Non-Toxic Crosslinking of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering and Biomedicine—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
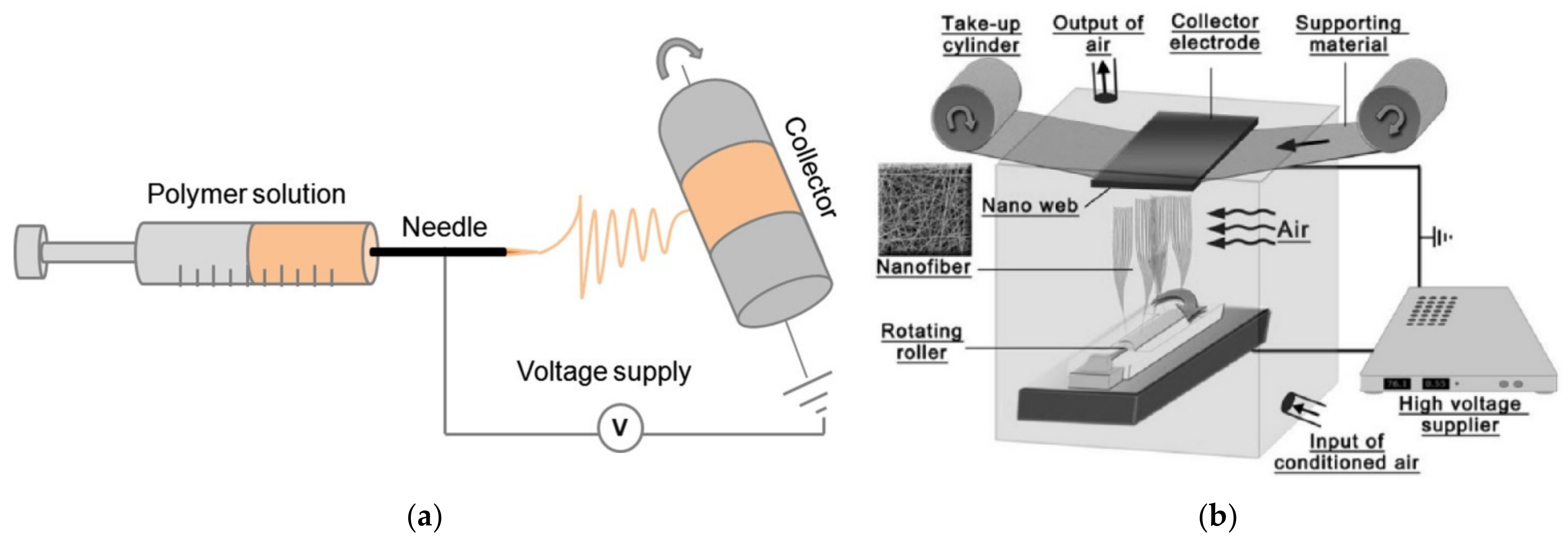
2. Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers—Production and Properties
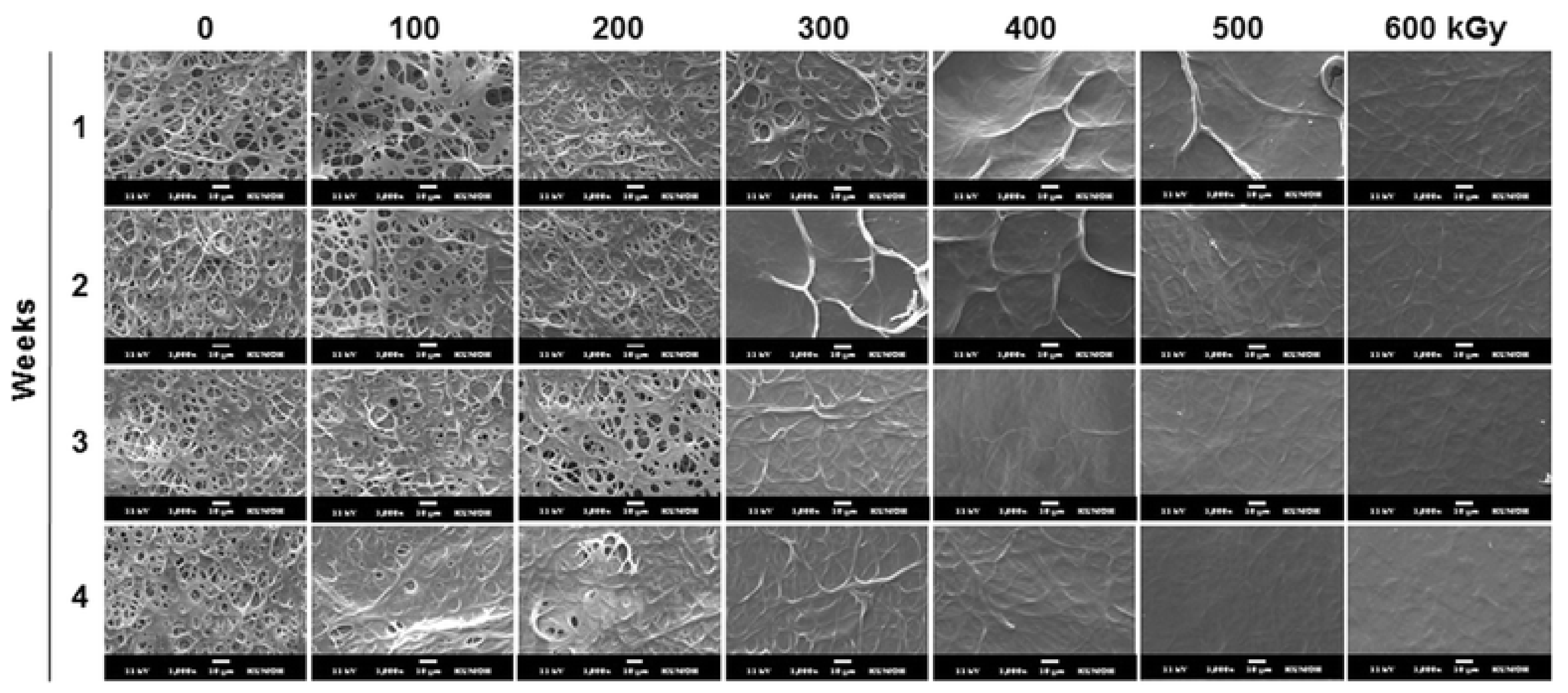
3. Physical Crosslinking
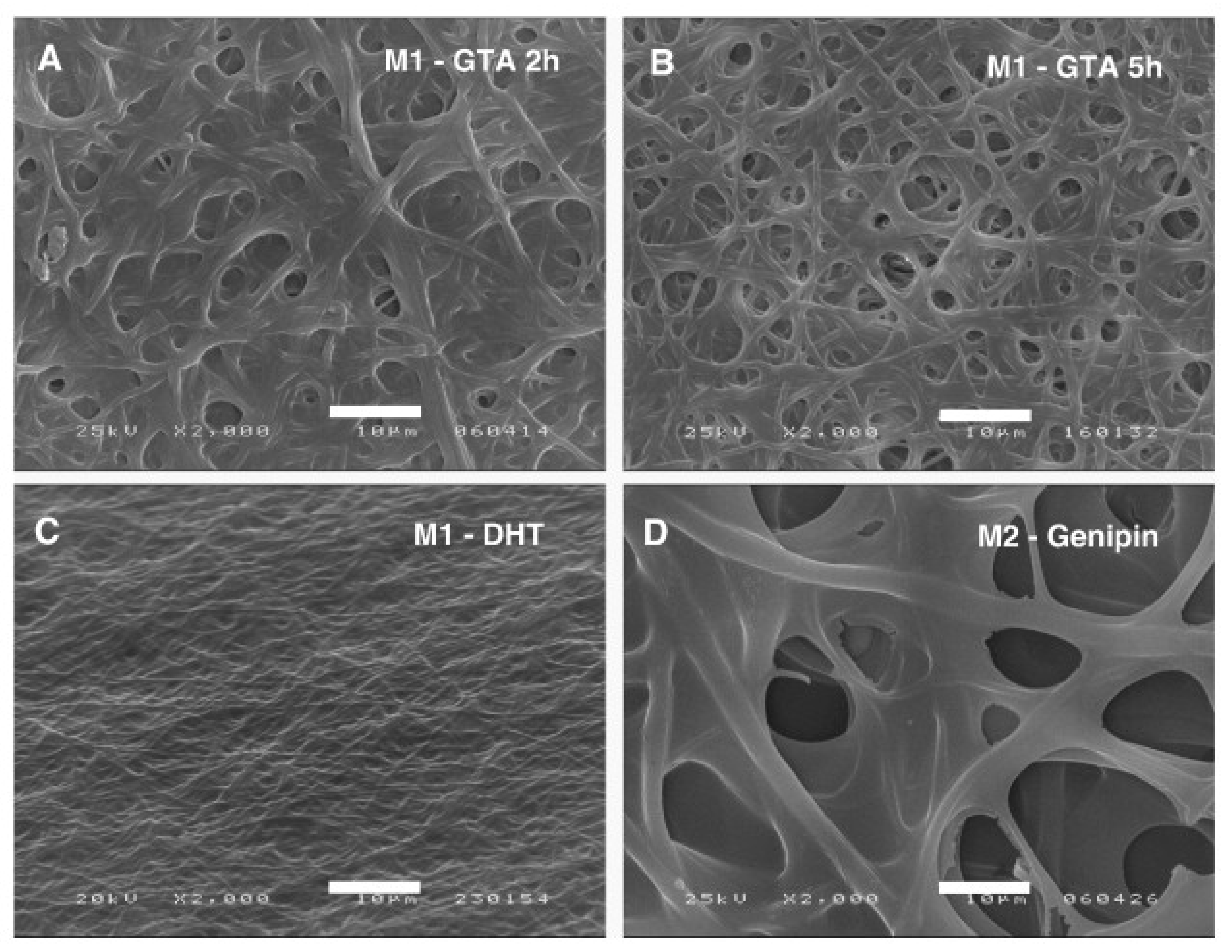
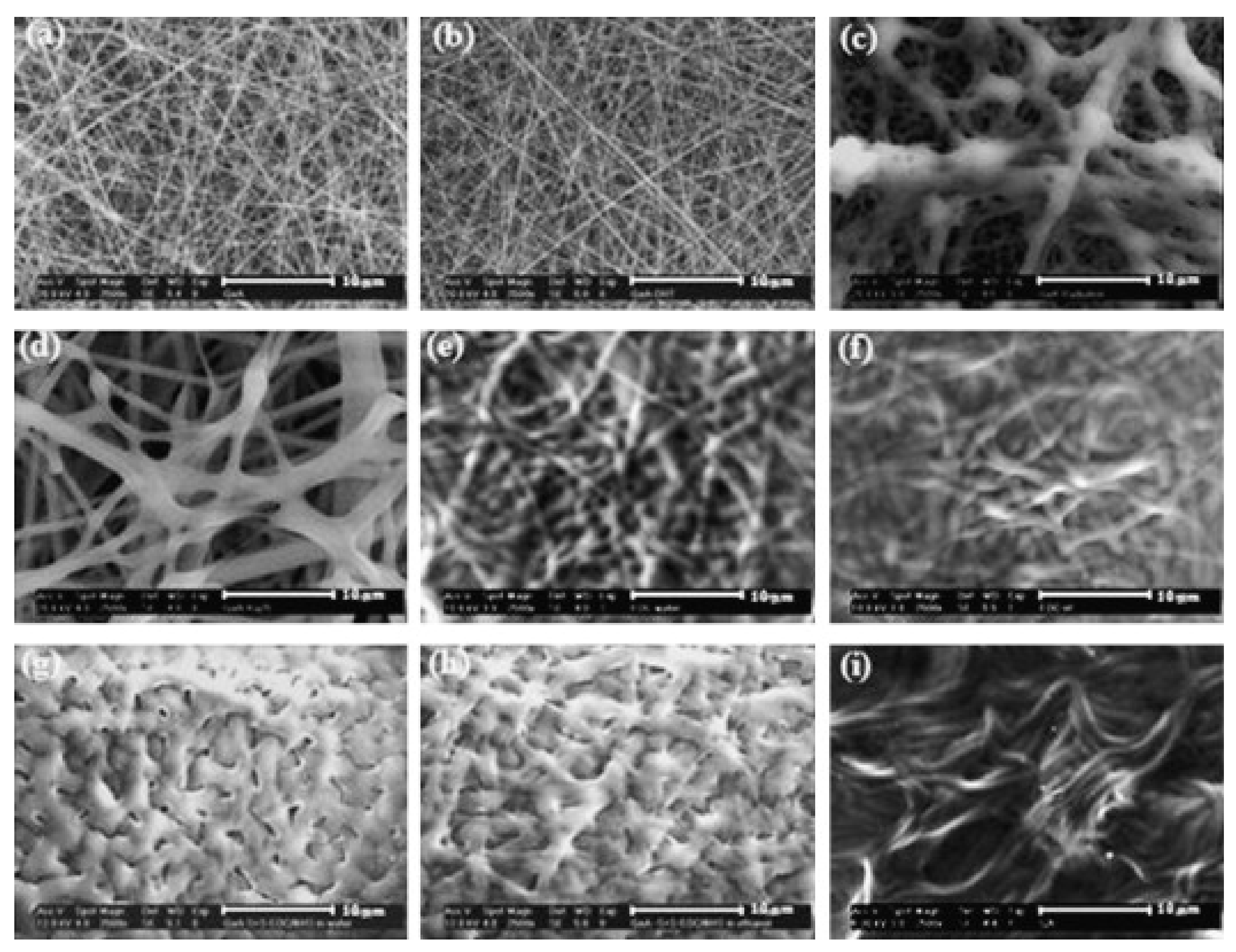
4. Chemical Crosslinking
5. Enzymatic Crosslinking
6. Blending Gelatin with Other Polymers
7. Biomedical Applications of Crosslinked Gelatin Nanofiber Mats
8. Conclusions and Outlook
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keenan, T.R. Gelatin. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Muyonga, J.H.; Cole, C.G.B.; Duodu, K.G. Extraction and physico-chemical characterisation of Nile perch (Lates niloticus) skin and bone gelatin. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, M. Rheological properties of fish gelatins. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 2172–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sompie, M.; Surtiono, S.E.; Pontoh, J.H.W.; Lontaan, N.N. The effect of acetic acid concentration and extraction temperature on physical and chemical properties of pigskin gelatin. Proc. Food Sci. 2015, 3, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Montero, P.; Fernández-Martín, F.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Physico-chemical and film-forming properties of bovine-hide and tuna-skin gelatin: A comparative study. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.E.; Nuge, T.; Yeow, T.K.; Nordin, N.; Prasad, R.G.S.V. Gelatin based scaffolds for tissue engineering—A review. Polym. Res. J. 2015, 9, 15–32. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Giner, S.; Gimeno-Alcañiz, J.V.; Ocio, M.J.; Lagaron, J.M. Comparative performance of electrospun collagen nanofibers cross-linked by means of different methods. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haugh, M.G.; Jaasma, M.J.; O’Brien, F.J. The effect of dehydrothermal treatment on the mechanical and structural properties of collagen-GAG scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2009, 89, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Cojazzi, G.; Panzavolta, S.; Rubini, K.; Roveri, N. Mechanical and thermal properties of gelatin films at different degrees of glutaraldehyde crosslinking. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.P.; Ma, M.; Xu, H.T.; Zhang, B.; Cao, X.F.; Guo, Y.C. Gelatin nanofibers prepared by spiral-electrospinning and cross-linked by vapor and liquid-phase glutaraldehyde. Mater. Lett. 2015, 140, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuijpers, A.J.; Engbers, G.H.M.; Krijgsveld, J.; Zaat, S.A.J.; Dankert, J.; Feijen, J. Cross-linking and characterisation of gelatin matrices for biomedical applications. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2000, 11, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.-Y.; Lin, J.-H.; Yao, C.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Lai, T.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S. In Vivo Evaluation of a Biodegradable EDC/NHS-Cross-Linked Gelatin Peripheral Nerve Guide Conduit Material. Macromol. Biosci. 2007, 7, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigi, A.; Cojazzi, G.; Panzavolta, S.; Roveri, N.; Rubini, K. Stabilization of gelatin films by crosslinking with genipin. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4827–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.B.; Kim, Y.T.; Bae, H.J.; Whiteside, W.S.; Park, H.J. Influence of transglutaminase-induced cross-linking on properties of fish gelatin films. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, E376–E383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopinska-Wisniewska, J.; Tuszynska, M.; Olewnik-Kruszkowska, E. Comparative study of gelatin hydrogels modified by various cross-linking agents. Materials 2021, 14, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisson, K.; Zhang, C.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Evaluation of cross-linking methods for electrospun gelatin on cell growth and viability. BioMacromolecules 2009, 10, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, P.; Gil, M.H.; Figueiredo, M. Tailoring the properties of gelatin films for drug delivery applications: Influence of the chemical cross-linking method. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 70, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of electrospinning technique for biomedical applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, F.; Krucinska, I.; Gliscinska, E.; Chrzanowski, M.; Göktepe, F. Comparative analysis of various electrospinning methods of nanofibre formation. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2009, 72, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Arkoun, M.; Daigle, F.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A. Antibacterial electrospun chitosan-based nanofibers: A bacterial membrane perforator. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, F. A review on advanced nanofiber technology for membrane distillation. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, Y.Q.; Yang, X.P.; Mei, F.; Ma, Q.; Chen, G.Q.; Ryu, S.K.; Deng, X.L. Gelatin nanofibrous membrane fabricated by electrospinning of aqueous gelatin solution for guided tissue regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2009, 90, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.W.; Shin, M.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Yun, H.S.; Song, D.W.; Yang, Y.; Shin, B.-S.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, K.H. Fabrication of an ultrafine fish gelatin nanofibrous web from an aqueous solution by electrospinning. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki, C.S.; Baek, D.H.; Gang, K.D.; Lee, K.H.; Um, I.C.; Park, Y.H. Characterization of gelatin nanofiber prepared from gelatin–formic acid solution. Polymer 2005, 46, 5094–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.-Y.; Wang, Z.-M.; Ren, J.; Zhang, C.-Y. Electrospinning of gelatin and gelatin/poly(l-lactide) blend and its characteristics for wound dressing. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2009, 29, 1822–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.-H.; Kim, H.-E.; Kim, H.-W. Production of electrospun gelatin nanofiber by water-based co-solvent approach. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2008, 19, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lim, C.T. Electrospinning and mechanical characterization of gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 5361–5368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.H.; Yin, H.Y.; An, J.H.; Chung, D.J. Characterization of cross-linked gelatin nanofibers through electrospinning. Macromol. Res. 2010, 18, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beishenaliev, A.; Lim, S.S.; Tshai, K.Y.; Khiew, P.S.; Moh’d Sghayyar, H.N.; Loh, H.-S. Fabrication and preliminary in vitro evaluation of ultraviolet-crosslinked electrospun fish scale gelatin nanofibrous scaffolds. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2019, 30, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.R.; Davidson, R.J. The effect of ultraviolet irradiation on soluble collagen. Biochem. J. 1965, 97, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichimaru, H.; Taguchi, T. Improved tissue adhesion property of a hydrophobically modified Alaska pollock derived gelatin sheet by UV treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, K.; Kimura, Y.; Miyata, S. Improvement of adhesion and proliferation of mouse embryonic stem cells cultured on ozone/UV surface-modified substrates. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumura, Y.; Kasai, K.; Miyata, S. Feeder-free culture for mouse induced pluripotent stem cells by using UV/ozone surface-modified substrates. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 92, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratanavaraporn, J.; Rangkupan, R.; Jeeratawatchai, H.; Kanokpanont, S.; Damrongsakkul, S. Influences of physical and chemical crosslinking techniques on electrospun type A and B gelatin fiber mats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, S.R.; Rodrigues, G.; Martins, G.G.; Henriques, C.M.R.; Silva, J.C. In vitro evaluaton of crosslinked electrospun fish gelatin scaffolds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, Z.; Slaughter, G. Cross-linked electrospun gelatin nanofibers for cell-based assays. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mozaffari, A.; Gashti, M.P.; Mirjalili, M.; Parsania, M. Argon and argon-oxygen plasma surface modification of gelatin nanofibers for tissue engineering applications. Membranes 2021, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Do, M.D.; Casey, P.; Sulistio, A.; Qiao, G.G.; Lundin, L.; Lillford, P.; Kosaraju, S. Chemical Modification of Gelatin by a Natural Phenolic Cross-Linker, Tannic Acid. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 6809–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, F.; Hossein Goli, S.A. Encapsulation of flaxseed oil in the tertiary conjugate of oxidized tannic acid-gelatin and flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum) mucilage. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozafari, A.; Mirjalili, M.; Gashti, M.P.; Parsania, M. Effect of tannic acid on properties of electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2020, 45, 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo, F.; Ursini, O.; Lilla, E.; Angelini, G. Radiation-induced crosslinking of collagen gelatin into a stable hydrogel. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2008, 275, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, T.; Bessho, M.; Furuta, M.; Okuda, S.; Hara, M. Characterization of biopolymer hydrogels produced by γ-ray irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2004, 71, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nho, Y.C.; Lim, Y.M.; Lee, Y.M. Preparation, properties and biological application of pH-sensitive poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) hydrogels grafted with acrylic acid(AAc) using gamma-ray irradiation. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2004, 71, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terao, K.; Nagasawa, N.; Nishida, H.; Furusawa, K.; Mori, Y.; Yoshii, F.; Dobashi, T. Reagent-free crosslinking of aqueous gelatin: Manufacture and characteristics of gelatin gels irradiated with gamma-ray and electron beam. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2003, 14, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisotzki, E.I.; Hennes, M.; Schuldt, C.; Engert, F.; Knolle, W.; Decker, U.; Käs, J.A.; Zink, M.; Mayr, S.G. Tailoring the material properties of gelatin hydrogels by high energy electron irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 27, 4297–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vlierberghe, S. Crosslinking strategies for porous gelatin scaffolds. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 4349–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Ko, Y.-G.; Cho, D.W.; Park, W.H.; Kwon, O.H. Modification and optimization of electrospun gelatin sheets by electron beam irradiation for soft tissue engineering. Biomater. Res. 2017, 21, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufay, M.; Jimenez, M.; Degoutin, S. Effect of cold plasma treatment on electrospun nanofibers properties: A review. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 4696–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertsung, I.; Damrongsakkul, S.; Saito, N. Crosslinking of a gelatin solutions induced by pulsed electrical discharges in solutions. Plasma Process. Polym. 2013, 10, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, A.; Bigi, A.; Colombo, V.; Focarete, M.L.; Gherardi, M.; Gualandi, C.; Oleari, M.C.; Panzavolta, S. Atmospheric pressure non-equilibrium plasma as a green tool to crosslink gelatin nanofibers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, A.; Yadav, S.; Majmdar, S.; Sharma, C.S. In-vitro release study of hydrophobic drug using electrospun cross-linked gelatin nanofibers. Biochem. Eng. J. 2016, 105, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Veugopal, J.; Huang, Z.-M.; Lim, C.T.; Ramakrishna, S. Crosslinking of the electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Polymer 2006, 47, 2911–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohammadzadehmoghadam, S.; Dong, Y. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun silk fibroin/gelatin scaffolds crosslinked with glutaraldehyde vapor. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angarano, M.; Schulz, S.; Fabritius, M.; Vogt, R.; Steinberg, T.; Tomakidi, P.; Friedrich, C.; Mülhaupt, R. Layered gradient nonwovens of in situ crosslinked electrospun collagenous nanofibers used as modular scaffold systems for soft tissue regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3277–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-C.; Jao, W.-C.; Yang, M.-C. Characterization of gelatin nanofibers electrospun using ethanol/formid acid/water as a solvent. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2009, 20, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takigawa, T.; Endo, Y. Effects of glutaraldehyde exposure on human health. J. Occup. Health 2006, 48, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballantyne, B.; Myers, R.C. The acute toxicity and primary irritancy of glutaraldehyde solutions. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 2001, 43, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeiger, E.; Gollapudi, B.; Spencer, P. Genetic toxicity and carcinogenicity studies of glutaraldehyde—A review. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2005, 589, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damink, L.H.H.O.; Dijkstra, P.J.; van Luyn, M.J.A.; van Wachem, P.B.; Nieuwenhuis, P.; Feijen, J. Cross-linking of dermal sheep collagen using a water-soluble carbodiimide. Biomaterials 1996, 17, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agheb, M.; Dinari, M.; Rafienia, M.; Salehi, H. Novel electrospun nanofibers of modified gelatin-tyrosine in cartilage tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiabbas, M.; Alemzadeh, I.; Vossoughi, M.; Shamloo, A. In-situ crosslinking of electrospun gelatin-carbodiimide nanofibers: Fabrication, characterization, and modeling of solution parameters. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2020, 208, 976–992, online first. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, Z.; Slaughter, G. Storage stability of electrospun pure gelatin stabilized with EDC/Sulfo-NHS. Biopolymers 2018, 109, e23232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, K.W.; Kimura, T.; Kishida, A. Controlling coupling reaction of EDC and NHS for preparation of collagen gels using ethanol/water co-solvents. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.-I.; Kuffova, L.; Merrett, K.; Mitra, D.; Forrester, J.V.; Li, F.; Griffith, M. Crosslinked collagen hydrogels as corneal implants: Effects of sterically bulky vs. non-bulky carbodiimides as crosslinkers. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7796–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, C.; Nakajima, N.; Ikada, Y. In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity of diepoxy compounds used for biomaterial modification. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1995, 29, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, J.C.; Li, Z.; Xia, W.; Yang, N.; Gong, J.X.; Zhang, J.F.; Qiao, C.S. Preparation and properties of EDC/NHS mediated crosslinking poly(gamma-glutamic acid)/epsilon-polylysine hydrogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 61, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdal, E.; Capanoglu, F. A review on protein-phenolic interactions and associated changes. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 954–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscarat, J.; Charmette, C.; Masquelez, N.; Sanchez, J.; Pochat-Bohatier, C. Cross-linking of gelatin membranes with ferrulic acid or glutaraldehyde: Relationship between gas permeability and renaturation level of gelatin triple helices. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2015, 53, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassoli-Kafrani, E.; Goli, S.A.H.; Fathi, M. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun gelatin nanofibers crosslinked with oxidized phenolic compounds. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavassoli-Kafrani, E.; Goli, S.A.H.; Fathi, M. Encapsulation of orange essential oil using cross-linked electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2018, 11, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.M.; Dhand, C.; Dwivedi, N.; Xiao, A.; Ong, S.T.; Chalasani, M.L.S.; Sriram, H.; Balakrishnan, Y.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Orive, G.; et al. Combating microbial contamination with robust polymeric nanofibers: Elemental effect on the mussel-inspired cross-linking of electrospun gelatin. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhand, C.; Venkatesh, M.; Barathi, V.A.; Harini, S.; Bairagi, S.; Leng, E.G.T.; Muruganandham, N.; Low, K.Z.W.; Fazil, M.H.U.T.; Loh, X.J.; et al. Bio-inspired crosslinking and matrix-drug interactions for advanced wound dressings with long-term antimicrobial activity. Biomaterials 2017, 138, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.H.; Park, C.B. Human endothelial cell growth on mussel-inspired nanofiber scaffold for vascular tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9431–9437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Michael, P.L.; Zhong, S.; Ma, B.; MacEwan, M.R.; Lim, C.T. Mussel inspired protein-mediated surface modification to electrospun fibers and their potential biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, H.; Nam, Y.S. Silver-polydopamine hybrid coatings of electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.J.; Fazil, M.H.; Dhand, C.; Venkatesh, M.; Goh, E.T.; Harini, S.; Eugene, C.; Lim, R.R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chaurasia, S.S.; et al. Insight into membrane selectivity of linear and branched polyethylenimines and their potential as biocides for advanced wound dressings. Acta Biomater. 2016, 37, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihli, J.; Bots, P.; Kulak, A.; Benning, L.G.; Meldrum, F.C. Elucidating mechanisms of diffusion-based calcium carbonate synthesis leads to controlled mesocrystal formation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhand, C.; Barathi, V.A.; Ong, S.T.; Venkatesh, M.; Harini, S.; Dwivedi, N.; Goh, E.T.; Nandhakumar, M.; Venugopal, J.R.; Diaz, S.M.; et al. Latent oxidative polymerization of catecholamines as potential cross-linkers for biocompatible and multifunctional biopolymer scaffolds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 32266–32281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, R.A.; Grosso, C.R.F. Characterization of gelatin based films modified with transglutaminase, glyoxal and formaldehyde. Food Hydrocoll. 2004, 18, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callioglu, F.C. The effect of glyoxal cross-linker and NaCl salt addition on the roller electrospinning of poly(vinyl alcohol). Tekst. Konfeksiyon 2014, 24, 15–20. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, P.; Tabor, B.E. Kinetic study of the crosslinking of gelatin by formaldehyde and glyoxal. J. Polym. Sci. A 1963, 1, 799–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhus, G.; Peptu, C.; Popa, M.; Desbrières, J. Controlled release of water soluble antibiotics by carboxymethylcellulose- and gelatin-based hydrogels crosslinked with epichlorohydrin. Cell. Chem. Technol. 2009, 43, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Tataru, G.; Popa, M.; Desbrieres, J. Microparticles of hydrogel type based on carboxymethylcellulose and gelatin for controlled release of water soluble drugs. Rev. Roum. Chim. 2011, 56, 399–409. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.W.; Xue, Z.X.; Yan, M.; Liu, J.J.; Xia, Y.Z. Effect of epichlorohydrin on the wet spinning of carrageenan fibers under optimal parameter conditions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.-S. Fabrication and evaluation of a biodegradable proanthocyanidin-crosslinked gelatin conduit in peripheral nerve repair. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 87, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanzadeh, E.; Mahmoodi, N.; Basiri, A.; Ranjbar, F.E.; Hassannejad, Z.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S.; Azami, M.; Ai, J.; Rahimi-Movaghar, V. Proanthocyanidin as a crosslinking agent for fibrin, collagen hydrogels and their composites with decellularized Wharton’s-jelly-extract for tissue engineering applications. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2020, 35, 554–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-R.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chao, A.-C.; Lin, C.-W.; Tsai, M.-L.; Mi, F.-L. Effect of grape seed proanthocyanidin-gelatin colloidal complexes on stability and in vitro digestion of fish oil emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-H.; Chi, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-S.; Chen, K.-Y.; Chen, P.-L.; Yao, C.-H. Evaluation of proanthocyanidin-crosslinked electrospun gelatin nanofibers for drug delivering system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2476–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; Wang, L.Q.; Jiang, H.L. The effect of procyanidine crosslinking on the properties of the electrospun gelatin membranes. Biofabrication 2012, 4, 035007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranga, J.; Leceta, I.; Etxabide, A.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. Cross-linking of fish gelatins to develop sustainable films with enhanced properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 78, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranga, J.; Nguyen, B.T.; Si, T.T.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K. The effect of cross-linking with citric acid on the properties of agar/fish gelatin films. Polymers 2020, 12, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguoiri, A.; Uranga, J.; Panzavolta, S.; Guerrero, P.; de la Caba, K.; Focarete, M.L. Electrospinning of fish gelatin solution containing citric acid: An environmentally friendly approach to prepare crosslinked gelatin fibers. Materials 2019, 12, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banner, J.; Dautzenberg, M.; Feldhans, T.; Hofmann, J.; Plümer, P.; Ehrmann, A. Water resistance and morphology of electrospun gelatine blended with citric acid and coconut oil. Tekstilec 2018, 61, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxabide, A.; Kilmartin, P.A.; Maté, J.I.; Prabakar, S.; Brimble, M.; Naffa, R. Analysis of advanced glycation end products in ribose-, glucose- and lactose-crosslinked gelatin to correlate the physical changes induced by Maillard reaction in films. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siimon, K.; Siimon, H.; Järvekülg, M. Mechanical characterization of electrospun gelatin scaffolds cross-linked by glucose. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2015, 26, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsy, R.; Hosny, M.; Reicha, F.; Elnimr, T. Developing a potential antibacterial long-term degradable electrospun gelatin-based composites mat for wound dressing applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 114, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, H.W.; Park, J.S.; Yun, H.S.; Jeon, K.H.; Kang, D.-W. Effect of crosslinkable sugar molecules on the physico-chemical and antioxidant properties of fish gelatin nanofibers. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siimon, K.; Reemann, P.; Pöder, A.; Pook, M.; Kangur, T.; Kingo, K.; Jaks, V.; Mäeorg, U.; Järvekülg, M. Effect of glucose content on thermally cross-linked fibrous gelatin scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 42, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-H.; Chang, Y.; Lai, P.-H.; Sung, H.-W. A genipin-crosslinked gelatin membrane as wound-dressing material: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2003, 14, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solorio, L.; Zwolinski, C.; Lund, A.W.; Farrell, M.J.; Stegemann, J.P. Gelatin microspheres crosslinked with genipin for local delivery of growth factors. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2010, 4, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasceanu, G.M.; Crica, L.E.; Pandele, A.M.; Ionita, M. Graphene oxide reinforcing genipin crosslinked chitosan-gelatin blend films. Coatings 2020, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yung, C.W.; Wu, L.Q.; Tullman, J.A.; Payne, G.F.; Bentley, W.E.; Barbari, T.A. Transglutaminase crosslinked gelatin as a tissue engineering scaffold. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 83, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, M.K.; Chen, T.H.; Williams, C.M.; Markley, K.M.; Payne, G.F. Mechanical properties of biomimetic tissue adhesive based on the microbial transglutaminase-catalyzed crosslinking of gelatin. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Weng, R.R.; Wang, W.H.; Wie, X.H.; Li, J.L.; Chen, X.J.; Liu, Y.H.; Lu, F.P.; Li, Y. Tunable physical and mechanical properties of gelatin hydrogel after transglutaminase crosslinking on two gelatin types. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzavolta, S.; Gioffrè, M.; Focarete, M.L.; Gualandi, C.; Foroni, L.; Gibi, A. Electrospun gelatin nanofibers: Optimization of genipin cross-linking to preserve fiber morphology after exposure to water. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1702–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Mo, X.M. Genipin crosslinked gelatin nanofibers for tissue engineering. J. Control Release 2011, 152, e230–e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, C.; Baiguera, S.; Boieri, M.; Mazzanti, B.; Ribatti, D.; Bianco, A.; Macchiarini, P. Induction of angiogenesis using VEGF releasing genipin-crosslinked electrospun gelatin mats. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7754–7765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gualandi, C.; Torricelli, P.; Panzavolta, S.; Pagani, S.; Focarete, M.L.; Bigi, A. An innovative co-axial system to electrospin in situ crosslinked gelatin nanofibers. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 11, 025007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, B.L.; Limaye, A.; Yarborough, J.; Freeman, J.W. Investigating processing techniques for bovine gelatin electrospun scaffolds for bone tissue regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2017, 105, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.J.; Lake, R.; Park, S.; Edwards, S.; Jones, C.; Jeong, K.J. Injectable macroporous hydrogel formed by enzymatic cross-linking of gelatin microgels. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2018, 1, 1430–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.Q.; Hu, S.X.; Yu, B.R.; Cai, Y.L.; Yang, J.M.; Li, F.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Shi, X.N. Transglutaminase-catalyzed preparation of crosslinked carboxymethyl chitosan/carboxymethyl cellulose/collagen composite membrane for postsurgical peritoneal adhesion prevention. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 201, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-T.; Chen, L.-C.; Lin, S.-B.; Chen, H.-H. Nano-biomaterials application: Morphology and physical properties of bacterial cellulose/gelatin composites via crosslinking. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 27, 137–144. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, L.S.M.; Feijen, J.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Karperien, M. Enzyme-catalyzed crosslinkable hydrogels: Emerging strategies for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, M.; Ishii, O.; Sueda, T.; Vacanti, J.P. Contractile cardiac grafts using a novel nanofibrous mesh. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 3717–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandayuthapani, B.; Krishna, U.M.; Sethuraman, S. Fabrication and characterization of chitosan-gelatin blend nanofibers for skin tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2010, 94, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, -G.; Zhang, -Y.; Bao, -W.; Wu, -J.; Shi, D.-B.; Dong, Z.-h.; Fu, W.-G. Study on the properties of the electrospun silk fibroin/gelatin blend nanofibers for scaffolds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 111, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, L.H.; Lim, M.M.; Sultana, N. Fabrication and evaluation of polycaprolactone/gelatin-based electrospun nanofibers with antibacterial properties. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 970542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.E.; Heo, D.N.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, J.R.; Park, S.H.; Jeon, S.H.; Kwon, I.K. Electrospun gelatin/polyurethane blended nanofibers for wound healing. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 4, 044106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-W.; Yu, H.-S.; Lee, H.-H. Nanofibrous matrices of poly(lactic acid) and gelatin polymeric blends for the improvement of cellular responses. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2008, 87, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Xiaoqiang, L.; Shuiping, L.; Hongsheng, W.; Chuanglong, H. Fabrication and properties of PLLA-gelatin nanofibers by electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 117, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.X.; Wang, Y.S.; Ma, C.; Zheng, W.; Li, L.; Zheng, Y.F. Electrospinning of PLGA/gelatin randomly-oriented and aligned nanofibers as potential scaffold in tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 1204–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Wehlage, D.; Klöcker, M.; Mamun, A.; Grothe, T.; García-Mateos, F.J.; Rodríguez-Mirasol, J.; Cordero, T.; Finsterbusch, K.; Ehrmann, A. Stabilization of electrospun PAN/gelatin nanofiber mats for carbonization. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 6131085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehlage, D.; Blattner, H.; Mamun, A.; Kutzli, I.; Diestelhorst, E.; Rattenholl, A.; Gudermann, F.; Lütkemeyer, D.; Ehrmann, A. Cell growth on electrospun nanofiber mats from polyacrylonitrile (PAN) blends. AIMS Bioeng. 2020, 7, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehlage, D.; Blattner, H.; Sabantina, L.; Böttjer, R.; Grothe, T.; Rattenholl, A.; Gudermann, F.; Lütkemeyer, D.; Ehrmann, A. Sterilization of PAN/gelatin nanofibrous mats for cell growth. Tekstilec 2019, 62, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Kai, D.; Ye, H.Y.; Tian, L.L.; Ding, X.; Ramakrishna, S.; Loh, X.J. Electrospinning of poly(glycerol sebacate)-based nanofibers for nerve tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, G.R.; Li, Y.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Tian, W.M.; Ramakrishna, S. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the wound healing capability of electrospun gelatin/PLLCL nanofibers. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2014, 29, 628–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalaja, K.; Anil Kumar, P.R.; Dey, T.; Kundu, S.C.; James, N.R. Modified dextran cross-linked electrospun gelatin nanofibres for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, X.T.; Hu, J.L.; Han, Y.T. Random and aligned electrospun gelatin nanofiber mats for human mesenchymal stem cells. Mater. Res. Innov. 2019, 23, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padrao, J.; Silva, J.P.; Dourado, F.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Sencadas, V. Modifying fish gelatin electrospun membranes for biomedical applications: Cross-linking and swelling behavior. Soft Mater. 2014, 12, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.S.; Guo, Z.Z.; He, P.; Chen, T.; Li, L.H.; Ding, S.; Li, H. Study on structure, mechanical property and cell cytocompatibility of electrospun collagen nanofibers crosslinked by common agents. Inter. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 476–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hivechi, A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Siegel, R.A. Investigation of morphological, mechanical and biological properties of cellulose nanocrystal reinforced electrospun gelatin nanofibers. Intern. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, A.; Majumdar, S.; Sharma, C.S. Controlled drug release formulation by sequential crosslinking of multilayered electrospun gelatin nanofiber mat. MRS Adv. 2016, 1, 2107–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inal, M.; Mülazimoglu, G. Production and characterization of bactericidal wound dressing material based on gelatin nanofiber. Intern. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 137, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, G.; Hussain, T.; Chauhan, G.; Garg, T.; Goyal, M.K. Development and characterization of cefazolin loaded zinc oxide nanoparticles composite gelatin nanofiber mats for postoperative surgical wounds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
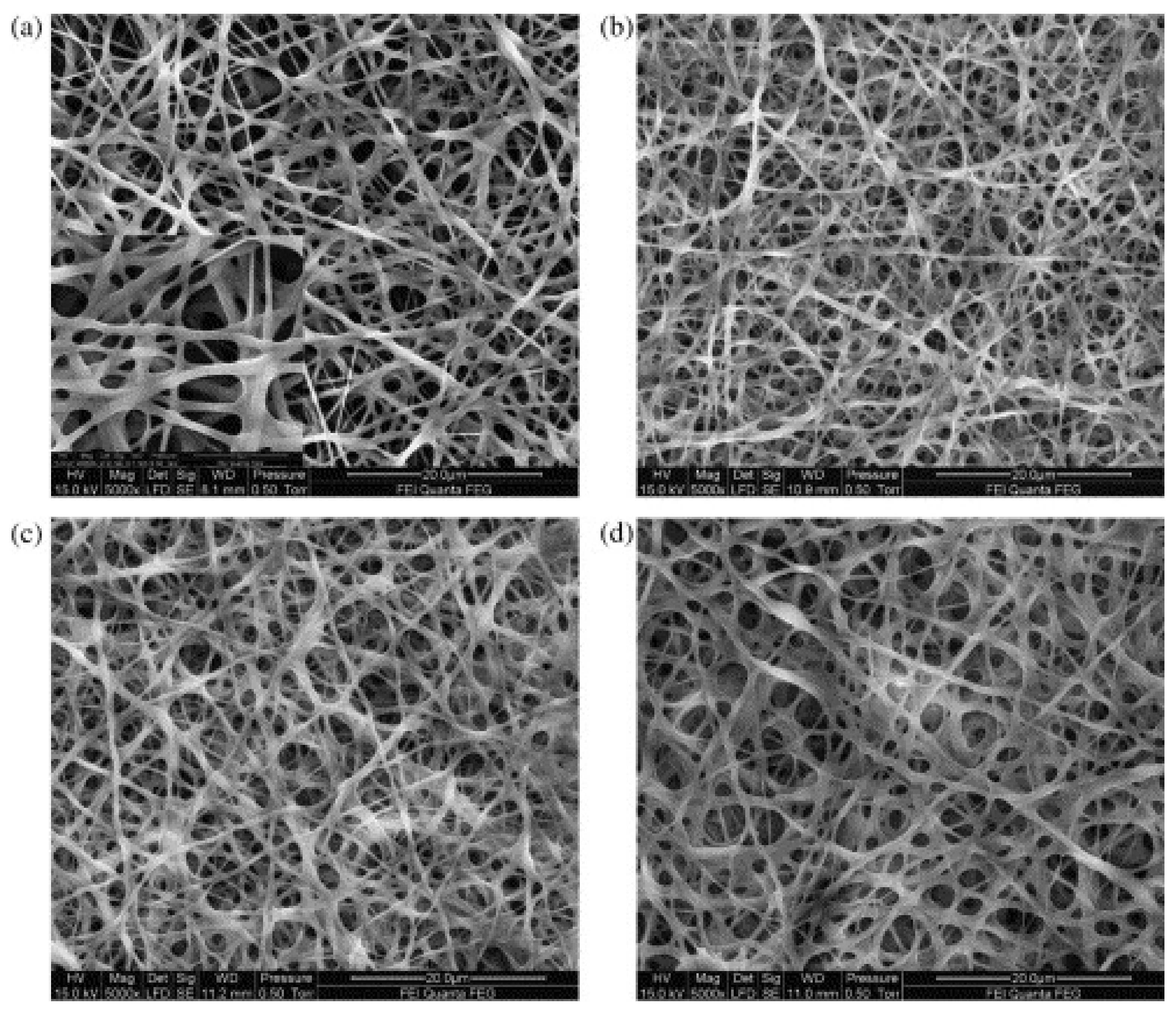
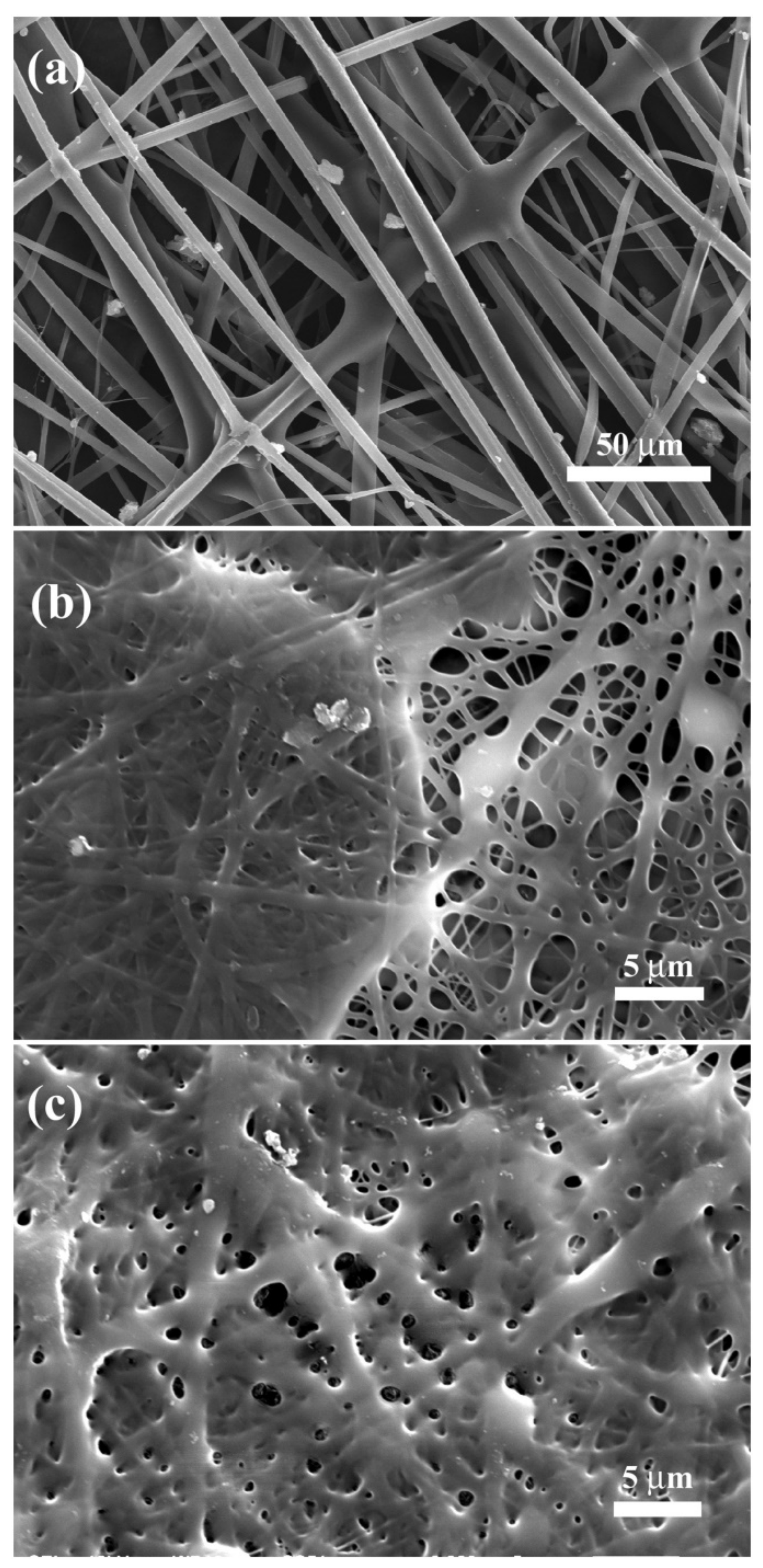
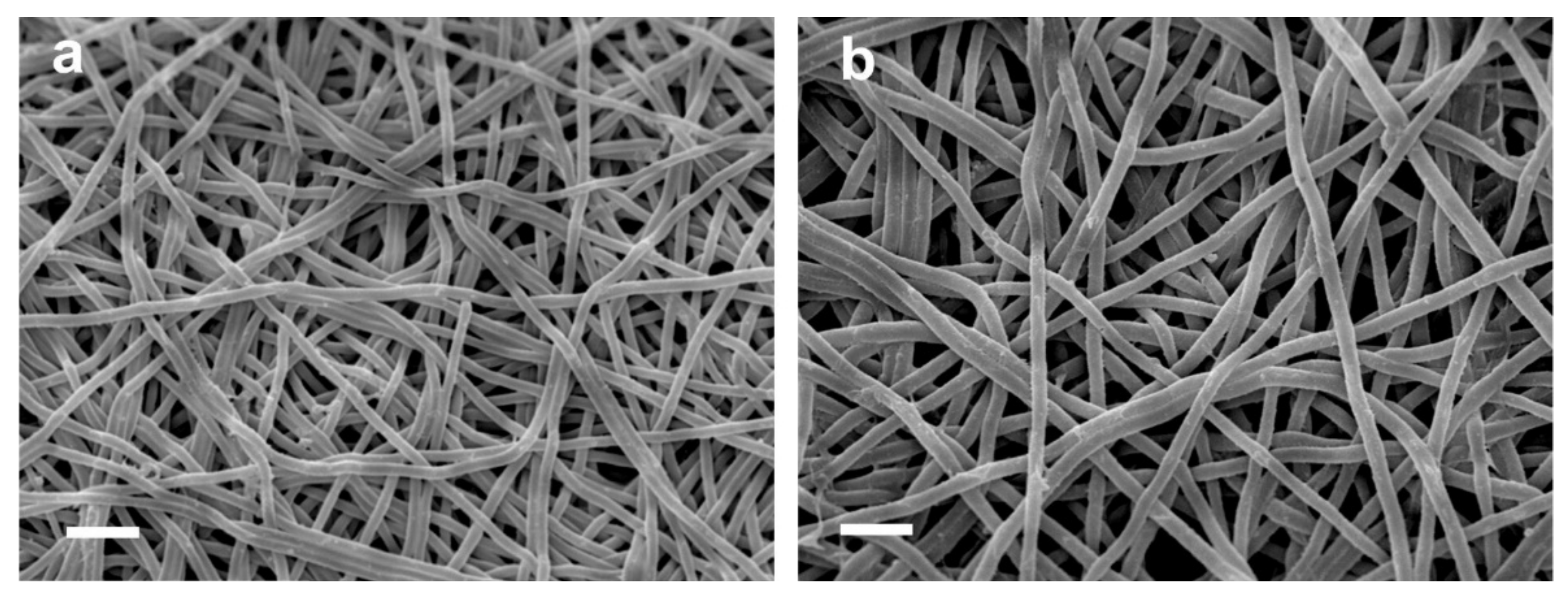
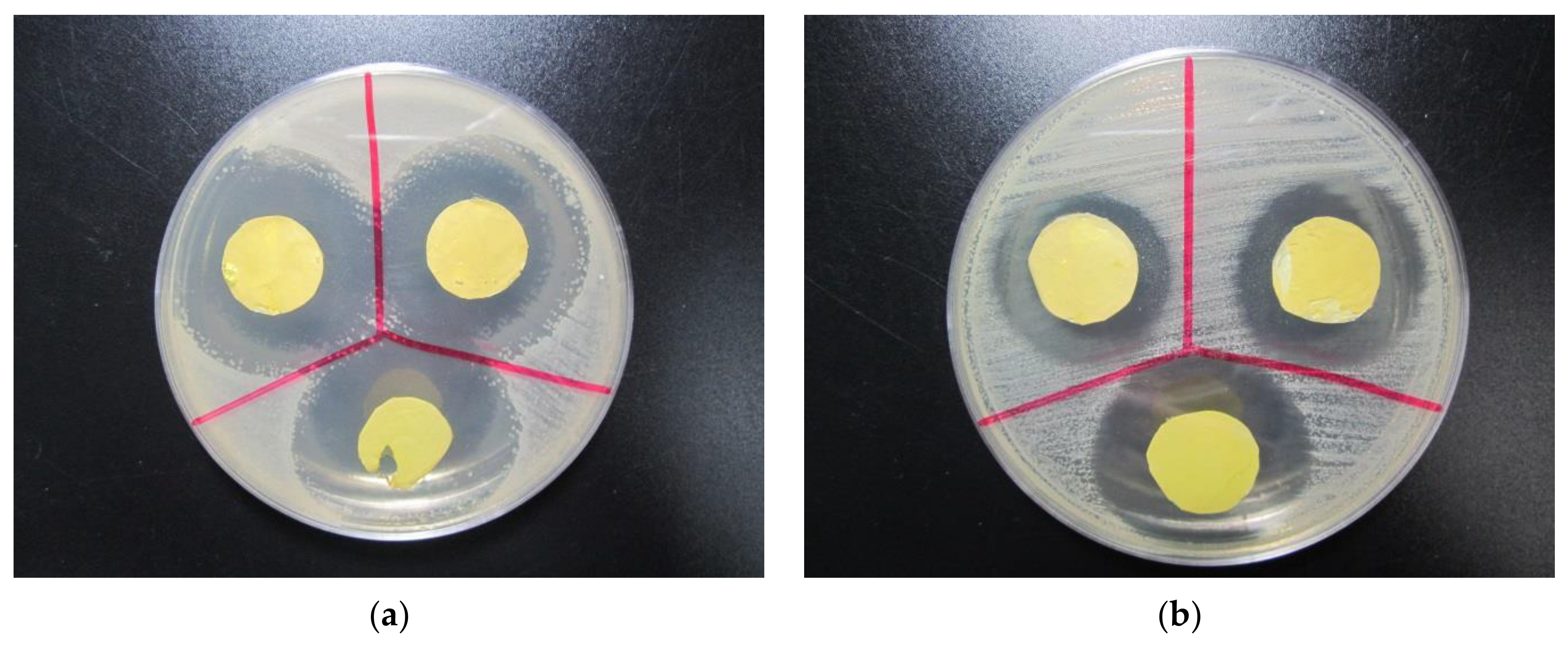
| Electrospinning Process | Crosslinking | Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marine fish-scale gelatin spun from acetic acid/water | UV crosslinker added in petri dish, UV irradiation at 254 nm for 5–20 min | 30% surface area lost after 14 day in medium | [30] |
| Alaska Pollock gelatin spun from water/ethanol at 55 °C | UV irradiation at 185 nm and 254 nm for 15–60 min without crosslinker | Increased burst strength and remaining mass after 60–150 min in collagenase solution | [32] |
| Gelatin type A and B spun from formic acid | Dehydrothermal treatment (DHT) | 80% efficiency for type B, 55% for type A | [35] |
| Cold water fish skin gelatin spun from acetic acid/water | DHT | Weight loss reduced to 15%, modified fiber morphology | [36] |
| Type B electrospun from acetic acid/distilled water | DHT | Immersion in PBS or DMEM dissolved fibers | [37] |
| Type A from porcine skin spun from acetic acid/water | Dielectric barrier discharge plasma in air at room temperature | Increased mechanical properties and morphological stability in aqueous solution | [51] |
| Gelatin type A and B spun from formic acid | Pulsed inductively coupled plasma in argon atmosphere at 5 Pa | Lower degree than DHT | [35] |
| Type B from bovine skin spun from acetic acid/water | EDC/NHS | Long-term stability in PBS and medium | [63] |
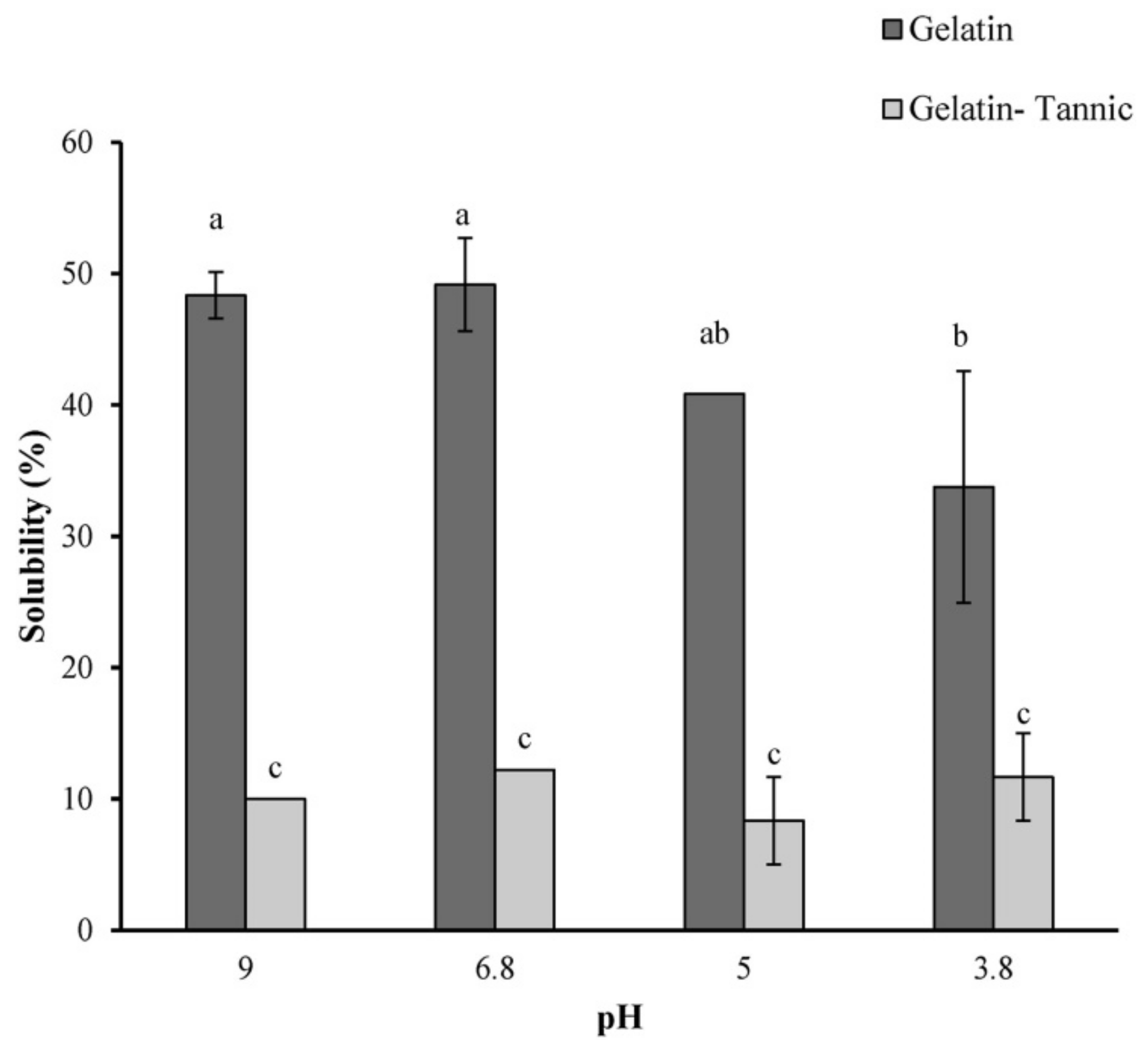
| Type A from porcine skin spun from acetic acid/water | Tannic acid | Increased tensile strength, reduced elongation at break | [71] |
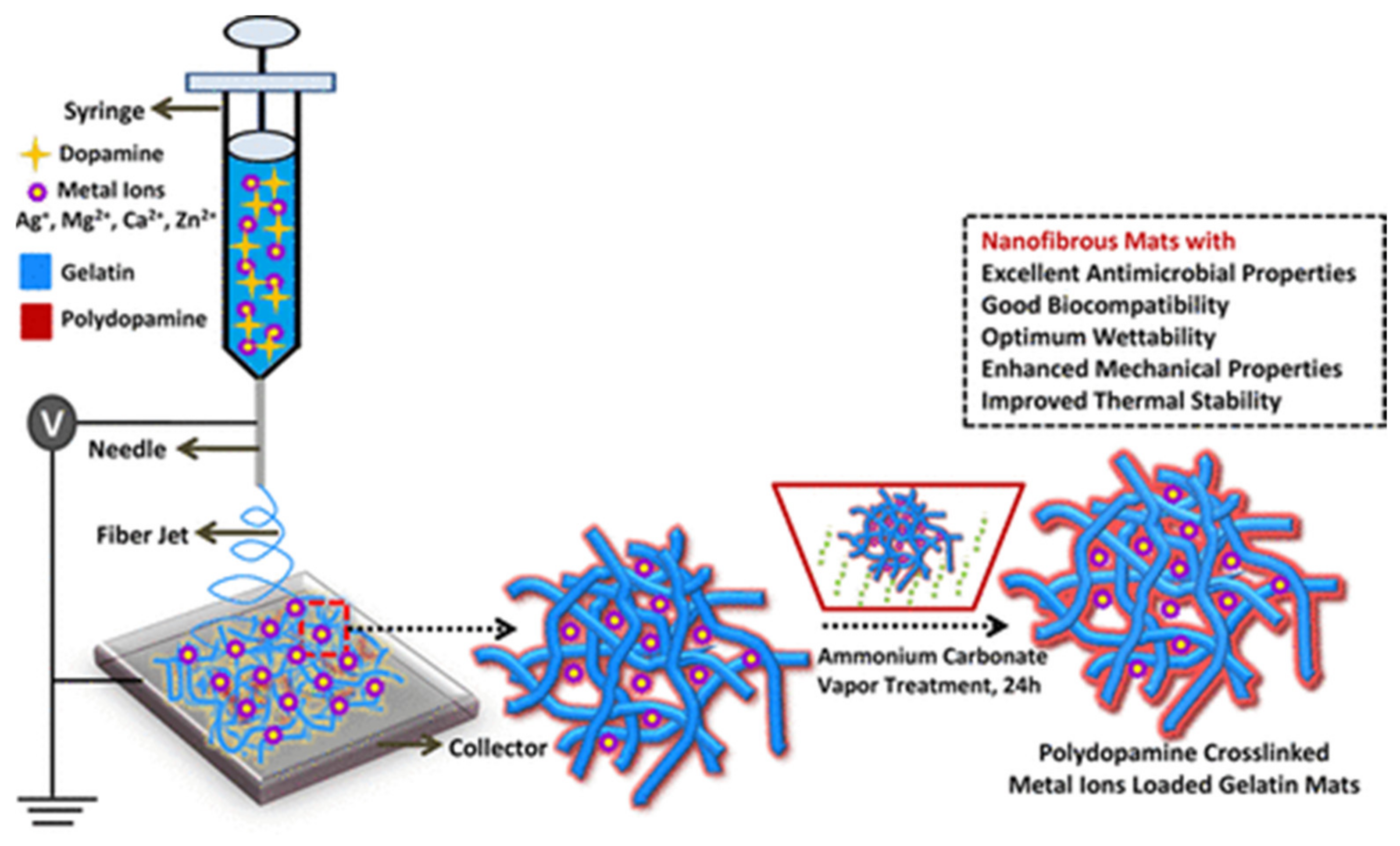
| Type A from porcine skin from 2,2,2-trifluoroethanol (TFE) | Polydopamine + ammonium carbonate vapor | Good retaining of the original fiber morphology | [73] |
| Type A spun from TFE | Proanthocyanidin (procyanidine) | High remaining mass after enzymatic degradation and retaining morphology well | [90] |
| Type A spun from glacial acetic acid | Glucose and glycerol | Strong modifications of surface morphology, reduced degradation in water | [97] |
| Cold water fish gelatin spun from water + sugar | Fructose and other sugars at 100 °C for 4 h | Nearly unaltered sample mass after 10 days for fructose crosslinking | [98] |
| Type A from porcine skin sun from acetic acid/water | Genipin | >90% for optimized parameters | [106] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ehrmann, A. Non-Toxic Crosslinking of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering and Biomedicine—A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121973
Ehrmann A. Non-Toxic Crosslinking of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering and Biomedicine—A Review. Polymers. 2021; 13(12):1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121973
Chicago/Turabian StyleEhrmann, Andrea. 2021. "Non-Toxic Crosslinking of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering and Biomedicine—A Review" Polymers 13, no. 12: 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121973
APA StyleEhrmann, A. (2021). Non-Toxic Crosslinking of Electrospun Gelatin Nanofibers for Tissue Engineering and Biomedicine—A Review. Polymers, 13(12), 1973. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13121973






