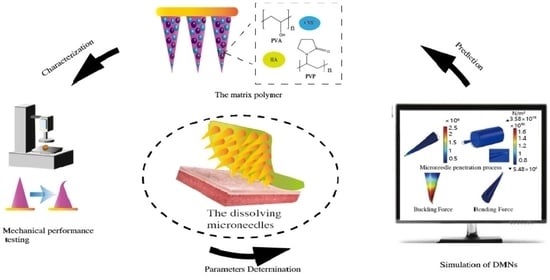
Finite Element Analysis for Biodegradable Dissolving Microneedle Materials on Skin Puncture and Mechanical Performance Evaluation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Animals
2.2. Preparation of the Composite Polymer Material
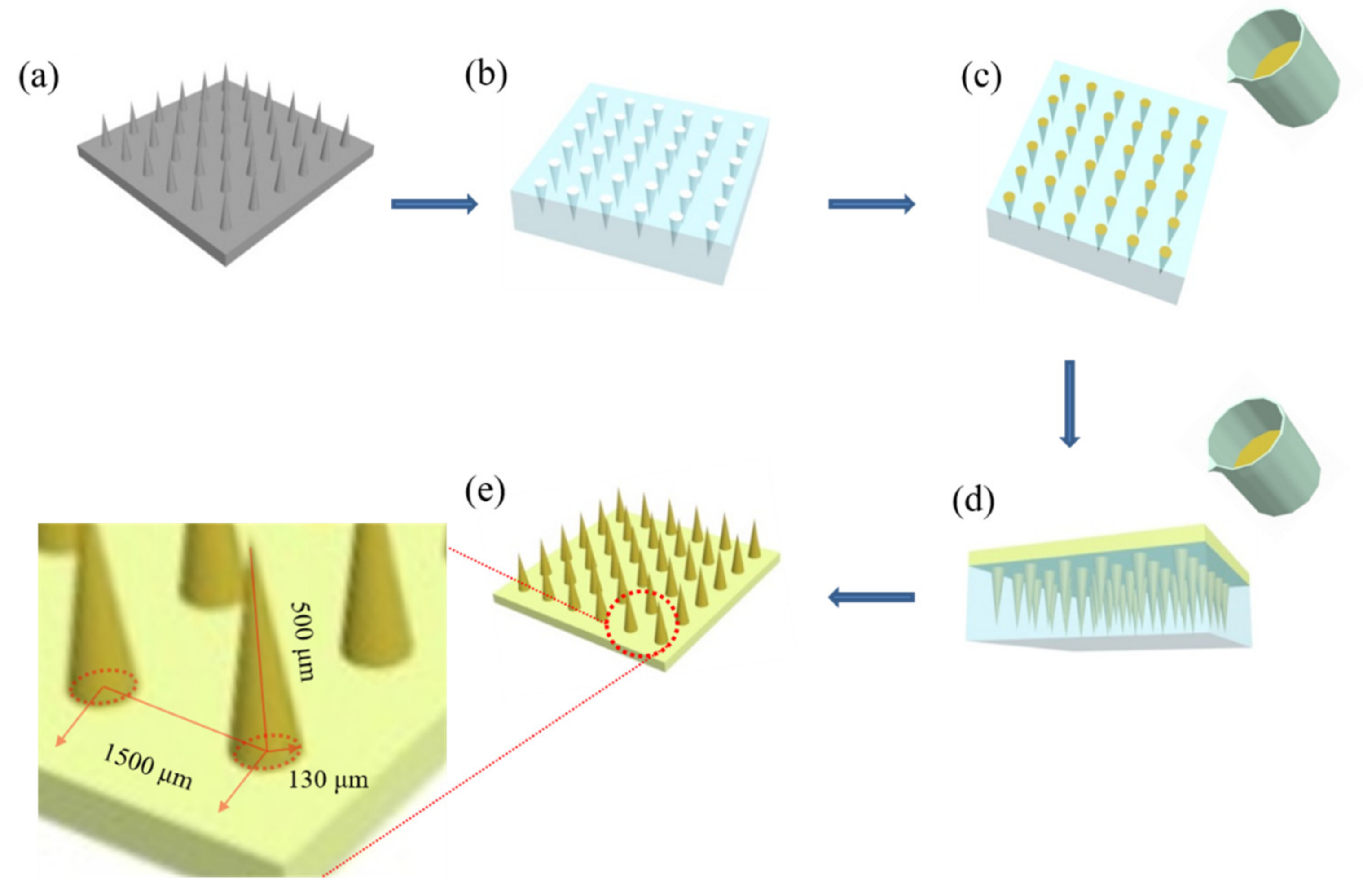
2.3. Preparation of the DMNs
2.4. Mechanical Properties of DMNs
2.4.1. Tensile Tests
2.4.2. Hardness Tests
2.5. Simulation of DMNs
2.5.1. Structure Model Construction
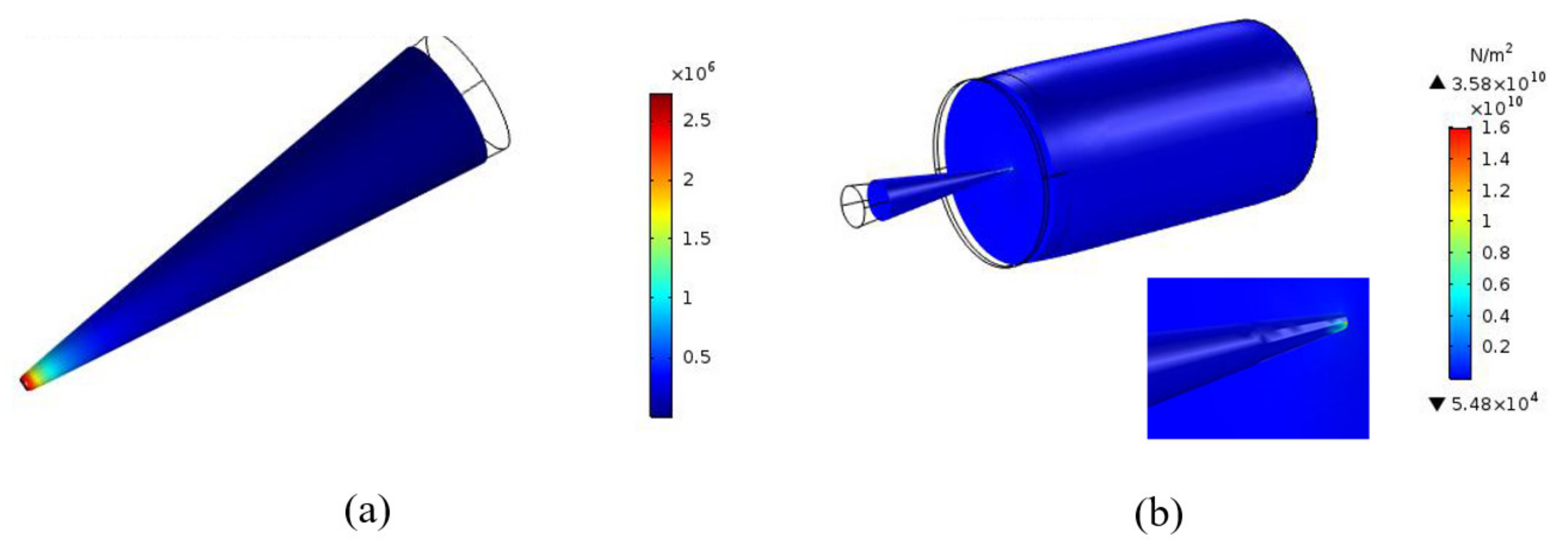
2.5.2. Von-Mises Stress
2.6. Swelling Tests
2.7. Skin Preparation
2.8. Skin Tests
2.8.1. Isolated Skin Penetration
2.8.2. Living Skin Irritation and Rehabilitation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Simulation
3.2. Puncture Tests
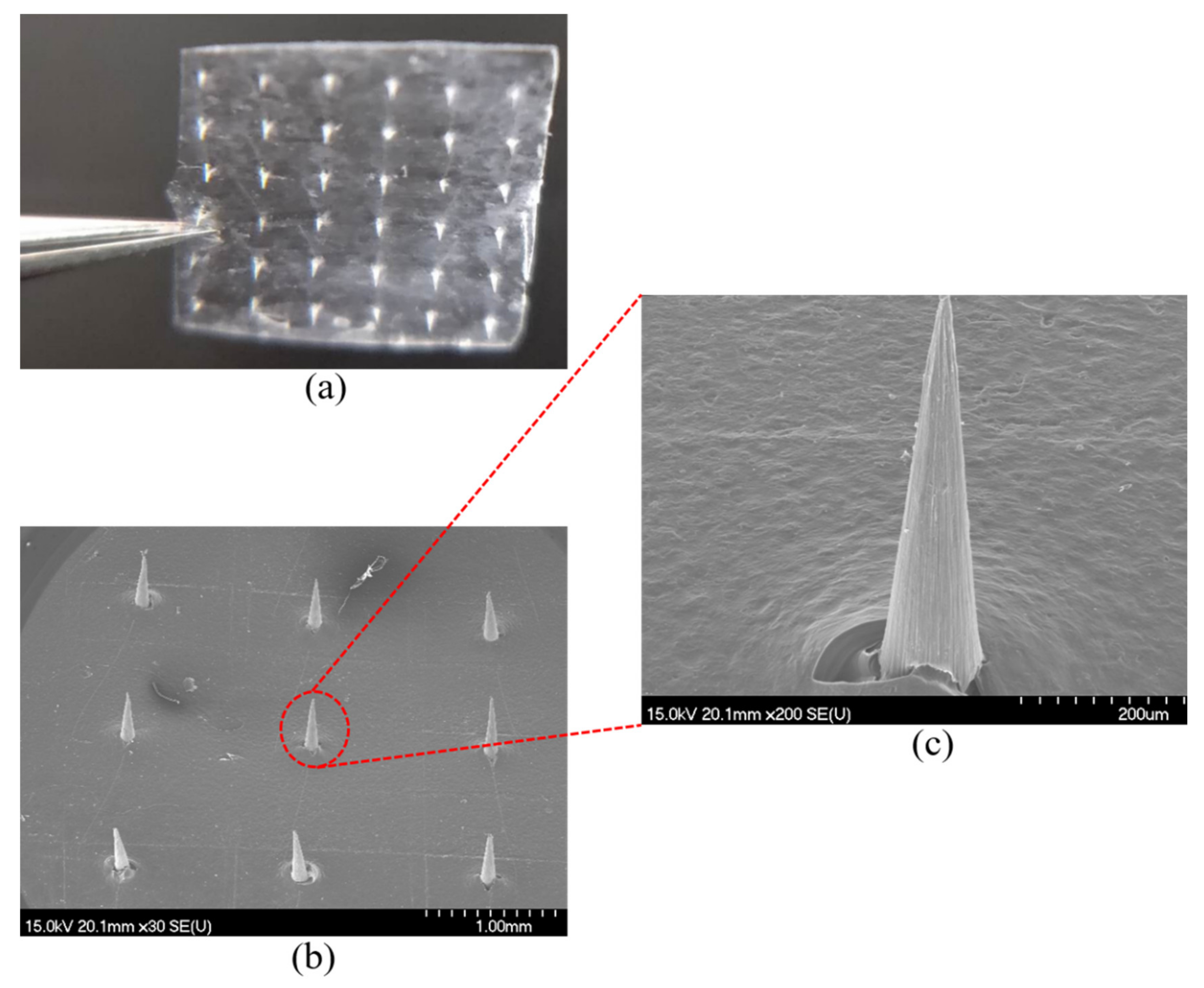
3.3. DMNs Images and Characterization
3.4. Structural Analysis
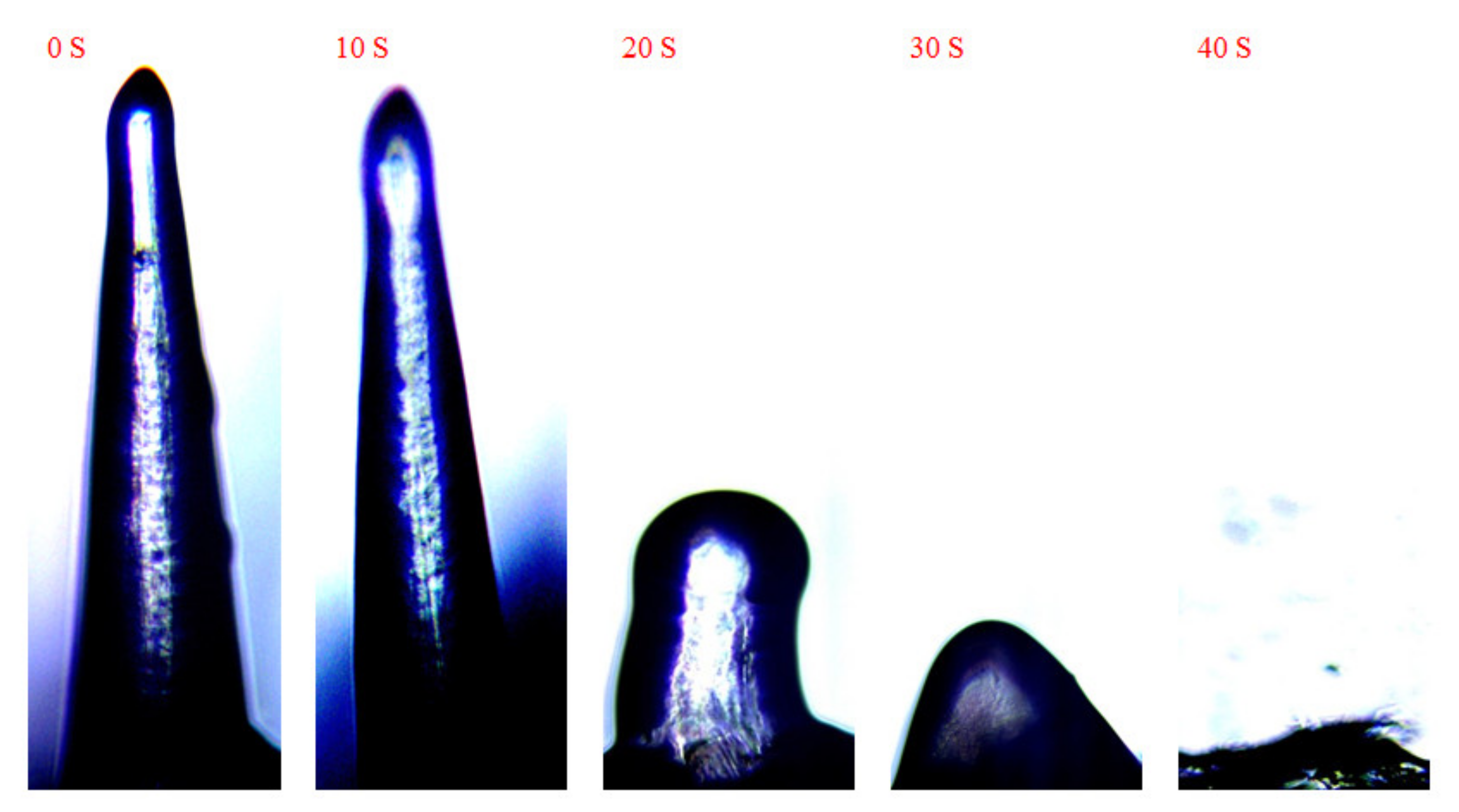
3.5. Swelling Tests
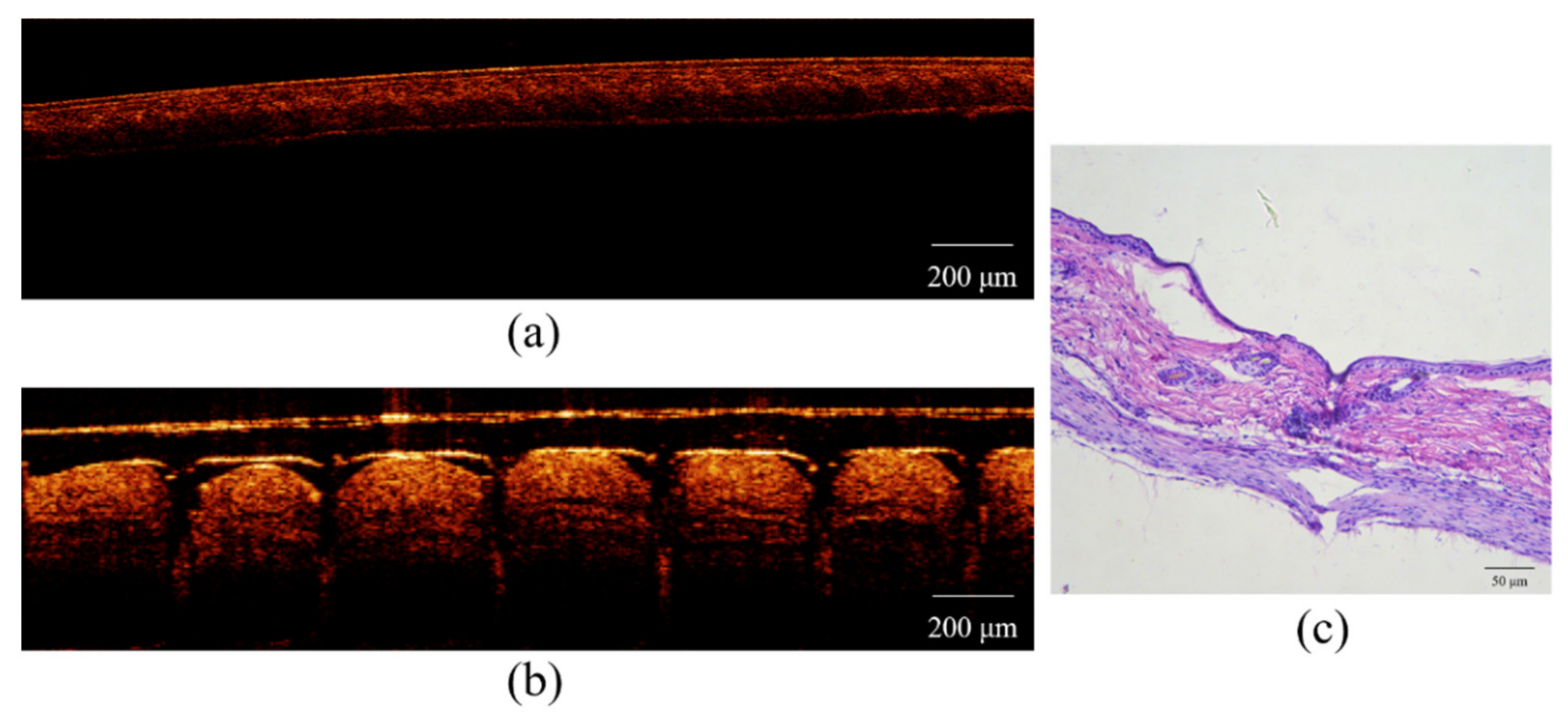
3.6. Skin Penetration Studies
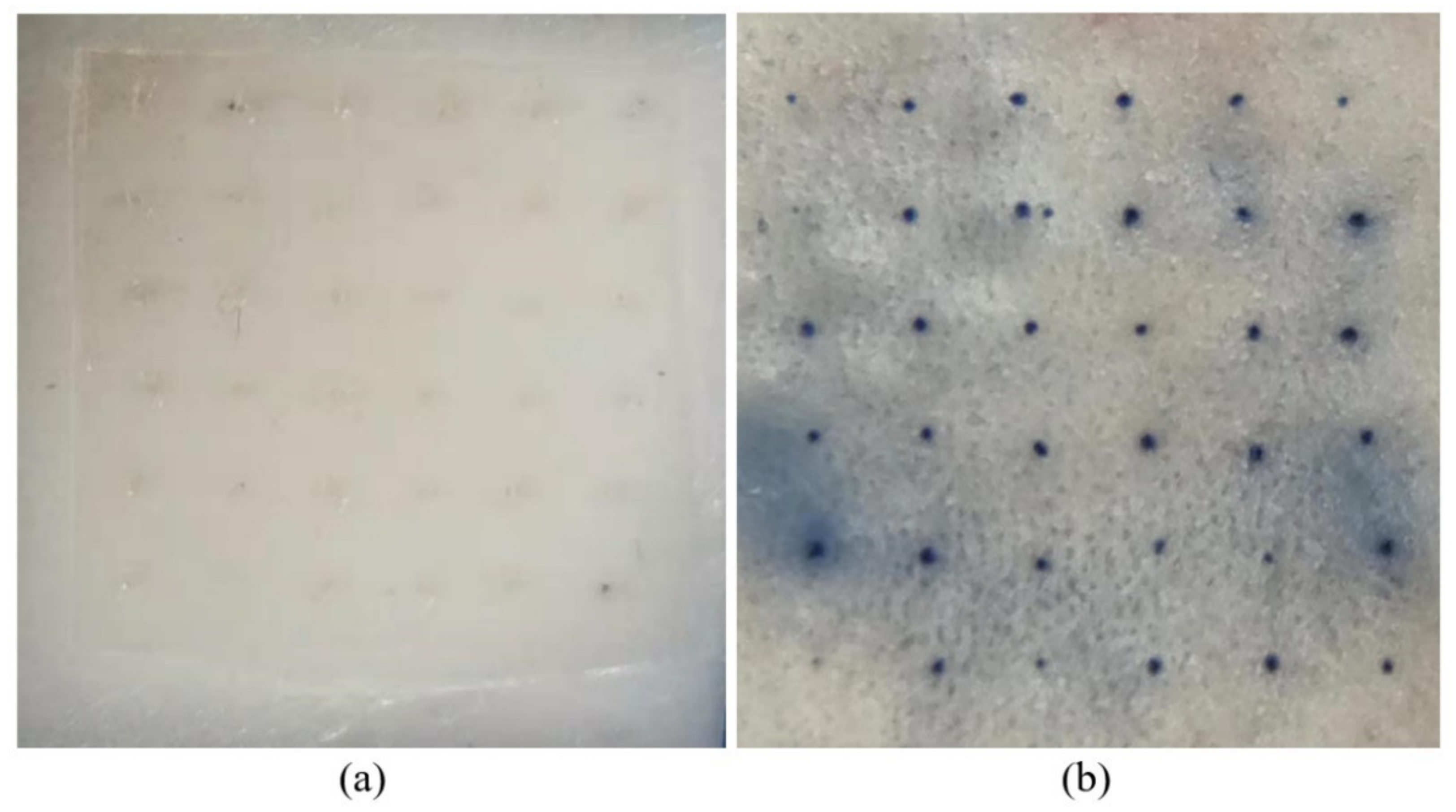
3.6.1. Isolated Skin Penetration
3.6.2. Living Skin Irritation and Rehabilitation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ravi, A.D.; Sadhna, D.; Nagpaal, D.; Chawla, L. Needle free injection technology: A complete insight. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, S.P.; Murthy, N.; Prausnitz, M.R. Minimally Invasive Protein Delivery with Rapidly Dissolving Polymer Microneedles. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuan-Mahmood, T.M.; McCrudden, M.T.; Torrisi, B.M.; McAlister, E.; Garland, M.J.; Singh, T.R.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedles for intradermal and transdermal drug delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 50, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, K.; Hirobe, S.; Yokota, Y.; Ayabe, Y.; Seto, M.; Quan, Y.S.; Kamiyama, F.; Tougan, T.; Horii, T.; Mukai, Y.; et al. Transcutaneous immunization using a dissolving microneedle array protects against tetanus, diphtheria, malaria, and influenza. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Jin, M.-N.; Quan, Y.-S.; Kamiyama, F.; Katsumi, H.; Sakane, T.; Yamamoto, A. The development and characteristics of novel microneedle arrays fabricated from hyaluronic acid, and their application in the transdermal delivery of insulin. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, Y.A.; Garland, M.J.; McInnes, F.; El-Khordagui, L.K.; Wilson, C.; Donnelly, R.F. Laser-engineered dissolving microneedles for active transdermal delivery of nadroparin calcium. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 82, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.L.; Zhu, D.D.; Liu, X.B.; Chen, B.Z.; Guo, X.D. Microneedles with Controlled Bubble Sizes and Drug Distributions for Efficient Transdermal Drug Delivery. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, W.-Z.; Huo, M.-R.; Zhou, J.-P.; Zhou, Y.-Q.; Hao, B.-H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y. Super-short solid silicon microneedles for transdermal drug delivery applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 389, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chong, R.H.; Gonzalez-Gonzalez, E.; Lara, M.F.; Speaker, T.J.; Contag, C.H.; Kaspar, R.L.; Coulman, S.A.; Hargest, R.; Birchall, J.C. Gene silencing following siRNA delivery to skin via coated steel microneedles: In vitro and in vivo proof-of-concept. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jun, H.; Han, M.-R.; Kang, N.-G.; Park, J.-H.; Park, J.H. Use of hollow microneedles for targeted delivery of phenylephrine to treat fecal incontinence. J. Control. Release 2015, 207, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, G.; McCaffrey, J.; Ali, A.A.; McBride, J.W.; McCrudden, C.M.; Vincente-Perez, E.M.; Donnelly, R.F.; McCarthy, H.O. Dissolving microneedles for DNA vaccination: Improving functionality via polymer characterization and RALA complexation. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2017, 13, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumbar, S.G.; Kulkarni, A.R.; Aminabhavi, M. Crosslinked chitosan microspheres for encapsulation of diclofenac sodium: Effect of crosslinking agent. J. Microencapsul. 2002, 19, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Allen, M.G.; Prausnitz, M.R. Polymer microneedles for controlled-release drug delivery. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Lee, S.S.; Lee, H.S.; Kwon, T.H. Fabrication of microneedle array using LIGA and hot embossing process. Microsyst. Technol. 2005, 11, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizidou, E.Z.; Williams, N.A.; Barrow, D.A.; Eaton, M.J.; McCrory, J.; Evans, S.L.; Allender, C.J. Structural characterisation and transdermal delivery studies on sugar microneedles: Experimental and finite element modelling analyses. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrudden, M.T.; Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, C.M.; McAlister, E.; McCarthy, H.O.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Design and physicochemical characterisation of novel dissolving polymeric microneedle arrays for transdermal delivery of high dose, low molecular weight drugs. J. Control. Release 2014, 180, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larran, E.; Lutton, R.E.M.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. Microneedle arrays as transdermal and intradermal drug delivery systems: Materials science, manufacture and commercial development. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2016, 104, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Yan, Q.; Yu, Y.; Wu, M.X. BCG vaccine powder-laden and dissolvable microneedle arrays for lesion-free vaccination. J. Control. Release 2017, 255, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Gadeela, P.R.; Thathireddy, P.; Venuganti, V.V.K. Microneedle-based drug delivery: Materials of construction. J. Chem. Sci. 2019, 131, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brogden, N.K.; Milewski, M.; Ghosh, P.; Hardi, L.; Crofford, L.J.; Stinchcomb, A.L. Diclofenac delays micropore closure following microneedle treatment in human subjects. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z. Synchronous fingerprint acquisition system based on total internal reflection and optical coherence tomography. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 8452–8465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draize, J.H. Appraisal of the Safety of Chemicals in Foods, Drugs and Cosmetics- Dermal Toxicity. 1965. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/joem/Citation/1960/02000/APPRAISAL_OF_THE_SAFETY_OF_CHEMICALS_IN_FOODS,.10.aspx (accessed on 28 March 2020).
- Olatunji, O.; Das, D.B.; Garland, M.J.; Belaid, L.U.; Donnelly, R.F. Influence of Array Interspacing on the Force Required for Successful Microneedle Skin Penetration Theoretical and Practical Approaches. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Composition | Proportion |
|---|---|
| CMC-PVP | CMC:PVP = 1:2 |
| CMC:PVP = 1:5 | |
| CMC:PVP = 2:1 | |
| CMC:PVP = 5:1 | |
| CMC-HA | CMC:HA = 1:2 |
| CMC:HA = 1:5 | |
| CMC:HA = 2:1 | |
| CMC:HA = 5:1 | |
| CMC-PVA | CMC:PVA = 1:2 |
| CMC:PVA = 1:5 | |
| CMC:PVA = 2:1 | |
| CMC:PVA = 5:1 |
| Erythema and Eschar/Formation | Value |
|---|---|
| No erythema | 0 |
| Very slight erythema (barely perceptible. Edges of area not well defined) | 1 |
| slight erythema (pare red in color and area well defined) | 2 |
| Moderate to severe erythema (defined in color and area well defined) | 3 |
| Severe erythema (beet to crimson red) to slight eschar formation (injures in depth) | 4 |
| CMC:PVA | CMC:PVP | CMC:HA | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:5 | 5:1 | 1:2 | 2:1 | 1:5 | 5:1 | 1:2 | 2:1 | 1:5 | 5:1 | 1:2 | 2:1 | |
| Tensile breaking force (N) | 22.5 | 5.6 | 14 | 8.5 | 5.1 | 12.7 | 11 | 11.2 | 9.7 | 5.3 | 33.2 | 8.8 |
| Elongation (mm) | 1.36 | 0.35 | 1.42 | 2.78 | 0.24 | 0.36 | 0.62 | 0.48 | 0.43 | 1.30 | 0.48 | 0.24 |
| Young’s modulus (Mpa) | 5454 | 2206 | 5514 | 1457 | 2912 | 5934 | 2710 | 3712 | 3370 | 1351 | 10853 | 4783 |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.40 | 0.04 | 0.37 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.43 | 0.33 | 0.12 |
| Compression breaking force (N) | 0.29 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.10 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.48 | 0.27 |
| Von-Mises stress (Mpa) | 555 | 192 | 581 | 142 | 263 | 555 | 246 | 359 | 300 | 116 | 980 | 413 |
| Penetration force (N) | 0.049 | 0.047 | 0.049 | 0.046 | 0.049 | 0.049 | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.047 | 0.048 | 0.048 |
| Max-penetration depth (μm) | 469 | 214 | 500 | 164 | 306 | 500 | 285 | 398 | 336 | 108 | 500 | 459 |
| Actual penetration depth (μm) | 477 | 285 | 458 | 262 | 328 | 469 | 317 | 391 | 395 | 202 | 448 | 455 |
| Mice’ Serial Number | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | |||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Q.; Weng, J.; Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Fang, M.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Q.; Yang, G. Finite Element Analysis for Biodegradable Dissolving Microneedle Materials on Skin Puncture and Mechanical Performance Evaluation. Polymers 2021, 13, 3043. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183043
Yan Q, Weng J, Shen S, Wang Y, Fang M, Zheng G, Yang Q, Yang G. Finite Element Analysis for Biodegradable Dissolving Microneedle Materials on Skin Puncture and Mechanical Performance Evaluation. Polymers. 2021; 13(18):3043. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183043
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Qinying, Jiaqi Weng, Shulin Shen, Yan Wang, Min Fang, Gensuo Zheng, Qingliang Yang, and Gensheng Yang. 2021. "Finite Element Analysis for Biodegradable Dissolving Microneedle Materials on Skin Puncture and Mechanical Performance Evaluation" Polymers 13, no. 18: 3043. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183043
APA StyleYan, Q., Weng, J., Shen, S., Wang, Y., Fang, M., Zheng, G., Yang, Q., & Yang, G. (2021). Finite Element Analysis for Biodegradable Dissolving Microneedle Materials on Skin Puncture and Mechanical Performance Evaluation. Polymers, 13(18), 3043. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13183043