Abstract
This work theoretically determined the high-energy photon shielding properties of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) composites containing rare-earth oxides, namely samarium oxide (Sm2O3), europium oxide (Eu2O3), and gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3), for potential use as lead-free X-ray-shielding and gamma-shielding materials using the XCOM software package. The considered properties were the mass attenuation coefficient (µm), linear attenuation coefficient (µ), half value layer (HVL), and lead equivalence (Pbeq) that were investigated at varying photon energies (0.001–5 MeV) and filler contents (0–60 wt.%). The results were in good agreement (less than 2% differences) with other available programs (Phy-X/PSD) and Monte Carlo particle transport simulation code, namely PHITS, which showed that the overall high-energy photon shielding abilities of the composites considerably increased with increasing rare-earth oxide contents but reduced with increasing photon energies. In particular, the Gd2O3/HDPE composites had the highest µm values at photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, and 5 MeV, due to having the highest atomic number (Z). Furthermore, the Pbeq determination of the composites within the X-ray energy ranges indicated that the 10 mm thick samples with filler contents of 40 wt.% and 50 wt.% had Pbeq values greater than the minimum requirements for shielding materials used in general diagnostic X-ray rooms and computerized tomography rooms, which required Pbeq values of at least 1.0 and 1.5 mmPb, respectively. In addition, the comparisons of µm, µ, and HVL among the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites investigated in this work and other lead-free X-ray shielding composites revealed that the materials developed in this work exhibited comparable X-ray shielding properties in comparison with that of the latter, implying great potential to be used as effective X-ray shielding materials in actual applications.
1. Introduction
High-energy photon technologies, especially those related to X-rays and gamma rays, have been extensively used in several applications such as X-ray and gamma imaging for medical diagnostic and material characterization [1,2,3,4], gamma-induced mutation breeding in plants [5,6], quality control and quality assurance for industrial products [7], and gemstone irradiation for color enhancement [8,9]. Despite the great benefits of such applications, excessive exposure to high-energy photons could severely harm users and others, with the effects varying from mild symptoms (rash, skin burn, nausea, and headache) to fatal diseases (cancers and genetic mutations) that could cause permanent disabilities or possible death [10,11]. To reduce and/or prevent such risks, a radiation safety principle called As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARA), must be strictly followed in all nuclear-related facilities that consist of proper time management, operational distance, and use of shielding equipment [12,13].
Particularly for shielding, the development of novel materials that offer not only enhanced shielding capabilities but also additionally preferred properties, such as exceptional strength and being environmentally friendly, has become a necessity in the fast-growing radiation technology to ensure the highest safety for all related personnel and users. Generally, materials containing heavy metals, especially lead (Pb), are commonly used to attenuate high-energy photons due to Pb being economically accessible and having a relatively high atomic number (Z = 82) and density (ρ = 11.34 g/cm3), which greatly enhances the interaction probability of the materials with incident photons that result in superior high-energy photon shielding properties [14,15]. Examples of Pb-containing materials used for high-energy photon shielding are Pb-borate glasses doped with aluminum oxide [16], Pb-fly ash concrete [17], and nano-PbO/EPDM composites [18]. However, it has been proven that Pb and Pb-containing materials have serious drawbacks due to their toxicity, with prolonged exposure to Pb being potentially harmful to almost every important organ and part of humans, animals, and plants [19,20]. To reduce such health concerns, new and safe Pb-free shielding materials have been constantly pursued, such that the developed materials offer better photon attenuation and are safer for production and use. Examples of reported Pb-free shielding materials are self-healable Bi2O3/PVA hydrogels [21], flexible EPDM and NR composites containing Bi2O3, WO3, and Fe3O4 particles [22,23], and transparent Bi2O3/B2O3/BaO glasses [24], for which the efficiencies of the mentioned materials in photon attenuation varied depending on the filler type, content, and size [25].
In addition to the Bi, W, and Fe compounds commonly used as fillers for the production of Pb-free shielding materials, rare-earth oxides have gained considered attention from researchers and product developers, especially samarium oxide (Sm2O3), europium oxide (Eu2O3), and gadolinium oxide (Gd2O3), for use as alternative high-energy photon protective fillers, due to their relatively high densities (7.40–8.35 g/cm3) and atomic numbers (ZSm = 62, ZEu = 63, and ZGd = 64). Examples of rare-earth-oxide-containing materials, previously developed for use as high-energy photon shielding materials, are TeO2-ZnF2-As2O3-Sm2O3 glasses [26], waste soda-lime glass doped with La2O3 and Gd2O3 [27], Eu2O3-reinforced zinc-borate glasses [28], erbium (III)- and terbium (III)-containing silicate-based bioactive glass [29], and rare-earth/glassy alloys [30], which all had highly promising photon shielding ability. Another important advantage of rare-earth oxides (Sm2O3, Eu2O3, and Gd2O3) over the common Pb, Bi2O3, WO3, and Fe2O3 fillers is that the former are able to attenuate not only high-energy photons but also thermal neutrons with exceptional efficiency (even higher than common borated materials) [31]. These dual shielding properties of the materials containing Sm2O3, Eu2O3, or Gd2O3 are crucially useful for workers in proximity to nuclear facilities, such as nuclear reactors and ion accelerators that have a photon–neutron-mixed environment [32]. The superior neutron attenuation abilities of Sm2O3, Eu2O3, and Gd2O3 are due to their relatively high neutron absorption cross sections (σabs) of the Sm, Eu, and Gd in the compounds, which are 5922, 4530, and 49,700 barns, respectively, compared to Bi, W, and Fe, which have much lower σabs values of 0.0338, 18.3, and 2.56 barns, respectively. The abilities of Sm2O3, Eu2O3, and Gd2O3 to simultaneously attenuate both high-energy photons and thermal neutrons, as well as being self-gamma attenuators, have led to considerably simpler material designs and fewer chemicals and processes needed to produce the individual shielding materials required for the attenuation of photons and neutrons. Examples of rare-earth-oxide-containing materials to attenuate neutron shielding are Sm2O3/PVA and Gd2O3/PVA composites [33], Sm2O3/UHMWPE composites [34], Sm2O3/HDPE and Gd2O3/HDPE composites [35], and ZnO-B2O3-TeO2-Eu2O3 glasses [36].
In addition to attenuation effects from fillers, the main matrices used for the production of the shielding materials also play an important role in defining mechanical properties of the materials. For example, in applications requiring high strength, such as structural parts (walls, partitions, and equipment enclosures) and transporting casks for nuclear sources, an HDPE having a chemical formula of (C2H4)n is one of the preferred choices due to its superior tensile strength compared to other thermoplastics, its excellent electrical insulation, its low water absorption, and its good processibility [37,38]. As a result, HDPE composites filled with different radiation protective fillers have been continuously developed and used as shielding materials to achieve both mechanical strength and enhanced shielding properties. Examples of HDPE composites used in radiation protection are Bi2O3/HDPE [39] and ZnO/HDPE [40] for gamma shielding and CdO/HDPE [41] and h-BN/Gd2O3/HDPE [42] for neutron shielding.
As previously mentioned, the current work theoretically determined the high-energy photon shielding properties of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites using XCOM, based on the mass attenuation coefficient (µm), linear attenuation coefficient (µ), half value layer (HVL), and lead equivalence (Pbeq) [43,44]. To fully understand the effects of filler types and contents, and incident photon energies on shielding properties, the contents of Sm2O3, Eu2O3, and Gd2O3 in HDPE composites were varied (0–60 wt.%) for a range of photon energies (0.001–5 MeV). To verify the correctness and reliability of the investigation, the µ values obtained from XCOM were compared with results from available online software (Phy-X/PSD) and Monte Carlo code (Particle and Heavy Ion Transport Code System; PHITS), and differences between their results were investigated. Furthermore, to assess the useability of the developed composites in actual applications, the Pbeq for all samples were determined at photon energies of 0.06, 0.08, and 0.1 MeV (X-ray ranges) and the results were compared with the minimum requirements for use in general diagnostic X-ray rooms and CT rooms, which are 1 mmPb and 1.5 mmPb, respectively. Lastly, to benchmark the shielding ability of the materials from this work with other common Pb-free composites, such as HDPE composites containing Bi2O3, WO3, and Fe2O3, and glassy alloys containing rare-earth elements, values of µm, µ, and HVL at filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.% and photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 MeV were compared and discussed. The outcomes of this work should not only reveal theoretically the effectiveness of rare-earth oxides to attenuate high-energy photons but also increase the availability of the currently limited information on the use of rare-earth oxides for radiation protection.
2. Determination of High-Energy Photon Shielding Properties
2.1. Determination of Mass Attenuation Coefficient (µm)
The XCOM software provided by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) (Gaithersburg, MD, USA), was used to determine the values of µm in the HDPE composites filled with either rare-earth oxides (Sm2O3, Eu2O3, or Gd2O3) or common Pb-free fillers (Bi2O3, WO3, and Fe2O3) at filler contents of 0–60 wt.% and photon energies of 0.001–5 MeV. In addition, the µm values of a pure Pb sheet were also determined at photon energies of 0.06, 0.08, and 0.1 MeV to provide comparative X-ray shielding properties of rare-earth oxides/HDPE composites with respect to a standard Pb sheet. The photon cross-section database used in this work was the NIST standard reference database 8 (XGAM), released in November 2010. The values of µm reported in this work were calculated from the total attenuation with the inclusion of coherent scattering [45]. Furthermore, to be able to determine µm for any filler content, simple mathematical relationships were developed between µm and the filler content at the photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 MeV in the form shown in Equation (1):
where µm is the mass attenuation coefficient, x is the filler content, and A (B) is the mathematical coefficient, determined using a trendline function available in the Microsoft Excel software package.
2.2. Verification of XCOM Results by Phy-X/PSD and PHITS
To verify the correctness and the reliability of the results obtained from XCOM for further investigation, other programs, namely Phy-X/PSD [46] and PHITS [47], were used to calculate the µm values of HDPE composites containing Sm2O3, Eu2O3, or Gd2O3 at filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.% and photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 MeV. In particular, for the determination of µm from PHITS, the Monte Carlo code (version 3.22) was set up such that the photon beam with a diameter of 1 mm was directed at the center of the sample, which had the surface area of 20 cm × 20 cm and the thickness of 1 cm, to minimize effects from build-up factor. Furthermore, the detector was set up in such a way that its size was the same as the photon beam and had 100% detection efficiency in order to capture all primary transmitted photons. More details of the setup for PHITS could be found in the previous reports of Toyen and Saenboonruang [25] and Poltabtim et al. [35] To verify the results obtained from this work, their results were compared and differences between the values were calculated using Equation (2):
where Difference (%) is the percentage difference between the µm values obtained from XCOM and Phy-X/PSD (PHITS), µm,XCOM is the mass attenuation coefficient obtained from XCOM, and µm,ref is the mass attenuation coefficient obtained from either Phy-X/PSD or PHITS.
2.3. Determination of Linear Attenuation Coefficient (µ) and Half Value Layer (HVL)
The values of µ and HVL of the HDPE composites, which represent the fraction of attenuated incident photons in a monoenergetic beam per unit thickness and the thickness of the materials required to attenuate 50% of incident photons, respectively, were determined from the obtained values of µm (XCOM) in Section 2.1 using Equations (3) and (4), respectively [43]:
where ρ is the density of the composites theoretically estimated using Equation (5):
where ρHDPE (ρF) is the density of HDPE (radiation protective filler with individual densities shown in Table 1) and cHDPE (cF) are the contents of the HDPE (radiation protective fillers). It should be noted that cHDPE + cF = 100 wt.%. Similar to µm, simple mathematical relationships were developed between µ (HVL) and the filler content in the form shown in Equation (6):
where µ (HVL) is the linear attenuation coefficient (half value layer), x is the filler content, and A (B) is the mathematical coefficient, determined using a trendline function available in the Microsoft Excel software package.

Table 1.
Individual density of a pristine HDPE, rare-earth oxides, metal oxides, and Pb used for determination of densities for HDPE composites [22,35].
2.4. Determination of Lead Equivalence (Pbeq)
The Pb equivalence (Pbeq) of the Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites at photon energies of 0.06, 0.08, and 0.1 MeV, which are common X-ray energy ranges in general medical diagnostic and CT facilities, were determined using Equation (7):
where µPb (µRO/HDPE) is the linear attenuation of pure Pb sheet (rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites), Pbeq is the Pb equivalence (in mmPb), and x is the thickness of the sample (in mm), which was fixed at 10 mm in this work [48,49].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mass Attenuation Coefficient (µm)
The µm values for the Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites at photon energies of 0.001–5 MeV and filler contents of 0, 20, 40, and 60 wt.% are shown in Figure 1 (raw data are available in supplementary; Tables S1–S4). The results indicated that the HDPE composites containing Sm2O3, Eu2O3, or Gd2O3 had notably higher µm values than the pristine HDPE composites at lower photon energies (0.001–0.2 MeV), as shown in Figure 1a,c,e. Furthermore, it was found that the µm values tended to increase with increasing filler contents but decreased with increasing photon energies. The shielding properties after the addition of rare-earth oxides were enhanced because the fillers could greatly increase the interaction probabilities between the incident photons and the composites from their relatively high Z values of Sm, Eu, and Gd, in Sm2O3, Eu2O3, or Gd2O3, respectively, through the process of photoelectric absorption, the cross section of which, a nuclear quantity representing the interaction probabilities of an element or a material with incident radiation, relates to the photon and material characteristics as shown in Equation (8):
where σpe is the photoelectric cross section, h is Planck’s constant, and ν is the frequency of the photon that directly relates to the energy () [50].
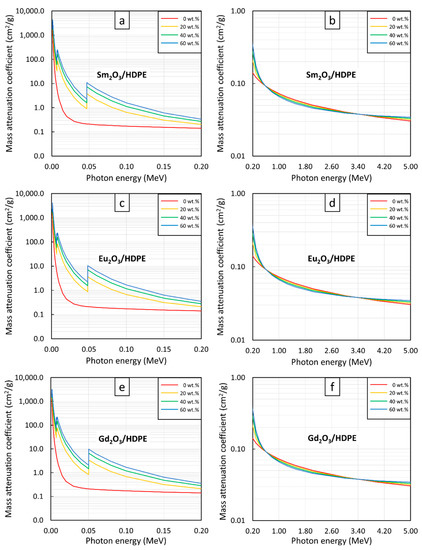
Figure 1.
µm values of (a,b) Sm2O3/HDPE, (c,d) Eu2O3/HDPE, and (e,f) Gd2O3/HDPE composites with filler contents of 0, 20, 40, and 60 wt.%, determined at photon energies of (a,c,e) 0.001–0.2 MeV and (b,d,f) 0.2–5 MeV using XCOM.
However, in contrast to distinct µm variations for different filler contents at lower photon energies, the pristine HDPE and rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites had less pronounced differences in their µm values for all filler contents at photon energies greater than 0.5 MeV (Figure 1b,d,f). This was due to the rapid decrease in the photoelectric cross section with photon energies () that greatly suppressed the roles of the added rare-earth oxides in photon attenuation through photoelectric absorption. It should be noted that at photon energies of 0.5–3.4 MeV, the pristine HDPE had slightly higher µm values than the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites. This was due to the underlying principles of Compton scattering (a dominant attenuation mechanism for photons having energies in the range 0.5–3 MeV), which suggest that the Compton scattering cross section (σcomp) is inversely proportional to the electron density (ne) of the materials, as shown in Equation (9):
As a result, materials containing high contents of light elements such as the pristine HDPE would have higher σcomp values and, subsequently, better photon attenuation abilities than those containing heavy elements, such as the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites investigated in this work [43]. Nonetheless, at photon energies greater than 3.4 MeV, the µm values of the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites began to regain their superior shielding properties, compared to the pristine HDPE. This was mainly due to the initiation of pair production at a photon energy of 1.022 MeV, with its cross section (σpp) being directly proportional to the square of Z, as shown in Equation (10) [43,50]:
and the value also tends to increase with increasing photon energies [51]. Thus, the added rare-earth oxides in the HDPE composites resumed their roles as active photon attenuators, resulting in enhanced µm values in the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites at photon energies greater than 3.4 MeV.
Additionally, Figure 1a,c,e reveal uncharacteristically sharp increases in µm values at photon energies of 0.006–0.008 MeV and 0.04–0.05 MeV for all rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites. These phenomena were observed due to the K-edge and L-edge absorptions of Sm, Eu, and Gd atoms (Figure 2), for which the incident photon energies were just above the binding energy of the electron shells inside the atoms, resulting in immensely enhanced interaction probabilities between the incident photons and the materials through photoelectric absorption at these particular energies [52].
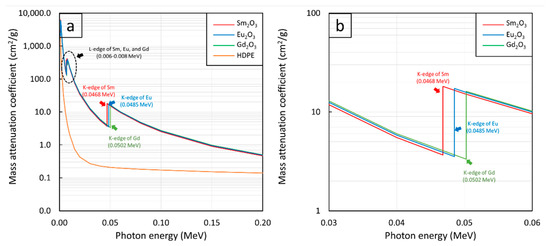
Figure 2.
µm values of Sm2O3, Eu2O3, Gd2O3, and HDPE showing K-edge and L-edge behaviors of Sm, Eu, and Gd at photon energies of (a) 0.001–0.2 MeV and (b) 0.03–0.06 MeV.
The µm values for the Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with filler contents of 0–60 wt.%, determined at the photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 MeV, are shown in Figure 3, with strong linear correlations evidenced between the filler contents and the µm values at all investigated energies. In particular, as shown in Figure 3a,b,d, there were positive correlations between the µm values and filler contents, mainly due to the potent roles of the Sm2O3, Eu2O3, or Gd2O3 particles in photon attenuation through the dominant photoelectric absorption at 0.1 and 0.5 MeV and the pair production at 5 MeV (the two mechanisms were highly dependent on the Z value). This positive correlation implied that higher filler contents would result in more available rare-earth elements to interact with the incident photons, resulting in enhanced interaction probabilities and, consequently, improved shielding abilities. The schemes showing effects of radiation-protective fillers and their contents on photon attenuation can be viewed elsewhere [43,53].
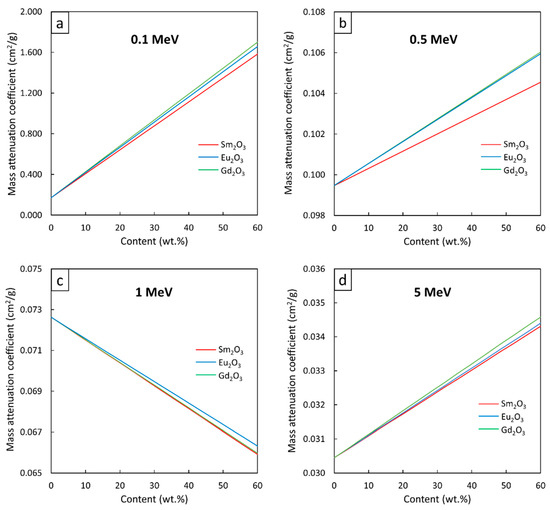
Figure 3.
µm values of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with filler contents varied from 0–60 wt.%, determined at photon energies of (a) 0.1 MeV, (b) 0.5 MeV, (c) 1 MeV, and (d) 5 MeV using XCOM.
On the other hand, Figure 3c shows negative correlations between the variables, as higher filler contents led to lower µm values. This trend in behavior was because the pristine HDPE, which is a hydrogen-rich material, could interact with the incident photons through Compton scattering, a dominant photon interaction at 1 MeV, at higher probabilities than those of the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites, which had less light-element contents due to the dilution effects from the added rare-earth oxides. This phenomenon could be mathematically explained using Equation (7) as σcomp is inversely proportional to the electron densities of the composites.
To determine the µm values for all filler contents at photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 MeV (Figure 3), linear mathematical equations in the form of µm = Ax + B (Equation (1)) were determined using a trendline function in Microsoft Excel. The results, as shown in Table 2, indicated that the Gd2O3/HDPE composites had the strongest correlations between µm values and filler contents among all the investigated rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites, as seen by the highest slopes (coefficient A) for all photon energies. These were due to Gd having the highest Z value (Z = 64) compared to Sm (Z = 62) and Eu (Z = 63), which resulted in more chances of interaction between the incident photons and the materials and, hence, a greater effect of the filler on enhancing the shielding ability. Notably, both coefficients A and B for the 0.1-MeV photon attenuations were higher than those at higher energies for all composites. This was due to the photoelectric absorption, which is a dominant interaction at 0.1 MeV and heavily reliant on the Z values of the composites (Equation (6)) than those from Compton scattering (Equation (7)) and pair production (Equation (8)), leading to more pronounced changes in the µm values as more filler was added to each HDPE composite.

Table 2.
Mathematical coefficients (A and B) for µm in form µm = Ax + B (Equation (1)) from Figure 3.
To validate the results from XCOM in this work, other available programs, namely Phy-X/PSD and PHITS, were used to calculate the µm values of the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites with filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.% at photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 MeV. The results of the comparisons, as well as the percentage of differences (Difference (%)) between µm values obtained from each software package (Equation (2)) are shown in Table 3, which indicated that the range for Difference (%) between XCOM vs. Phy-X/PSD and XCOM vs. PHITS were 0.00–0.05% with the average being 0.02% and 0.02–1.24% with the average being 0.56%, respectively. These comparisons clearly showed that the determined results from XCOM were in very good agreement with those using the other software packages; hence, they could be reliably used in later determinations of µ, HVL, and Pbeq. It should be noted that the differences in results obtained from the three methods could have been due to several factors, including possible deviations in the cross-section databases, use of incoherent/coherent scattering for the calculations, or the mathematical corrections used for the calculation of µm [44,46,47].

Table 3.
Comparative µm values obtained from XCOM and other programs (Phy-X/PSD and PHITS) for HDPE composites containing rare-earth oxides at various photon energies.
3.2. Linear Attenuation Coefficients (µ) and Half Value Layer (HVL)
The densities for each filler content were measured to determine the µ and HVL values of the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites. The results of the density calculations based on Equation (5) are shown in Table 4, which suggested that the densities of the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites generally increased with filler contents due to the high densities of the rare-earth oxide fillers. It was notable that the Sm2O3/HDPE composites had slightly higher densities than the Eu2O3/HDPE and Gd2O3/HDPE composites at the same filler content due to higher density of Sm2O3 than for Eu2O3 and Gd2O3 (Table 1).

Table 4.
Densities of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with filler contents varying from 0 to 60 wt.% (in 4 wt.% increments), calculated using Equation (5).
Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the µ and HVL values of the Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with varying fillers contents and photon energies. The results in Figure 4 indicated that the µ values for all composites had similar trends, namely increasing with filler content but decreasing with photon energy. These results agreed with the behavior of µm (Figure 1) due to the abilities of the rare-earth oxides to enhance the interaction probabilities between the incident photons and the materials. Furthermore, Figure 5 and Figure 6 suggest that the effects of the additional filler contents on the µ and HVL values for all composites were more pronounced than those observed in µm, as seen by the exponential correlations between the µ (HVL) values and the filler contents (the relationships between µm and filler contents were linearly dependent (Figure 3)). This stronger dependence of the µ and HVL values on the filler content was mainly due to the relatively high densities of Sm2O3, Eu2O3, and Gd2O3 that increased the densities of the composites at higher filler contents, which subsequently amplified the µ values according to Equations (3) and (4).
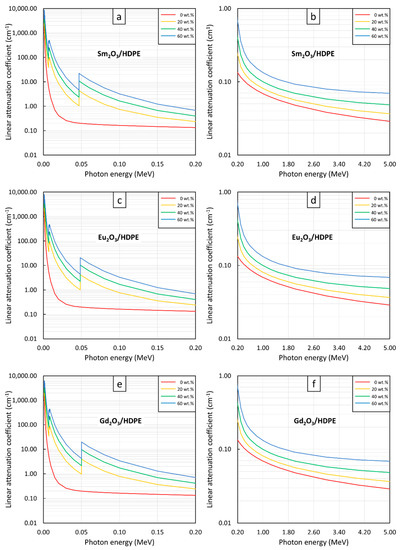
Figure 4.
µ values of (a,b) Sm2O3/HDPE, (c,d) Eu2O3/HDPE, and (e,f) Gd2O3/HDPE composites with filler contents of 0, 20, 40, and 60 wt.%, determined at photon energies of (a,c,e) 0.001–0.2 MeV and (b,d,f) 0.2–5 MeV using XCOM.
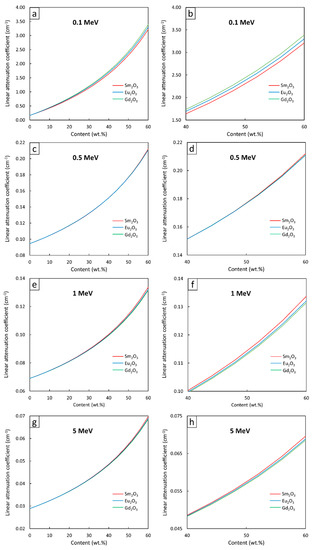
Figure 5.
µ values of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites using XCOM, with filler contents varied from (a,c,e,g) 0–60 wt.%, and (b,d,f,h) 40–60 wt.%, determined at photon energies of (a,b) 0.1 MeV, (c,d) 0.5 MeV, (e,f) 1 MeV, and (g,h) 5 MeV.
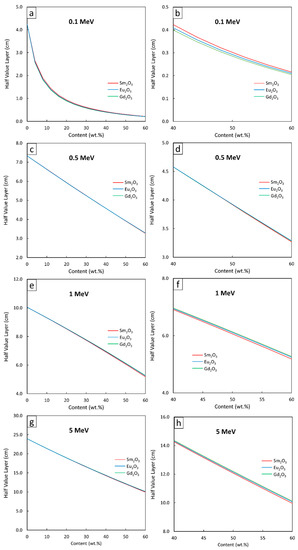
Figure 6.
HVL values of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites using XCOM, with filler contents varied from (a,c,e,g) 0–60 wt.%, and (b,d,f,h) 40–60 wt.%, determined at photon energies of (a,b) 0.1 MeV, (c,d) 0.5 MeV, (e,f) 1 MeV, and (g,h) 5 MeV.
Similar to µm, mathematical correlations between µ (HVL) values and the filler contents were determined at photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 MeV and the results are shown in Table 5 and Table 6, respectively. It should be noted that the absolute values of coefficient B, which indicate the strength of the correlation between µ (HVL) and filler contents, determined at 0.1-MeV photons, were higher than those of 0.5-, 1-, and 5-MeV photons. This was because the additional rare-earth oxides could greatly increase the photon interactions of the composites through the most effective photoelectric absorption at lower photon energies, leading to more pronounced enhancement in the µ and HVL values.

Table 5.
Mathematical constants (A and B) of µ in the form µ = AeBx (Equation (6)) from Figure 5.

Table 6.
Mathematical constants (A and B) of HVL in the form HVL = AeBx (Equation (6)) from Figure 6.
3.3. Lead Equivalence (Pbeq)
To determine the useability of the developed composites for actual applications, especially in medical applications, the Pb equivalence (Pbeq) values were determined for all composites at photon energies of 0.06, 0.08, and 0.1 MeV and filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.%, and are shown in Table 7. The results indicated that the Pbeq values increased with increasing filler content, which was consistent with the behaviors of µm and µ, with the highest Pbeq values being 2.17, 2.17, and 0.54 mmPb at the photon energies of 0.06, 0.08, and 0.1 MeV, respectively, achieved in 60 wt.%-Gd2O3/HDPE composites. Although the requirement of minimum Pbeq for X-ray shielding materials varied, depending on the photon energy, equipment, and applications, most of the general medical diagnostic X-ray and CT facilities require Pbeq values of at least 1 mmPb at 100 kVp (0.06–0.08 MeV) and 1.5 mmPb at 120 kVp (~0.08 MeV), respectively [54]. Hence, Table 7 suggests that the HDPE composites with at least 40 wt.% and 50 wt.% (interpolated from the composites with 40 wt.% and 60 wt.%) were the recommended formulations for applications in general medical diagnostic X-ray and CT rooms, respectively. It should be noted that the actual photon energies inside the facilities were distributed as a spectrum, with their average energies varying depending on the type, design, and manufacturer of the X-ray equipment and facilities.

Table 7.
Pbeq of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with filler contents of 0, 20, 40, and 60 wt.%, determined at photon energies of 0.06, 0.08, and 0.1 MeV using XCOM.
3.4. Comparative µm, µ, and HVL of Rare-Earth Oxide/HDPE and Other Common Pb-Free Composites
To compare the high-energy photon shielding capabilities of the Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with other common Pb-free HDPE composites (Bi2O3/HDPE, WO3/HDPE, and Fe2O3/HDPE), the µm, µ, and HVL values for all the composites of interest were determined and are shown in Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9, respectively (raw data are available in supplementary; Table S5). The results revealed that Bi2O3/HDPE composites had the highest shielding abilities among all the composites as seen by their highest values of µm and µ, and their lowest values of HVL. This was because the Bi atoms and Bi2O3 in the Bi2O3/HDPE composites have a higher Z (Z = 83) and density (8.90 g/cm3) than the other fillers, leading to higher chances of interactions with incident photons. In contrast, the Fe2O3/HDPE composites had the lowest shielding properties, mainly due to the low Z (Z = 26) of the Fe atoms and the lowest density (ρ = 5.24 g/cm3) of Fe2O3 that resulted in lower interaction probabilities, and consequently, inferior overall shielding properties. Notably, the rare-earth oxides/HDPE and WO3/HDPE composites attenuated high-energy photons with comparable shielding capabilities. For example, the µ values of the WO3/HDPE composites were higher than those of the Gd2O3/HDPE composites by 24%, 8%, 3%, and 1% at photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 MeV, respectively, implying promising utilization of the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites as Pb-free shielding materials, especially where the photon energy is greater than 0.5 MeV.
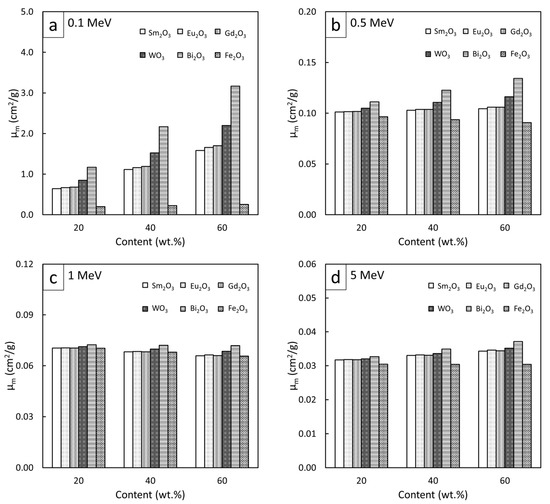
Figure 7.
Comparative µm values of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with other common Pb-free HDPE composites (Bi2O3/HDPE, WO3/HDPE, and Fe2O3/HDPE) at filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.% and photon energies of (a) 0.1 MeV, (b) 0.5 MeV, (c) 1 MeV, and (d) 5 MeV.
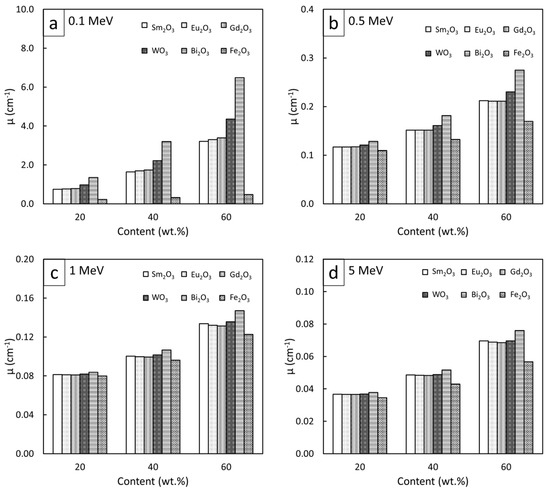
Figure 8.
Comparative µ values of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with other common Pb-free HDPE composites (Bi2O3/HDPE, WO3/HDPE, and Fe2O3/HDPE) at filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.% and photon energies of (a) 0.1 MeV, (b) 0.5 MeV, (c) 1 MeV, and (d) 5 MeV.
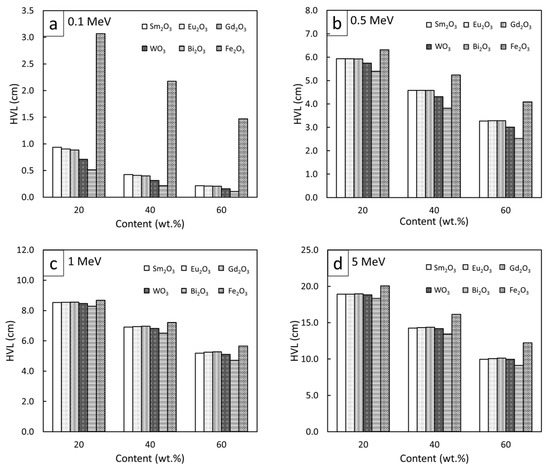
Figure 9.
Comparative HVL values of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with other common Pb-free HDPE composites (Bi2O3/HDPE, WO3/HDPE, and Fe2O3/HDPE) at filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.% and photon energies of (a) 0.1 MeV, (b) 0.5 MeV, (c) 1 MeV, and (d) 5 MeV.
Another interesting advantage of the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites over other common Pb-free shielding materials was the simultaneous ability of the former to competently attenuate both high-energy photons and thermal neutrons because Sm, Eu, and Gd have relatively high Z values (making them suitable for photon attenuation) and excellent σabs values (making them suitable for thermal neutron absorption). Furthermore Bi, W, and Fe have considerably smaller σabs values than Sm, Eu, and Gd; hence, they are not suitable for thermal neutron attenuation [55,56]. This dual shielding property of the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites would enable the developed materials to be used in neutron–photon-mixed environments, such as near nuclear reactors or ion accelerators, which could subsequently reduce the required amount of individual shielding material, as well as allowing a simplified design for the shielding setup [32].
In addition to the comparison between the results obtained from this work and those from common HDPE composites, our results were also compared with previously reported high-energy photon shielding properties of glassy alloys containing different types and contents of rare-earth elements, namely Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, and Tm. The results of the comparison are shown in Table 8, which indicated that the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites investigated in this work exhibited lower overall photon shielding properties than glassy alloys, as seen by lower µm and µ values and higher HVL values at the same photon energy. These results were mainly observed due to higher weight fractions of rare-earth elements in glassy alloys (total weight fractions of rare-earth elements in the alloys were approximately 0.8–0.85) than those in HDPE composites (weight fractions of Sm, Eu, and Gd were approximately 0.5) as well as their much higher densities of glassy alloys (ρ = 6.898–7.68 g/cm3) in comparison to HDPE composites (the highest ρ was approximately 2 g/cm3 for those with 60 wt.% rare-earth oxides), which resulted in higher photon interaction probabilities and overall shielding abilities in glassy alloys. Nonetheless, the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites in this work could still be useful in actual applications, especially for medical purposes, for which the HDPE composites offer not only sufficient photon attenuation abilities for the safety of the users but also their lighter weight and high strength, which enabled the materials to be used as structural parts and transporting casks.

Table 8.
Comparative µm, µ, and HVL values of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with glassy alloys containing different types and contents of rare-earth elements (Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, and Tm) at photon energies of 0.1 and 5 MeV.
4. Conclusions
This work determined the theoretical high-energy photon shielding properties (µm, µ, HVL, and Pbeq) for Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with filler contents in the range 0–60 wt.% and photon energies in the range 0.001–5 MeV for the development of Pb-free materials to shield against X-rays and gamma rays with exceptional strength and rigidity. The XCOM simulation software was used in this work and the results were verified with other programs, namely Phy-X/PSD and PHITS, which showed very good agreement among the three methods. The results showed that the overall high-energy photon shielding properties and densities of the composites increased with the addition of rare-earth oxide fillers, as seen by the increases (decreases) in µm, µ, and ρ (HVL), but these properties were lowered with increasing photon energies. Furthermore, the Pbeq determination indicated that the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites with 40 wt.% and 50 wt.% filler contents were suitable for use in general diagnostic X-ray and CT facilities as their Pbeq values at these recommended contents were higher than 1 mmPb and 1.5 mmPb, respectively. Compared to other Pb-free shielding materials, namely HDPE composites and glassy alloys, the developed rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites could attenuate incident photons with comparable efficiencies to some of the common materials, for example, to WO3/HDPE composites, especially at photon energies greater than 0.5 MeV, implying the promising potential of utilizing rare-earth oxide as alternative radiation protective fillers. Additionally, the rare-earth oxide/HDPE composites had advantages compared to other materials due to these composites with the dual capabilities of efficient high-energy photon and thermal neutron attenuations.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/polym13121930/s1, Table S1: Mass attenuation coefficients (µm) of HDPE composites at photon energies of 0.001–5 MeV, Table S2: Mass attenuation coefficients (µm) of Sm2O3/HDPE composites at filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.% and photon energies of 0.001–5 MeV, Table S3: Mass attenuation coefficients (µm) of Eu2O3/HDPE composites at filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.% and photon energies of 0.001–5 MeV, Table S4: Mass attenuation coefficients (µm) of Gd2O3/HDPE composites at filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.% and photon energies of 0.001–5 MeV, Table S5: Comparative µm, µ, and HVL values of Sm2O3/HDPE, Eu2O3/HDPE, and Gd2O3/HDPE composites with other common Pb-free HDPE composites (Bi2O3/HDPE, WO3/HDPE, and Fe2O3/HDPE) at filler contents of 20, 40, and 60 wt.% and photon energies of 0.1, 0.5, 1, and 5 MeV.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.S.; Formal analysis, K.S., W.P., A.T., T.P. and C.R.; Funding acquisition, K.S.; Investigation, K.S., W.P., A.T., T.P. and C.R.; Methodology, K.S., W.P., A.T., T.P. and C.R.; Supervision, K.S.; Validation, K.S.; Visualization, K.S.; Writing—original draft, K.S.; Writing—review and editing, K.S., W.P., A.T., T.P. and C.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI), Bangkok, Thailand, grant number FF(KU)25.64.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Technical support was provided by the Department of Applied Radiation and Isotopes, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand. The Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI) and Specialized Center of Rubber and Polymer Materials in Agriculture and Industry (RPM), Faculty of Science, Kasetsart University, provided publication support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; the writing of the manuscript; or the decision to publish the results.
References
- Matsuyama, S.; Maeshima, K.; Shimura, M. Development of X-ray imaging of intracellular elements and structure. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 1279–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitz, A.; Hoevels, M.; Hellerbach, A.; Gierich, A.; Luyken, K.; Dembek, T.A.; Klehr, M.; Wirths, J.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Treuer, H. Determining the orientation angle of directional leads for deep brain stimulation using computed tomography and digital x-ray imaging: A phantom study. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 4463–4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrick, R.E.; Tredennick, T. Benefit to radiation risk of breast-specific gamma imaging compared with mammography in screening asymptomatic women with dense breasts. Radiology 2016, 281, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, E.; Tashima, H.; Nagatsu, K.; Tsuji, A.; Kamada, K.; Parodi, K.; Yamaya, T. Whole gamma imaging: A new concept of PET combined with Compton imaging. Phys. Med. Biol. 2020, 65, 125013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulukapi, K.; Ozmen, S.F. Study of the effect of irradiation (60Co) on M1 plants of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cultivars and determined [sic] of proper doses for mutation breeding. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2018, 11, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, J.; Alisha, A.; Bhatt, V.; Chandanshive, S.; Kumar, N.; Mir, Z.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Shivaraj, S.M.; Sonah, H.; et al. Mutation breeding in tomato: Advances, applicability and challenges. Plants 2019, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, Y.N.; Pak, D.Y. Solid fuel quality control by the pulsed neutron-gamma method. Solid Fuel Chem. 2017, 51, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phichaikamjornwut, B.; Pongkrapan, S.; Intarasiri, S.; Bootkul, D. Conclusive comparison of gamma irradiation and heat treatment for color enhancement of Rubellite from Mozambique. Vib. Spectrosc. 2019, 103, 102926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunnag, N.; Sripoonjan, T. Gamma irradiation on Rubellite Tourmaline. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2019, 46, 1249–1255. [Google Scholar]
- Bastian, C.; Muller, J.B.; Lortat-Jacob, S.; Nihoul-Fekete, C.; Bignon-Topalovic, J.; McElreavey, K.; Bashamboo, A.; Brauner, R. Genetic mutations and somatic anomalies in association with 46, XY gonadal dysgenesis. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103, 1297–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, E.S.; van Eck, A.T.C.J.; Sauerland, C.; Schipmann, S.; Horstmann, G.; Stummer, W.; Brokinkel, B. Local tumor control and clinical symptoms after gamma knife radiosurgery for residual and recurrent vestibular schwannomas. World Neurosurg. 2019, 122, e1240–e1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyen, D.; Saenboonruang, K. Development of paraffin and paraffin/bitumen composites with additions of B2O3 for thermal neutron shielding applications. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkhout, W.E. The ALARA-principle. Backgrounds and enforcement in dental practices. Ned. Tijdschr. Tandheelkd. 2015, 122, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninyong, K.; Wimolmala, E.; Sombatsompop, N.; Saenboonruang, K. Properties of natural rubber (NR) and wood/NR composites as gamma shielding materials. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 526, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, S.A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Faghihi, R.; Arjmand, M.; Sina, S.; Amani, A.M. Lead oxide-decorated graphene oxide/epoxy composite towards X-ray radiation shielding. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 146, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Singh, K.J. Investigation of lead borate glasses doped with aluminium oxide as gamma ray shielding materials. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2014, 63, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Singh, S.; Dhaliwal, A.S.; Singh, G. Gamma radiation shielding analysis of lead-flyash concretes. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2015, 95, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, T.; Gungor, A.; Akbay, I.K.; Uzun, H.; Babuccupglu, Y. Nano lead oxide and epdm composite for development of polymer-based radiation shielding material: Gamma irradiation and attenuation tests. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 144, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, A.L.; Ara, A.; Usmani, J.A. Lead toxicity: A review. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, L.H.T.; Beardall, J. Effects of lead on growth, photosynthetic characteristics and production of reactive oxygen species of two freshwater green algae. Chemosphere 2016, 147, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiamduangtawan, P.; Kamkaew, C.; Kuntonwatchara, S.; Wimolmala, E.; Saenboonruang, K. Comparative mechanical, self-healing, and gamma attenuation properties of PVA hydrogels containing either nano-or micro-sized Bi2O3 for use as gamma-shielding materials. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 177, 109164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltabtim, W.; Wimolmala, E.; Saenboonruang, K. Properties of lead-free gamma-ray shielding materials from metal oxide/EPDM rubber composites. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 153, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyen, W.; Rittirong, A.; Poltabtim, W.; Saenboonruang, K. Flexible, lead-free, gamma-shielding materials based on natural rubber/metal oxide composites. Iranian Polym. J. 2018, 27, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marltan, W.; Rao, P.V.; Klement, R.; Galusek, D.; Sayyed, M.I.; Tekin, H.O.; Prasad, P.S.; Veeraiah, N. Spectroscopic and thermal analysis of lead-free multipurpose radiation shielding glasses. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 5332–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyen, D.; Saenboonruang, K. Comparative X-ray shielding properties of bismuth oxide/natural rubber composites using a Monte Carlo code of PHITS. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 773, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaikwad, D.K.; Sayyed, M.I.; Obaid, S.S.; Issa, S.A.M.; Pawar, P.P. Gamma ray shielding properties of TeO2-ZnF2-As2O3-Sm2O3 glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 765, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtulus, R.; Kavas, T.; Akkurt, I.; Gunoglu, K. Theoretical and experimental gamma-rays attenuation characteristics of waste soda-lime glass doped with La2O3 and Gd2O3. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 8424–8432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, G.; Issa, S.A.M.; Ilik, E.; Kilicoglu, O.; Tekin, H.O. A journey for exploration of Eu2O3 reinforcement effect on zinc-borate glasses: Synthesis, optical, physical and nuclear radiation shielding properties. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 2572–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deliormanli, A.M.; Issa, S.A.M.; Al-Buriahi, M.S.; Rahman, B.; Zakaly, H.M.H.; Tekin, H.O. Erbium (III)- and Terbium (III)-containing silicate-based bioactive glass powders: Physical, structural and nuclear radiation shielding characteristics. Appl. Phys. A 2021, 127, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perisanoglu, U.; El-Agawany, F.I.; Tekin, H.O.; Kavaz, E.; Zakaly, H.M.H.; Issa, S.A.M.; Zaid, M.H.M.; Sidek, H.A.A.; Matori, K.A.; Rammah, Y.S. Multiple characterization of some glassy-alloys as photon and neutron shields: In-silico Monte Carlo investigation. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 035202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florez, R.; Colorado, H.A.; Giraldo, C.H.C.; Alajo, A. Preparation and characterization of Portland cement pastes with Sm2O3 microparticle additions for neutron shielding applications. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 191, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonay, A.; Deniz, M.; Wong, H.T.; Agartioglu, M.; Asryan, G.; Chen, J.H.; Kerman, S.; Li, H.B.; Li, J.; Lin, S.T.; et al. Neutron background measurements with a hybrid neutron detector at the Kuo-Sheng Reactor Neutrino Laboratory. Phys. Rev. C 2018, 98, 024602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiamduangtawan, P.; Wimolmala, E.; Meesat, R.; Saenboonruang, K. Effects of Sm2O3 and Gd2O3 in poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels for potential use as self-healing thermal neutron shielding materials. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 172, 108818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyen, D.; Wimolmala, E.; Sombatsompop, N.; Markpin, T.; Saenboonruang, K. Sm2O3/UHMWPE composites for radiation shielding applications: Mechanical and dielectric properties under gamma irradiation and thermal neutron shielding. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 164, 108366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltabtim, W.; Toyen, D.; Saenboonruang, K. Comparative neutron-shielding properties of metal oxide/HDPE composites using a Monte Carlo Code of PHITS. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 526, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammah, Y.S.; Sayyed, M.I.; El-bashir, B.O.; Asiri, S.M.; Al-Haseethi, Y. Linear optical features and radiation shielding competence of ZnO–B2O3–TeO2-Eu2O3 glasses: Role of Eu3+ ions. Opt. Mater. 2021, 111, 110525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, A.; Grasso, A.; Recca, G.; Carbone, D.C.; Pistone, A. Mechanical, wear and thermal behavior of polyethylene blended with graphite treated in ball milling. Polymers 2021, 13, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekhta, P.; Sedliačik, J. Environmentally friendly high-density polyethylene-bonded plywood panels. Polymers 2019, 11, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalsalam, A.H.; Sakar, E.; Kaky, K.M.; Mhareb, M.H.A.; Sakar, B.C.; Sayyed, M.I.; Gurol, A. Investigation of gamma ray attenuation features of bismuth oxide nano powder reinforced high-density polyethylene matrix composites. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 168, 108537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayed, Z.; Badawi, M.S.; Awad, R.; Thabet, A.A.; El-Khatib, A.M. Study of some γ-ray attenuation parameters for new shielding materials composed of nano ZnO blended with high density polyethylene. Nucl. Technol. Radiat. Prot. 2019, 34, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulsoom, U.; Gursal, S.A.; Khurshid, M.S.; Saif-ur-Rehman, M.; Minhas, A.S.; Yasin, T.; Mehboob, N.; Mehmood, M.S. Investigating the effect of adding CdO nano particles on neutron shielding efficacy of HDPE. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 177, 109145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irim, S.G.; Wis, A.A.; Keskin, M.A.; Baykara, O.; Ozkoc, G.; Avci, A.; Dogru, M.; Karakoc, M. Physical, mechanical and neutron shielding properties of h-BN/Gd2O3/HDPE ternary nanocomposites. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2018, 144, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltabtim, W.; Toyen, D.; Saenboonruang, K. Theoretical determination of high-energy photon attenuation and recommended protective filler contents for flexible and enhanced dimensionally stable wood/NR and NR composites. Polymers 2021, 13, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, M.J.; Hubbell, J.H.; Seltzer, S.M.; Chang, J.; Coursey, J.S.; Sukumar, R.; Zucker, D.S.; Olsen, K. XCOM: Photon Cross Section Database (version 1.5); National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2010.
- Livet, F.; Sutton, M. X-ray coherent scattering in metal physics. C. R. Phys. 2012, 13, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakar, E.; Ozpolar, O.F.; Alim, B.; Sayyed, M.I.; Kurudirek, M. Phy-X/PSD: Development of a user-friendly online software for calculation of parameters relevant to radiation shielding and dosimetry. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 166, 108496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Iwamoto, Y.; Hasimoto, S.; Ogawa, T.; Furuta, T.; Abe, S.; Kai, T.; Tsai, P.; Matsuda, N.; Iwase, H.; et al. Features of Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS) version 3.02. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.K.; Wagner, L.K. On the (f)utility of measuring the lead equivalence of protective garments. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 063902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljabal, A.F.; Wargo, R.R.; Lin, P.J.P. Evaluation of lead equivalence of radiation protection apparatuses as a function of tube potential and spectral shaping filter. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2019, 20, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, H. Lecture Note on Photon Interactions and Cross Sections. Available online: http://rcwww.kek.jp/research/shield/photon_r.pdf (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Blokhin, A.I.; Ignatyuk, A.V.; Lunev, V.P.; Manokhin, V.N.; Tertychnyi, G.Y.; Zolotarev, K.I. New evaluations of gamma-ray production cross-sections for lead and bismuth. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2000, 37, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si-Mohamed, S.; Cormode, D.P.; Bar-Ness, D.; Sigovan, M.; Naha, P.C.; Langlois, J.B.; Chalabreysse, L.; Coulon, P.; Blevis, I.; Roessl, E.; et al. Evaluation of spectral photon counting computed tomography K-edge imaging for determination of gold nanoparticle biodistribution in vivo. Nanoscale 2017, 46, 18246–18257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninyong, K.; Wimolmala, E.; Sombatsompop, N.; Saenboonruang, K. Potential use of NR and wood/NR composites as thermal neutron shielding materials. Polym. Test. 2017, 59, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winstone Wallboards Limited. GIB X-Block Radiation Shielding Systems. Available online: https://www.usgboral.com/content/dam/USGBoral/Australia/Website/Documents/English/brochures-catalogues/XBlockRadiationSheildingSystemsApril091.pdf (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Adib, M.; Kilany, M. On the use of bismuth as a neutron filter. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2003, 66, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayana, G.; Kebaili, I.; Dong, M.G.; Al-Buriahi, M.S.; Dahshan, A.; Kityk, I.V.; Lee, D.E.; Yoon, J.; Park, T. Estimation of gamma-rays, and fast and the thermal neutrons attenuation characteristics for bismuth tellurite and bismuth boro-tellurite glass systems. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 5750–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).