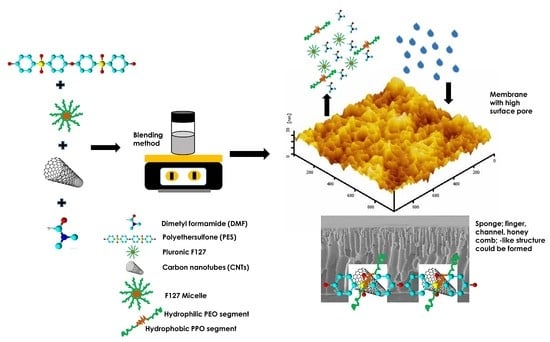
Ultrafiltration of α-Lactalbumin Protein: Acquaintance of the Filtration Performance by Membrane Structure and Surface Alteration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
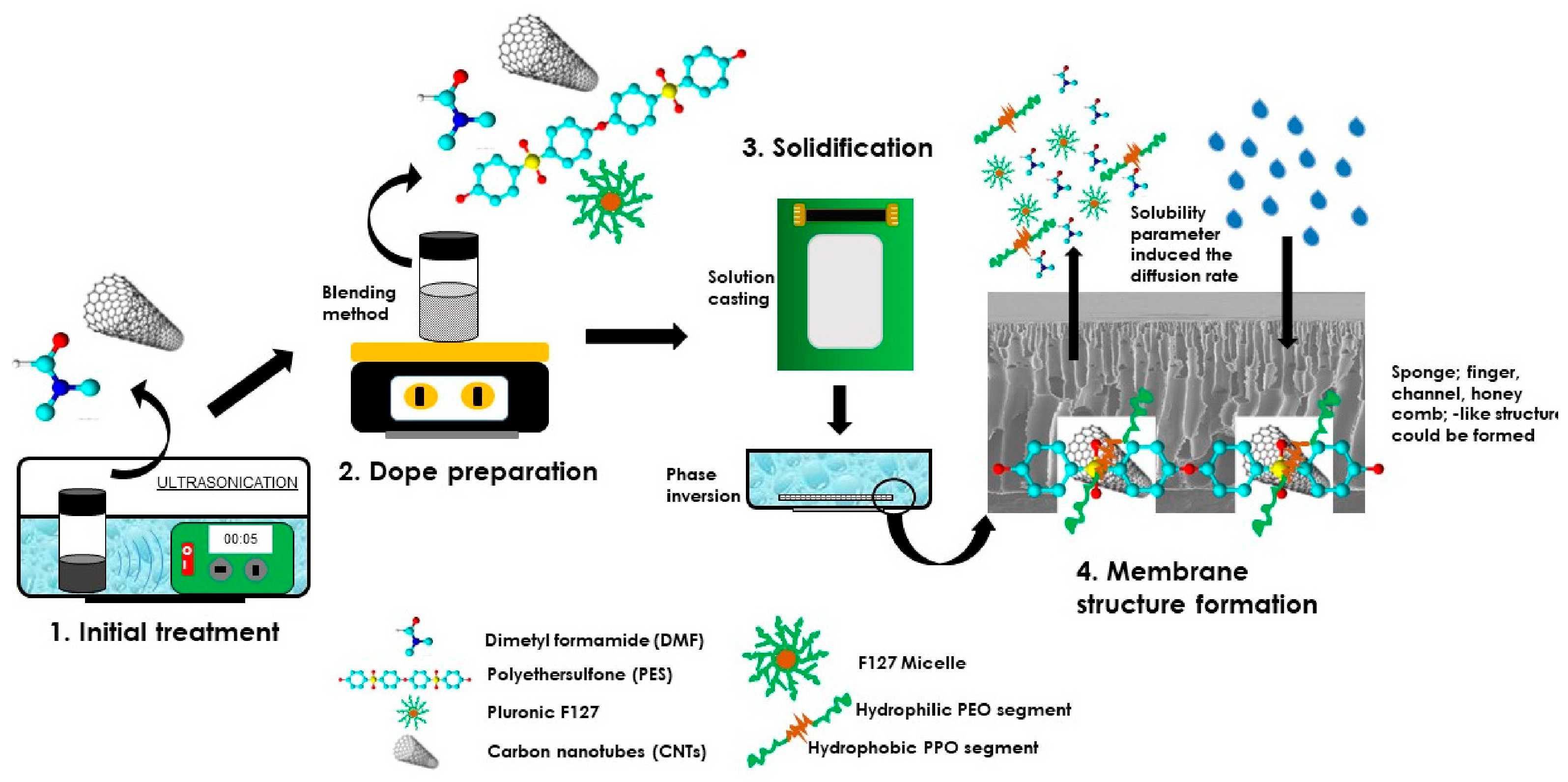
2.2. Membrane Fabrication
2.3. Membrane Characterization
2.3.1. Microstructure Investigation
2.3.2. Water Contact Angle (WCA)
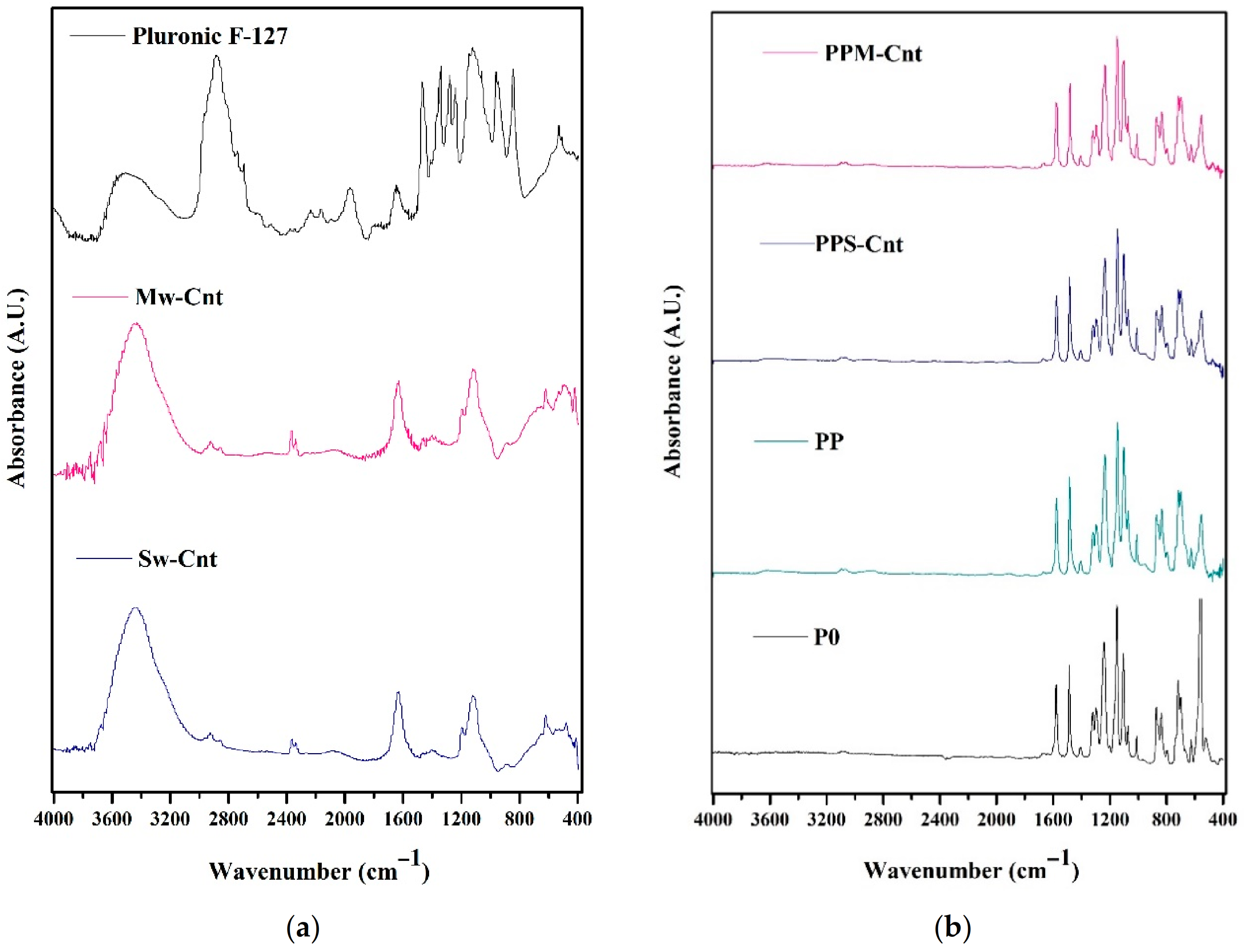
2.3.3. Chemical Groups
2.4. Membrane Filtration Performance
2.4.1. Water Permeability
2.4.2. Filtration of Lactalbumin Solution
3. Results and Discussion
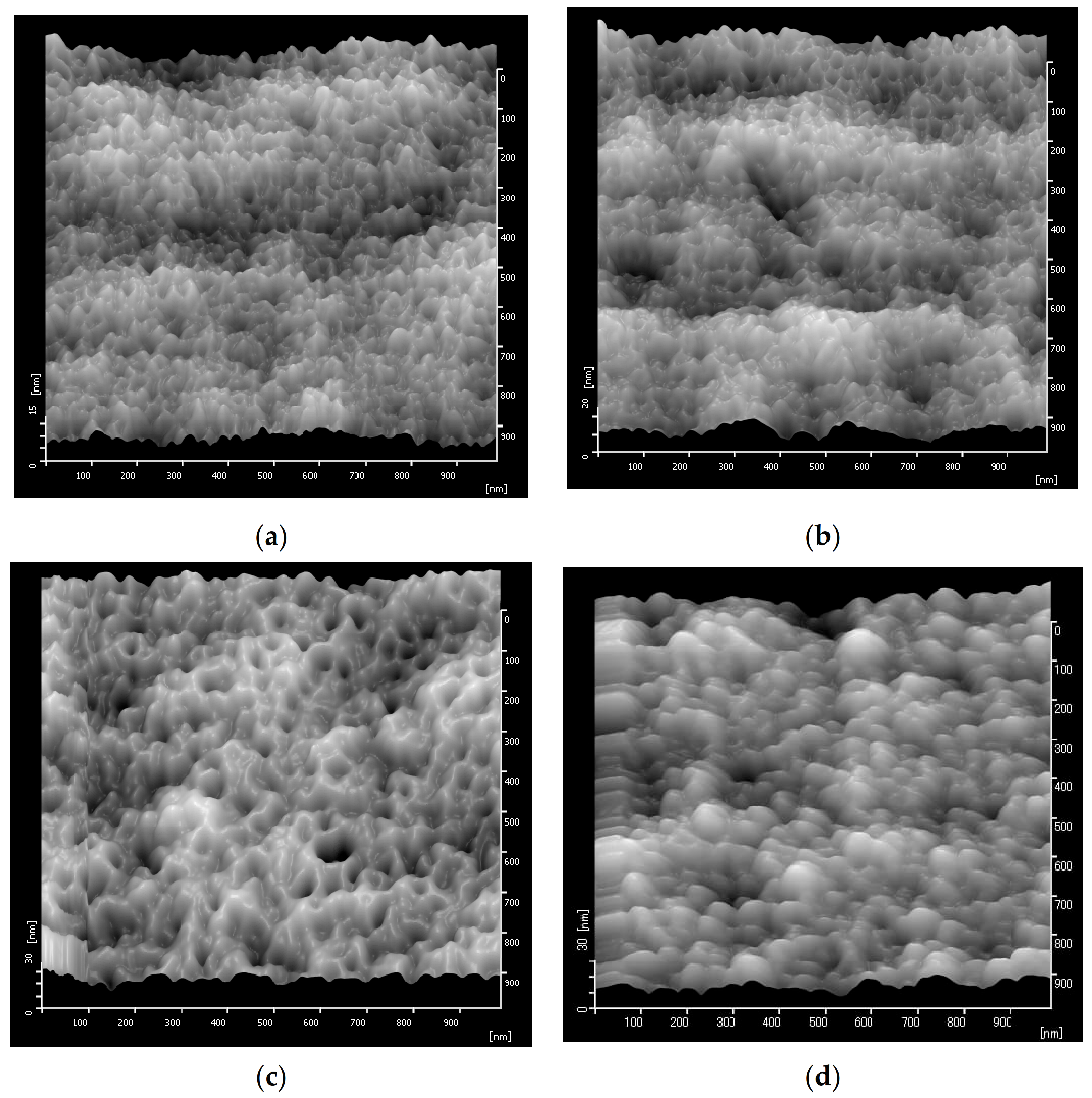
3.1. Membrane Morphological Structure

3.2. Membrane Surface Roughness
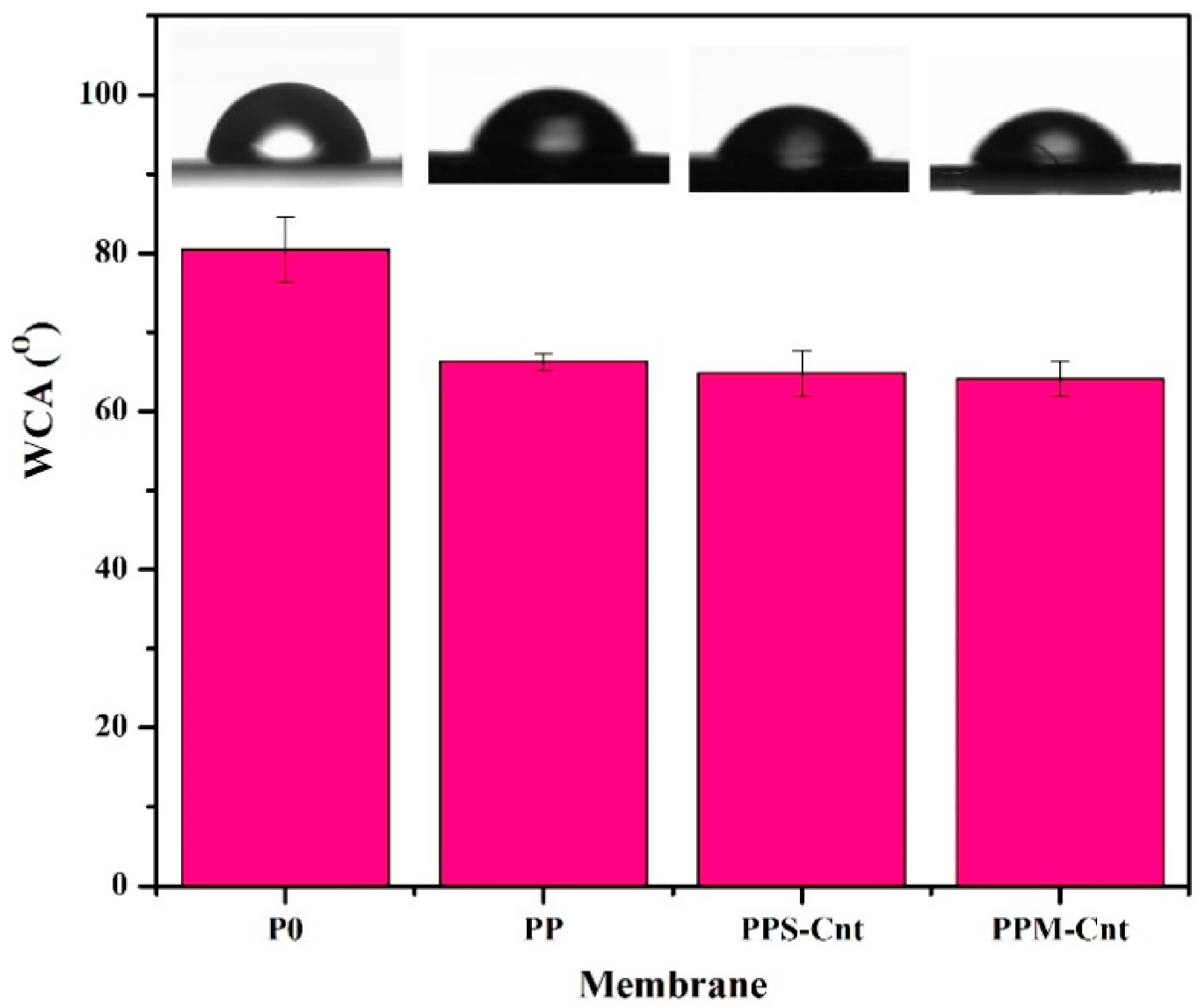
3.3. Membrane Surface Wettability
3.4. Membrane Chemical Groups
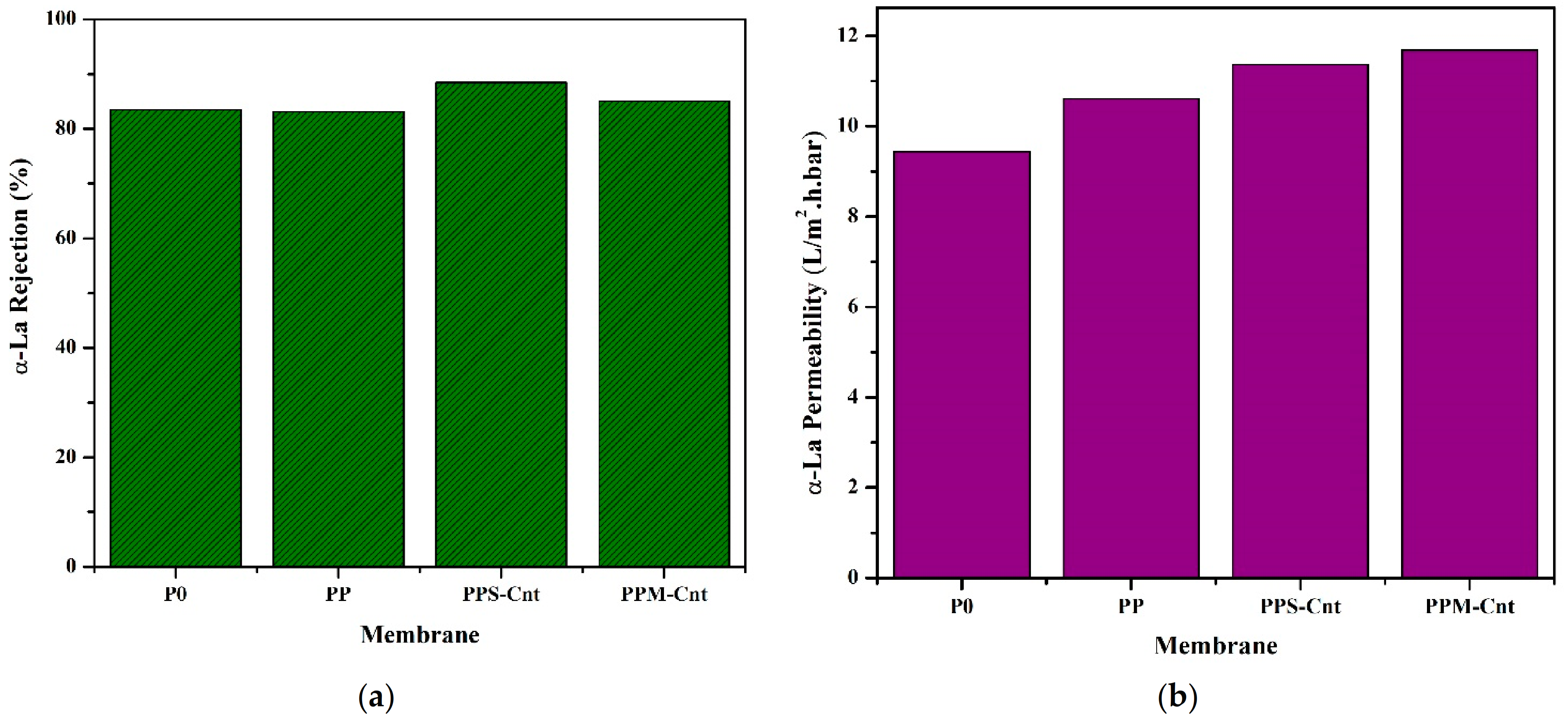
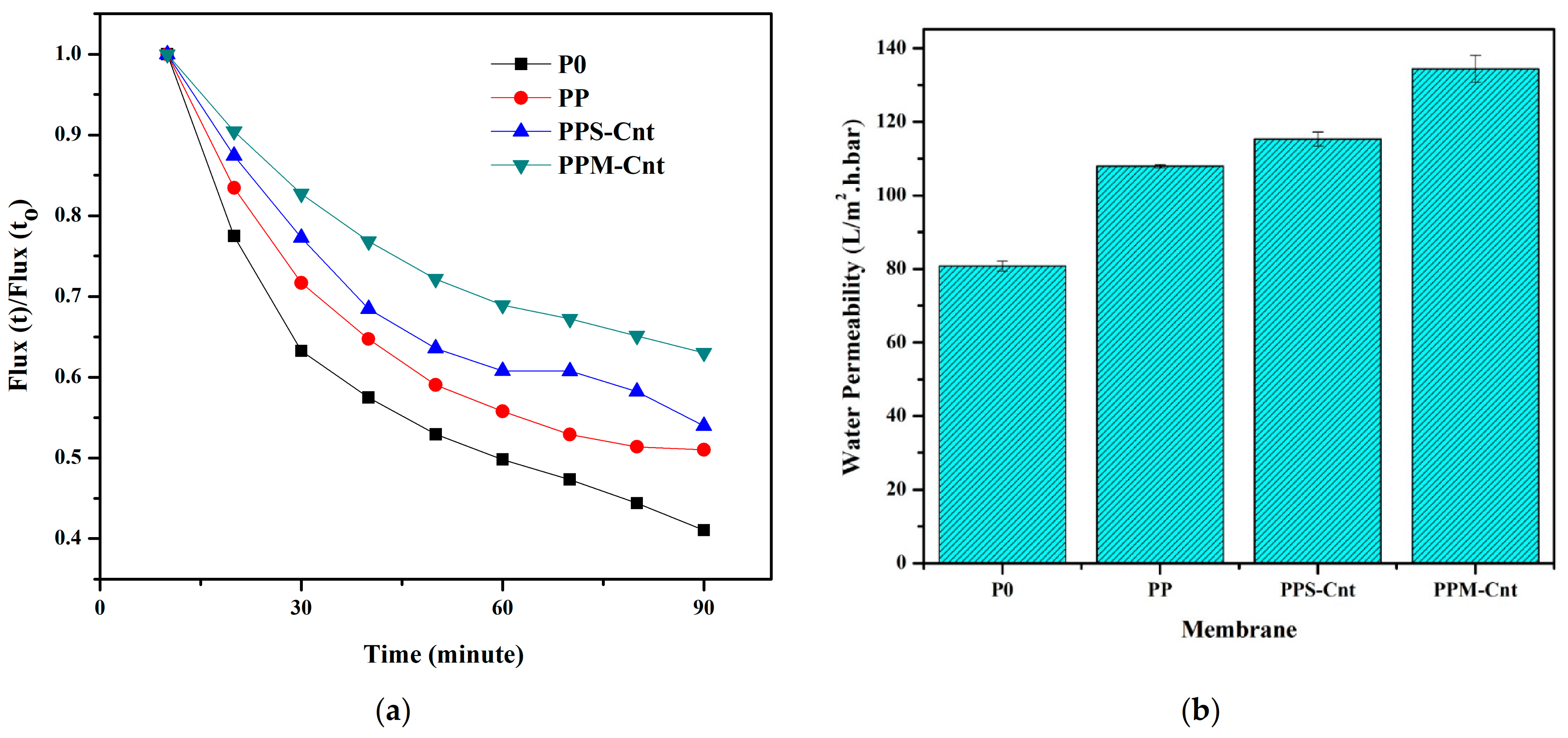
3.5. Membrane Permeability and Rejection Performance
3.6. Membrane Performance in α-La Solution Filtration
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gerd Konrad, T.K. A new method for isolation of native a—Lactalbumin from sweet whey. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Bin, J.; Zhibiao, F.; Yuxiao, Q.U.; Xuan, L.I. Separation of α—Lactalbumin and β—Lactoglobulin in Whey Protein Isolate by Aqueous Two—phase System of Polymer/Phosphate. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2016, 44, 754–759. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, L.; Na, J.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, C.; Feng, Z. Environmentally-friendly strategy for separation of α-lactalbumin from whey by aqueous two phase flotation. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puthia, M.; Storm, P.; Nadeem, A.; Hsiung, S.; Svanborg, C. P0127 Treatment and prevention of colon cancer by peroral HAMLET (human alpha-lactalbumin made lethal to tumour cells). Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, M.M.H.; Chase, H.A. Trends in whey protein fractionation. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 1501–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunkumar, A.; Etzel, M.R. Fractionation of α-lactalbumin and β-lactoglobulin from bovine milk serum using staged, positively charged, tangential fl ow ultra fi ltration membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 454, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, D.; Rabiller-baudry, M.; Millesime, L.; Chaufer, B.; Dau, G. Extraction of—lactalbumin from whey protein concentrate with modi ® ed inorganic membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 1998, 148, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.; Chaufer, B.; Merin, U.; Daufin, G. Purification of α-lactalbumin from a prepurified acid whey: Ultrafiltration or precipitation. Lait 2003, 83, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.M.; Haufer, B.C.; Erin, U.M.; Aufin, G.D. Original article Prepurification of a-lactalbumin with ultrafiltration ceramic membranes from acid casein whey: Study of operating conditions. Lait 2003, 83, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsämuuronen, S.; Nyström, M. Evaluation of six flat sheet ultrafiltration membranes for fractionation of whey proteins. Desalination 2006, 200, 290–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Abdulkarim, A.; Ooi, B.S.; Ismail, S. Recent development in additives modifications of polyethersulfone membrane for flux enhancement. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 246–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Wang, W.; Zhang, X.; Long, G.; Fan, J.; Chen, H.; Deng, L. A novel fractal solution for permeability and Kozeny-Carman constant of fi brous porous media made up of solid particles and porous fi bers. Powder Technol. 2019, 349, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, B.; Yang, S.; Wang, Z.; Han, H. An analytical model for the transverse permeability of gas diffusion layer with electrical double layer effects in proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 17880–17888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Moghareh Abed, M.R.; Li, K. Progress in the production and modification of PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, E.; Karpati, S.; Gassara, S.; Deratani, A.; Beaume, F.; Lorain, O.; Tencé-Girault, S.; Norvez, S. Localization of antifouling surface additives in the pore structure of hollow fiber PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 538, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikooe, N.; Saljoughi, E. Preparation and characterization of novel PVDF nanofiltration membranes with hydrophilic property for filtration of dye aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 413, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrul, A.; Bastian, A.; Sri, M.; Yoshikage, O.; Hideto, M. Improved fouling redction of P ES hollow fiber membranes by incorporation with non-ionic s urfactant. Res. J. Chem. Environ. 2011, 15, 2–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fahrina, A.; Arahman, N.; Mulyati, S.; Aprilia, S.; Nawi, N.I.M.; Aqsha, A.; Bilad, M.R.; Takagi, R.; Matsuyama, H. Development of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane by Incorporating Bio-Based Ginger Extract as Additive. Polymers 2020, 12, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, M.Y.; Muchtar, S.; Jeon, S.; Fang, L.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Takagi, R.; Arahman, N.; Mulyati, S.; Riza, M.; Matsuyama, H. Synergistic effects of organic and inorganic additives in preparation of composite poly (vinylidene fl uoride) antifouling ultra fi ltration membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 47737, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ziel, R.; Haus, A.; Tulke, A. Quantification of the pore size distribution (porosity profiles) in microfiltration membranes by SEM, TEM and computer image analysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 323, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Su, Y.; Li, C.; Shi, Q.; Ning, X.; Jiang, Z. Fabrication of antifouling polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes using Pluronic F127 as both surface modifier and pore-forming agent. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 318, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pylypchuk, I.; Selyanchyn, R.; Budnyak, T.; Zhao, Y.; Lindström, M.; Fujikawa, S.; Sevastyanova, O. “Artificial Wood” Lignocellulosic Membranes: Influence of Kraft Lignin on the Properties and Gas Transport in Tunicate-Based Nanocellulose Composites. Membranes 2021, 11, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teow, Y.; Ahmad, A.; Lim, J.; Ooi, B. Preparation and characterization of PVDF/TiO2 mixed matrix membrane via in situ colloidal precipitation method. Desalination 2012, 295, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falath, W.; Sabir, A.; Jacob, K.I. Highly improved reverse osmosis performance of novel PVA/DGEBA cross-linked membranes by incorporation of Pluronic F-127 and MWCNTs for water desalination. Desalination 2016, 397, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, L.; Shan, B.; Xie, C.; Liu, C.; Cui, F.; Li, G. Preparation and characterization of SLS-CNT/PES ultrafiltration membrane with antifouling and antibacterial properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, Z.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.L.; Zinadini, S. Preparation of high antibiofouling amino functionalized MWCNTs/PES nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane for application in membrane bioreactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Sun, X.; Gao, C. Antifouling polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes with sulfobetaine polyimides as novel additive for the enhancement of both water flux and protein rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.J.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B. An improved method for surface modification of porous water purification membranes. Polymers 2014, 55, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raslan, R.; Mohammad, A.W. Polysulfone/Pluronic F127 Blend Ultrafiltration Membranes: Preparation and Characterizations. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 2628–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Twibell, B.; Somerville, K.; Manani, G.; Duszynski, M.; Wanekaya, A.; Schweiger, P. Influence of CNTRENE® C100LM carbon nanotube material on the growth and regulation of Escherichia coli. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Idris, A.; Nasiri, R.; Almaki, J.H. Fabrication and evaluation of polymeric membranes for blood dialysis treatments using functionalized MWCNT based nanocomposite and sulphonated-PES. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 101513–101525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouhestani, F.; Torangi, M.A.; Motavalizadehkakhky, A.; Karazhyan, R.; Zhiani, R. Enhancement strategy of polyethersulfone (Pes) membrane by introducing pluronic f127/graphene oxide and phytic acid/graphene oxide blended additives: Preparation, characterization and wastewater filtration assessment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 171, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrenko, M.; Penkova, A.; Atta, R.; Zolotarev, A.; Plisko, T.; Mazur, A.; Solovyev, N.; Ermakov, S. The development and study of novel membrane materials based on polyphenylene isophthalamide—Pluronic F127 composite. Mater. Des. 2019, 165, 107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, H.; Shawuti, S.; Siddiq, M.; Niazi, J.H.; Qureshi, A. PEG functionalized graphene oxide-silver nano-additive for enhanced hydrophilicity, permeability and fouling resistance properties of PVDF-co-HFP membranes. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 579, 123646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.H.; Min, B.R.; Lee, J.S. Change of surface morphology, permeate flux, surface roughness and water contact angle for membranes with similar physicochemical characteristics (except surface roughness) during microfiltration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 187, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Wintgens, T.; Sherman, P.; Zaricky, J.; Schäfer, A. Removal of hormones and pharmaceuticals in the Advanced Water Recycling Demonstration Plant in Queensland, Australia. Water Sci. Technol. 2004, 50, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, B.; Sinha, M.K.; Dash, S.K. Mitigation of HA, BSA and oil/water emulsion fouling of PVDF Ultrafiltration Membranes by SiO2-g-PEGMA nanoparticles. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 30, 100603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Membrane | Concentration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PES | Pluronic F-127 | Sw-Cnt | Mw-Cnt | DMF | |
| P0 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 84 |
| PP | 16 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 81 |
| PPS-Cnt | 16 | 3 | 0.01 | 0 | 80.99 |
| PPM-Cnt | 16 | 3 | 0 | 0.01 | 80.99 |
| Membrane | Ra (nm) | RMS (nm) |
|---|---|---|
| P0 | 2.04 | 2.54 |
| PP | 6.04 | 7.51 |
| PPS-Cnt | 6.23 | 8.69 |
| PPM-Cnt | 6.85 | 8.85 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arahman, N.; Rosnelly, C.M.; Yusni, Y.; Fahrina, A.; Silmina, S.; Ambarita, A.C.; Bilad, M.R.; Gunawan, P.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Takagi, R.; et al. Ultrafiltration of α-Lactalbumin Protein: Acquaintance of the Filtration Performance by Membrane Structure and Surface Alteration. Polymers 2021, 13, 3632. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213632
Arahman N, Rosnelly CM, Yusni Y, Fahrina A, Silmina S, Ambarita AC, Bilad MR, Gunawan P, Rajabzadeh S, Takagi R, et al. Ultrafiltration of α-Lactalbumin Protein: Acquaintance of the Filtration Performance by Membrane Structure and Surface Alteration. Polymers. 2021; 13(21):3632. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213632
Chicago/Turabian StyleArahman, Nasrul, Cut Meurah Rosnelly, Yusni Yusni, Afrillia Fahrina, Silmina Silmina, Aulia Chintia Ambarita, Muhammad Roil Bilad, Poernomo Gunawan, Saeid Rajabzadeh, Ryosuke Takagi, and et al. 2021. "Ultrafiltration of α-Lactalbumin Protein: Acquaintance of the Filtration Performance by Membrane Structure and Surface Alteration" Polymers 13, no. 21: 3632. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213632
APA StyleArahman, N., Rosnelly, C. M., Yusni, Y., Fahrina, A., Silmina, S., Ambarita, A. C., Bilad, M. R., Gunawan, P., Rajabzadeh, S., Takagi, R., Matsuyama, H., & Aziz, M. (2021). Ultrafiltration of α-Lactalbumin Protein: Acquaintance of the Filtration Performance by Membrane Structure and Surface Alteration. Polymers, 13(21), 3632. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213632