Investigation of Flexible Arrayed Lactate Biosensor Based on Copper Doped Zinc Oxide Films Modified by Iron–Platinum Nanoparticles
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
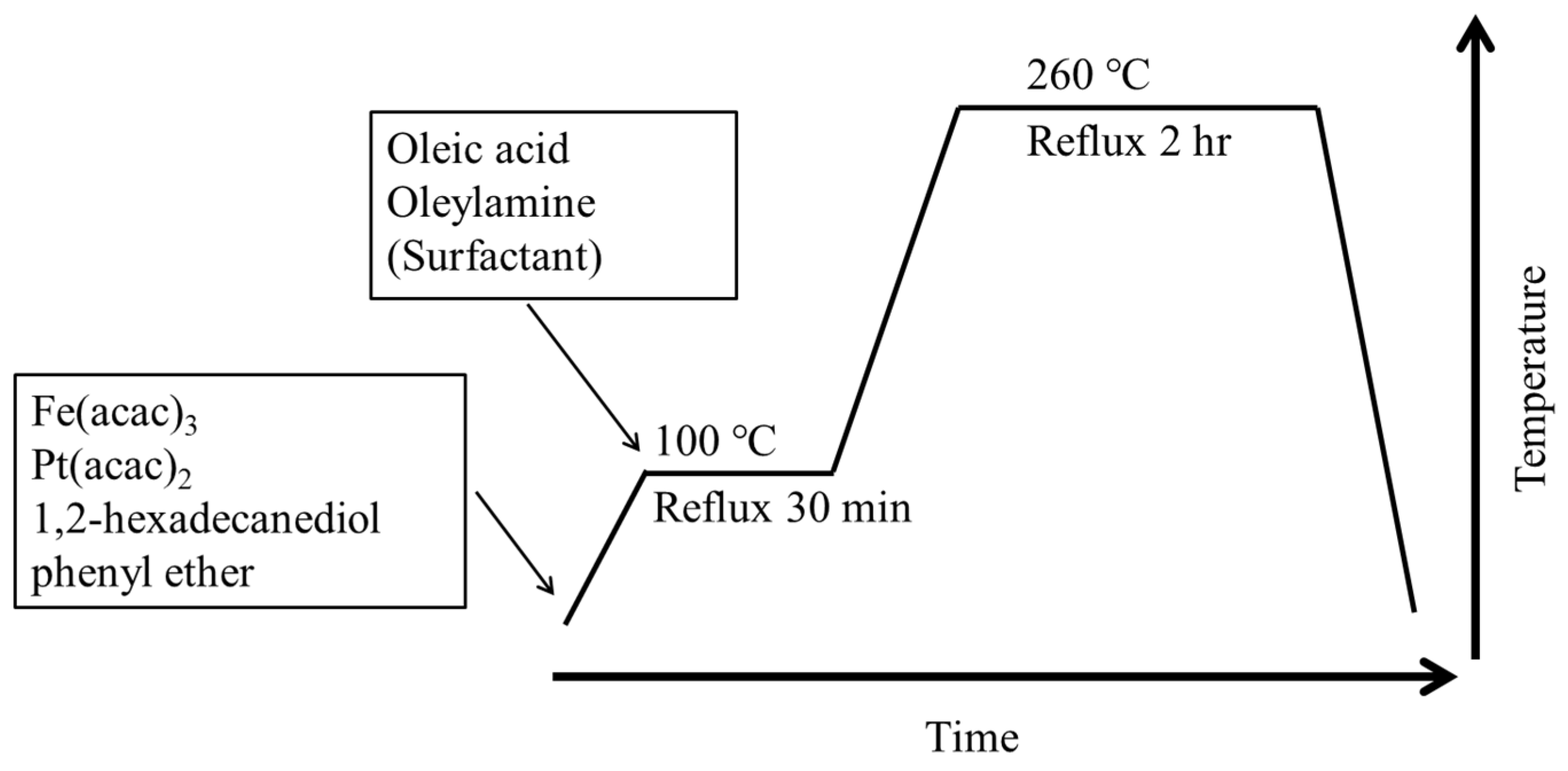
2.2. Fabrication of Oil-Soluble FePt NPs
2.3. Fabrication of Water-Soluble FePt NPs
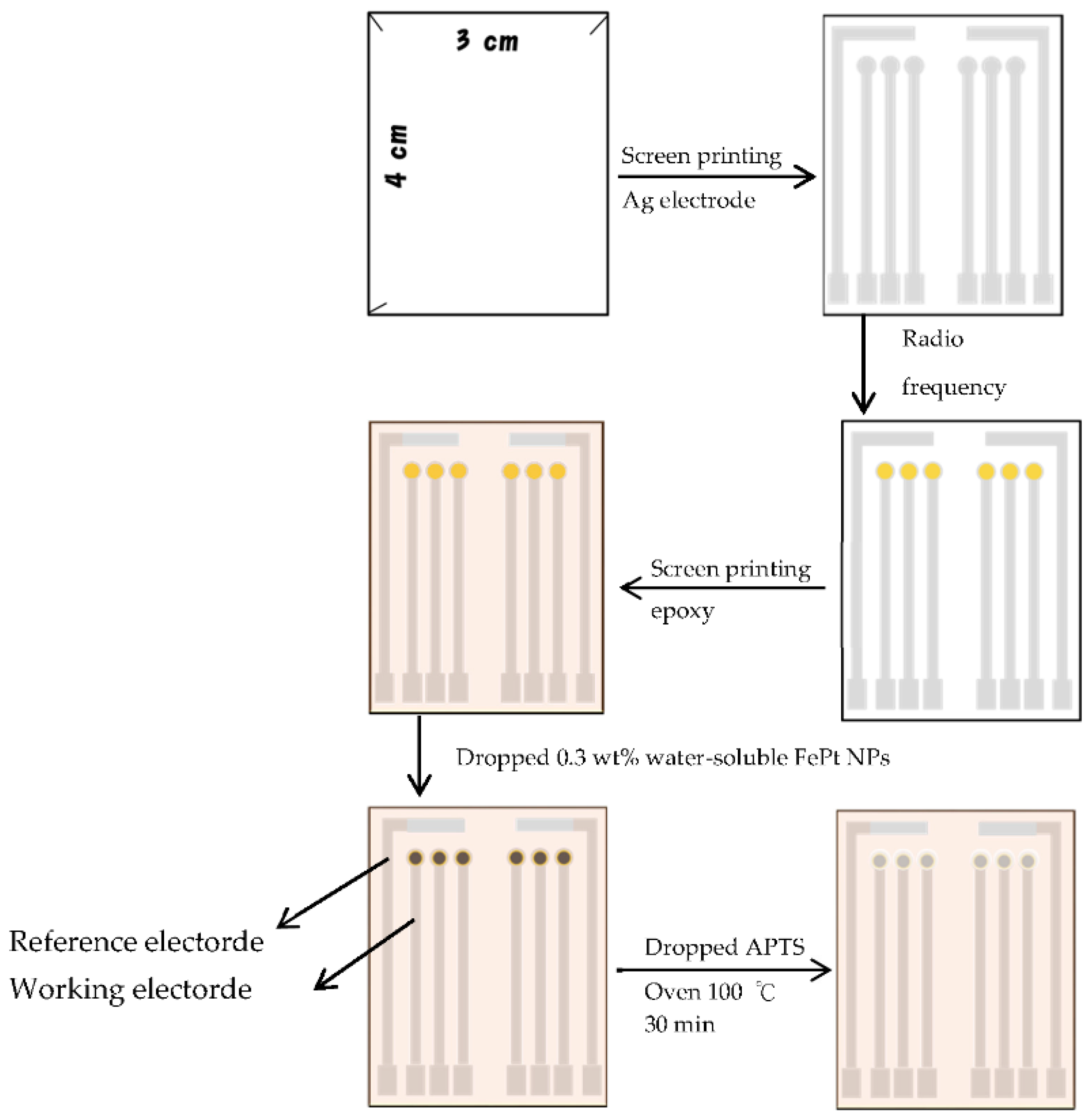
2.4. Fabrication of Flexible Lactate Biosensors Based on FePt NPs/CZO Sensing Films
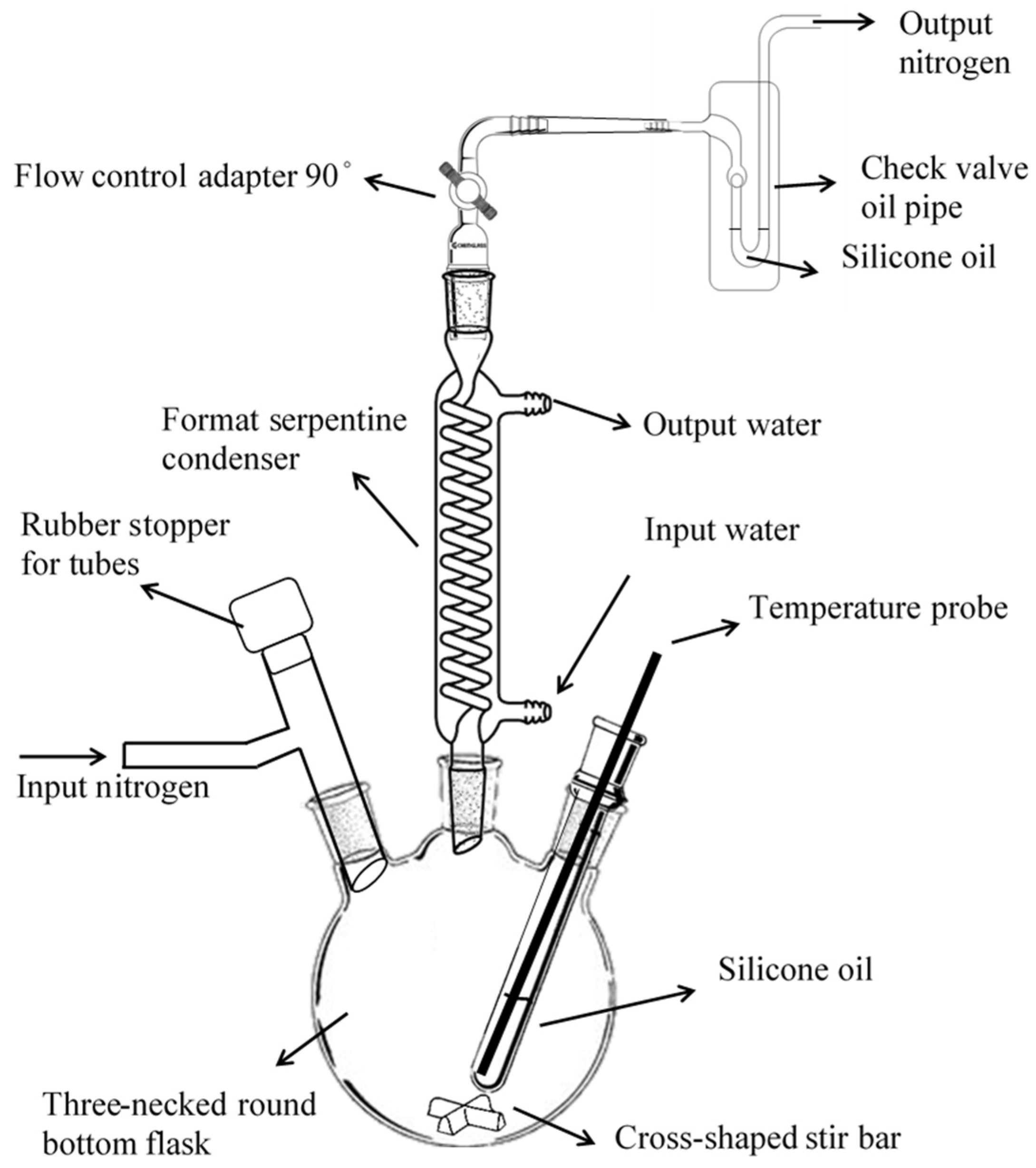
2.5. The V-T Measurement System
2.6. Description of the Conditions Used for the Characterization of CZO Film Modified by FePt NPs
3. Results
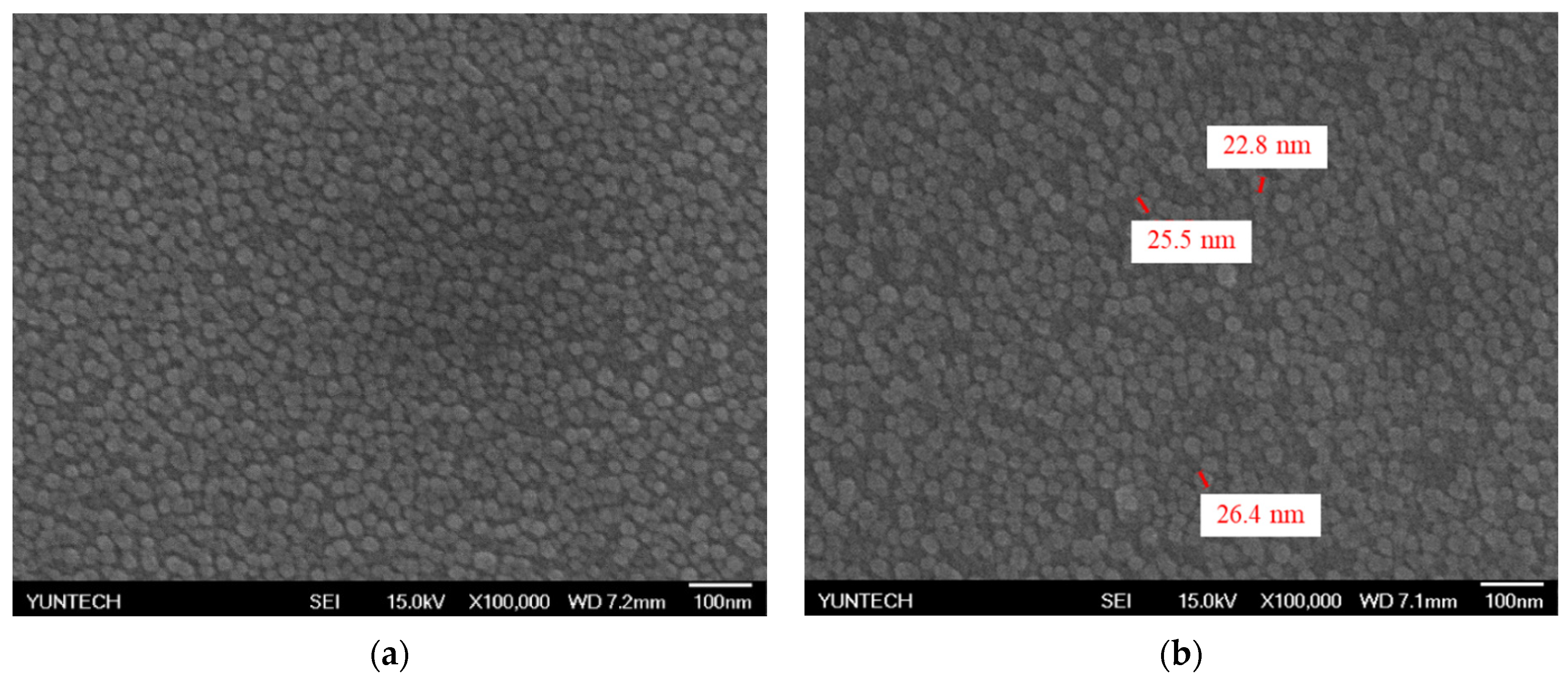
3.1. The SEM and EDS of the CZO Sensing Film
3.2. X-ray Diffraction of the FePt NPs
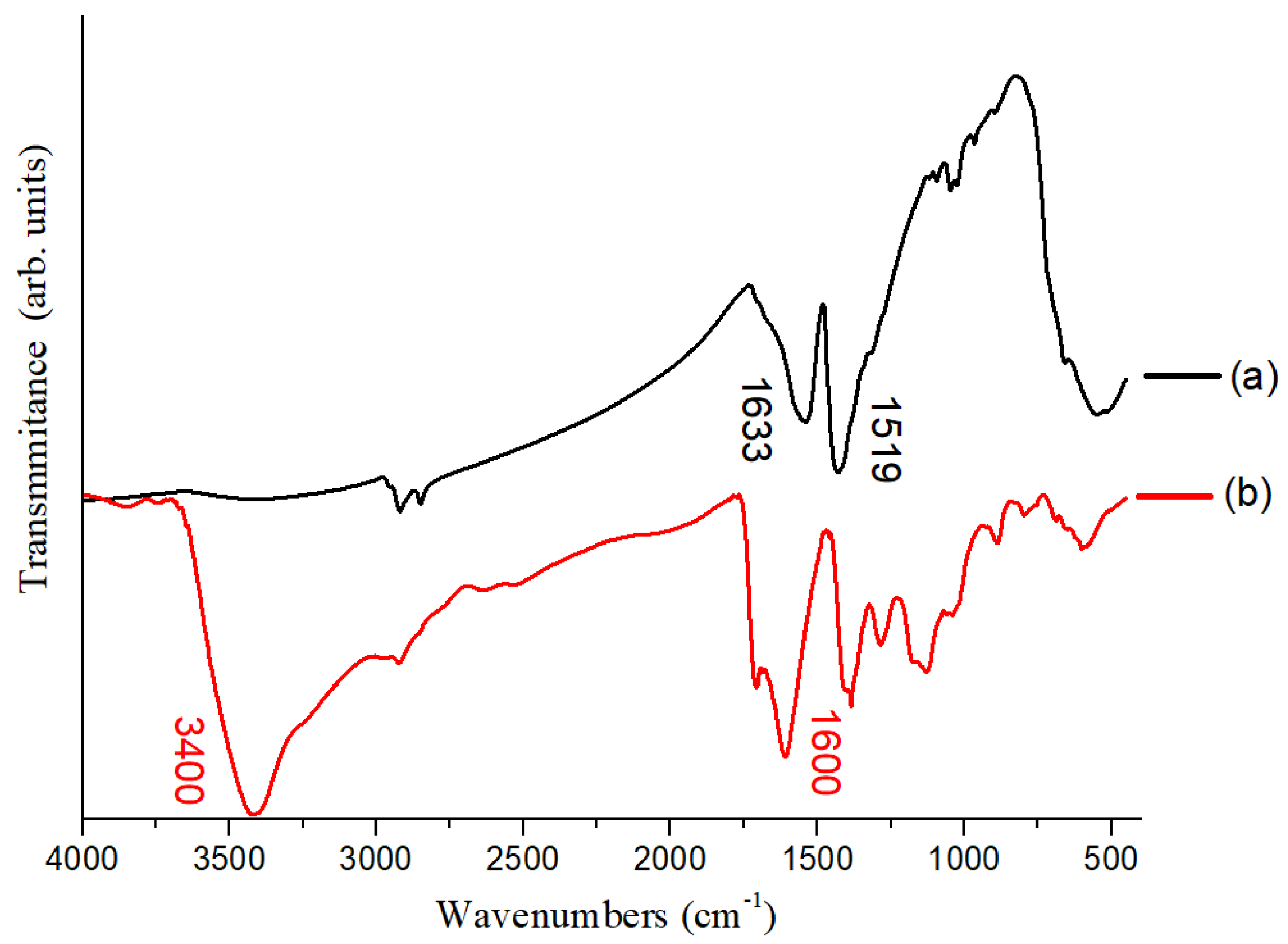
3.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) of the FePt NPs
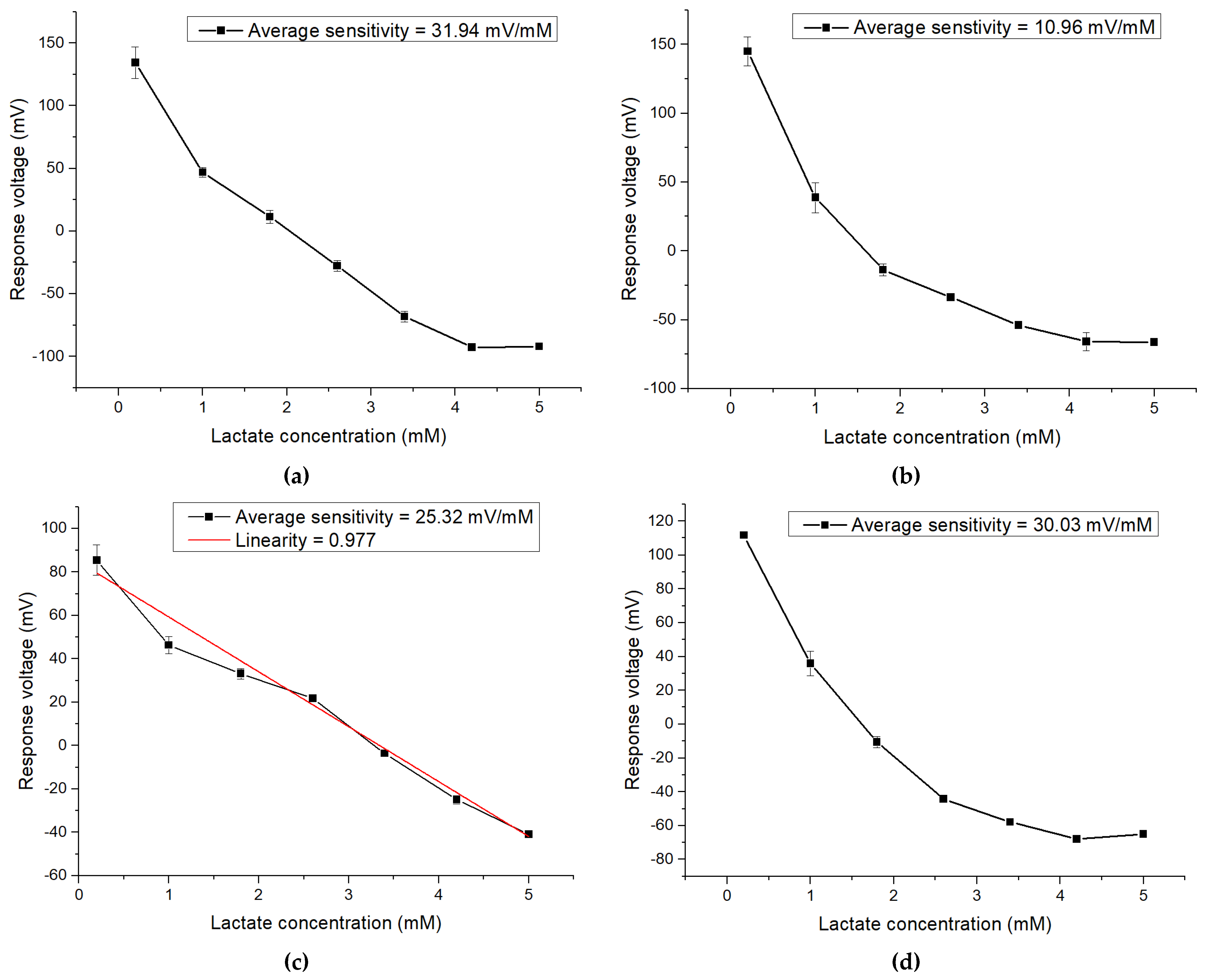
3.4. The Sensing Characteristics of Flexible Lactate Biosensor Based on FePt NPs/CZO Sensing Films
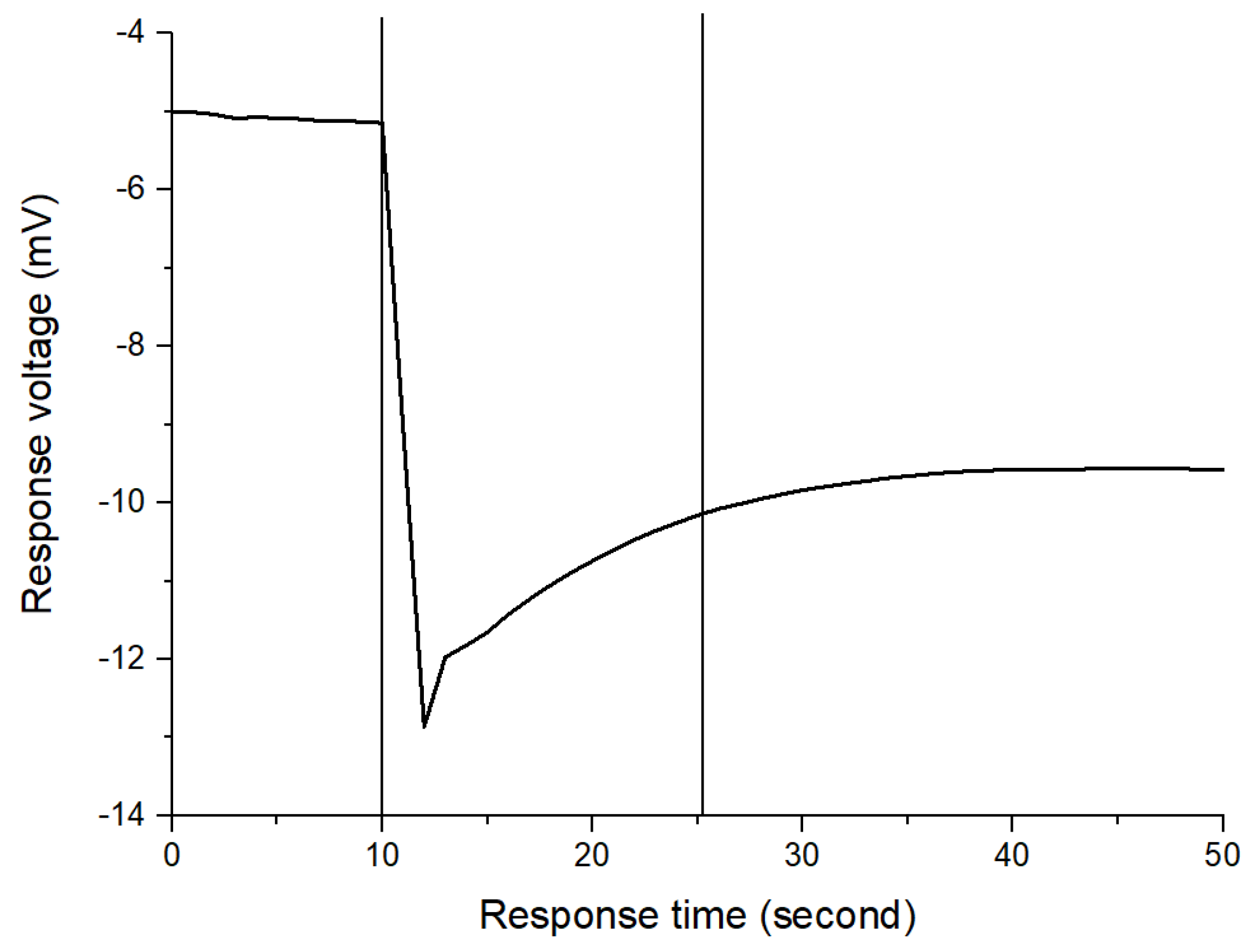
3.5. Response Time
3.6. Interference Effect
3.7. The Analysis of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy of Lactate Biosensor Based on Different Sensing Membrane
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamel, K.S.; Oh, M.S.; Halperin, M.L. L-Lactic Acidosis: Pathophysiology, Classification, and Causes; Emphasis on Biochemical and Metabolic Basis. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, D.; Deichsel, G.; Schmulling, R.-M.; Stein, W.; Eggstein, M. Definition of Clinically Relevant Lactic Acidosis in Patients with Internal Diseases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1983, 80, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robergs, R.A.; Ghiasvand, F.; Parker, D. Biochemistry of Exercise-Induced Metabolic Acidosis. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 287, R502–R516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conlay, L.A.; Loewenstein, J.E. Phenformin and Hyperamylasemia in Lactic Acidosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1977, 87, 312–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.-D.; Sun, B.; Bian, X.-C.; Chen, Z.-M.; Chen, X.-S. Determination of D-Lactate Content in Poly(Lactic Acid) Using Polarimetry. Polym. Test. 2010, 29, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teaford, M.E.; Kaplan, A. Measurement of Blood Lactate by Gas Chromatography. Clin. Chim. Acta 1967, 15, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-L.; Akita, T.; Mita, M.; Ide, T.; Lee, J.-A.; Hamase, K. Development of a Selective Three-Dimensional HPLC System for Enantiomer Discriminated Analysis of Lactate and 3-Hydroxybutyrate in Human Plasma and Urine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 195, 113871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.B.; Cerdán, S.; García-Martín, M.L. A Method to Measure Lactate Recycling in Cultured Cells by Edited 1H Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 370, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Kim, C.-S.; Choi, M. Oxidase-Coupled Amperometric Glucose and Lactate Sensors with Integrated Electrochemical Actuation System. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2006, 55, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Hu, C.; Ji, Z.; Ma, W.; Wang, H. A Solid Ionic Lactate Biosensor Using Doped Graphene-like Membrane of Au-EVIMC-Titania Nanotubes-Polyaniline. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 118, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, F.; Jalal, A.H.; Forouzanfar, S.; Karabiyik, M.; Baboukani, A.R.; Pala, N. Flexible and Linker-Free Enzymatic Sensors Based on Zinc Oxide Nanoflakes for Noninvasive L-Lactate Sensing in Sweat. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 5102–5109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugo, S.M.; Dhanjai; Alberkant, J. A Biomimetric Lactate Imprinted Smart Polymers as Capacitive Sweat Sensors. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 5741–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Tahira, A.; Solangi, A.; Mazzaro, R.; Ibupoto, Z.H.; Vomiero, A. A Sensitive Enzyme-Free Lactic Acid Sensor Based on NiO Nanoparticles for Practical Applications. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 3578–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Kong, Y.; Liu, C.; Huang, G.; Xiao, Z.; Zhu, H.; Bao, Z.; Mei, Y. Atomic Layer Deposition-Assisted Fabrication of 3D Co-Doped Carbon Framework for Sensitive Enzyme-Free Lactic Acid Sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 129285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanto, H.; Minami, T.; Takata, S. Zinc-oxide Thin-film Ammonia Gas Sensors with High Sensitivity and Excellent Selectivity. J. Appl. Phys. 1986, 60, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahşi, Z.B.; Oral, A.Y. Effects of Mn and Cu Doping on the Microstructures and Optical Properties of Sol–Gel Derived ZnO Thin Films. Opt. Mater. 2007, 29, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, Y.S.; Kanade, K.G.; Kale, B.B.; Aiyer, R.C. Electrical and Gas Sensing Properties of Self-Aligned Copper-Doped Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 2008, 43, 2719–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, N.; Leung, K.T. FePt Alloy Nanoparticles for Biosensing: Enhancement of Vitamin C Sensor Performance and Selectivity by Nanoalloying. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 5974–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkins, K.E.; Vedantam, T.S.; Liu, J.P.; Zeng, H.; Sun, S.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Ultrafine FePt Nanoparticles Prepared by the Chemical Reduction Method. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.C.W.; Nie, S. Quantum Dot Bioconjugates for Ultrasensitive Nonisotopic Detection. Science 1998, 281, 2016–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar Sahu, N.; Bahadur, D. Influence of Excess Fe Accumulation over the Surface of FePt Nanoparticles: Structural and Magnetic Properties. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 134303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.-C.; Lin, S.-H.; Kuo, P.-Y.; Lai, C.-H.; Nien, Y.-H.; Lai, T.-Y.; Su, T.-Y. A Sensitive Potentiometric Biosensor Using MBs-AO/GO/ZnO Membranes-Based Arrayed Screen-Printed Electrodes for AA Detection and Remote Monitoring. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 105962–105972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nien, Y.-H.; Su, T.-Y.; Chou, J.-C.; Lai, C.-H.; Kuo, P.-Y.; Lin, S.-H.; Lai, T.-Y.; Rangasamy, M. Investigation of Flexible Arrayed Urea Biosensor Based on Graphene Oxide/Nickel Oxide Films Modified by Au Nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.-C.; Lin, S.-H.; Kuo, P.-Y.; Lai, C.-H.; Nien, Y.-H.; Lai, T.-Y.; Su, T.-Y. Integrating a Plastic Glucose Biosensor Based on Arrayed Screen-Printed Electrodes Utilizing Magnetic Beads with a Microfluidic Device. IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 2019, 7, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Liao, Y.-H.; Lai, C.-H.; Huang, M.-S.; Chen, J.-S.; Yan, S.-J.; Wu, C.-Y. Sensing Characteristic of Arrayed Flexible Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Lactate Biosensor Modified by Magnetic Beads. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 5920–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.-C.; Yan, S.-J.; Liao, Y.-H.; Lai, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-X.; Wu, C.-Y. Remote Detection for Glucose and Lactate Based on Flexible Sensor Array. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 3467–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Liao, Y.-H.; Lai, C.-H.; Yan, S.-J.; Wu, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-X. Sensing Characteristic of Arrayed Flexible Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Lactate Biosensor Modified by GO and Magnetic Beads. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2018, 17, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Element Series | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unnormalized Weight % | Normalized Weight % | Atomic % | Error | |
| (wt. %) | (wt. %) | (at. %) | (wt. %) | |
| Copper | 0.87 | 3.73 | 2.77 | 0.2 |
| Zinc | 19.63 | 83.81 | 60.47 | 1.8 |
| Oxygen | 2.92 | 12.46 | 36.76 | 1.4 |
| Total | 23.43 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
| Concentration of FePt NPs (wt%) | Average Sensitivity (mV/mM) | Linearity |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 12.76 | Nonlinear |
| 0.05 | 31.94 | Nonlinear |
| 0.10 | 10.96 | Nonlinear |
| 0.30 | 25.32 | 0.977 |
| 0.50 | 30.03 | Nonlinear |
| Interference Substances | Concentration (mM) |
|---|---|
| Glucose | 5.00 |
| Urea | 5.00 |
| Dopamine (DA) | 0.06 |
| Uric Acid (UA) | 0.30 |
| Ascorbic Acid (AA) | 0.02 |
| Sensing Members | Linear Range (mM) | Average Sensitivity (mV/mM) | Linearity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDH NAD+-IGZO | 0.3–3 | 56.09 | 0.998 | [25] |
| LDH NAD+-MBs/GPTS/GO/NiO | 0.2–3 | 45.40 | 0.992 | [26] |
| MBs-LDHNAD+-GO/IGZO | 0.2–3 | 69.08 | 0.997 | [27] |
| γ-APTS/0.3%FePt NPs/CZO | 0.2–5 | 25.31 | 0.977 | This study |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nien, Y.-H.; Kang, Z.-X.; Su, T.-Y.; Ho, C.-S.; Chou, J.-C.; Lai, C.-H.; Kuo, P.-Y.; Lai, T.-Y.; Dong, Z.-X.; Chen, Y.-Y.; et al. Investigation of Flexible Arrayed Lactate Biosensor Based on Copper Doped Zinc Oxide Films Modified by Iron–Platinum Nanoparticles. Polymers 2021, 13, 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132062
Nien Y-H, Kang Z-X, Su T-Y, Ho C-S, Chou J-C, Lai C-H, Kuo P-Y, Lai T-Y, Dong Z-X, Chen Y-Y, et al. Investigation of Flexible Arrayed Lactate Biosensor Based on Copper Doped Zinc Oxide Films Modified by Iron–Platinum Nanoparticles. Polymers. 2021; 13(13):2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132062
Chicago/Turabian StyleNien, Yu-Hsun, Zhi-Xuan Kang, Tzu-Yu Su, Chih-Sung Ho, Jung-Chuan Chou, Chih-Hsien Lai, Po-Yu Kuo, Tsu-Yang Lai, Zhe-Xin Dong, Yung-Yu Chen, and et al. 2021. "Investigation of Flexible Arrayed Lactate Biosensor Based on Copper Doped Zinc Oxide Films Modified by Iron–Platinum Nanoparticles" Polymers 13, no. 13: 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132062
APA StyleNien, Y.-H., Kang, Z.-X., Su, T.-Y., Ho, C.-S., Chou, J.-C., Lai, C.-H., Kuo, P.-Y., Lai, T.-Y., Dong, Z.-X., Chen, Y.-Y., & Huang, Y.-H. (2021). Investigation of Flexible Arrayed Lactate Biosensor Based on Copper Doped Zinc Oxide Films Modified by Iron–Platinum Nanoparticles. Polymers, 13(13), 2062. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13132062









