Multipurpose Processing Additives for Silica/Rubber Composites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
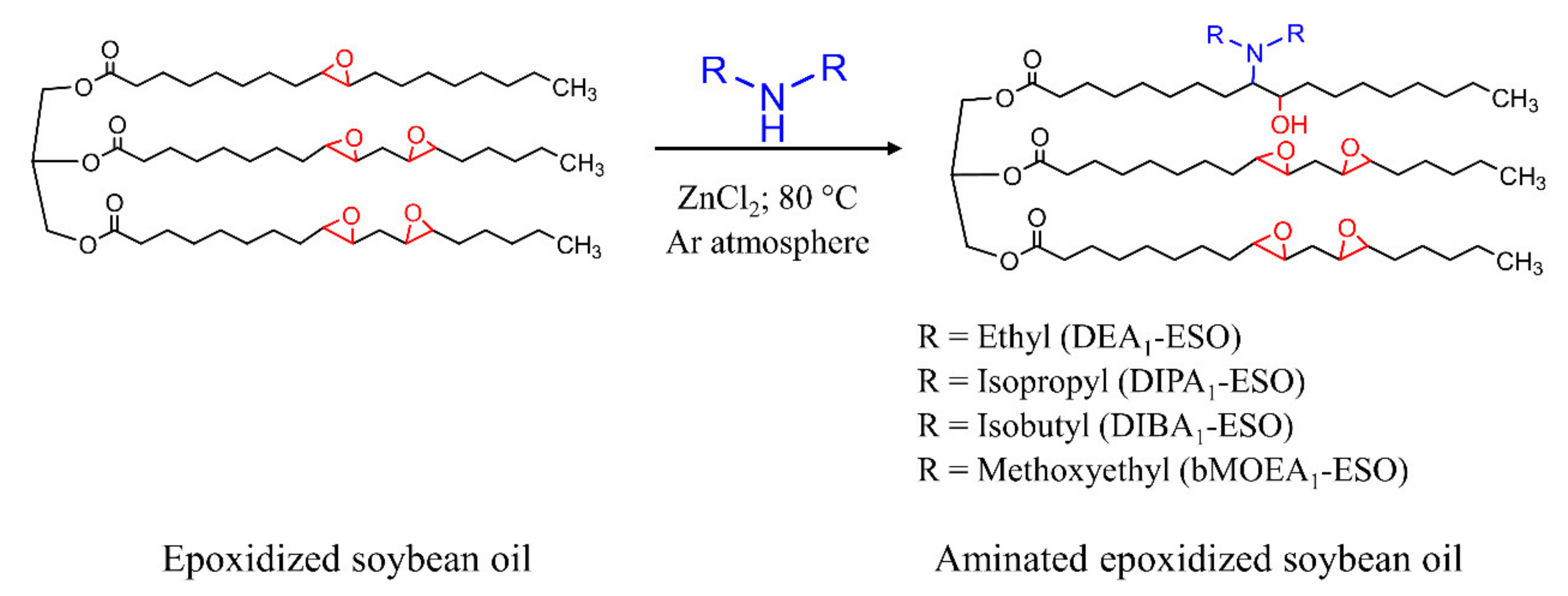
2.2. Synthesis of Aminated Epoxidized Soybean Oil
2.3. Incorporation of Aminated Epoxidized Soybean Oils in Silica-Loaded Rubber Formulations
2.4. Cure Kinetics and Vulcanization of Rubber Compounds
2.5. Specific Equilibrium Swelling of Cured Rubber Materials
2.6. Mechanical Properties of Rubber Compounds
2.7. Micro-Computed X-ray Tomography (µCT) to Assess Microscale Dispersion of Silica
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
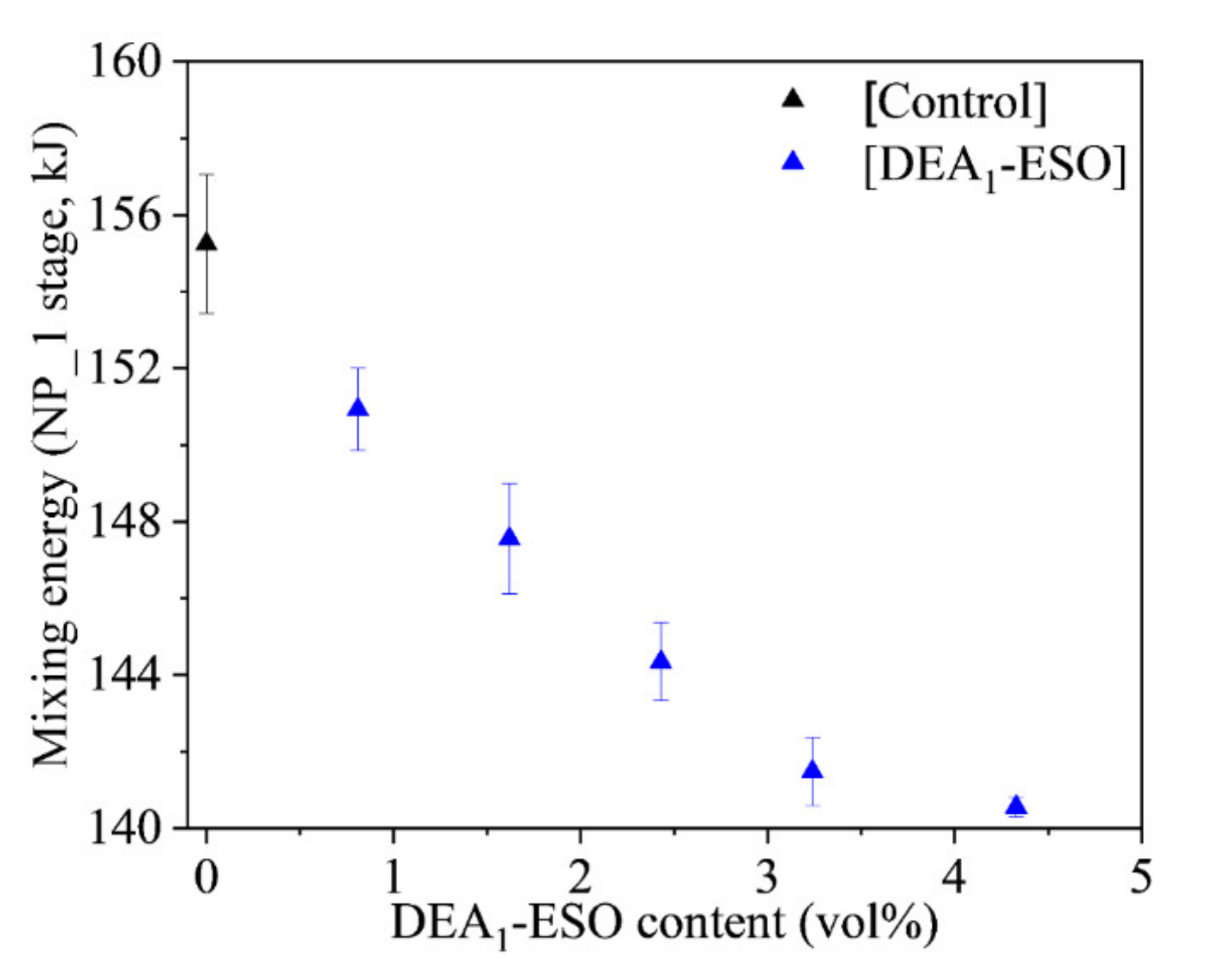
3.1. Effect of DEA1-ESO on the Processability of Silica-Filled Rubber System
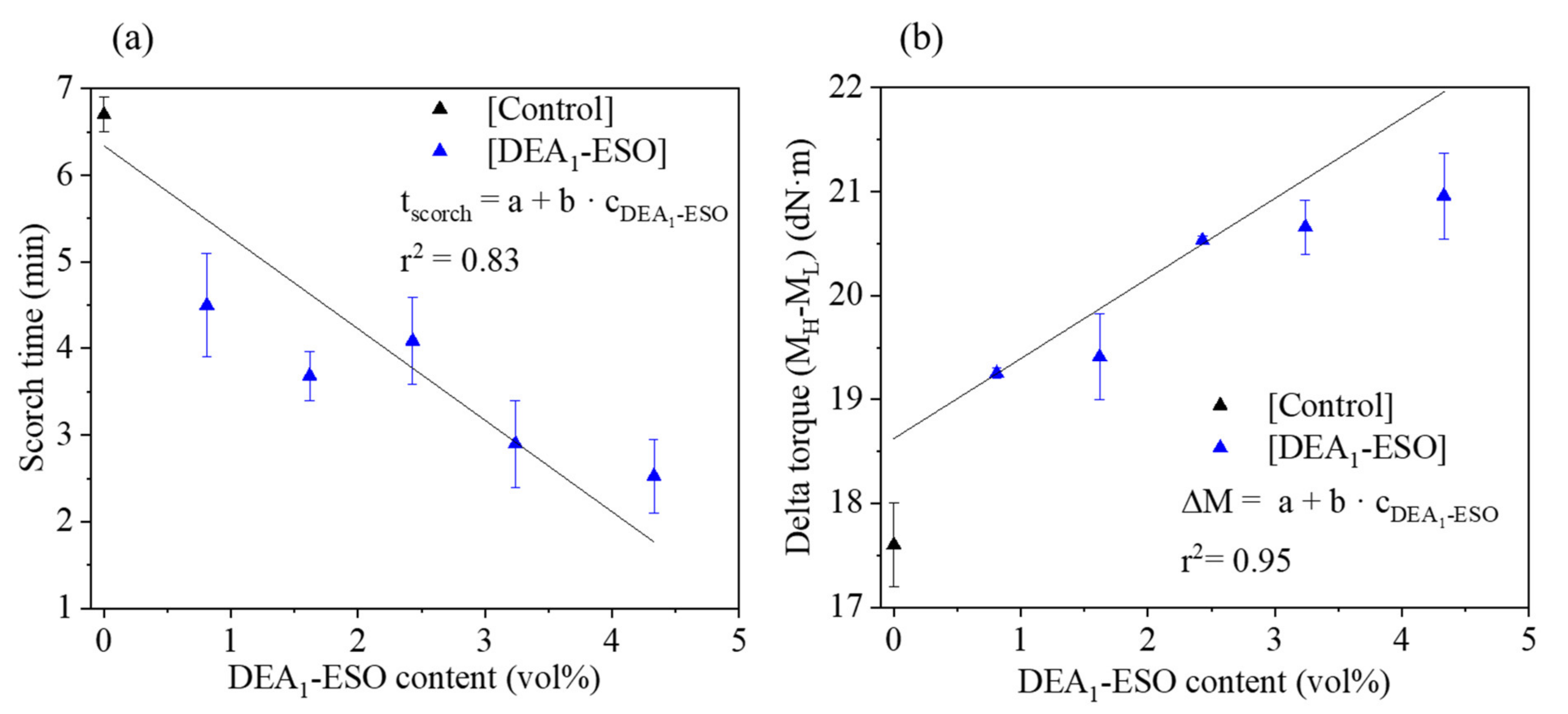
3.2. Effects of DEA1-ESO on Cure Rate and Cure State of Silica-Filled Rubber Compounds
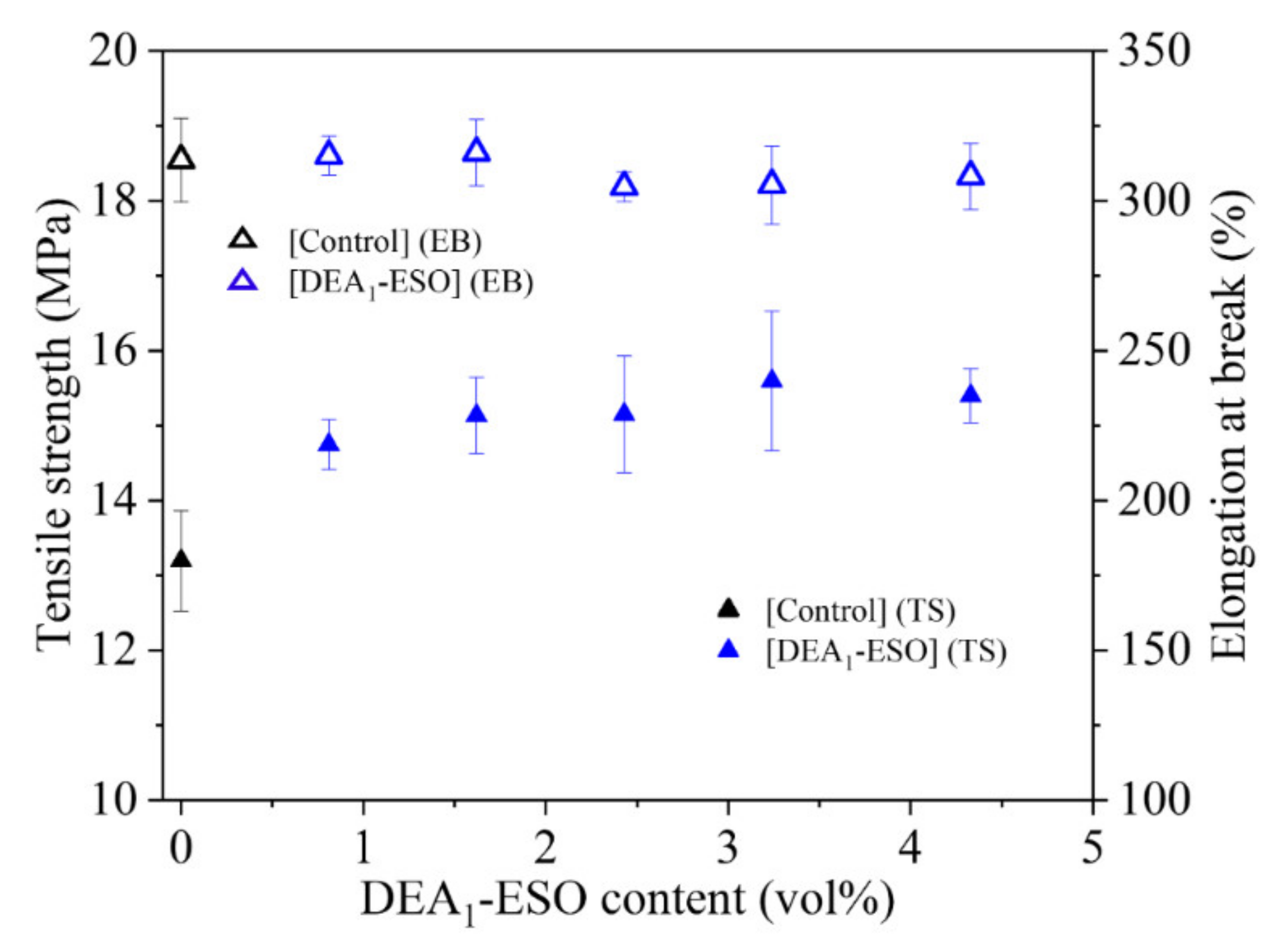
3.3. Quasistatic Mechanical Properties of Silica-Filled Rubber System Compounded with DEA1-ESO
3.4. Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Silica-Filled Rubber System Compounded with DEA1-ESO and its Relationship with Silica-Rubber Morphology
3.5. Properties of Silica-Filled Rubber Compound Formulated with Different Aminated Epoxidized Soybean Oils
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szeluga, U.; Kumanek, B.; Trzebicka, B. Synergy in hybrid polymer/nanocarbon composites. A review. Compos. Part A 2015, 73, 204–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, S.; Peng, J.; Liu, L. The filler–rubber interface and reinforcement in styrene butadiene rubber composites with graphene/silica hybrids: A quantitative correlation with the constrained region. Compos. Part A 2016, 86, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Zhang, C.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Niu, L.; Ding, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z. Preparation of hexamethyl disilazane-surface functionalized nano-silica by controlling surface chemistry and its “agglomeration-collapse” behavior in solution polymerized styrene butadiene rubber/butadiene rubber composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2021, 201, 108482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Formela, K.; Wang, S. Enhanced interfacial and mechanical performance of styrene-butadiene rubber/silica composites compatibilized by soybean oil derived silanized plasticization. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 197, 108271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa, H.M.; Abrantes, T.A.S.; Nunes, R.C.R.; Visconte, L.L.Y.; Furtado, C.R.G. Design and analysis of experiments in silica filled natural rubber compounds—Effect of castor oil. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandanan, V.; Joseph, R.; George, K.E. Rubber seed oil: A multipurpose additive in NR and SBR compounds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 72, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Isayev, A.I.; Ren, X.; Soucek, M.D. Toward replacement of petroleum oils by modified soybean oils in elastomers. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2016, 89, 608–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwarote, B.; Sae-Oui, P.; Wirasate, S.; Suchiva, K. Effects of bio-based oils on processing properties and cure characteristics of silica-filled natural rubber compounds. J. Rubber Res. 2017, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodyear Soybean Oil Technology Wins ‘Environmental Achievement of the Year’ Award—News Release. Available online: https://corporate.goodyear.com/en-US/media/news/goodyear-soybean-oil-technology-wins-environmental-achievement-of-the-year-award.html (accessed on 24 February 2021).
- Hayichelaeh, C.; Reuvekamp, L.A.E.M.; Dierkes, W.K.; Blume, A.; Noordermeer, J.W.M.; Sahakaro, K. Silica-reinforced natural rubber tire tread compounds containing bio-based process oils. I: Aspects of mixing sequence and epoxide content. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2020, 93, 360–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espósito, L.H.; Marzocca, A.J. Silica-filled S-SBR with epoxidized soybean oil: Influence of the mixing process on rheological and mechanical properties of the compound. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta Sarma, A.; Eloy Federico, C.; Staropoli, M.; Nzulu, F.; Weydert, M.; Verge, P.; Schmidt, D.F. Properties of silica-filled rubber compounds vs. epoxidized oil content and degree of epoxidation. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 168, 113600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-L.; Futamura, S.; Bates, K.A.; Halasa, A.F.; Hua, K.-C.; Hahn, B.R. Preparation of Silica Reinforced Polyisoprene-Rich Rubber Composition and Tire with Component Thereof. U.S. Patent 7,473,724, 6 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, W.-L.; Futamura, S.; Hua, K.-C.; Bates, K.A.; Zhang, P. Tire with Component Comprised of Rubber Composition Containing Hydrophobated, Pre-Silanized Silica. U.S. Patent 7285584, 23 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Weydert, M.; Frantzen, A.; Kunysz, P.W.S. Pneumatic Tire with Rubber Component Containing Epoxidized Palm Oil. EP2340946B1, 6 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hayichelaeh, C.; Reuvekamp, L.A.E.M.; Dierkes, W.K.; Blume, A.; Noordermeer, J.W.M.; Sahakaro, K. Reinforcement of natural rubber by silica/silane in dependence of different amine types. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2017, 90, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, S.T.; Robertson, R.E. Thermodynamics of basic ionization of some aminoethers in water. Can. J. Chem. 1976, 54, 3600–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, H.K. Correlation of the base strengths of amines 1. JACS 1957, 79, 5441–5444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S. Science and Technology of Rubber, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1978; pp. 529–551. [Google Scholar]
- Braum, M.V.; Jacobi, M.A. Silica grafted with epoxidized liquid polybutadienes: Its behavior as filler for tire tread compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2017, 90, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Adhvaryu, A.; Gordon, S.H.; Erhan, S.Z.; Willett, J.L. Synthesis of diethylamine-functionalized soybean oil. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2005, 53, 9485–9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D3616—95. Standard Test Method for Rubber—Determination of Gel, Swelling Index, and Dilute Solution Viscosity; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcea, S.C.; Wang, Y.; Withers, P.J. X-ray computed tomography of polymer composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2018, 156, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, S.C.; Stevenson, A.W.; Wilkins, S.W. In-line phase-contrast X-ray imaging and tomography for materials science. Materials 2012, 5, 937–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.S.; Barry, C.M.F.; Mead, J.L. Microscopic measurement of the degree of mixing for nanoparticles in polymer nanocomposites by TEM images. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2007, 70, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.S.; Barry, C.M.F.; Mead, J.L. Effect of fill factor and validation of characterizing the degree of mixing in polymer nanocomposites. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2007, 47, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Lee, J.S.; Barry, C.F.; Mead, J.L. Evaluation and prediction of the effects of melt-processing conditions on the degree of mixing in alumina/poly(ethylene terephthalate) nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 2924–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D1566—20. Standard Terminology Relating to Rubber; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengloyluan, K.; Sahakaro, K.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W. Reduced ethanol emissions by a combination of epoxidized natural rubber and silane coupling agent for silica-reinforced natural rubber-based tire treads. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2016, 89, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewsakul, W.; Sahakaro, K.; Dierkes, W.K.; Noordermeer, J.W. Cooperative effects of epoxide functional groups on natural rubber and silane coupling agents on reinforcing efficiency of silica. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2014, 87, 291–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-g.; Saha, P.; Kim, J.-H.; Jo, S.-H.; Kim, J.K. Novel elastomer nanocomposite with uniform silica dispersion from polybutadiene rubber treated with epoxidized soybean oil. J. Compos. Mater. 2015, 49, 3005–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Datta Sarma, A.; Moretto, E.; Thomann, J.-S.; Verge, P.; Schmidt, D.; Kayser, F.; Dieden, R. Semi-quantitative solid-state NMR study of the adsorption of soybean oils on silica and its significance for rubber processing. Langmuir 2021, 37, 10298–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Sun, Y.; He, J.; Tang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Luo, Y.; Liu, F. Enhancing mechanical properties of styrene–butadiene rubber/silica nanocomposites by in situ interfacial modification with a novel rare-earth complex. Compos. Part A 2016, 87, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramier, J.; Chazeau, L.; Gauthier, C.; Guy, L.; Bouchereau, M.N. Influence of silica and its different surface treatments on the vulcanization process of silica filled SBR. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2007, 80, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanasom, N.; Saowapark, T.; Deeprasertkul, C. Reinforcement of natural rubber with silica/carbon black hybrid filler. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Fan, X.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Reinforcement and Payne effect of hydrophobic silica filled natural rubber nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 187, 107943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Sun, S.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, H.; Zuo, M.; Song, Y.; Zheng, Q. Influence of carbon black on the Payne effect of filled natural rubber compounds. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 203, 108586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Nie, H.; Wang, R.; He, A. Multi-block copolymer as reactive multifunctional compatibilizer for NR/BR blends with desired network structures and dynamical properties: Compatibility, co-vulcanization and filler dispersion. Compos. Part A 2019, 116, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhu, S.; Liu, M.; Zhong, B.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Liu, F.; Jia, Z.; Jia, D. A high-performance, thermal and electrical conductive elastomer composite based on Ti3C2 MXene. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 145, 106292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Rubber Compound | Experimental Oil | Vol% of A-ESO b | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Content a (phr) | ||
| [Control] | - | - | 0 |
| [DEA1-ESO]1.5–8 | DEA1-ESO | 1.5/3/4.5/6/8 | 0.8/1.6/2.4/3.2/4.3 |
| [DIPA1-ESO]4.5 | DIPA1-ESO | 4.5 | 2.4 |
| [DIBA1-ESO]4.5 | DIBA1-ESO | 4.5 | 2.4 |
| [bMOEA1-ESO]4.5 | bMOEA1-ESO | 4.5 | 2.4 |
| Non-Productive Stage_1 | Non-Productive Stage_2 | Productive Stage |
|---|---|---|
| Rubber (SBR, BR) + ZnO (0.5 phr) + Stearic acid + Oil (TDAE, modified oil) + Silica (65 phr) | Silica (15 phr) + Silane coupling agent (TESPD) + Anti-oxidant (6-PPD) | Sulfur + Accelerators (MBT, DPG, and CBS)+ ZnO (2 phr) |
| Sample Name | Magnitude of Payne Effect (MPa) | Equivalent Diameter (µm) | Skewness |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Control] | 0.30 ± 0.01 | 10.15 ± 0.17 | 2.77 ± 0.13 |
| [DEA1-ESO]1.5 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 9.98 ± 0.09 | 1.89 ± 0.11 |
| [DEA1-ESO]3 | 0.27 ± 0.01 | 9.76 ± 0.19 | 2.36 ± 0.09 |
| [DEA1-ESO]4.5 | 0.32 ± 0.01 | 8.95 ± 0.07 | 2.71 ± 0.20 |
| [DEA1-ESO]6 | 0.33 ± 0.04 | 8.65 ± 0.05 | 2.68 ± 0.16 |
| [DEA1-ESO]8 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 9.06 ± 0.05 | 3.03 ± 0.15 |
| Sample Name | Mixing Energy (kJ) | Cure Kinetics | Specific Swelling (%) | Quasi-Static Mechanical Properties | Dynamic Mechanical Properties | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ∆M (dN·m) | Scorch Time (min) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | ∆G′ (MPa) | |||
| [Control] | 155 ± 2 | 17.6 ± 0.6 | 6.7 ± 0.2 | 187.0 ± 5.0 | 13.2 ± 0.6 | 313 ± 14 | 0.30 ± 0.01 |
| [DEA1-ESO]4.5 | 144 ± 1 | 20.5 ± 0.4 | 4.1 ± 0.5 | 174.9 ± 0.8 | 15.2 ± 0.8 | 304 ± 5 | 0.32 ± 0.00 |
| [DIPA1-ESO]4.5 | 147 ± 1 | 20.1 ± 1.0 | 4.9 ± 0.8 | 173.7 ± 1.3 | 15.0 ± 0.7 | 305 ± 10 | 0.32 ± 0.09 |
| [DIBA1-ESO]4.5 | 146 ± 1 | 19.8 ± 1.0 | 4.7 ± 0.6 | 175.0 ± 1.5 | 15.5 ± 0.3 | 304 ± 2 | 0.31 ± 0.05 |
| [bMOEA1-ESO]4.5 | 144 ± 1 | 18.9 ± 0.0 | 5.7 ± 0.1 | 185.0 ± 4.0 | 13.8 ± 0.8 | 292 ± 13 | 0.26 ± 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Datta Sarma, A.; Federico, C.E.; Nzulu, F.; Weydert, M.; Verge, P.; Schmidt, D.F. Multipurpose Processing Additives for Silica/Rubber Composites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application. Polymers 2021, 13, 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213608
Datta Sarma A, Federico CE, Nzulu F, Weydert M, Verge P, Schmidt DF. Multipurpose Processing Additives for Silica/Rubber Composites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application. Polymers. 2021; 13(21):3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213608
Chicago/Turabian StyleDatta Sarma, Arpan, Carlos Eloy Federico, Frida Nzulu, Marc Weydert, Pierre Verge, and Daniel Frederick Schmidt. 2021. "Multipurpose Processing Additives for Silica/Rubber Composites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application" Polymers 13, no. 21: 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213608
APA StyleDatta Sarma, A., Federico, C. E., Nzulu, F., Weydert, M., Verge, P., & Schmidt, D. F. (2021). Multipurpose Processing Additives for Silica/Rubber Composites: Synthesis, Characterization, and Application. Polymers, 13(21), 3608. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13213608






