Poly(lactic acid)–Poly(butylene succinate)–Sugar Beet Pulp Composites; Part II: Water Absorption Characteristics with Fine and Coarse Sugar Beet Pulp Particles; A Phenomenological Investigation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Compounding
2.3. Injection Molding
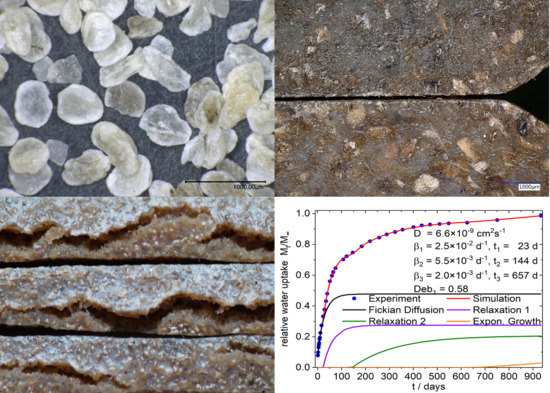
2.4. Microscopy
2.5. Water Absorption
3. Background: Penetrant Sorption in Polymers
4. Results
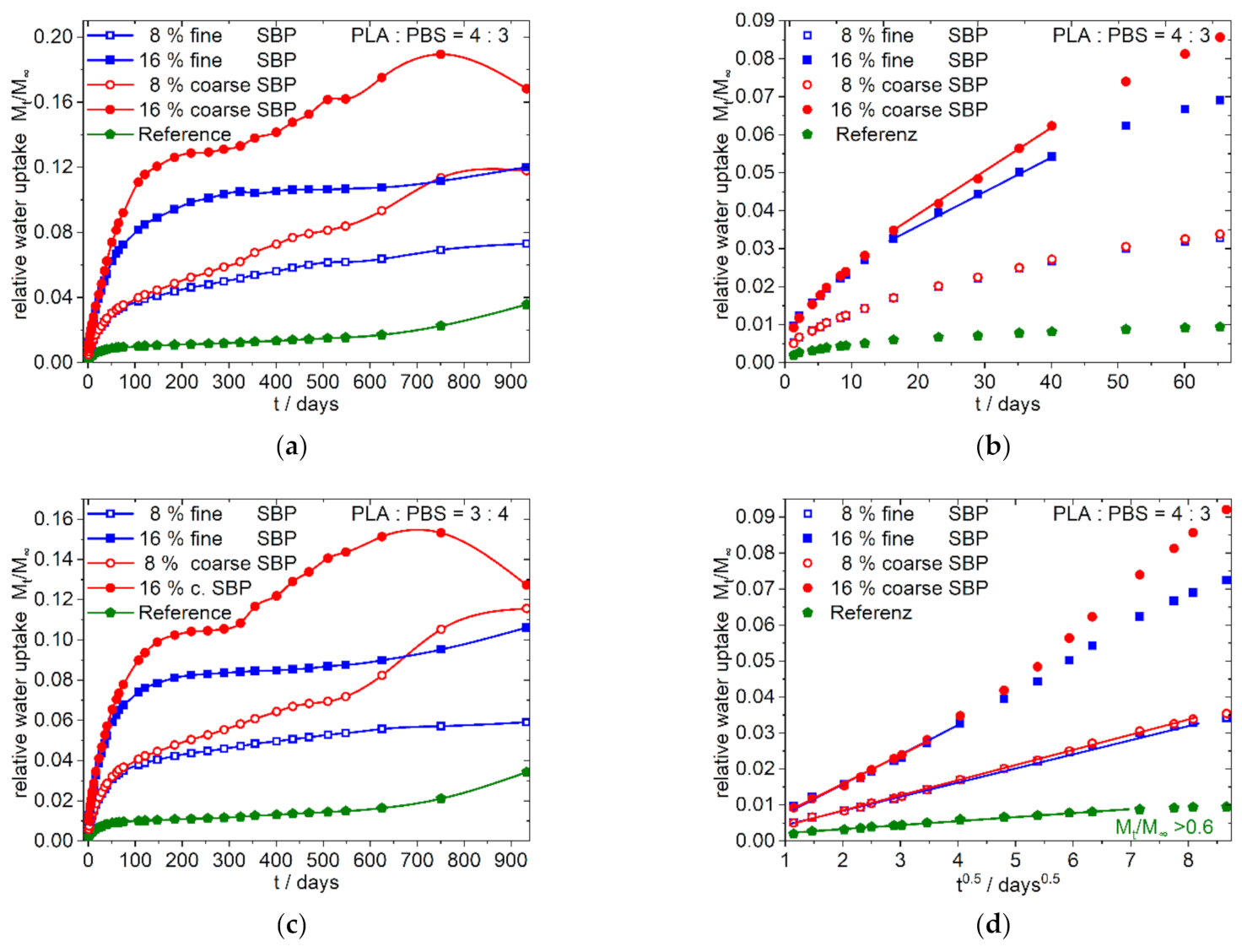
4.1. Water Sorption in Sugar Beet Pulp Containing Composites
4.1.1. Phenomenological Description
4.1.2. Water Sorption Curves, Description
Overall Sorption Characteristics
Sorption Characteristics at the Beginning
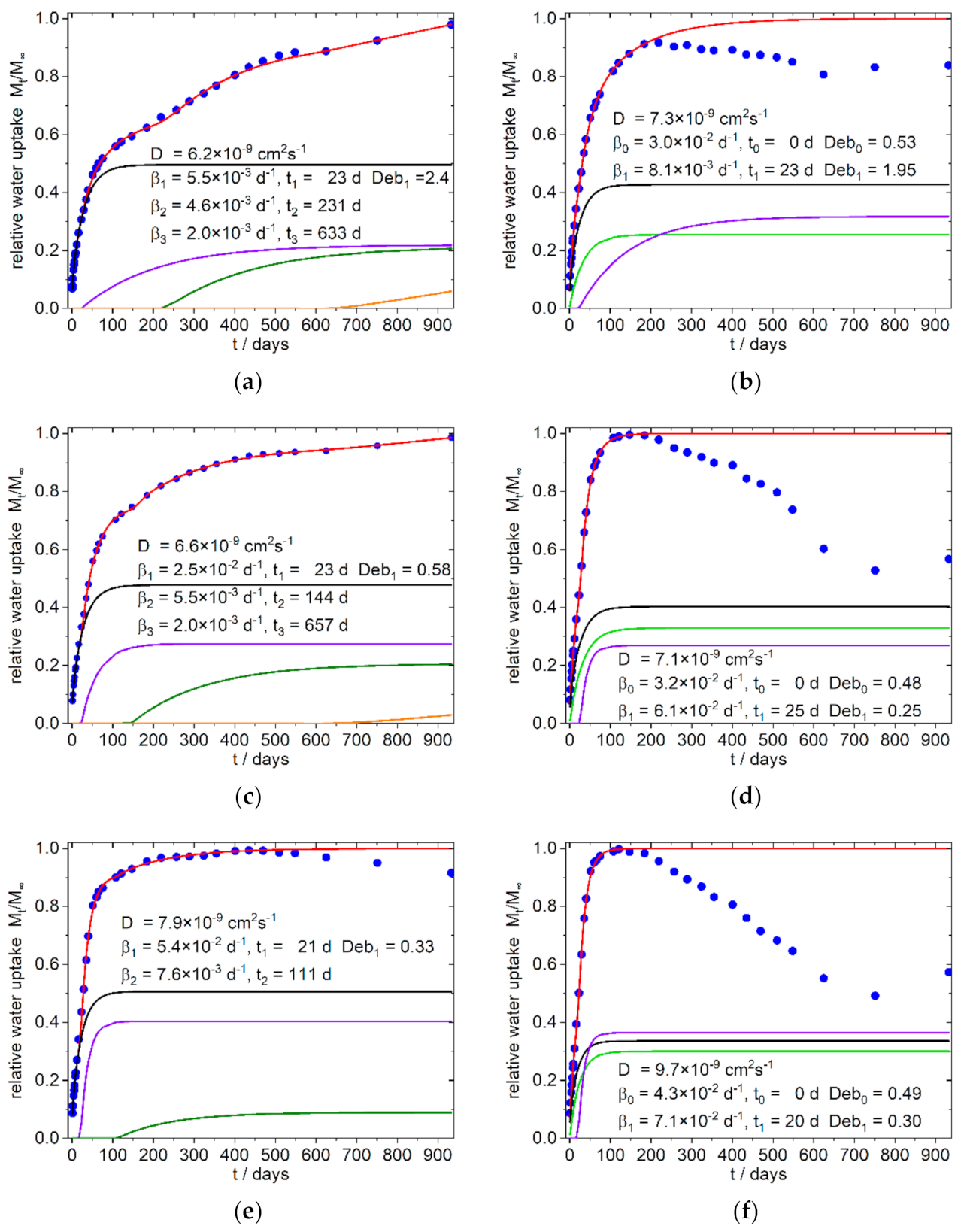
4.2. Phenomenological Simulation of Sorption Curves
4.2.1. 9:1-f/c/-X Composites
4.2.2. 4:3/3:4-f/c-Xcomposites
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculure Organisation of the United Nations. FAOSTAT Data. Available online: http://fenix.fao.org/faostat/internal/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 18 August 2021).
- Rouilly, A.; Jorda, J.; Rigal, L. Thermo-Mechanical processing of sugar beet pulp. I. Twin-screw extrusion process. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 66, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Poel, P.W.; Schiweck, H.; Schwartz, T. Zuckertechnologie: Rüben-und Rohrzuckergewinnung; Verlag Dr. Albert Bartens KG: Berlin, Germany, 2000; pp. 123–125. ISBN 3-87040-070-6. [Google Scholar]
- van der Poel, P.W.; Schiweck, H.; Schwartz, T. Sugar Technology: Beet and Cane SUGAR Manufacture, 1st ed.; Verlag Dr. Albert Bartens KG: Berlin, Germany, 1998; pp. 115–117. ISBN 978-3-87040-065-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kopitzky, R. Poly(Lactic Acid)–Poly(Butylene Succinate)–Sugar Beet Pulp Composites; Part I: Mechanics of Composites with Fine and Coarse Sugar Beet Pulp Particles. Polymer 2021, 13, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Liu, L.; Cooke, P.H.; Hicks, K.B.; Zhang, J. Performance Enhancement of Poly(lactic acid) and Sugar Beet Pulp Composites by Improving Interfacial Adhesion and Penetration. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 8667–8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Hotchkiss, A.T. Preparation and Properties of Water and Glycerol-plasticized Sugar Beet Pulp Plastics. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouilly, A.; Geneau-Sbartaï, C.; Rigal, L. Thermo-mechanical processing of sugar beet pulp. III. Study of extruded films improvement with various plasticizers and cross-linkers. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3076–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rouilly, A.; Jorda, J.; Rigal, L. Thermo-mechanical processing of sugar beet pulp. II. Thermal and rheological properties of thermoplastic SBP. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 66, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dea, I.; Madden, J.K. Acetylated pectic polysaccharides of sugar beet. Food Hydrocoll. 1986, 1, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, C.M.; Thibault, J.-F. Structure and properties of apple and sugar-beet pectins extracted by chelating agents. Carbohydr. Res. 1993, 244, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Chavarría-Hernández, N.; Inés Rodríguez Hernández, A.; Pagliaro, M. Pectin: A new perspective from the biorefinery standpoint. Biofuels Bioprod. Bioref. 2015, 9, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciriminna, R.; Fidalgo, A.; Delisi, R.; Ilharco, L.M.; Pagliaro, M. Pectin production and global market. Agro. Food Ind. Hi-Tech. 2016, 27, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Pippen, E.L.; McCready, R.M.; Owens, H.S. Gelation Properties of Partially Acetylated Pectins 2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejaii, M.; Salehi, E.A. Properties of sugar beet pulp pectin: A systemic review. Int. J. PharmTech Res. 2016, 9, 364–368. [Google Scholar]
- Rombouts, F.M.; Thibault, J.-F. Feruloylated pectic substances from sugar-beet pulp. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 154, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibault, J.-F. Some physicochemical properties of sugar-beet pectins modified by oxidative cross-linking. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 155, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Bhaladhare, S.; Zhan, P.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Hotchkiss, A.T. Morphology and Properties of Thermoplastic Sugar Beet Pulp and Poly(butylene adipate-co-terepthalate) Blends. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 13859–13865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buxbaum, L.H. Der Abbau von Polyäthylenterephthalat. Angew. Chem. 1968, 80, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.A.; Smith, P.A. Modeling the Transport of Low-Molecular-Weight Penetrants within Polymer Matrix Composites. Polymer 2006, 59, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensitieri, G.; Del Nobile, M.A.; Apicella, A.; Nicolais, L. Moisture-Matrix Interactions in Polymer Based Composite Materials. Rev. Inst. Fr. Pét. 1995, 50, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, J.H.; Sanopoulou, M.; Papadokostaki, K.G. Physically insightful modeling of non-Fickian kinetic regimes encountered in fundamental studies of isothermal sorption of swelling agents in polymeric media. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed.; reprint; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1975; ISBN 0198533446. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, J.; Tsige, M.; Taylor, P.L. Generalized model for the diffusion of solvents in glassy polymers: From Fickian to Super Case II. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 147, 44904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loh, W.K.; Crocombe, A.D.; Abdel Wahab, M.M.; Ashcroft, I.A. Modelling anomalous moisture uptake, swelling and thermal characteristics of a rubber toughened epoxy adhesive. Intern. J. Adhesi. Adhesi. 2005, 25, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placette, M.D.; Fan, X.; Zhao, J.-H.; Edwards, D. Dual stage modeling of moisture absorption and desorption in epoxy mold compounds. Microelectron. Reliab. 2012, 52, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Windle, A. A theory of case II diffusion. Polymer 1982, 23, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Sparer, R.; Untereker, D. Analytical solutions to mathematical models of the surface and bulk erosion of solid polymers. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2005, 43, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Burkersroda, F.; Schedl, L.; Göpferich, A. Why degradable polymers undergo surface erosion or bulk erosion. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4221–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample Designation | PLA:PBS | PLA | PBS | SBP, Fine (f) or Coarse (c) Type | Chalk | Talc | Coupling Agent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix composition | X | Y | |||||
| 9:1-f-X-Y | 9:1 | 67.5 | 7.5 | 0/8.3/16.7/25 | 25/16.7/8.3/0 | 0 | 0.5/1.0/1.5/4 |
| 9:1-c-X-Y | 0/8.3/16.7/25 | 25/16.7/8.3/0 | 0 | 0.5/1.0/1.5/4 | |||
| 4:3-f-X-Y | 4:3 | 48 | 36 | 0/8/16 | 0 | 16/8/0 | 1.0/1.5 |
| 4:3-c-X-Y | 0/8/16 | 0 | 16/8/0 | 1.0/1.5 | |||
| 3:4-f-X-Y | 3:4 | 36 | 48 | 0/8/16 | 0 | 16/8/0 | 1.0/1.5 |
| 3:4-c-X-Y | 0/8/16 | 0 | 16/8/0 | 1.0/1.5 | |||
| Sample Designation | Day | Observation | Day | Observation | Day | Observation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9:1-0-0-0.0 | ||||||
| 9:1-f-8.3-1.0 | 257 | bump | 289 | bump with crevice | ||
| 9:1-f-16.7-1.0 | 257 | bump with crevices | ||||
| 9:1-f-25-1.0 | 219 | bump with crevices | ||||
| 9:1-c-8.3-1.0 | 12 | crevices/cracks | 51 | cracks | 510 | edge breaking |
| 9:1-c-16.7-1.0 | 12 | crevices/cracks | 29 | cracks | ||
| 9:1-c-25-1.0 | 12 | crevices/cracks | 29 | cracks | 751 | embrittlement |
| 4:3-0-0-0.0 | 933 | bump | ||||
| 4:3-f-8-1.0 | 625 | bump | 933 | crevices | ||
| 4:3-f-16-1.0 | 219–289 | bump with crevices | 625 | crevices | 933 | crevices |
| 4:3-c-8-1.0 | 355 | crevices/cracks | 401 | cracks | 625 | long cracks |
| 4:3-c-16-1.0 | 107 | crack | 401 | long crack | 625–933 | embrittl. delamination |
| 3:4-0-0-0.0 | 933 | bump | ||||
| 3:4-f-8-1.0 | 355 | beginning bump | 933 | crevices | ||
| 3:4-f-16-1.0 | 355–455 | bump | 625 | crevices | 751–933 | embrittlement |
| 3:4-c-8-1.0 | 625 | crevices | 751 | embrittlement | ||
| 3:4-c-16-1.0 | 147 | crevices | 184 | crevices/cracks | 751 | embrittlement |
| Sample Designation | Diffusion-Coefficient 10−9 cm2s−1 | Relaxation/Expon. Growth | Frequency Coefficient Beta/ 10−3 d−1 | Deb | ∅ Error Per DataPoint | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day | Relaxation | Growth | |||||||||||
| d0 | d1 | d2 | d3 | β0 | β1 | β2 | β3 | β3 | β0 | β1 | |||
| 9:1-0-0 | 13 | 27 | 112 | 438 | 12 | 6.0 | 1.8 | 2.3 | 0.0022 | ||||
| 9:1-f-8.3 | 6.2 | 23 | 231 | 633 | 5.5 | 4.6 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 0.0051 | ||||
| 9:1-f-16.7 | 6.6 | 23 | 144 | 657 | 25 | 5.5 | 2.0 | 0.58 | 0.0034 | ||||
| 9:1-f-25 | 7.9 | 21 | 111 | 54 | 7.6 | 0.33 | 0.0071 | ||||||
| 9:1-c-8.3 | 7.3 | 0 | 23 | 30 | 8.1 | 0.53 | 2.0 | 0.0032 | |||||
| 9:1-c-16.7 | 7.1 | 0 | 26 | 32 | 61 | 0.48 | 0.25 | 0.0036 | |||||
| 9:1-c-25 | 9.7 | 0 | 20 | 43 | 71 | 0.49 | 0.30 | 0.0069 | |||||
| 4:3-0-0 | 9.5 | 35 | 318 | 599 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 9.8 | 0.0032 | ||||
| 4:3-f-8 | 7.2 | 20 | 307 | 599 | 3.5 | 8.1 | 2.2 | 4.4 | 0.0037 | ||||
| 4:3-f-16 | 7.0 | 18 | 645 | 8.1 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 0.0035 | ||||||
| 4:3-c-8 | 8.3 | 18 | 311 | 612 | 3.4 | 10 | 5.3 | 0.0020 | |||||
| 4:3-c-16 | 11 | 22 | 328 | 526 | 14 | 5.9 | 1.7 | 0.0060 | |||||
| 3:4-0-0 | 11 | 20 | 293 | 600 | 2.4 | 1.4 | 2.3 | 9.8 | 0.0042 | ||||
| 3:4-f-8 | 6.5 | 23 | 305 | 405 | 3.4 | 4.2 | 1.7 | 4.1 | 0.0030 | ||||
| 3:4-f-16 | 5.9 | 19 | 419 | 582 | 11 | 4.2 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 0.0023 | ||||
| 3:4-c-8 | 8.1 | 25 | 285 | 597 | 4.0 | 4.3 | 8.4 | 4.4 | 0.0015 | ||||
| 3:4-c-16 | 18 | 18 | 318 | 408 | 15 | 12 | 6.3 | 2.5 | 0.0038 | ||||
| Sample Designation | Satu-Ration | Mass Fraction 1 | Relative Sorption Per Percent SBP 1 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XD | X0 | XR1 | XR2 | XR3 | Xe.gro. | Sum | D | R0 | R1 | R2 | R3 | e.gro. | ||
| 9:1-0-0 | 1.61% | 0.43 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.21 | |||||||||
| 9:1-f-8.3 | 7.81% | 0.50 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 0.94 | 0.46 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 0.07 | ||||
| 9:1-f-16.7 | 13.5% | 0.48 | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.81 | 0.39 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.03 | ||||
| 9:1-f-25 | 19.5% | 0.51 | 0.40 | 0.09 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 0.32 | 0.07 | ||||||
| 9:1-c-8.3 | 7.69% | 0.43 | 0.26 | 0.32 | 0.92 | 0.39 | 0.24 | 0.29 | ||||||
| 9:1-c-16.7 | 13.9% | 0.40 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.83 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.22 | ||||||
| 9:1-c-25 | 22.8% | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.91 | 0.31 | 0.27 | 0.33 | ||||||
| 4:3-0-0 | 3.76% | 0.24 | 0.18 | 0.12 | 0.45 | |||||||||
| 4:3-f-8 | 7.38% | 0.40 | 0.44 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.92 | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.07 | 0.08 | ||||
| 4:3-f-16 | 12.6% | 0.44 | 0.41 | 0.15 | 0.79 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.11 | ||||||
| 4:3-c-8 | 11.9% | 0.23 | 0.43 | 0.13 | 0.22 | 1.49 | 0.34 | 0.64 | 0.19 | 0.32 | ||||
| 4:3-c-16 | 19.5% | 0.24 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 1.22 | 0.29 | 0.55 | 0.19 | 0.20 | ||||
| 3:4-0-0 | 3.61% | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.42 | |||||||||
| 3:4-f-8 | 5.95% | 0.56 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 0.74 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.02 | ||||
| 3:4-f-16 | 10.7% | 0.58 | 0.22 | 0.05 | 0.15 | 0.67 | 0.39 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.10 | ||||
| 3:4-c-8 | 12.0% | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.33 | 1.50 | 0.39 | 0.45 | 0.17 | 0.49 | ||||
| 3:4-c-16 | 15.6% | 0.24 | 0.45 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.98 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.15 | 0.16 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopitzky, R. Poly(lactic acid)–Poly(butylene succinate)–Sugar Beet Pulp Composites; Part II: Water Absorption Characteristics with Fine and Coarse Sugar Beet Pulp Particles; A Phenomenological Investigation. Polymers 2021, 13, 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203558
Kopitzky R. Poly(lactic acid)–Poly(butylene succinate)–Sugar Beet Pulp Composites; Part II: Water Absorption Characteristics with Fine and Coarse Sugar Beet Pulp Particles; A Phenomenological Investigation. Polymers. 2021; 13(20):3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203558
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopitzky, Rodion. 2021. "Poly(lactic acid)–Poly(butylene succinate)–Sugar Beet Pulp Composites; Part II: Water Absorption Characteristics with Fine and Coarse Sugar Beet Pulp Particles; A Phenomenological Investigation" Polymers 13, no. 20: 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203558
APA StyleKopitzky, R. (2021). Poly(lactic acid)–Poly(butylene succinate)–Sugar Beet Pulp Composites; Part II: Water Absorption Characteristics with Fine and Coarse Sugar Beet Pulp Particles; A Phenomenological Investigation. Polymers, 13(20), 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13203558