Increase of Solid Polymer Electrolyte Ionic Conductivity Using Nano-SiO2 Synthesized from Sugarcane Bagasse as Filler
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Solid Polymer Electrolytes
2.3. Synthesis of Nano-SiO2 from Sugarcane Bagasse
2.4. Preparation of Solid Polymer Electrolytes PEO/NaClO4 with Nano-SiO2 as Filler
2.5. Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of Nano-SiO2 from Sugarcane Bagasse
3.2. Preparation of Solid Polymer Electrolyte
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, H.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Yang, B.; Mei, S.; Zhang, W.; Xie, F.; Wei, W.; et al. Narrow band-gap cathode Fe3(PO4)2 for sodium-ion battery with enhanced sodium storage. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 591, 124561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni’Mah, Y.L.; Cheng, M.-Y.; Cheng, J.-H.; Rick, J.; Hwang, B.-J. Solid-state polymer nanocomposite electrolyte of TiO2/PEO/NaClO4 for sodium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 278, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, S.; Xu, C.; Hu, N.; Molenda, J.; Lu, L. Development of solid-state electrolytes for sodium-ion battery–A short review. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Shao, D.; Luo, K.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z.; Luo, Z.; Wang, X. Preparation and application of poly(ethylene oxide)_based all soli _state electrolyte with a walnut_like SiO2 as nano_fillers. J. Appl. Polymer Sci. 2020, 137, 48810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Judez, X.; Rojo, T.; Armand, M.; Zhang, H. Review—Polymer Electrolytes for Sodium Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 070534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meabe, L.; Huynh, T.V.; Lago, N.; Sardon, H.; Li, C.; O’Dell, L.A.; Armand, M.; Forsyth, M.; Mecerreyes, D. Poly(ethylene oxide carbonates) solid polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 264, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.G.; Son, B.; Mukherjee, S.; Schuppert, N.; Bates, A.; Kwon, O.; Choi, M.J.; Chung, H.Y.; Park, S. A review of lithium and non-lithium based solid state batteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 282, 299–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhu, P.; Fang, Q.; Jing, M.; Shen, X.; Yang, L. A novel solid PEO/LLTO-nanowires polymer composite electrolyte for solid-state lithium-ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 292, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.C.; Pandey, G.P. Solid polymer electrolytes: Materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: An overview. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2008, 41, 055409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, M.A.K.L.; Rupasinghe, W.N.S.; Jayasundara, J.M.N.I.; Ekanayake, P.; Bandara, T.M.W.J.; Thalawala, S.N.; Seneviratne, V.A. Ionic conductivity enhancement in the solid polymer electrolyte PEO9LiTf by nanosilica filler from rice husk ash. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2012, 17, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Chen, L. All solid-state polymer electrolytes for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2016, 5, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.; Tsai, M.-C.; Lin, M.-H.; Ni’Mah, Y.L.; Hy, S.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Cheng, J.-H.; Rick, J.; Su, W.-N.; Hwang, B.-J. Capacity retention of lithium sulfur batteries enhanced with nano-sized TiO2-embedded polyethylene oxide. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 6708–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni’Mah, Y.L.; Taufik, M.F.; Maezah, A.; Kurniawan, F. Increasing the ionic conductivity of solid state polymer electrolyte using fly ash as a filler. Malays. J. Fundam. Appl. Sci. 2018, 14, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yap, Y.L.; You, A.H.; Teo, L.L.; Hanapei, H. Inorganic Filler Sizes Effect on Ionic Conductivity in Polyethylene Oxide (PEO) Composite Polymer Electrolyte. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Masoud, E.M. Montmorillonite incorporated polymethylmethacrylate matrix containing lithium trifluoromethanesulphonate (LTF) salt: Thermally stable polymer nanocomposite electrolyte for lithium-ion batteries application. Ionics 2018, 25, 2645–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoud, E.M.; El-Bellihi, A.-A.; Bayoumy, W.A.; Mohamed, E.A. Polymer composite containing nano magnesium oxide filler and lithiumtriflate salt: An efficient polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries application. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 260, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ab Rahman, I.; Padavettan, V. Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles by Sol-Gel: Size-Dependent Properties, Surface Modification, and Applications in Silica-Polymer Nanocomposites—A Review. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghorbani, F.; Younesi, H.; Mehraban, Z.; Çelik, M.S.; Ghoreyshi, A.A.; Anbia, M. Preparation and characterization of highly pure silica from sedge as agricultural waste and its utilization in the synthesis of mesoporous silica MCM-41. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2013, 44, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Rattanasak, U. Eco-production of silica from sugarcane bagasse ash for use as a photochromic pigment filler. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affandi, S.; Setyawan, H.; Winardi, S.; Purwanto, A.; Balgis, R. A facile method for production of high-purity silica xerogels from bagasse ash. Adv. Powder Technol. 2009, 20, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Lee, H.R.; Hsu, P.-C.; Liu, K.; Cui, Y. High Ionic Conductivity of Composite Solid Polymer Electrolyte via In Situ Synthesis of Monodispersed SiO2 Nanospheres in Poly(ethylene oxide). Nano Lett. 2015, 16, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falk, G.; Shinhe, G.; Teixeira, L.; de Moraes, E.G.; de Oliveira, A.N. Synthesis of silica nanoparticles from sugarcane bagasse ash and nano-silicon via magnesiothermic reactions. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 21618–21624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.; Datta, A. Synthesis of SiO2-Nanoparticles from Rice Husk Ash and its Comparison with Commercial Amorphous Silica through Material Characterization. Silicon 2020, 13, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Hashmi, S. Ion transport and ion–filler-polymer interaction in poly(methyl methacrylate)-based, sodium ion conducting, gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with silica nanoparticles. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 5101–5108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, K.-S.; Moon, H.-S.; Kim, J.-W.; Park, J.-W. Role of functional nano-sized inorganic fillers in poly(ethylene) oxide-based polymer electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2003, 117, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElBellihi, A.A.; Bayoumy, W.A.; Masoud, E.M.; Mousa, M.A. Preparation, Characterizations and Conductivity of Composite Polymer Electrolytes Based on PEO-LiClO4 and Nano ZnO Filler. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 2949–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, J.; Qiu, X.; Cui, M.; Tang, X.; Zhu, W.; Chen, L. Enhanced electrochemical properties of PEO-based composite polymer electrolyte with shape-selective molecular sieves. J. Power Sources 2006, 156, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Nellutla, S.; Thokchom, J.; Chen, C. Ionic conduction through heterogeneous solids: Delineation of the blocking and space charge effects. J. Power Sources 2006, 160, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Ren, Y.; Wang, M.; He, J.; Huo, W.; Tang, H. Improving the Conductivity of Solid Polymer Electrolyte by Grain Reforming. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
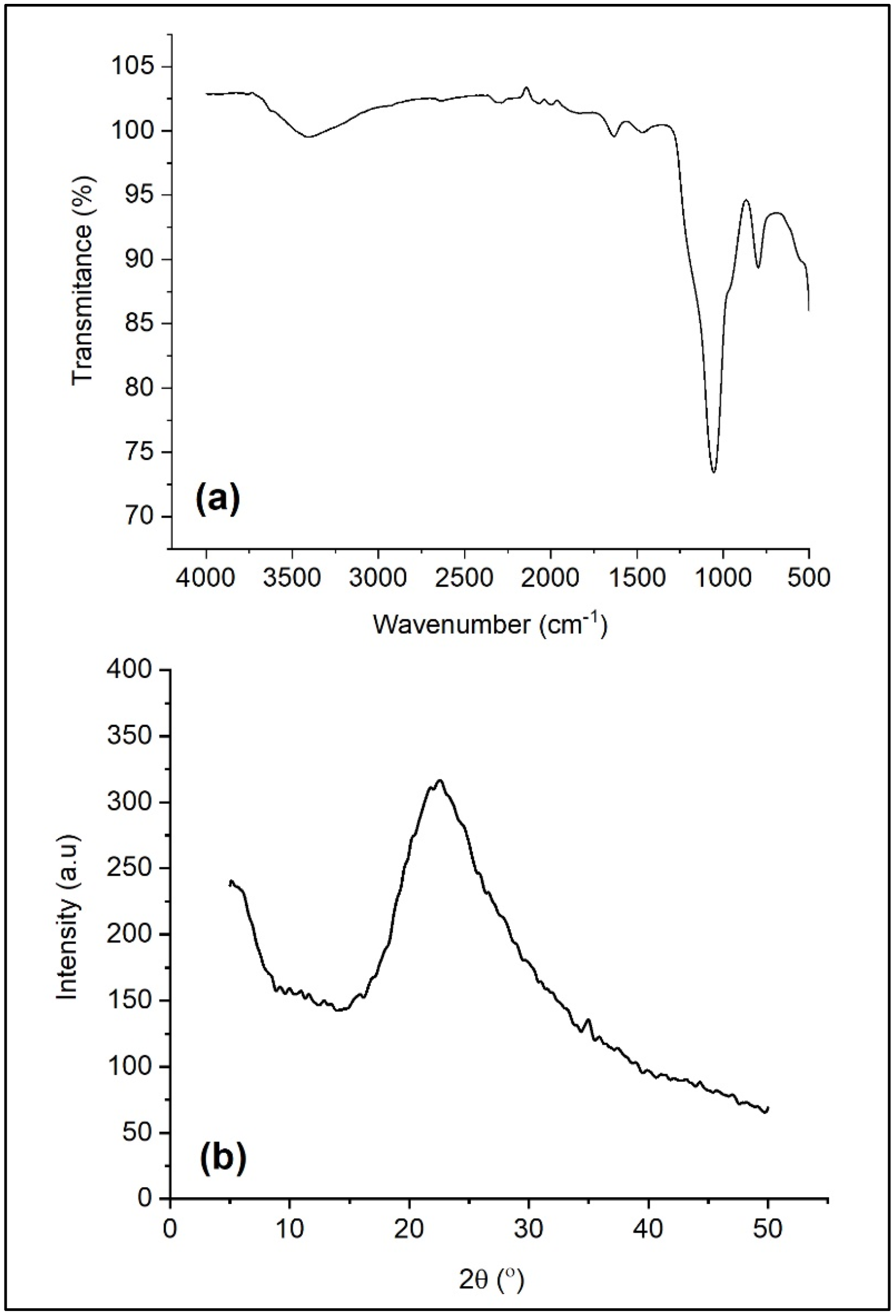

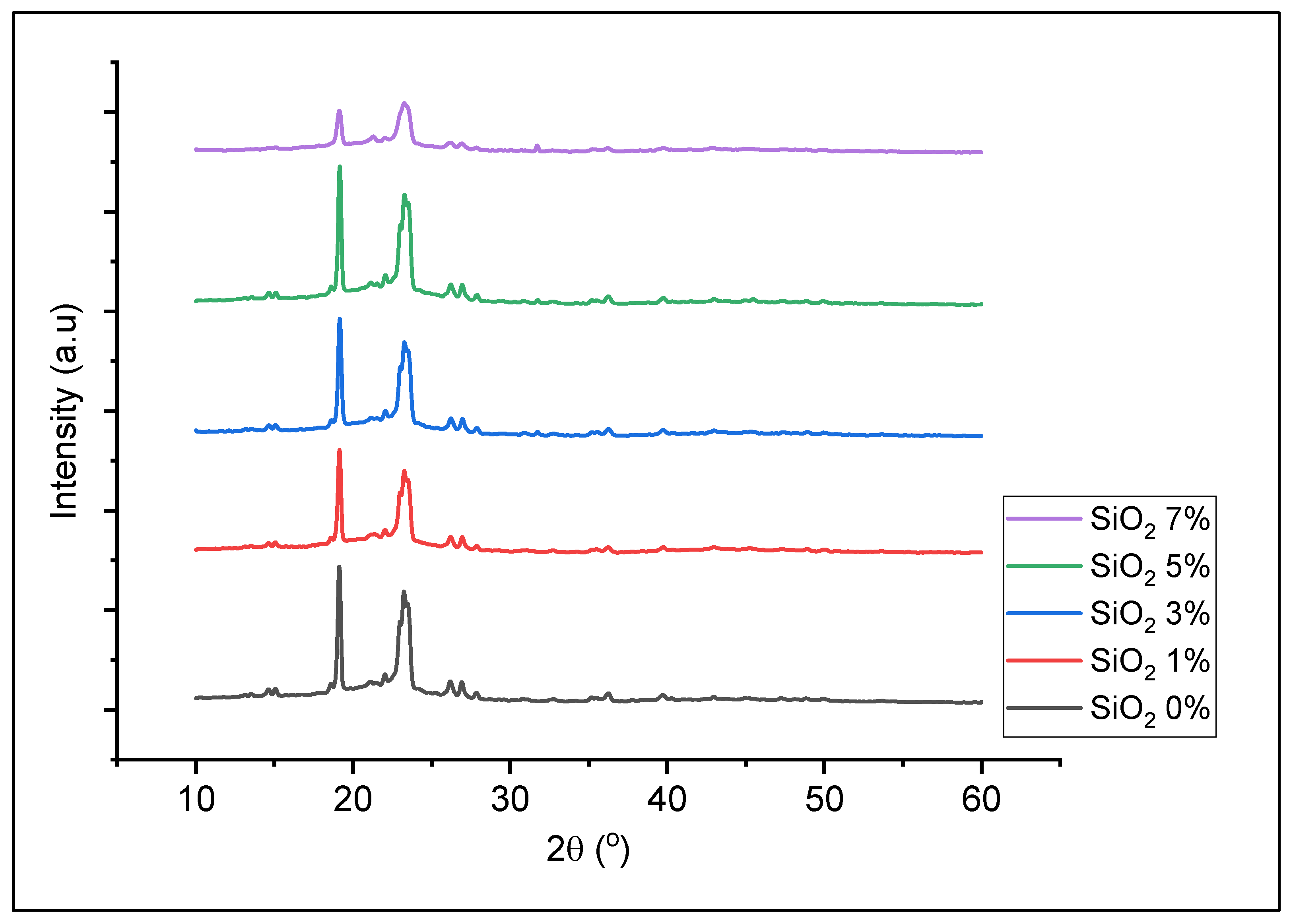
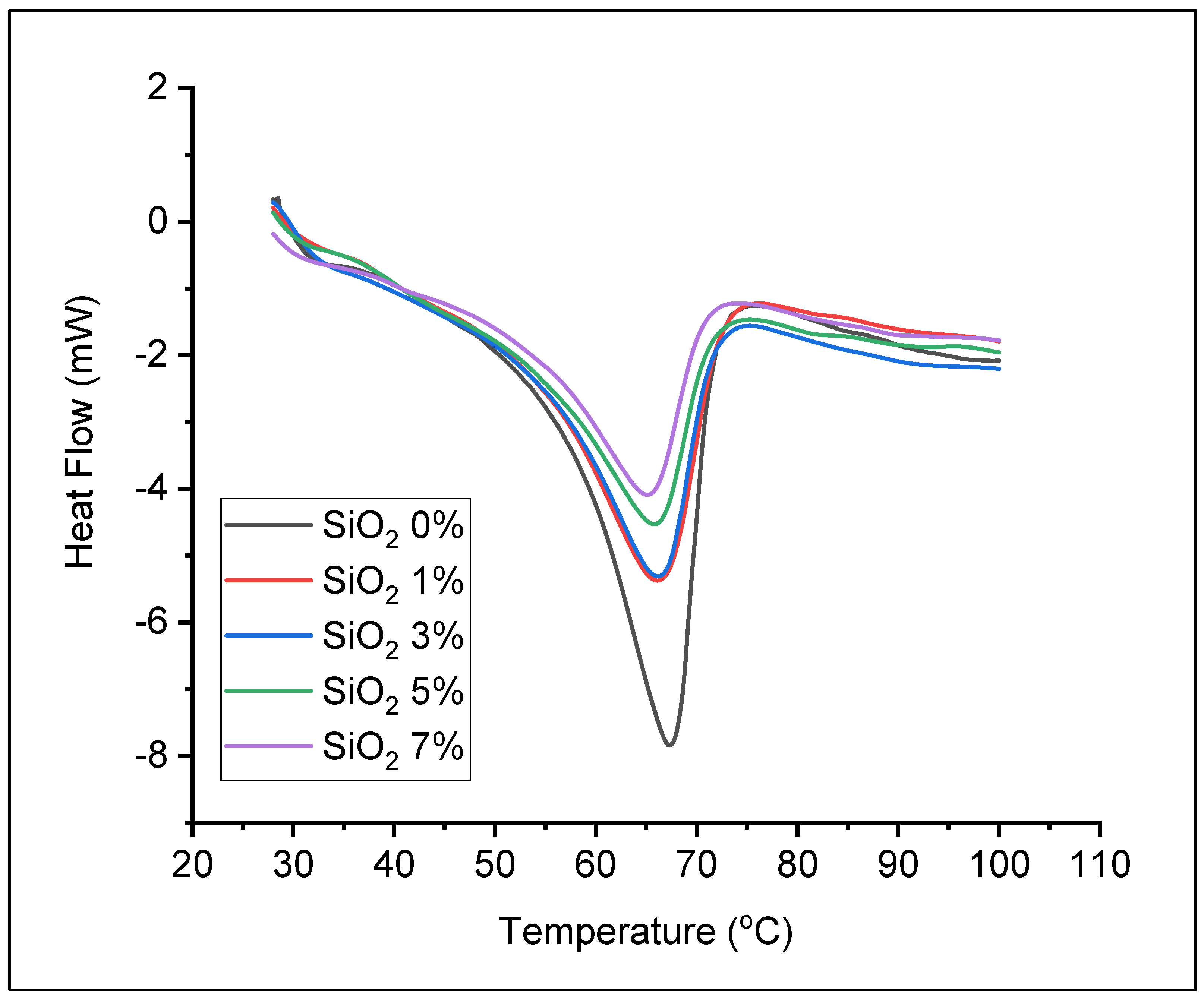


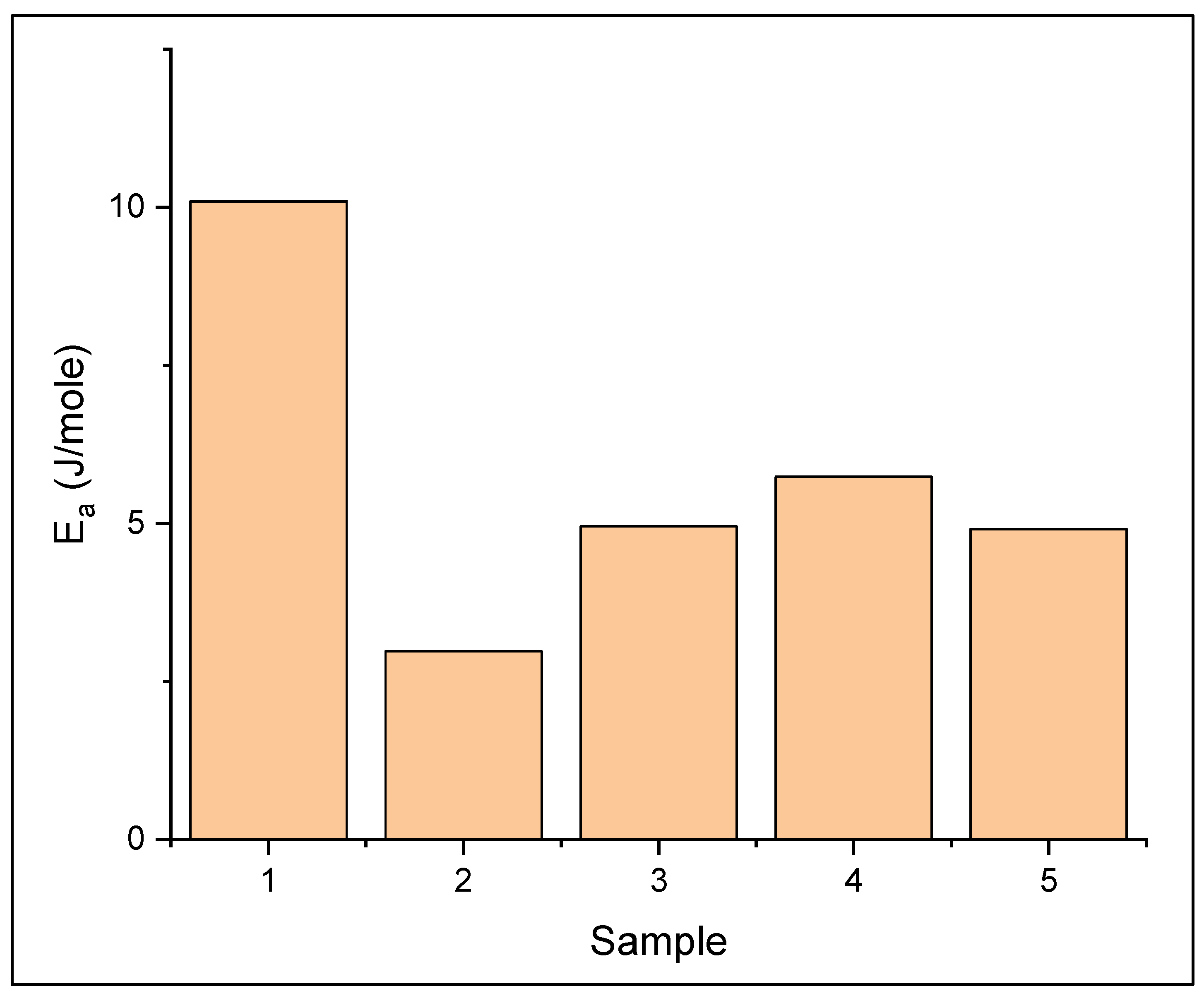
| Sample | Tm (°C) | ΔHm (J/g) | Xc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 0% | 67.17 | 68.48 | 33.73 |
| SiO2 1% | 66.17 | 46.24 | 22.78 |
| SiO2 3% | 66.17 | 45.72 | 22.52 |
| SiO2 5% | 65.83 | 38.80 | 19.11 |
| SiO2 7% | 65.17 | 34.65 | 17.07 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | % Elongation | |
|---|---|---|
| PEO/NaClO4 | 0.31 | 270 |
| PEO/NaClO4 + nano-SiO2 5% | 0.29 | 260 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ni’mah, Y.L.; Muhaiminah, Z.H.; Suprapto, S. Increase of Solid Polymer Electrolyte Ionic Conductivity Using Nano-SiO2 Synthesized from Sugarcane Bagasse as Filler. Polymers 2021, 13, 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234240
Ni’mah YL, Muhaiminah ZH, Suprapto S. Increase of Solid Polymer Electrolyte Ionic Conductivity Using Nano-SiO2 Synthesized from Sugarcane Bagasse as Filler. Polymers. 2021; 13(23):4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234240
Chicago/Turabian StyleNi’mah, Yatim Lailun, Zakkiyyah Hidayatul Muhaiminah, and Suprapto Suprapto. 2021. "Increase of Solid Polymer Electrolyte Ionic Conductivity Using Nano-SiO2 Synthesized from Sugarcane Bagasse as Filler" Polymers 13, no. 23: 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234240
APA StyleNi’mah, Y. L., Muhaiminah, Z. H., & Suprapto, S. (2021). Increase of Solid Polymer Electrolyte Ionic Conductivity Using Nano-SiO2 Synthesized from Sugarcane Bagasse as Filler. Polymers, 13(23), 4240. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13234240






