Influence of Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles and Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles-Xanthan Gum Complexes on the Stability of O/W Emulsions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles Preparation
2.3. Particle Size Distribution Measurements of WPMPs
2.4. WPMP-XG Complexes Preparation
2.5. Micro-Rheology Measurements of WPMP Dispersions and WPMP-XG Complexes
2.6. Emulsion Preparation
2.7. Short-Term Stability Measurement of Emulsions
2.8. Mean Droplet Size of Emulsions
2.9. Determination of the Peroxide Values (PVs) of the Emulsions
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size Distribution of WPMPs
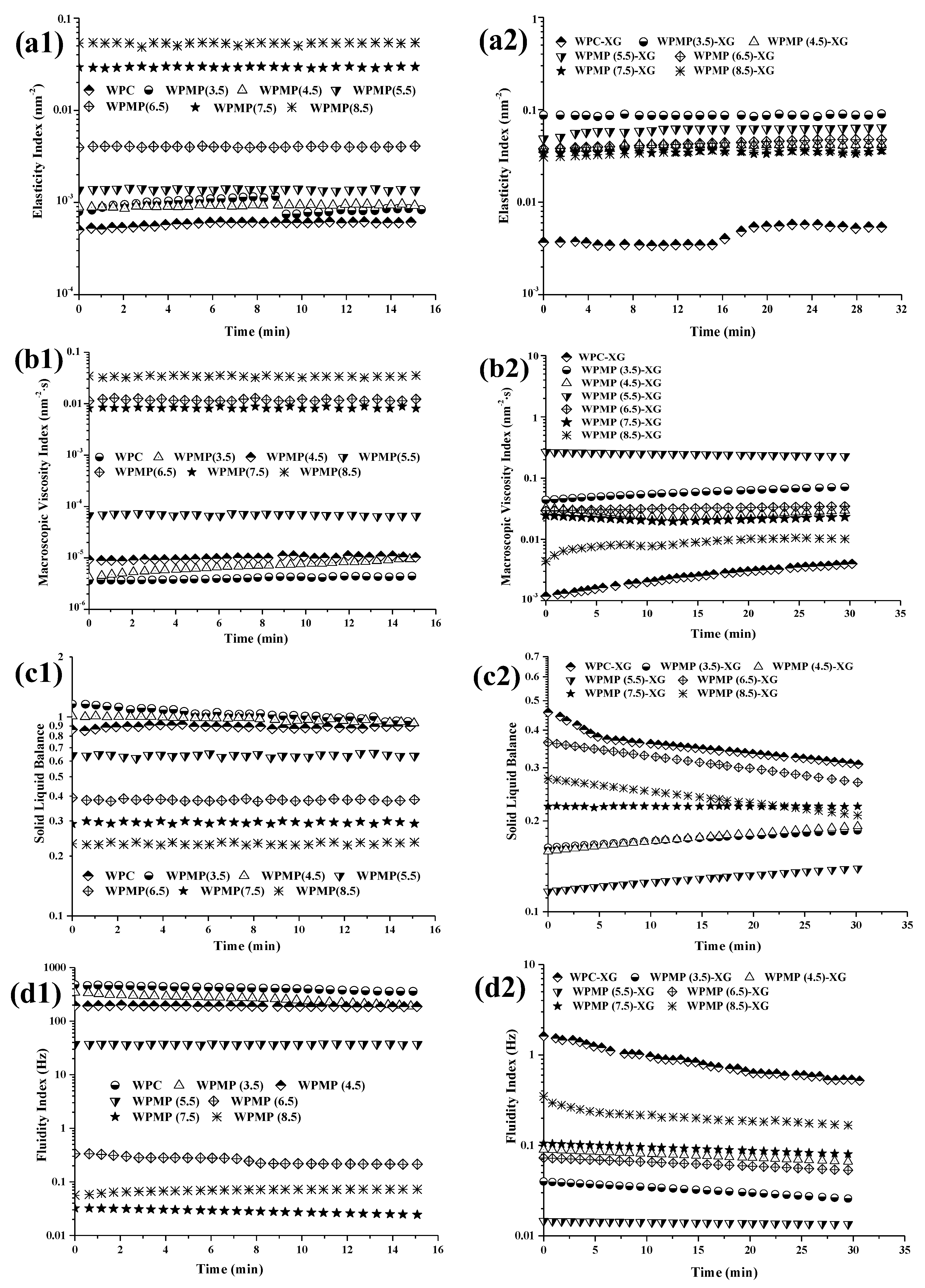
3.2. Micro-Rheology Measurements of WPMP Dispersions and WPMP-XG Complexes
3.2.1. EI and MVI of Samples
3.2.2. SLB and FI of Samples
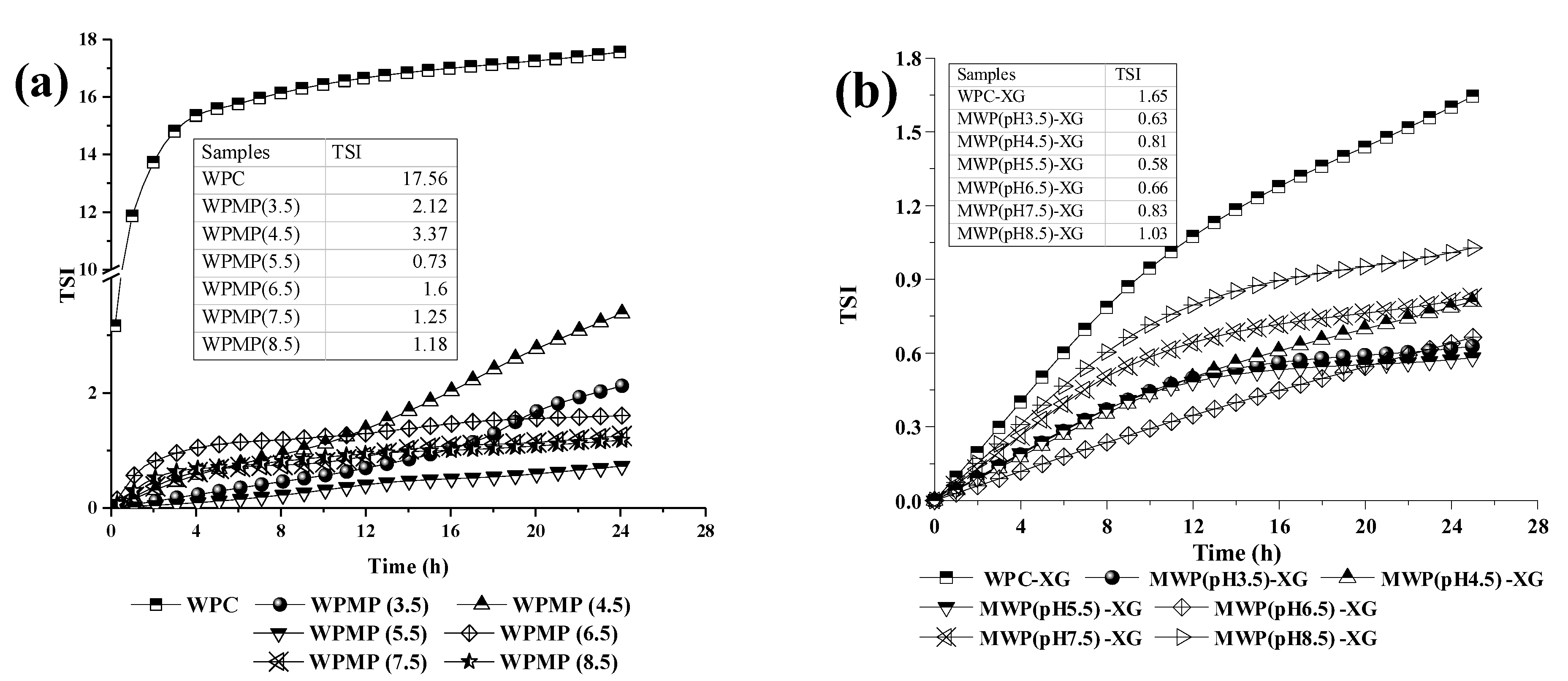
3.3. Analysis of Stability and Mean Droplet Size
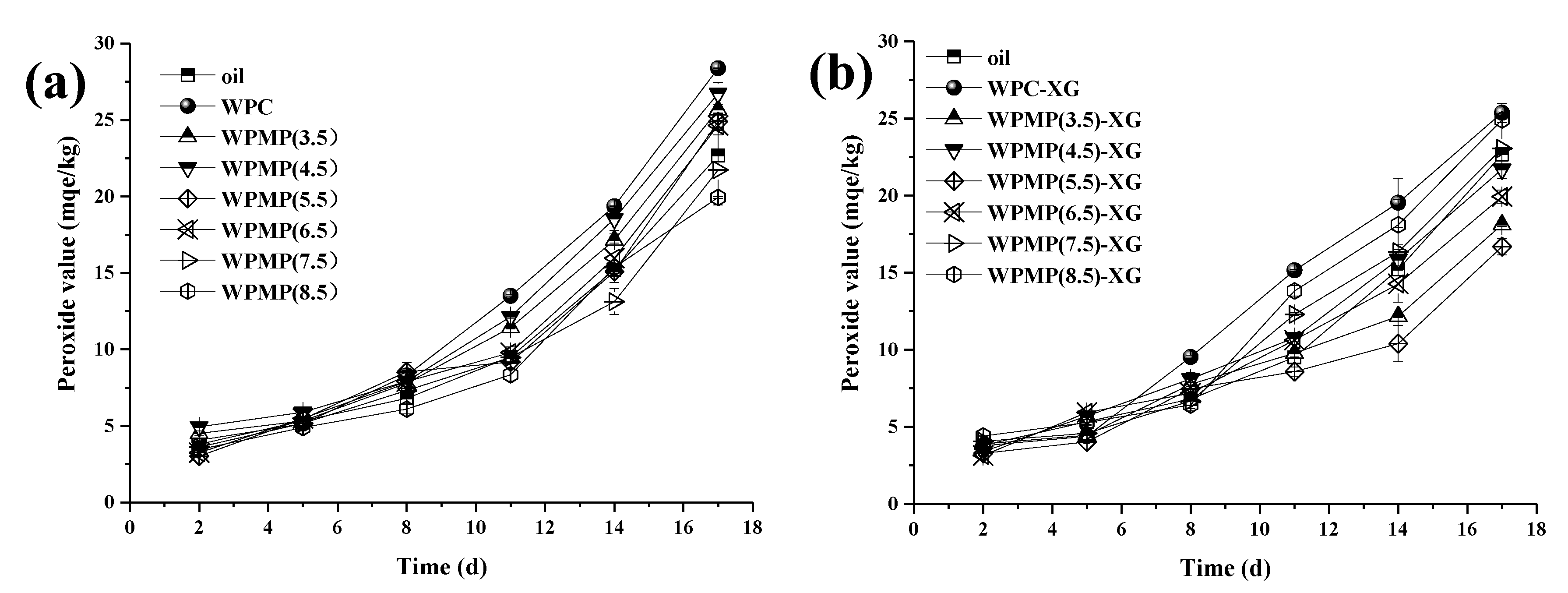
3.4. Measuring the PVs of the Emulsions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klinchongkon, K.; Khuwijitjaru, P.; Adachi, S.; Bindereif, B.; Karbstein, H.P.; van der Schaaf, U.S. Emulsifying properties of conjugates formed between whey protein isolate and subcritical-water hydrolyzed pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 91, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Zhao, M.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of protein type on oxidation and digestibility of fish oil-in-water emulsions: Gliadin, caseinate, and whey protein. Food Chem. 2015, 175 (Suppl. C), 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obando, M.; Papastergiadis, A.; Li, S.; De Meulenaer, B. Impact of Lipid and Protein Co-oxidation on Digestibility of Dairy Proteins in Oil-in-Water (O/W) Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9820–9830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qayum, A.; Li, M.; Shi, R.; Bilawal, A.; Gantumur, M.-A.; Hussain, M.; Ishfaq, M.; Waqas Ali Shah, S.; Jiang, Z.; Hou, J. Laccase cross-linking of sonicated α-Lactalbumin improves physical and oxidative stability of CLA oil in water emulsion. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 71, 105365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wu, T.; Liu, R.; Liang, B.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, E.; Zhang, M. Effects of superfine grinding and microparticulation on the surface hydrophobicity of whey protein concentrate and its relation toemulsions stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gunasekaran, S. Rheology and Oxidative Stability of Whey Protein Isolate-Stabilized Menhaden Oil-in-Water Emulsions as a Function of Heat Treatment. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, C1–C8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noello, C.; Carvalho, A.G.S.; Silva, V.M.; Hubinger, M.D. Spray dried microparticles of chia oil using emulsion stabilized by whey protein concentrate and pectin by electrostatic deposition. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Luo, L.; Liu, C.; McClements, D.J. Influence of anionic polysaccharides on the physical and oxidative stability of hydrolyzed rice glutelin emulsions: Impact of polysaccharide type and pH. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72 (Suppl. C), 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, K.; Khouryieh, H. Influence of electrostatic interactions on the formation and stability of multilayer fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein-xanthan-locust bean complexes. J. Food Eng. 2020, 277, 109893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, C.; Li, Q. Interaction between the Polysaccharides and Proteins in Semisolid Food Systems. In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Melton, L., Shahidi, F., Varelis, P., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 439–445. [Google Scholar]
- Le, X.T.; Rioux, L.E.; Turgeon, S.L. Formation and functional properties of protein-polysaccharide electrostatic hydrogels in comparison to protein or polysaccharide hydrogels. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 239, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisserand, C.; Fleury, M.; Brunel, L.; Bru, P.; Meunier, G. Passive Microrheology for Measurement of the Concentrated Dispersions Stability. In UK Colloids 2011: An International Colloid and Surface Science Symposium; Starov, V., Griffiths, P., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 101–105. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwar, A.; Aziz, T.; Al-Dalali, S.; Zhang, J.; Din Ju Chen, C.; Cao, Y.; Fatima, H.; Yang, Z. Characterization of synbiotic ice cream made with probiotic yeast Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 in combination with inulin. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 141, 110910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikos, V. Encapsulation of vitamin E in edible orange oil-in-water emulsion beverages: Influence of heating temperature on physicochemical stability during chilled storage. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 72 (Suppl. C), 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-R.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chao, A.-C.; Lin, C.-W.; Tsai, M.-L.; Mi, F.-L. Effect of Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin-Gelatin Colloidal Complexes on Stability and in Vitro Digestion of Fish Oil Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 10200–10208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Standard GB/T5009.37-2003. Method for Analysis of Hygienic Standard of Edible Oils; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Lin, L.; Sun, W.; Zhao, M. Stable and pH-Sensitive Protein Nanogels Made by Self-Assembly of Heat Denatured Soy Protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 9553–9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Kong, X.L.; Li, Q.M.; Zhang, H.L.; Zha, X.Q.; Luo, J.P. Stability and bioavailability of vitamin D3 encapsulated in composite gels of whey protein isolate and lotus root amylopectin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 227, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Ma, T.; Zhang, W.; Su, E.; Cao, F.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y. Heat-induced gel formation by whey protein isolate-Lycium barbarum polysaccharides at varying pHs. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 115, 106607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, R.; Sheng, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, M. Effect of microparticulation and xanthan gum on the stability and lipid digestion of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4683–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazt, B.; Bassani, H.P.; Elias-Machado, J.P.; Aldinucci Buzzo, J.L.; Silveira, J.L.M.; de Freitas, R.A. Effect of pH and protein particle shape on the stability of amylopectin–xyloglucan water-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 104, 105769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceniti, C.; Froiio, F.; Britti, D.; Paolino, D.; Costanz, N. Rheological characteristics of bovine colostrum and their correlation with immunoglobulin G. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2019, 72, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chihi, M.-L.; Mession, J.-L.; Sok, N.; Saurel, R. Heat-Induced Soluble Protein Aggregates from Mixed Pea Globulins and β-Lactoglobulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2780–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-M.; Ma, C.-Y. Conformational study of globulin from common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8046–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, C.M.; Mcclements, D.J. Influence of xanthan gum on physical characteristics of heat-denatured whey protein solutions and gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2000, 14, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laneuville, S.I.; Paquin, P.; Turgeon, S.L. Effect of preparation conditions on the characteristics of whey protein—Xanthan gum complexes. Food Hydrocoll. 2000, 14, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.C.; Liu, R.; Liang, B.; Wu, T.; Sui, W.J.; Zhang, M. Microparticulated whey protein-pectin complex: A texture-controllable gel for low-fat mayonnaise. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Niu, S.; Yu, J. Effect of protein oxidation on kinetics of droplets stability probed by microrheology in O/W and W/O emulsions of whey protein concentrate. Food Res. Int. 2016, 85, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.-S.; Azuma, N.; Yang, H. Effects of pH and ionic strength on the rheology and microstructure of a pressure-induced whey protein gel. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Liu, R.; Wu, T.; Liang, B.; Shi, C.; Cong, X.; Zhang, M. Combined Superfine Grinding and Heat-Shearing Treatment for the Microparticulation of Whey Proteins. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Ratcliffe, I.; Williams, P.A. Emulsion stabilisation using polysaccharide–protein complexes. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 18, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Q.; Wang, S.; Lyu, F.; Liu, J.; Ding, Y. The interfacial covalent bonding of whey protein hydrolysate and pectin under high temperature sterilization: Effect on emulsion stability. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2021, 206, 111936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Lu, L.; Li, M.; Xu, J.; Deng, H. Expert analysis of the biological demulsification of a water-in-oil emulsion by two biodemulsifiers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakos, A.; Kiosseoglou, V. Stability of Acidic Egg White Protein Emulsions Containing Xanthan Gum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 10164–10169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, W.; Zhao, Q.; Selomulya, C.; Zhu, X.; Xiong, H. Physical and oxidative stabilities of o/w emulsions formed with rice dreg protein hydrolysate: Effect of xanthan gum rheology. Food Bioprocess Tech. 2016, 9, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noon, J.; Mills, T.B.; Norton, I.T. The use of antioxidant rutin hydrate Pickering particles to combat lipid oxidation in O/W emulsions. J. Food Eng. 2020, 274, 109830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Moreno, P.J.; Guadix, A.; Guadix, E.M.; Jacobsen, C. Physical and oxidative stability of fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized with fish protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2016, 203 (Suppl. C), 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimada, K.; Muta, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Okada, H.; Matsuo, K.; Yoshioka, S.; Nakamura, T. Iron-binding property and antioxidative activity of xanthan on the autoxidation of soybean oil in emulsion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1607–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gunasekaran, S. Effects of protein concentration and oil-phase volume fraction on the stability and rheology of menhaden oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein isolate with xanthan gum. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Gunasekaran, S.; Richards, M.P. Effect of xanthan gum on physicochemical properties of whey protein isolate stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
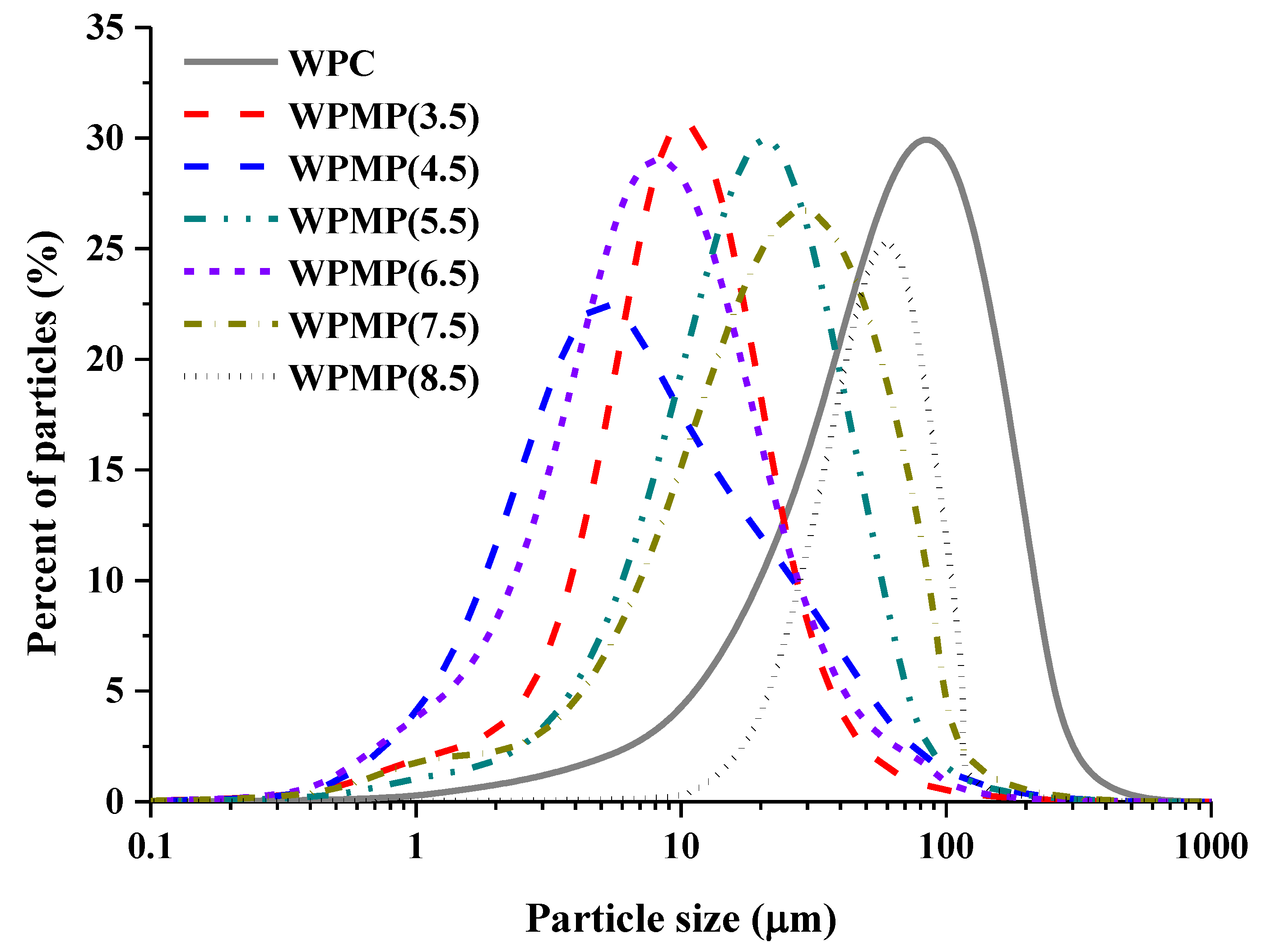


| Samples | D50 (μm) | D[2,1] | D[3,2] | D[4,3] | SSA * (m2/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WPC | 45.86 ± 1.22 a | 4.19 ± 0.02 a | 23.83 ± 0.25 a | 50.90 ± 2.18 a | 0.08 ± 0.01 a |
| WPMP(3.5) | 7.54 ± 0.11 b | 1.80 ± 0.05 b,c | 4.83 ± 0.06 b | 8.39 ± 0.3 1b | 0.40 ± 0.01 b |
| WPMP(4.5) | 4.91 ± 0.21 c | 1.52 ± 0.12 b,d | 3.36 ± 0.03 c | 8.32 ± 0.76 b | 0.58 ± 0.01 c |
| WPMP(5.5) | 13.96 ± 0.10 d | 2.12 ± 0.05 c | 7.91 ± 0.11 d | 15.91 ± 0.16 c | 0.24 ± 0.01 d |
| WPMP(6.5) | 6.19 ± 0.42 e | 1.42 ± 0.08 d | 3.71 ± 0.15 c | 8.78 ± 0.38 b | 0.52 ± 0.02 e |
| WPMP(7.5) | 17.74 ± 0.13 f | 1.51 ± 0.01 b,d | 7.75 ± 0.06 d | 21.99 ± 0.22 e | 0.25 ± 0.01 d |
| WPMP(8.5) | 46.68 ± 0.56 a | 31.05 ± 0.31 e | 39.84 ± 0.43 e | 48.91 ± 0.50 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 f |
| Samples | y = a(1 + x)b | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | R2 | |
| oil | 0.51 | 1.58 | 0.93 |
| WPC | 0.24 | 1.64 | 0.97 |
| WPMP(3.5) | 0.25 | 1.58 | 0.94 |
| WPMP(4.5) | 0.29 | 1.59 | 0.94 |
| WPMP(5.5) | 0.18 | 1.67 | 0.92 |
| WPMP(6.5) | 0.20 | 1.65 | 0.94 |
| WPMP(7.5) | 0.28 | 1.48 | 0.91 |
| WPMP(8.5) | 0.23 | 1.53 | 0.93 |
| WPC-XG | 0.48 | 1.37 | 0.98 |
| WPMP(3.5)-XG | 0.60 | 1.15 | 0.93 |
| WPMP(4.5)-XG | 0.46 | 1.32 | 0.97 |
| WPMP(5.5)-XG | 0.52 | 1.17 | 0.91 |
| WPMP(6.5)-XG | 0.51 | 1.25 | 0.96 |
| WPMP(7.5)-XG | 0.40 | 1.50 | 0.96 |
| WPMP(8.5)-XG | 0.41 | 1.51 | 0.95 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Liang, B.; He, H.; Ji, C.; Cui, T.; Sun, C. Influence of Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles and Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles-Xanthan Gum Complexes on the Stability of O/W Emulsions. Polymers 2021, 13, 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142301
Zhang M, Liang B, He H, Ji C, Cui T, Sun C. Influence of Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles and Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles-Xanthan Gum Complexes on the Stability of O/W Emulsions. Polymers. 2021; 13(14):2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142301
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Man, Bin Liang, Hongjun He, Changjian Ji, Tingting Cui, and Chanchan Sun. 2021. "Influence of Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles and Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles-Xanthan Gum Complexes on the Stability of O/W Emulsions" Polymers 13, no. 14: 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142301
APA StyleZhang, M., Liang, B., He, H., Ji, C., Cui, T., & Sun, C. (2021). Influence of Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles and Whey Protein Micro-Gel Particles-Xanthan Gum Complexes on the Stability of O/W Emulsions. Polymers, 13(14), 2301. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13142301








