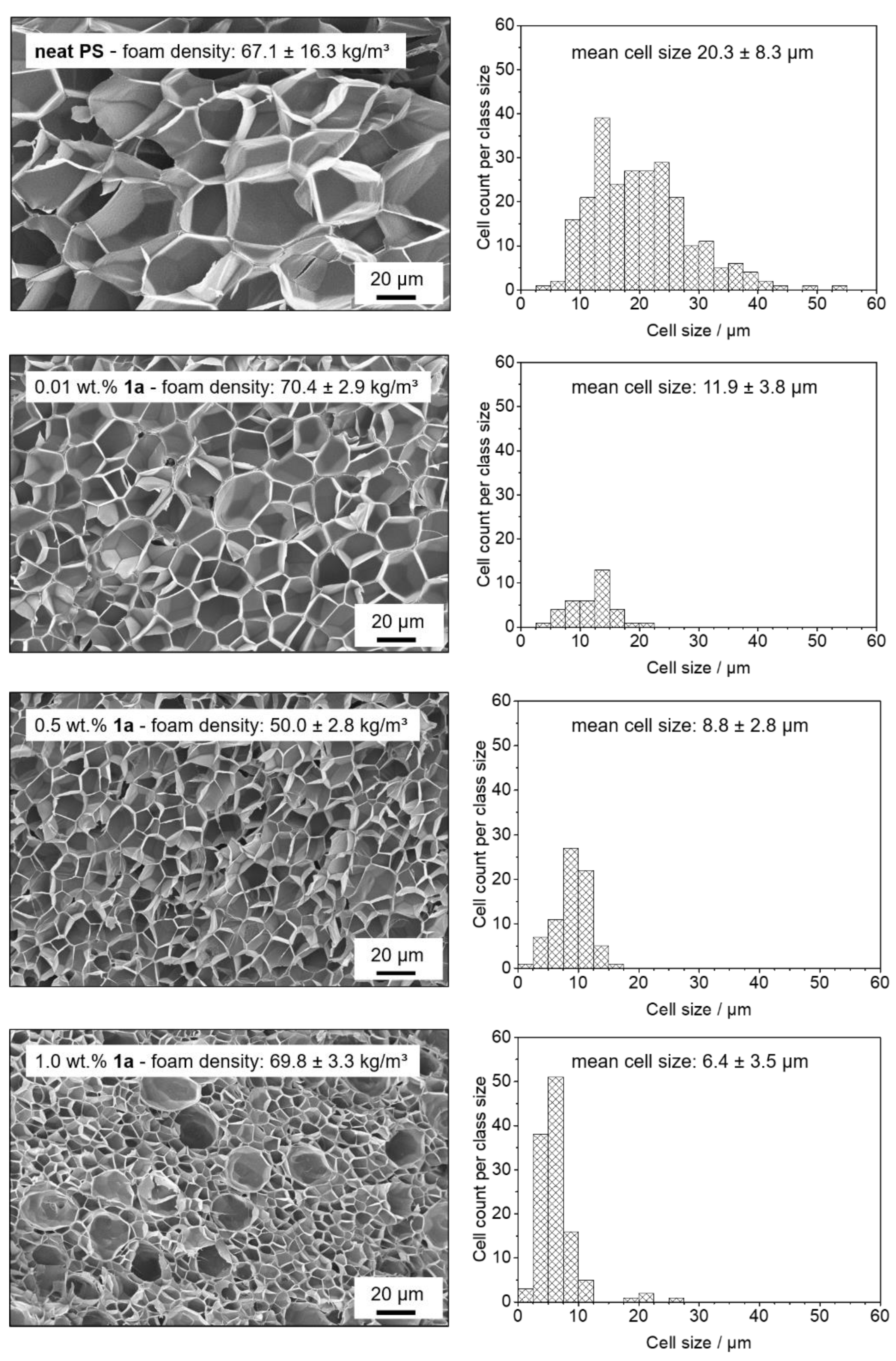
2.5.1. Foam Morphology
2.5.2. Foam Density
2.5.3. Cell Density
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis, Characterization, and Thermal Properties of Kinked Bisamides
3.2. Self-Assembly of Kinked Bisamides from Xylene
3.3. Crystal Structure Solution of 3a
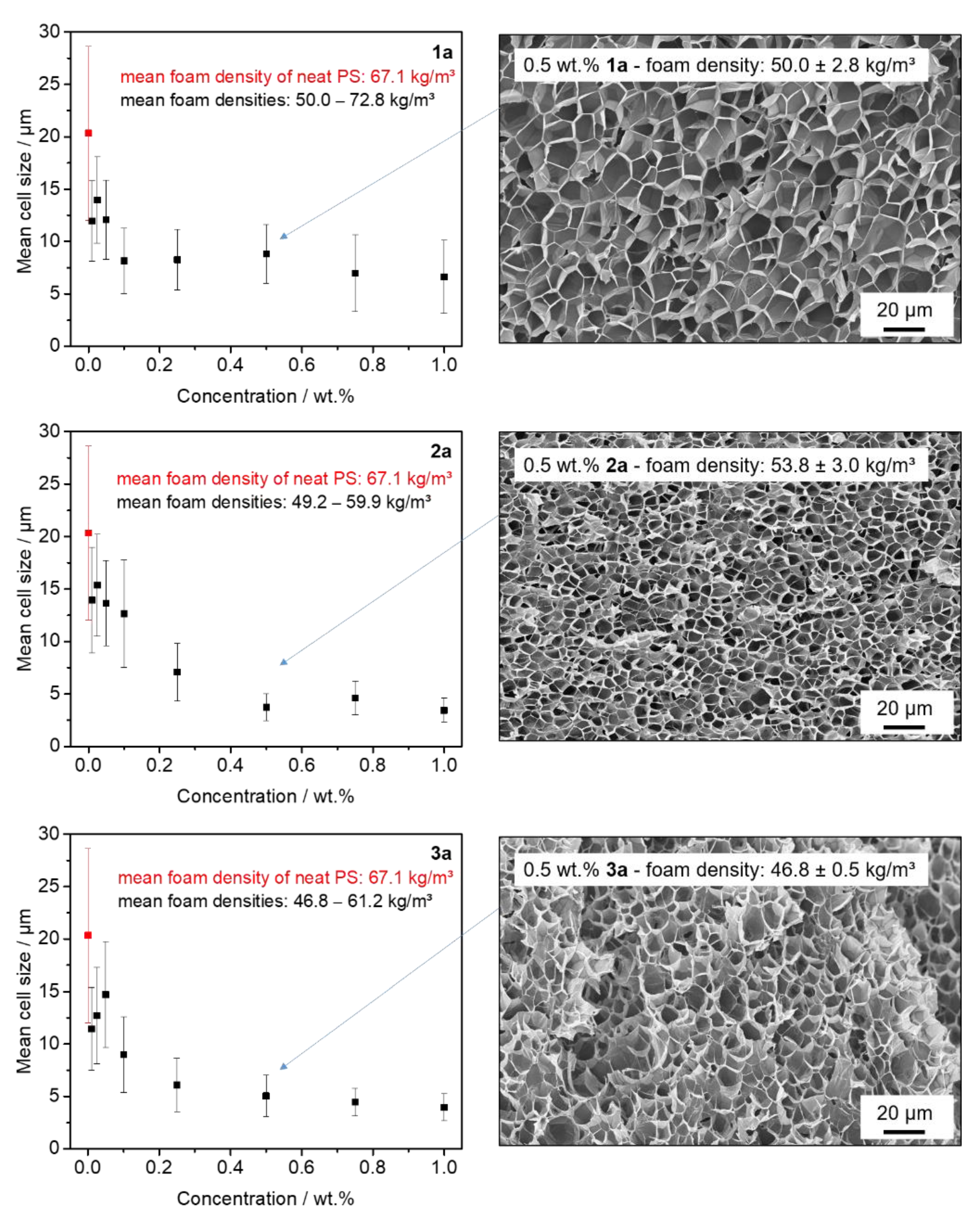
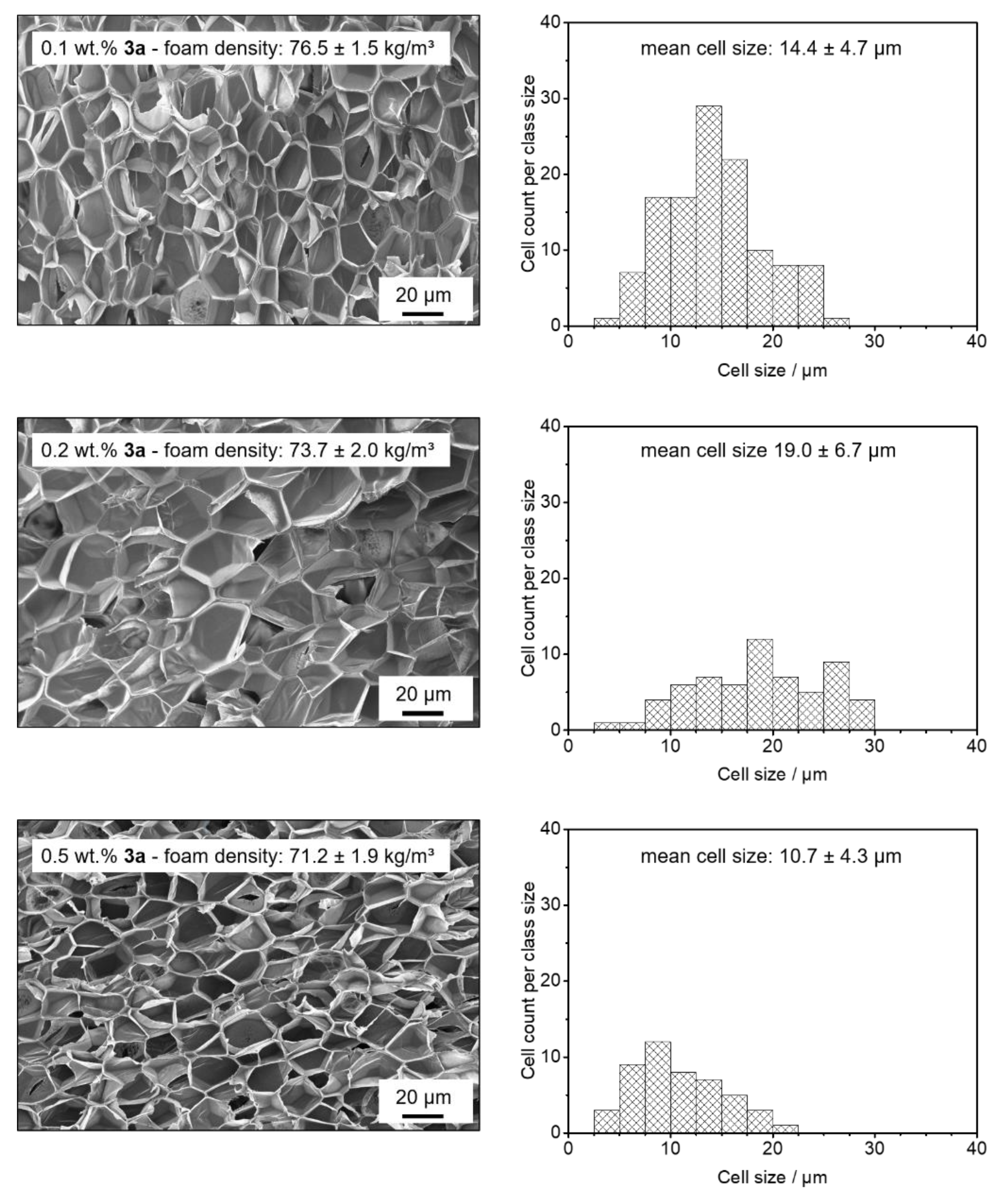
3.4. Batch Foaming of Polystyrene Using Kinked Bisamides
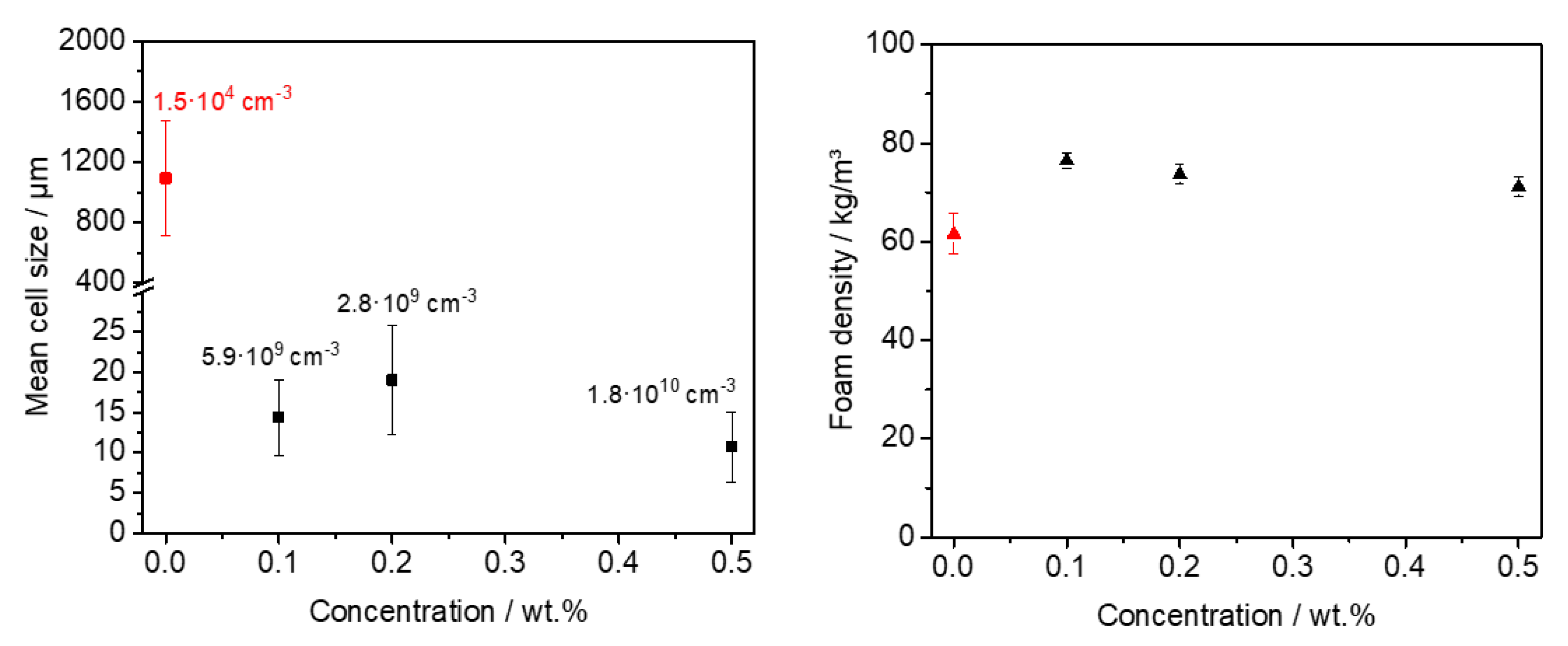
3.5. Extrusion Foaming of Polystyrene Using Kinked Bisamides
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, A.; Patham, B.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Polyolefinic nanocomposite foams: Review of microstructure-property relationships, applications, and processing considerations. J. Cell. Plast. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugad, R.; Radhakrishna, G.; Gandhi, A. Recent advancements in manufacturing technologies of microcellular polymers: A review. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Mark, L.H.; Kim, S.; Chang, E.; Park, C.B.; Lee, P.C. Recent progress in micro-/nano-fibrillar reinforced polymeric composite foams. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolieocha, C.; Raps, D.; Subramaniam, K.; Altstädt, V. Microcellular to nanocellular polymer foams: Progress (2004–2015) and future directions—A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 73, 500–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Li, F. Effect of microstructure on the properties of polystyrene microporous foaming material. e-Polymers 2020, 20, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Park, C.B. The effects of extensional stresses on the foamability of polystyrene-talc composites blown with carbon dioxide. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 75, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Park, C.B.; Kontopoulou, M. Nanosilica Addition Dramatically Improves the Cell Morphology and Expansion Ratio of Polypropylene Heterophasic Copolymer Foams Blown in Continuous Extrusion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 7282–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Zhong, M. Mesoporous silica particles grafted with polystyrene brushes as a nucleation agent for polystyrene supercritical carbon dioxide foaming. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 4308–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Kuboki, T.; Wang, L.; Park, C.B.; Lee, E.K.; Naguib, H.E. Cell Structure Evolution and the Crystallization Behavior of Polypropylene/Clay Nanocomposites Foams Blown in Continuous Extrusion. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 9834–9845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Y.; Zhu, R.M.; Zhou, N.Q.; Park, C.B. Effects of Nanoclay and CO2 Content on Foaming Behaviors of PP/PS Alloys. Adv. Mat. Res. 2014, 898, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Okolieocha, C.; Köppl, T.; Kerling, S.; Tölle, F.J.; Fathi, A.; Mülhaupt, R.; Altstädt, V. Influence of graphene on the cell morphology and mechanical properties of extruded polystyrene foam. J. Cell. Plast. 2015, 51, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A. Synthesis and properties of novel polystyrene/polyurea and functional graphene-based nanocomposite foams. J. Cell. Plast. 2017, 53, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, B.; Lee, L.J. Extrusion foaming of polystyrene/carbon particles using carbon dioxide and water as co-blowing agents. Polymer 2011, 52, 1847–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Buahom, P.; Tran, M.-P.; Saniei, M.; Park, C.B.; Pötschke, P. Heat transfer in microcellular polystyrene/multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite foams. Carbon 2015, 93, 819–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.; Kuang, T.; Yen, Y.-C.; Li, D.; Benatar, A.; Peng, X.F.; Lee, L.J. Polystyrene/multi-wall carbon nanotube composite and its foam assisted by ultrasound vibration. J. Cell. Plast. 2017, 53, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.; Gedler, G.; Velasco, J.I. Multifunctional nanocomposite foams based on polypropylene with carbon nanofillers. J. Cell. Plast. 2013, 49, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, C.; Garcia, M.T.; Mencía, R.; Garrido, I.; Rodríguez, J.F. Clean preparation of tailored microcellular foams of polystyrene using nucleating agents and supercritical CO2. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 4825–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-G.; Su, B.; Turng, L.-S. Mechanical properties, fiber orientation, and length distribution of glass fiber-reinforced polypropylene parts: Influence of water-foaming technology. Polym. Compos. 2018, 39, 4386–4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, A.; Park, C.B. Dispersed polypropylene fibrils improve the foaming ability of a polyethylene matrix. Polymer 2014, 55, 4199–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, A.; Tabatabaei, A.; Barzegari, M.R.; Mahmood, S.H.; Park, C.B. In situ fibrillation of CO2-philic polymers: Sustainable route to polymer foams in a continuous process. Polymer 2013, 54, 4645–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakroodi, A.R.; Kazemi, Y.; Ding, W.; Ameli, A.; Park, C.B. Poly(lactic acid)-Based in Situ Microfibrillar Composites with Enhanced Crystallization Kinetics, Mechanical Properties, Rheological Behavior, and Foaming Ability. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3925–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libster, D.; Aserin, A.; Garti, N. Advanced nucleating agents for polypropylene. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2007, 18, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahleitner, M.; Grein, C.; Kheirandish, S.; Wolfschwenger, J. Nucleation of Polypropylene Homo- and Copolymers. Int. Polym. Process. 2011, 26, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomenhofer, M.; Ganzleben, S.; Hanft, D.; Schmidt, H.-W.; Kristiansen, M.; Smith, P.; Stoll, K.; Mäder, D.; Hoffmann, K. “Designer” Nucleating Agents for Polypropylene. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 3688–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, F.; Ganzleben, S.; Hanft, D.; Smith, P.; Schmidt, H.-W. Synthesis and Structure-Efficiency Relations of 1,3,5-Benzenetrisamides as Nucleating Agents and Clarifiers for Isotactic Poly(propylene). Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2010, 211, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, F.; Schmidt, H.-W. Supramolecular Nucleating Agents for Poly(butylene terephthalate) Based on 1,3,5-Benzenetrisamides. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, Z.; Na, H.; Zhu, J. Effect of 1,3,5-trialkyl-benzenetricarboxylamide on the crystallization of poly(lactic acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, F.; Schmidt, H.-W. 1,3,5-Benzenetrisamide based nucleating agents for poly(vinylidene fluoride). Polymer 2010, 51, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksit, M.; Zhao, C.; Klose, B.; Kreger, K.; Schmidt, H.-W.; Altstädt, V. Extruded Polystyrene Foams with Enhanced Insulation and Mechanical Properties by a Benzene-Trisamide-Based Additive. Polymers 2019, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksit, M.; Klose, B.; Zhao, C.; Kreger, K.; Schmidt, H.-W.; Altstädt, V. Morphology control of extruded polystyrene foams with benzene-trisamide-based nucleating agents. J. Cell. Plast. 2019, 55, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksit, M.; Gröschel, S.; Kuhn, U.; Aksit, A.; Kreger, K.; Schmidt, H.-W.; Altstädt, V. Low-Density Polybutylene Terephthalate Foams with Enhanced Compressive Strength via a Reactive-Extrusion Process. Polymers 2020, 12, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mörl, M.; Steinlein, C.; Kreger, K.; Schmidt, H.-W.; Altstädt, V. Improved compression properties of polypropylene extrusion foams by supramolecular additives. J. Cell. Plast. 2018, 54, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, M.; Spörrer, A.; Schmidt, H.-W.; Altstädt, V. Influence of supramolecular additives on foam morphology of injection-molded i-PP. J. Cell. Plast. 2011, 47, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urushihara, T.; Ueda, N.; Kawamoto, N. Polyolefin Resin Composition. U.S. Patent 2010/0240815A1, 23 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Material Data Sheet, Polystyrene 168N, Ineos Styrolution. Available online: https://www.ineos-styrolution.com/Product/GPPS_Styrolution-PS-168N-L_SKU200300060596.html, (accessed on 3 March 2021).
- Xu, X.; Park, C.B.; Xu, D.; Pop-Iliev, R. Effects of die geometry on cell nucleation of PS foams blown with CO2. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2003, 43, 1378–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Weller, J. Production of Microcellular Polycarbonate Using Carbon Dioxide for Bubble Nucleation. J. Eng. Ind. 1994, 116, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, T. The Hydrogen Bond in the Solid State. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 48–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüninger, H.; Schmutzler, A.; Siegel, R.; Armstrong, K.; Frost, D.J.; Senker, J. Quantitative description of 1H SQ and DQ coherences for the hydroxyl disorder within hydrous ringwoodite. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 15098–15105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-M.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, S.G.; Park, C.B.; Naguib, H.E. Bi-cellular Foam Structure of Polystyrene from Extrusion Foaming Process. J. Cell. Plast. 2009, 45, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
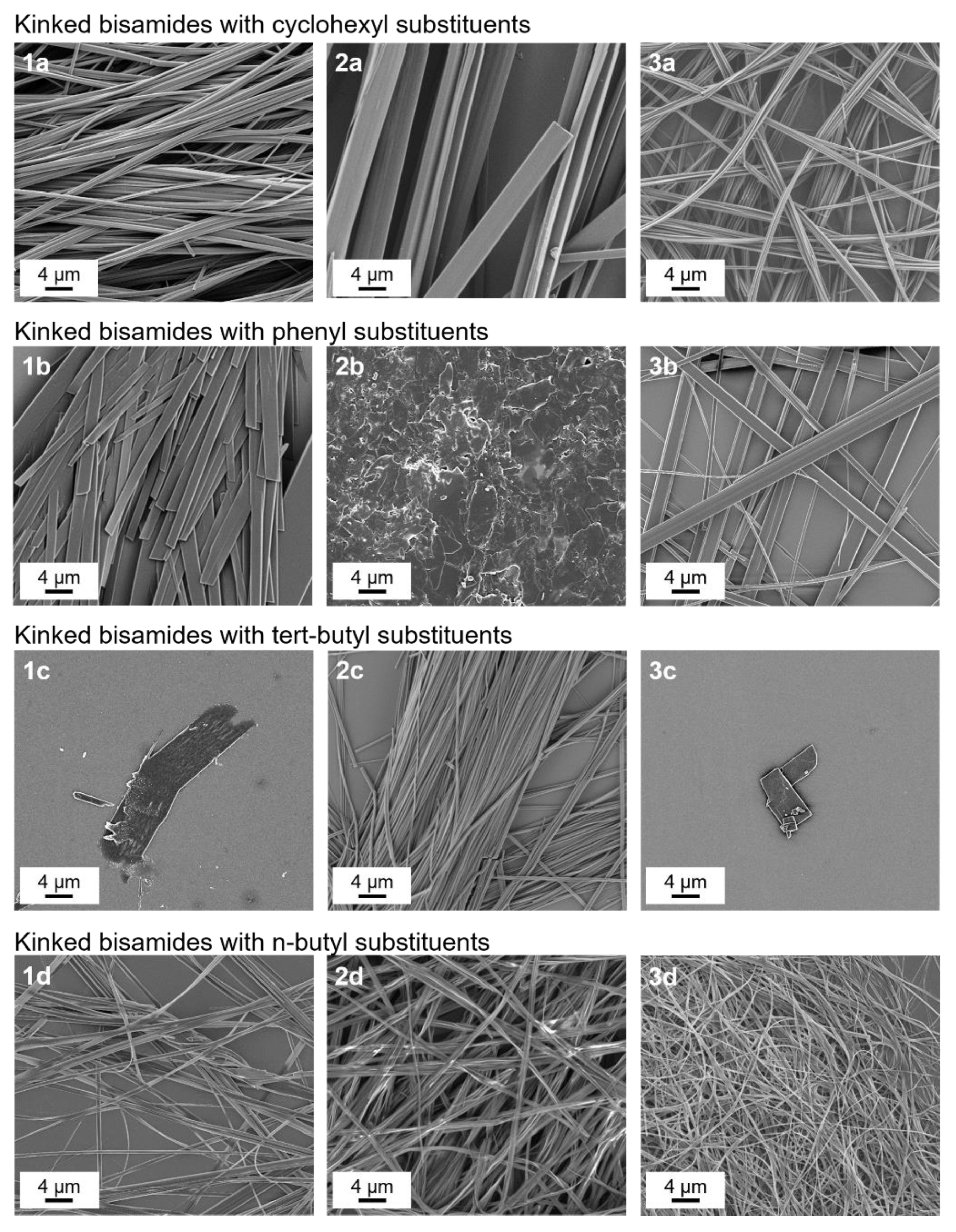

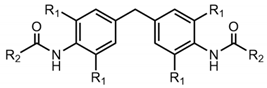
| R2 | Cyclohexyl | Phenyl | Tert-Butyl | N-Butyl | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | |||||
| H | 1a | 1b | 1c | 1d | |
| methyl | 2a | 2b | 2b | 2d | |
| ethyl | 3a | 3b | 3b | 3d | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klose, B.; Kremer, D.; Aksit, M.; Zwan, K.P.v.d.; Kreger, K.; Senker, J.; Altstädt, V.; Schmidt, H.-W. Kinked Bisamides as Efficient Supramolecular Foam Cell Nucleating Agents for Low-Density Polystyrene Foams with Homogeneous Microcellular Morphology. Polymers 2021, 13, 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071094
Klose B, Kremer D, Aksit M, Zwan KPvd, Kreger K, Senker J, Altstädt V, Schmidt H-W. Kinked Bisamides as Efficient Supramolecular Foam Cell Nucleating Agents for Low-Density Polystyrene Foams with Homogeneous Microcellular Morphology. Polymers. 2021; 13(7):1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071094
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlose, Bastian, Daniel Kremer, Merve Aksit, Kasper P. van der Zwan, Klaus Kreger, Jürgen Senker, Volker Altstädt, and Hans-Werner Schmidt. 2021. "Kinked Bisamides as Efficient Supramolecular Foam Cell Nucleating Agents for Low-Density Polystyrene Foams with Homogeneous Microcellular Morphology" Polymers 13, no. 7: 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071094
APA StyleKlose, B., Kremer, D., Aksit, M., Zwan, K. P. v. d., Kreger, K., Senker, J., Altstädt, V., & Schmidt, H.-W. (2021). Kinked Bisamides as Efficient Supramolecular Foam Cell Nucleating Agents for Low-Density Polystyrene Foams with Homogeneous Microcellular Morphology. Polymers, 13(7), 1094. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13071094








