A Facile Approach of Fabricating Electrically Conductive Knitted Fabrics Using Graphene Oxide and Textile-Based Waste Material
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of the Knitted Fabrics
2.3. Synthesis, Coating, and Reduction of Graphene Oxide (GO)
2.4. Characterisation Techniques
3. Results
3.1. Morphology of the Knitted Fabrics
3.2. FTIR and XRD Analysis of the Knitted Fabrics
3.3. Colour Change Properties of the Knitted Fabrics
3.4. Electrical Conductivity of the Knitted Fabrics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B.; Shu, L.; Yang, Y.; Ren, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, W. Smart textile-integrated microelectronic systems for wearable applications. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1901958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes-Riley, T.; Dias, T.; Cork, C. A historical review of the development of electronic textiles. Fibers 2018, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tadesse, M.G.; Mengistie, D.A.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Loghin, C.; Nierstrasz, V. Electrically conductive highly elastic polyamide/lycra fabric treated with PEDOT: PSS and polyurethane. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 9591–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Lu, S. Screen printed silver patterns on functionalised aramid fabric. Fibers Polym. 2017, 18, 1975–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J.; Esteves, M.; Fernández, J.; Bonastre, J.; Cases, F. Polyaniline coated conducting fabrics. Chemical and electrochemical characterization. Eur. Polym. J. 2011, 47, 2003–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weng, W.; Chen, P.; He, S.; Sun, X.; Peng, H. Smart electronic textiles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6140–6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.; Wu, L.; Li, P.; Guo, F.; Men, X.; Liu, W. Coupling hybrid of BN nanosheets and carbon nanotubes to enhance the mechanical and tribological properties of fabric composites. Compos. Part. A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2019, 123, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Shang, S.; Yuen, C.W.M.; Jiang, S.-X. Graphene nanoribbon coated flexible and conductive cotton fabric. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2015, 117, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Jeerapan, I.; Tehrani, F.; Yin, L.; Silva-Lopez, C.A.; Jang, J.-H.; Joshuia, D.; Shah, R.; Liang, Y.; Xie, L. Sweat-based wearable energy harvesting-storage hybrid textile devices. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 3431–3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.O.; Kim, S.K.; Lim, Y.R.; Han, J.K.; Yoon, Y.; Ji, S.; Lee, M.; Kim, S.-W.; Song, W.; Myung, S. Foldable and water-resist electrodes based on carbon nanotubes/methyl cellulose hybrid conducting papers. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 160, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchley, L. Could the Focus on Sustainability Help Drive the Graphene Market? Available online: https://www.azonano.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=5652 (accessed on 5 August 2021).
- Molina, J.; Fernández, J.; Del Rio, A.; Bonastre, J.; Cases, F. Chemical and electrochemical study of fabrics coated with reduced graphene oxide. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 279, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azim, A.; Sowrov, K.; Ahmed, M.; Hasan, H.R.U.; Al Faruque, M.A. Effect of elastane on single jersey knit fabric properties-physical & dimensional properties. Int. J. Text. Sci. 2014, 3, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Shateri-Khalilabad, M.; Yazdanshenas, M.E. Fabricating electroconductive cotton textiles using graphene. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, K.; Galib, C.; Yang, F.; Chen, C.-M.; Wang, C. A new approach to fabricate graphene electro-conductive networks on natural fibers by ultraviolet curing method. Synth. Met. 2014, 193, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stempien, Z.; Khalid, M.; Kozicki, M.; Kozanecki, M.; Varela, H.; Filipczak, P.; Pawlak, R.; Korzeniewska, E.; Sąsiadek, E. In-situ deposition of reduced graphene oxide layers on textile surfaces by the reactive inkjet printing technique and their use in supercapacitor applications. Synth. Met. 2019, 256, 116144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Bordes, R. Conductive textiles prepared by spray coating of water-based graphene dispersions. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 2396–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H.; Cao, J.; Jiang, L.; Chen, G. Functional finishing of viscose knitted fabrics via graphene coating. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2017, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Faruque, M.A.; Remadevi, R.; Guirguis, A.; Kiziltas, A.; Mielewski, D.; Naebe, M. Graphene oxide incorporated waste wool/PAN hybrid fibres. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naebe, M.; Tester, D.; McGregor, B.A. The effect of plasma treatment and loop length on the handle of lightweight jersey fabrics as assessed by the Wool HandleMeter. Text. Res. J. 2015, 85, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pei, S.; Cheng, H.-M. The reduction of graphene oxide. Carbon 2012, 50, 3210–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maryniak, W.A.; Uehara, T.; Noras, M.A. Surface resistivity and surface resistance measurements using a concentric ring probe technique. Trek Appl. Note 2003, 1005, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Lu, Y. Fabrication and properties of conductive conjugated polymers/silk fibroin composite fibers. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 1471–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Shim, E.; Noro, J.; Fu, J.; Wang, Q.; Kim, H.R.; Silva, C.; Cavaco-Paulo, A. Conductive cotton by in situ laccase-polymerization of aniline. Polymers 2018, 10, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rani, K.V.; Sarma, B.; Sarma, A. Plasma treatment on cotton fabrics to enhance the adhesion of Reduced Graphene Oxide for electro-conductive properties. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 84, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, J. Graphene-based fabrics and their applications: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68261–68291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongahge, D.; Foroughi, J.; Gambhir, S.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G. Fabrication of a graphene coated nonwoven textile for industrial applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 73203–73209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.; Mao, C.; Zhang, H. Highly conductive graphene-coated silk fabricated via a repeated coating-reduction approach. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 4265–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Su, B.; Gao, C. Declining flux and narrowing nanochannels under wrinkles of compacted graphene oxide nanofiltration membranes. Carbon 2016, 108, 568–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirguis, A.; Maina, J.W.; Kong, L.; Henderson, L.C.; Rana, A.; Li, L.H.; Majumder, M.; Dumée, L.F. Perforation routes towards practical nano-porous graphene and analogous materials engineering. Carbon 2019, 155, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Faruque, M.A.; Remadevi, R.; Wang, X.; Naebe, M. Preparation and characterisation of mechanically milled particles from waste alpaca fibres. Powder Technol. 2019, 342, 848–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Faruque, M.A.; Remadevi, R.; Razal, J.; Wang, X.; Naebe, M. Investigation on structure and characteristics of alpaca-based wet-spun polyacrylonitrile composite fibers by utilizing natural textile waste. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Faruque, M.A.; Remadevi, R.; Razal, J.M.; Naebe, M. Impact of the wet spinning parameters on the alpaca-based polyacrylonitrile composite fibers: Morphology and enhanced mechanical properties study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ogale, A.A. Carbon fibers derived from wet-spinning of equi-component lignin/polyacrylonitrile blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Guo, S.; Xu, L.; Xiao, S.; Shen, Z. Microwave treatment of pre-oxidized fibers for improving their structure and mechanical properties. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Guo, C.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Jin, M. Comparison of microwave and conventional heating methods in carbonization of polyacrylonitrile-based stabilized fibers at different temperature measured by an in-situ process temperature control ring. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 140, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, S.; Shen, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Peng, J. Study on the oxidative stabilization of polyacrylonitrile fibers by microwave heating. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 150, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, W. Properties of partially hydrolyzed PAN fibers. Front. Chem. China 2009, 4, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, D.; Gupta, A.; Saha, S.K. Removal of toxic Cr (VI) by UV-active functionalized graphene oxide for water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11221–11228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Salihi, E.C.; Šiller, L. Green reduction of graphene oxide using alanine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 72, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Gong, P.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ren, J.; Wang, H.; Yang, S. Synthesis of fluorinated graphene with tunable degree of fluorination. Carbon 2012, 50, 5403–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, J.; Ku, B.-C.; Kim, J.; Joh, H.-I. Structural evolution of polyacrylonitrile fibers in stabilization and carbonization. Adv. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 2, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, H.K.; Jeun, J.P.; Kang, P.H. The characterization of polyacrylonitrile fibers stabilized by electron beam irradiation. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.-J.; Bai, Y.-J.; Wang, C.-G.; Xu, Y.; Guo, P.-Z. A new method for the evaluation of stabilization index of polyacrylonitrile fibers. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 2292–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouadil, B.; Cherkaoui, O.; Safi, M.; Zahouily, M. Surface modification of knit polyester fabric for mechanical, electrical and UV protection properties by coating with graphene oxide, graphene and graphene/silver nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Carey, T.; Chen, K.; Yin, Y.; Torrisi, F. Environmentally-friendly conductive cotton fabric as flexible strain sensor based on hot press reduced graphene oxide. Carbon 2017, 111, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rossi, T.; Silva, P.; De Moura, L.; Araújo, M.; Brito, J.; Freeman, H. Waste from eucalyptus wood steaming as a natural dye source for textile fibers. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.B.; Santhana Krishnan, S.; Bhattacharyya, D. Manufacturing and characterization of novel silicone/natural fabric/graphene-based functional composites for human body motion sensing. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 3493–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remadevi, R.; Al Faruque, M.A.; Zhang, J.; Naebe, M. Electrically conductive honeycomb structured graphene composites from natural protein fibre waste. Mater. Lett. 2020, 264, 127311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guirguis, A.; Maina, J.W.; Zhang, X.; Henderson, L.C.; Kong, L.; Shon, H.; Dumée, L.F. Applications of nano-porous graphene materials–critical review on performance and challenges. Mater. Horiz. 2020, 7, 1218–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Y.J.; Ah, C.S.; Hong, W.G.; Kim, H.J.; Shin, J.-H.; Jun, Y. Highly conductive and environmentally stable gold/graphene yarns for flexible and wearable electronics. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 11439–11445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulan, L.; Zhi, L.; Lan, C.; Sihao, C.; Dayang, W.; Fangyin, D. Reduced graphene oxide coated silk fabrics with conductive property for wearable electronic textiles application. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriche, R.; Jiménez-Suárez, A.; Sánchez, M.; Prolongo, S.; Ureña, A. Graphene nanoplatelets coated glass fibre fabrics as strain sensors. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 146, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
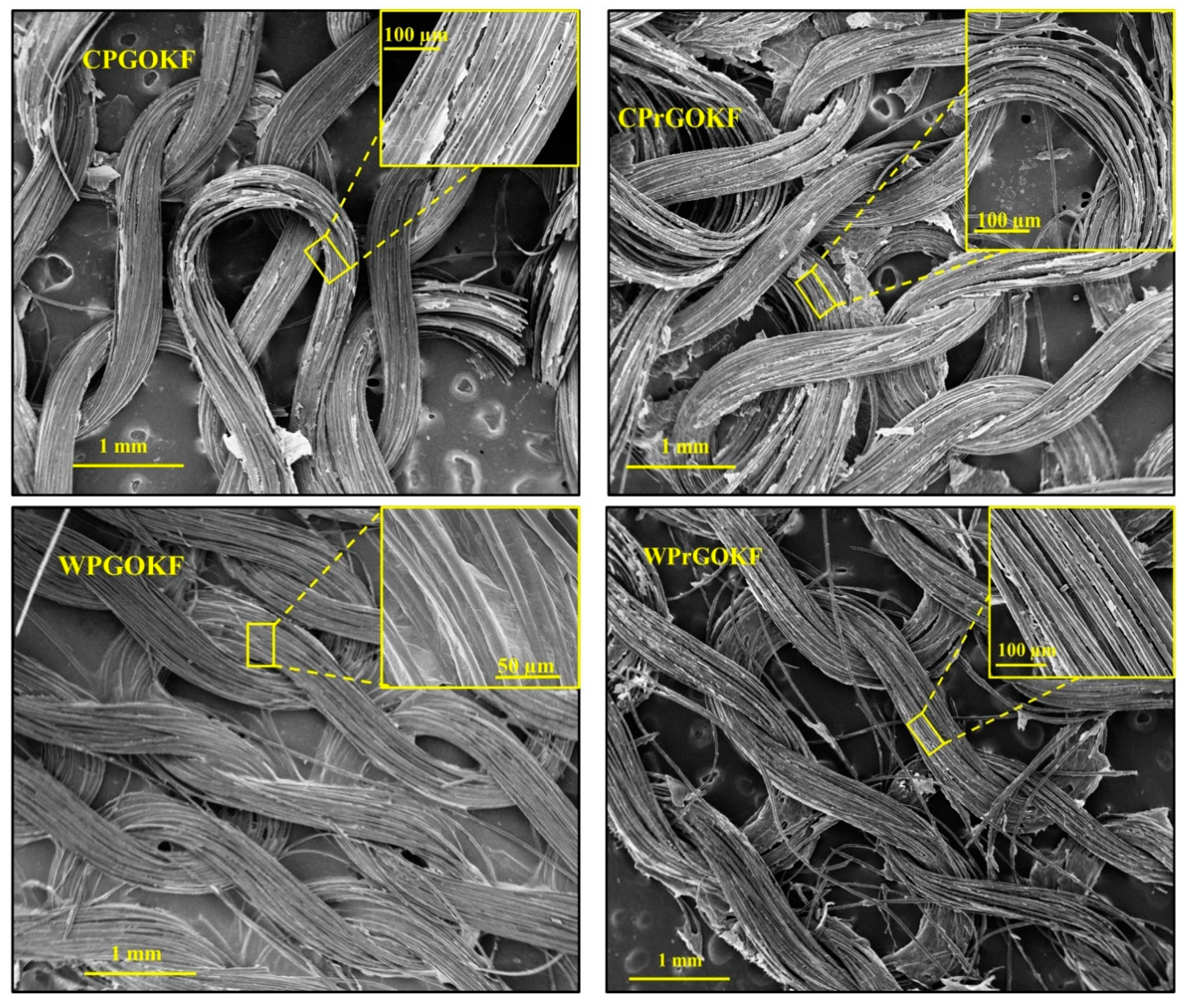
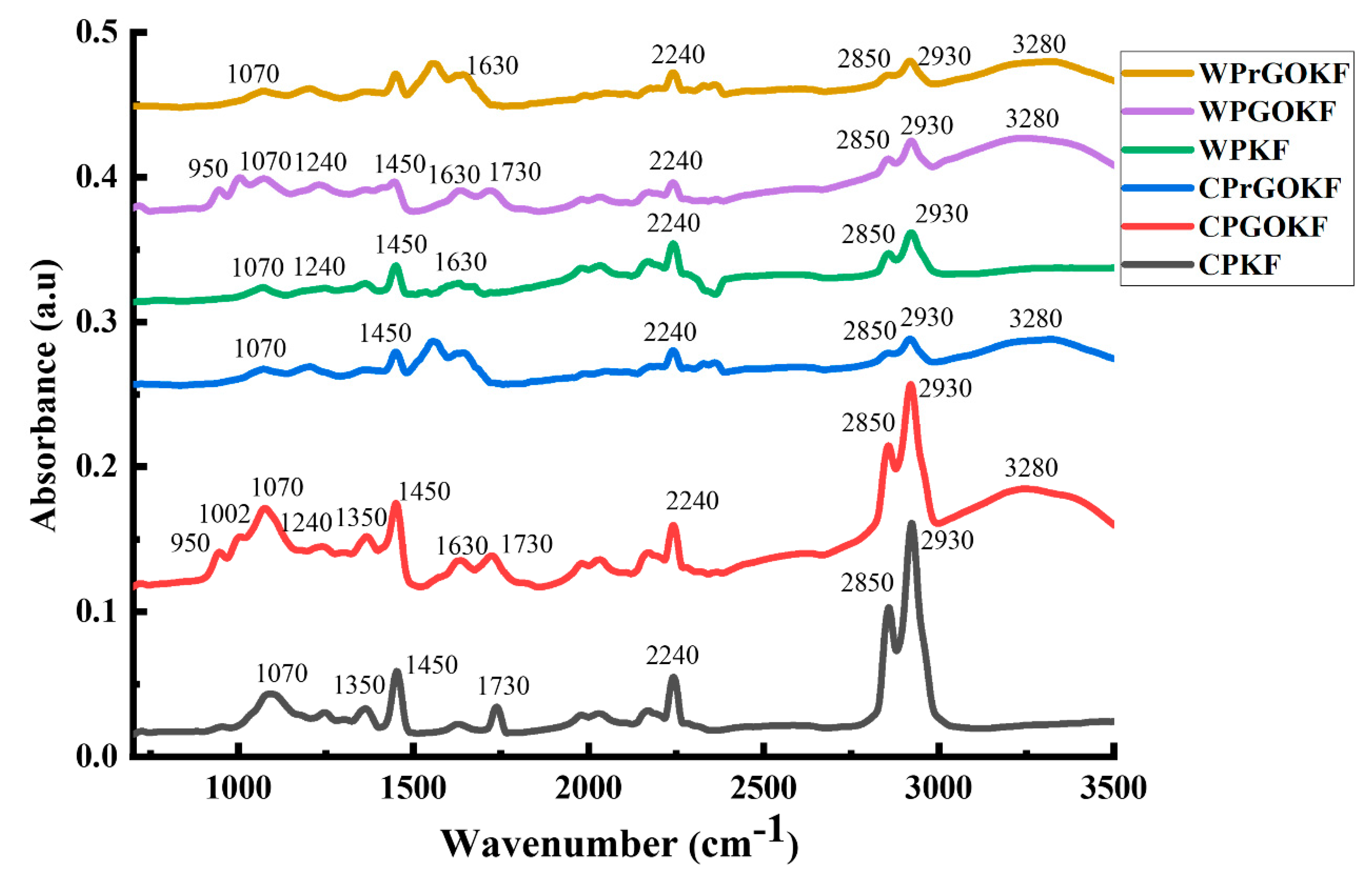
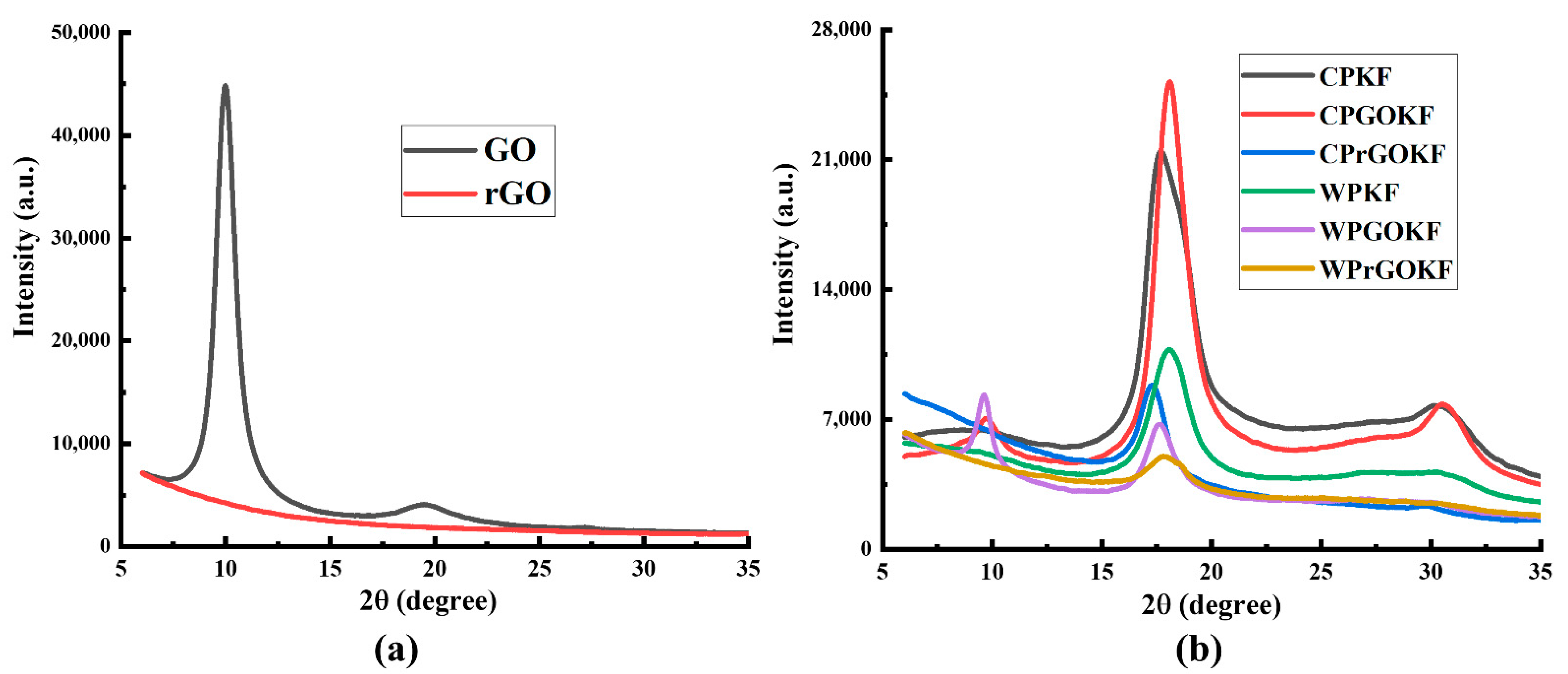
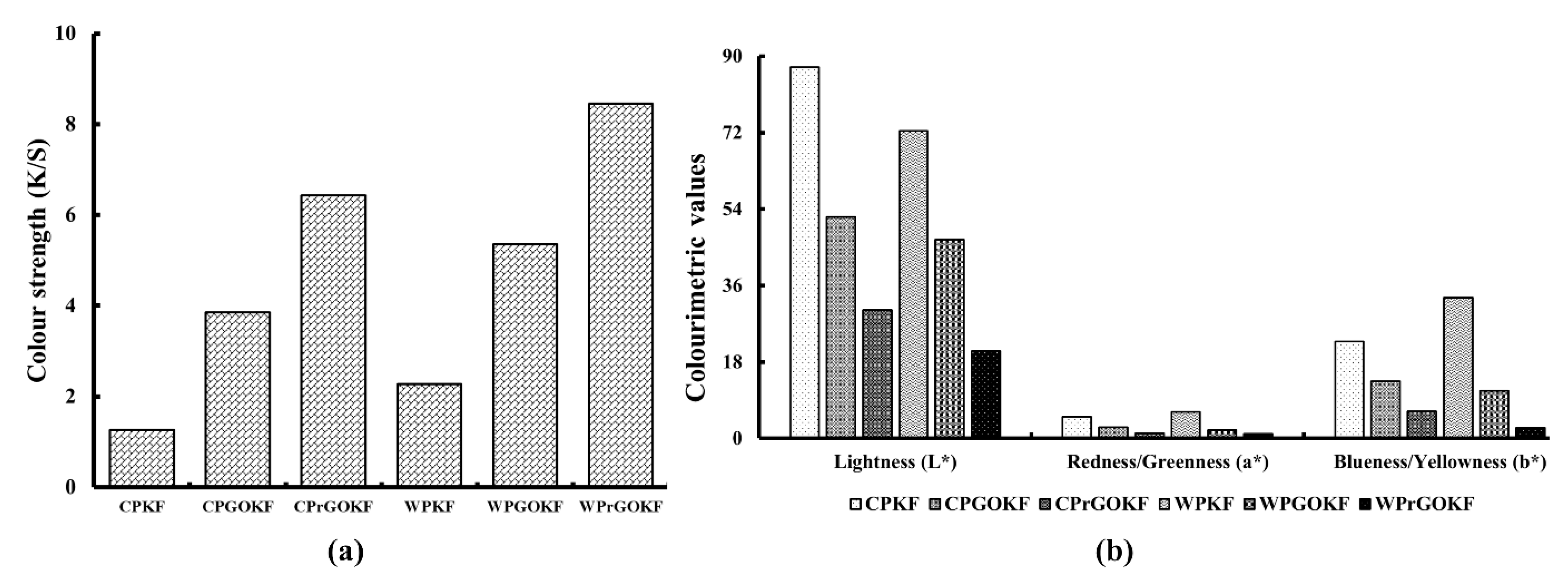
| Sample | Course Per Inch (CPI) | Wales Per Inch (WPI) | GSM (g/m2) | Loop Length (mm) | Yarn Diameter (µm) | Yarn Count (tex) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPKF | 16 | 18 | 108 | 2.90 | 17 | 20 |
| WPKF | 18 | 22 | 116 | 2.90 | 20 | 26 |
| Fabric Sample | Reduction Process | Resistance (Ω) | Conductivity (S/cm) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyester/graphene (woven) | Thermal reduction (200 °C, 2 h) | - | 1.28 × 10−5 | [17] |
| Polyester/graphene (woven) | Chemical reduction (L-ascorbic acid) | - | 8.3 × 10−6 | [17] |
| Cotton/graphene (knitted) | Conductive graphene with SDBS * surfactants | - | 0.359 | [48] |
| Flax/graphene (knitted) | Conductive graphene with SDBS * surfactants | - | 0.040 | [48] |
| Wool/graphene (knitted) | Conductive graphene with SDBS * surfactants | - | 0.426 | [48] |
| Cotton/graphene (woven) | Chemical reduction (hydrazine) | 1,070,000 | 2.1 × 10−5 | [25] |
| Silk/graphene (woven) | Thermal reduction (200 °C, 30 min) | 130,400 | 7.89 × 10−6 | [52] |
| Glass/graphene nanoplatelets (woven) | - | - | 0.0005 | [53] |
| polyacrylonitrile/graphene (knitted) | Chemical reduction (hydrazine) | 285 | 0.35 | This study |
| Wool/PAN/graphene (knitted) | Chemical reduction (hydrazine) | 50 | 1.67 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al Faruque, M.A.; Kiziltas, A.; Mielewski, D.; Naebe, M. A Facile Approach of Fabricating Electrically Conductive Knitted Fabrics Using Graphene Oxide and Textile-Based Waste Material. Polymers 2021, 13, 3003. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13173003
Al Faruque MA, Kiziltas A, Mielewski D, Naebe M. A Facile Approach of Fabricating Electrically Conductive Knitted Fabrics Using Graphene Oxide and Textile-Based Waste Material. Polymers. 2021; 13(17):3003. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13173003
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl Faruque, Md Abdullah, Alper Kiziltas, Deborah Mielewski, and Maryam Naebe. 2021. "A Facile Approach of Fabricating Electrically Conductive Knitted Fabrics Using Graphene Oxide and Textile-Based Waste Material" Polymers 13, no. 17: 3003. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13173003
APA StyleAl Faruque, M. A., Kiziltas, A., Mielewski, D., & Naebe, M. (2021). A Facile Approach of Fabricating Electrically Conductive Knitted Fabrics Using Graphene Oxide and Textile-Based Waste Material. Polymers, 13(17), 3003. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13173003








